To define the compartments of the leg
To describe the calf muscles & layers
To follow the tibial nerve & posterior tibial artery in the leg
To relate the deep & superficial veins of the leg & determine
their pathology
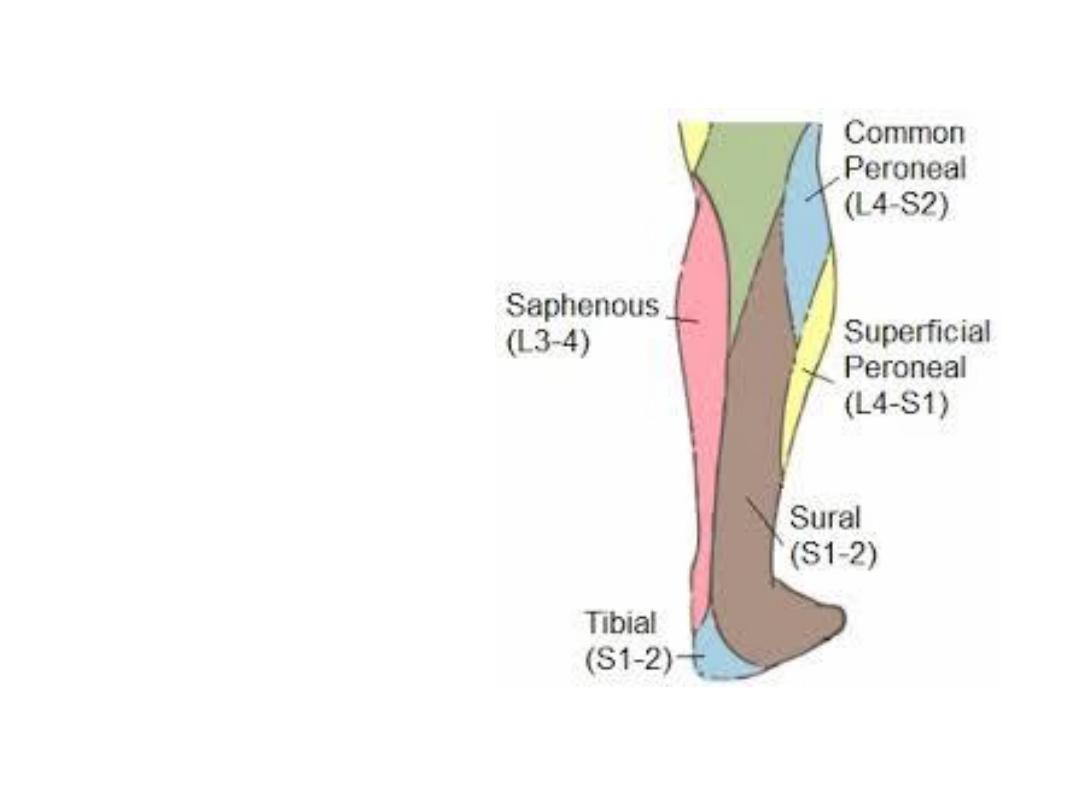
Superficial structures:
-
Small saphenous v
-
Sural nerve
Cutaneous innervation
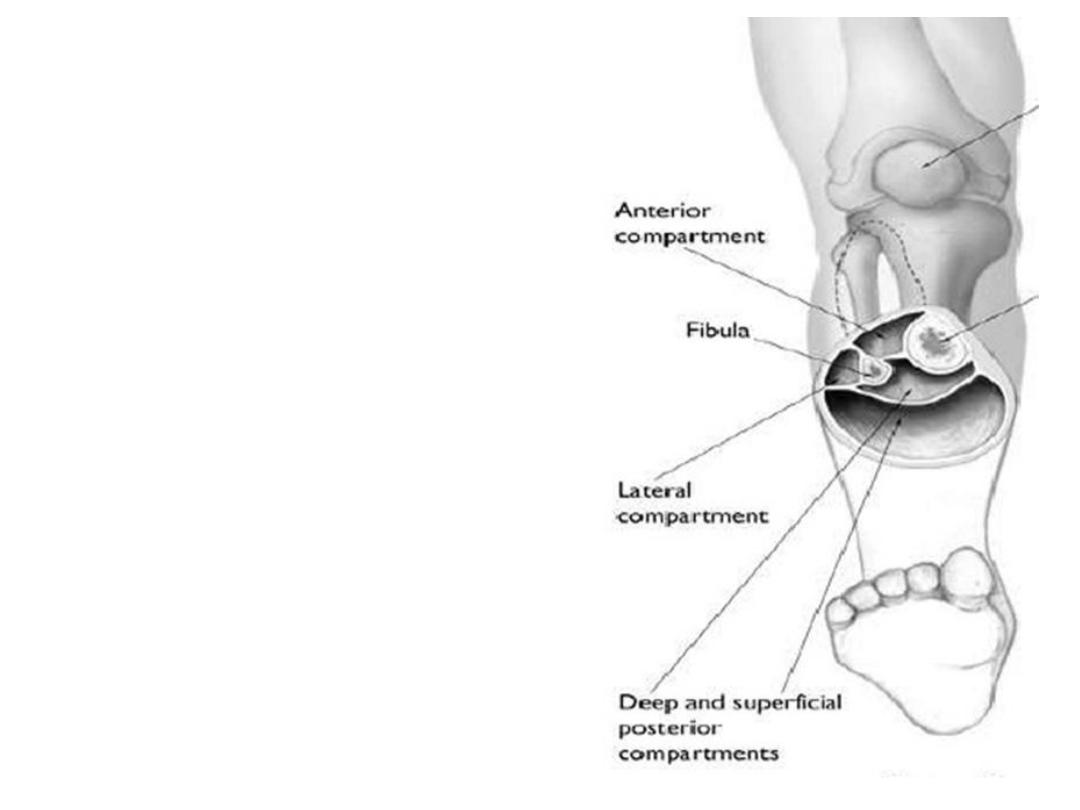
The leg fascia:
•Fascia lata continues over the leg as the
crural fascia
•Superiorly the fascia is attached to the
bones in the upper leg, reinforced by the
patellar retinacula
•Lower down it is attached to the
