
ASSESSMENT OF FETAL WELLBEING & FETAL DISTRESS
Assessment of fetal well-being:
Aims:
-
Ensure fetal wellbeing (Identify patients at risk of fetal asphyxia) and
-
To prevent prenatal mortality & morbidity
Screening for high risk pregnancy:
History
•
Age.
•
Social burden.
•
Smoking.
•
Past medical conditions e.g D.M, HTN.
•
Past Obstetric history
When to start fetal Assessment:
•
Risk assessed individually.
•
For D.M. fetal assessment should start from 32 weeks onward if uncomplicated.
•
If complicated D.M. start at 24 weeks onward.
•
For Post date pregnancy start at 40 weeks.
•
For any patient with decrease fetal movement start immediately.
•
Fetal assessment is done once or twice weekly.
FETAL AND NEONATAL COMPLICATIONS OF ANTEPARTUM ASPHYXIA:
1. Fetal Outcomes Neonatal Outcomes.
2. Stillbirth Mortality.
3. Metabolic acidosis at birth Metabolic acidosis.
4. Hypoxic renal damage.
5. Necrotizing enterocolitis.
6. Intracranial haemorrhage.
7. Seizures.
8. Cerebral palsy.
Components of Fetal Assessment:
1. Fetal movement counting
2. Ultrasound fetal assessment
3. Non stress test
4. Contraction stress test
5. Umbilical Doppler Velocimetry
Fetal movement counting:
I. Kick cout:
•
Done in the morning, patient should calculate how long it takes to have 10 fetal
movement:
•
10 movements should be appreciated in 12 hours.
•
For one hour after meal the woman should lie down and concentrate on fetal
movement.
•
4 movement should be felt in one hour.
•
If not, she should count for another hour.
•
If after 2 hours four movements are not felt, she should have fetal monitoring.
II. Ultrasound fetal assessment:
A. Assessment of growth:
1. Biometry:
a) Biparietal diameter (BPD).
b) Abdominal Circumference (AC).
