Popliteal fossa
anatomy
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Dr.Muayad j. Al-Haris

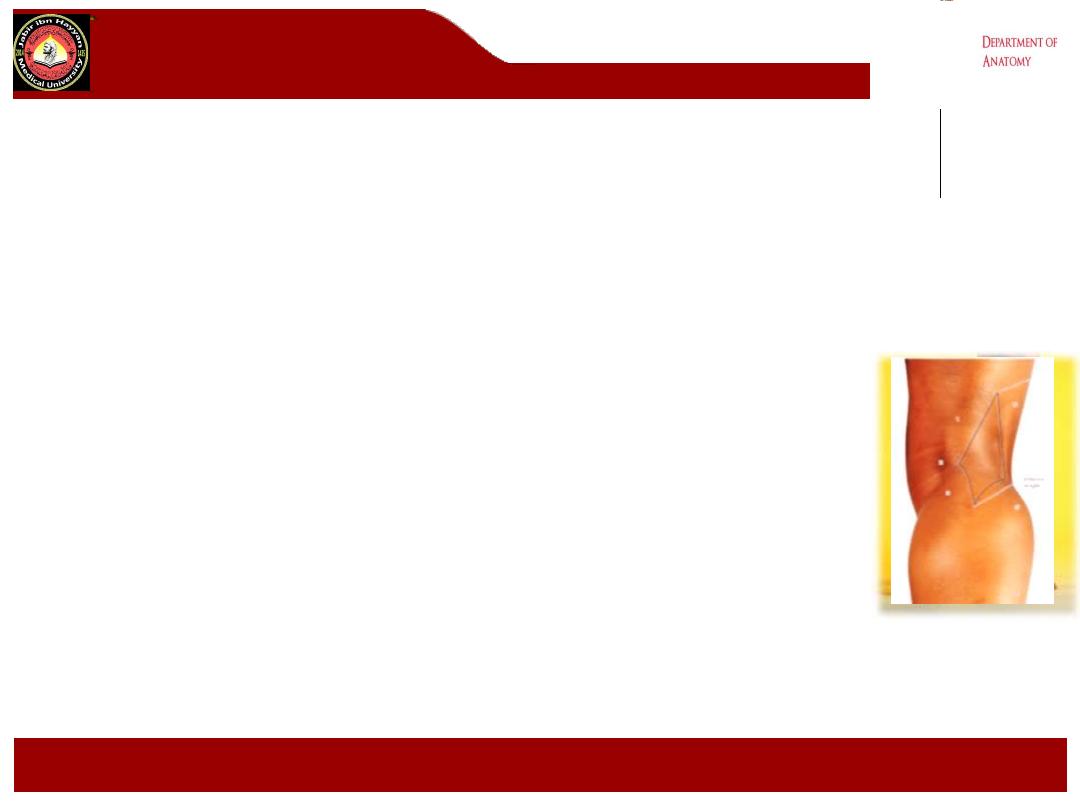
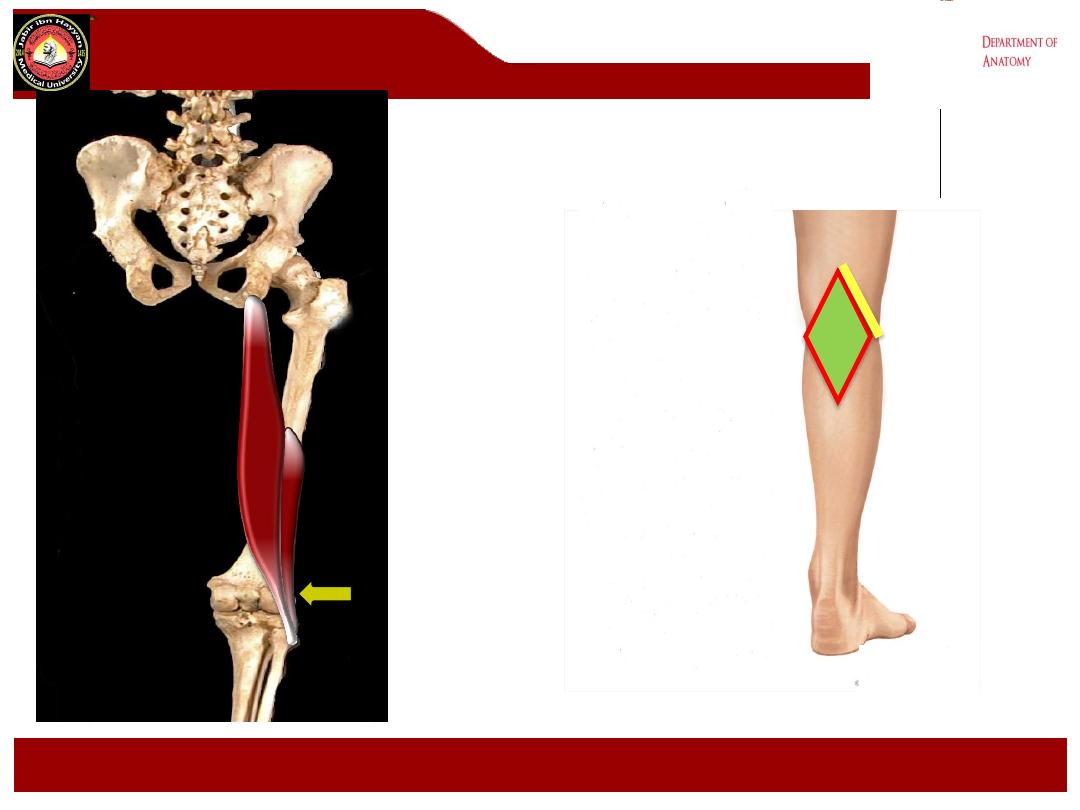
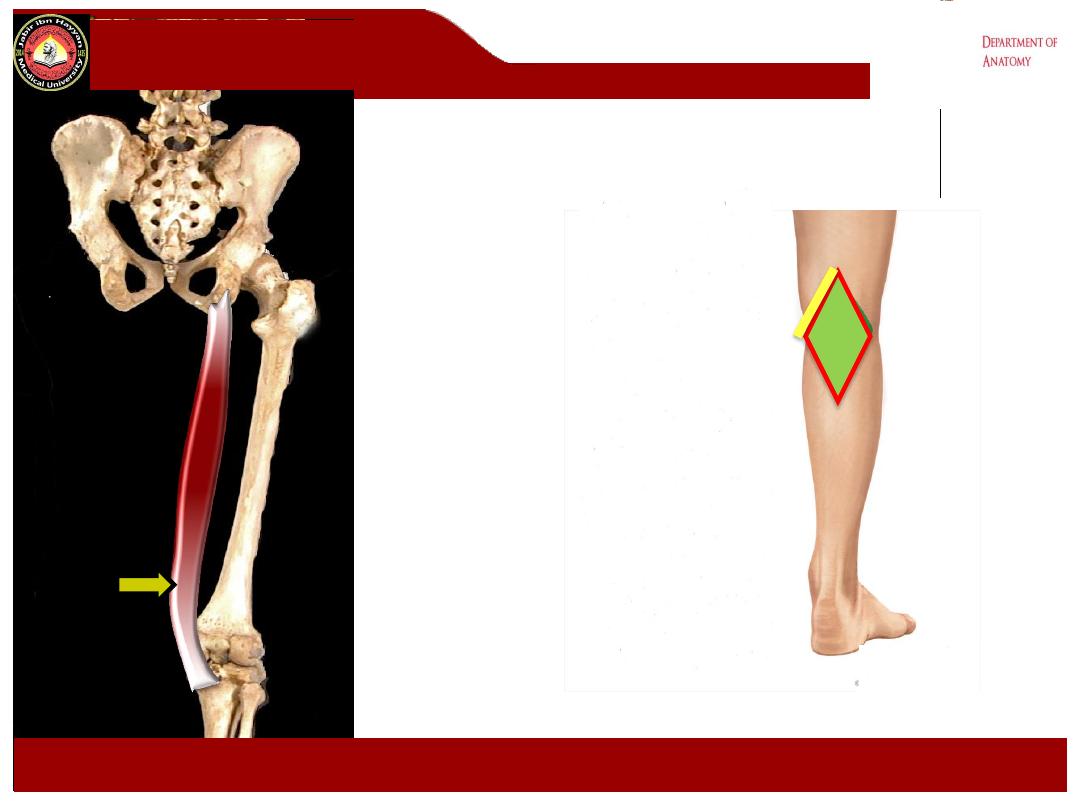
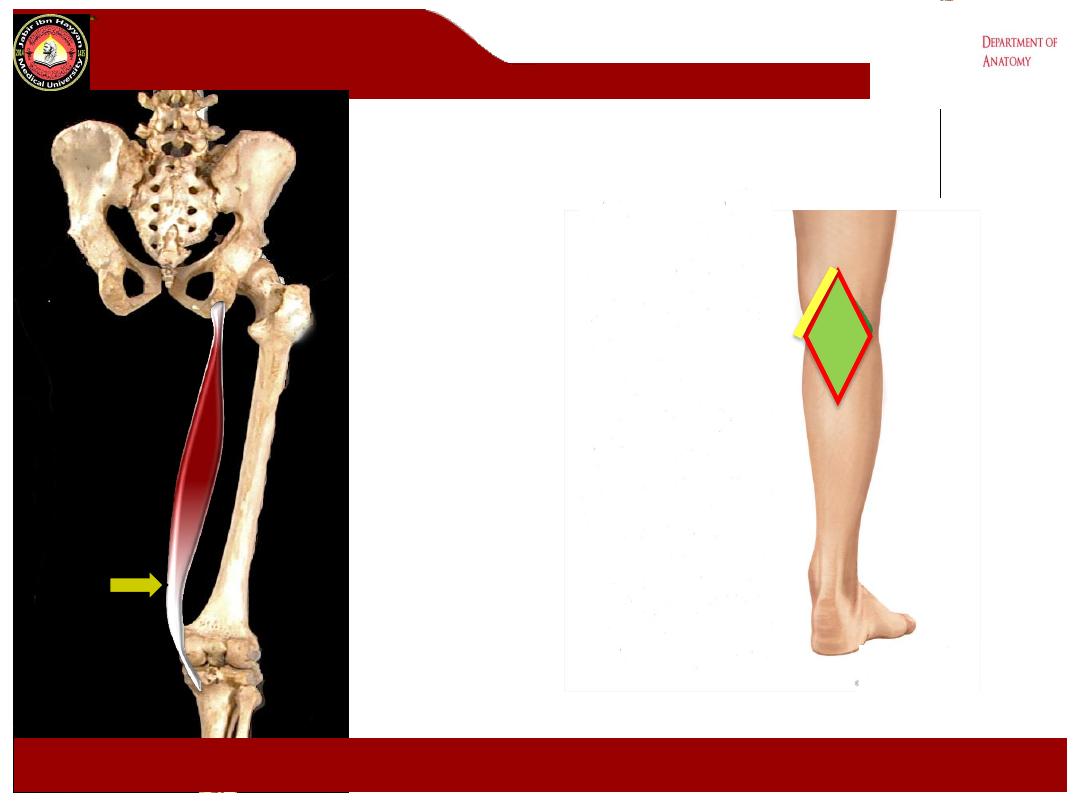
The popliteal fossa
1- It is a
diamond
-shaped intermuscular space ( depression) lies behind
the knee, the lower 1/3 of the femur and the upper part of the tibia.
