-To describes the gluteal region
-To list its muscles, vessels & nerves
-To specify the site of injection
-To demonstrate some important pathologies affecting the
structures in the region
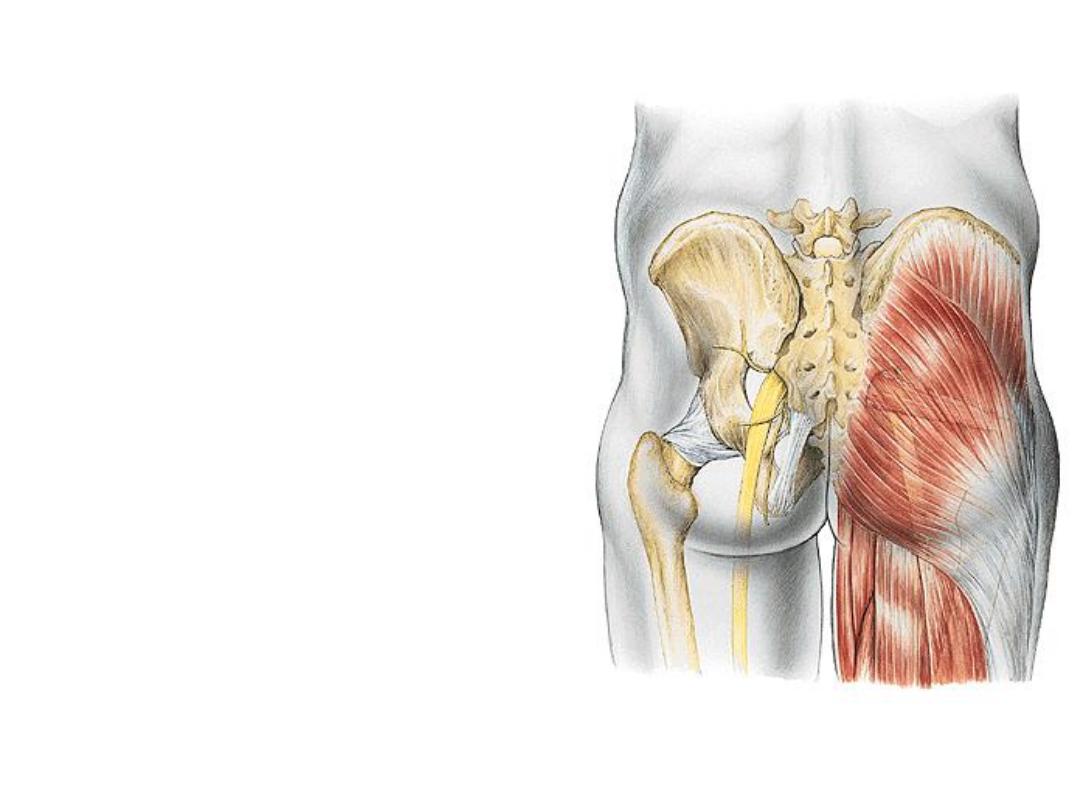
-This region is anatomically related to
the trunk & functionally to the LL
-It is bounded by the iliac crest above
& G fold below
-Muscles in the region are mainly
extensors,
abductors
&
lateral
rotators of the femur on the hip
-The region communicates with the
pelvic cavity and perineum through
the
greater
and
lesser
sciatic
foramina
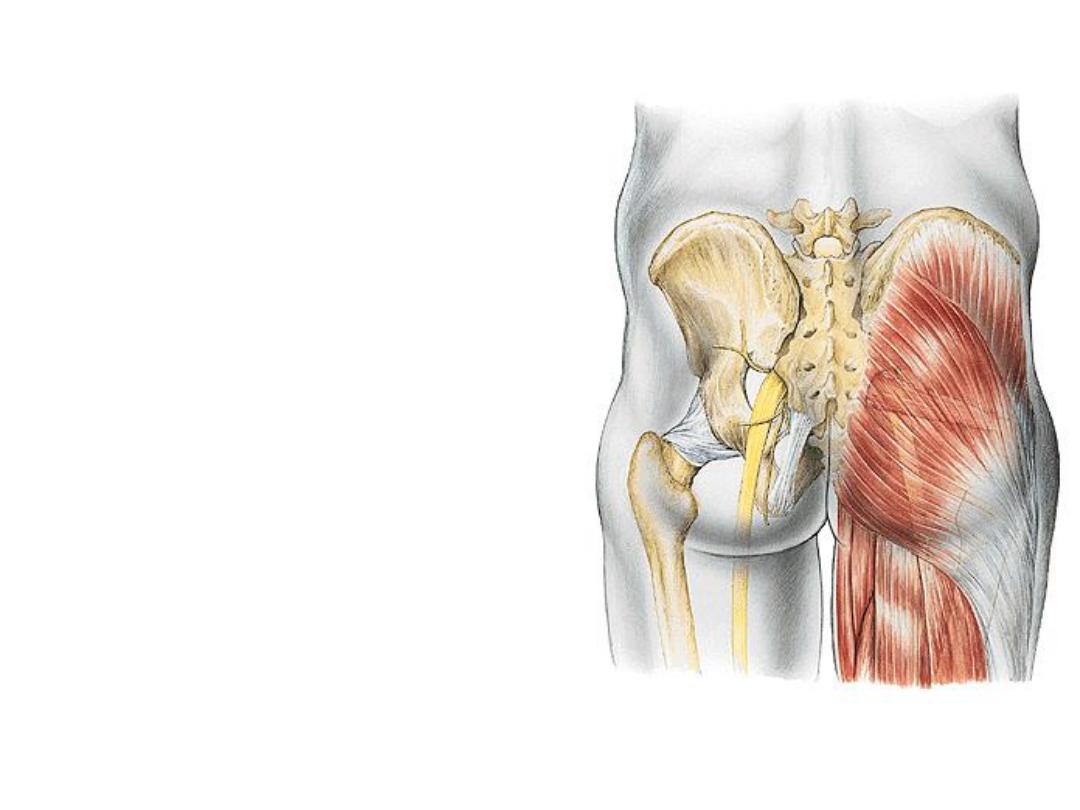
-Inferiorly, it is continuous with the
posterior thigh (hamstring comp).
