Cardiovascular SystemDevelopment
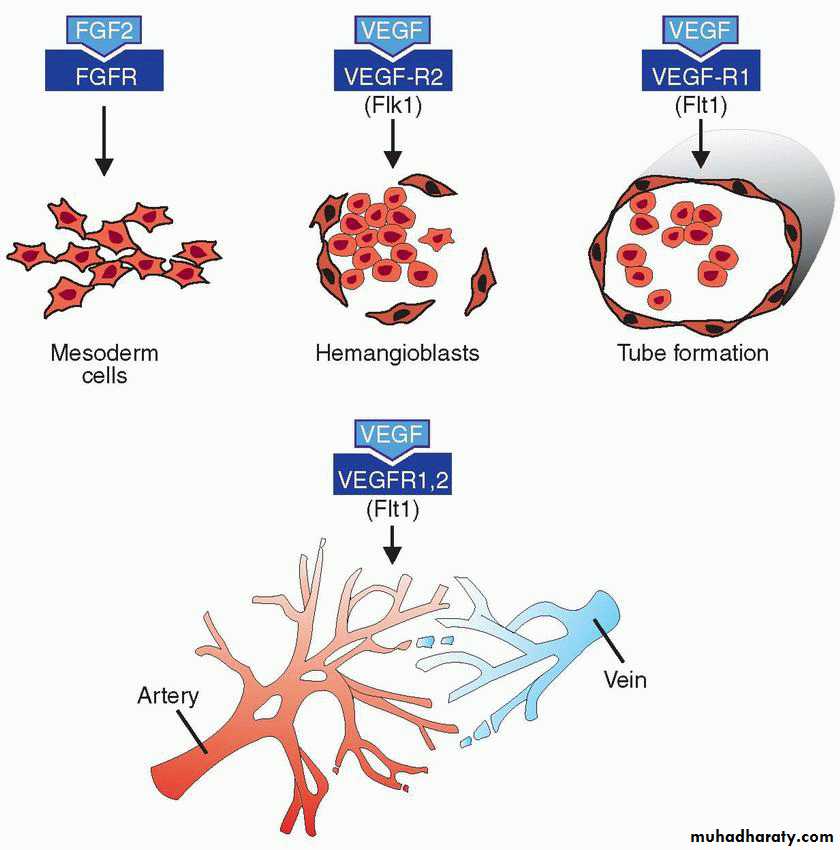
Formation of blood vessels• vasculogenesis:
Blood islands (mesoderm of the yolk sac) 3rd week
~~~~ induced to form the hemangioblast
In the center of the bl island
Hemopoitic stem cell
In the periphery
angioblasts
2. angiogenesis:
Sprouting of new vessels from the existing one
Hemangioblasts are induced by the VEGF
These bl islands in the yolk sac are transitory.
The definitive hematopoitic stem cells arise from mesoderm surrounding the aorta, region known as aorta gonad mesonephrous (AGM):- colonize the liver ( fetus)
- colonize the bone marrow ( adult)
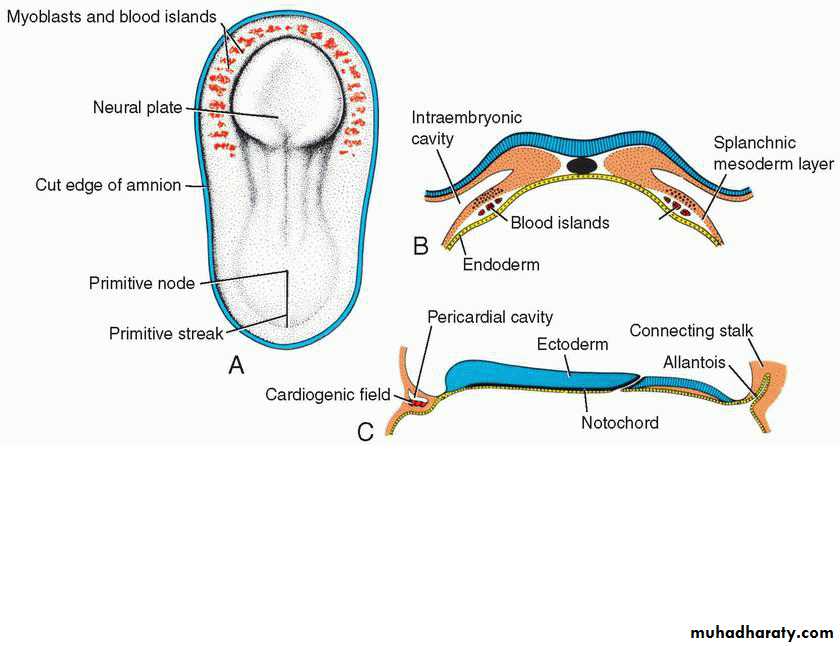
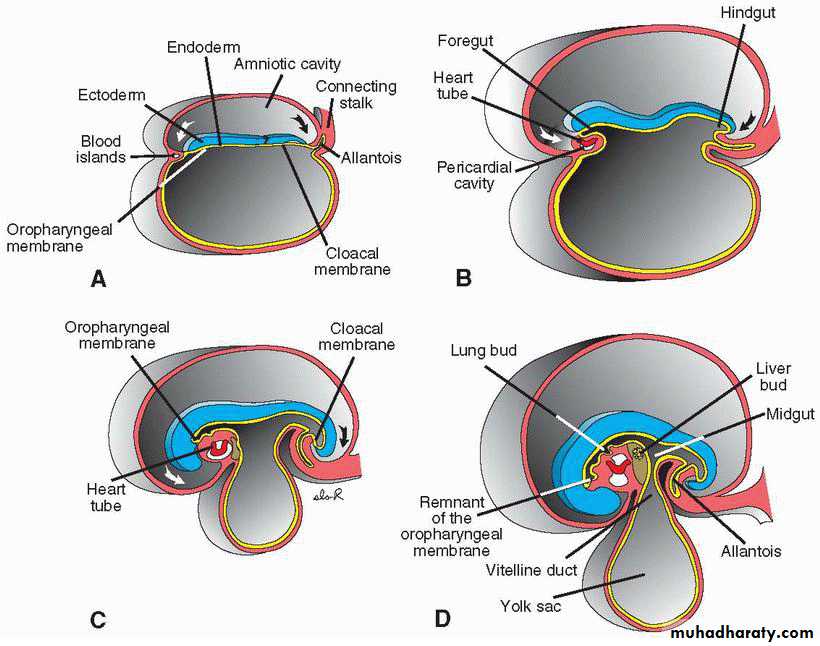
Formation of Cardiogenic Field
Appearance: Middle of the 3rd weekCardiogenic progenitor cells in epiblast lateral to the primitive streak.
Migrate to form angiogenetic clusters rostral to the buccopharyngeal membrane and neural folds
(splanchnic layer)
Formation of Cardiogenic Field
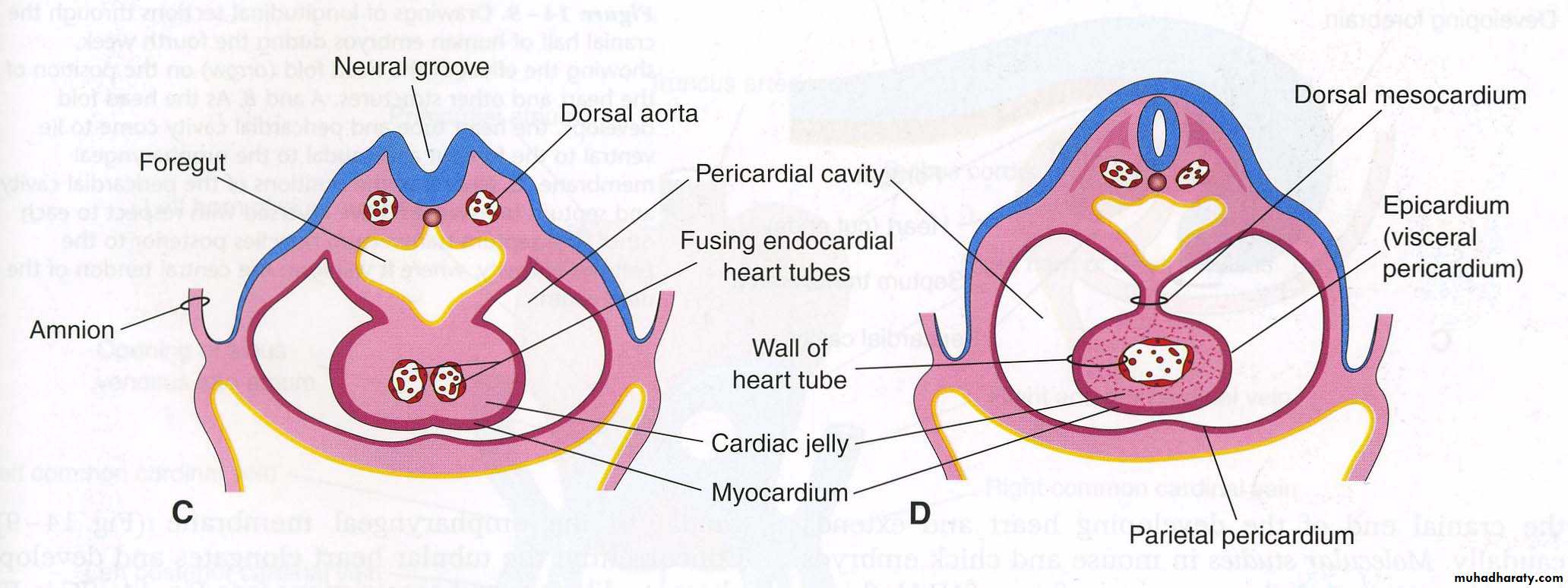
angiogenetic clusters induced by pharyngeal endo to form Cardiac myoblastthe cardiogenic field: horse-shoe shaped endothelial lined tube surrounded by myoblasts.