2- The superficial fascia of the fossa contain little fat, while the deep
fascia is thin and strong. The popliteal fascia is continuous
Proximally with the deep fascia of the thigh
–
Fascia Lata
Distally with the deep fascia of the leg -
Crural Fascia
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY

The popliteal fossa
3-
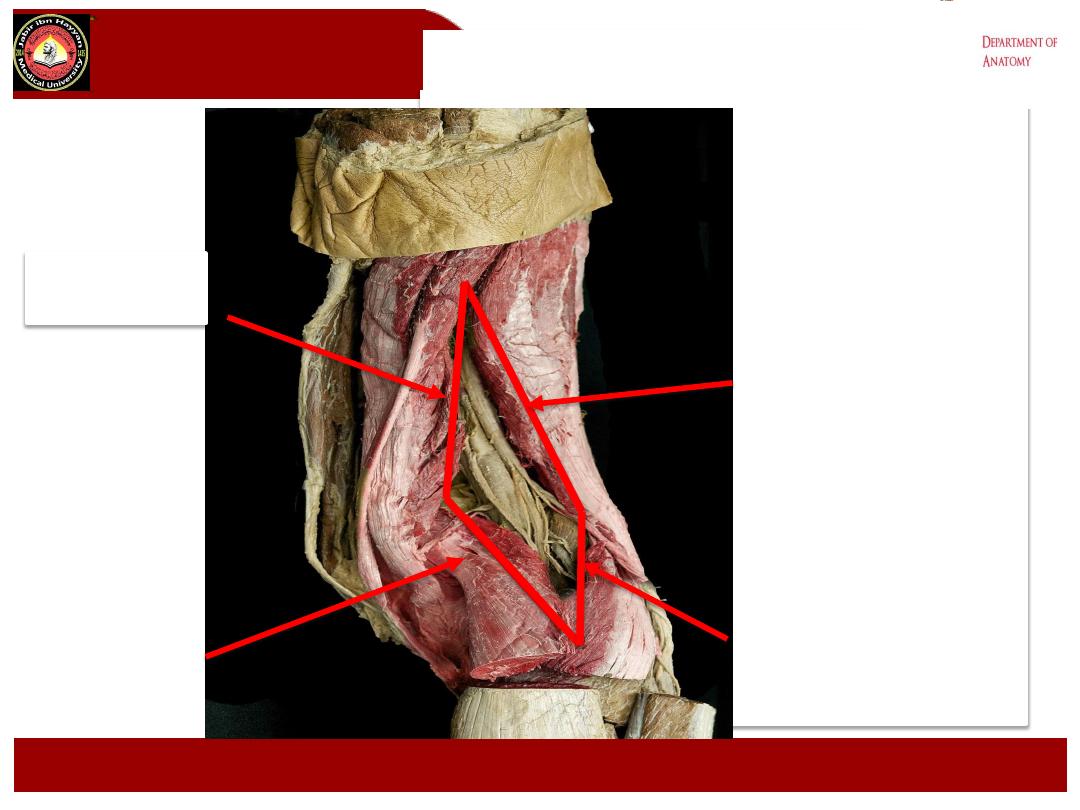
Boundaries
:
a- superolaterally biceps femoris m.
b- superomedially semimembranosus and semitendinosus ms.
c- Inferolaterally lateral head of the gastrocnemius m.
d- Inferomedially Medial head of the gastrocnemius m.
e- The anterior wall ( floor) : from above downward is
the popliteal surface of the femur, popliteus m, the posterior capsule of
the knee joint and oblique popliteal ligament
f- The posterior wall ( roof) is the skin and deep fascia of the fossa
which is here strongly reinforced by transverse fibers. It is pierced by
small saphenous vein & posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
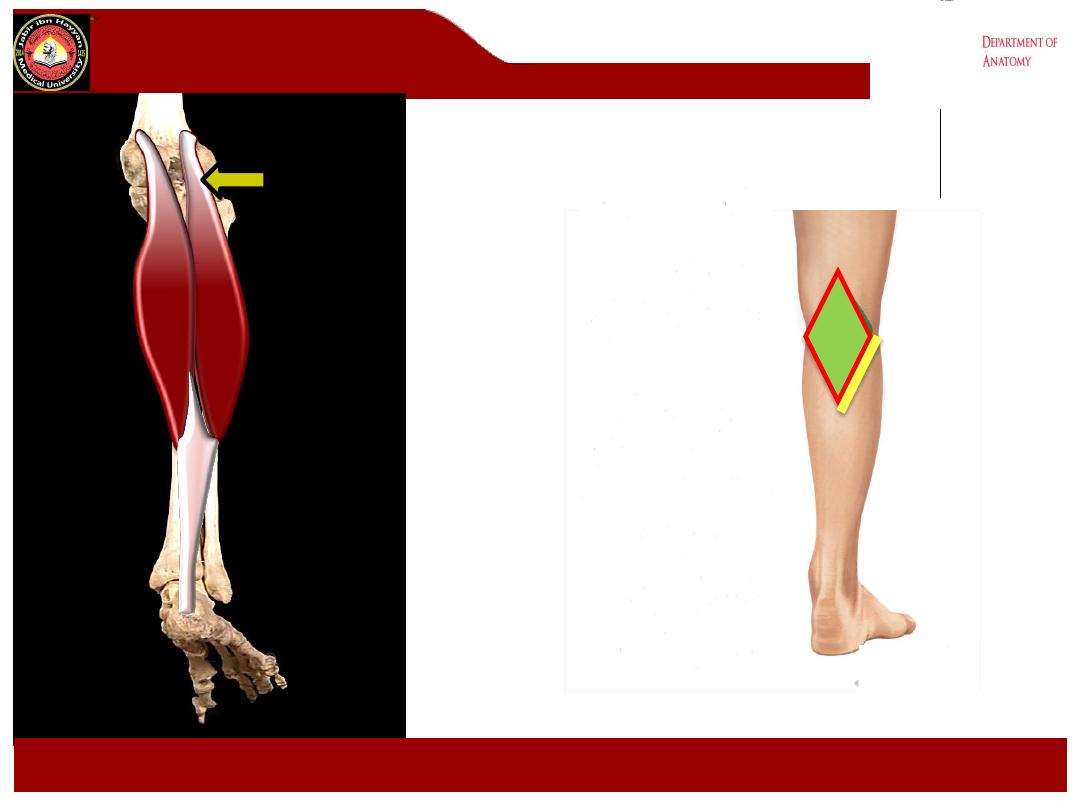
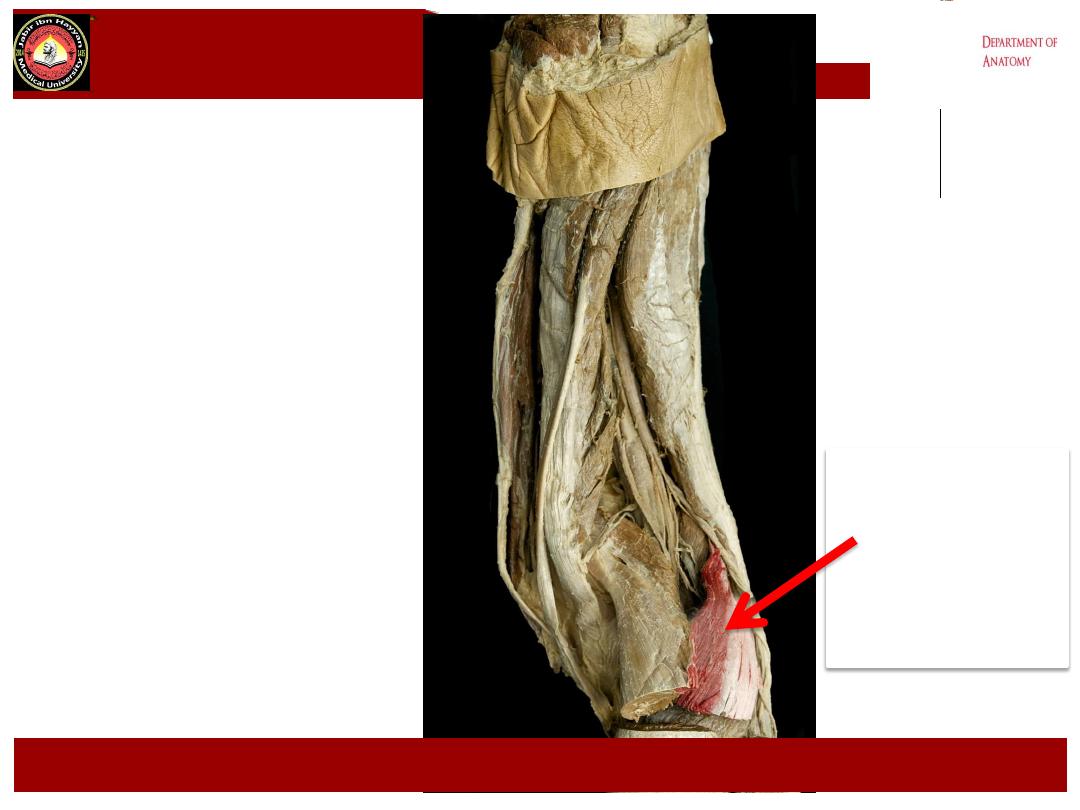
Lateral head of
Gastrocnemius
.