malleoli & posterior surface of calcaneus
•The fascia sends 2 intermuscular septa,
anterior & posterior dividing the leg into
3 compartments, flexor (superficial &
deep), extensor & peroneal
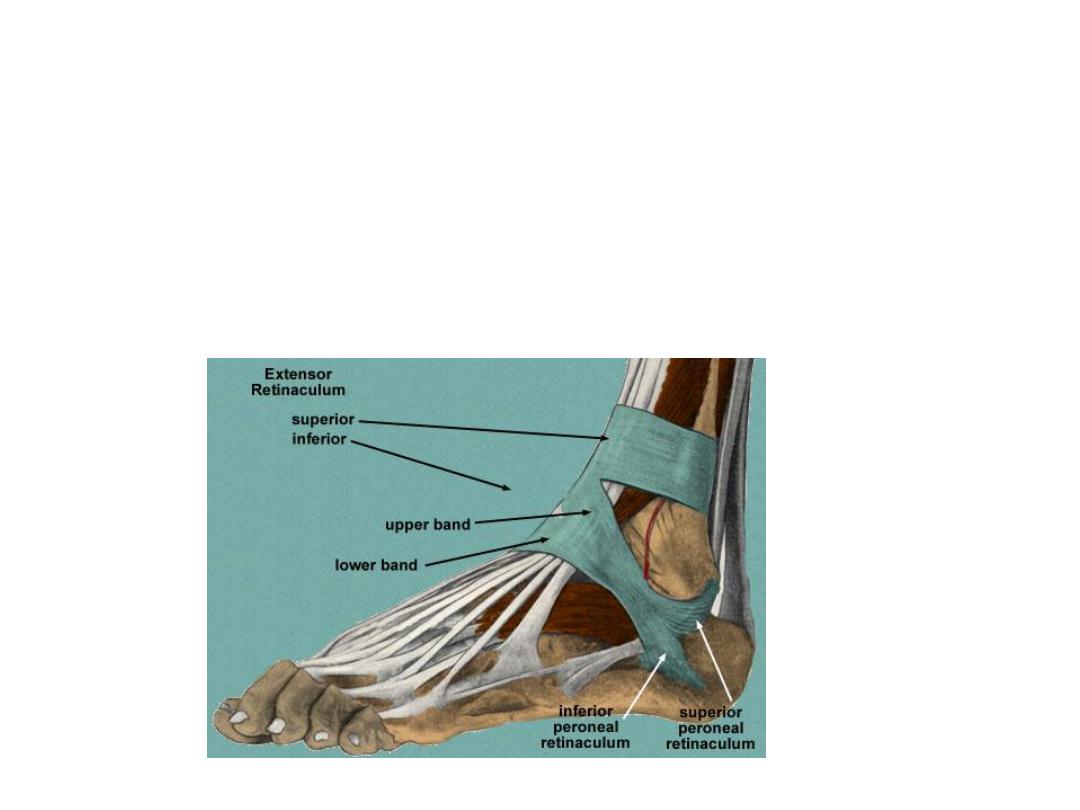
Ankle retinacula:
Around the ankle joint the crural fascia is thickened as many retinacula:
1- superior extensor R;
between tibia & fibula
2- Inferior extensor R;
Y-shaped, the stem is attached to calcaneus, the upper
limb to medial malleolus & the lower limb blends medially with the fascia of the
sole
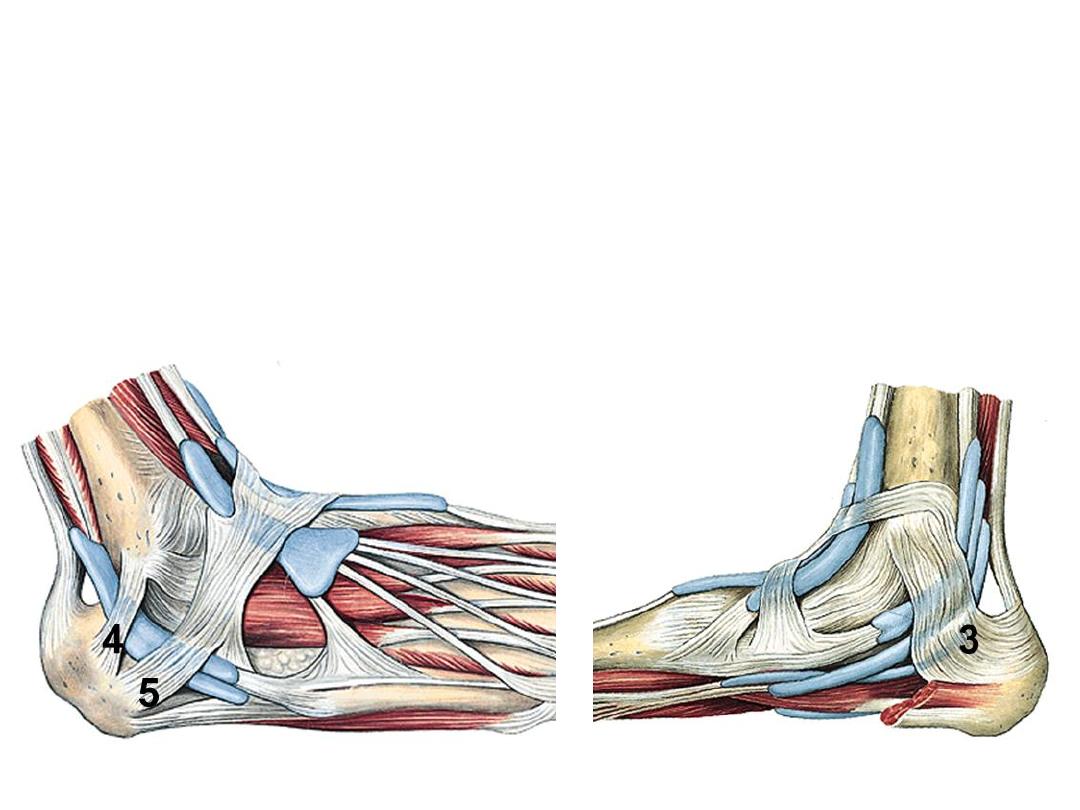
3- Flexor R;
between the medial alleolus & medial calcaneal tubercle