-The sciatic nerve enters the lower limb
after crossing the inferomedial part of
the G region
-The
subcutaneous
fat
is
well
developed in this region as it is the site
where one sits on
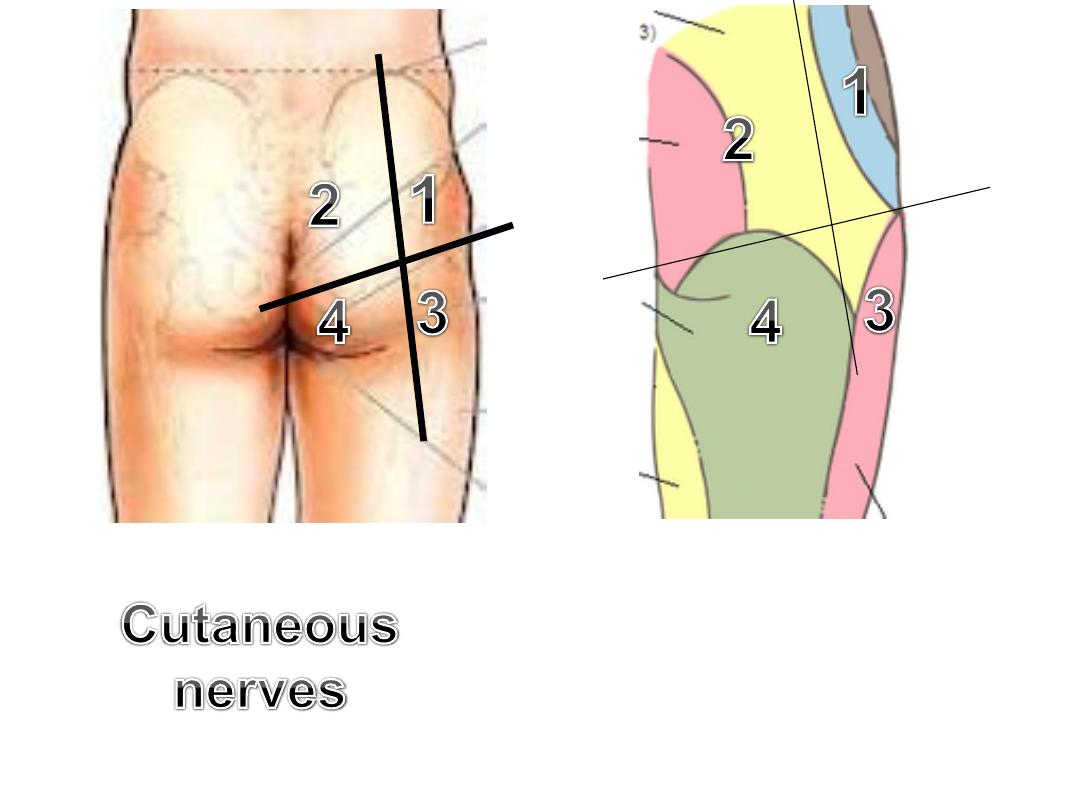
1-
Subcostal (T12)
&
iliohypogastric (L1)
2-
Superior cluneal (L1,2,3)
&
middle
cluneal (S1,2,3)
3- LFCT (L2,3)
4- PFCN (S2,3)
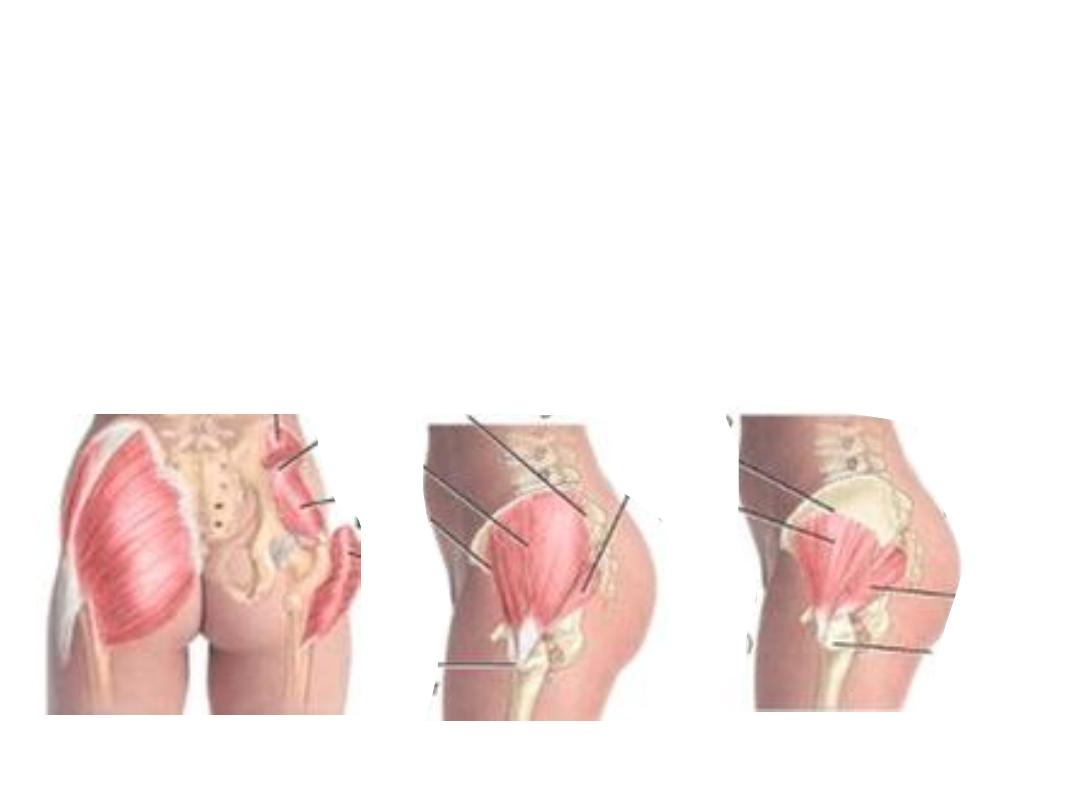
Muscle arrangement:
-The outermost & bulkiest is the gluteus maximus
-Next is the G medius
-After removing G medius a series of muscles appear they are from above
downward:
G minimus, piriformis, gemellus superior, obturator internus, G inferior the
quadratus femoris
-Tensor fascia latae lies anterior to the glutei, lateral to the ASIS
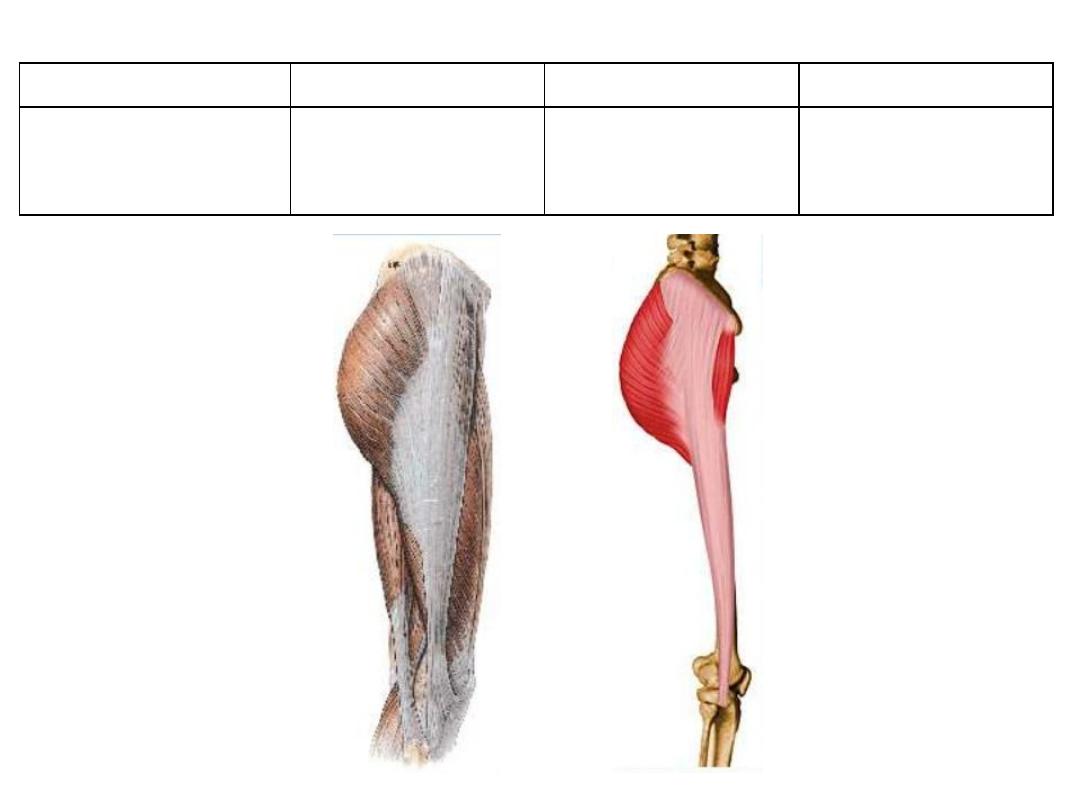
Tensor fascia latae:
Action
Innervation
Insertion
Origin
Stabilizes the
extended knee
Superior gluteal
n. L4,5,S1
Iliotibial tract
Lateral aspect of
iliac crest
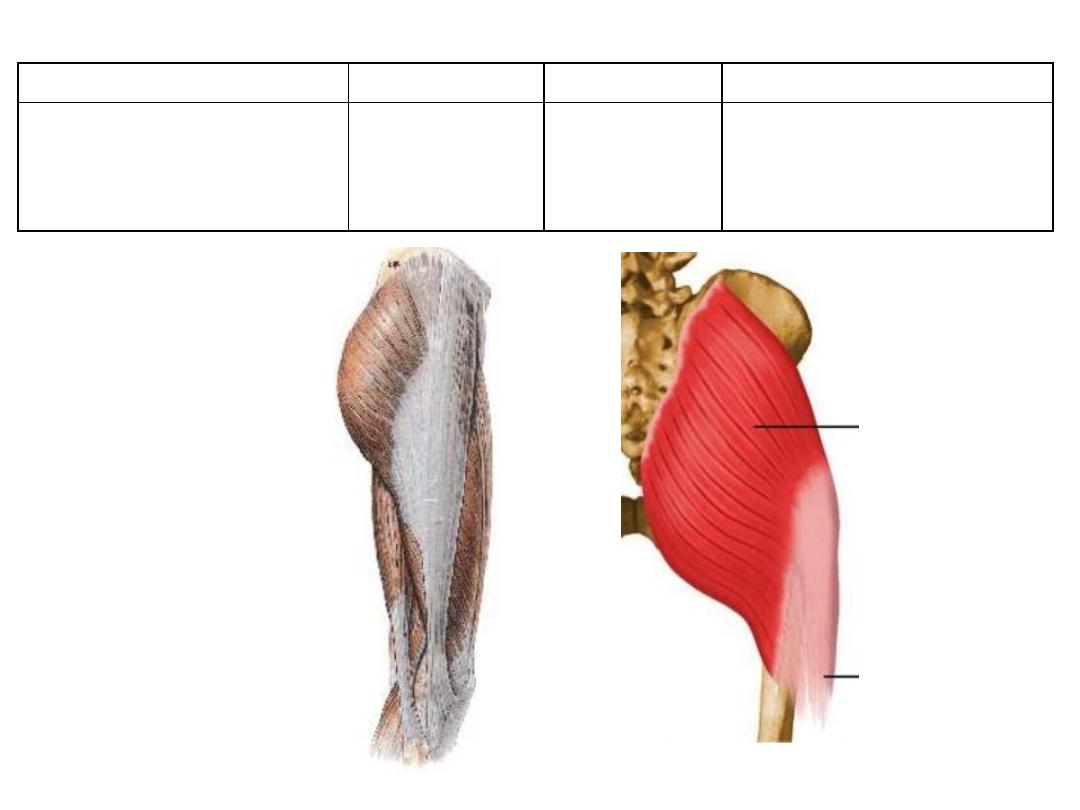
Action
Innervation
Insertion
Origin
-
Extensor, abductor &
lateral rotator of femur
-
Act on IT tract
Inferior
gluteal n.
