
1
Fifth stage
Pediatrics
Lec2
د.أثل
2016
Lower Airway Diseases
• Lower air way disease often result in air way obstruction. Obstruction below the
thoracic inlet manifist mainly as wheezing.
• A wheeze is a continuous musical sound that is produced by vibration of airway walls
mainly on expiration.
• Intrathoracic pressure is increased relative to atmospheric pressure during exhalation,
which tends to collapse the intrathoracic airways and accentuates airway narrowing on
expiration. This manifests as expiratory wheeze, prolonged expiratory phase, and
increased expiratory work of breathing.
Causes of Wheezing in Childhood
:
1- Reactive airway disease
Asthma
Hypersensitivity reactions
2- Bronchial edema
Infection (e.g., bronchiolitis)
Inhalation of irritant gases or particulates
3- Bronchial hypersecretion
Infection
Inhalation of irritant gases or particulates
Cholinergic drugs
4- Aspiration
Foreign body
Aspiration of gastric contents
Chronic or recurrent :
1. Reactive airway disease.
2. Hypersensitivity reactions, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis.
3. Dynamic airway collapse.
Bronchomalacia/tracheomalacia
Vocal cord adduction
4. Airway compression by mass or blood vessel
Vascular ring/sling
Lymph nodes
5. Aspiration
Foreign body
Swallowing dysfunction
GER

2
6. Bronchial hypersecretion or failure to clear secretions
Bronchitis, bronchiectasis
Cystic fibrosis
7. Intrinsic airway lesions
Endobronchial tumors
8. Endobronchial tuberculosis
Bronchial or tracheal stenosis
Bronchiolitis obliterans
9. Congestive heart failure
Asthma ~
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition of the lung airways resulting in episodic airflow
obstruction. This chronic inflammation heightens the airways hyperresponsiveness (AHR) to
provocative exposures.
Epedemiology :-
Asthma is a common chronic disease, causing considerable morbidity.
Male gender and living in poverty are demographic risk factors for having childhood
asthma.
Childhood asthma is among the most common causes of childhood emergency
department visits, hospitalizations, and missed school days .
Approximately 80% of all asthmatic patients report disease onset prior to 6 yr of age.
However, of all young children who experience recurrent wheezing, only a minority
go on to have persistent asthma in later childhood.
Risk factors :-
Early childhood risk factors for persistent asthma have been identified and have been
described as:
Major: (parent asthma, eczema, inhalant allergen sensitization) and
Minor: (allergic rhinitis, wheezing apart from colds, ≥4% peripheral blood
eosinophils, food allergen sensitization .)
Allergy in young children with recurrent cough and/or wheeze is the strongest identifiable
factor for the persistence of childhood asthma.

3
Etiology :-
A combination of environmental exposures and inherent biologic and genetic susceptibilities
can trigger airway hyperresponsiveness.
1- Genetics:
To date, more than 100 genetic loci have been linked to asthma,although relatively few have
consistently been linked to asthma
2- Environment
:
Common viral infections of the respiratory tract
Animal dander
Indoor allergens (Dust mites , Cockroaches )
Seasonal aeroallergens ( trees, grasses, weeds )
Air pollutants ) dust, Wood- or coal-burning smoke )
Strong or noxious odors or fumes
Cold air, dry air
Exercise and psychological factors
Types of childhood asthma :-
There are 2 common types of childhood asthma based on different natural courses :
Recurrent wheezing in early childhood, primarily triggered by common respiratory
viral infections, usually resolves during the preschool/lower school years.
Chronic asthma associated with allergy that persists into later childhood and often
adulthood.