4- Superior peroneal R;
between lateral malleolus & lateral surface of
calcaneus
5- Inferior peroneal R;
lies on the side of calcaneus
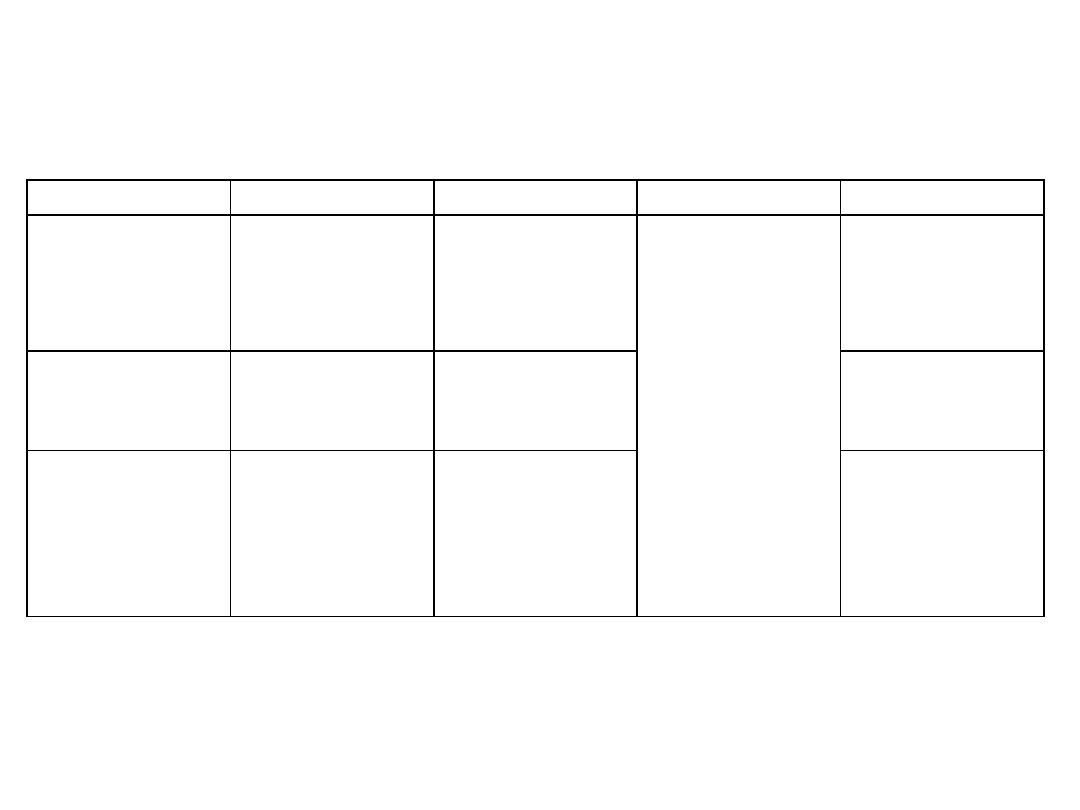
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
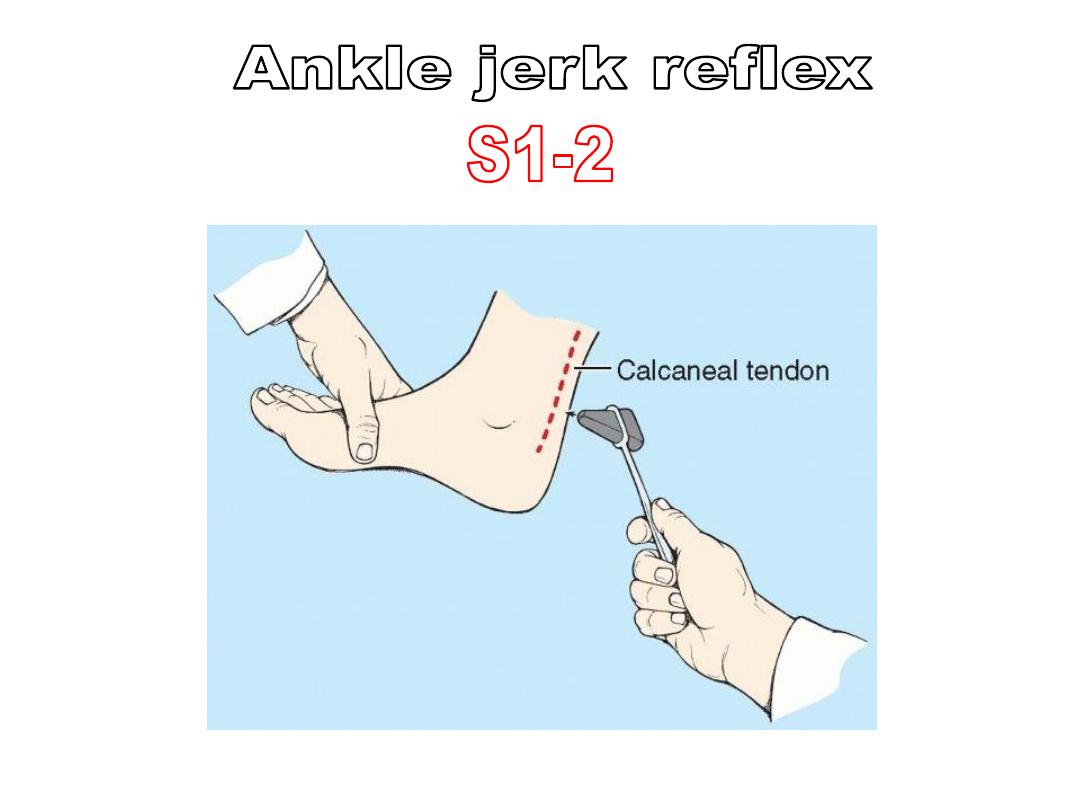
Gastrocnemius
(Top gear)
Medial & lateral
heads from back of
femur above
corresponding
condyles
Via calcaneal
tendon, to
the back of
calcaneus
Tibial nerve
S1,2
- Plantarflex
the foot
- Gn
flexes
the knee
Plantaris
Lateral
supracondylar line of
femur
Soleus
(Bottom gear)
- Soleal line
- Fibular head
- Tendinous arch in
between
