
Parasitic Skin Diseases
By
Dr. Salam Altemimi

Leishmaniasis
• Leishmania are flagellate protozoans.
• The pathogenic one present in Iraq is Leishmania
tropica.
• The protozoan is transferred by sandflies
(Phlebotomus).
• The average incubation period is 2–4 weeks.
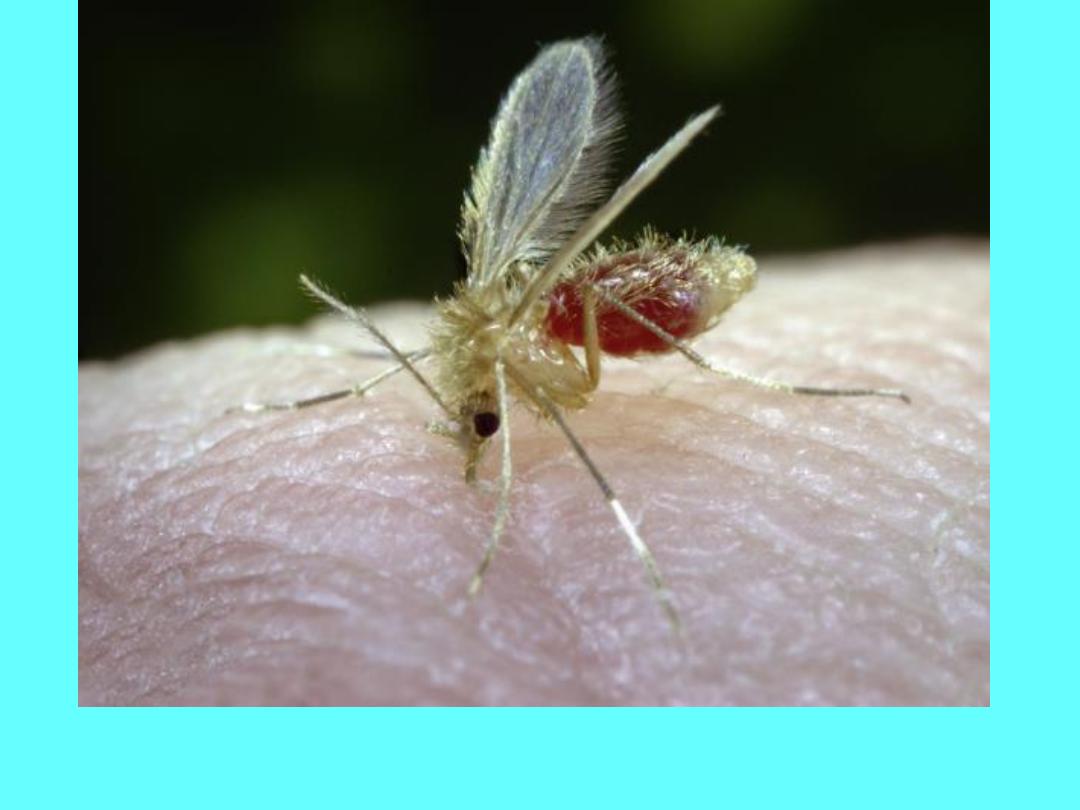

Blood-sucking Phlebotomus papatasi sandfly, it is one third the size of
a mosquito. Sandflies are most active from dusk to dawn.