pericardial cavity
Formation of Cardiogenic Field
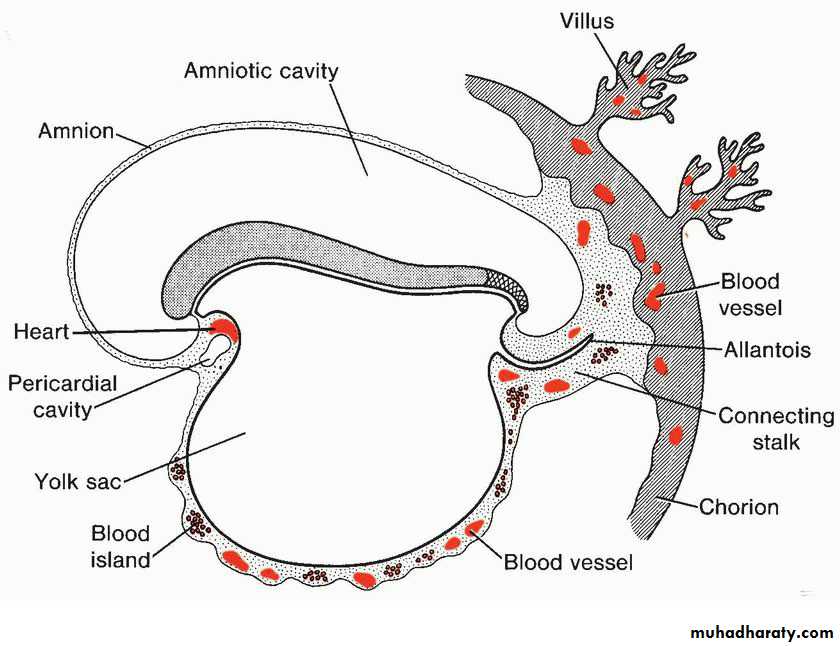
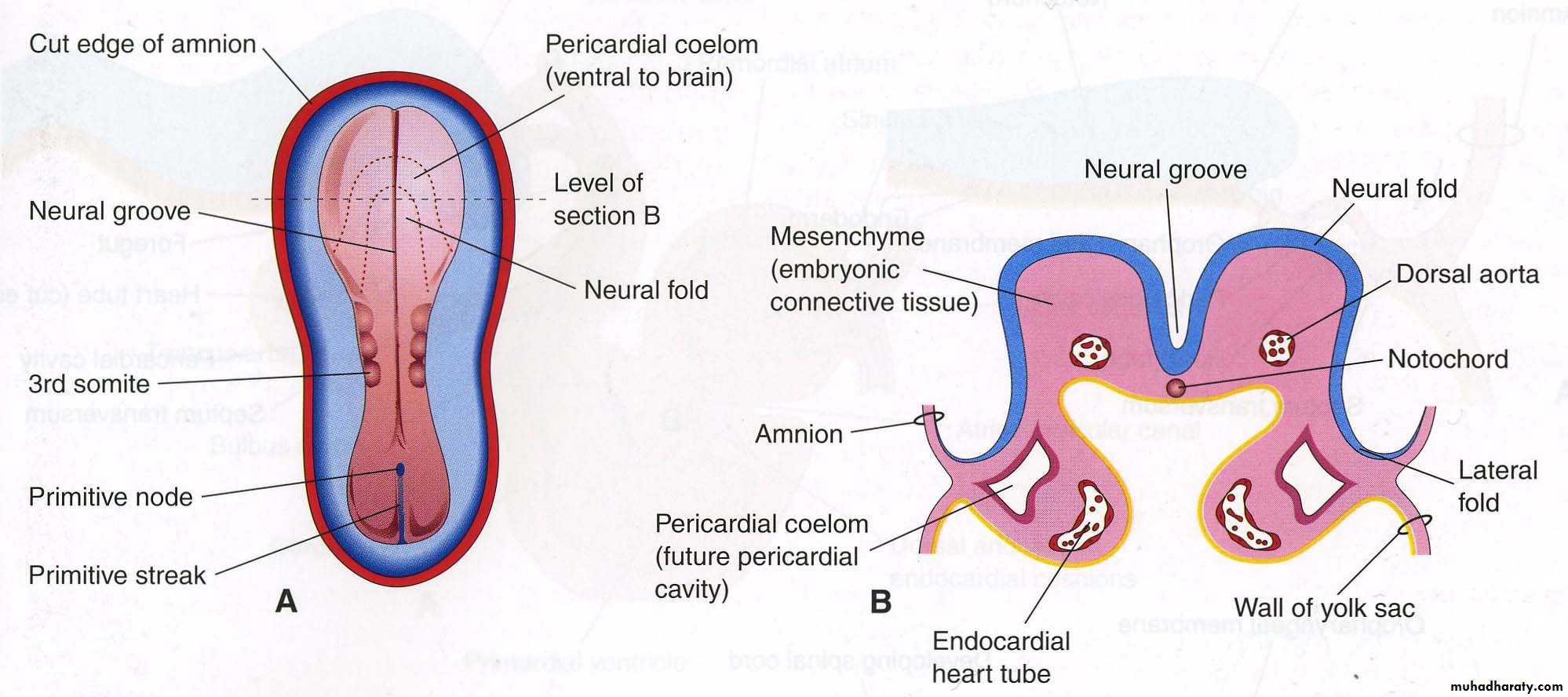
Bilateral blood islands appear close to the midline of the embryonic shield. These islands form a pair of longitudinal vessels, the dorsal aortaeFormation and position of the endocardiac heart tube
Formation and position of the endocardiac heart tube
Heart tube consists of3 layers:
• Endocardium
• Myocardium
• Epicardium
(visceral pericardium);
Responsible for coronaries
formation
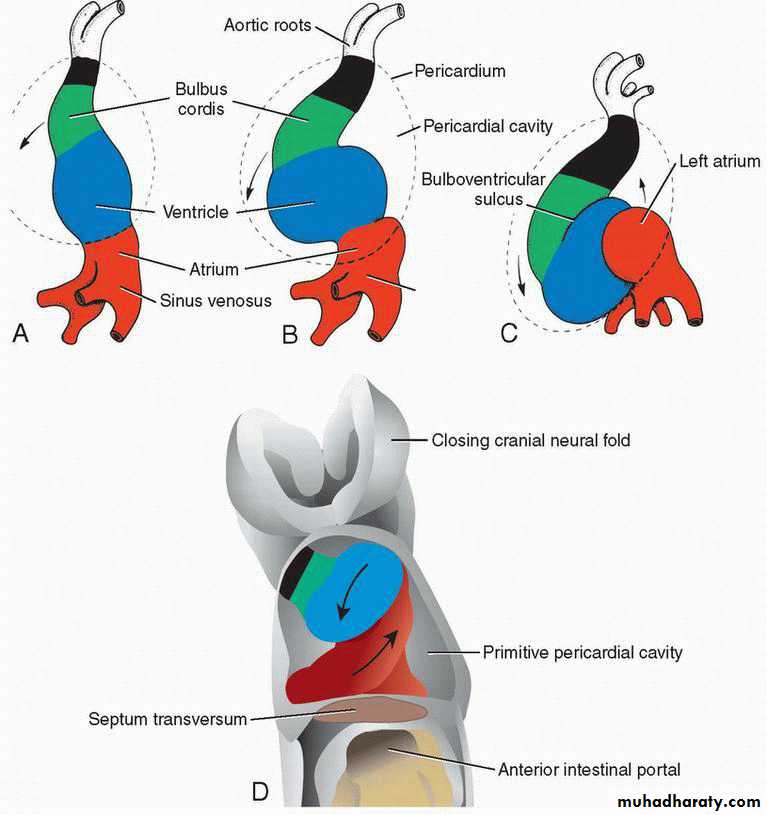
Formation of heart loop
Four parts :1. The bulbus cordis.
