Fourth Class University of Mosul
Dr. Rasha Al-Shamaa (Operative Dentistry)
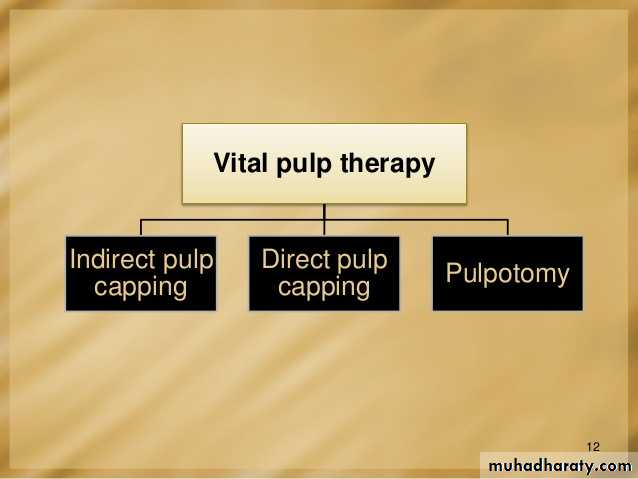
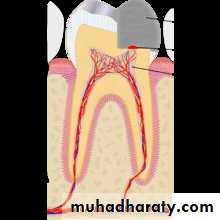
Vital Pulp Therapy
Introduction:
Endodontic therapy, also known as root canal treatment, is one of the most commonly used techniques in dental clinics. Endodontic therapy is a procedure for removing contaminated or injured dental tissue, refilling, and sealing off the created void with synthetic material to eliminate future contamination. With advancements in antibiotic therapies, dental materials, and endodontic technology, the success rate of endodontic therapy has increased dramatically.
Current endodontic procedures replace the vital pulp with synthetic materials . Extruded endodontic materials can cause a foreign body reaction . Pulpless teeth lose their ability to sense environmental changes, making the progression of caries unnoticeable by patients. Another advantage of maintained dental pulp vitality is to maintain the capacity for limited dentin regeneration. Reparative dentin formation is particularly important for immature permanent teeth, because of their incomplete apical and dentinal wall development. The structural integrity of endodontically treated teeth may also be undermined if they are not properly restored, making them more vulnerable to masticatory forces . In terms of aesthetics, endodontic therapy can often result in discoloration of the tooth crown, mainly due to staining from endodontic filling material. Maintaining the vital pulp also helps reduce the occurrence of apical periodontitis by blocking bacterial infections. Based on these issues and concerns, the ability to maintain dental pulp vitality would be preferable to current endodontic treatments .
Definition:
Vital pulp therapy is defined as a treatment initiated to preserve and maintain pulp tissue in a healthy state → tissue that has been compromised by caries, trauma or restorative procedures.
Pulp Capping Materials:
Calcium Hydroxide Ca(OH)2, Mineral Trioxide Aggregate MTA, Tri-Calcium Phosphate, Bioaggregate, Biodentin, Bonding Systems, polycarboxylate cement, collagen fiber, Enamel matrix derivative.Requirements for Successful Vital Pulp Therapy:
Treatment of healthy pulp has been shown to be an essential requirement for successful therapy, treatment of inflamed pulp have lower successful rate, therefore, the optimal time for treatment is within 24hrs .
Bacterial tight seal is the most critical factor for successful treatment .
A proper pulp dressing is important.