Superficial group of muscles
(Act on ankle)
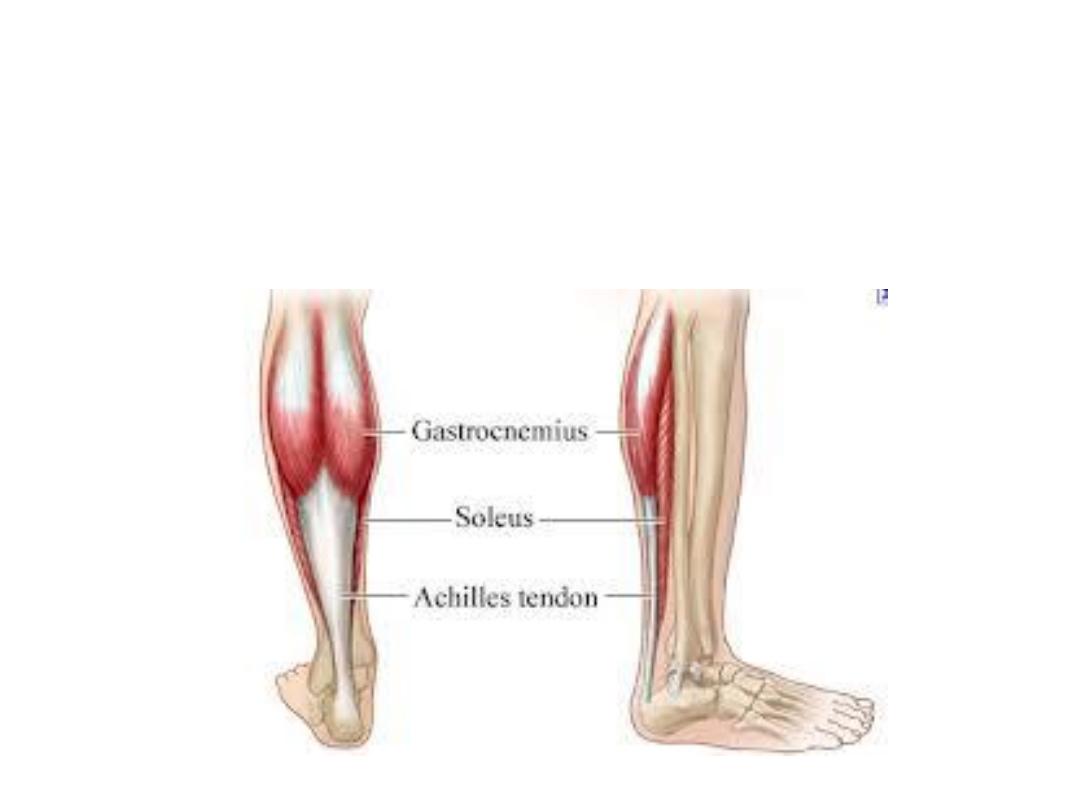
The peripheral heart:
-Soleus is a powerful muscle which participate in venous return
-When venous stagnation takes place it reflexly contracts (with other
muscles of yawning) to pump blood back to the circulation
Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Function
Tibialis
posterior
Interosseous
membrane &
adjacent bony
borders
- Navicular
tuberosity
- Tarsal
*
metatarsals
Tibial nerve L4-
S1
- Inversion
- Support the
foot arch
Flexor
digitorum
longus
Posterior
surface of tibia
(below soleus)
Distal
phalanges of