L5,S1,2
G tuberosity &
iliotibial tract
-
Outer surface of ilium
-
Adjacent sacrum & STL
Gluteus maximus:
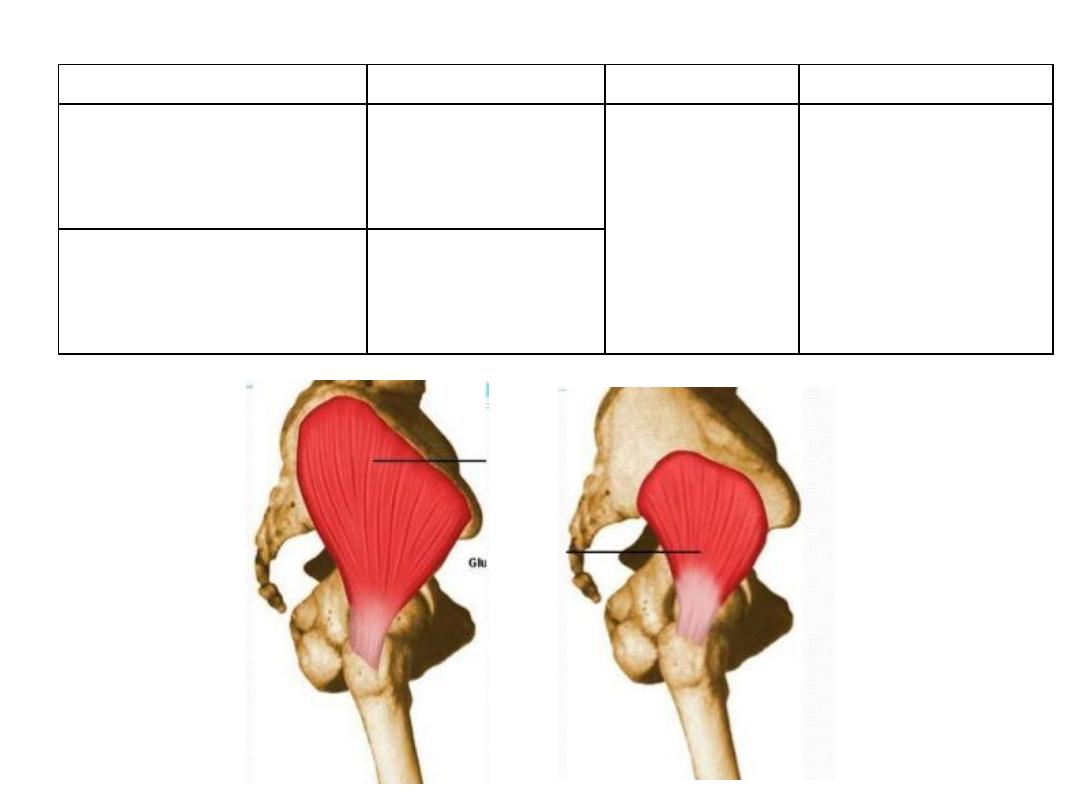
Action
Innervation
Insertion
Origin
Abductor & medial
rotator of the thigh
?
Superior
gluteal n.
L4,5,S1
lateral surface of
the greater
trochanter
External surface of ilium
between anterior and
posterior gluteal lines
anterior surface of
the greater
trochanter
External surface of ilium
between inferior and
anterior gluteal lines
Gluteus medius & minimus:
Me
d
iu
s
Min
imu
s
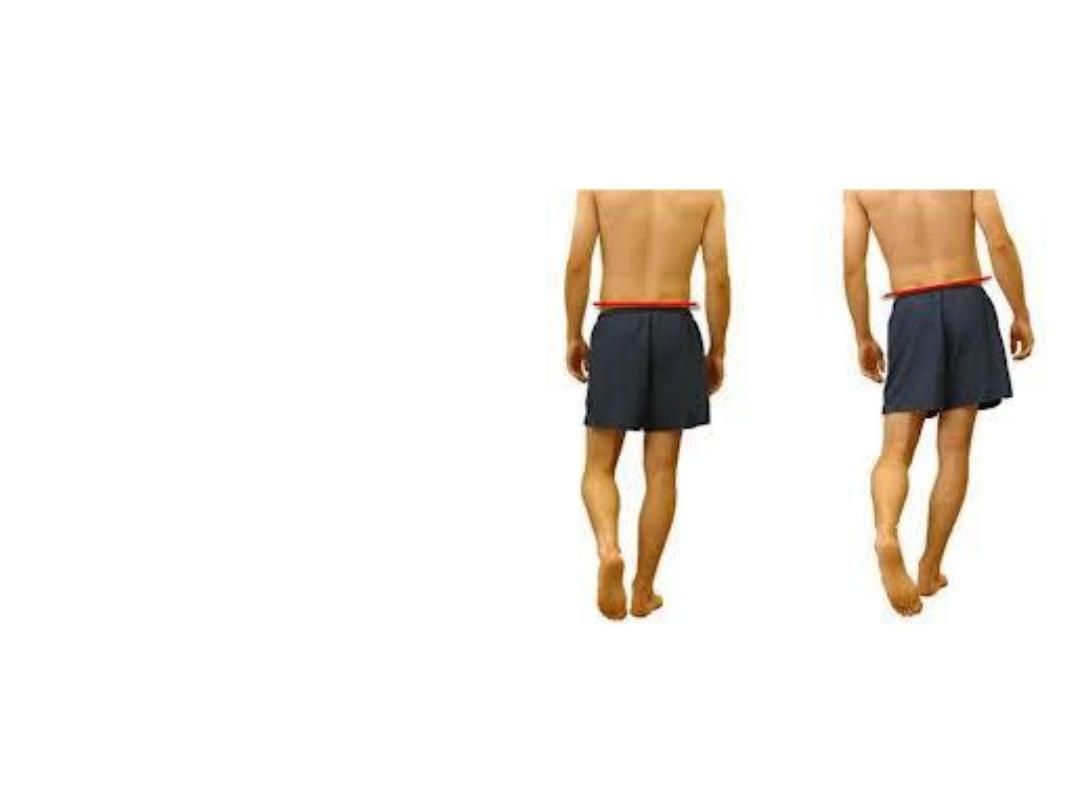

Is thigh abduction so an important
movement?