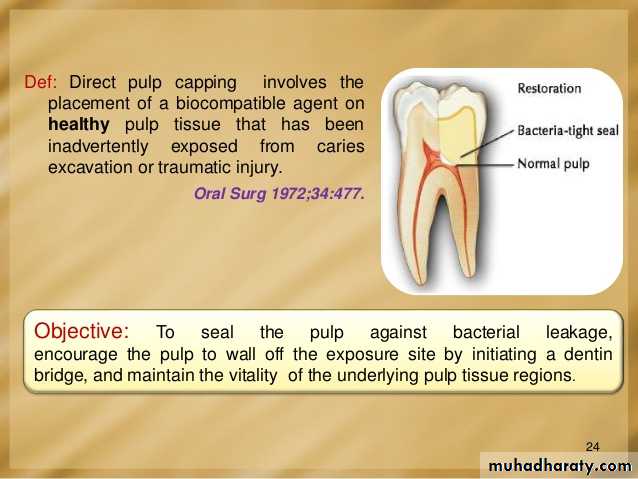
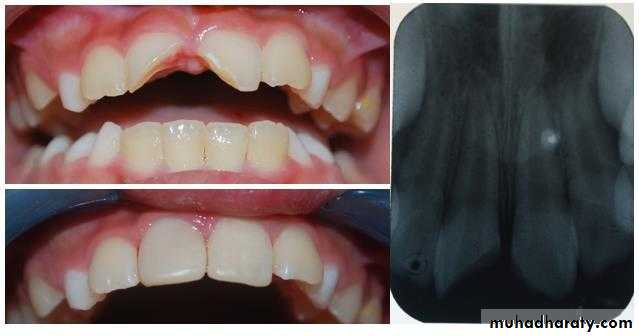
Direct pulp cap
DefinitionThe procedure in which the small exposure of the pulp, encountered during cavity preparation or following a traumatic injuries or due to caries, with a sound surrounding dentin, is dressed with an appropriate biocompatible radiopaque base in contact with exposed pulp tissue prior to placing a restoration.
Indication:
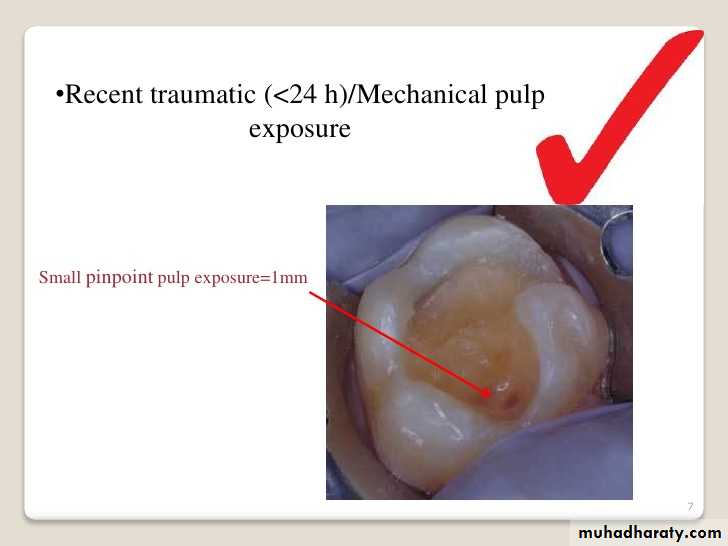
Small pin point mechanical pulp exposure of diameter less than 1mm .Traumatic exposure in a dry , clean field which reported to the dental office within 24 hours ( without previous symptoms of pulpitis with normal radiographical finding ) .
Small pin point pulp exposure= 1mm
Technique
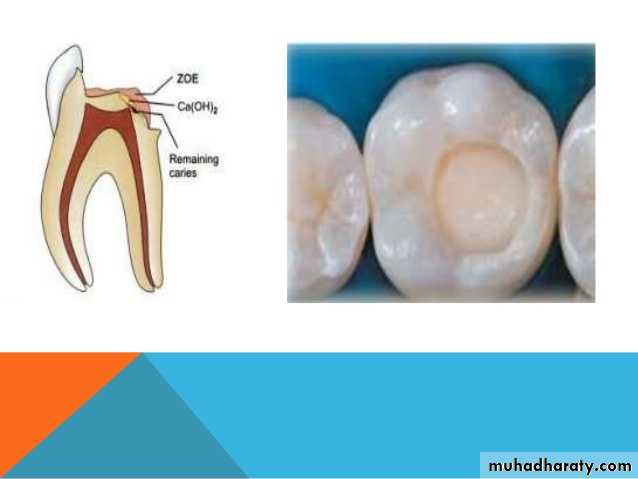
Once the exposure is made, the tooth is isolated from saliva to prevent contamination by use of a dental dam, if it was not already in place. The tooth is then washed and dried, and the protective material placed (calcium hydroxide is the material of choice for capping the exposure site , zinc oxide eugenol is placed over the calcium hydroxide as sealant then zinc phosphate cement , followed finally by a dental restoration which gives a bacteria-tight seal to prevent infection. Since pulp capping is not always successful in maintaining the vitality of the pulp, the dentist will usually keep the status of the tooth under review for about 1 year after the procedure.Indirect pulp cap (stepwise caries removal)
A procedure in which a material is placed over a thin portion of remaining carious dentin, that if removed may exposed the pulp.