lateral 4 toes
Flexor lateral 4
toes
Flexor hallucis
longus
Posterior
surface of
fibula
Distal phalanx
of big toe
Flexor big toe
Deep group of muscles
(Act on the foot)
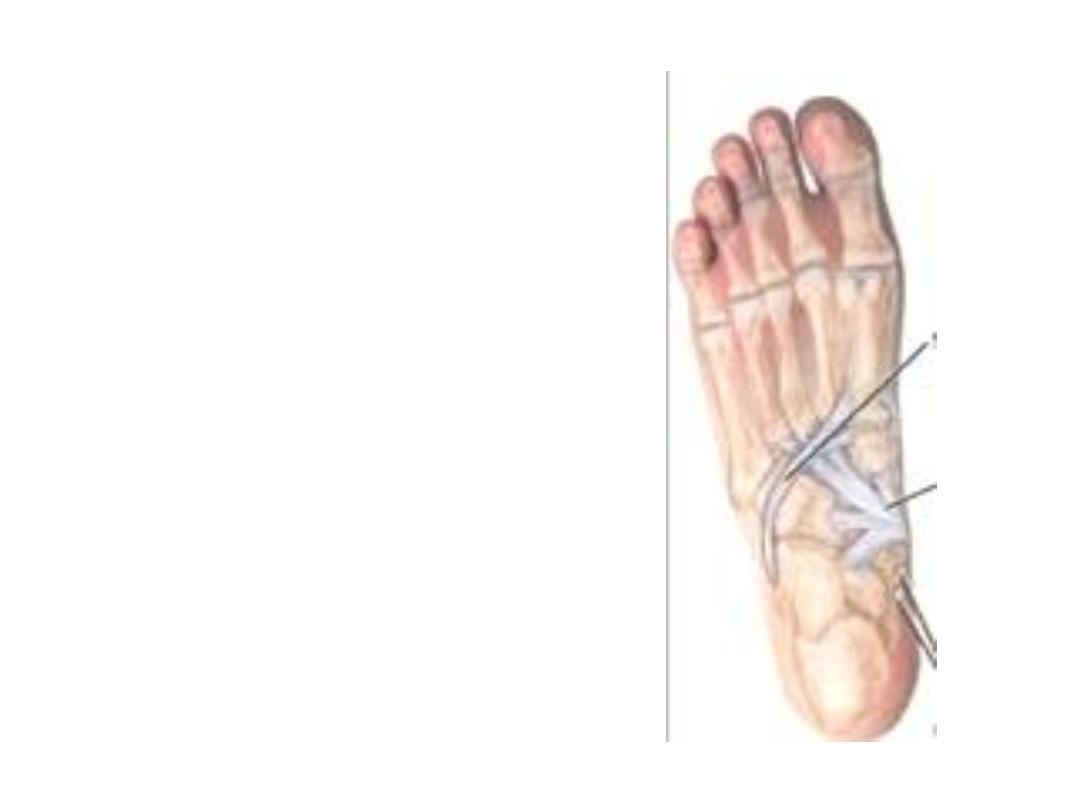
Notes:
- Tibialis
posterior
tendon
after passing deep to the
flexor R inserted by slips as
follows:
Main part in the navicular
tuberosity
Plantar portion is inserted
into the cuboid, cuneiforms
&
bases
of
2
&
3
metatarsals
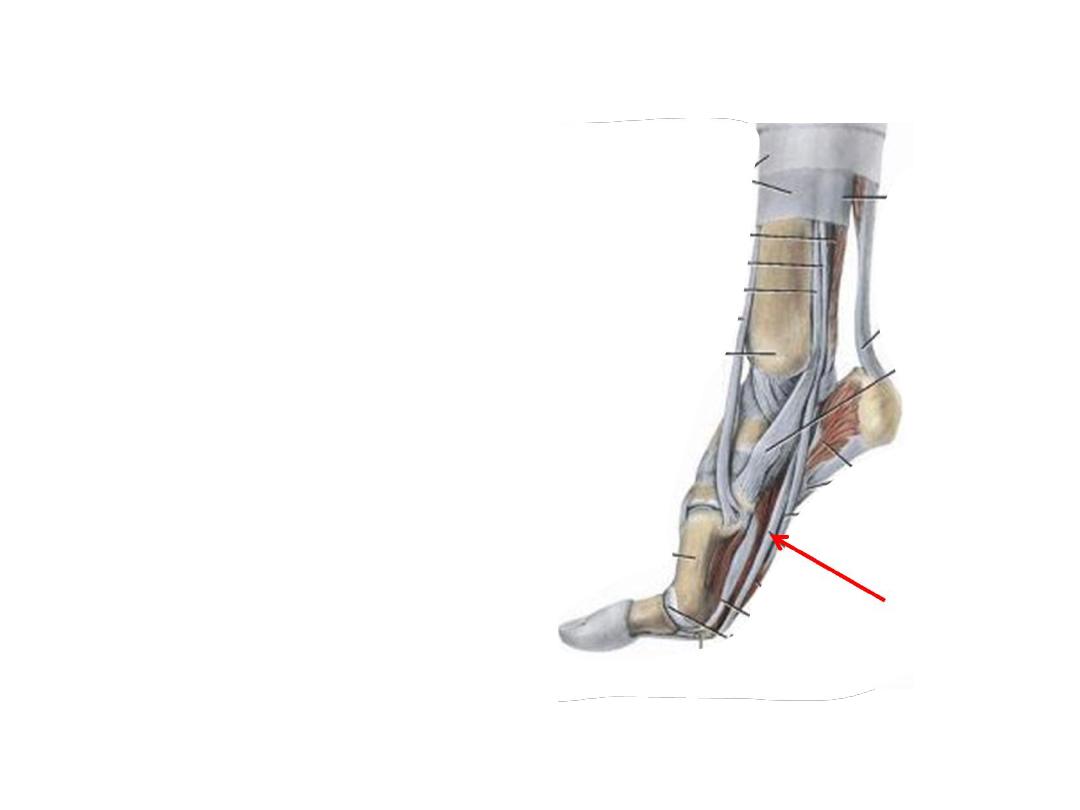
Notes:
- FHL & FDL tendons cross
over in the sole
- FHL tendon grooves the
talus & calcaneus
- FHL is the take off muscle
