
Microbiology-P-1 D. Esraa D. T.
1
Streptococcus pneumonia
INTRODUCTION:
Common name Pneumococcus.
Formerly known as Diplococcus pneumoniae.
Has been reclassified as S. pneumoniae because of its genetic relatedness to
streptococcus.
Normal inhabitants of the upper respiratory tract of human beings.
MORPHOLOGY:
Pneumococci are Gram positive small(1μm), slightly elongated cocci, with one end
broad & other end pointed, presenting a flame shaped or lanceolate appearance.
They occur in pairs, with the broad ends opposing each other.
They are capsulated & the capsule encloses each pair.
They are nonmotile & nonsporing.
CULTURE & CULTURAL CHARACTERISTICS:
They grow only in enriched media.
They are aerobes & facultative anaerobes.
The optimum temperature being 37ºC & pH 7.8.
Microbiology-P-1 D. Esraa D. T.
2
Growth is improved by 5-10% CO2.
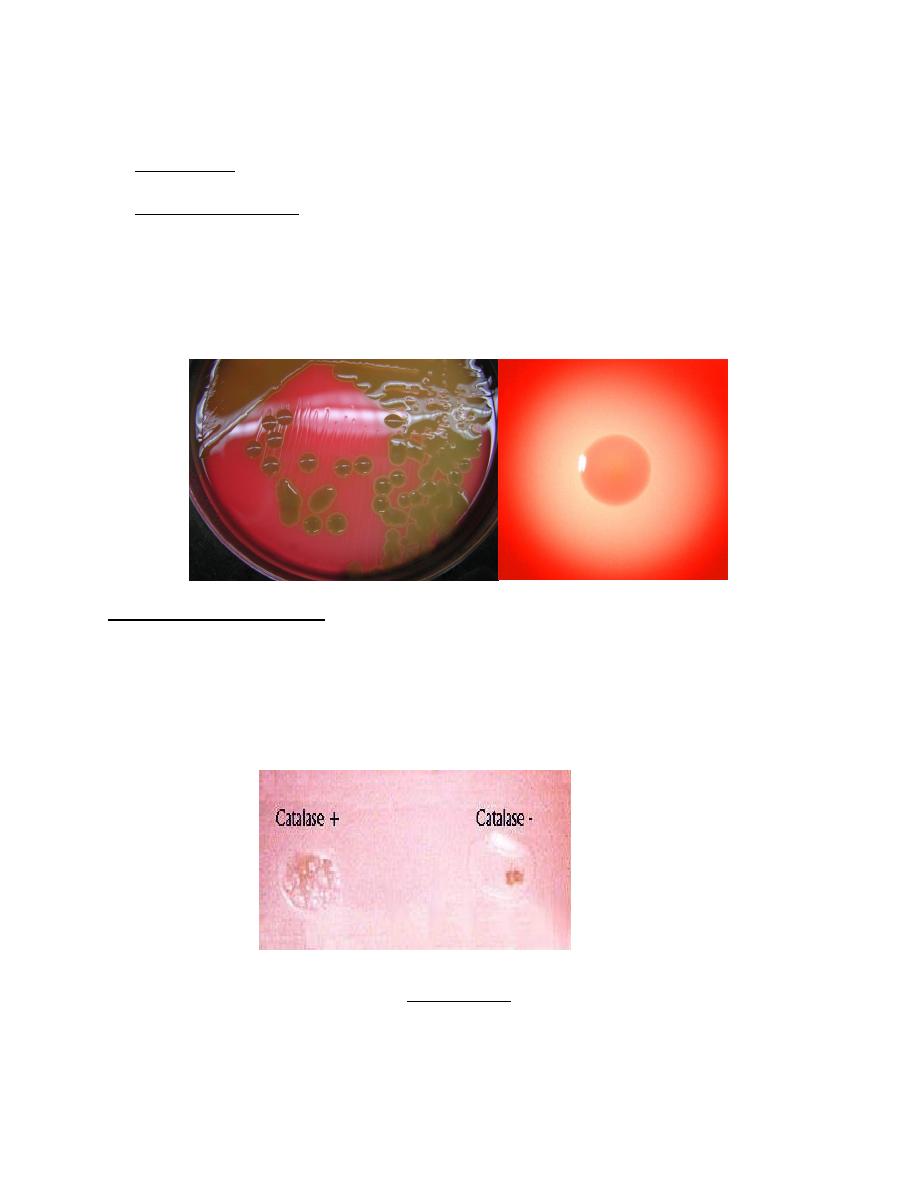
Media used: Blood agar
Colony morphology: On blood agar, after incubation for 18 hours, the colonies are
small, dome shaped & glistening, with an area of α-haemolysis.