-Glutei medius & minimus are
important in holding both hips at
the same level & preventing drop
of the lifted side during walking
-Their
paralysis
causes
+ve
Trendelenburg sign (pelvis sags
down when the limb is not weight
bearing0
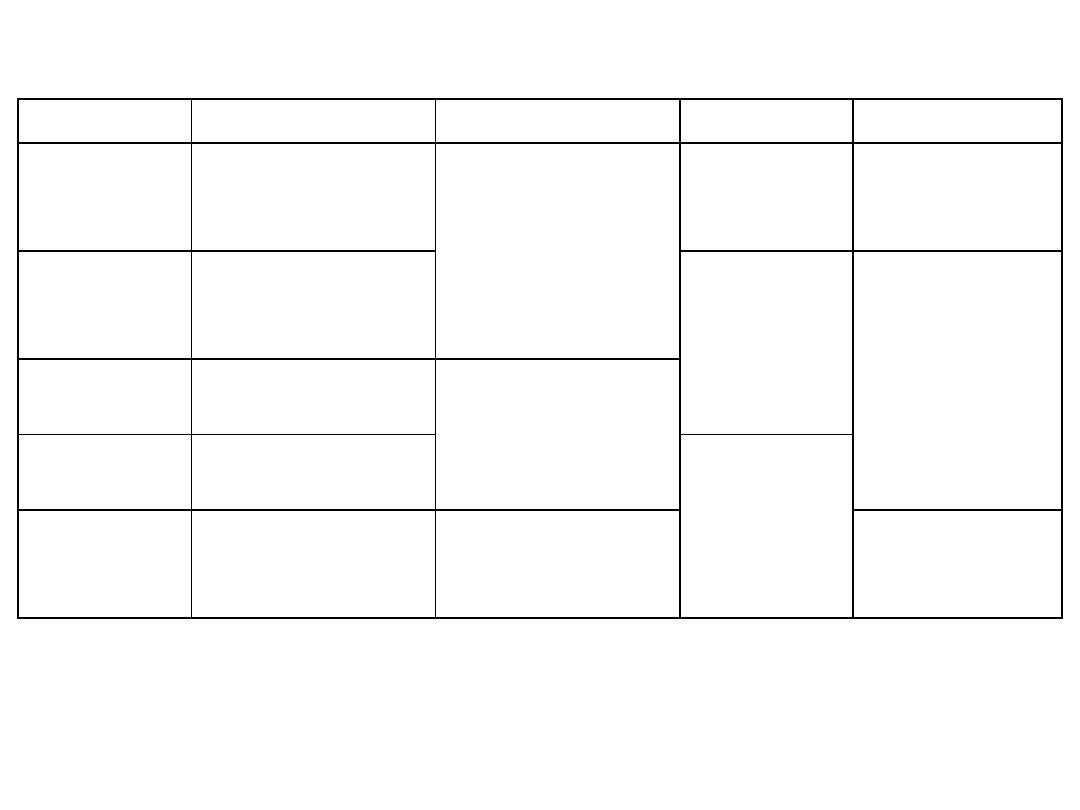
Action
Innervation
Insertion
Origin
Muscle
Lateral rotator
& extensor of
hip
S1,2
Medial side of G
trochanter
Anterior surface
of middle 3
pieces of sacrum
Piriformis
Laterally
rotate the
extended
femur &
abduct the
flexed femur
Nerve to OI
(L5,S1)
Deep surface of
obturator
membrane
Obturator
internus
OI tendon
Ischial spine
Gemellus
superior
Nerve to
QF (L5,S1)
Ischial tuberosity
Gemellus
inferior
Lateral
rotation of
femur
Intertrochanteric
crest
Lateral surface
of iscjium
Quadratus
femoris