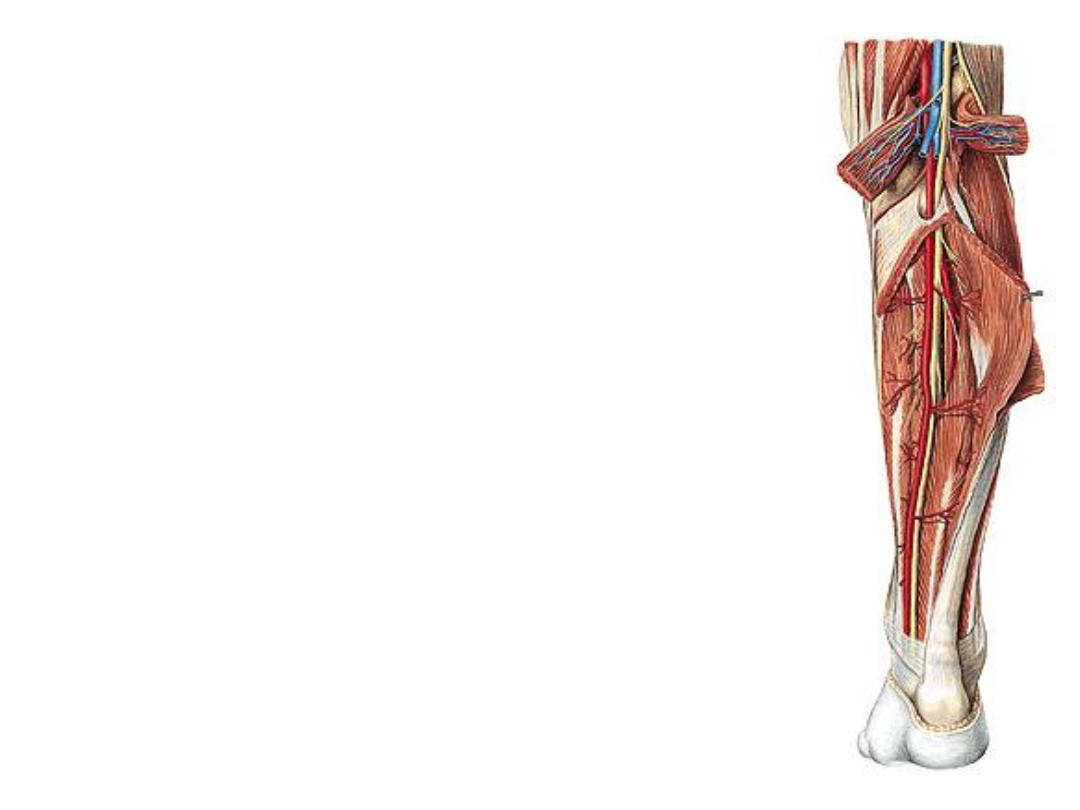
The posterior tibial artery:
-The continuation of popliteal a. after giving the anterior TA
-Descends deep to soleus, where at the lower leg it lies
behind the medial malleolus
-Ends in the foot by dividing into medial & lateral planter
arteries
-Accompanied by two deep veins & the tibial nerve
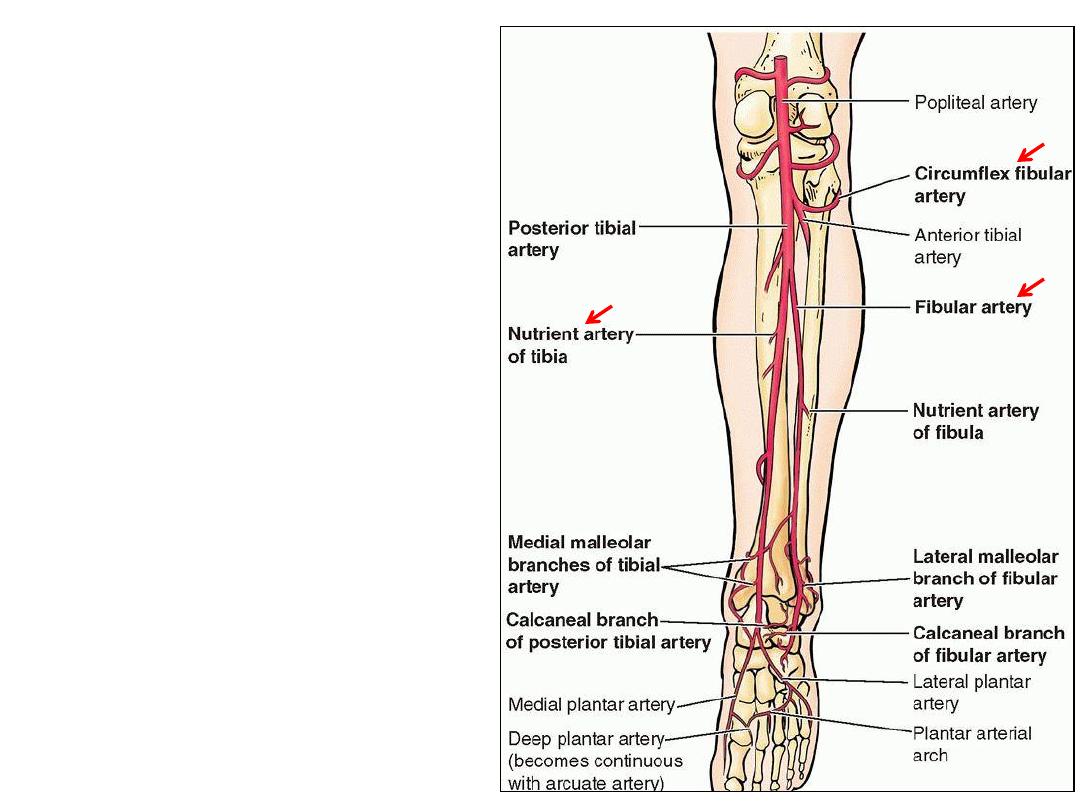
Branches:
1- Circumflex fibular a.; einds
around fibular neck to anastomose
with anterior tibial recurrent &
genicular arteries
2- Posterior tibial recurrent a.; to
the anastomosis around the knee
3- Peroneal artery
4- Muscular arteries