Lower Lateral:
Lateral head of
Gastrocnemius
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
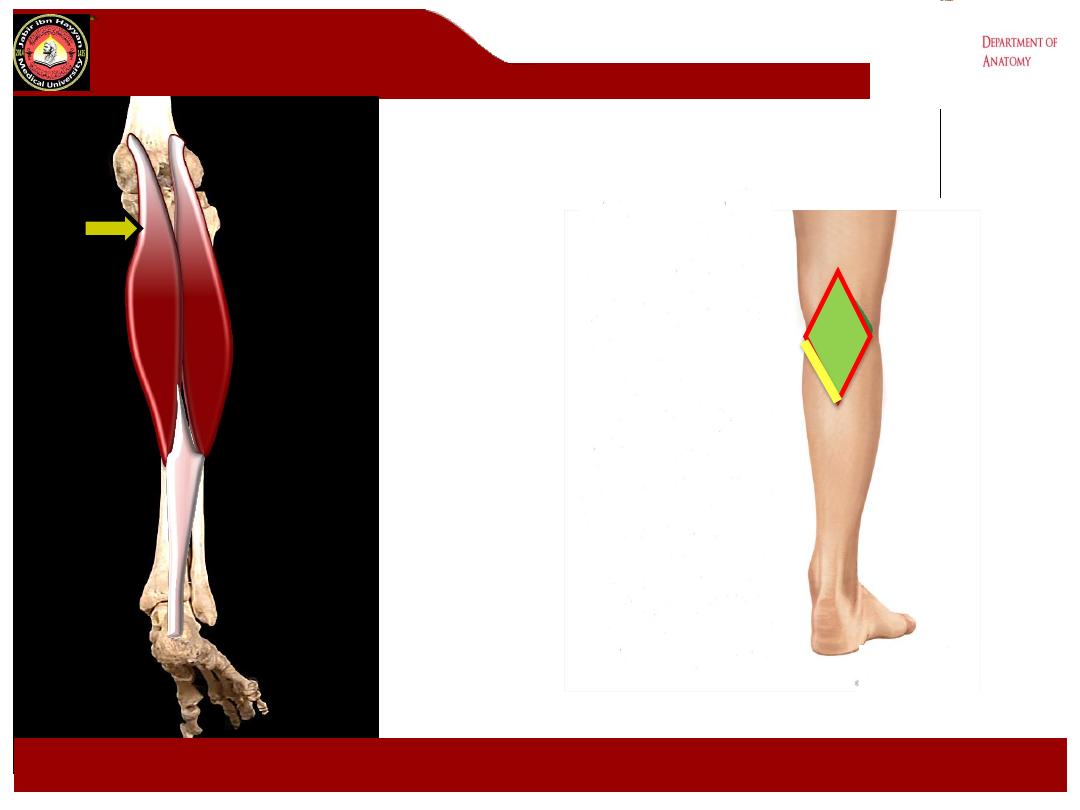
Medial head of
Gastrocnemius
.
Lower Medial:
Medial head of
Gastrocnemius
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
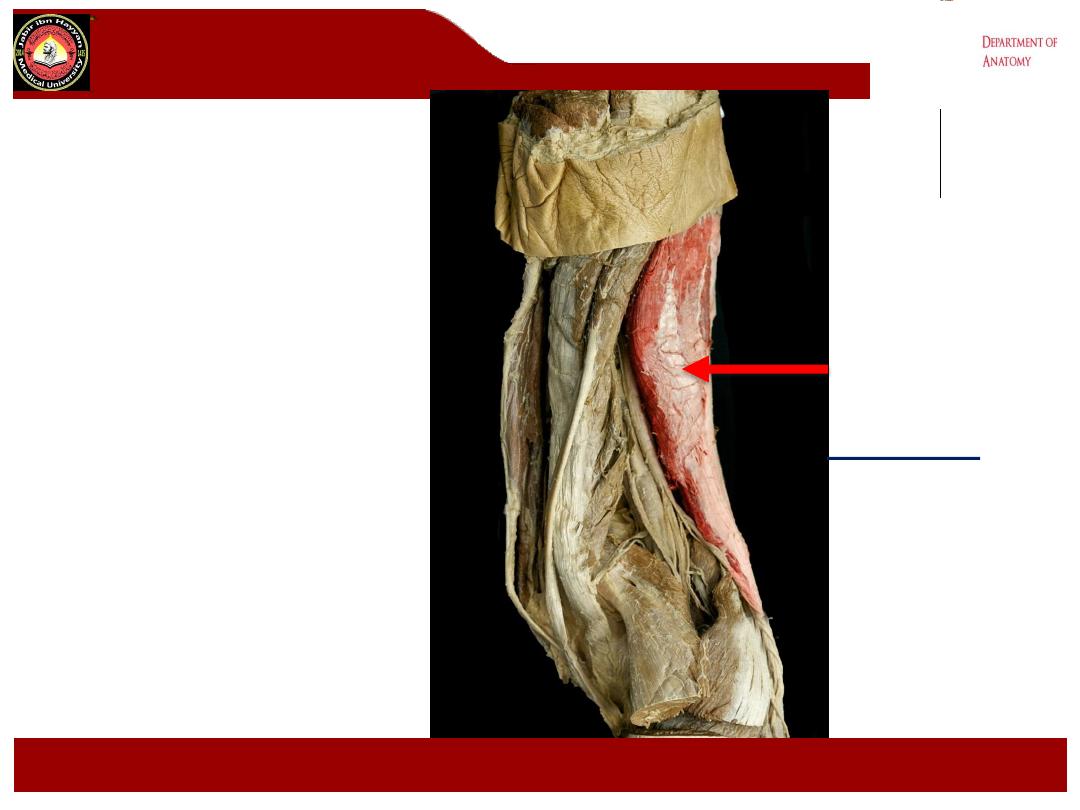
Biceps
femoris
.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
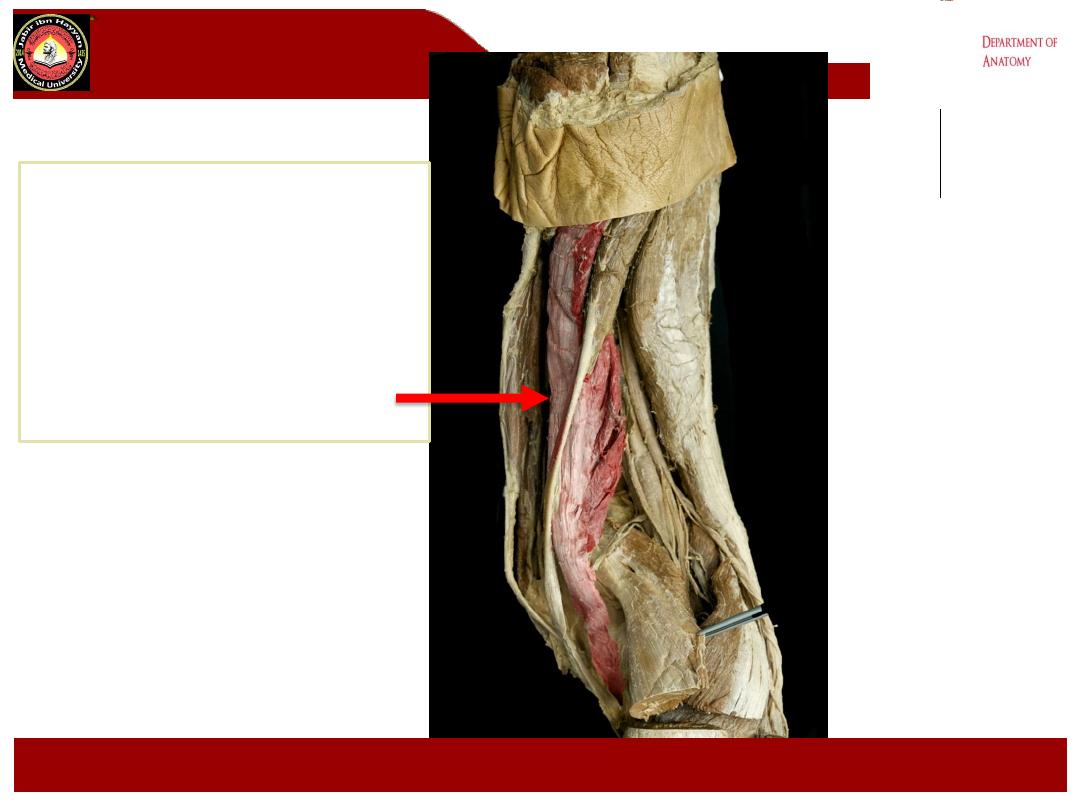
Semimembranosus
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
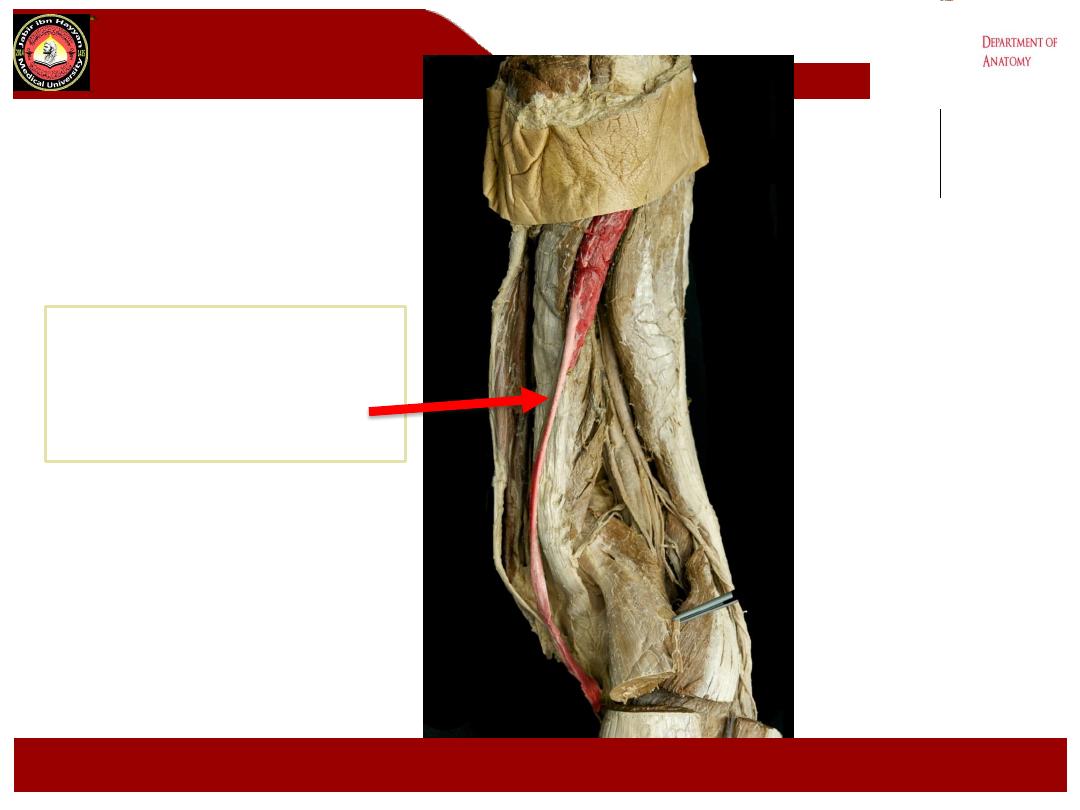
Semitendinosus
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY

Lateral
head
gastrocnemius