4
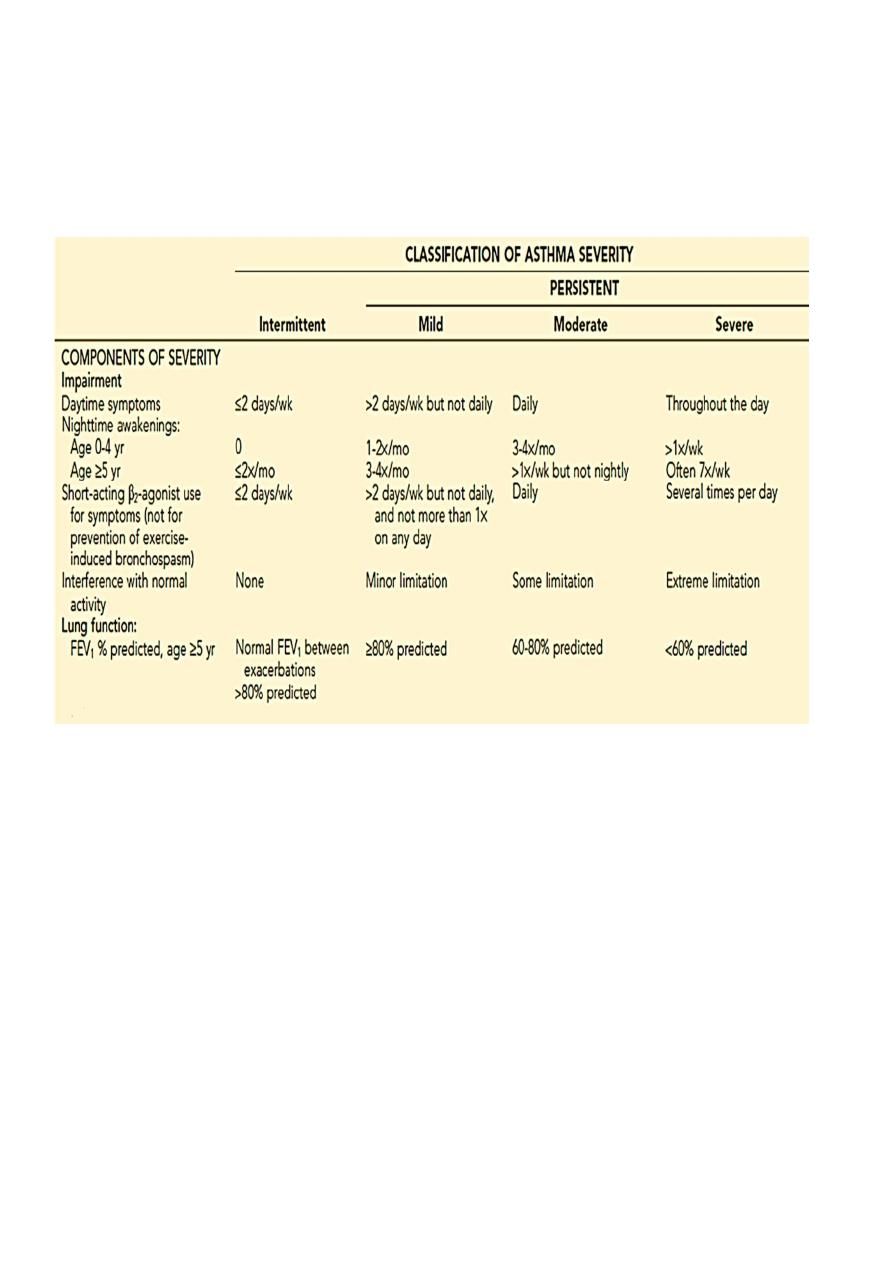
Asthma is also classified by disease severity:
Intermittent disease :
Persistent :
Mild
Moderate
Severe
Clinical manifestation :-
The history should elicit the frequency, severity, and factors that worsen the child's
symptoms. Exacerbating factors include viral infections, exposure to allergens and
irritants. Rhinosinusitis, gastroesophageal reflux, and sensitivity to NSAID(especially
aspirin) can aggravate asthma. Obtaining a family history of allergy and asthma is
useful .
Children with asthma have symptoms of coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath or
rapid breathing, and chest tightness. Nighttime symptoms are common.