5- Nutrient artery to the tibia
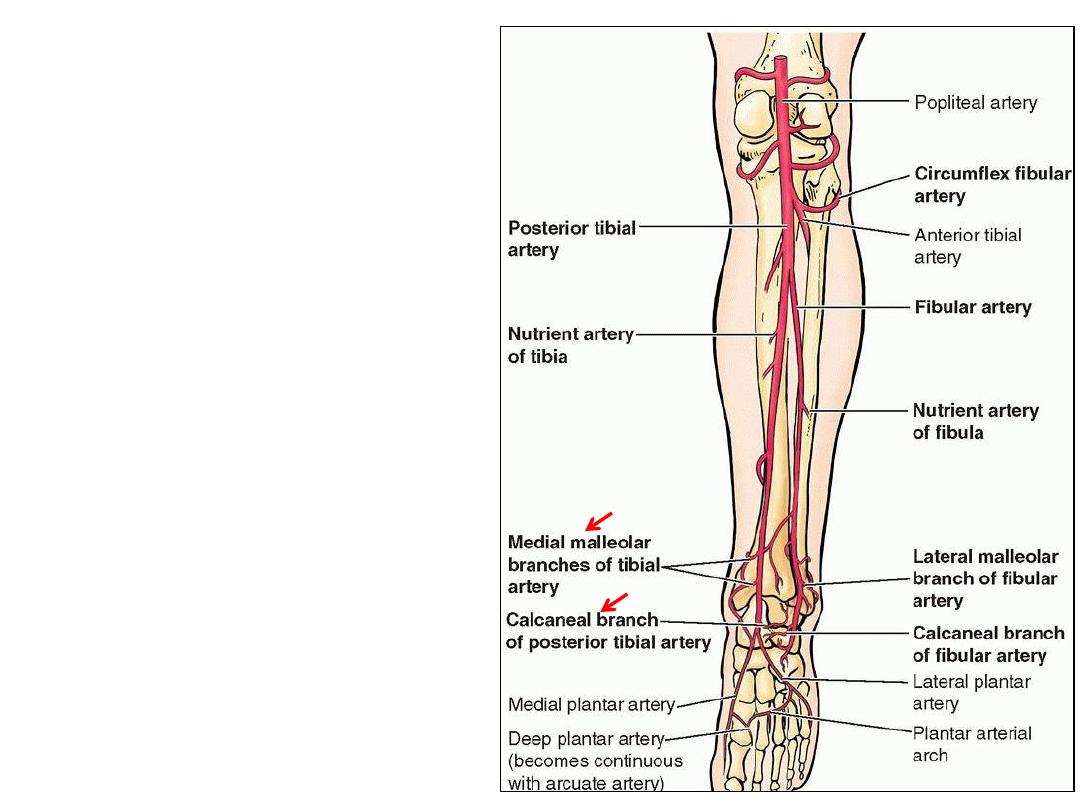
6- Perforating arteries; 5 in number,
perforate the deep fascia to supply
superficial structures & skin
7- Medila malleolar artery; to the
malleolar network
8- Medial calcaneal branches; to the
skin of the heel & adjacent areas
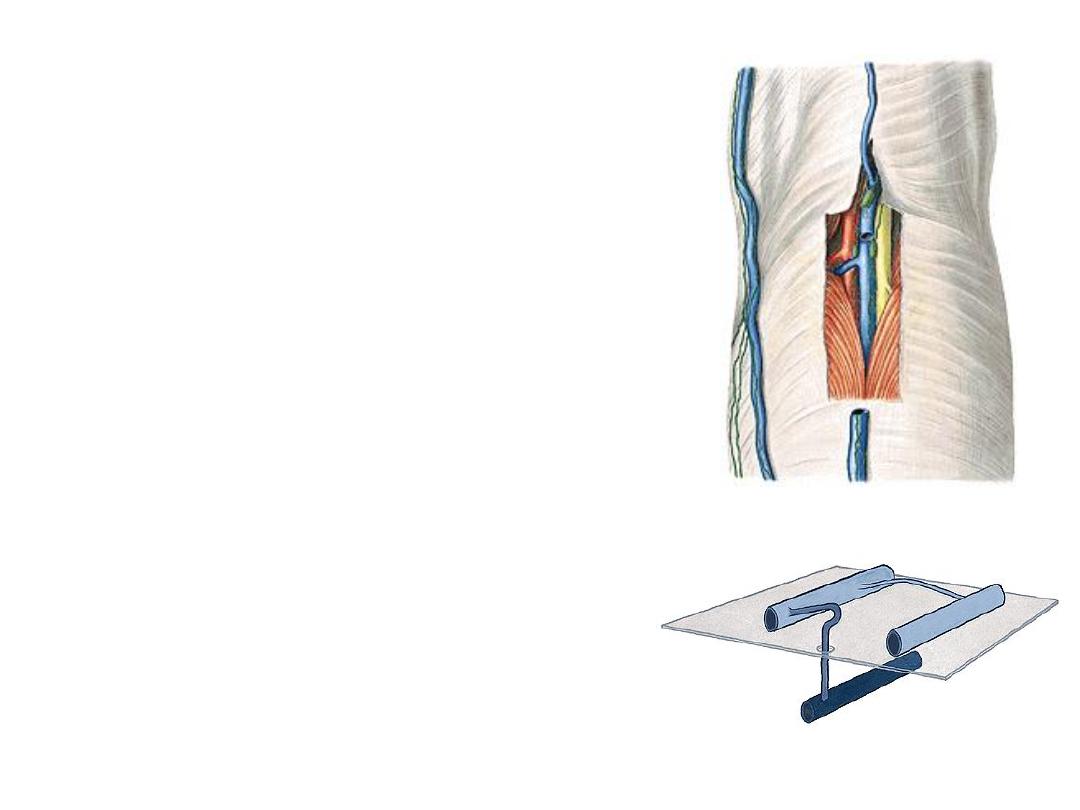
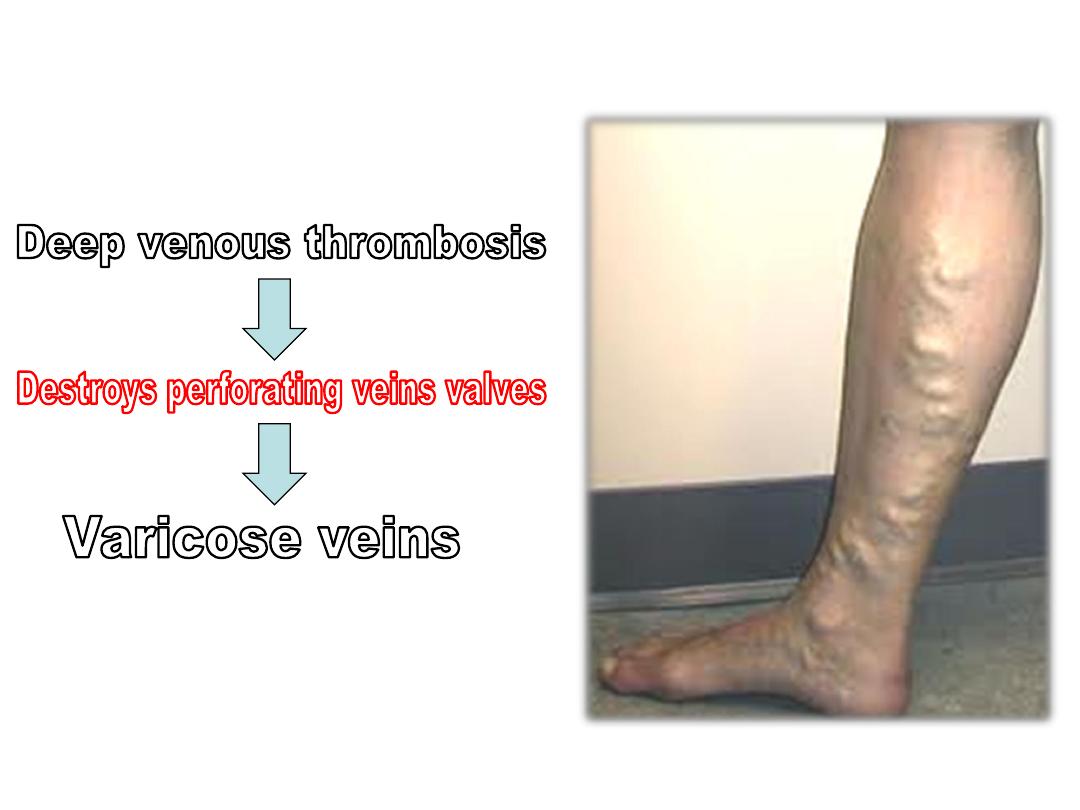
Veins of the leg:
-Saphenous veins are superficial
-Two deep veins accompany the PTA
-These veins are valved to aid venous
return
-Perforating
veins
communicate
these
veins with superficial ones
-Perforating veins valves permit blood flow
