
The Face

To list facial muscles
To follow the course & branches of facial vessels
To define pterygoid plexus & its clinical importance
To follow the course & branches of facial nerve
To follow the course & branches of trigeminal nerve
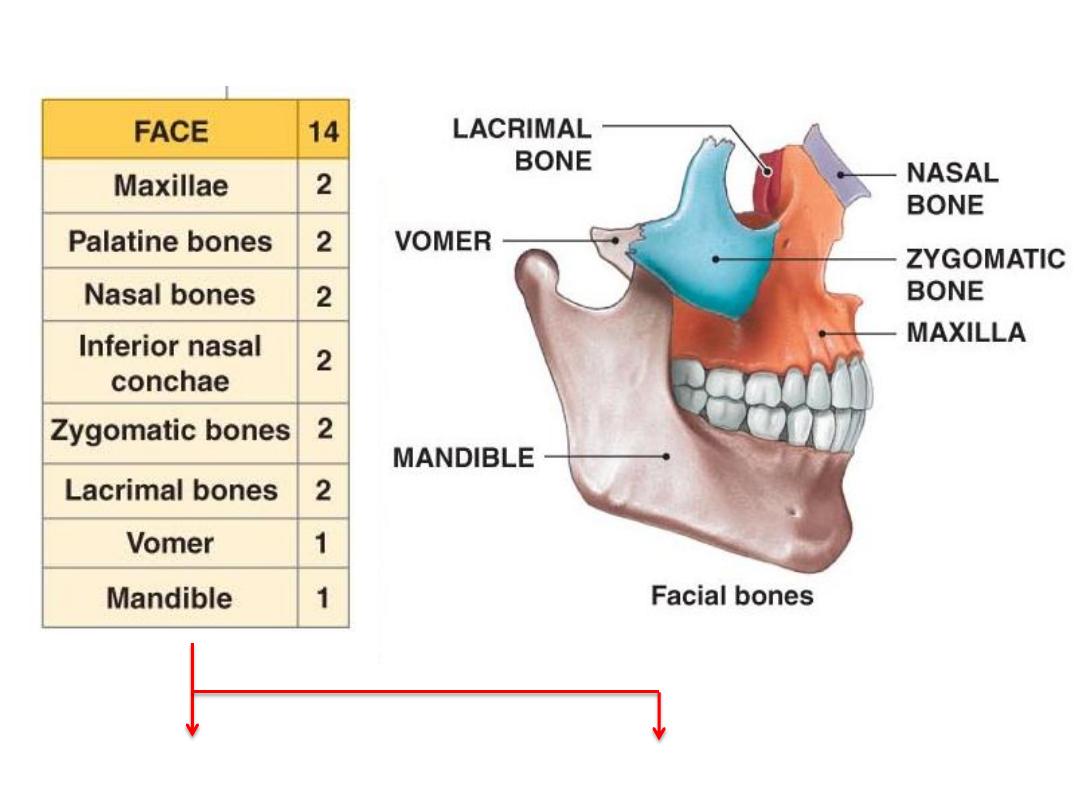
The viscerocranium
Provide facial skeleton
Provide muscle attachment
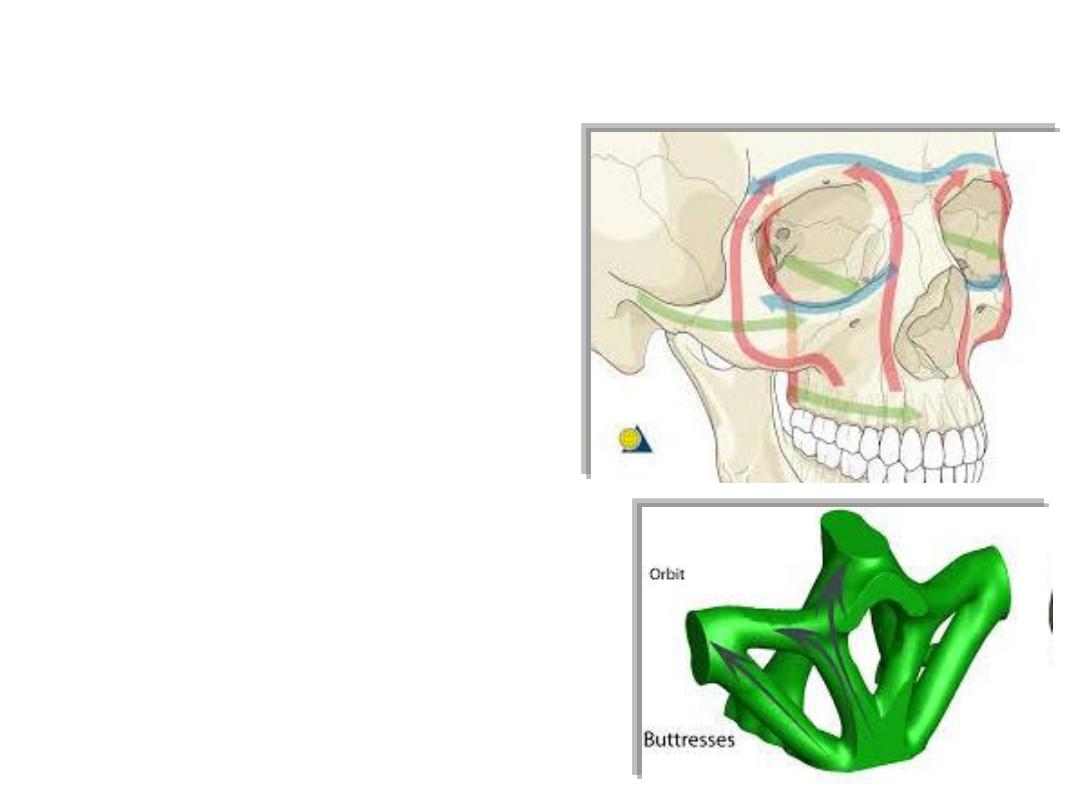
Buttresses:
The midface is anchored to the
cranium through a rigid buttress
framework
The buttress system