(Technique in which caries is removed in increments in two or three appointments over a few months to a year rather than removing the caries in one sitting ) .
Indication
Deep carious lesion in vital asymptimatic restorable teeth.
Presence of sclerotic dentin in chronic slow progressing lesion.
Desire for final restoration in the same appiontement.
Recurrent caries under deep existing restoration with thin remaining dentinal thickness.
Technique:
The tooth is anesthetized and isolated with the rubber dam
All the caries except that immediately over the pulp is removed(use large round bur at low speed)Azone of AFFECTED demineralized dentin is left behind
Not all undermind enamel is removed
Asedative dressing is placed then the tooth restored with ZOE or amalgum
The formation of reparative dentin beanath the caries (average rate 1.4 micron per day)The treated tooth is re-entered after 6-8 weeks and the remainig caries is excavated
Pulpal protection with adequate base and permanent restoration
Sedative Material placed over exposed or nearly exposed pulp1)crown 2)root 3)Restoration 4)pulp capp 5) pulp chamber.
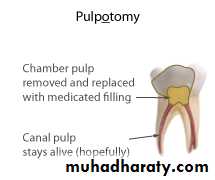
Full Pulpotomy
DefinitionThe complete removal of the coronal portion of the dentinal pulp, followed by placement of suitable dressing or medicament will promote healing and preserve vitality of the pulp.
The procedure is usually reserved for teeth:
With little or no history of pain .
Absence of radiographic signs of periapical pathosis or resorption .
Lack of percussion sensitivity , swelling, or mobility.
Technique:
Two stage procedure involve of placement of paraformaldehyde to fix the entire coronal and radicular pulp tissue, the medicaments used in this technique have a devitalizing , mummifying and bactericidal action .Indication: profuse bleeding, difficulty of control bleeding, spontaneous bleeding, slight purulence discharge, thickened periodontal ligament .
The agents used in this technique are Gysi triopaste formula, paraformaldehyde paste .
First appiontement:
Isolation of the affected teeth with the rubber dam.
Preparation of cavity , excavate the caries .
On excavation of deep caries the exposure encountered , ensure that the exposure site is free of debris .
Enlarge the cavity with the round bur .
Cotton pellet with the paraformaldeyde is placed in the exposure site, seal it for 1-2 weeks .
Second appointment :
The procedure is carried with help of local anesthesia , the roof of pulp chamber is removed and cleaned with saline and dried with the cotton pellet .
The pulp chamber is then filled with antiseptic paste and the tooth is restored .
Follow up
Due to loss of coronal pulp , the sensitivity test is not possible , therefore , radiographic follow up is extremely important to asses sign of apical priodontitis and to ensure the continuation of root formation .
Partial Pulpotomy
The procedure in which the inflamed pulp tissue beneath an exposure is removed to a depth of 1-3mm to reach the deeper healthy pulp tissue .
Indicated for a vital, traumatically exposed, young permanent tooth, especially one with an incompletely formed apex .
When a baby teeth or young permanent teeth is traumatized , it can be broken in such a way that the pulp is exposed, a partial pulpotomy may help it to finish developing and be saved .
Technique
Anesthesia, rubber dam, 1-2 mm deep cavity prepared into the pulp .
If the bleeding is excessive, the pulp is amputated deeper until only moderate hemorrhage is seen , then rinsing with sterile saline or anesthetic solution .
Dried with sterile cotton pellet .
Suitable medicament used (Calcium Hydroxide or MTA ), all exposed dentinal tubules are covered .
Follow up
Maintenance of positive sensitivity tests and radiograph .