2. The ventricle.
3. The atrium.
4. The sinus venosus
• day 23
• cephalic portion :ventrally, caudally, and Rt
• caudal (atrial) portion: dorsocranially and Lt
• Completed on day 28
Formation of Heart Loop
day 23cephalic portion :ventrally, caudally, and Rt
caudal (atrial) portion: dorsocranially and Lt
Completed on day 28
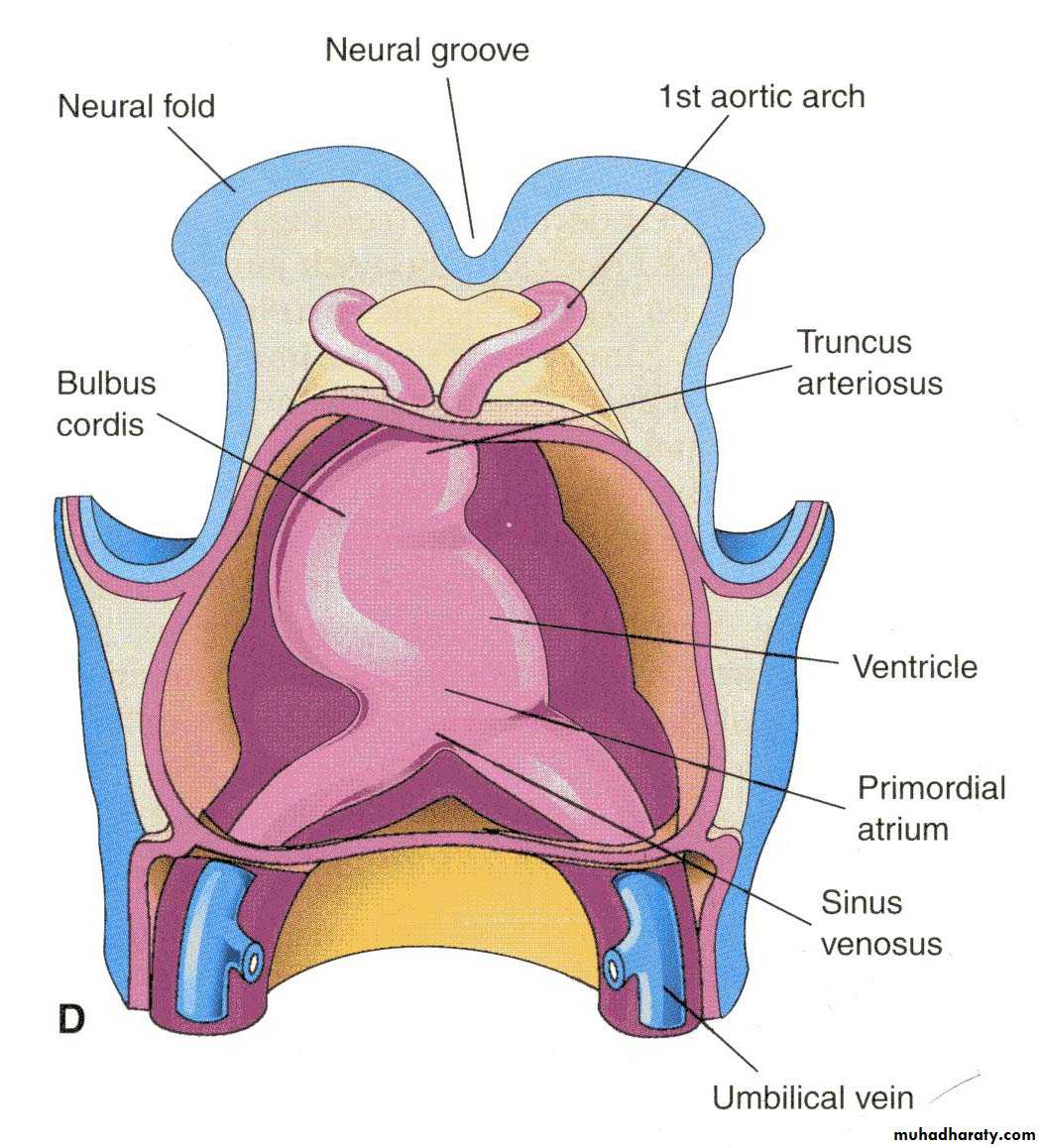
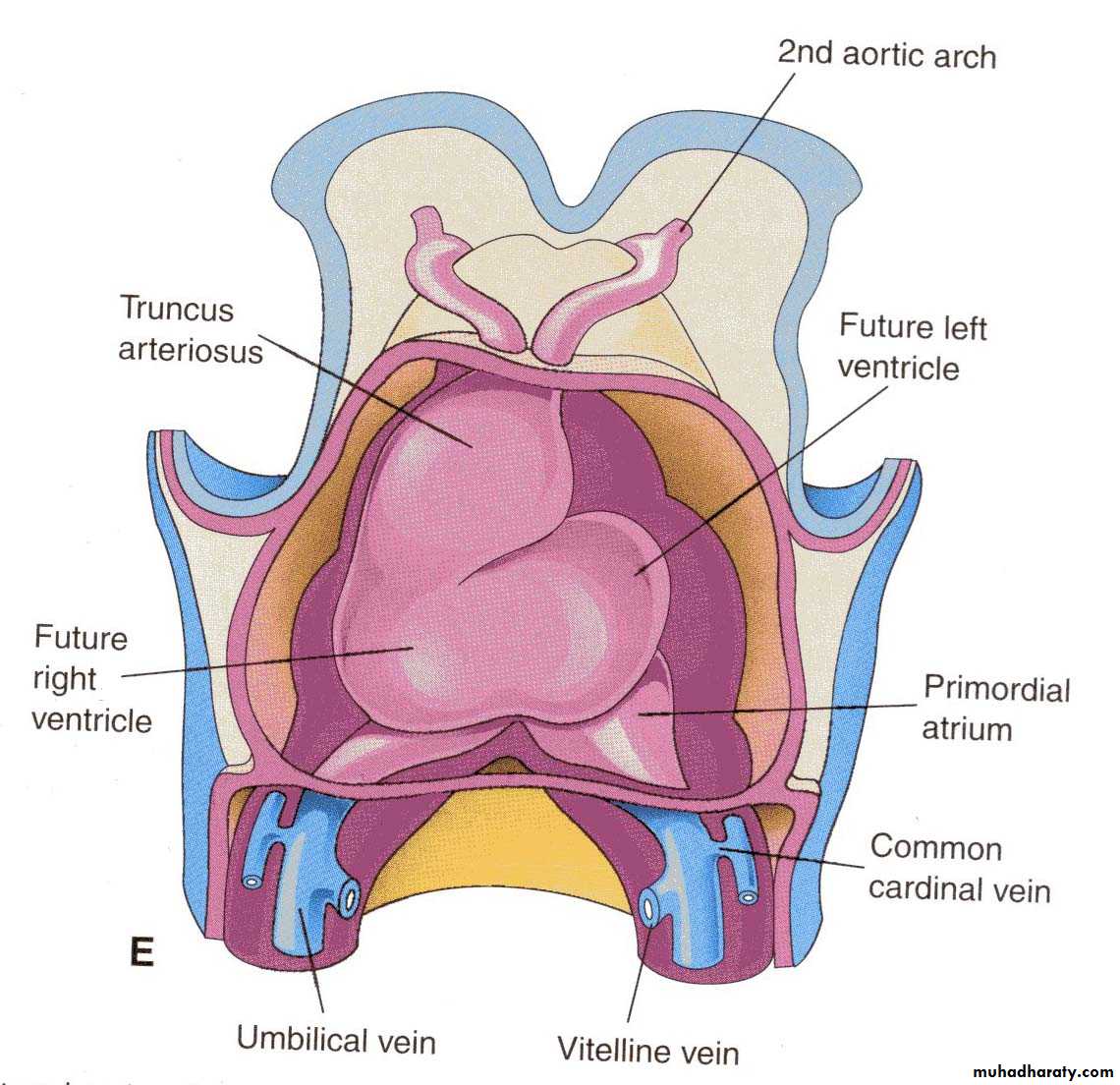
Sinus Venosus
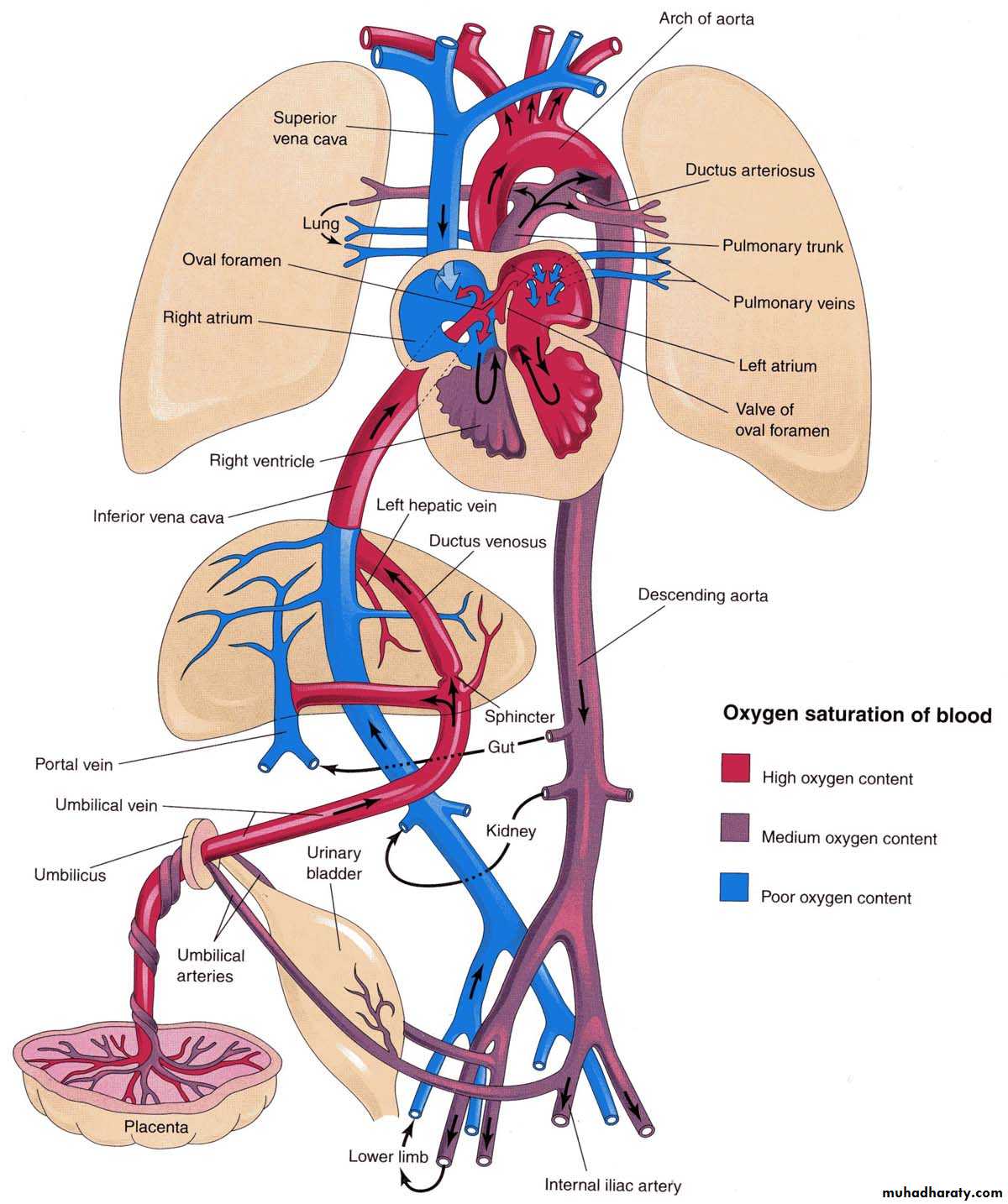
The sinus venosus receives:• The umbilical vein, from the chorion
• The vitelline vein from the yolk sac
• The common cardinal veins from the embryo
Derivatives of Heart Tube
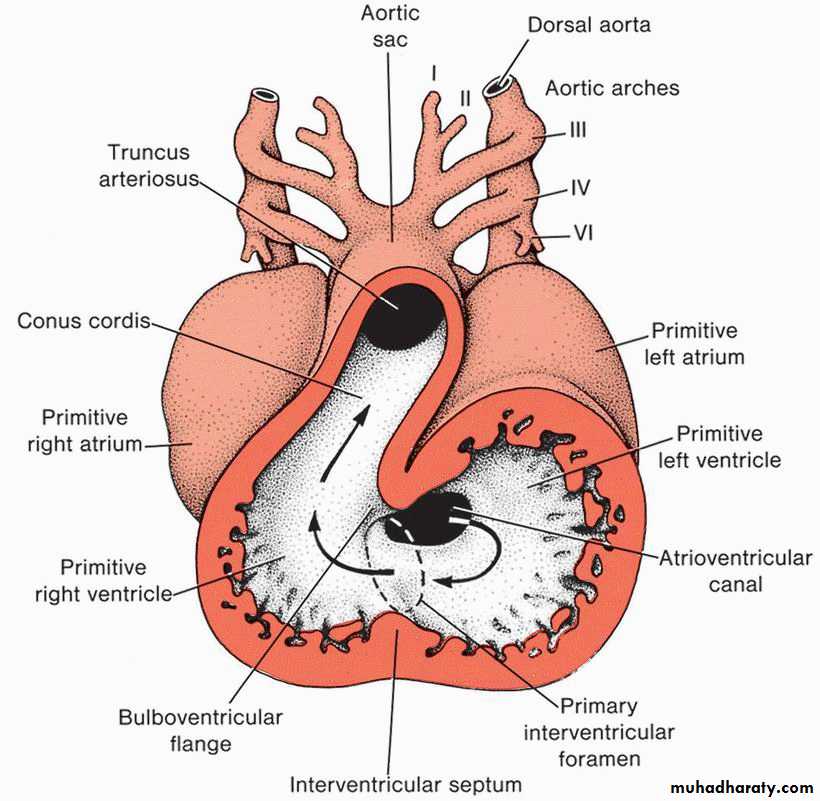
• Bulbus cordis:• proximal third :trabeculated part of Rt ventricle,
• middle third (the conus cordis) forms the out flow of both ventricles,
• distal third (the truncus arteriosus) forms the root of the aorta and pulmonary arteries.