Physical examination: tachypnea, tachycardia, cough, wheezing, and a prolonged
expiratory phase & the finding may be subtle. Physical examination may show
evidence of other atopic diseases such as eczema or allergic rhinitis .
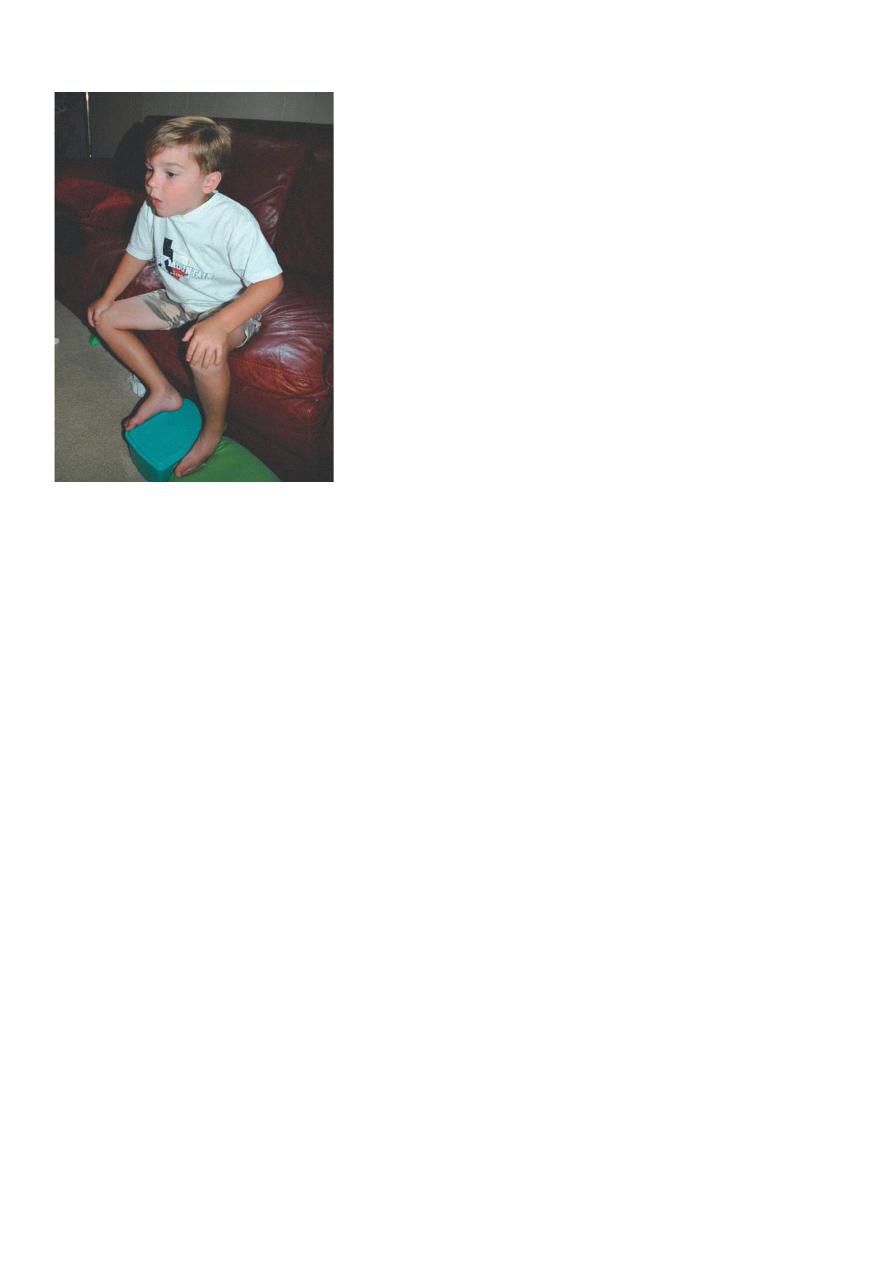
In severe attack: cyanosis, diminished air movement, retractions, agitation, inability to
speak, tripod sitting position, diaphoresis, and pulsus paradoxus (decrease in blood
pressure with inspiration of >15 mm Hg) may be observed.

5
Tripod position
Investigations :-
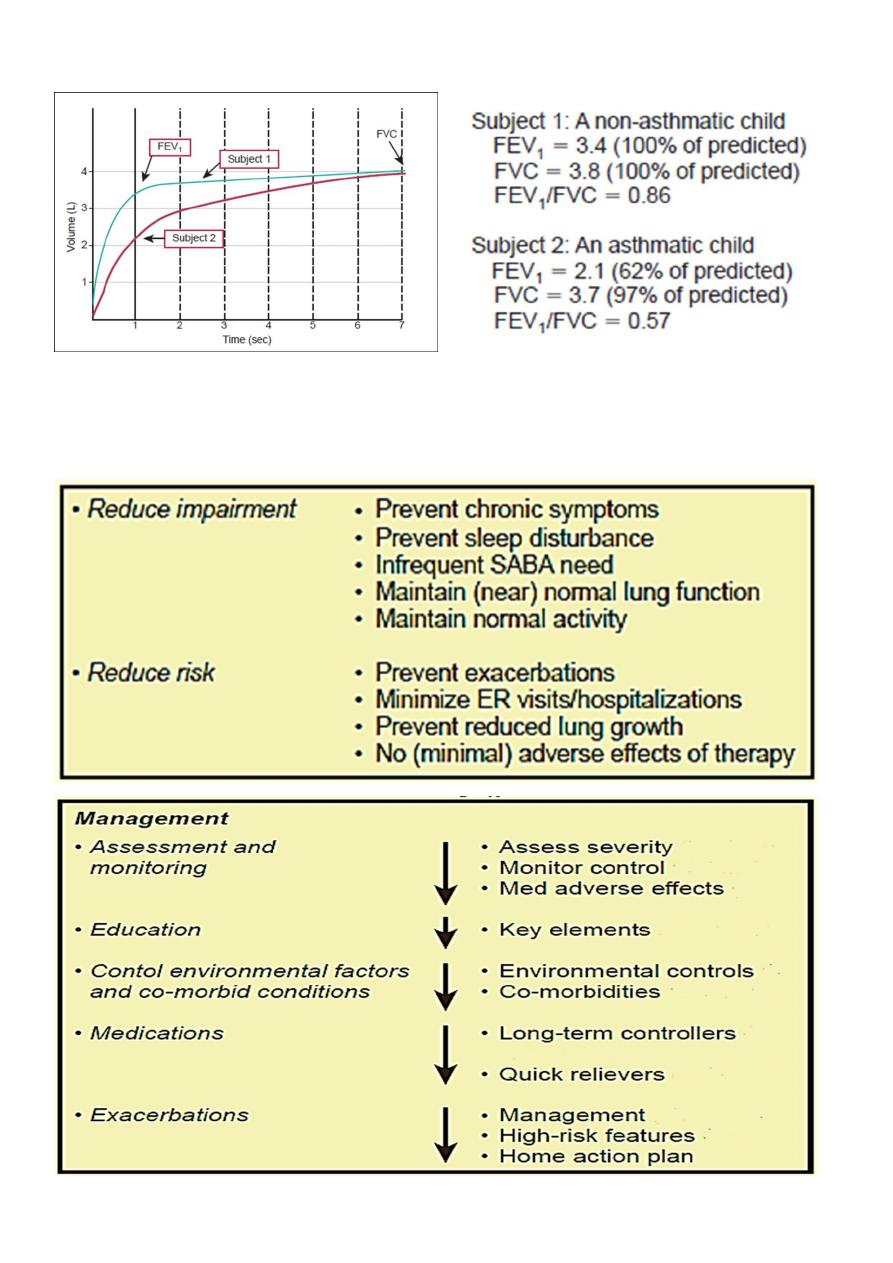
1- Lung Function:
Spirometry: children older than 5 years of age can perform spirometry maneuvers .