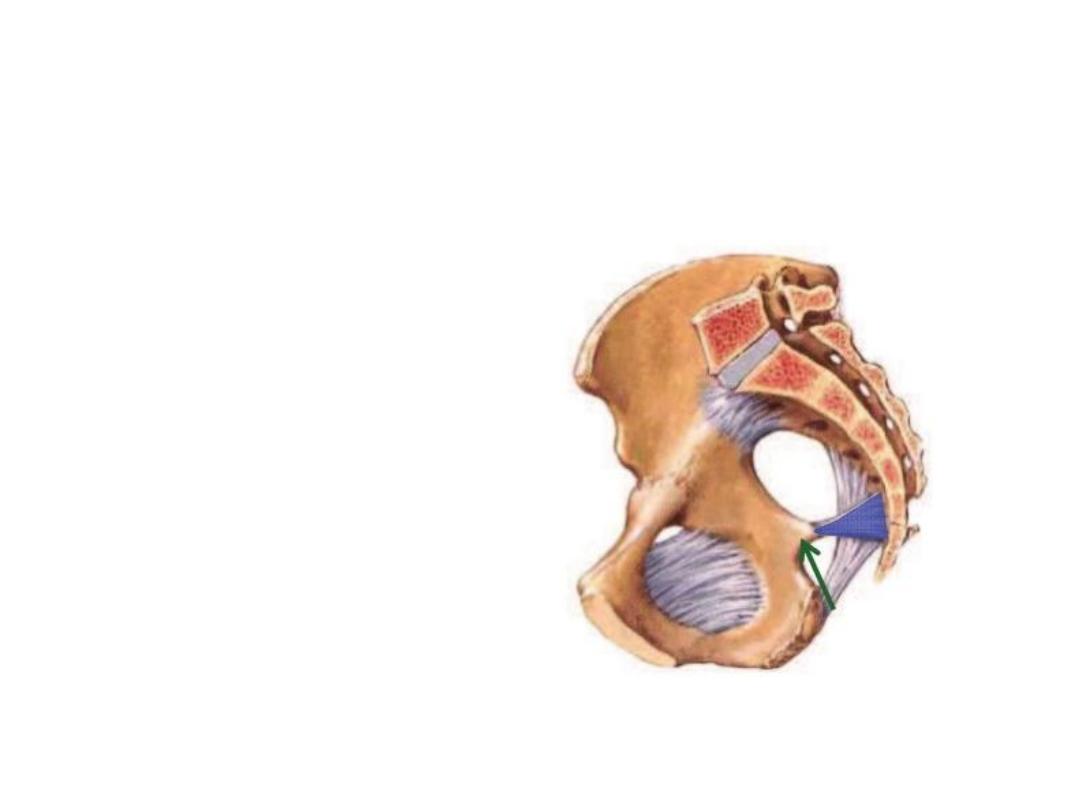
Sacrotuberous & sacrospinous ligaments
convert the sciatic notches of the hip to
foramina:
GSF leads to the pelvis
LSF leads to the perineum
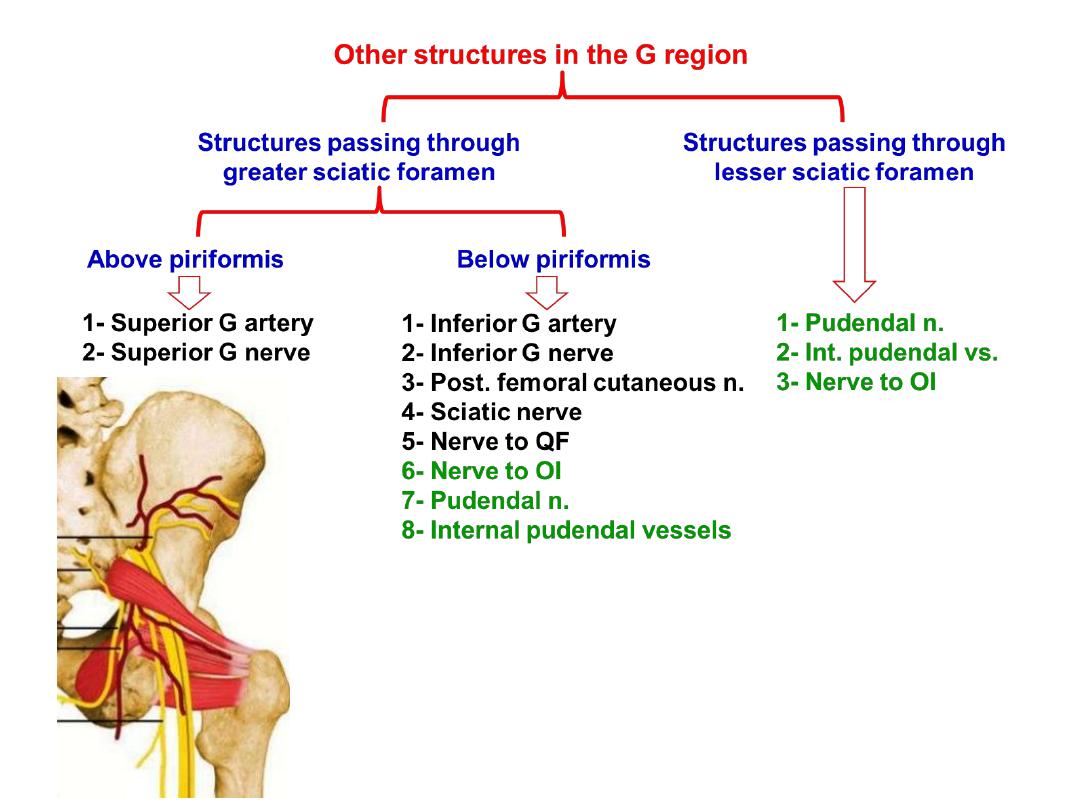
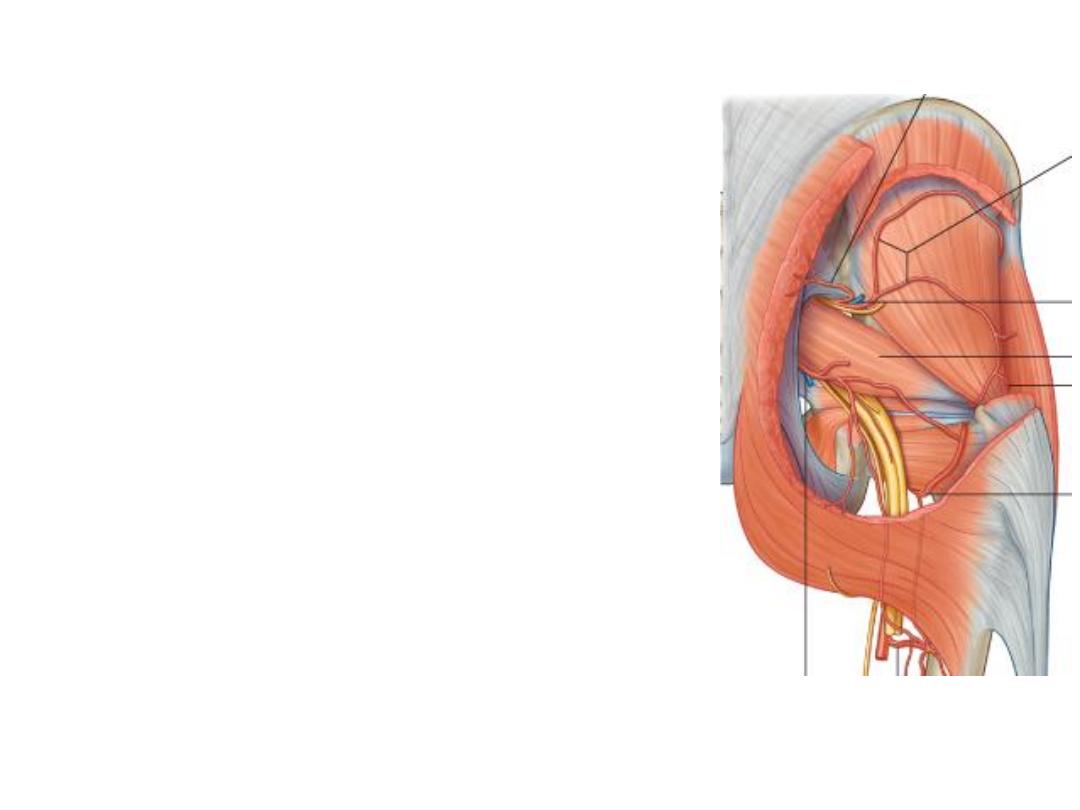
Superior gluteal artery:
-From the posterior division of the internal iliac a.
-In the G region it gives superficial & deep branches
-Superficial; enters G. maximus
-Deep; passes between other 2 glutei supplying
both with TFL & share in the anastomosis around
ASIS
Superior gluteal nerve:
-Arises from the posterior divisions of L4,5,S1
-Passes between the glutei medius & minimus
supplying both with TFL
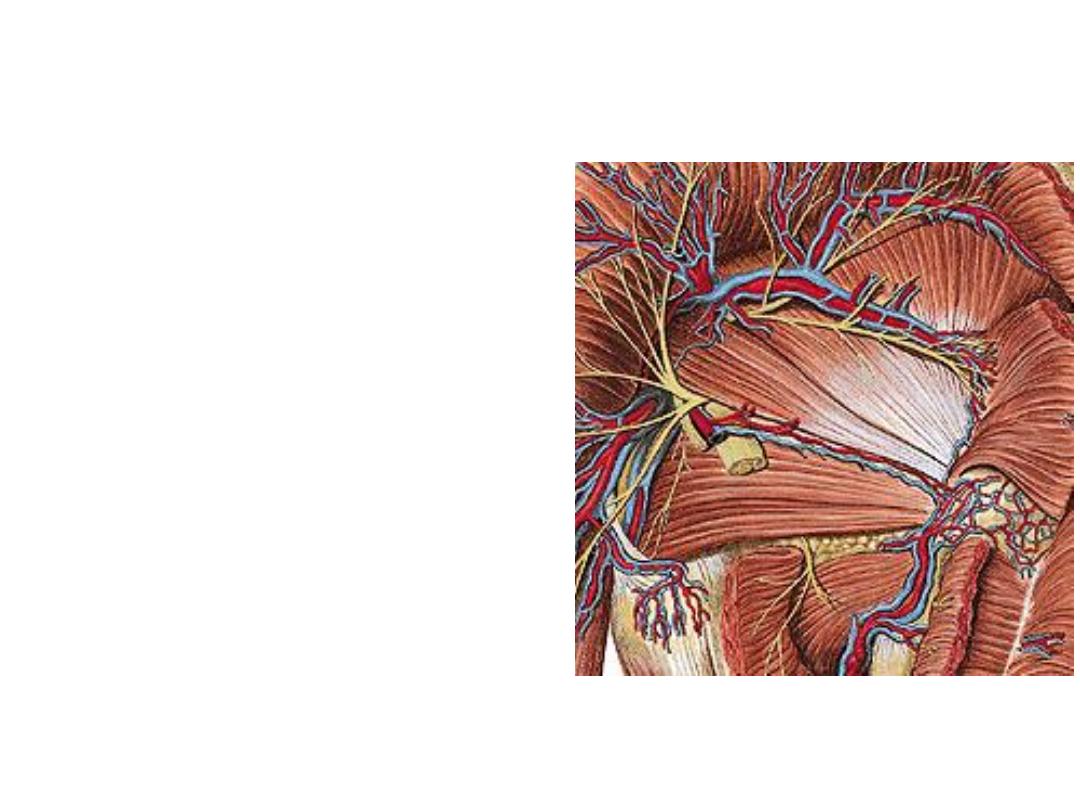
Inferior gluteal artery:
-The largest of the 2 terminal divisions of
the internal iliac a.