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
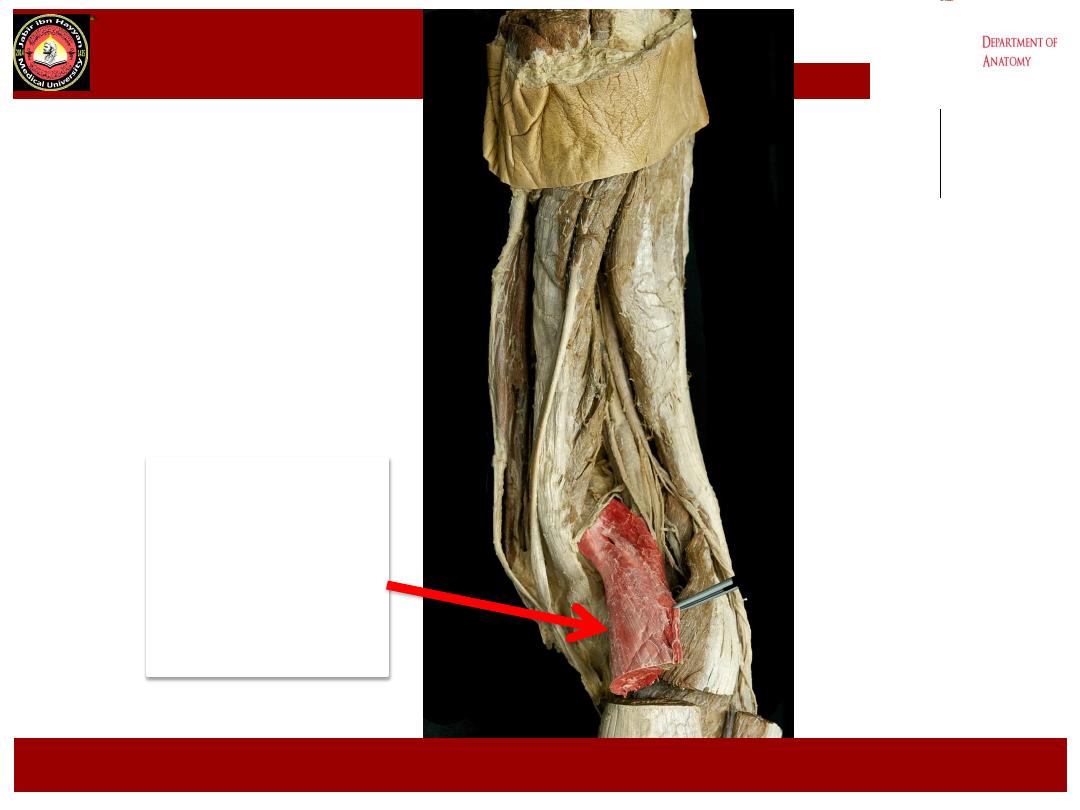
Medial
head
gastrocnemius
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
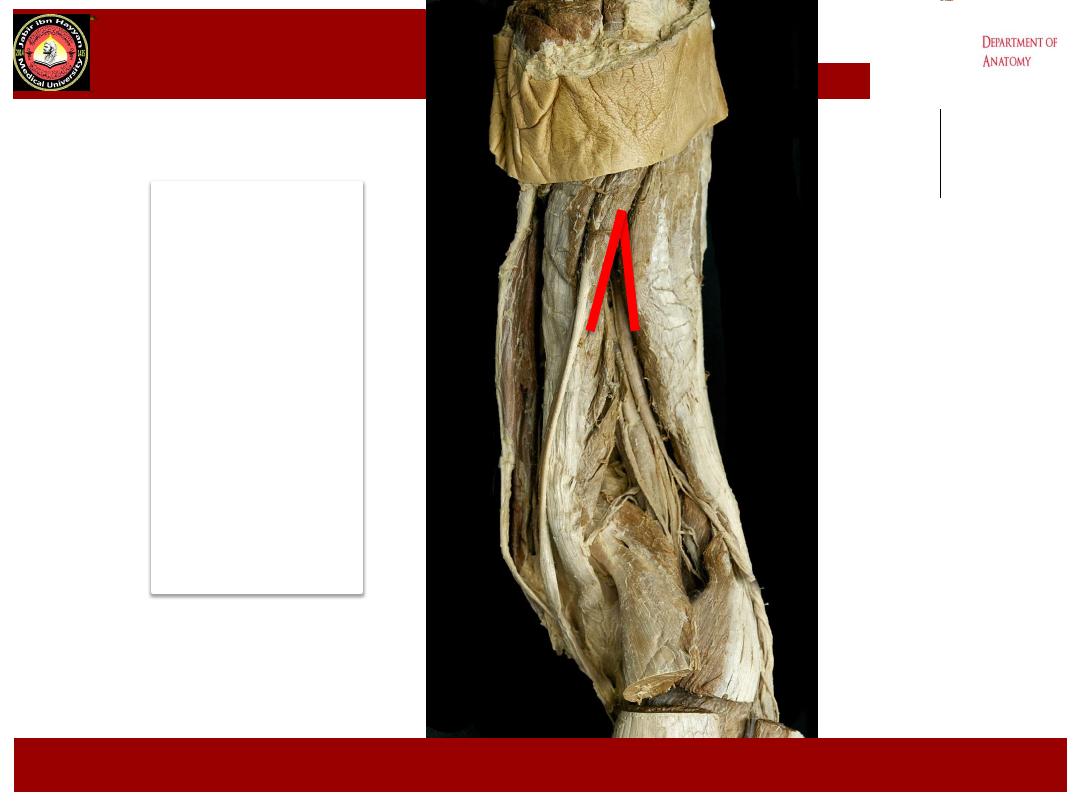

Upper
angle
Of
Popliteal
fossa
,
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
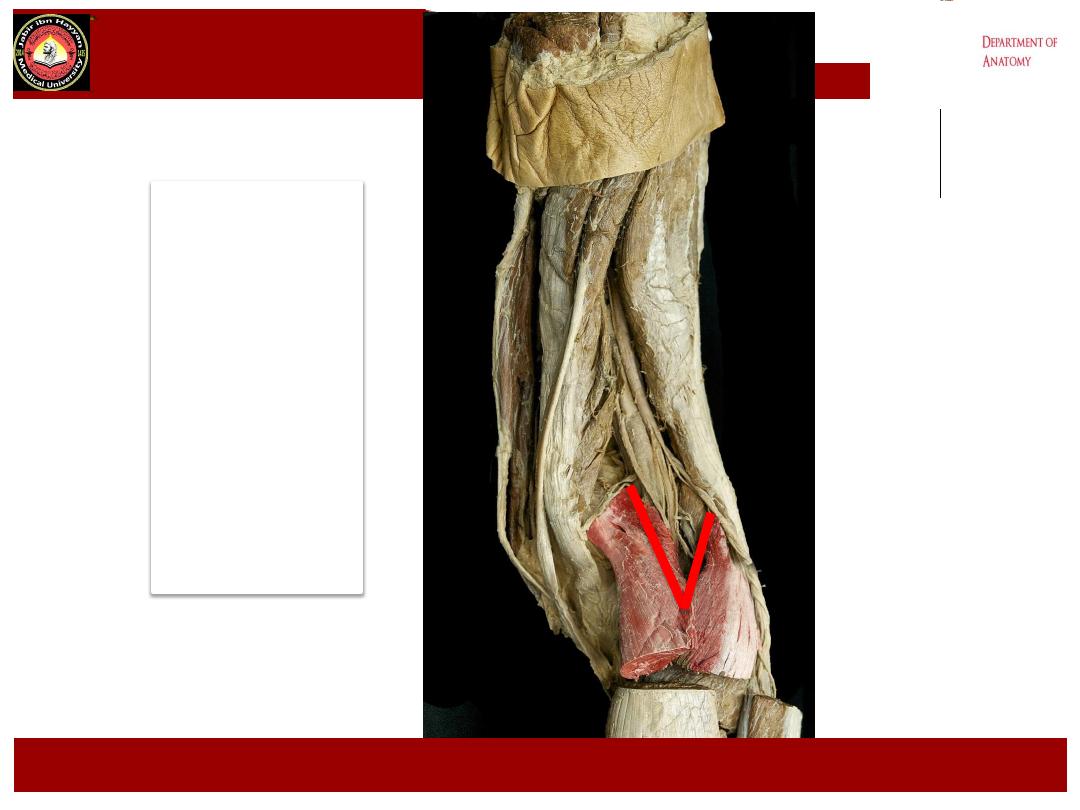
lower
angle
Of
Popliteal
fossa
,
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Upper medial
Boundary
Lower Medial
Boundary
Upper Lateral
Boundary
Lower Lateral
Boundary

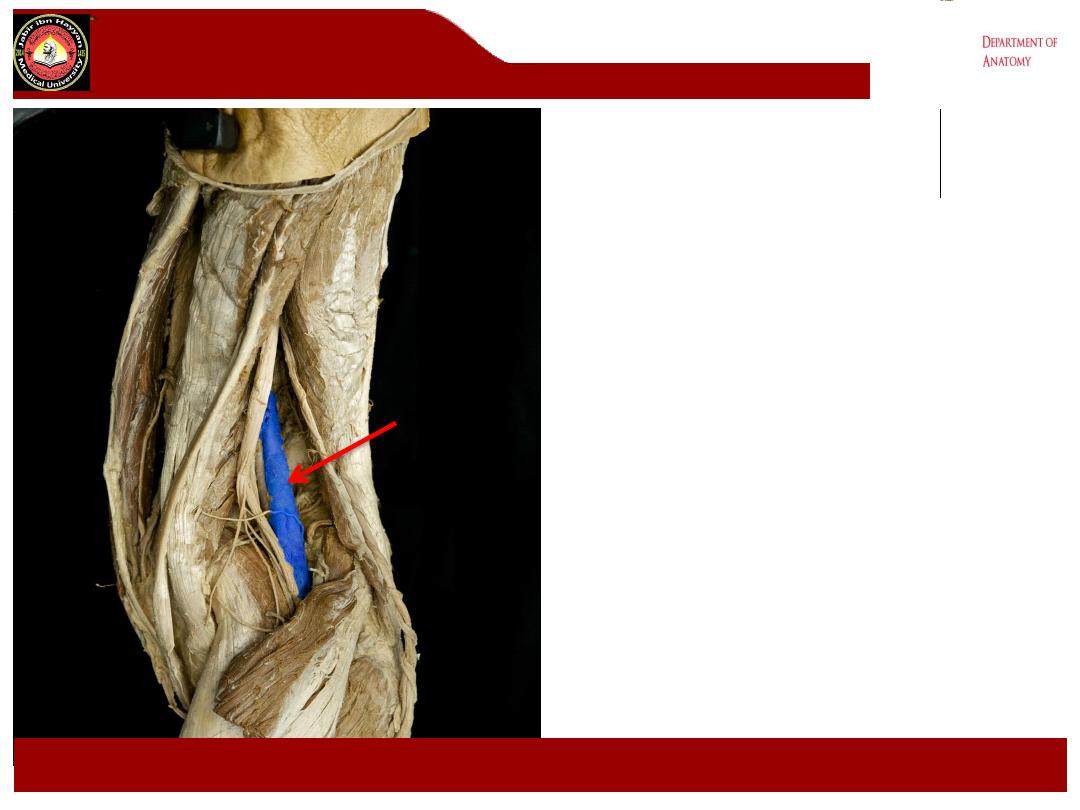
Contents of the fossa
These include:
1-
The popliteal vessels(artery &
vein).