absorbs and
transmits forces applied to the
facial
skeleton to stronger bones
Fractures of buttresses are serious &
may be fatal
Langer lines
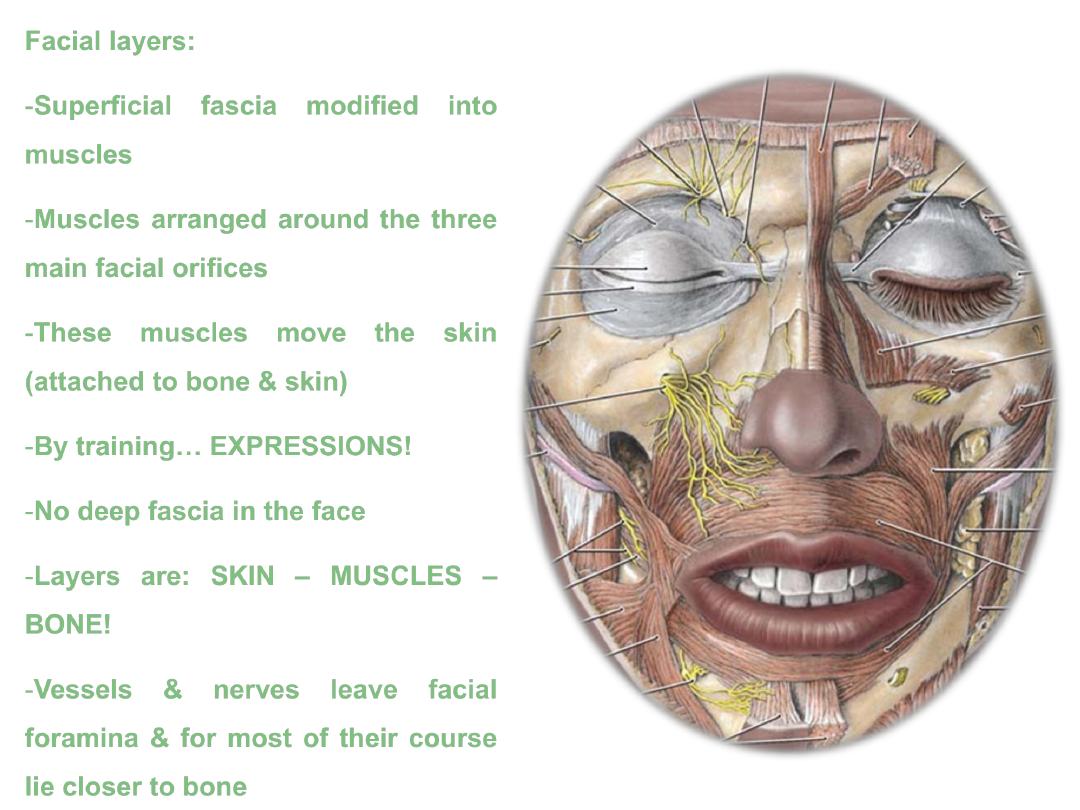
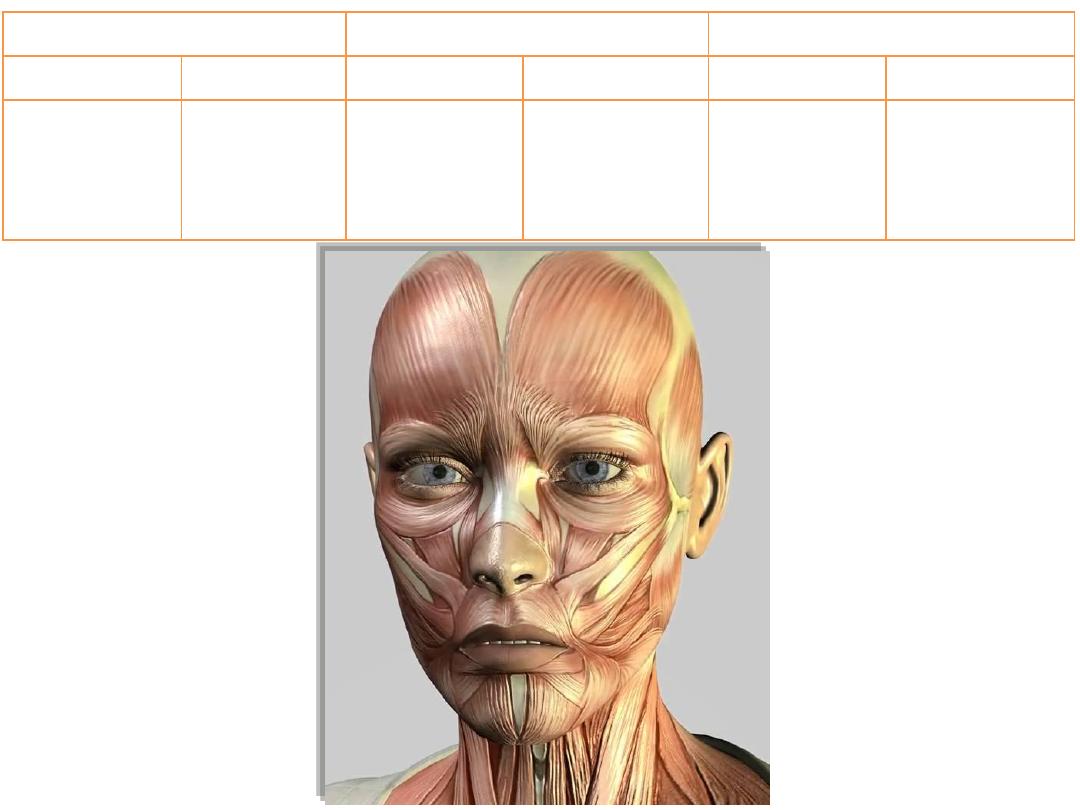
Facial layers:
-Superficial fascia modified into
muscles
-Muscles arranged around the three
main facial orifices
-These muscles move the skin
(attached to bone & skin)
-By training
…
EXPRESSIONS!
-No deep fascia in the face
-Layers are:
SKIN
– MUSCLES –
BONE!
-Vessels & nerves leave facial