On further incubation the colonies become flat with raised edges & central
umbonation called as Draughtsman or carom coin appearance.
BIOCHEMICAL REACTIONS:
1) Catalase test: Negative.
2) Bile solubility test: Positive.
3) It ferments inulin.
Catalase test

Microbiology-P-1 D. Esraa D. T.
3
Bile solubility test
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS:
Specimens to be collected:
Sputum,
CSF,
Blood,
Synovial fluid,
In children laryngeal swab can be taken if sputum can not be collected.
Microbiology-P-1 D. Esraa D. T.
4
Methods of examination:
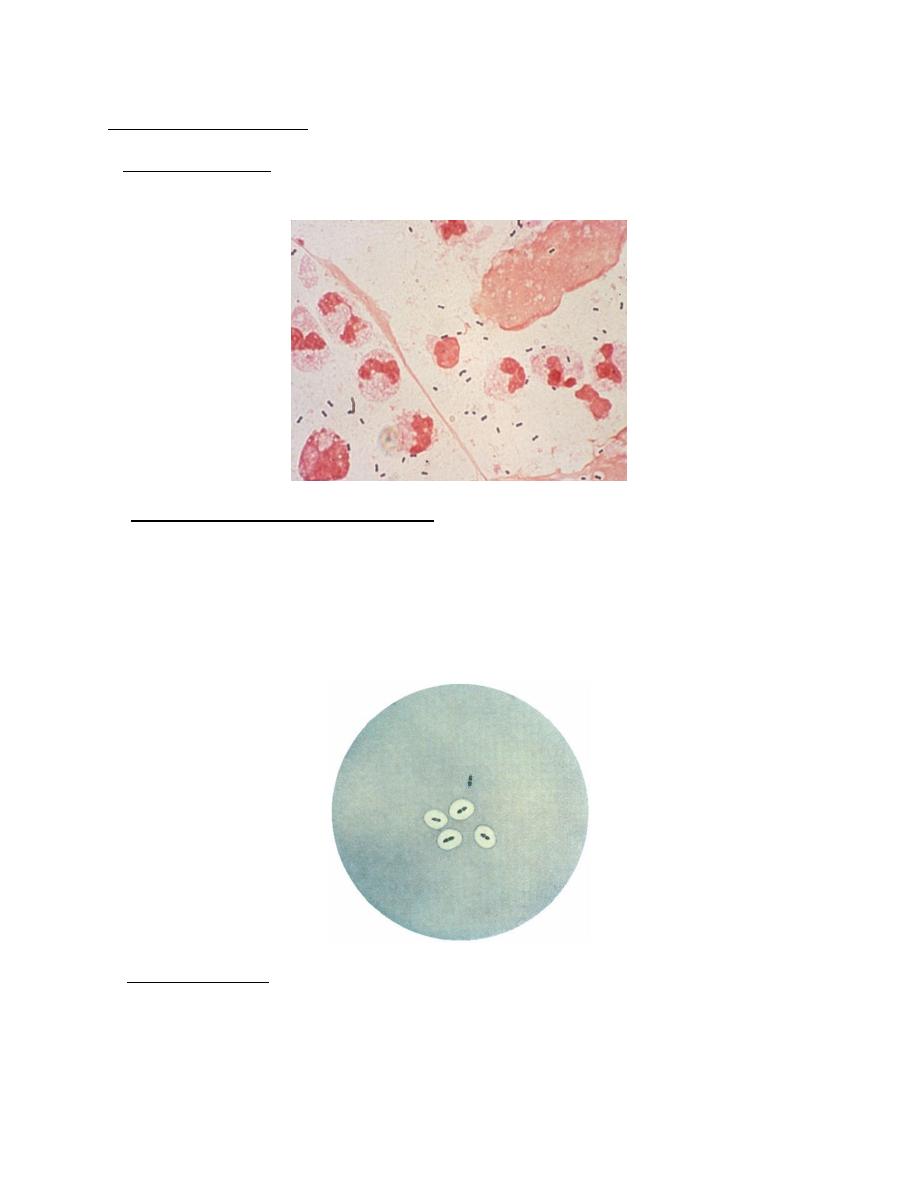
1.Direct microscopy:Gram stained smears reveals Gram positive lanceolate shaped
diplococci with numerous pus cells.