The popliteal art. is most
anteriorly , it gives 5 genicular
branches in the fossa and bifurcates
at lower border of popliteus m. into
anterior and posterior tibial arteries
2- Branches of the sciatic nerve the
tibial and common peroneal nerves
.
3-
Popliteal lymph nodes
.
4-
Posterior cutaneous nerve
of the
thigh.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY

A- The popliteal artery
1- These are the direct continuation of the femoral art. enter
the fossa through the adductor hiatus.
2- They lie anterior to the tibial nerve,.
3- it lies against the posterior part of the capsule of the knee
joint,
4- then it lies posterior to popliteus muscle in the upper part
of the leg.
5- The popliteal artery ends at the lower border of the
popliteus muscle by dividing into anterior and posterior tibial
arteries.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY

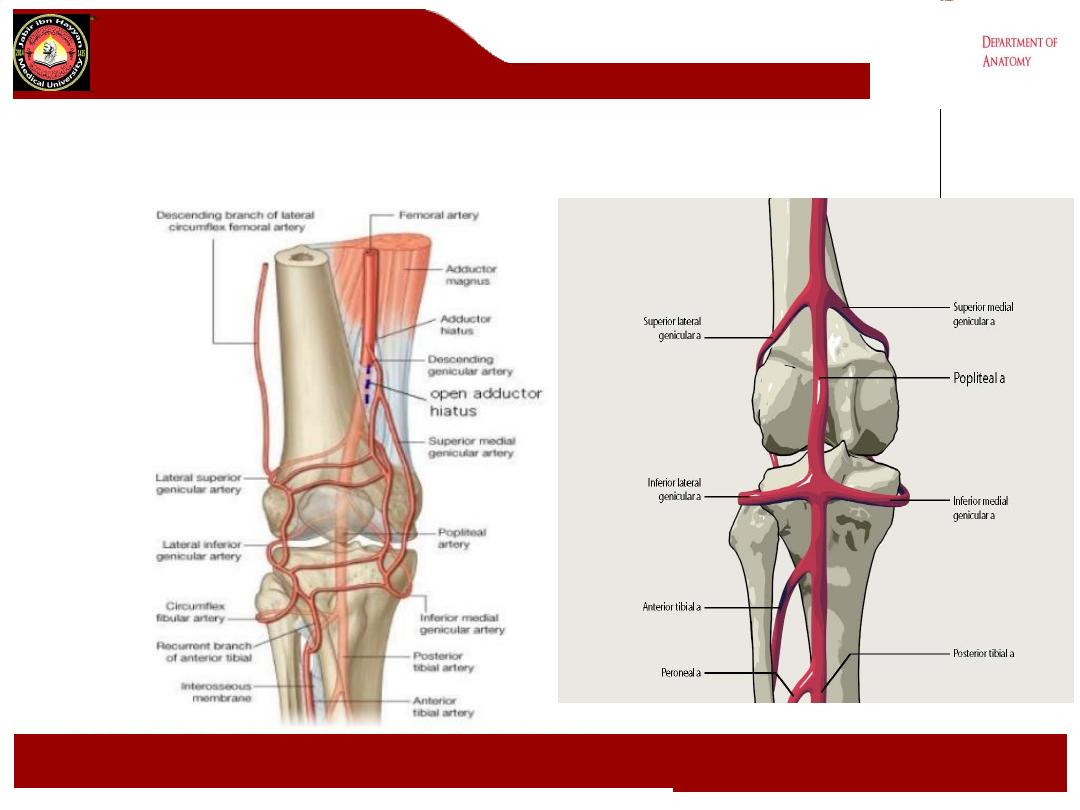
Branches of popliteal artery
:
1- muscular branches to the hamstring ms.
And to the muscles of the calf.
2- Articular branches these are :
a- the lateral and medial superior and inferior
genicular and middle genicular arteries to the
knee joint correspond to the genicular
branches from the tibial and common peroneal
nerves.
b- they anastomosed with the branches from
the lateral circumflex femoral, descending
genicular arteries, and the recurrent branches
of the anterior tibial artery.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
clinically
Popliteal pulsation against
the back of the femur, with
the fingertips of both hands
pressing into the centre of
the fossa
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
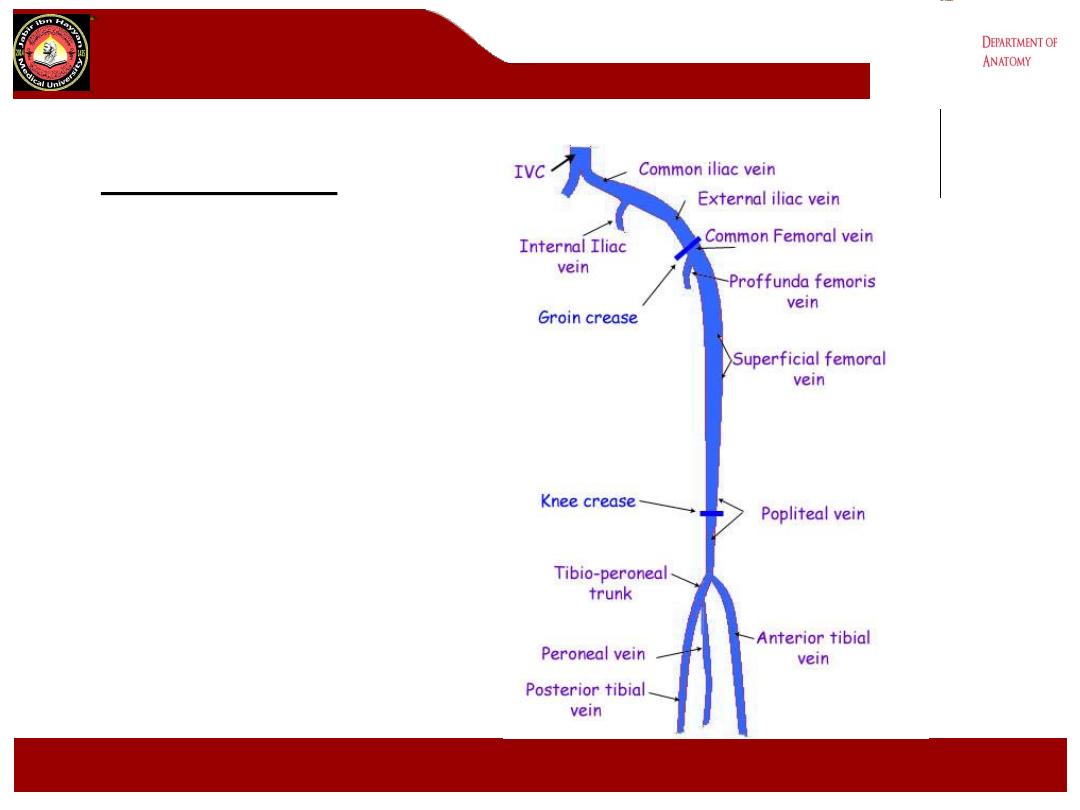
B- The popliteal vein:
1- formed by the union of the
anterior tibial, the posterior tibial
and the peroneal veins at the
lower border of the popliteus
muscle
2- it lies superficial to the artery
and between it and the tibial
nerve.
3- it receive tributaries
correspond to the branches of
the popliteal artery and the lesser
saphenous vein.
4- it become the femoral vein at
the adductor hiatus.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
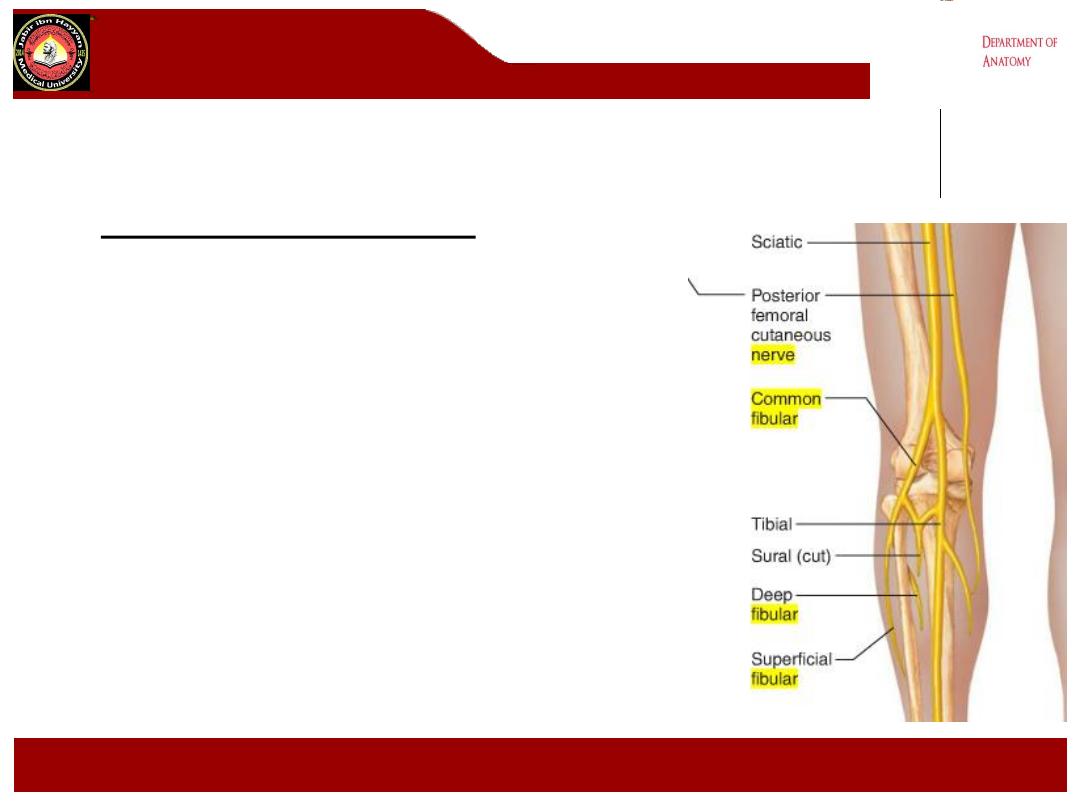
C- Tibial nerve (L4 L5 S1 S2 S3).
1- It is the largest of the two terminal branches
of the sciatic nerve
2- it begins above the popliteal fossa descends
vertically in the fossa, Lying first on the lateral
side of the popliteal artery then posterior to it
and finally medial to it.
3- it pass between the two heads of the
gastrocnemius muscle and under the soleus
muscle.