foramina & for most of their course
lie closer to bone
Palpebral orifice
Nasal orifice
Oral orifice
Sphincter
Dilator
Sphincter
Dilator
Sphincter
Dilator
Orbicularis
oculi
-Levator
palpebrae
superioris
-Frontalis
-Depressor
septi
-Procerus
-Corrugator
-Nasalis
-Orbicularis
oris
-Buccinator
-Elevators of
upper lip
-Depressors
of lower lip
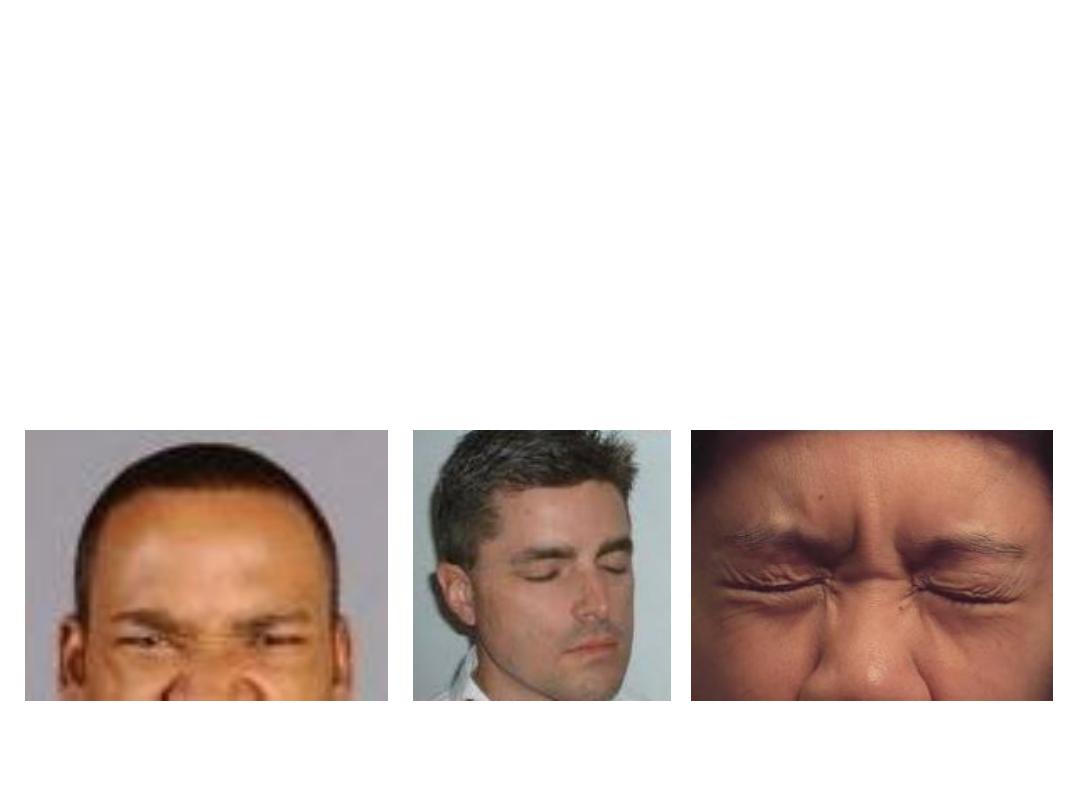
Orbicularis oculi:
-Concentric fibers which surround the
palpebral fissure
-Arise from medial palpebral ligament