Low FEV1
FEV1/FVC ratio <0.80
Bronchodilator response (to inhaled β-agonist) , Improvement in FEV1 ≥12% or
≥200 mL
Exercise challenge ---- worsening in FEV1 ≥15%
Daily peak flow or FEV 1 monitoring: day to day and/or AM-to-PM variation
≥20%
2- Allergy skin testing
3- Radiology:
CXR in children with asthma often appear to be normal, aside from subtle and
nonspecific findings of hyperinflation (flattening of the diaphragms) and
peribronchial thickening.
Indicated in 1st episode, in recurrent episode with fever(suggesting pneumonia)
or localized findings on physical examination & recurrent episode of cough or
wheeze to exclude anatomic abnormalities .
Two novel forms of monitoring asthma and airway inflammation directly include
exhaled nitric oxide analysis and quantitative analysis of expectorated sputum
for eosinophilia .
6
Spirometry
Treatment
Optimal goal: Well-controlled asthma

7
The key elements to optimal asthma management:
1- Assessment and monitoring:
o Assessing asthma severity as intermittent & persistent (mild, moderate, severe )
o Monitoring control with medications & SE of therapy
2. Education
o Specify goals of asthma management
o Explain basic facts about asthma:
• Contrast normal vs asthmatic airways
• Long-term-control and quick-relief medications
• Potential adverse effects of asthma pharmacotherapy
o Teach, demonstrate, and have patient show proper technique for:
• Inhaled medication use (spacer use with metered-dose inhaler)
• Peak flow measures
o Investigate and manage factors that contribute to asthma severity:
• Environmental exposures
• Comorbid conditions as rhinitis, sinusitis & GERD
o Create written 2-part asthma management plan:
• Daily management
• Action plan for asthma exacerbations
o Regular follow-up visits:
• Twice yearly (more often if asthma not well-controlled)
• Monitor lung function annually
3. Control environmental factors and co-morbid conditions

8
4. Medications: Long-term controllers & quick relievers.
A. Long-Term Control Medications:
Inhaled Corticosteroids
:
the most effective anti-inflammatory medications for the treatment of chronic,
persistent asthma and are the preferred therapy when initiating long-term control
therapy.
given by inhaler or nebulizer .
rinsing the mouth after inhalation lessen the local adverse effects of dysphonia
and candidiasis and decrease systemic absorption from the gastrointestinal tract.
Leukotriene Modifiers:
Leukotriene are potent mediators of inflammation and smooth muscle
bronchoconstriction.
Two classes of leukotriene modifiers include
• leukotriene receptor antagonists (zafirlukast and montelukast)
• leukotriene synthesis inhibitors (zileuton).
Zafirlukast is approved for children older than 5 years of age and is given twice
daily.
Montelukast is dosed once daily at night
• as 4-mg (6 months to 5 years)
• 5-mg (6 to 14 years)
• 10-mg tablets for adolescents 15 years of age or older.
Long-Acting β2-Agonists :
Long-acting β
2
-agonists, formoterol and salmeterol, have twice-daily dosing and relax
airway smooth muscle for 12 hours, but they do not have any significant anti-inflammatory
effects.
Theophylline :
It is mildly to moderately effective as a bronchodilator.
Adverse effects associated with elevated theophylline levels include nausea, headaches, and
seizures.
Omalizumab (Xolair) :
a humanized anti-IgE monoclonal antibody that prevents binding of IgE to high-affinity
receptors on basophils and mast cells. It is approved for moderate to severe allergic asthma
in children 12 years of age and older.

9
B.
Quick-Relief Medications :
Short-Acting β2-Agonists :
• Such as albuterol, levalbuterol, and pirbuterol, are effective bronchodilators
that exert their effect by relaxing bronchial smooth muscle within 5 to 10
minutes of administration. They last for 4 to 6 hours.
• Generally, a short-acting β
2
-agonist is prescribed for acute symptoms and as
prophylaxis before allergen exposure and exercise.
• The inhaled route is preferred because adverse effects-tremor, prolonged
tachycardia, and irritability-are fewer.