Derivatives of Heart Tube
• Ventricle :forms• trabeculated Lt ventricle
• The sulcus between the bulbus cordis and ventricle forms the primary interventricular foramen.
• The sulcus between ventricle and the atrium forms the atrioventricular canal
Derivatives of Heart Tube
• Atrium: formsthe common atrium, which is the primordium of trabeculated part of the Rt and Lt atria
Derivatives of Heart Tube
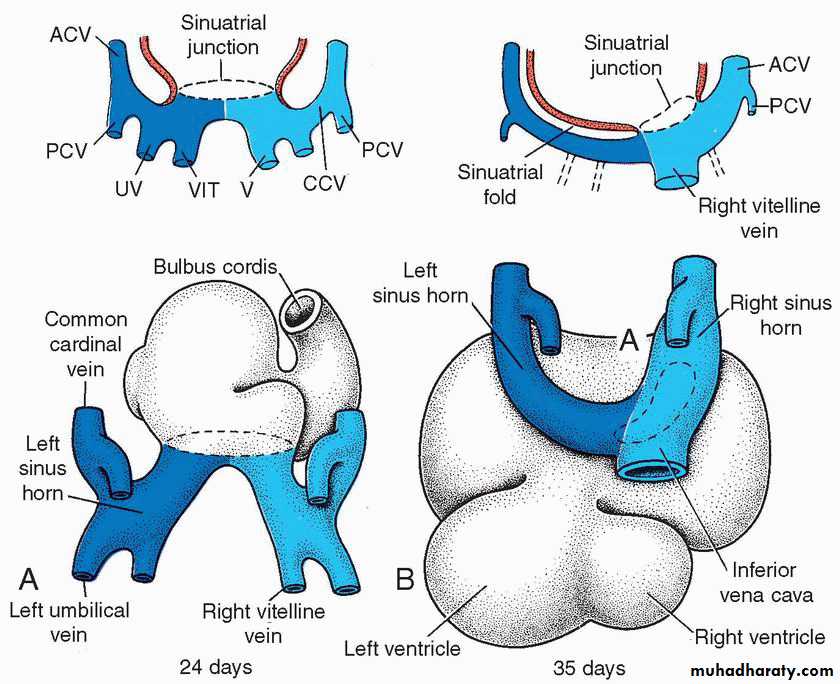
• Sinus venosus:consist of:
• transverse part (body)
• Lt and Rt sinus horns
• each horn recieves: -vitelline vein umbilical vein common cardinal vein
Fate of sinus venosus
On the left side:• Vitelline vein: disappear
• Umblical vein: disappear
• Common cardinal vein: disappear
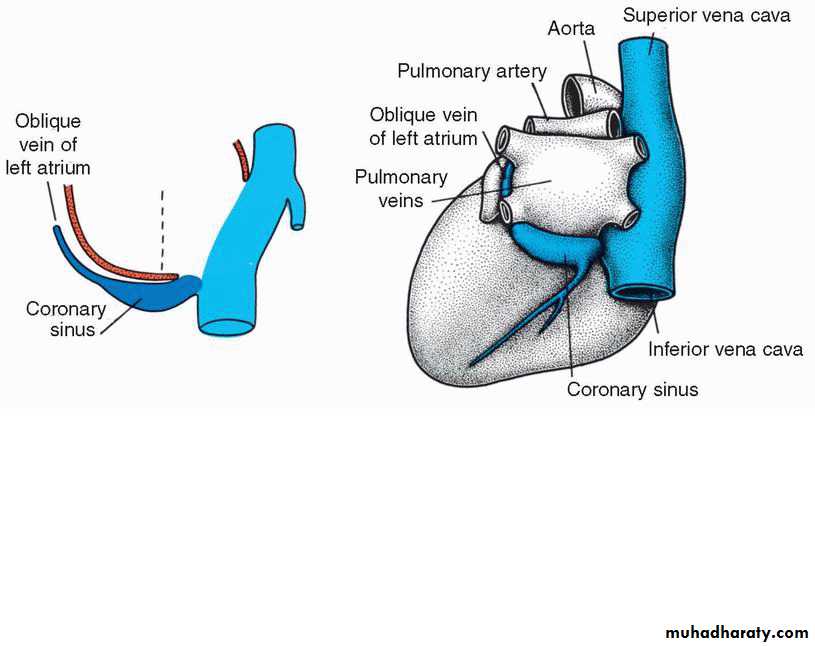
• Lt horn degenerate forming the coronary sinus and the oblique vein of the Lt atrium
Fate of sinus venosus