-Divided into:
1- Palpebral part; inside the lid
2- Orbital part; outside the lid
3- Lacrimal part; around lacrimal sac
-Action:
Orbital
Depress eyebrows
Palpebral
Blinking
Both
Forced closure
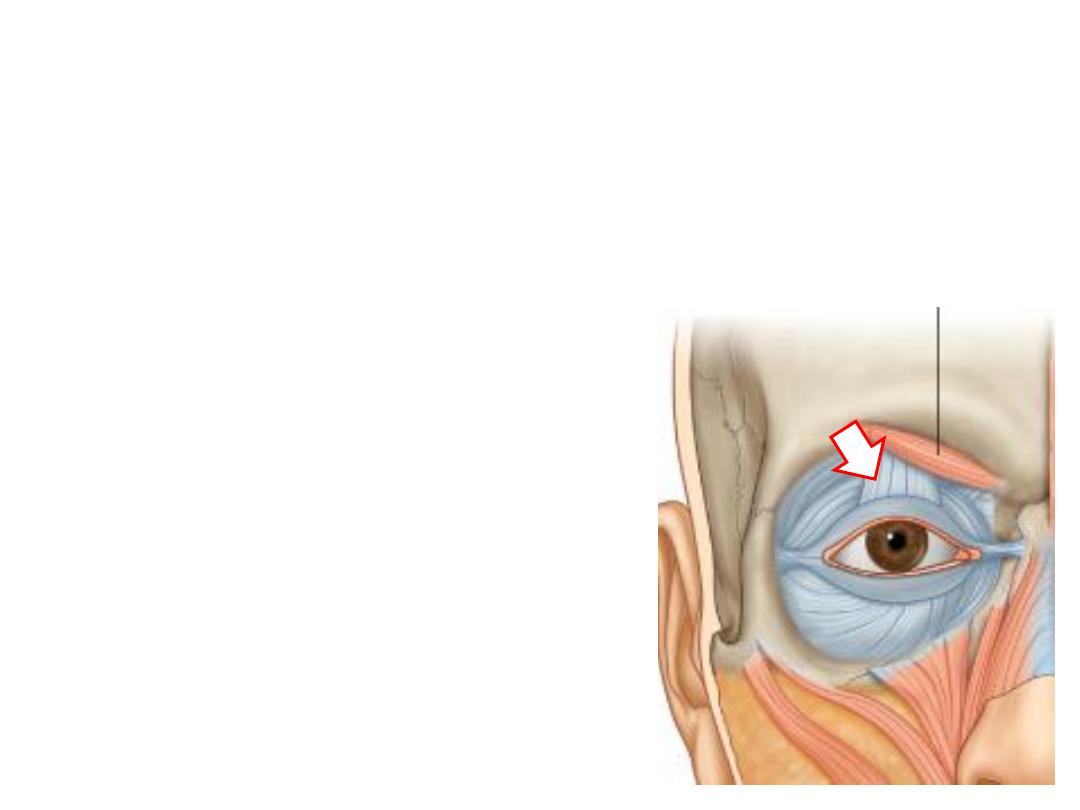
Levator palpebrae superioris:
-Arises from the back of the orbit
-Inserted into the orbital septum of upper lid
-Composed of smooth & skeletal muscles
-Supplied by oculomotor nerve (skeletal) & sympathetic trunk
– T1 (smooth)
Why this muscle is mixed?