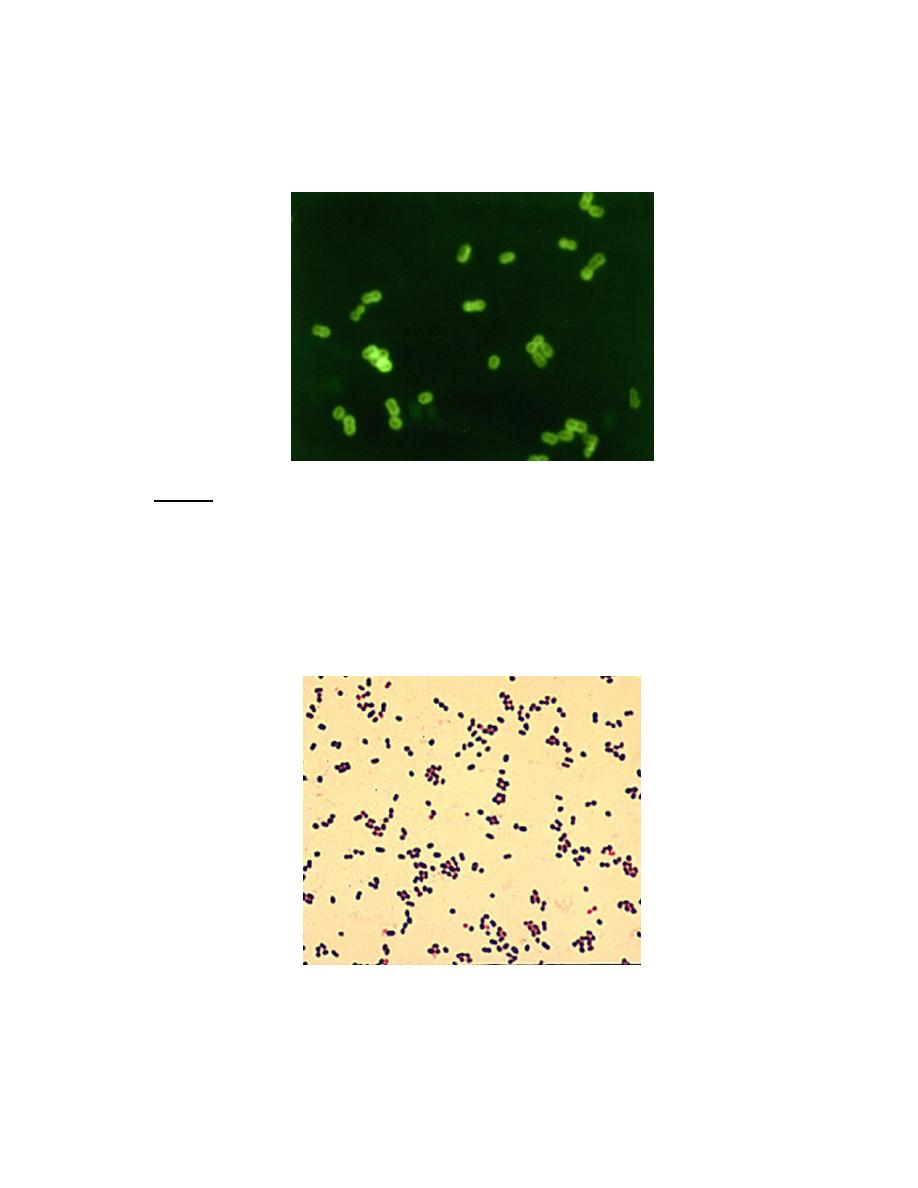
2. Quellung( capsular swelling ) reaction:
It is described by Neufeld.
On a slide the sputum is mixed with type specific antiserum against capsular
antigen & a loopful of methylene blue solution. The capsule becomes swollen &
refractile.
3. Antigen detection: Capsular polysaccharide
antigen in blood, CSF & urine can detected by
Passive latex agglutination,
Microbiology-P-1 D. Esraa D. T.
5
Counter immunoelectrophoresis,
Coaggutination.
4. Culture:
a) Media used:
b) Colony morphology:
c) Gram’s smear:Smears are examined from the culture plate and reveals Gram
positive lanceolate shaped diplococci.
d) Capsular swelling reaction: Positive.
It is done by mixing the suspension of colonies from the culture plate and a loopful
of type specific antiserum & a drop of methylene blue solution on a slide.

Microbiology-P-1 D. Esraa D. T.
6
e) Biochemical reactions:
f) Optochin sensitivity: Sensitive.
5. Animal inoculation: From specimens where organisms are expected to be scanty,
isolation may be obtained by intraperitoneal inoculation in mice.
6. Serology: Antibodies can be demonstrated by agglutination & precipitation test.