• Overuse: use of more than one metered dose inhaler canister per month or more
than eight puffs per day suggests poor control.
Anticholinergic Agent :
Ipratropium bromide is an anticholinergic bronchodilator that relieves bronchoconstriction,
decreases mucus hypersecretion, and counteracts cough-receptor irritability.
Oral Corticosteroids :
Short bursts of oral corticosteroids (3 to 10 days) are administered to children with acute
exacerbations.
Prolonged use of oral corticosteroids can result in systemic adverse effects such as:
hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal suppression, cushingoid features, weight gain, hypertension,
diabetes, cataracts, glaucoma, osteoporosis, and growth suppression.
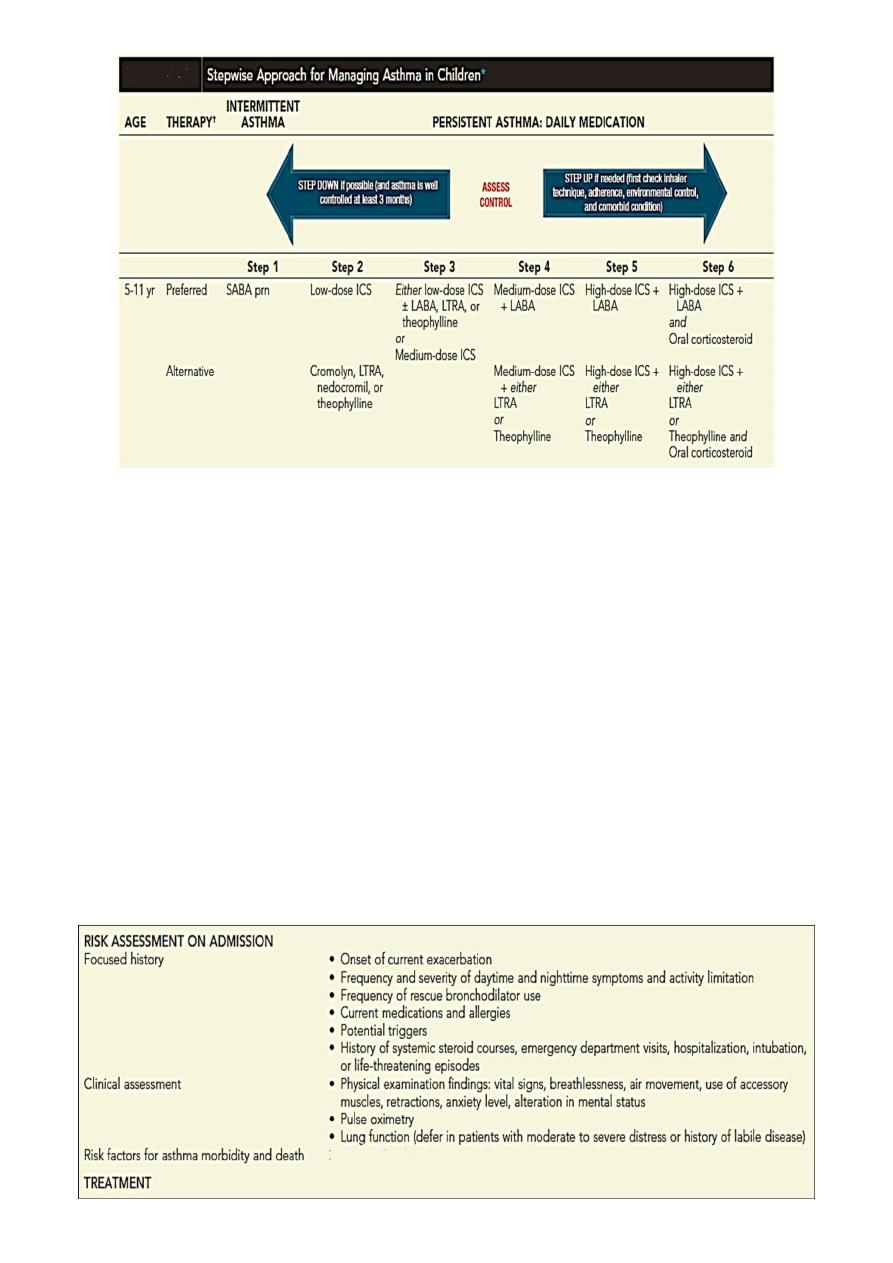
Approach to Therapy
A stepwise approach is used for management.
Medication type, amount, and scheduling are determined by the level of asthma
severity or asthma control.
Therapy is then increased (stepped up) as necessary and decreased (stepped down)
when possible .
A short-acting bronchodilator should be available for all children with asthma .
the rule of two is helpful: daytime symptoms occurring ≥2 / week or nighttime
awakening ≥2 / month implies a need for daily anti-inflammatory medication.
10
QUICK-RELIEF MEDICATION FOR ALL PATIENTS
SABA as needed for symptoms. Intensity of treatment depends on severity of
symptoms: up to 3 treatments at 20-min intervals as needed. Short course of oral
systemic corticosteroids may be needed.