4- It supply the muscles of the back of the thigh
and leg, the sole of the foot, the skin of the
lateral and lower half of the back of the leg and
sole of the foot.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
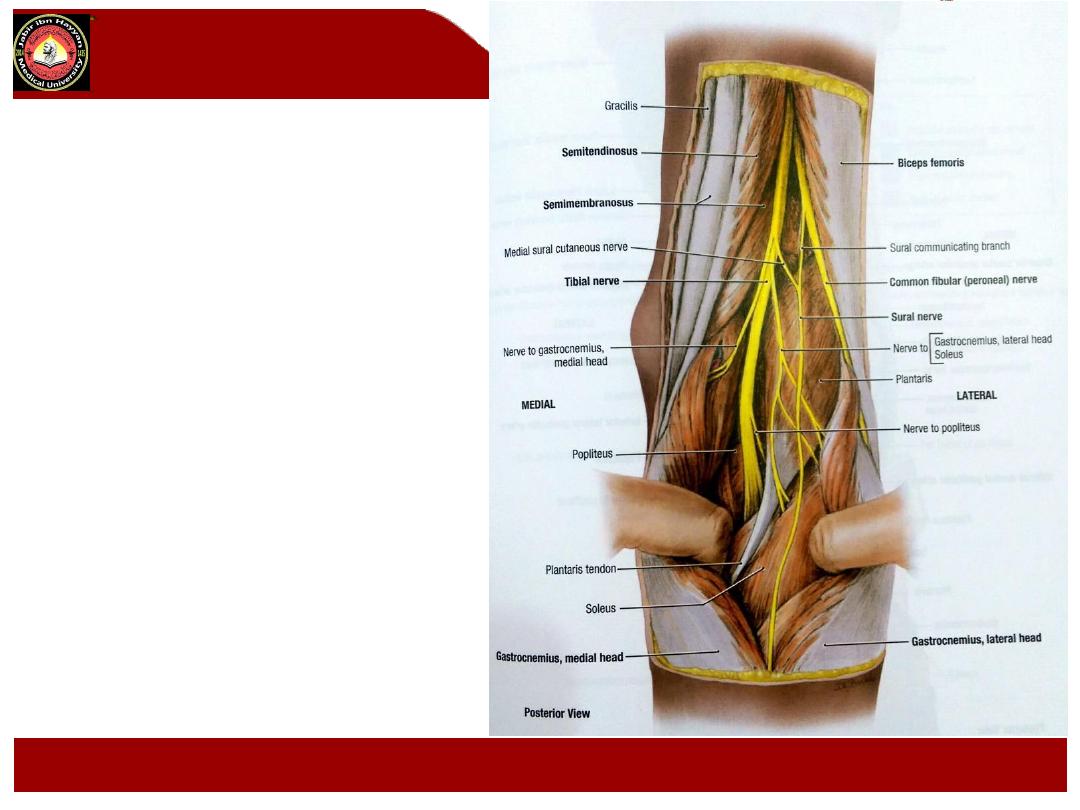
Branches in the popliteal fossa
:
1- Articular branches, it gives
superomedial, inferomedial and
middle genicular branches to the
knee joint, accompanied the
corresponding branches from the
popliteal artery
2- Muscular branches to the
muscles of the back of the thigh
and to the gastrocnemius, plantaris,
soleus and popliteus ms.
3- sural nerve:
a- it is a cutaneous branch descend
in the groove between the two
heads of the gastrocnemius m.
b- it pierce the deep fascia about
the middle of the back of the leg,
supply the skin of the lower
posterior part of the leg and the
skin of the lateral side of the
dorsum of the foot.
c- It accompany the small
saphenous vein.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY

D- Common peroneal nerve (L4 L5 S1 S2)
1- It is smaller than tibial nerve follow the tendon of biceps femoris m. along the upper lateral border of
the popliteal fossa to the back of the head of the fibula,
2- then curves forwards along the neck of the fibula deep to the peroneus longus m. here it divides into
deep and superficial branches.
Branches in the popliteal fossa:
1-
cutaneous branches
, these include
a-
the peroneal communicating
branch which arise in the upper part of the popliteal fossa descend
on the posterolateral side of the calf , it supply the proximal 2/3 of the posterolateral part of the leg.
b-
Lateral cutanous nerve of the calf
arise on the lateral head of the gastrocnemius m. supply the
lateral side of the leg.
2-
articular branches
, these include:
a-
the superior and the inferior lateral
genicular branches they are small branches accompany the