c) Femur Length (FL).
d) Head Circumference (HC).
2. Amniotic fluid.
3. Placental localization.
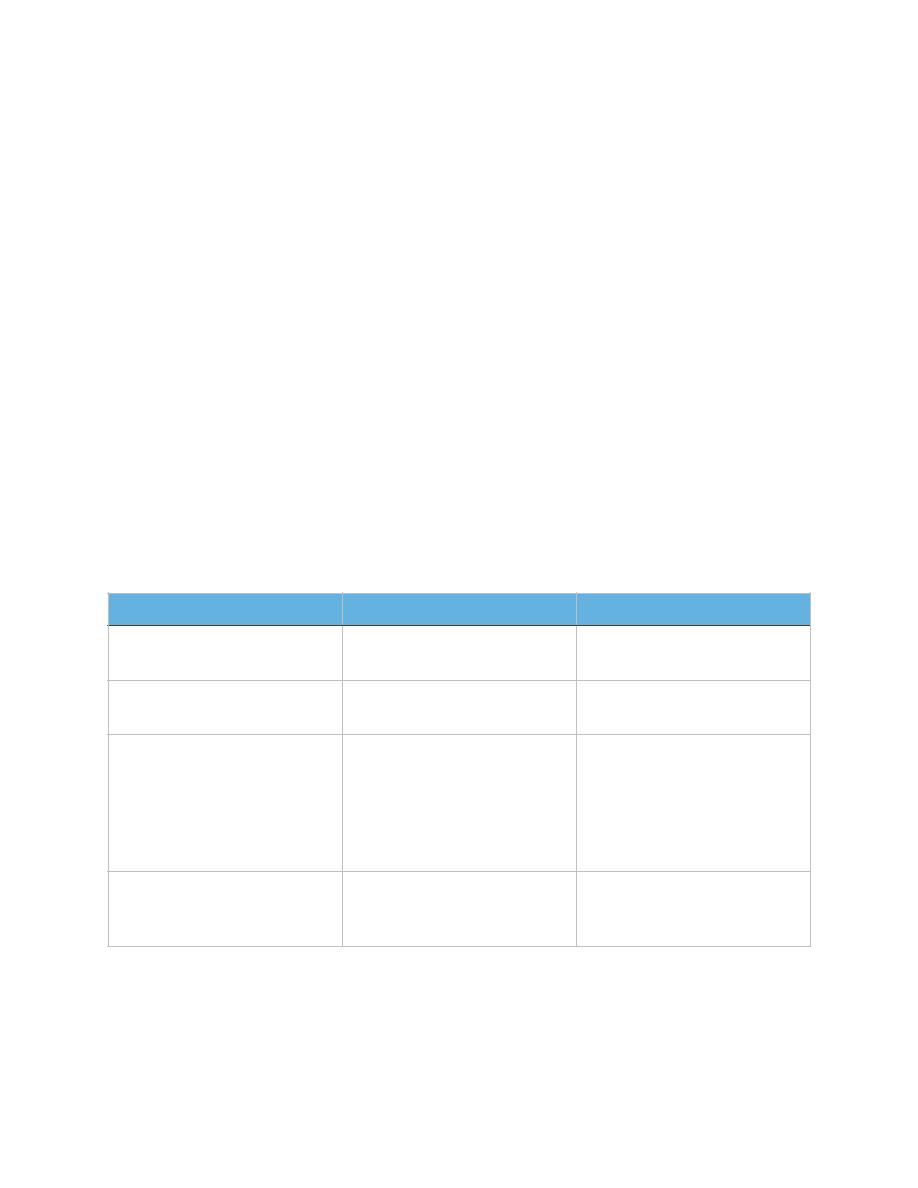
B. Biophysical profile (BPP):
1. Assessment of 5 variables:
a) Fetal breathing movements.
b) Fetal movements of body or limbs.
c) Fetal tone.
d) Amniotic fluid volume.
e) Reactive non-stress test.
2. Identifies compromised fetus.
3. Desired BPP score: 8-10 considered normal.
Biophysical Variable
Normal (score=2)
Abnormal (score=0)
Fetal breathing movements 1 episode FBM of at least
30 s duration in 30 min
Absent FBM or no episode
>30 s in 30 min
Fetal movements
3 discrete body/limb
movements in 30 min
2 or fewer body/limb
movement in 30 min
Fetal tone
1 episode of active
extension with return to
flexion of fetal limb(s) or
trunk. Opening and closing
of the hand considered
normal tone.
Either slow extension with
return to partial flexion or
movement of limb in full
extension Absent fetal
movement.
Amniotic fluid volume
1 pocket of AF that
measures at least 2 cm in 2
perpendicular planes.
Either no AF pockets or a
pocket<2 cm in 2
perpendicular planes.
III. Non stress test:
A. Done using the cardiotocometry with the patient in left lateral position.
B. Record for 20 minutes.
C. Assess fetal well being.
D. Procedure:
1. EFM to abdomen.
2. Fetal heart rate measured: at least 2 accelerations of 15 bpm lasting 15 sec
or more within 20 minutes.
3. Fetal movement is documented.
E. Possible clinical findings:
1. Fetus with adequate oxygenation and an intact central nervous system.
2. Fetus at risk.
3. *The base line 110-150 beats/minute.
F. Reactive: At least two accelerations from base line of 15 bpm for at least 15 sec
within 20 minutes.