Caution: Use of SABA >2 days/wk for symptom relief (not prevention of exercise-
induced bronchospasm) generally indicates inadequate control and the need to step up
treatment.
For ages 0-4 yr: With viral respiratory infection: SABA q4-6h up to 24 hr (longer with
physician consult). Consider short course of systemic corticosteroids if exacerbation is
severe or patient has history of previous severe exacerbations.
5.
Exacerbations (Status Asthmaticus)
A. Management

11
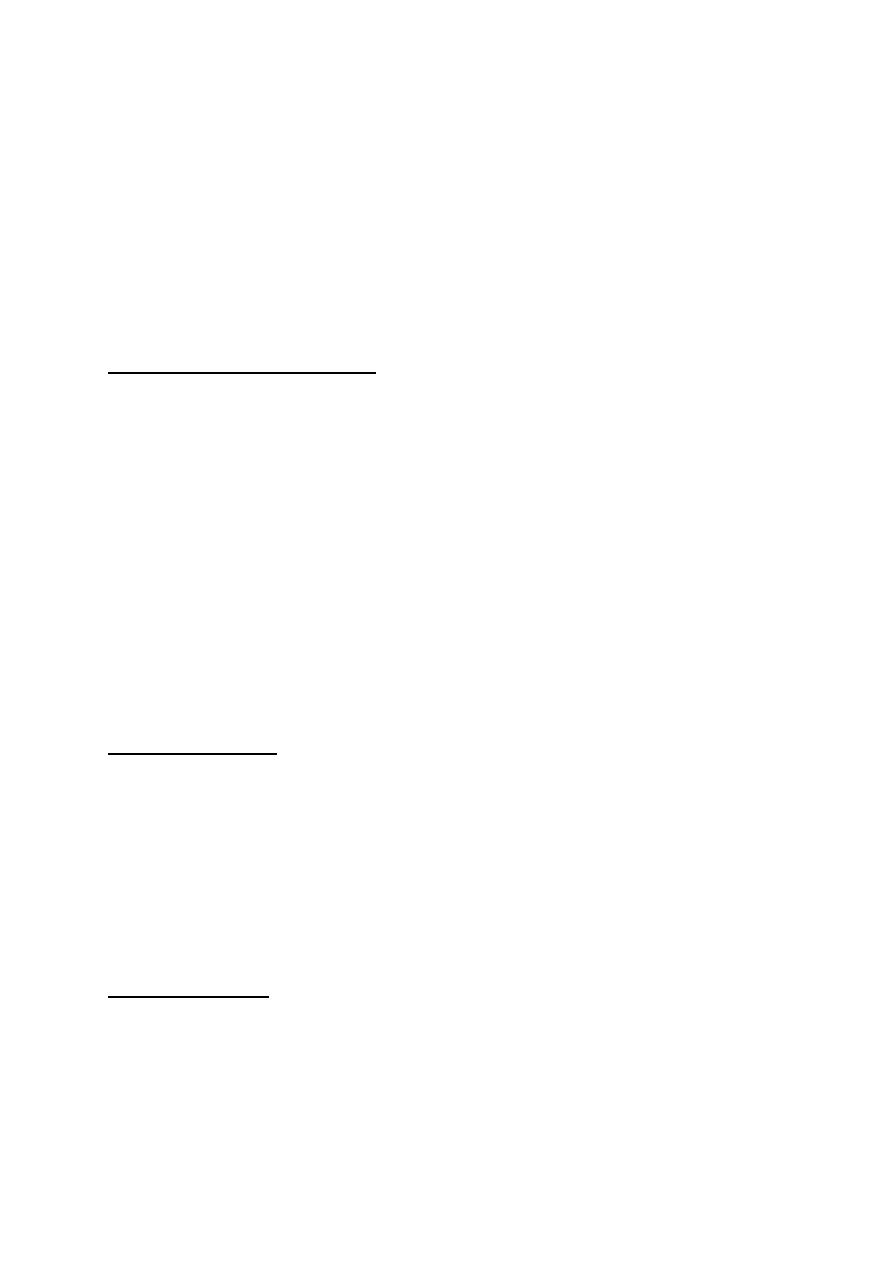
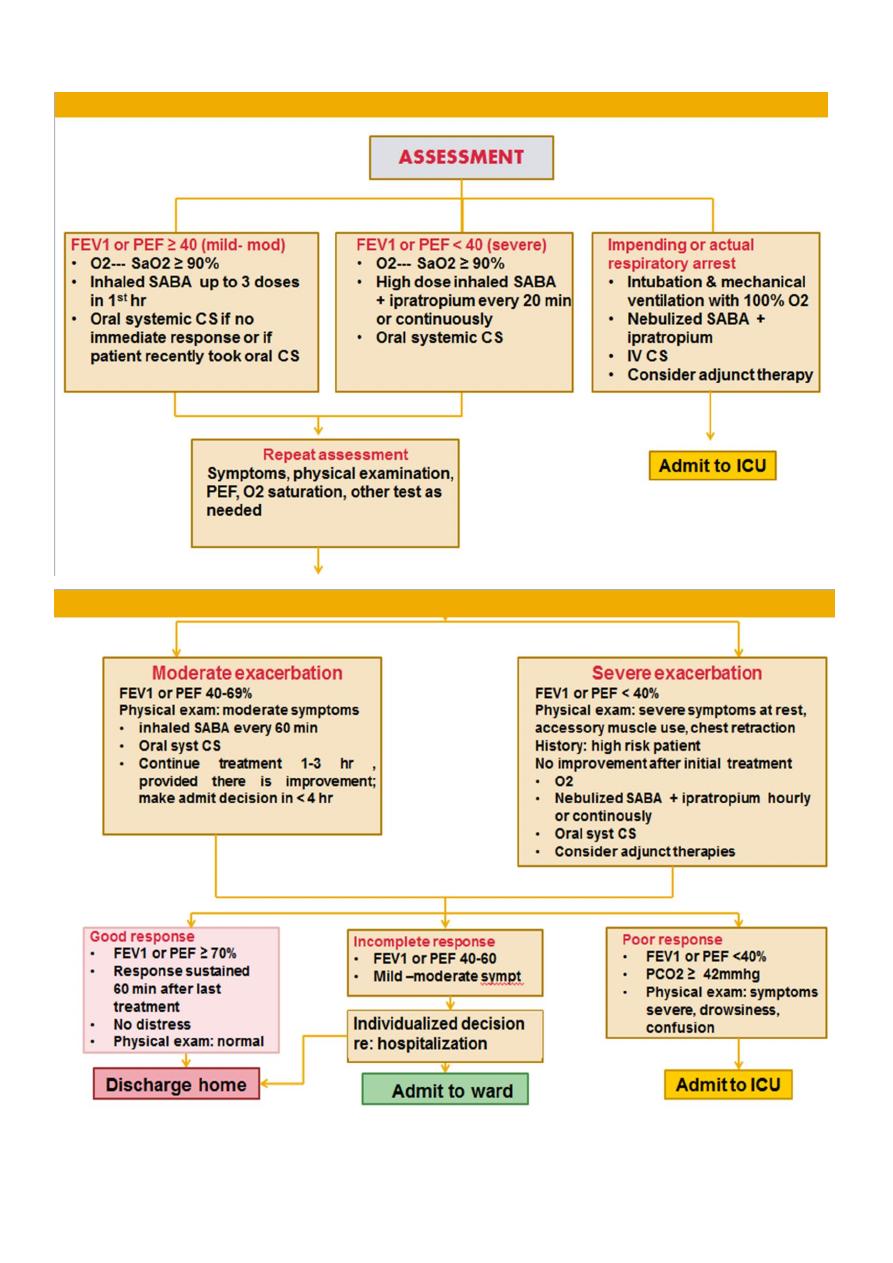
Emergency Department Management of Asthma Exacerbations.
The primary goals of asthma management include correction of hypoxemia, rapid
improvement of airflow obstruction, and prevention of progression or recurrence of
symptoms.
Indications of a severe exacerbation include:
• SOB, retractions, accessory muscle use, tachypnea,
• Cyanosis.
• Mental status changes.
• silent chest with poor air exchange.
• PEF or FEV1 value <50%
12
Initial treatment includes:
• O2
• Hydration
• Inhaled SABA every 20 min for 1 hr
• Systemic CS either orally or intravenously
• Inhaled ipratropium may be added to the β-agonist treatment if no significant
response.
• IM or SC adrenaline for impending respiratory failure or other adjunct therapy.
Discharged to home if there is:
• Sustained improvement in symptoms.
• Normal physical findings.
• PEF >70%
• O2 saturation >92% while the patient is breathing room air for 4 hr.