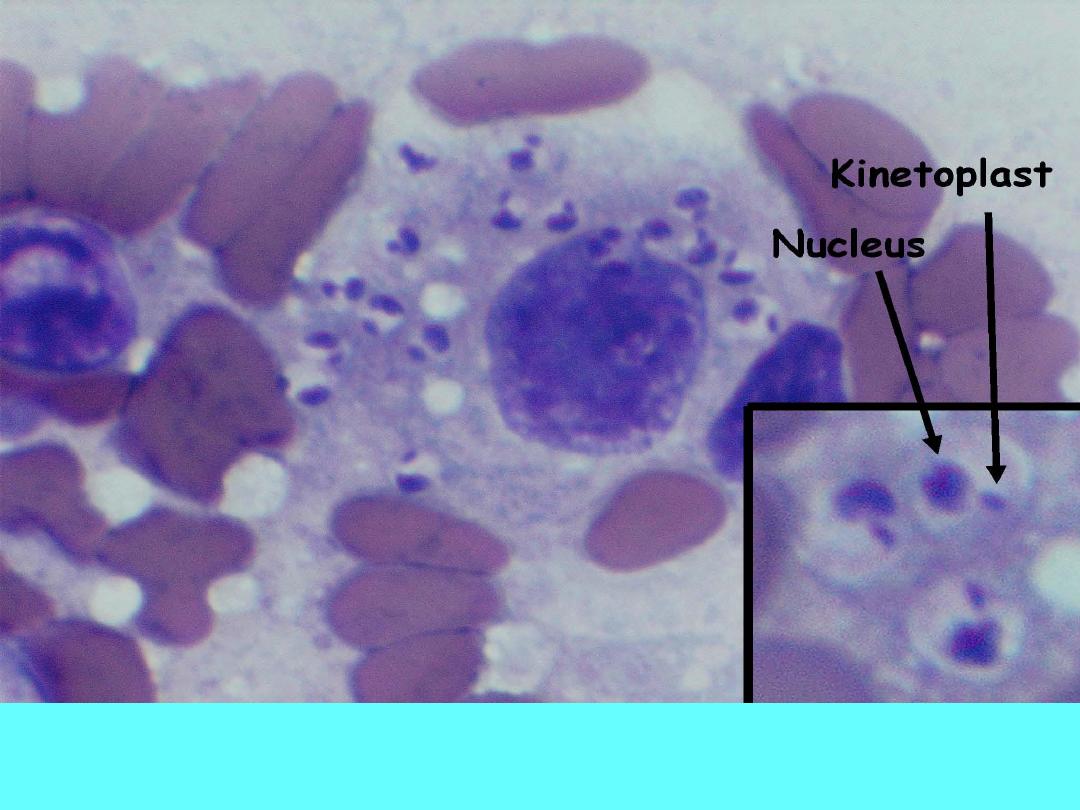
Leishmania: Amastigotes in a macrophage at 1000X, Inset shows the
cell membrane and points out the nucleus and kinetoplast.

Acute cutaneous leishmaniasis
• Following the bite, a papule develops, then
rapidly enlarges and breaks down in the
center. The ulcer usually has a rolled border
(volcano sign) and it is asymptomatic unless
secondarily infected.
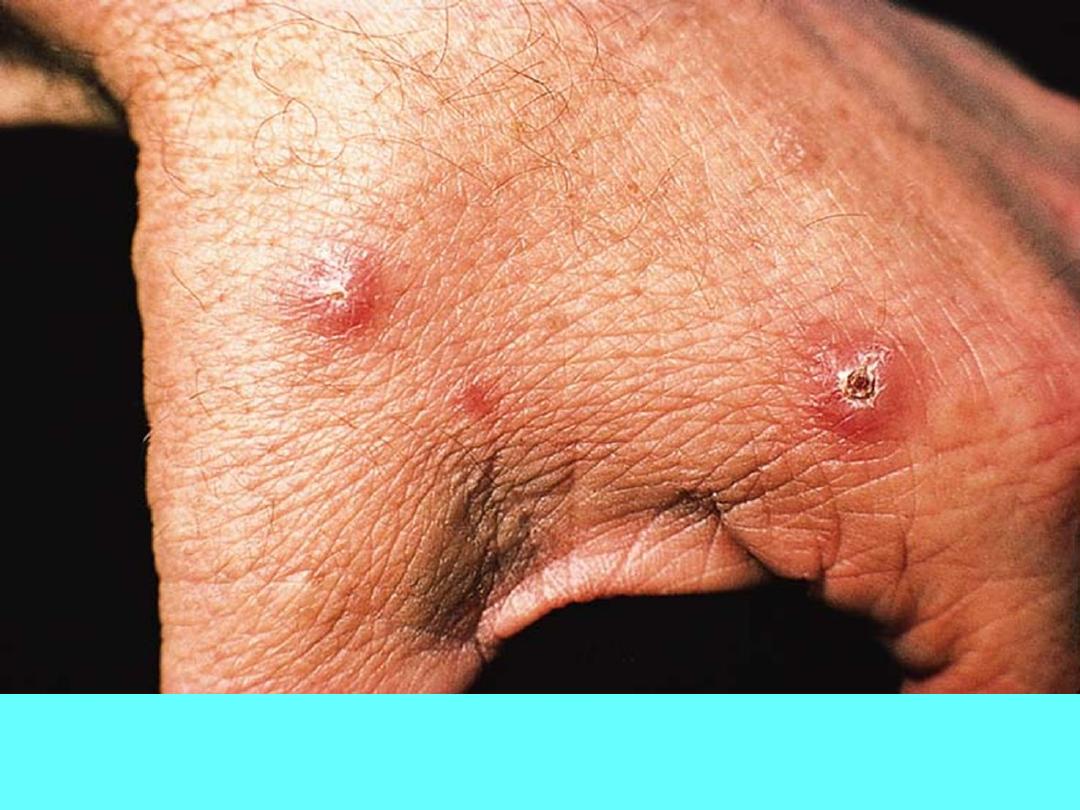
Cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania major: asymptomatic
early papules, one of which is starting to show central crusting.
