Ear Anatomy
Functions of Ear
The ear is the organ of hearing.plays an important role in maintaining the balance (equilibrium) of the body
Subdivisions
3 parts:-1. External ear.
2. Middle ear.
3. Internal ear
The external ear
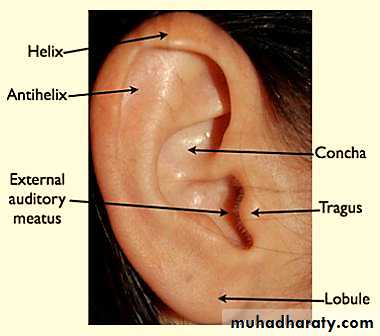
1- Auricle or pinna.
2- External auditory meatus.
3- Tympanic membrane (ear drum).
Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity)
Small air-filled space within the petrous part of the temporal bone.It contains the auditory ossicles.
It communicates with the nasopharynx through auditory tube & mastoid process by aditus to mastoid.
By its medial wall; it communicates with the internal ear (via oval or round windows).
The internal (Labyrinth)ear
It consists of:-1- bony labyrinth:- a complicated space in the
petrous part of the temporal bone.
2- fluid-filled membranous labyrinth.
The membranous labyrinth contains sensory receptors for hearing and balancing.
EXTERNAL EAR
The external ear consists of:-(a) pinna or auricle.
(b) external auditory meatus.
It is concerned with collection and transmission of sound waves to the tympanic membrane.
AURICLE/PINNA
Overview
The auricle is undulating projection on the side of the head
The entire pinna except its lobule is made up of a single piece of yellow elastic cartilageThe lobule of pinna is made of fibro-fatty tissue covered with skin
The External Auditory canal
It is a curved tube (S-shape) that leads from the auricle to the tympanic membrane.It has two components:-
1- Outer 1/3 is 1- cartilaginous
2- is provided with hairs and sebaceous and ceruminous glands (wax-producing glands).
The External Auditory canal
2- Inner 2/3 is :- 1- bony2- contains no appendages or hair
The sensory nerve supply of the lining skin is derived from 1- the auriculotemporal nerve (roof & ant.wall)
2- the auricular branch of vagus n.(floor & post.wall)
The lymph drainage:-
1- Superficial parotid
2- Mastoid and
3- Superficial cervical lymph nodes.
Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity)
It is an air-containing cavity in the petrous part of temporal bone
It is lined with mucous membrane.
It contains the auditory ossicles & muscles.
It communicates in front through the auditory tube with the nasopharynx and behind with the mastoid antrum.
.
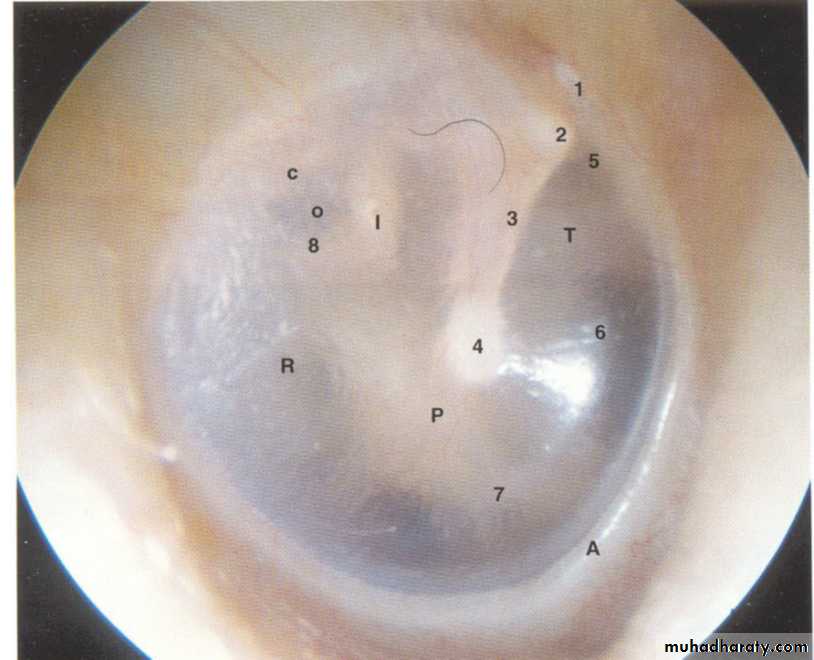
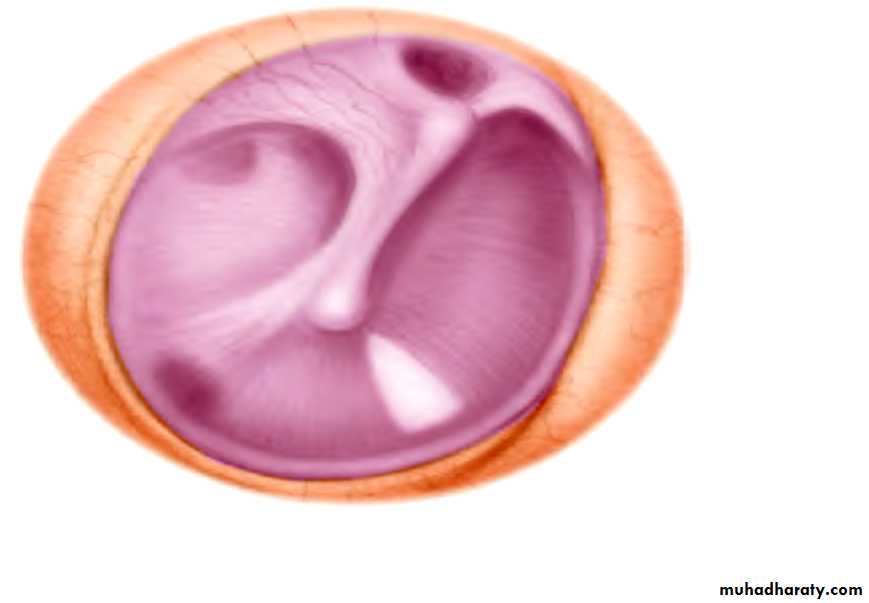
The tympanic membrane
It is a thin fibrous structure covered1-Externally with a thin layer of stratified squamous epith.