On the right side:• Umblical vein: disappear
• Vitelline vein: inf vena cava
• Common cardinal vein: sup vena cava
• Rt horn absorbed in the Rt atrium forming the smooth part of atrium(sinus venarum)
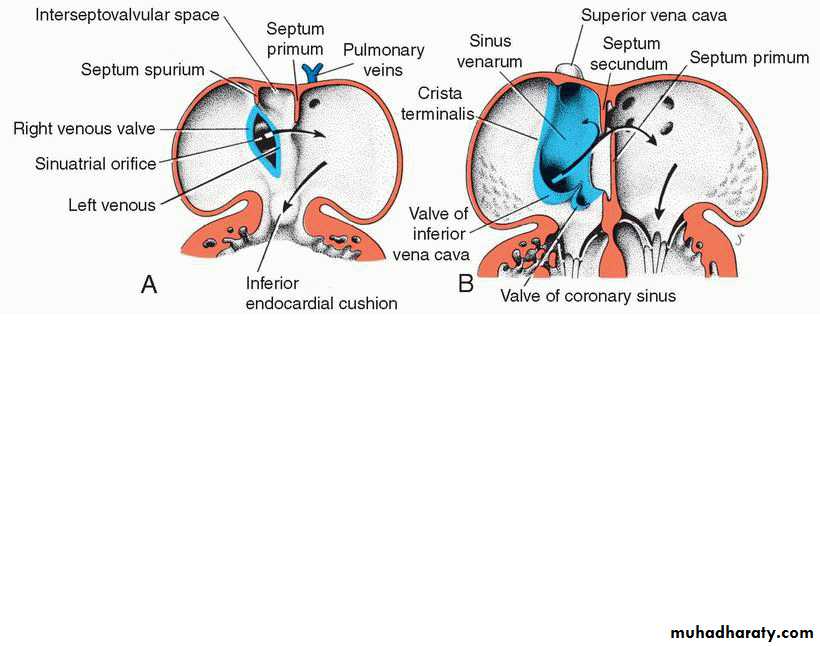
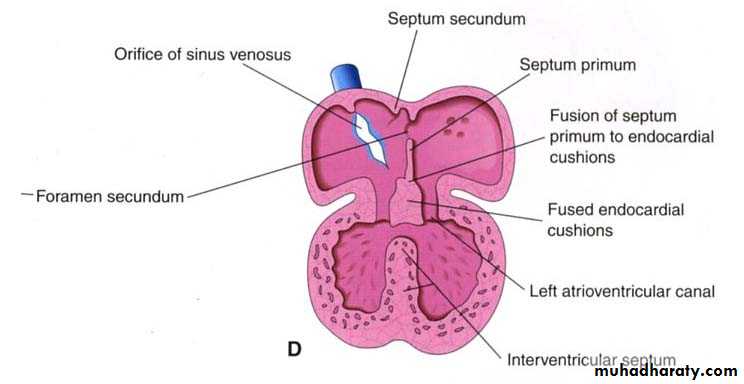
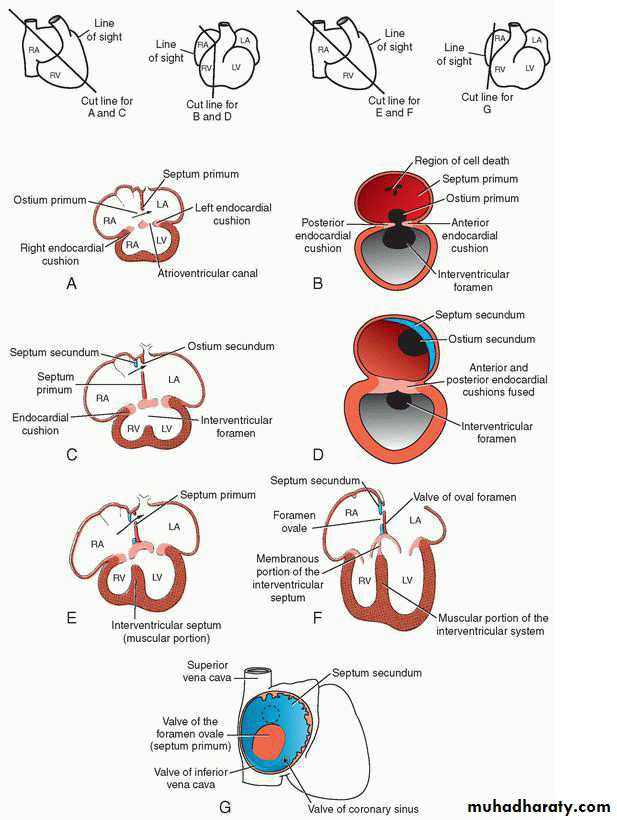
Septation of common atrium
4th w• Septum primum unites with the endocardial cushions.(ostium primum and ostium secondum)
• septum secundum.incomplete septa
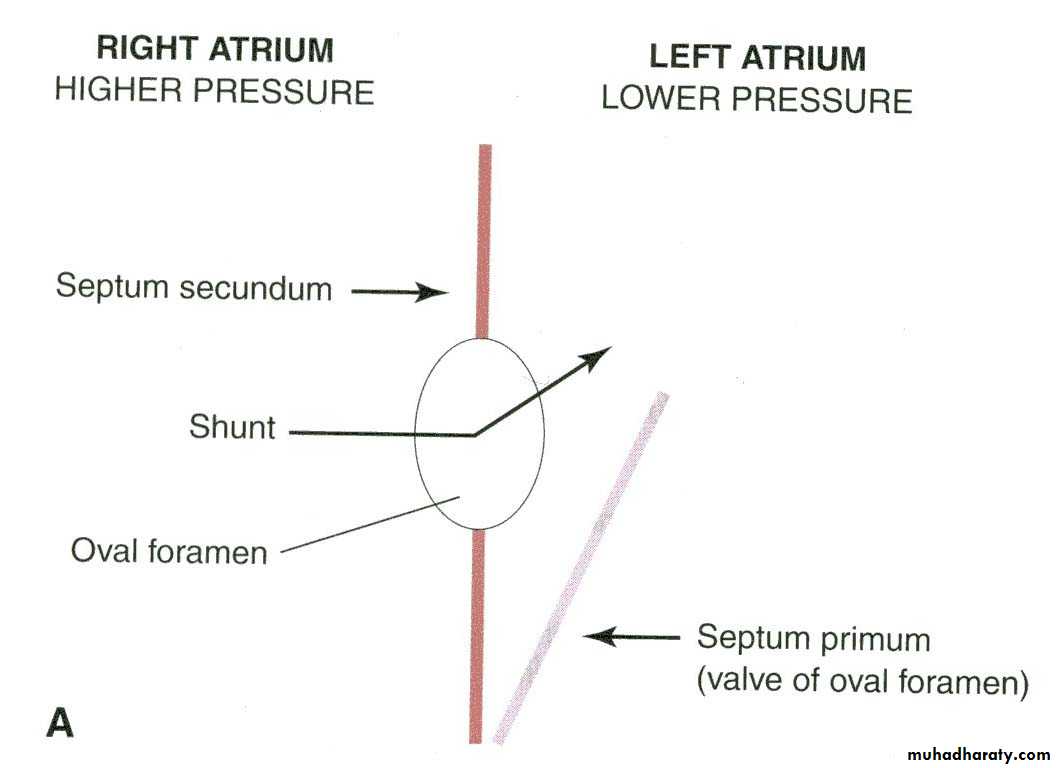
Septum secundum forms foramen ovale, opening between the atria.
Part of septum primum, forms valve for foramen ovale.
Septation of common atrium
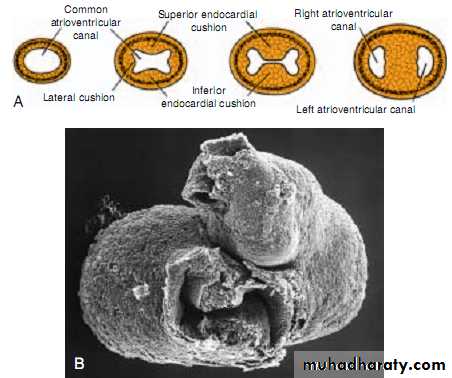
Septation of AtrioVentricular Canal
Endocardial cushions form on the dorsal and ventral walls of the atrioventricular canal.They fuse, dividing the atrioventricular canal into right and left atrioventricular canals.