corresponding arteries.
b-
Recurrent genicular branch
arise where the common peroneal nerve divides into superficial and
deep branches, it ascends to the knee joint.
3-
muscular branch
to the short head of the biceps femoris m. arise high up in the fossa
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY

popliteal fossa
contents
Popliteal lymph nodes: about six LNs. Are embedded in the
fatty connective tissue of pop. Fossa .they receive superficial
lymph vs. from lateral side of the foot & leg ,these accompany
small saphenous vein into pop. Fossa ,they also receive lymph
from knee joint&from deep lymph vs. accompanying the anterior
& posterior tibial arteries..
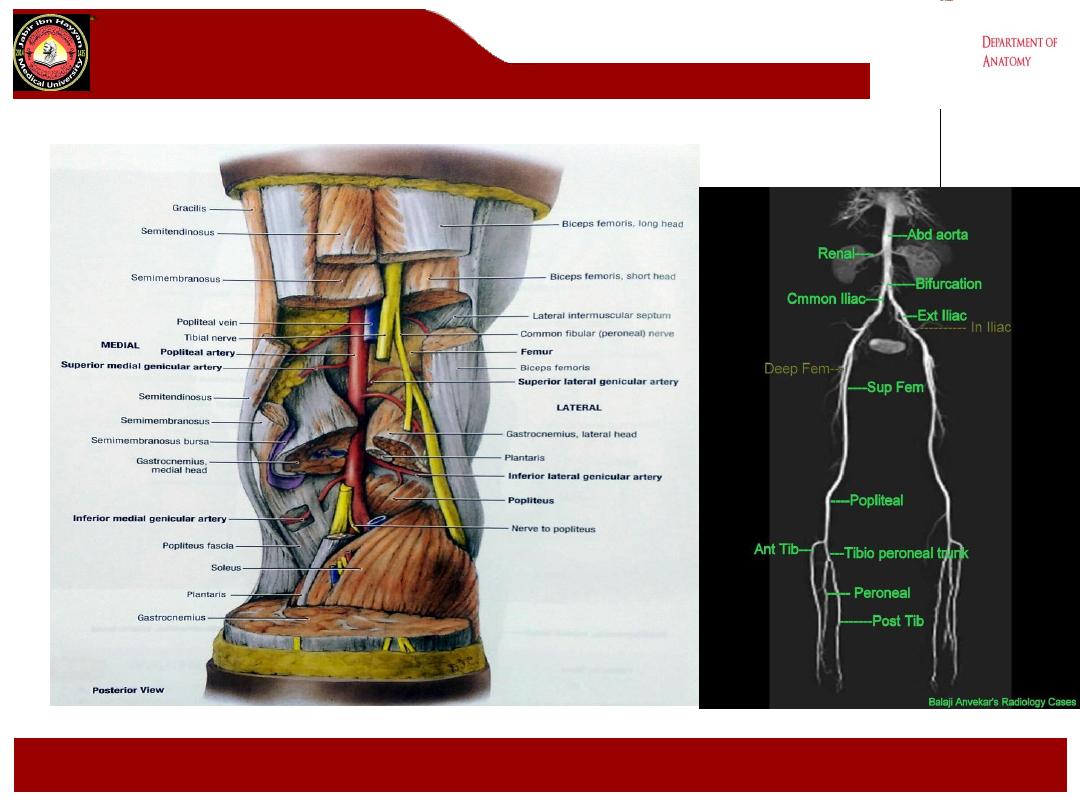
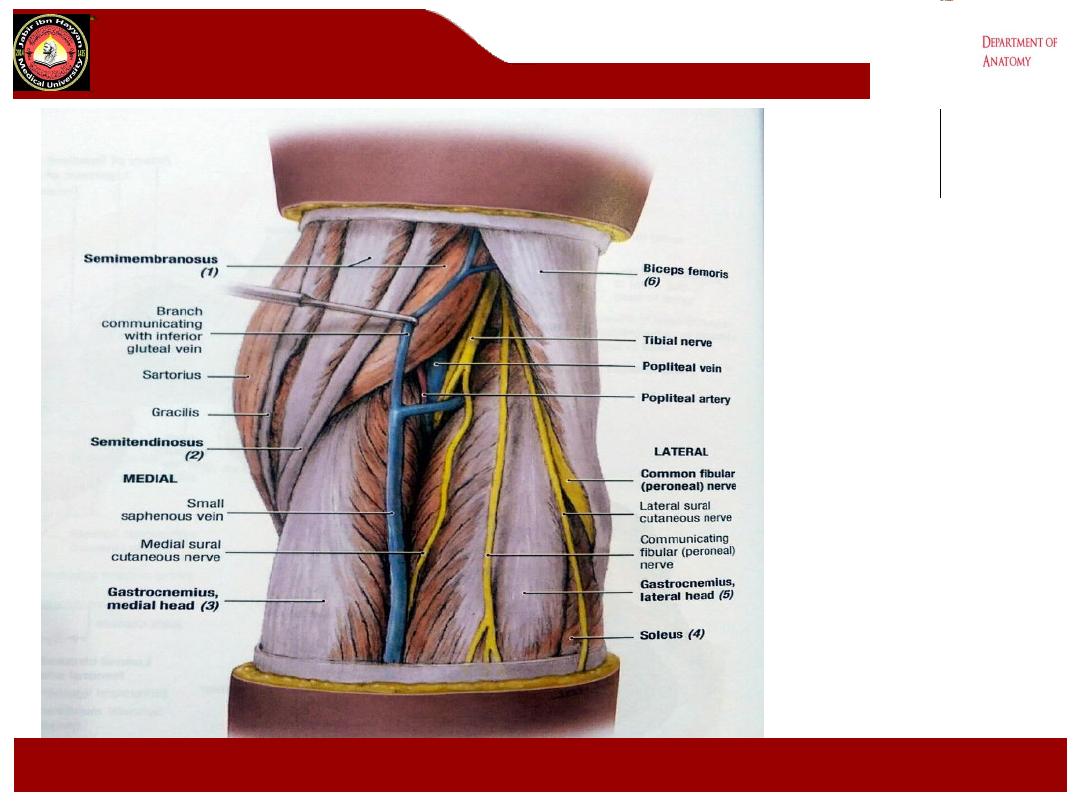
Note: Review the relationship of the nerves, veins, and arteries
within the popliteal fossa. The
common peroneal and tibial
nerves
are most superficial, the
popliteal vein
and its branches
are intermediate in position, and the
popliteal artery
and its
branches are most deep and lie adjacent to the femur, tibia, and
the knee joint capsule.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
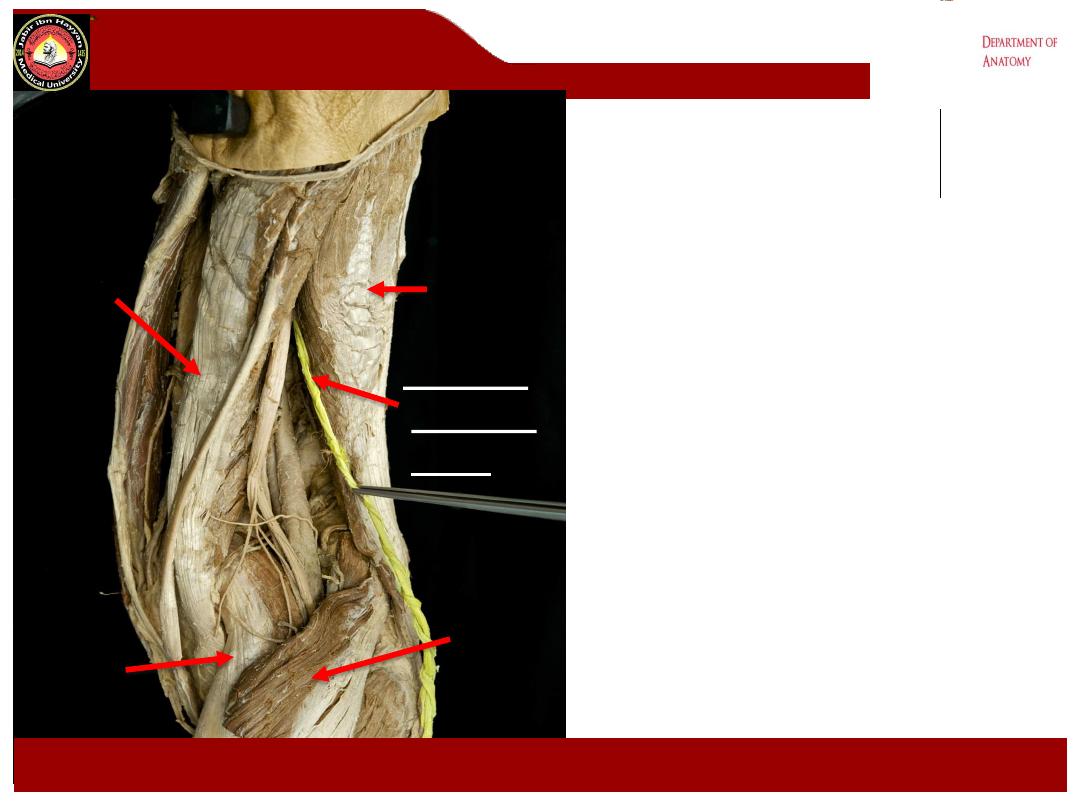
Posterior view of knee
SM Biceps
Tibial nerve
LG
MG
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
SM
Biceps
common
peroneal
nerve
LG
MG
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
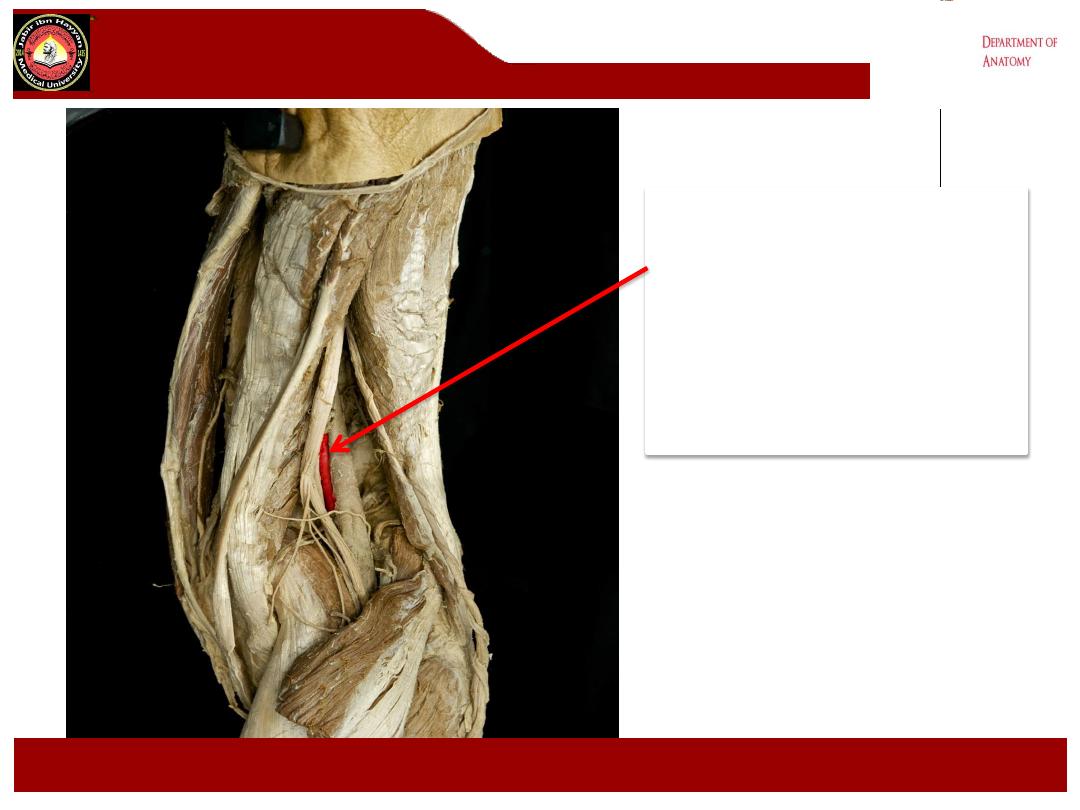
Popliteal artery
.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
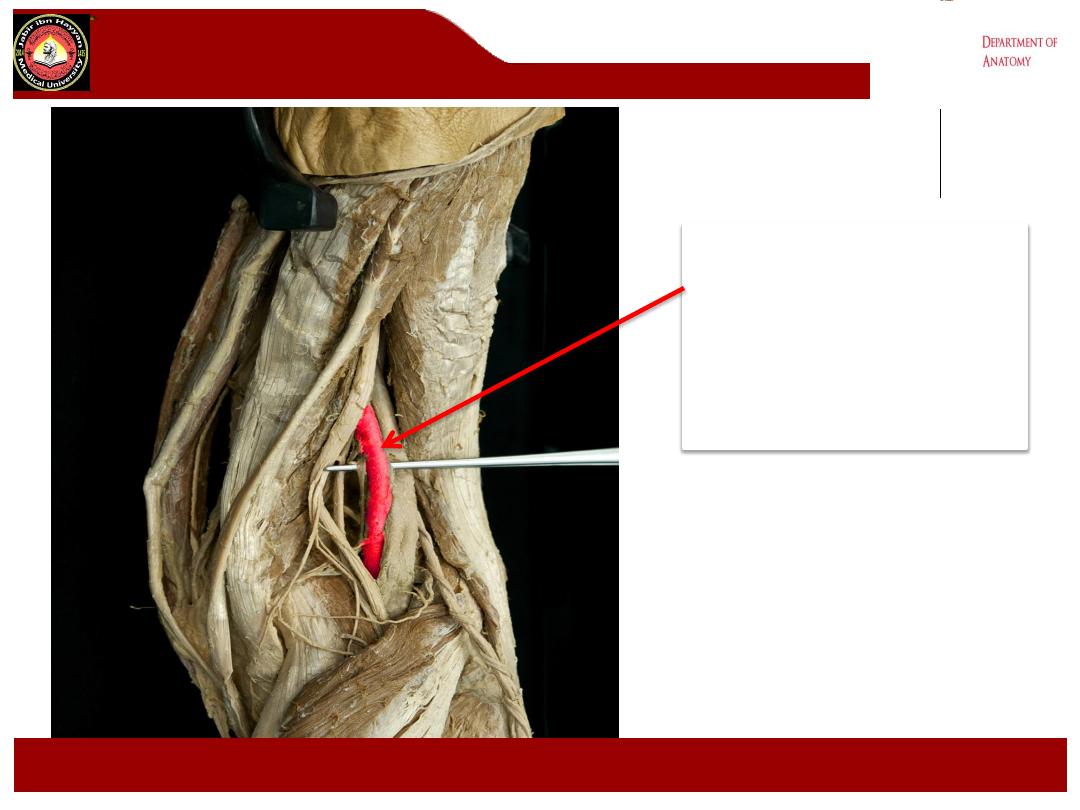
Popliteal artery
.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY

.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
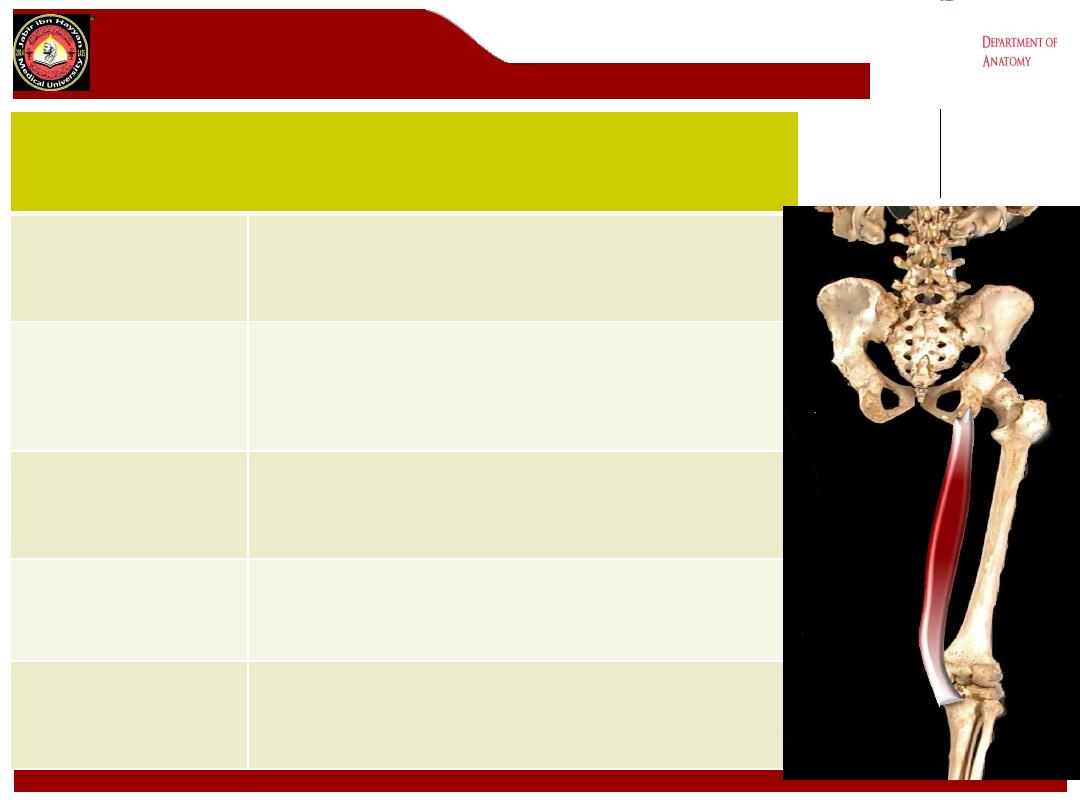
semimembranosus
Origin
Superior lateral quadrant of posterior surface
ischial tuberosity
Insertion
Posterior surface of the medial tibial condyle.