G. Non reactive: No acceleration after 20 minutes- proceed for another 20 minutes.
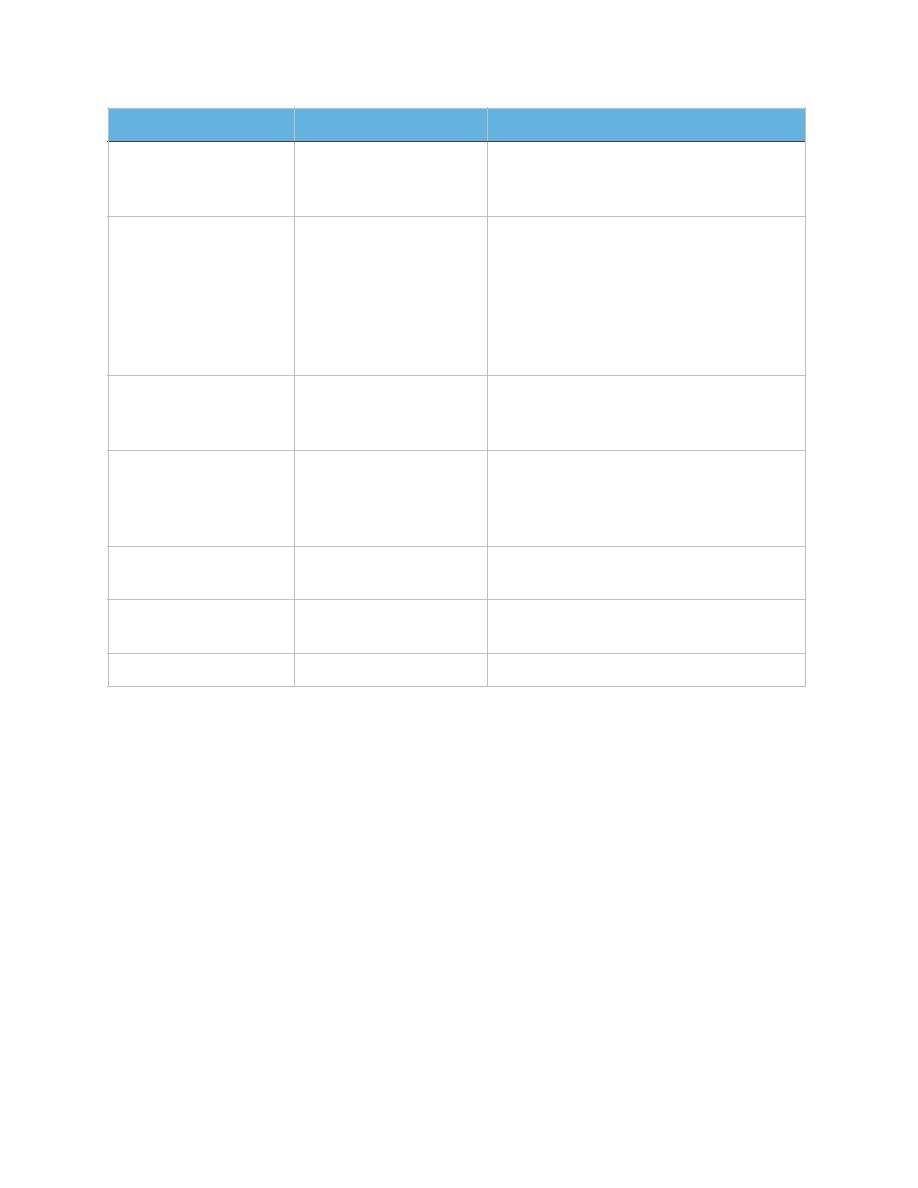
IV. Contraction stress test:
Test Score Result
Interpretation
Management
10 of 10
8 of 10 (normal fluid)
8 of 8 (NSF not done)
Risk of fetal asphyxia
extremely rare
Intervention for obstetric and maternal
factors
8 of 10 (abnormal
fluid)
Probable chronic fetal
compromise
Determine that there is functioning
renal tissue and intact membranes. If
so, delivery of the term fetus is
indicated. In the preterm fetus less
than 34 weeks, intensive surveillance
may be preferred to maximize fetal
maturity.
6 of 10 (normal fluid)
Equivocal test,
possible fetal
asphyxia.
Repeat test within 24 hr.
6 of 10 (abnormal
fluid)
Probable fetal
asphyxia.
Delivery of the term fetus. In the
preterm fetus less than 34 weeks,
intensive, surveillance may be
preferred to maximize fetal maturity.
4 of 10
High probability of
fetal asphyxia.
Deliver for fetal indications.
2 of 10
FetaI asphyxia almost
certain.
Deliver for fetal indications.
0 of 10
Fetal asphyxia certain. Deliver for fetal indications.

•
Fetal response to induced stress of uterine contraction and relative placental
insufficiency.
•
Should not be used in patients at risk of preterm labor or placenta previa.
•
Should be proceeded by NST.
•
Contraction is initiated by nipple stimulation or by oxytocin I.V.
•
The objective is 3 contractions in 10 minutes.
•
If late deceleration occur-----positive CST.
•
Positive CST results: (bad) with persistent late decelerations is evidence that the
fetus will not be able to withstand the hypoxic stress of the uterine contractions.
•
Negative CST results: (good) No persistent decelerations noted with at least 3
ctx.