Ventricular Septation
• After 4th week, grow of lateral ventriclular walls on outside and absorbed from inside forming the Trabeculae carnea and papillary muscles.• Medial walls of both ventricles fail to grow and fused with each other forming the muscular interventricular septum
•
Ventricular Septation
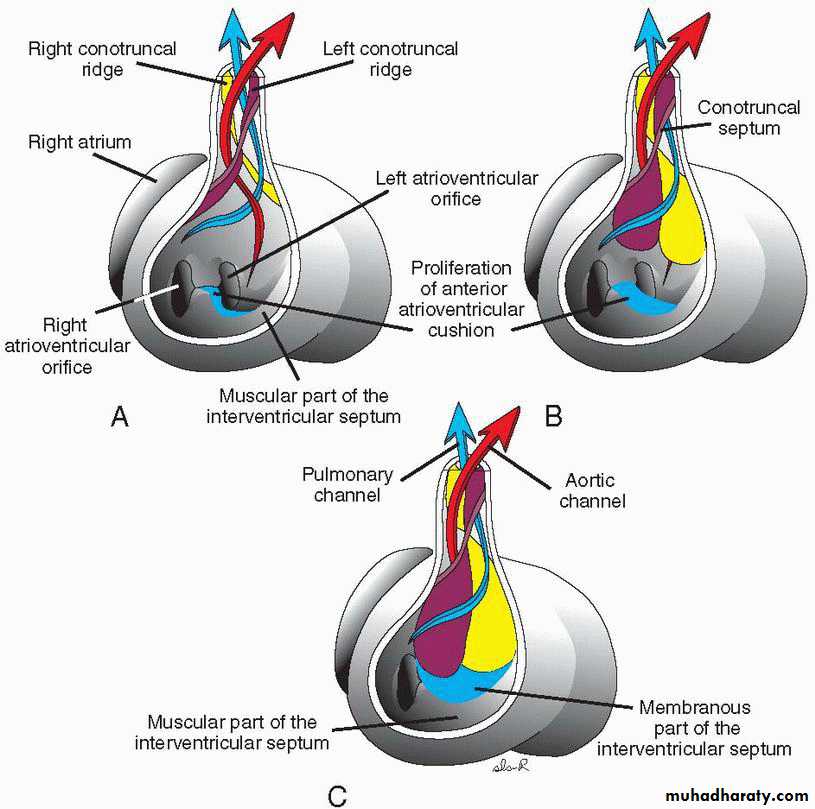
• 3. The opening between the upper free end of this septum and the endocardial cushions is closed by the membranous interventricular septum that is derived from the inferior cushion.• 4. The bulbus cordis is divided into: a. truncus arteriosus, b. conus cordis, and trabeculated part of the RT ventricle.
• 5. The conus and truncus swellings will contribute to the interventricular septum.
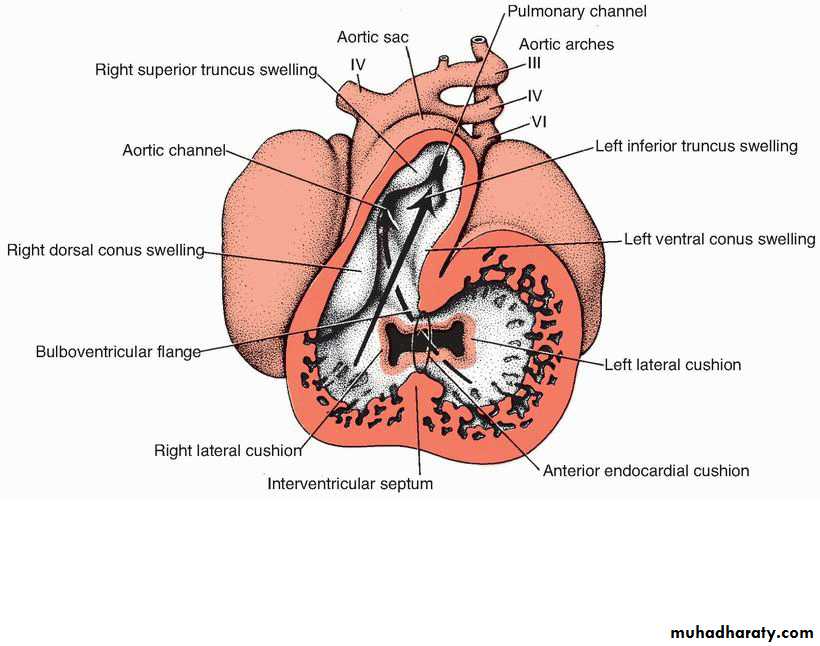
Septation of the truncus arteriosus and conus cordis
5th week, two swellings develop in the trucus arteriosus as a Rt superior and Lt inferior swellings.in the conus cordis as Rt dorsal and Lt ventral swellings.
Septation of the truncus arteriosus and conus cordis
These four swellings grow toward each other in a spiral way to separate the aorta from the pulmonary artery by a spiral septum that is connected with the septum derived from the conus swellings separating the out flow (smooth part) of the Lt and Rt ventricles.Tubercles of the semilunar valves develop inside the truncal swellings forming the semilunar valves
Fetal Circulation Course of the blood from the Placenta to the heart. Three shunts permits the blood to bypass the liver and lungs. 1-Ductus venosus 2-Oval foramen 3-Ductus arteriosus
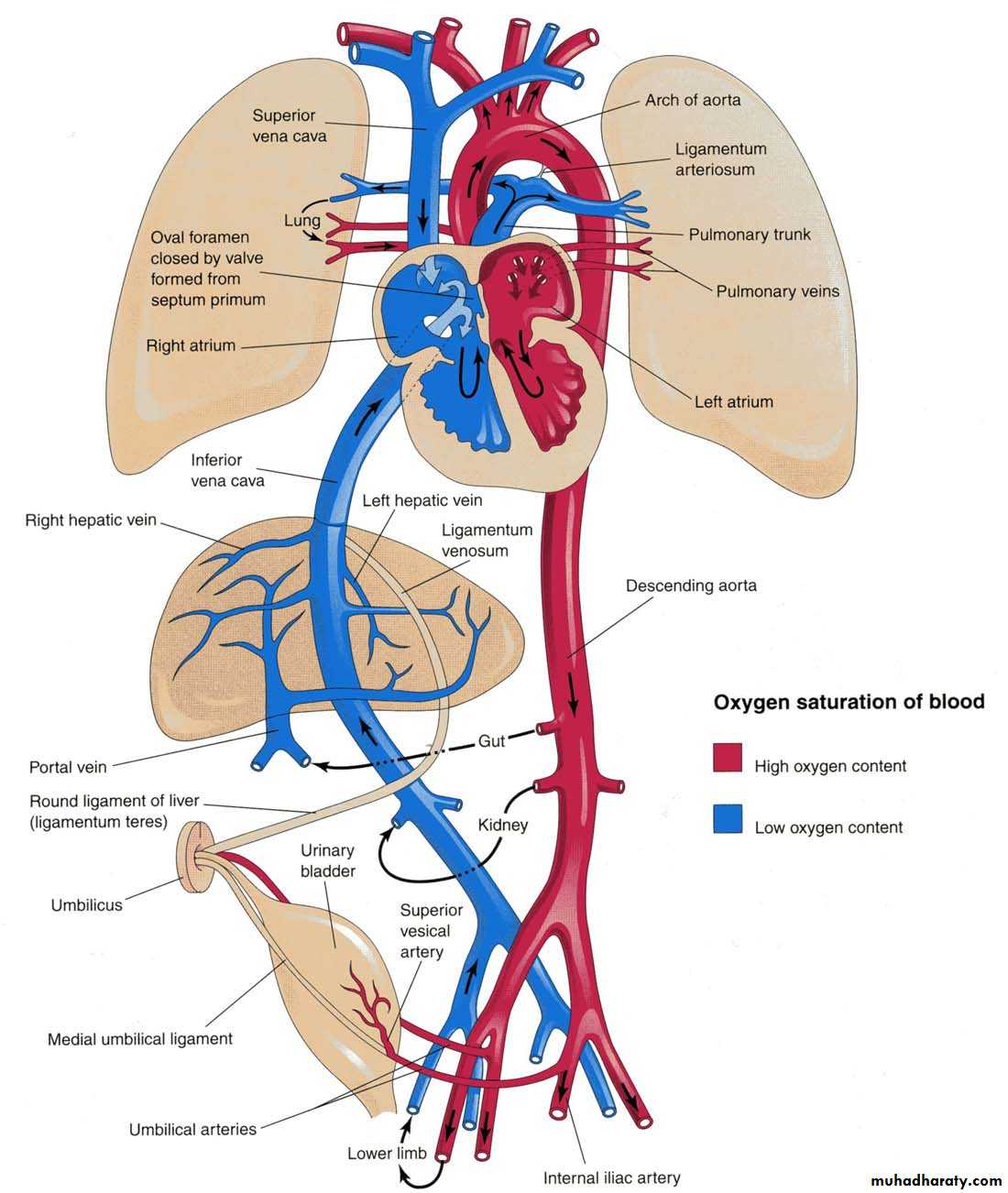
Neonatal Circulation
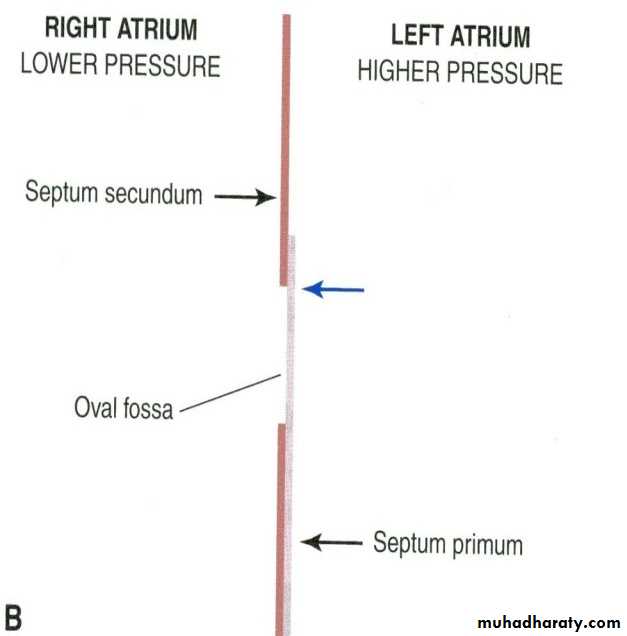
After birth the three shunt that short-circulated the blood during the fetal life cease to function they are 1-Ductus arteriosus became ligament. 2-Ductus venosus became ligament. 3-Oval foramen is closed by septum primum.Cynotic Cardiac Malformation
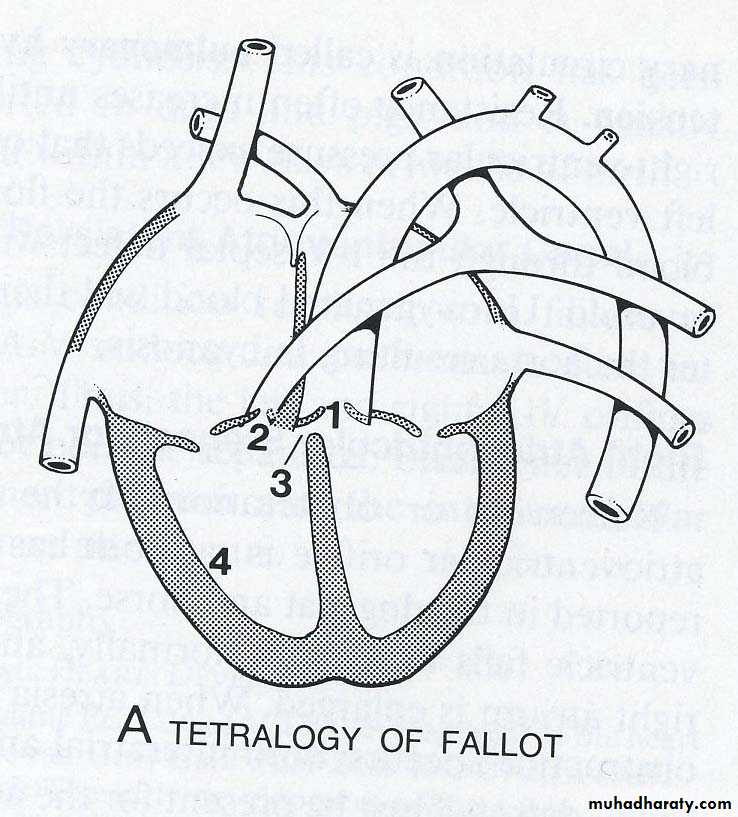
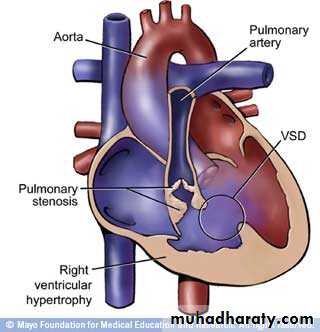
Teratology of Fallot1-overriding of aorta 2-Pulmonary stenosis 3- I-V Septal Defect