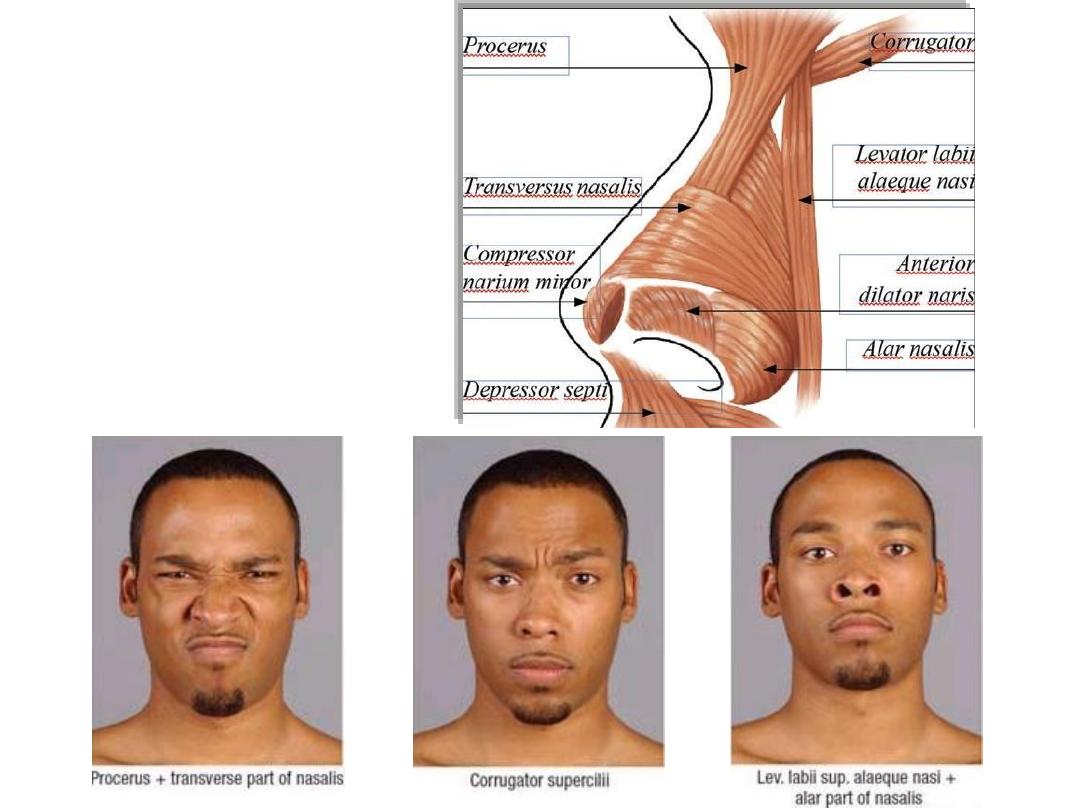
Nasal muscles
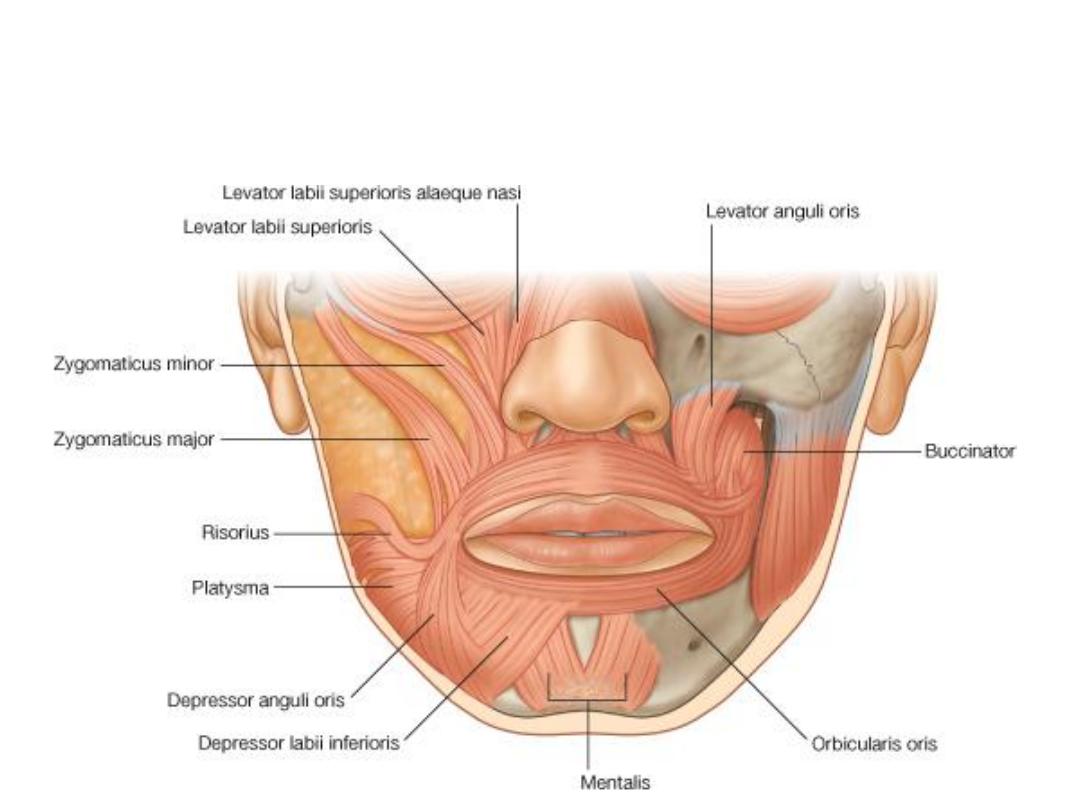
Oral muscles

Orbicularis oris:
-Arises by maxillary & mandibular fibers which form purse-string arrangement
-Receives contribution from buccinator called extrinsic part
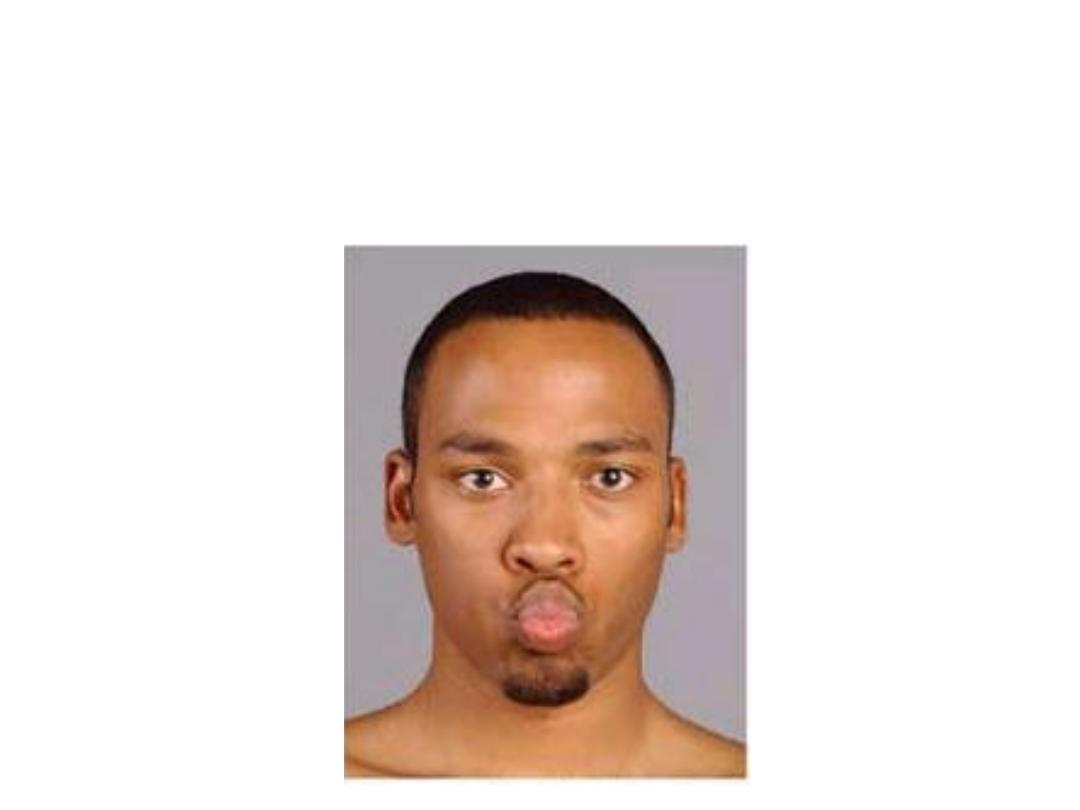
-It flattens & protrudes the lips
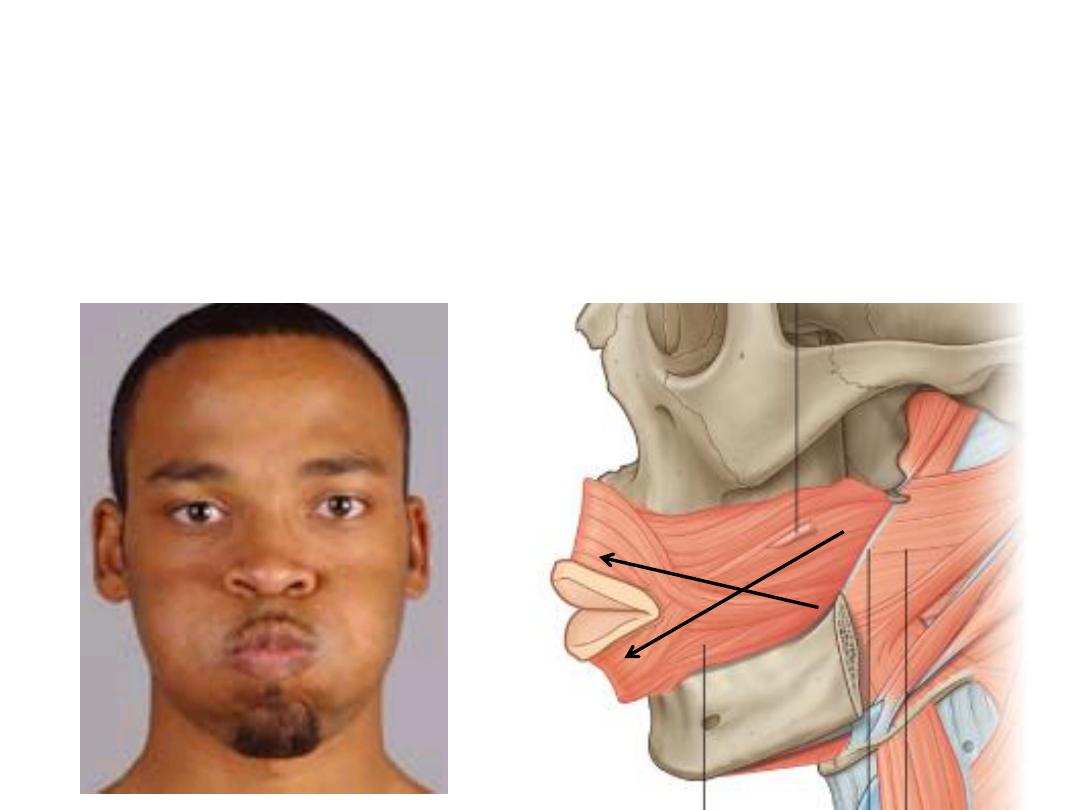
Buccinator:
-Arises from the alveolar process of maxilla & mandible
-Inserted into the substance of orbicularis oris
-Pierced by the parotid duct
-Increases intraoral pressure
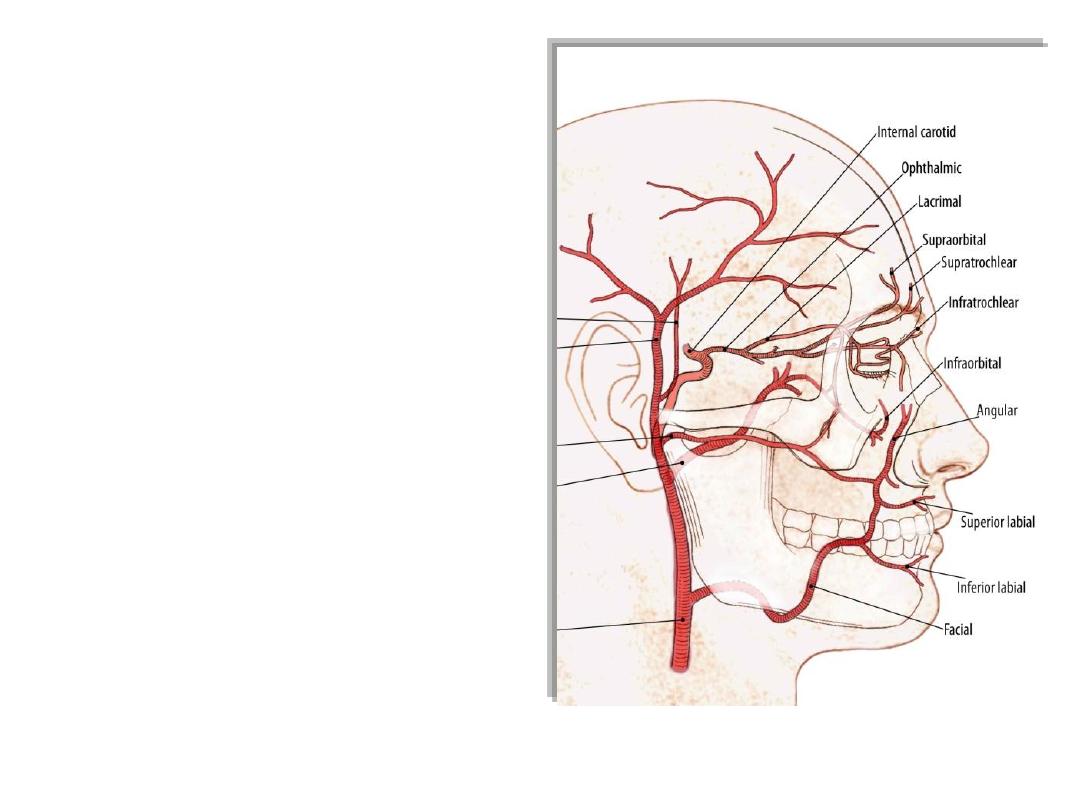
Arteries of the face:
1- Facial artery:
-After a course in the digastric triangle
-Enters the face at the anterior border