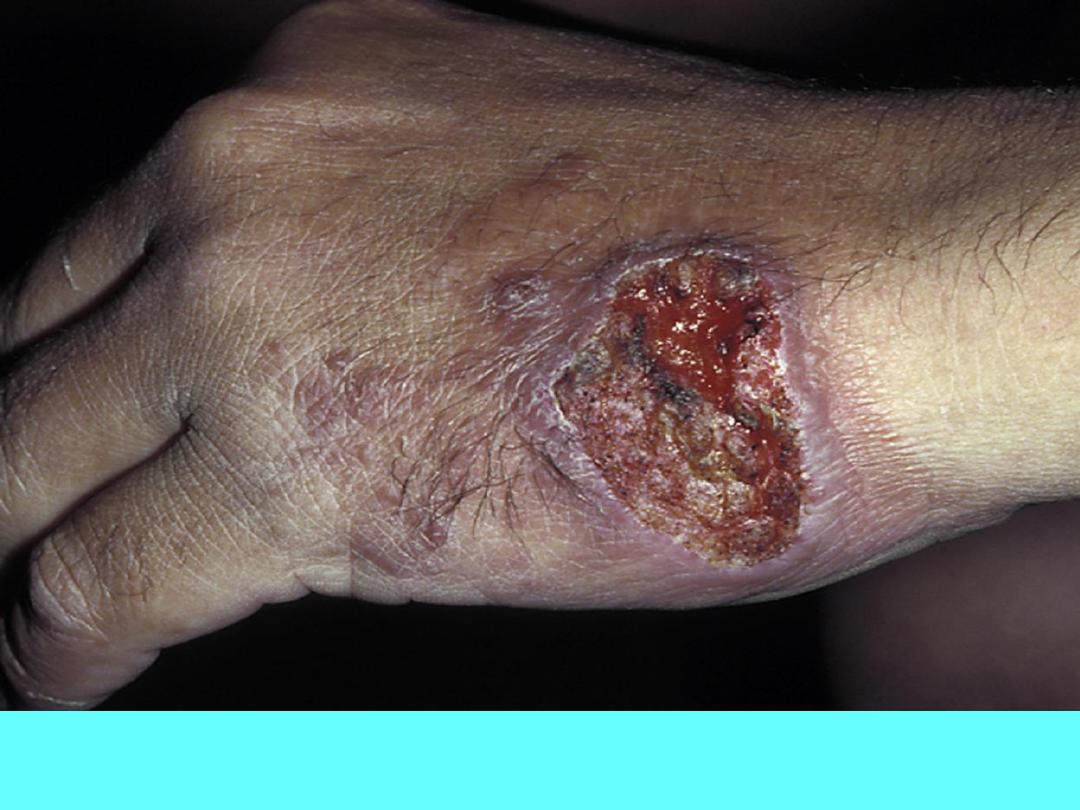
Cutaneous leishmaniasis. A red papule eventually ulcerates and forms
raised edges with surrounding dusky red skin.

Treatment
• Standard treatment is intralesional injection of
sodium stibogluconate (Pentostam) diluted
1:3 with a local anesthetic; 1–2 times weekly
for 2–4 weeks.
Pediculosis
• Lice (Pediculus spp.) are blood-sucking,
wingless, ectoparasitic insects.