4-Dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle
Causes of Defects
Unknown causes
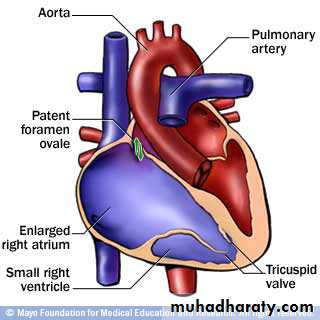
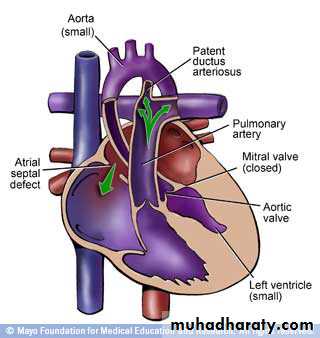
Genetic causes, e.g. ASD and hypoplastic left heart syndrom
Environmental factors:
Causes of Defects
• Infections• Exposure to chemicals
• Alcohol and cocaine
• drugs
• Chronic illneses
Causes of Defects
• Heart defects can be part of a wider pattern of birth defects. E.g. chromosomal abnormalities• Heart defects also are common in children with a variety of inherited disorders
Types of CHD
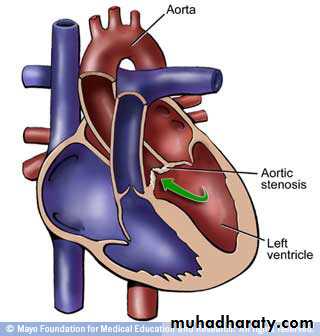
Obstructive defects:• Aortic stenosis
Types of CHD
Obstructive defects:
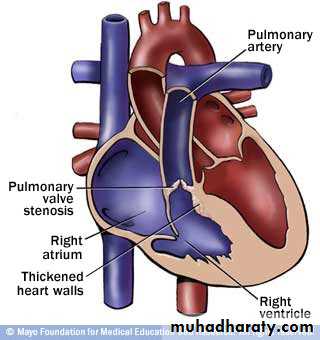
• Pulmonary stenosis
•
Types of CHD
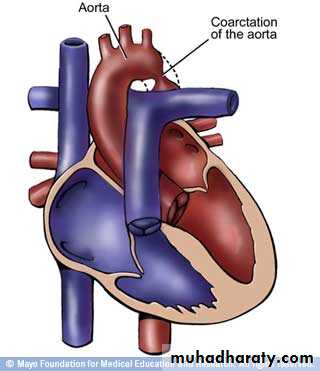
Obstructive defects:• Coarctation of aorta
•
Types of CHD
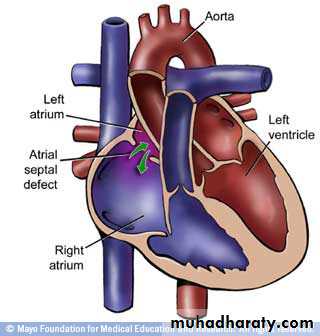
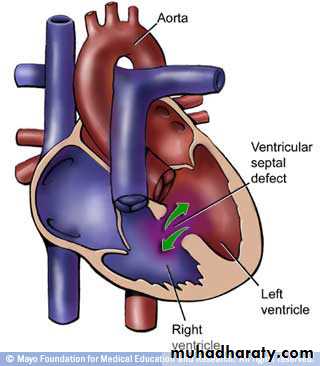
• ASD• VSD
•
Types of CHD
• VSD
•
Types of CHD
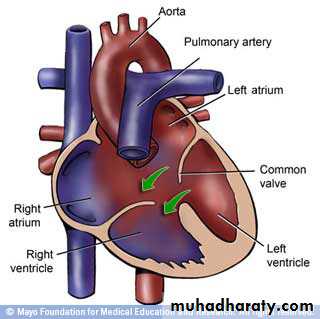
• VSD• Aterioventricular canal defect
Types of CHD
• canal defect• Ebestein anomaly
•
Types of CHD
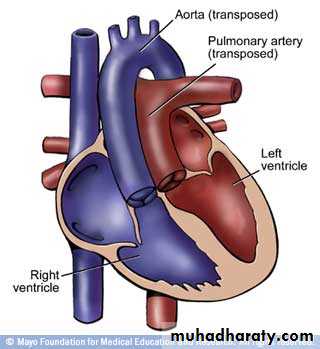
• TOF• Transposition of great vessels
Types of CHD
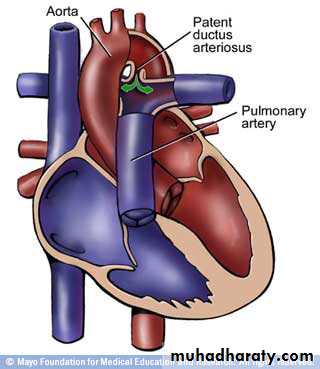
• PDA• Hypoplastic left heart syndrom
Types of CHD
• Dextrocardia• Ectopia cordis
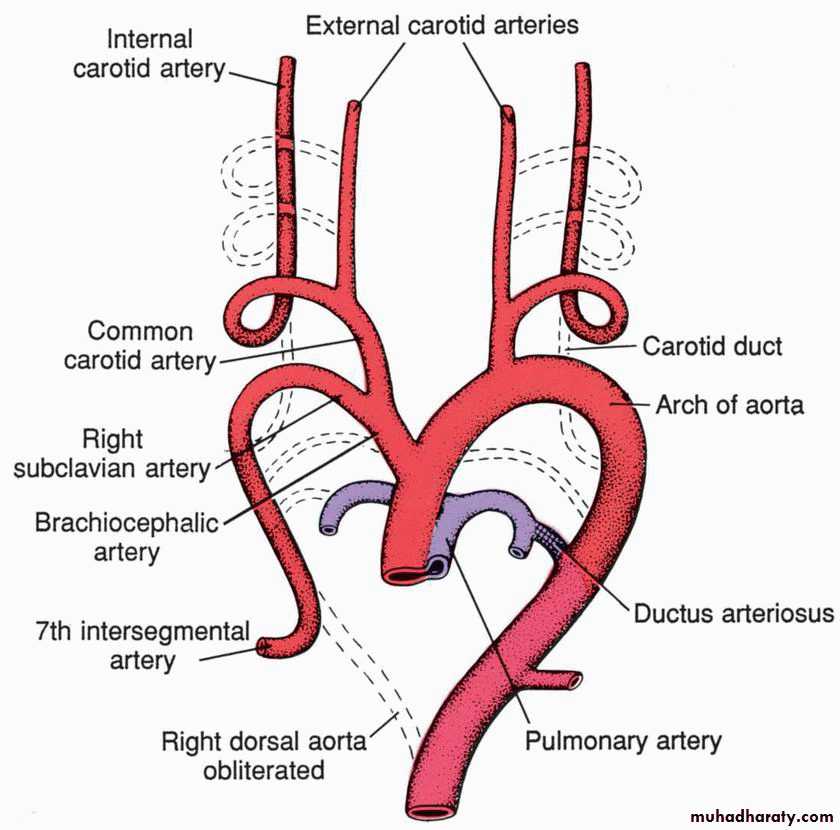
Arterial system
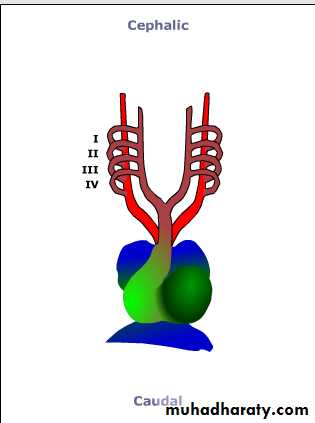
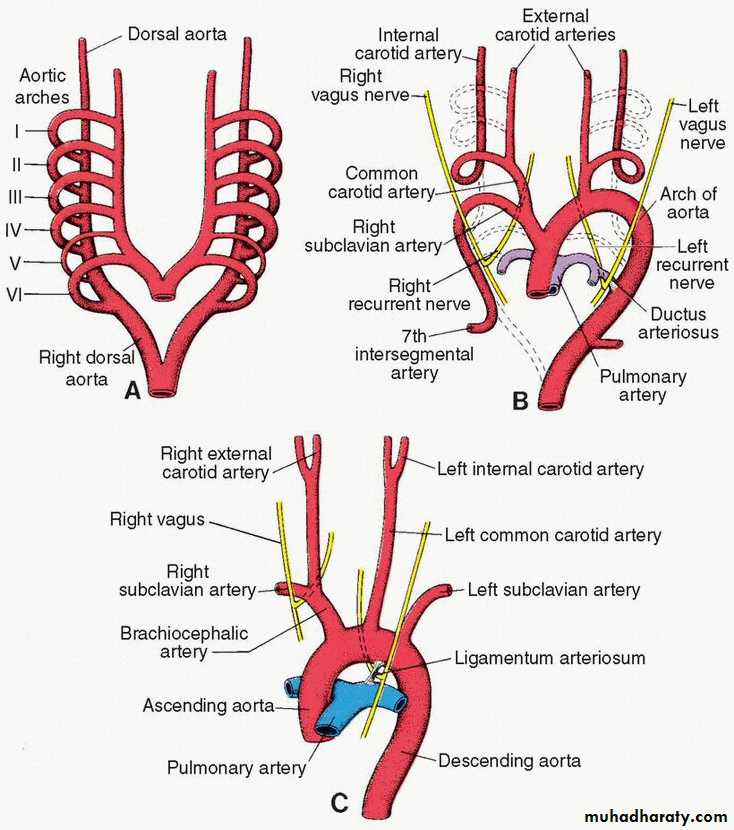
Each of the pharyngeal arches has its own arterycalled aortic arches that originate from root of aorta (the aortic sac), and end into the dorsal aorta.
There are 6 pairs of aortic arches
5th arch often underdeveloped or absent.
Aortic arches
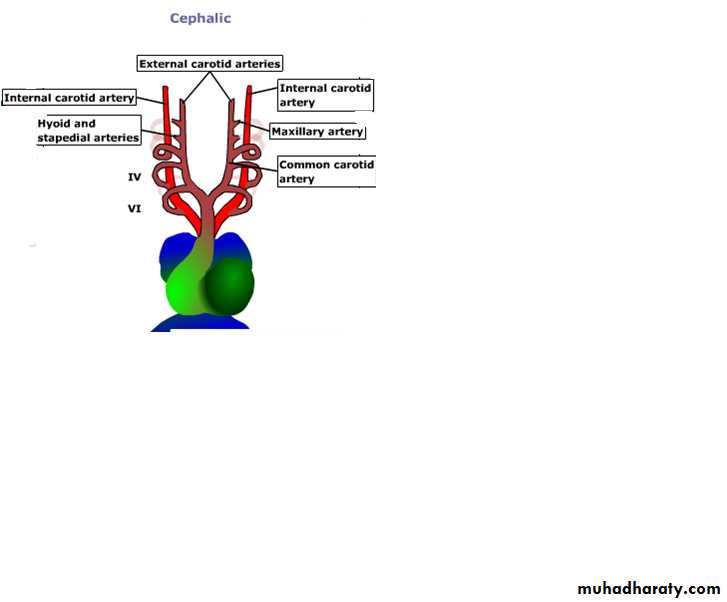
The first aortic arch: largely disappears, remnant of it forms the maxillary artery.The second aortic arch: also disappears, remnant of it forms the hyoidal and stapedial arteries.
Aortic arches
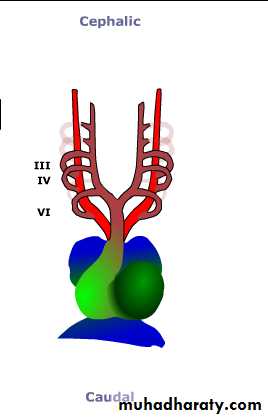
The third aortic arch: forms common carotid artery and the beginning of internal carotid artery. Continuation of internal carotid is derived from dorsal aorta distal to third arch.Aortic arches