of masseter
-Has tortuous course anterior to the
facial vein
-Gives labial & nasal branches
-Continues as the angular artery
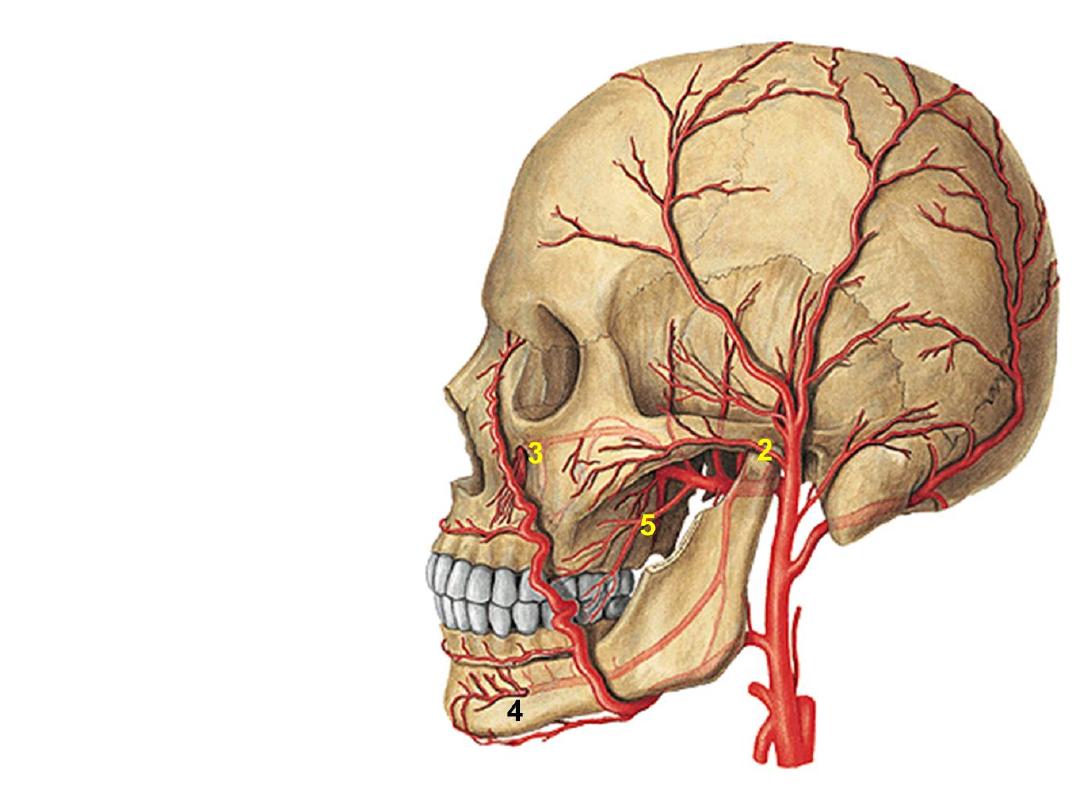
2- Transverse facial artery:
-Branch of superficial temporal
artery
3- Infraorbital artery:
-Continuation of maxillary artery
4- Mental artery:
-Continuation of inferior alveolar