• Pediculosis capitis (Head lice) is infestation
with Pediculus humanus capitis.
• Lice live on the scalp and suck blood there.
They firmly attach their eggs (nits) to the hair
shaft just at the skin surface.
• Malathion 0.5% lotion is most effective.
Applied twice, 7–14 days apart. Their
application is for 30 minutes and rinsed.
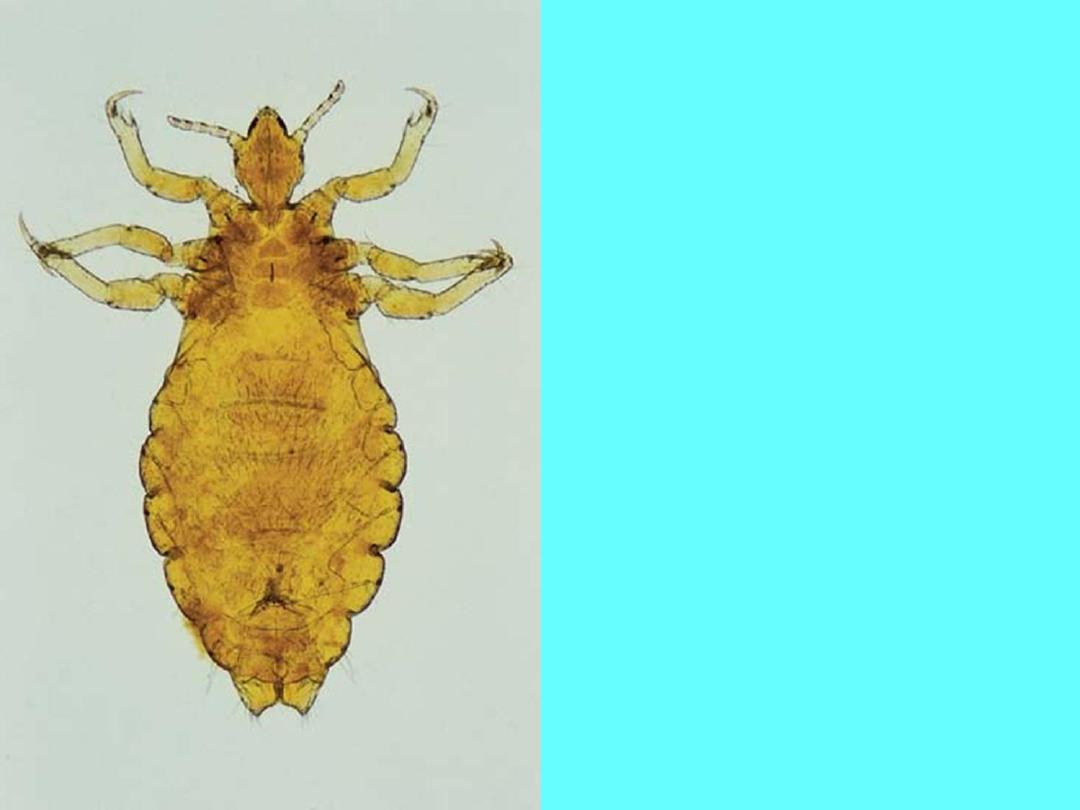

Head louse (Pediculus humanus
var. capitis)
Body louse (Pediculus humanus
var. corporis)
It is less than 2 mm, flat, wingless
insect with three pairs of legs
located on the anterior part of the
body directly behind the head. The
legs terminate in sharp claws.
Body louse is the largest in size.
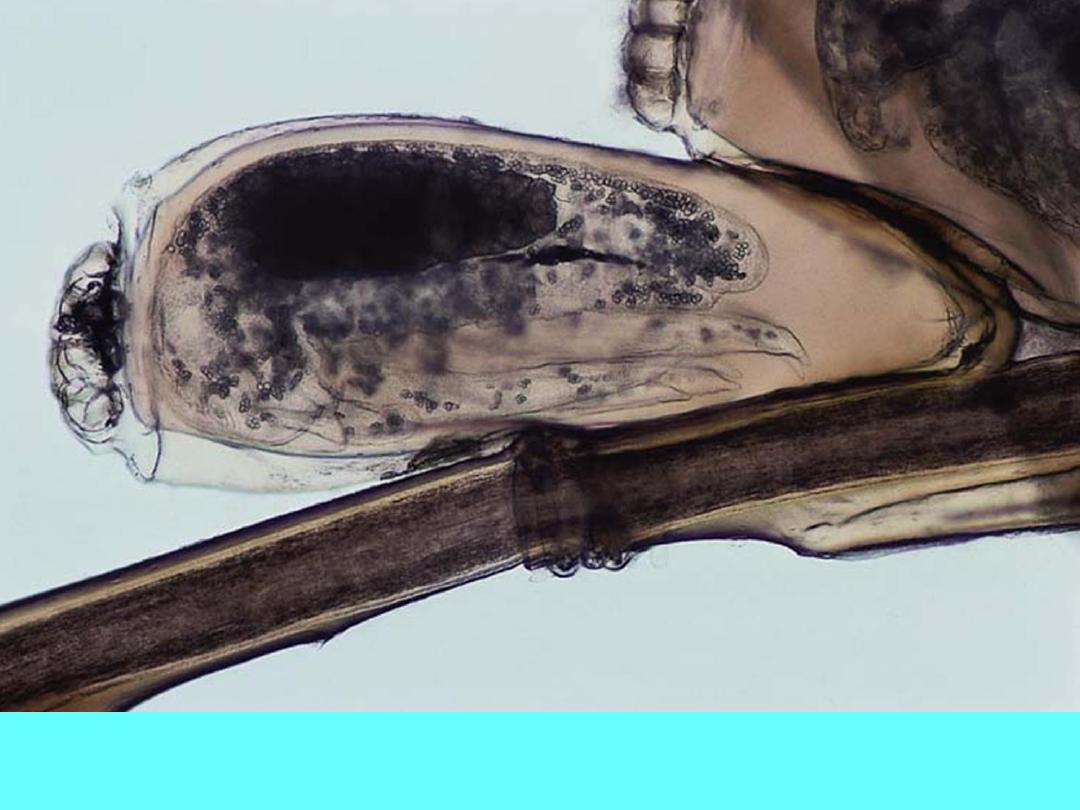
Head louse eggs (nits) cemented to a hair shaft.

• Pediculosis corporis (Body lice).
• Infestation with Pediculus humanus corporis.
• Pediculosis corporis is primarily a disease of
the unwashed.
• The lice feed on the body, but live in the
clothing and tend to lay their eggs along the
seams.
• Look for the lice and nits on the clothing, not
on the skin.
• Treatment: Disinfection of clothing and
bedding (boiling, hot ironing, fumigation).
Attempt to change living conditions.

• Pediculosis pubis (Pubic lice).
• Infestation with Phthirus pubis. Usually
transmitted by sexual contacts.
• Moving lice on their pubic hairs.
• Nits usually on pubic hair, but occasionally
elsewhere (axillary or body hairs; eyelashes,
eyebrows).
• Treatment: Permethrin cream or shampoo
applied for 30 minutes; repeat in 1 week.
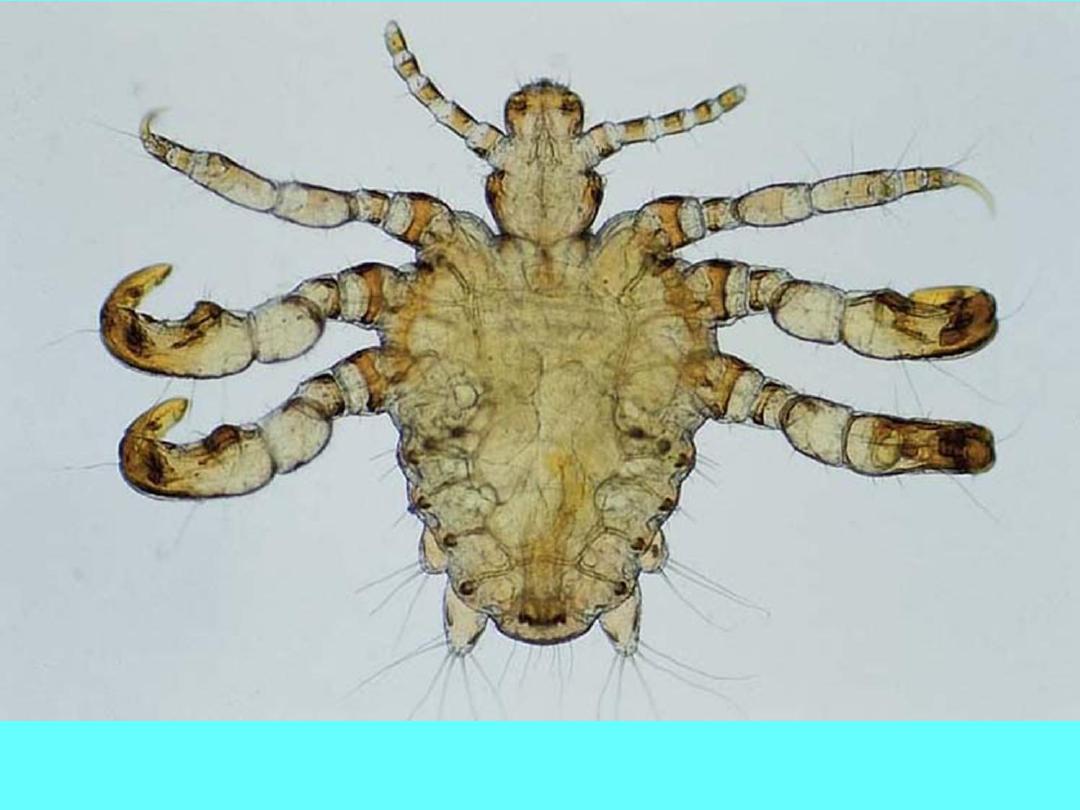

Crab or pubic louse (Phthirus pubis) with a short, oval body and
prominent claws resembling sea crabs.

Scabies
• Intensely pruritic infestation with the mite
Sarcoptes scabiei.
• It lives only on humans.
• Transmission is by close personal contact.
• Female mites burrow in the epidermis just
below the stratum corneum, depositing eggs
and feces as they move along.
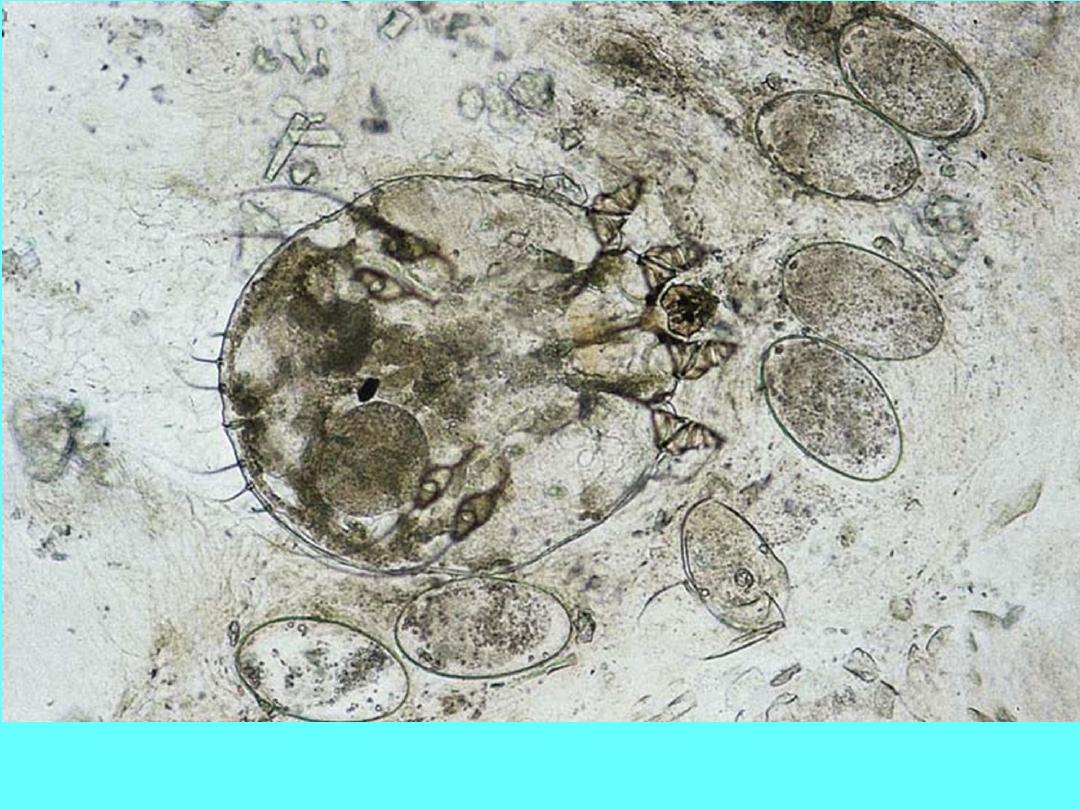
Sarcoptes scabiei: The scabies mite. Female with eggs. Ovoid body, flattened
dorsoventrally; four pairs of legs, the anterior 2 pairs tipped with suckers.