2- and internally lined with low columnar epith.
3- The framework consists of collagen fibres.
Tympanic membrane
General features of TM
It is circular, 1 cm in diameter.It lies obliquely at 55 ْwith external auditory meatus.
It is concave towards the meatus. At the depth of the concavity is a small depression, the umbo
The handle of the malleus is firmly attached
to the inner surface of the membrane.
Tympanic membrane
From the lateral process of the malleus two thickened fibrous folds (mallear folds) diverge up to the margins of the tympanic
bone;
Between them the small upper segment of the membrane is lax (pars flaccida).
The rest of TM is pars tensa
Tympanic membrane
Nerve supply:-1- Auriculotemporal nerve.
2- Vagus nerve.
Both lateral surface; while glossopharyngeal nerve (medial surface)
Walls of Middle Ear
6 walls;-1- lateral wall (tympanic):- tympanic membrane
2- medial wall (Labyrinthine):- lat. wall of inner ear
3- Anterior wall (carotid);- two openings:-
a- canal for tensor tympani b- Eustachian tube
4- Posterior wall (mastoid).
5- Superior wall (roof) Tegmen tympani
6- floor (inferior wall) jugular
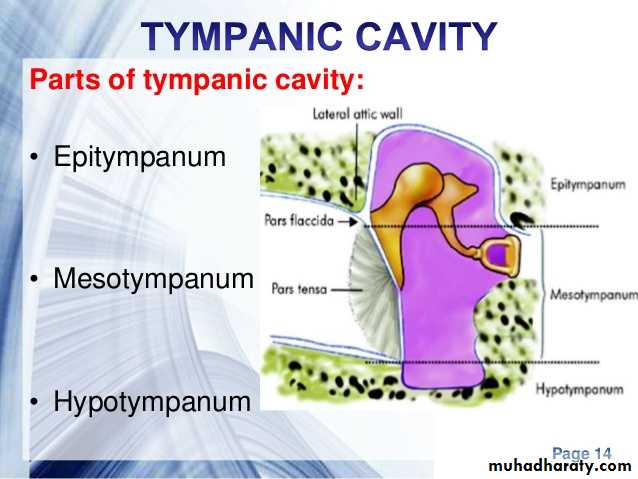
Compartments of ME
1- Epitympanum:- the part above the TM containing the head of malleus; body & short process of incus.
2- mesotympanum:- the part opposite the TM containing handle of malleus, long process of incus & stapes.
3- hypotympanum:- the part below the tympanic membrane
Auditory Ossicles
1- The malleus:-is the largest ossicle and possesses a head,
a neck, a long process or handle, an anterior process, and a
lateral process.
2- Incus:- it has a large body and two processes
3- The stapes:- smallest bone that has head, neck & two limbs
Auditory ossicles
3 ossiclesAuditory Ossicles
Auditory muscles
Two muscles1- Tensor tympani muscle.
2- Stapedius muscle. T T= tensor tympani
ET= eustachian tube
Nerve supply
Action
insertion
Origin
Muscle
Mandibular n.
Slow down vibration of TM (dampening effect)
Neck of malleusWall of
1- canal for T T.
2- wall for ET
Tensor tympani
Facial nerve
Slow down vibration of TM (dampening effect)
Neck of stapes
Pyramid
Stapedius
Tympanic cavity
Tympanic cavityInner Ear (Labyrinth)
The labyrinth is situated in the petrous part of the temporal bone, medial to the middle earIt consists of
The bony labyrinth, comprising a series of cavities within the bone.
The membranous labyrinth, comprising a series of
membranous sacs and ducts contained within the
bony labyrinth.
Bony labyrinth
It consists of three parts:-1- Cochlea:- anteriorly; it resembles snail shell
2- Vestibule:- central part
3- Semicircular canals:- posteriorly
They are lined by endosteum and contain a clear fluid, the perilymph,
in which is suspended the membranous labyrinth.
Membranous labyrinth
Membranous Labyrinth
It is lodged within the bony labyrinth.It is filled with endolymph and surrounded
by perilymph.
It consists of the utricle and saccule, which are
lodged in the bony vestibule;
the three semicircular ducts, which lie within the bony semicircular canals;
And the duct of the cochlea, which lies within the bony cochlea.
The scala media ( Cochlear duct)
It is a blind tube that divides the bony cochlear canal into two passagesThe upper chamber called scala vestibuli
The lower passage known as scala tympani.
The two passages communicate with each other at a narrow opening called the helicotrema.
Scala media
It is triangular in cross section.It is stretched between the Reissner’s membrane & basilar membrane.
It contains the sensory organ of hearing (i.e. organ of corti) which contains the hair cells as the receptors of hearing;
These cells are embedded in the thick gelatinous tectorial membrane.
Organ of Corti
Scala media is located between Reissner’s membrane & basilar membrane.
Organ of corti is the sense organ of hearing and lies on the basilar membrane
It is overlaid by the gelatinous tectorial membrane.