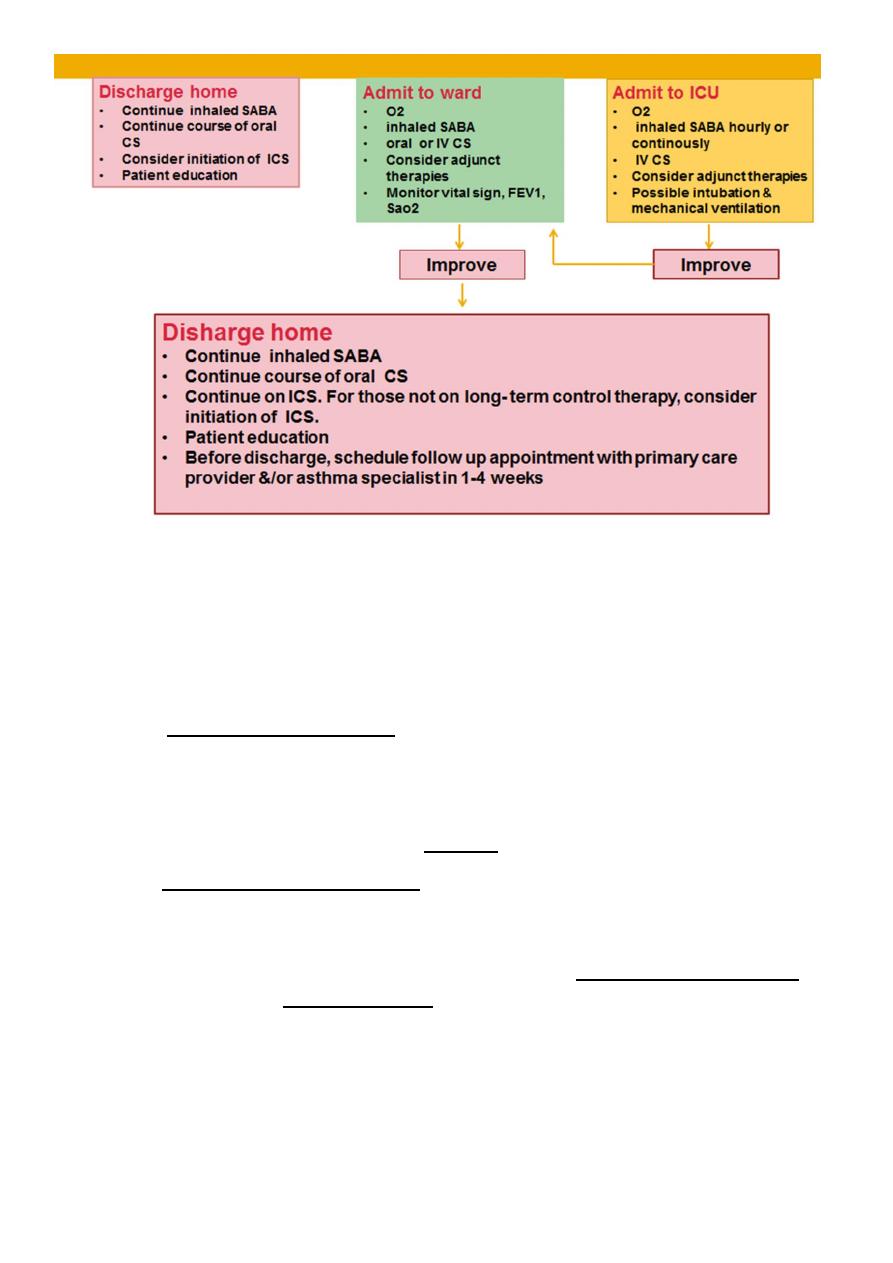
• Discharge medications:
• Include administration of an inhaled β-agonist up to every 3-4 hr .
• 3-7 day course of an oral corticosteroid.
• Consider initiation of ICS for those not on long- term control therapy.
Hospital Management of Asthma Exacerbations
Admission to ward:
• Patients with moderate to severe exacerbations that do not adequately improve
within 1-2 hr of intensive treatment.
• FEV1 or PEF 40-69%
• If there is high-risk features for asthma morbidity or death.
Continue treatment with monitoring & may need other adjunct therapy as magnesium or
inhaled heliox (helium and oxygen mixture) .
Admission to ICU:
• Patients with severe respiratory distress.
• Poor response to therapy.
• Potential respiratory failure & arrest.
• FEV1 <40%
• PCO2 ≥ 42 mmHg
13
Continue treatment & monitoring with possible intubation & mechanical ventilation.
14
B. Home action plan
• Families of all children with asthma should have a written action plan
• to guide their recognition and management of exacerbations, along
• with the necessary medications and tools to manage them.
• A written home action plan can reduce the risk of asthma death by 70%.
• The NIH guidelines recommend:
a. immediate inhaled SABA, up to 3 treatments in 1 hr. (A good response is
characterized by resolution of symptoms within 1 hr, no further symptoms over
the next 4 hr, and improvement in PEF value to at least 80% of personal best. )
b. If the child has an incomplete response (persistent symptoms and/or a PEF
value <80% of personal best), oral CS should be instituted.
c. Immediate medical attention if lack of expected response or high-risk factors
for asthma morbidity or mortality.
d. For patients with severe asthma and/or a history of life-threatening episodes,
especially if abrupt-onset in nature, providing an epinephrine autoinjector
and, possibly, portable oxygen at home should be considered & call for
emergency support.
Prognosis :-
• Children with moderate to severe asthma and with lower lung function
measures are likely to have persistent asthma as adults.
• Children with milder asthma and normal lung function are likely to improve
over time, with some becoming periodically asthmatic.

15
Prevention :-
• Education plays an important role in helping patients and their families adhere to the
prescribed therapy and needs to begin at the time of diagnosis.
• Peak flow monitoring is a self-assessment tool that is helpful for children older than 5
years of age. It is advisable for:
• children who have moderate to severe asthma.
• have a history of severe exacerbations.
• Peak flow monitoring also can be useful in children who are still learning to
recognize asthma symptoms.
SH.Jღ