from superficial to deep veins
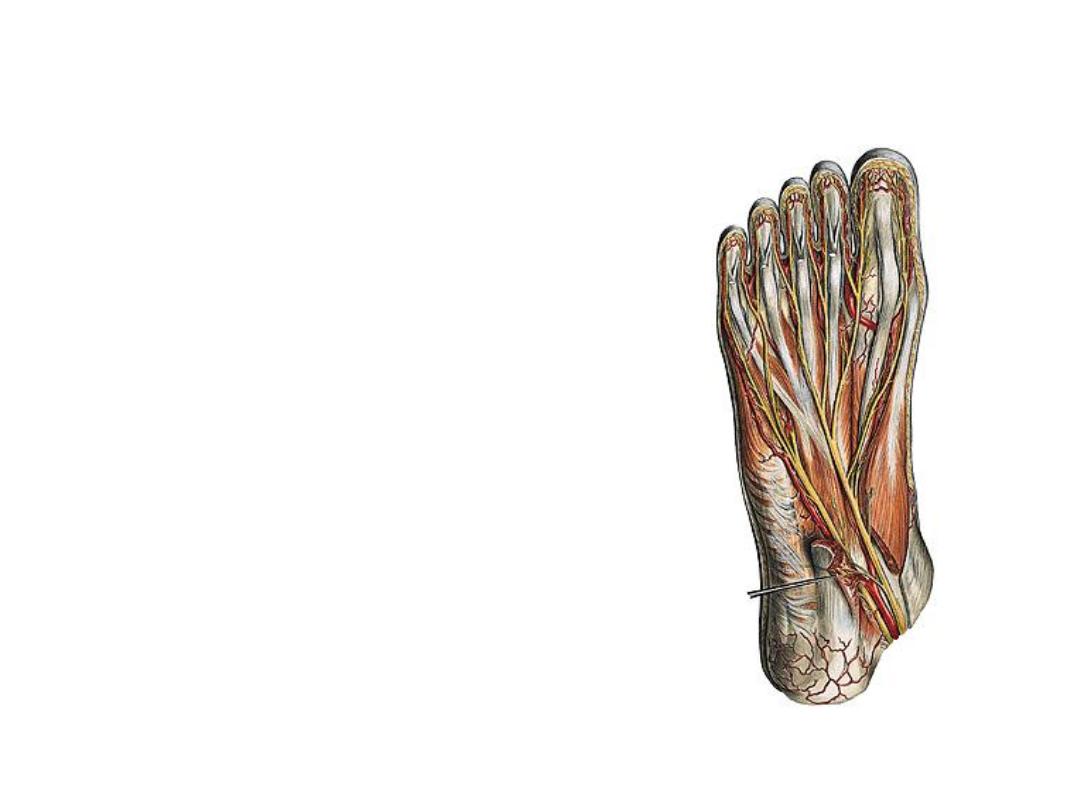
The tibial nerve:
-Lies at the same plane of the artery, superficial
to it
-The nerve passes underneath the flexor
retinaculum between FHL tendon & PTA to enter
the foot
-It divides into its 2 terminal divisions (medial &
lateral plantar) beneath the flexor retinaculum
-Branches:
1- Cutaneous
2- Muscular; to all calf muscles
3- Medial calcaneal branches; to supply the skin
over the medial aspect of the heel
4- Articular; to the knee & ankle joints
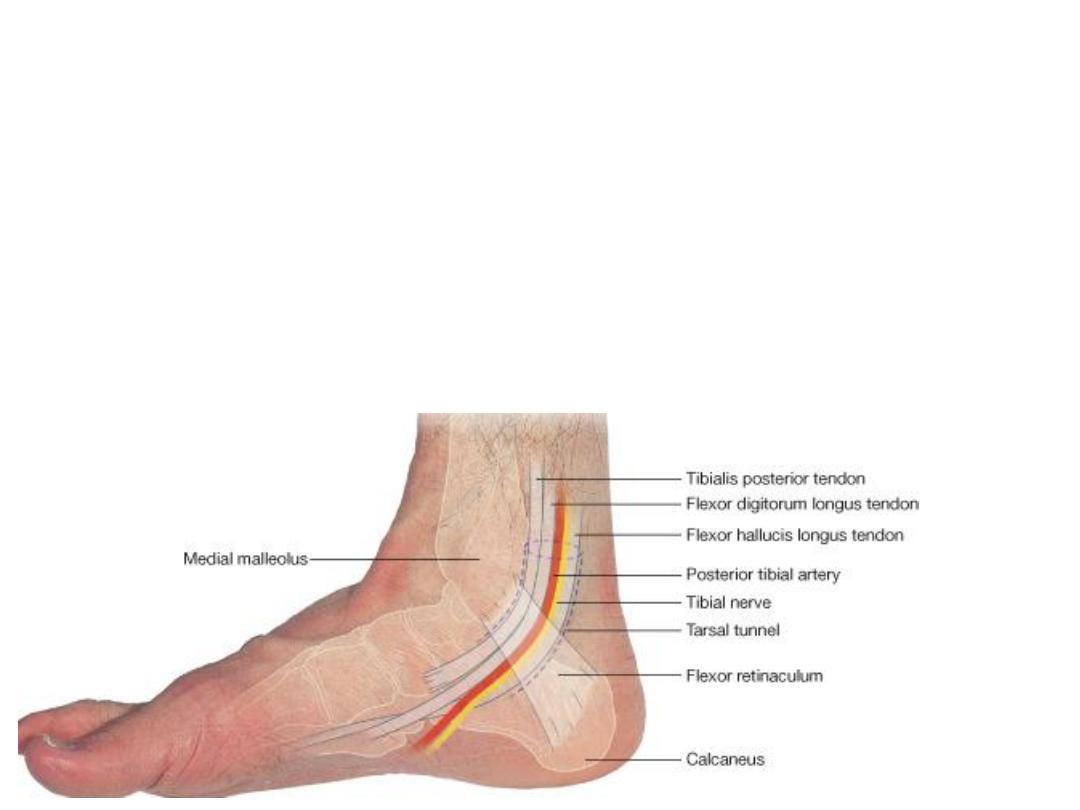
Structures deep to the FR
(The tarsal tunnel)