Sends fascial extension over popliteus, and
gives rise to oblique popliteal ligament
Action
Extends hip, flexes and medially rotates the
knee
Nerve supply
Tibial component of sciatic nerve
(L5, S1)
Blood supply
Perforating branches of profunda femoris
artery, inferior gluteal artery, and the superior
muscular branches of popliteal artery
.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
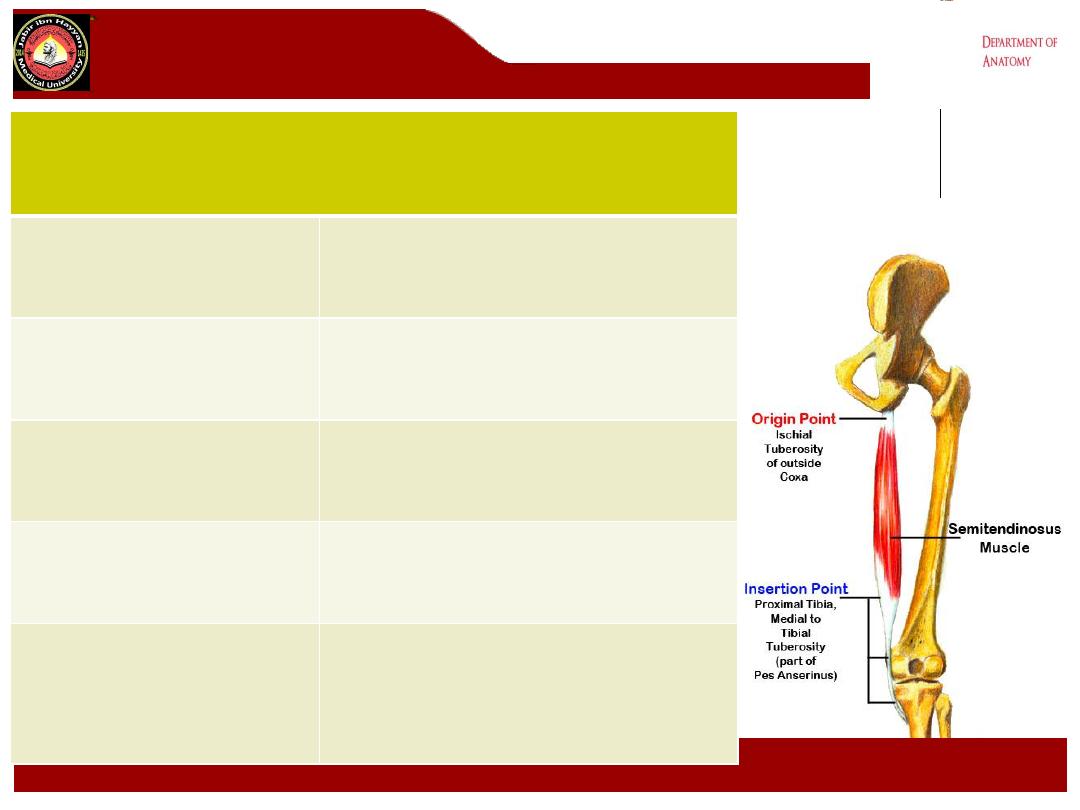
Semitendinosus
Origin
Superior medial quadrant,
posterior surface ischial tuberosity
Insertion
Superior part, medial tibial shaft
Action
Extends hip, flexes and medially
rotates knee
Nerve supply
Tibial component of sciatic nerve
(L5, S1)
Blood supply
Perforating branches of profunda
femoris artery, inferior gluteal
artery, superior muscular branches
of popliteal artery

.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Bi
ceps Femoris
Origin
Long Head: Superior medial quadrant of the
posterior surface of the ischial tuberosity
Short Head: Middle third linea aspera, lateral
supracondylar ridge of femur
Insertion
Fibular head, with extensions to lateral
collateral ligament and lateral tibial condyle
Action
Flexes the knee, rotates tibia laterally,
extends the hip joint
Nerve supply
Long head: tibial component of sciatic nerve,
Short head: common peroneal component of
sciatic nerve (L5, S1)
Blood supply
Perforating branches of profunda femoris
artery, inferior gluteal artery, superior
muscular branches of popliteal artery
.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
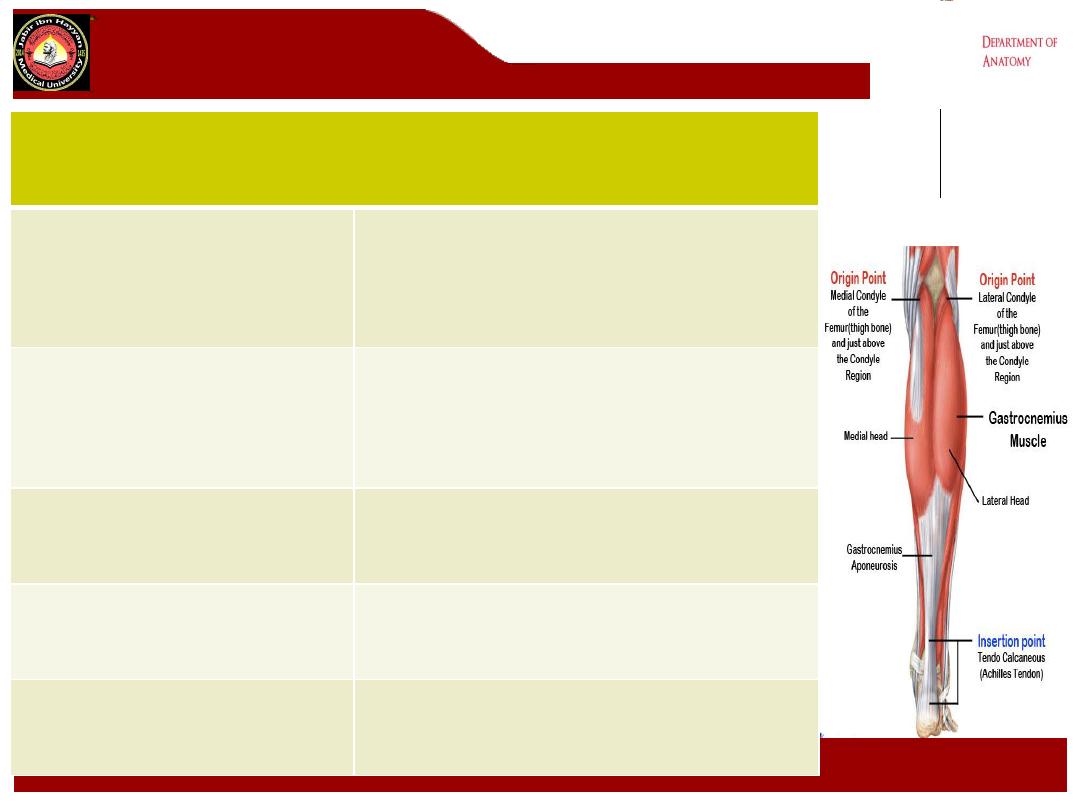
Gastrocnemius
Origin
Medial head: posterior surface of
medial femoral condyle
Lateral head: posterior surface of
lateral femoral condyle
Insertion
The two heads unite and with soleus
form the Achilles tendon, which inserts
onto the posterior and upper surface of
calcaneum
Action
Powerful plantar flexor of ankle
Nerve supply
Tibial nerve ( S1, S2)
Blood supply
Sural branches of the popliteal artery
.
Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
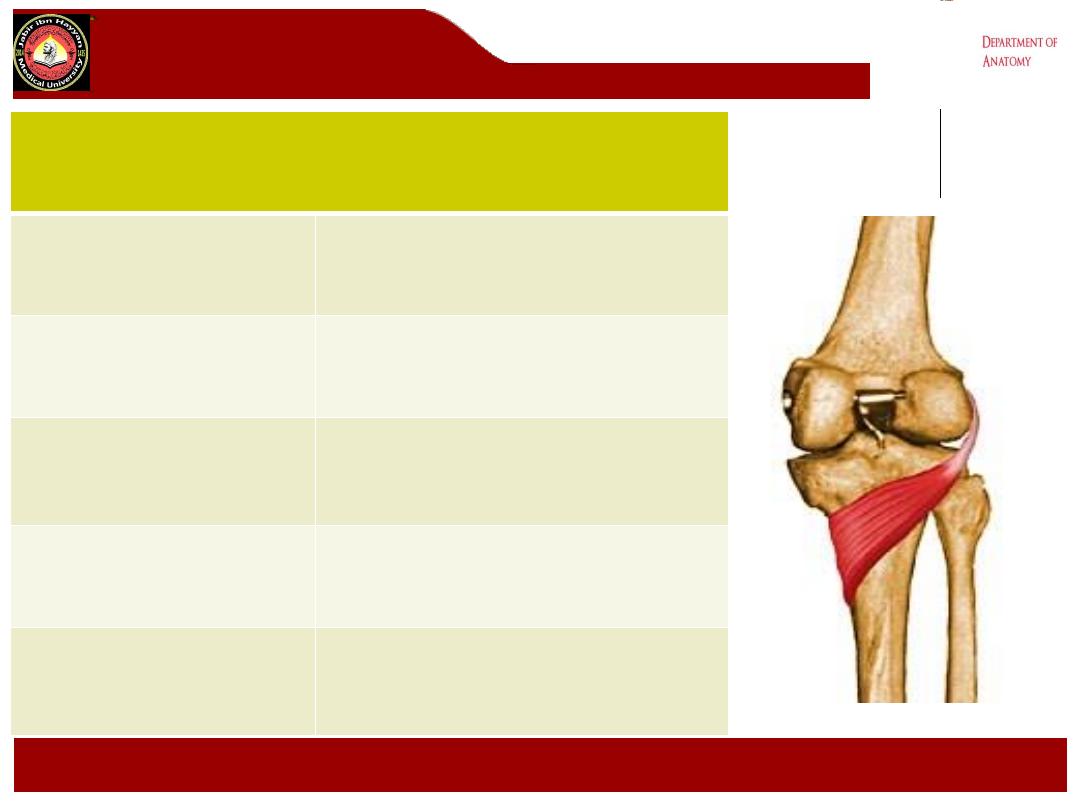
popliteus
Origin
Lateral surface of lateral femoral
condyle
Insertion
Posterior surface of the shaft of
the tibia above soleal line
Action
Flex knee joint,lateral rotation of
femur on tibia
(unlocking the knee joint)
Nerve supply
Tibial nerve (L4,L5,S1)
Blood supply
Medial inferior genicular branch of
popliteal artery and muscular
branch of posterior tibial artery

Jabir ibn Hayyan
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY