Urticaria
(hives, ‘nettle-rash’)Etiologic factors
DrugsPenicillin and related antibiotics
The incidence of aspirin-induced urticaria has fallen
Aspirin-sensitive persons tend to have cross-sensitivity withtartrazine, the yellow azo-benzone dye. These are common food additives and preservatives.
Aspirin exacerbates chronic urticaria in at least 30% of patients unknown.
Food
frequent in acute urticaria, less in chronic urticaria.chocolate, shellfish, nuts, peanuts, tomatoes, strawberries, melons, cheese, garlic, onions, eggs, milk,and spices.
Food allergens that may cross-react with latex include chestnuts, bananas, avocado, and kiwi.
Food additives
Fewer than 10% of cases of chronic urticaria.
Natural food additives :yeasts, salicylates, citric acid, egg, and fish albumin.
Synthetic additives include azo dyes, benzoic acid derivatives, sulfite, and penicillin.
Infections
Acute urticaria may be associated with upper respiratory infections,
localized infection in the tonsils, a tooth, the sinuses, gallbladder, prostate, bladder, or kidney.
treatment with antibiotics for Helicobacter
Chronic viral infections, such as hepatitis B and C.
Helminths may cause urticaria
Emotional stress
Neoplasms : carcinomas and Hodgkin disease.