-In the G region it lies deep to G maximus
-Accompanies the sciatic n. & PCNT
Inferior gluteal nerve:
-Arises from the posterior division of
L5,S1,2
-Lies superficial to the sciatic nerve
-After a short course it divides into many
branches which enter the deep surface of
G maximus supplying it
Posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh:
-Arises from posterior divisions of S2,3
-Lies behind the sciatic nerve
-Ends in the roof of the popliteal fossa
Branches;
1- Gluteal to the inferomedial quadrant of
G skin
2- Perineal to the skin of perineum
3- Perforating to the skin of the back of
the thigh
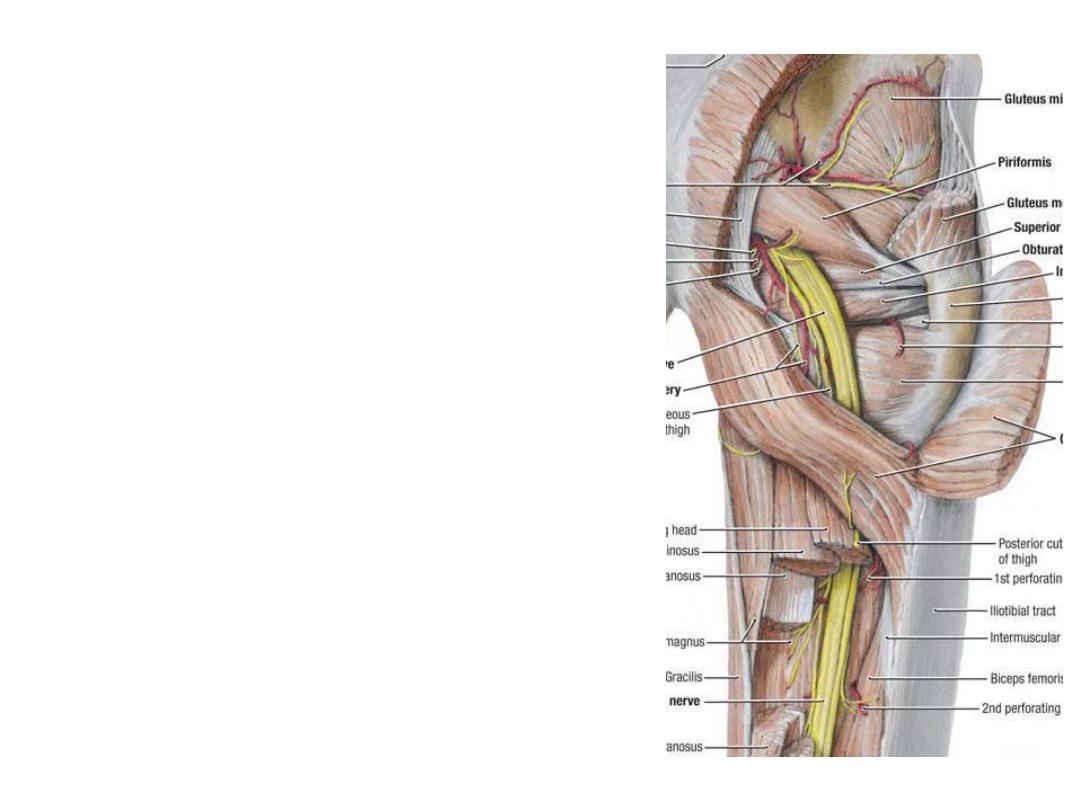
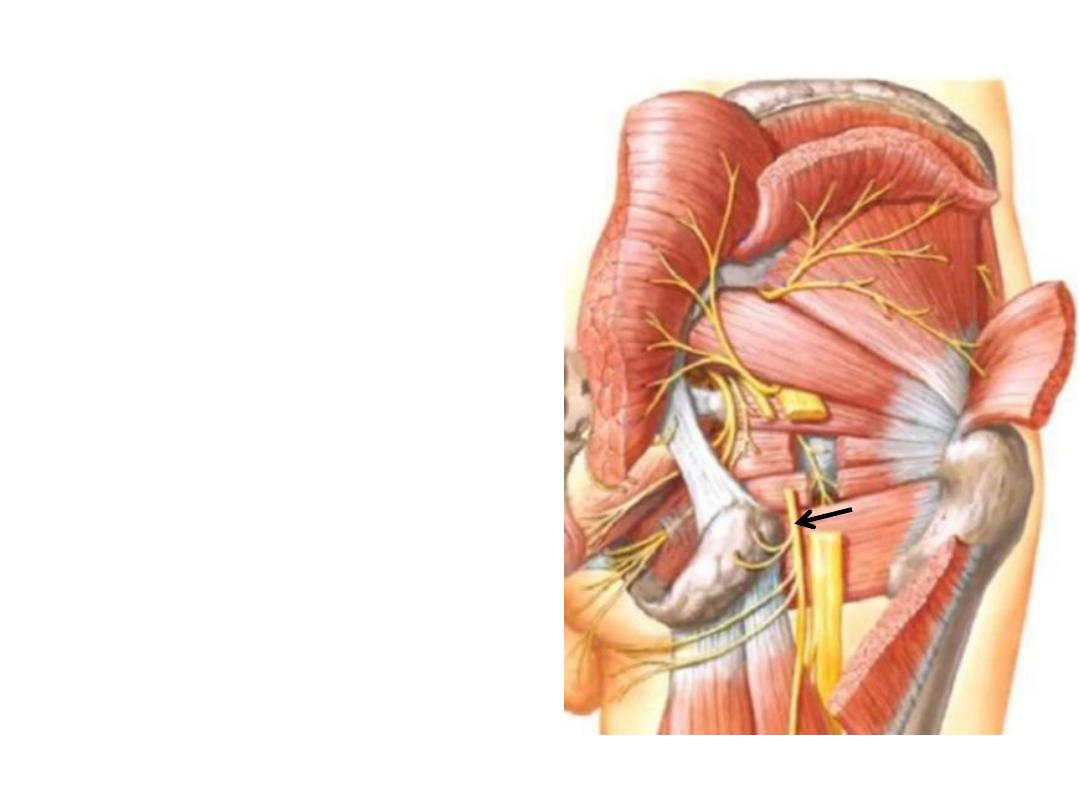
Sciatic nerve:
-The largest nerve in the body
-Lies midway between the ischial tuberosity &
greater trochanter
-Enters between the hanstring muscles where
it divides into its 2 original components at the
upper border of the popliteal fossa
-Components:
1- Tibial part (L4,5,S1,2,3 anterior)
2- Common peroneal part (L4,5,S1,2 posterior)
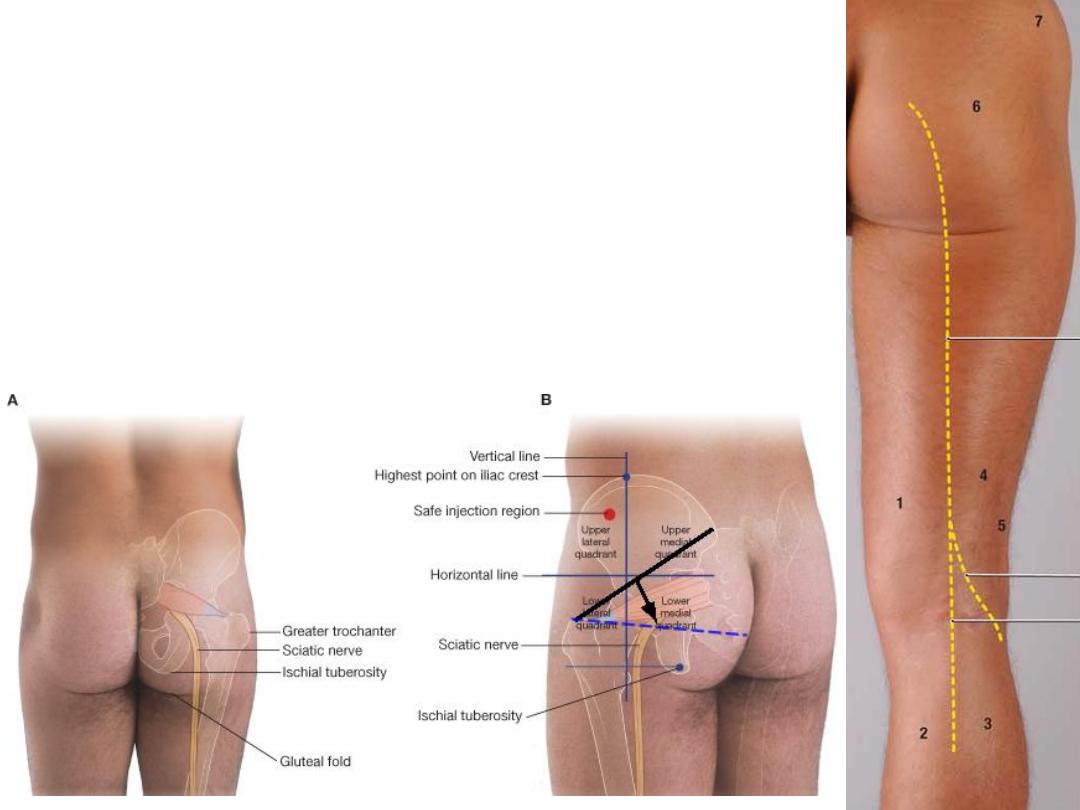
Surface markings of
the sciatic nerve &
the
safe site for i.m
injection
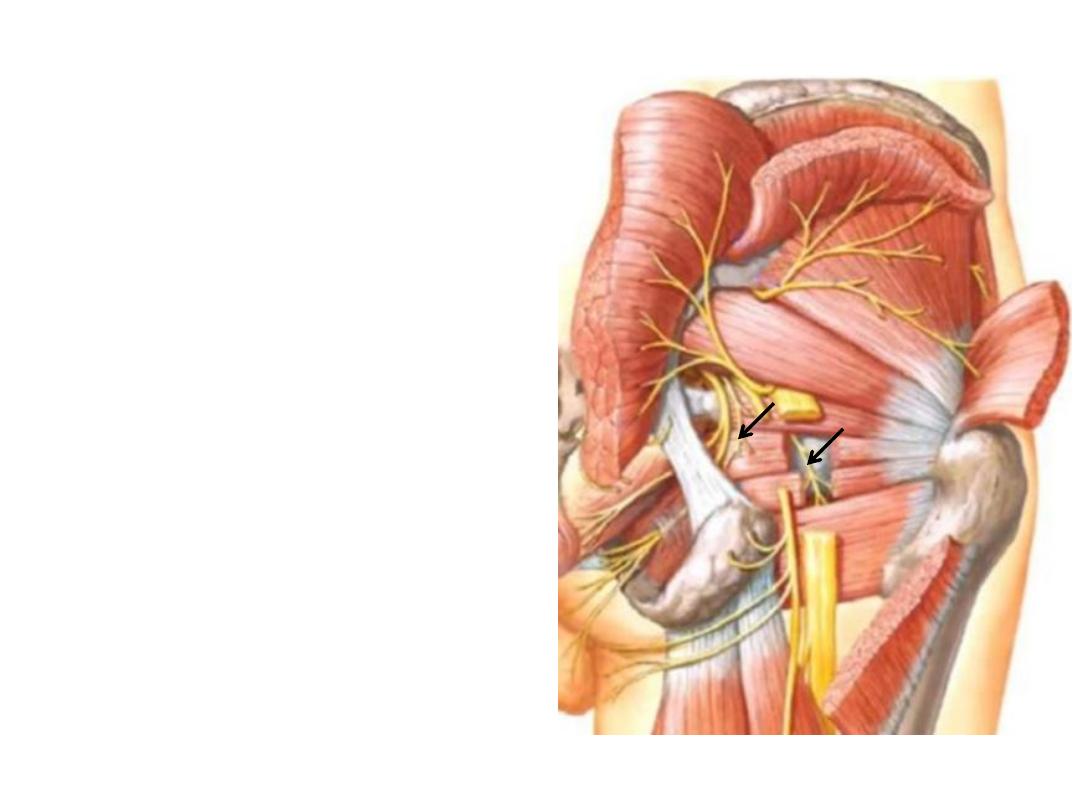
Nerve to obturator internus:
-Arises from anterior divisions of L5,S1
-Lies lateral to the pudendal vessels
-Crosses the ischial spine to enter the
perineum through LSF
-Supplies OI & G superior
Nerve to quadratus femoris:
-Arises from anterior divisions of L5,S1
-Descends anterior to OI & gemelli
-Enters QF at its anterior surface
-Supplies QF & G inferior
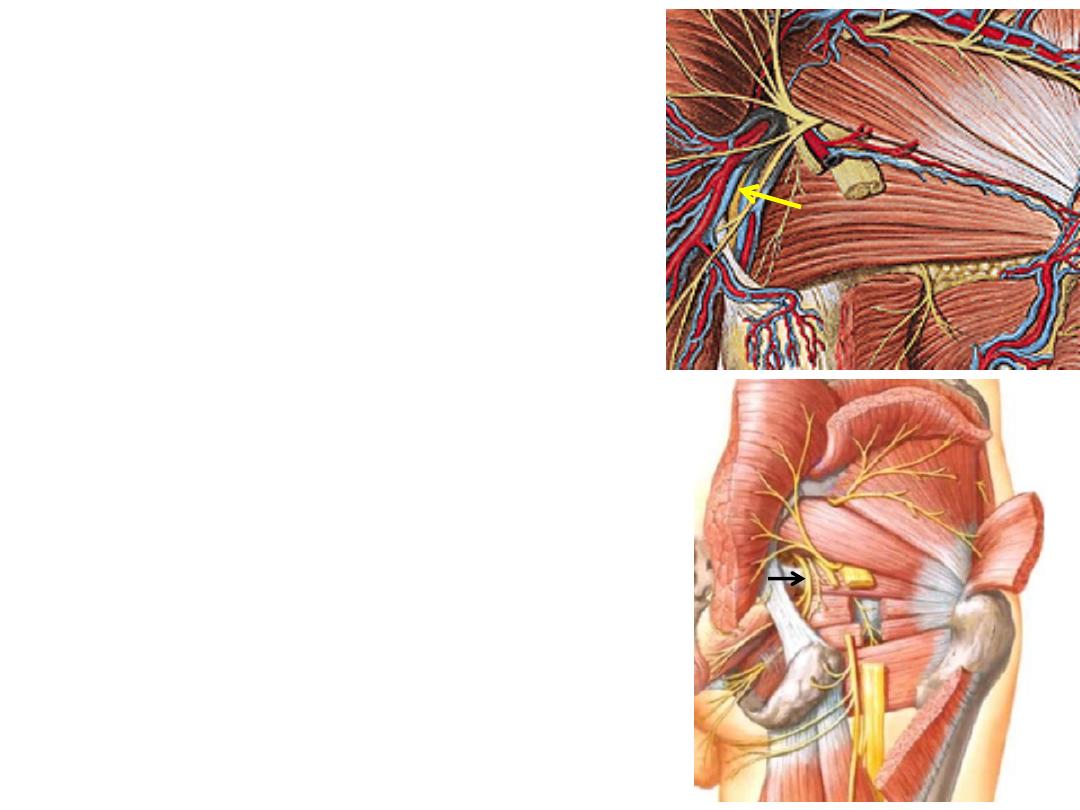
Internal pudendal artery:
-From the anterior division of internal iliac
artery
-Crosses the tip of the ischial spine (between
the pudendal n. & n. to OI)
-Enters the perineum where it is distributed
Pudendal nerve:
-Arises from anterior divisions of (S2,3,4)
-Crosses the sacrospinous ligament to enter
the perineum where it is distributed
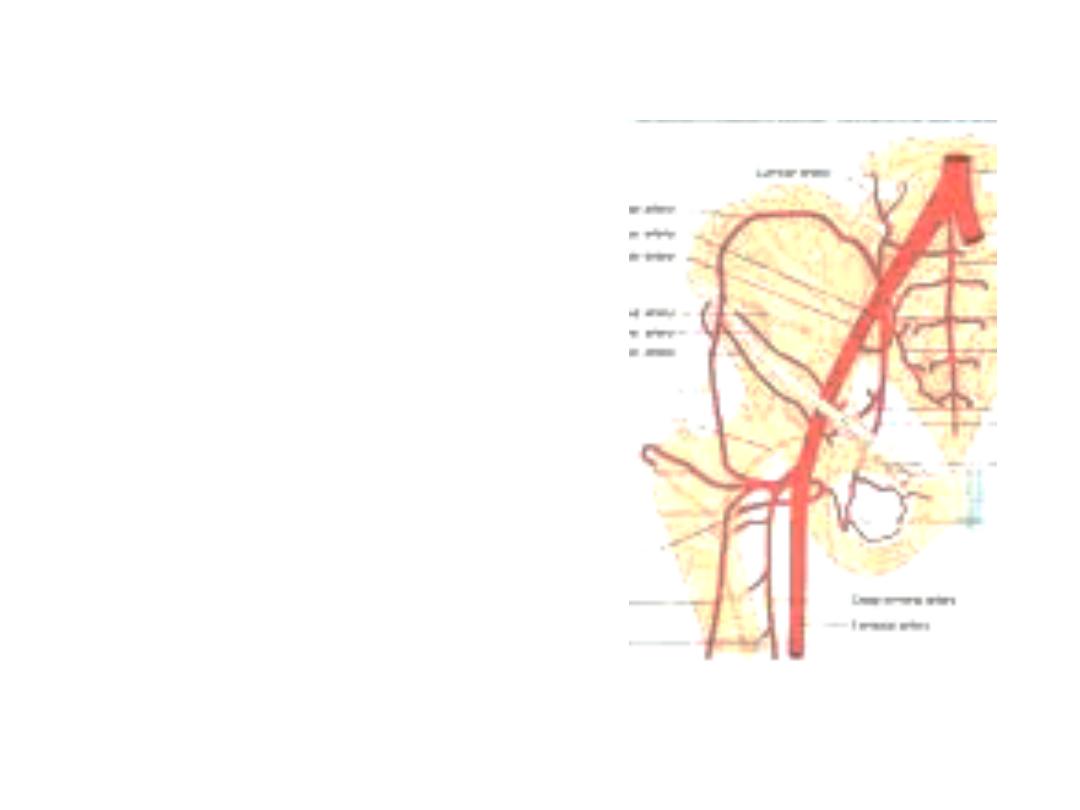
Anastomosis around the ASIS:
Connect the iliac arteries to the femoral &
profunda arteries
1- Iliac branch of iliolumbar artery
(internal internal iliac)
2- Deep circumflex iliac a. (external iliac)
3- Superficial circumflex iliac a. (femoral)
4- Ascending branch of LCF (profunda
femoris)
1
2
3
4
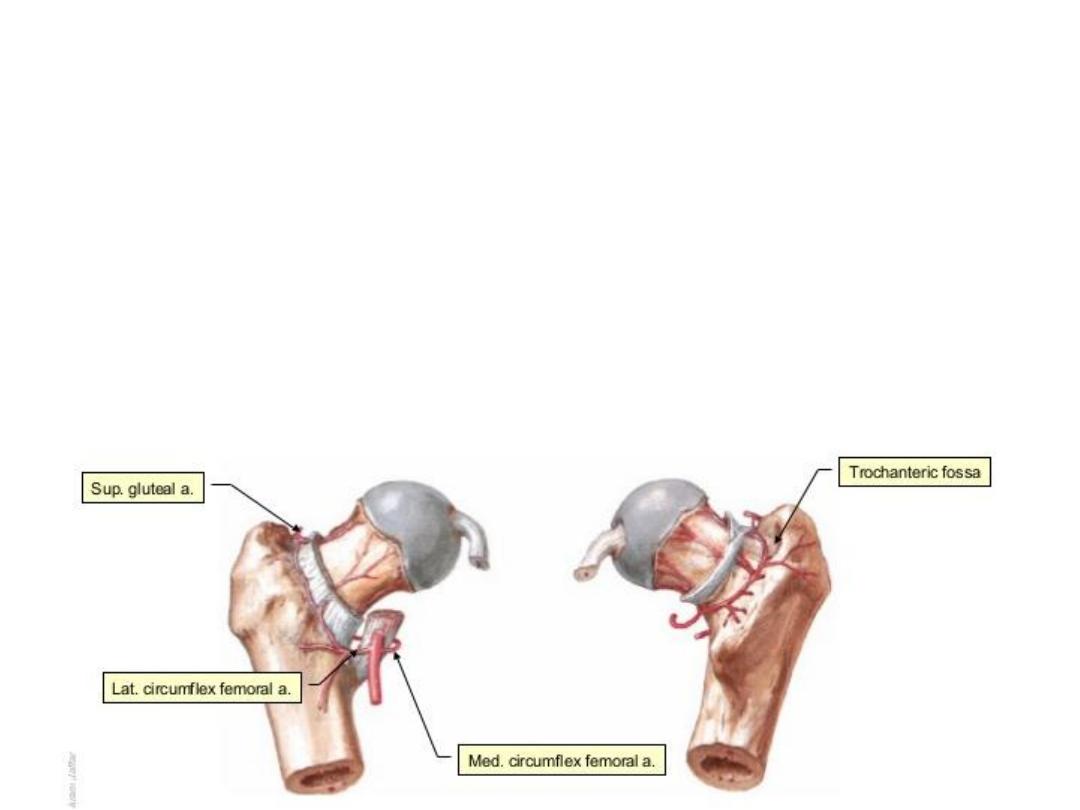
Trochanteric anastomosis:
-Lie in the trochanteric fossa
-Supplies the femoral head
-Formed by:
1- Ascending branch of LCF
2- Ascending branch of MCF
3- Branch from superior gluteal a.
4- Branch from inferior gluteal a.
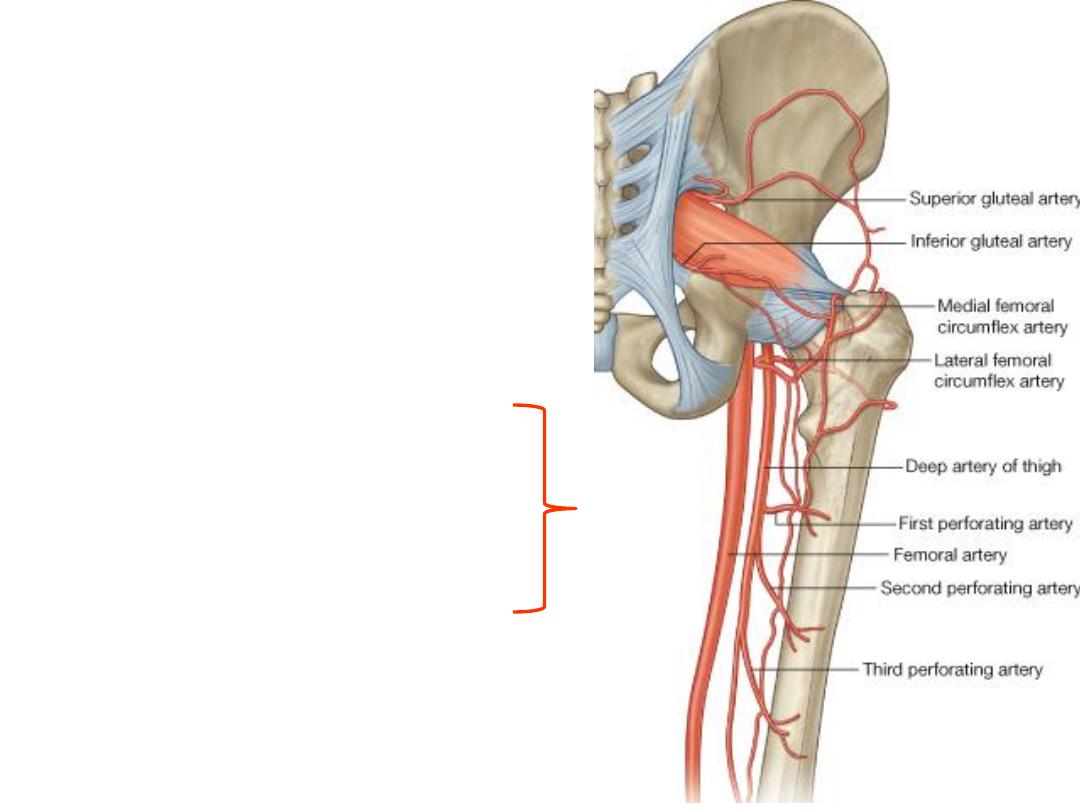
Cruciate anastomosis:
-Connects the internal iliac a. to the
profunda femoris
-Lies in the region of QF
-Formed by:
1- Transverse branch of LCF
2- Transverse branch of MCF
3- Ascending branch of 1
st
perforating a.
4-Descending branch of inferior gluteal a.
(internal iliac)
Profun
da
fem
oris