V. Doppler:
A. Doppler Blood Flow studies:
1. Assess uteroplacental function.
2. Beginning at 16 to 18 weeks gestation.
3. Procedure: woman in supine position and warmed gel to abdomen.
4. Pulsed-wave Doppler device is used.
5. Possible clinical findings: suspected uteroplacental insufficiency.
B. Umbilical Doppler Velocimetry:
1. Indication:
a) IUGR.
b) PET.
c) D.M.
d) Any high risk pregnancy.
2. Use a free loop of umbilical cord to measure blood flow in it.
C. Management of abnormal Doppler:
1. Depends on:
a) Fetal maturity.
b) Gestational age.
c) Obstetric history.
2. Management of Doppler results:
a) Reverse flow or absent end diastolic flow--- Immediate delivery.
b) High resistance index---- repeat in few days or delivery.
c) Normal flow---- repeat in 2 week if indicated
Fetal Distress:
Definition:
•
Fetal distress is defined as depletion of oxygen and accumulation of carbon
dioxide,leading to a state of “hypoxia and acidosis ” during intra-uterine life.
Etiology:
A. Maternal factors:
1. Microvascular ischaemia (PIH).
2. Low oxygen carried by RBC (severe anemia).
3. Acute bleeding(placenta previa, placental abruption).
4. Shock and acute infection.
5. Obstructed of Utero-placental blood flow .

B. Placental, umbilical factors:
1. Obstructed of umbilical blood flow.
2. Dysfunction of placenta.
C. Fetal factors:
1. Malformations of cardiovascular system.
2. Intrauterine infection
Pathogenesis:
Hypoxia - accumulation of carbon dioxide
Respiratory Acidosis
FHR → FHR → FHR
Intestinal peristalsis
Relaxation of the anal sphincter
Meconium aspiration
Fetal or neonatal pneumonia
Chronic Fetal distress -------\IUGR(intrauterine growth restriction
Interpretation of CTG:
1. Normal Baseline FHR 110–150 bpm.
2. Moderate bradycardia 100–109 bpm.
3. Moderate tachycardia 161–180 bpm.
4. Abnormal bradycardia < 100 bpm.
5. Abnormal tachycardia > 180 bpm
Acceleration: showing a transient increase of greater than 15 bpm.
Deceleration:
A. EARLY:
1. Head compression.
2. FHR decrease with onset of contraction and back to normal with end of
contraction.
B. LATE:
1. U-P Insufficiency.
2. Deceleration persist after end of contraction.
C. VARIABLE:
1. Cord compression.
2. Variable onset

Reduced variability: Tachycardia, Hypoxia, Chorioamnionitis
Baseline rate of above 150 bpm: Maternal fever ,Mimetic drugs , Fetal
anaemia,sepsis,ht failure,arrhythmias
Management:
A. Remove the induced factors actively.
B. Correct the acidosis: 5%NaHCO3 250ML stop oxytocin if present, give
oxygen ,iv fluid & place patient in left lateral position.
C. Terminate the pregnancy:
(1) FHR>160 or <120 bpm.
•
meconium staining (II~III).
(2) Meconium staining grade III.
•
amniotic fluid volume<2cm.
(3) FHR<100 bpm continually.
(4) Repeated LD and severe VD.
(5) Baseline variability disappear with LD.
(6) FBS pH<7.20.
D. Forceps delivery.
E. Caesarean section.
ُﻛﺭرﻭوﻩهَﻣ َوﻭ ٌبﺏوﻭﺑﺣَﻣ ثﺙِدﺩاﺍوﻭ َﺣﻟاﺍ ّﻲـطﻁ **** ﻲﻓ َوﻭ ءﺎﺿَﻘﻟاﺍ مﻡﻛُﺣ ﻰﻠَﻋ رﺭوﻭﻣَﻷاﺍ يﻱرﺭﺟَﺗ
ُﻭوﻩهــﺟرﺭَأﺃ ﱡتﺕﺑ ﺎـﻣ ﻲﻧَءﺎﺳ ﺎﻣَـّﺑُرﺭ َوﻭ **** ُهﻩرﺭَذﺫــﺣَأﺃ ّتﺕِﺑ ﺎـﻣ ﻲﻧﱠرﺭـــَﺳ ﺎﻣّﺑُرﺭَﻓ