Types of Dentin :
Primary dentin, the most prominent dentin in the tooth, lies between the enamel and the pulp chamber (near Dentinoenamel junction). The outer layer closest to enamel is known as mantle dentin. This layer is unique to the rest of primary dentin. Mantle dentin is formed by newly differentiated odontoblasts and forms a layer approximately 150 micrometers wide. Unlike primary dentin, mantle dentin lacks phosphorylation, has loosely packed collagen fibrils and is less mineralized. Below it lies the circumpulpal dentin, a more mineralized dentin which makes up most of the dentin layer and is secreted after the mantle dentin by the odontoblasts. Circumpulpal dentin is formed before the root formation is completed.secondary dentin is formed after root formation is complete, normally after the tooth has erupted and is functional. It grows much more slowly than primary dentin, but maintains its incremental aspect of growth. It has a similar structure to primary dentin, although its deposition is not always even around the pulp chamber. It is the growth of this dentin that causes the decrease in the size of the pulp chamber with age. This is clinically known as pulp recession
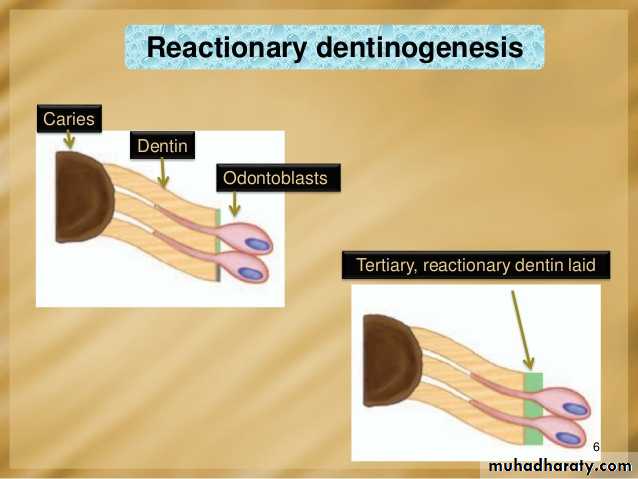
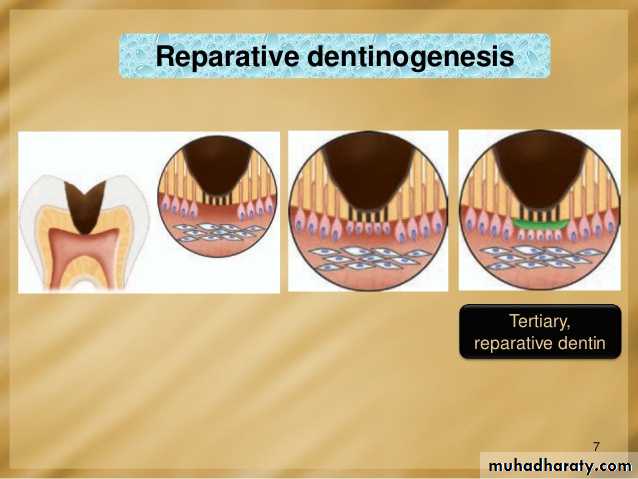
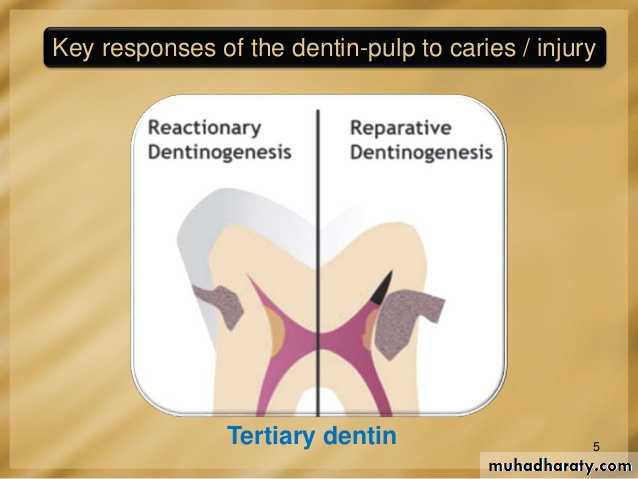
Tertiary dentin (including reparative dentin or sclerotic dentin)
Tertiary dentin is dentin formed as a reaction to external stimulation such as cavities. It is of two types, either reactionary, where dentin is formed from a pre-existing odontoblast, or reparative, where newly differentiated odontoblast-like cells are formed due to the death of the original odontoblasts, from a pulpal progenitor cell. Tertiary dentin is only formed by an odontoblast directly affected by a stimulus; therefore, the architecture and structure depend on the intensity and duration of the stimulus, e.g., if the stimulus is a carious lesion, there is extensive destruction of dentin and damage to the pulp, due to the differentiation of bacterial metabolites and toxins. Thus, tertiary dentin is deposited rapidly, with a sparse and irregular tubular pattern and some cellular inclusions; in this case it is referred to as "osteodentin". However, if the stimulus is less active, it is laid down less rapidly with a more regular tubular pattern and hardly any cellular inclusions.