The forth aortic arch:• left side :arch of aorta.
• right side: forms the beginning of the Rt subclavian artery, the continuation of it is derived from the Rt dorsal aorta connecting the 4th, 5th, and 6th aortic arches and also by the 7th intersegmental artery.
Aortic arches
The sixth aortic arch: (pulmonary arch) it forms pulmonary arteries.The connection of the RT sixth arch and the Rt dorsal aorta will disappears, while the connection of the 6th arch with the dorsal aorta forms the ductus arteriosus on the left side.
During aortic arches development, there will be disappearance of the following:
1.the bilateral dorsal aortae between the 3rd and the 4th arches (called the carotid arch).2.the Rt dorsal aorta between the origin of the Rt 7th intersegmental artery and the junction with the left dorsal aorta.
During heart descends from neck to thoracic cavity the following two changes occur:
1.the Lt subclavian artery (originating from the Lt 7th intersegmental artery) become nearer to the left common carotid artery.2.the recurrent laryngeal nerve (which is the nerve of the 6th pharyngeal arch) hooks around the distal part of the left 6th arch (forming the ductus arteriosus) to reach the larynx. On the right side, the nerve hook ascends superiorly because of the disappearance of the distal part of the 6th aortic arch, thus hooking around the Rt subclavian artery.
Venous System
• the vitelline system, which develops into the portal system;• the cardinal system, which forms the caval system
• the umbilical system, which disappears after birth.
The complicated caval system is characterized by many abnormalities, such as double inferior and superior vena cava and left superior vena cava.
Changes at Birth
In the circulatory system the following changes take place at birth and in the 1st postnatal months:• The ductus arteriosus closes; becomes ligamentum arteriosum
• The oval foramen closes;
• The ductus venosus close; becomes ligamentum venosum
• The umbilical vein obliterated forming the ligamentum teres hepatis
• The umbilical arteries form the medial umbilical ligaments.