Inhalants : Grass pollens, house dust mites, feathers, formaldehyde, cottonseed, animal dander, cosmetics, aerosols, and molds
Physical urticarias
Cold urticaria : on the face when cycling . reproduce the reaction by holding an ice cube, in a thin plastic bag against forearm skin.Solar urticaria : within minutes of sun exposure.
Heat urticaria : contact with hot objects or solutions.
Cholinergic urticaria : Anxiety, heat, sexual excitement or strenuous exercise. The vessels over-react to acetylcholine liberated from sympathetic nerves in the skin.
Aquagenic urticaria : precipitated by contact with water, irrespective of its temperature.
Dermographism
This is the most common type of physical urticaria,the skin mast cells releasing extrahistamine after rubbing or scratching. The linear wheals are therefore an exaggerated triple response of Lewis.
They can be reproduced by rubbing the skin of the back lightly at different pressures, or by scratching the back with a fingernail or blunt object.
Delayed pressure urticaria
Sustained pressure causes oedema of the underlying skin and subcutaneous tissue 3–6 h later.
The swelling may last up to 48 h and kinins or prostaglandins, rather than histamine, probably mediate it.
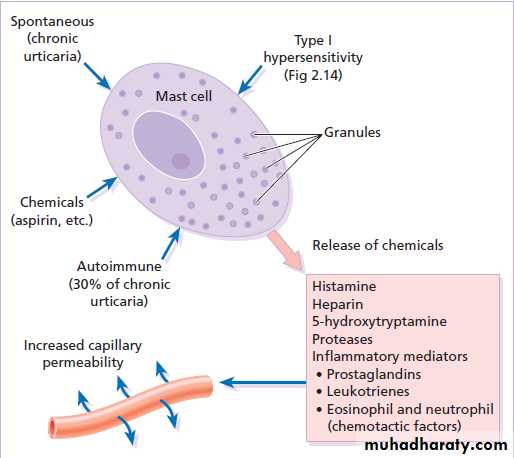
Hypersensitivity urticaria
IgE-mediated (type I) allergic reaction.Allergens may be encountered in 10 different ways :
Presentation
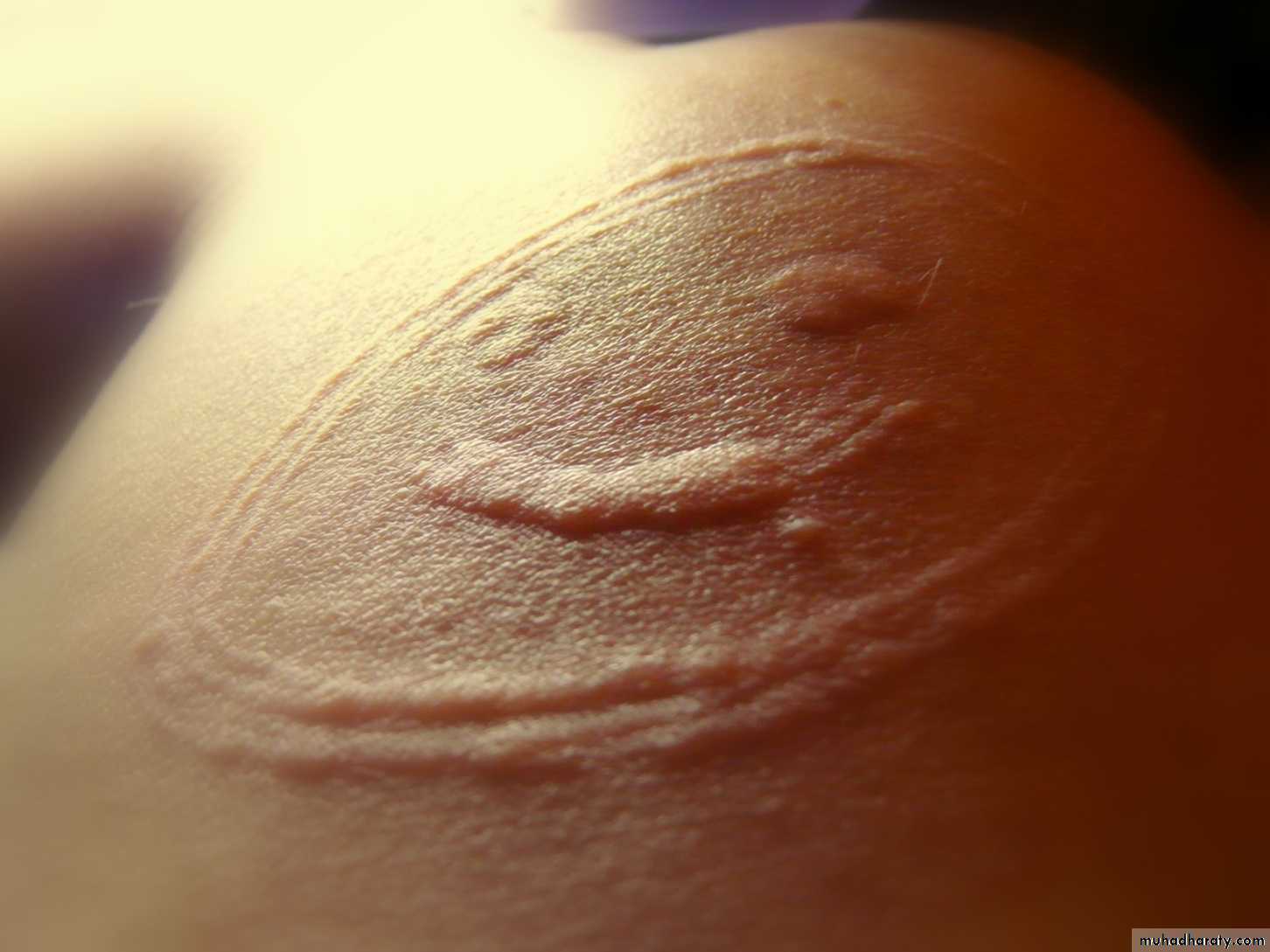
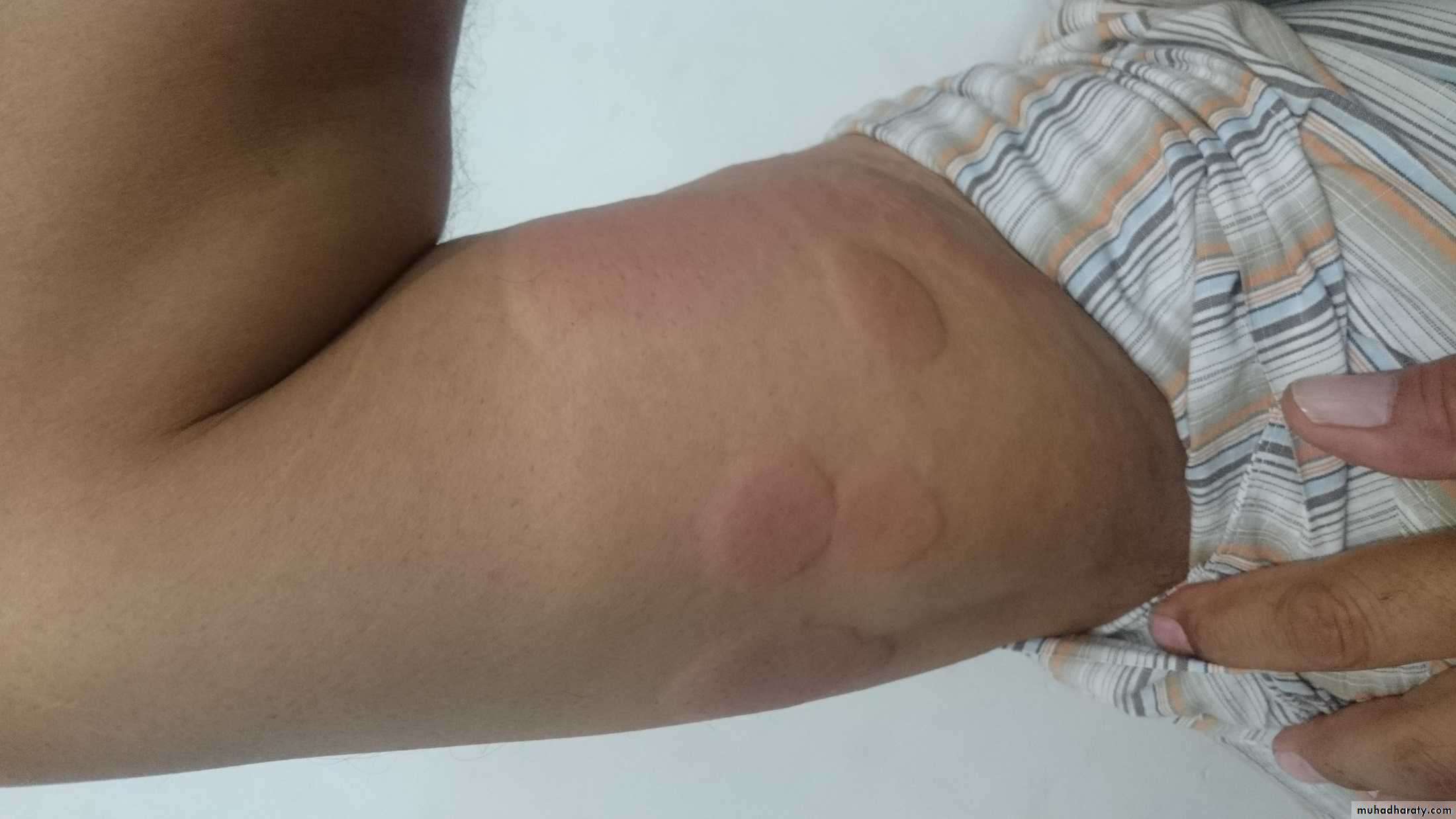
sudden appearance of pink itchy whealsanywhere on the skin surface.
Each lasts for less than a day
Lesions may take up an annular shape.
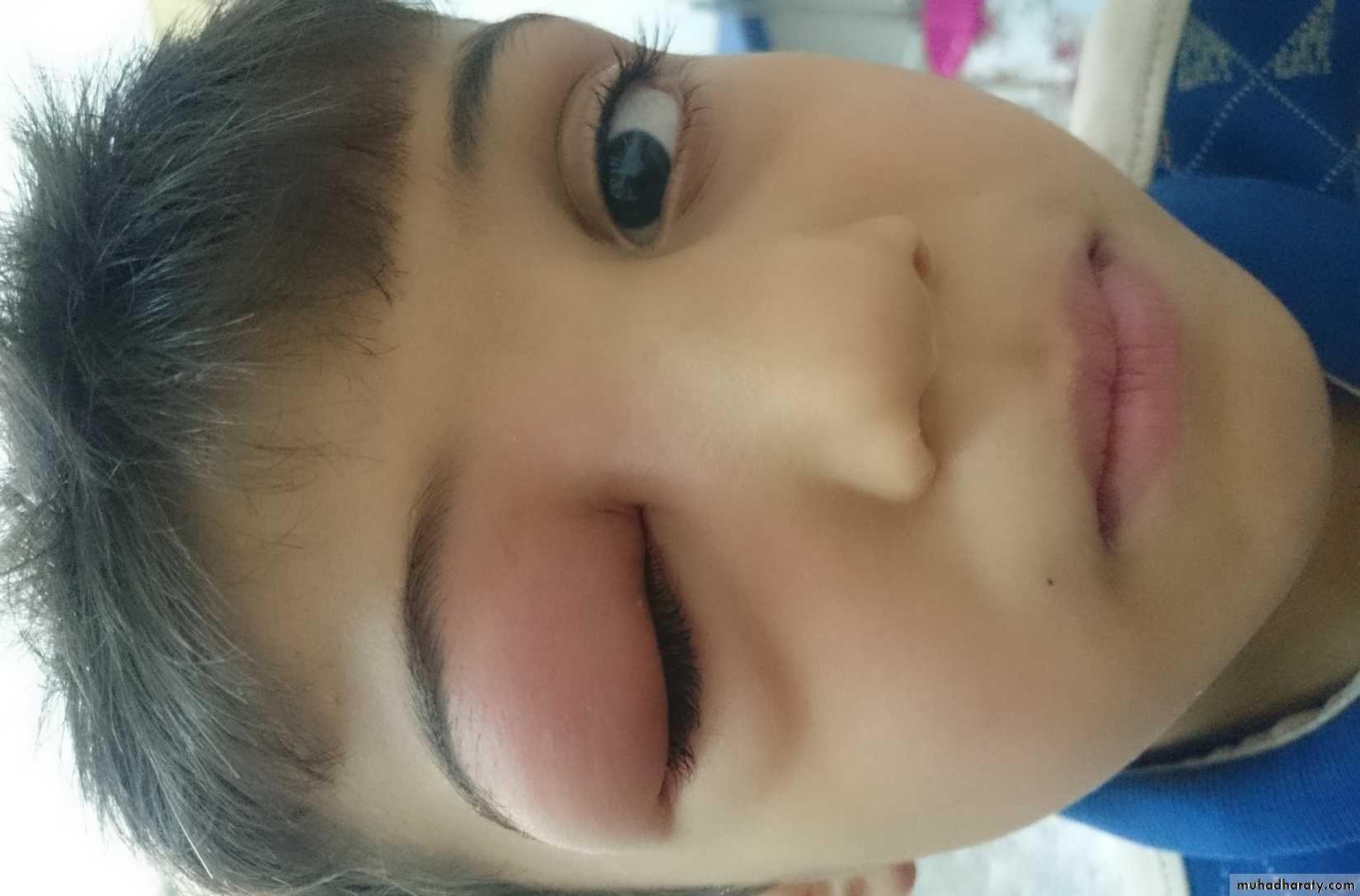
Angioedema is a variant of urticaria that primarily affects the subcutaneous tissues, so that the swelling is less demarcated and less red than an urticarial wheal.
Angioedema at junctions between skin and mucous membranes( peri-orbital, peri-oral and genital ).
The course depends on its cause.
If the urticaria is allergic, it will continue until the allergen is removed, tolerated or metabolized.Urticaria may recur if the allergen is met again. Only half of patients with chronic urticaria and angioedema will be clear 5 years later.
Those with urticarial lesions alone do better, half being clear after 6 months.
Differential diagnosis
Insect bites or stings and infestationsErythema multiforme can mimic an annular urticaria.
urticarial vasculitis: individual lesions last for longer than 24 h, blanch incompletely,leave bruising.
Some bullous diseases ( dermatitis herpetiformis, bullous pemphigoid and pemphigoid gestationis) begin as urticarial papules or plaques, but later bullae make the diagnosis obvious.
On the face,erysipelas can be distinguished from angioedema by its sharp margin, redder colour and accompanying pyrexia.
Investigations
more is learned from the history than laboratory.A review of systems.
Careful attention should be paid to drugs
investigations can be confined to a complete blood count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
An eosinophilia should lead to the exclusion of bullous and parasitic disease, and a
raised ESR might suggest urticarial vasculitis or a systemic cause.
Prick tests are unhelpful.
Treatment
The ideal is to find a cause and then to eliminate it.
antihistamines are the mainstays of symptomatic treatment.
Cetirizine 10 mg/day and loratadine 10 mg/day
shorter acting antihistamines( hydroxyzine 10–25 mg).
H2-blocking antihistamines (cimetidine)
Chlorphenamine or diphenhydramine are used during pregnancy
Sympathomimetic agents can help urticaria, adrenaline
A tapering course of systemic corticosteroids
Low doses of ciclosporine