• Burrows: Fine slightly raised, sometimes
erythematous, irregular lines with a terminal
swelling where the female mite can be found.
Typical sites include interdigital spaces, sides
of the hands and feet, flexural surface of the
wrist, anterior axillary line, penis, nipples.
• Intense pruritus usually worst at night.
• Dermatitis: Immune reaction (type IV) to
mites leads to both pruritus and diffuse
exanthem. Typical sites are thighs, buttocks,
trunk.
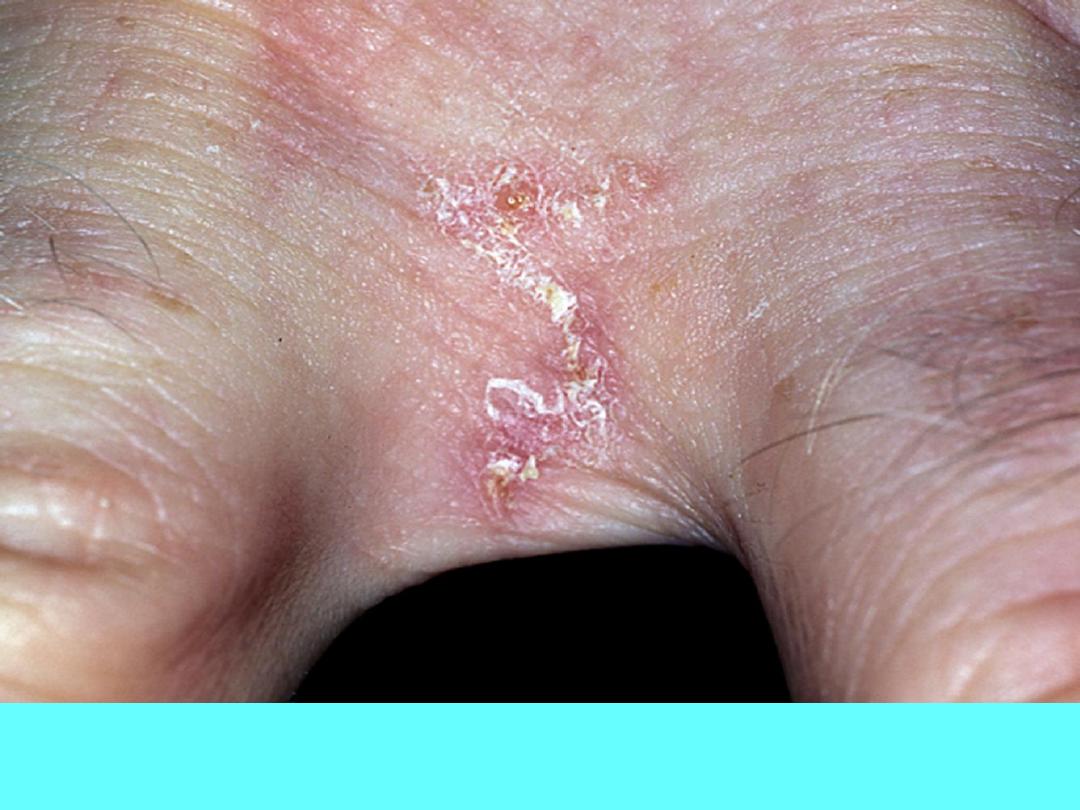
Scabies: Burrows appear as curved tracks and are most often found in
the finger webs and on the wrists.

• Treatment: Permethrin 5% cream is the agent
of choice. Apply at night, wash in morning;
repeat after 1 week.
• Bedding and clothing should be washed in hot
cycle of washing machine.