artery
5- Buccal artery:
-Branch of maxillary artery
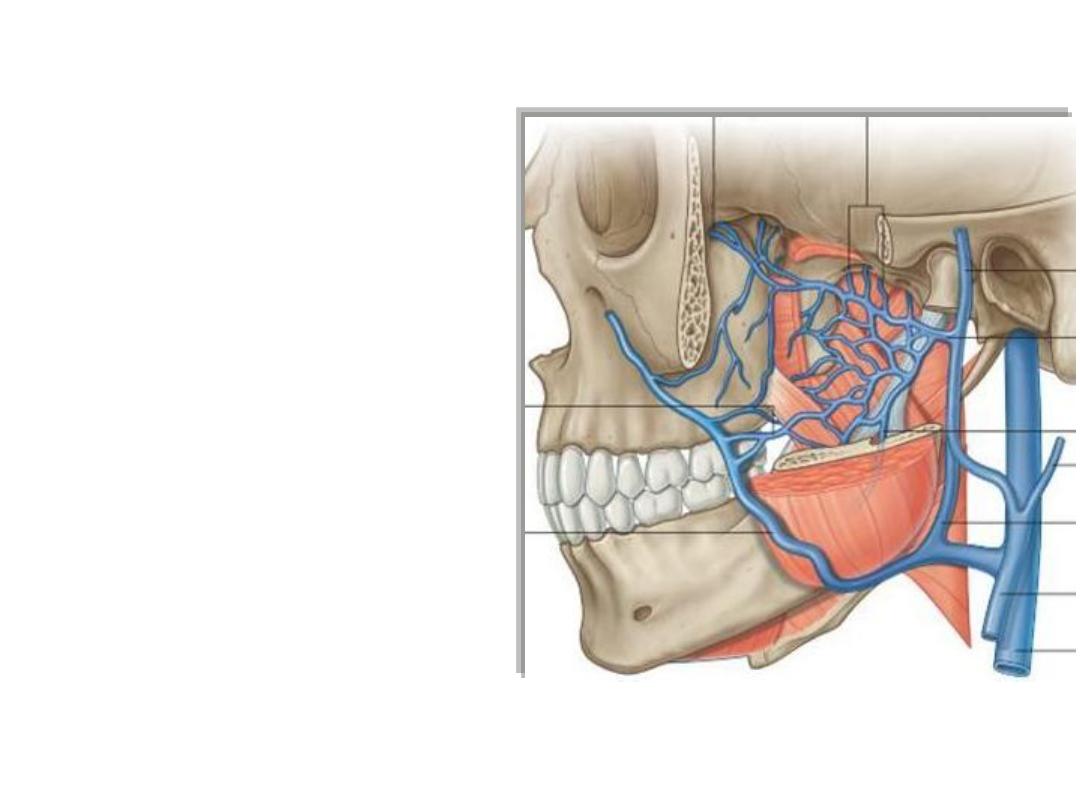
Veins of the face:
Correspond to arteries
The anterior facial vein (valveless):
•Begins as the angular vein
•Descends in a straight course
posterior to facial artery
•Meets the anterior division of
retromandibular vein to form the
common facial vein
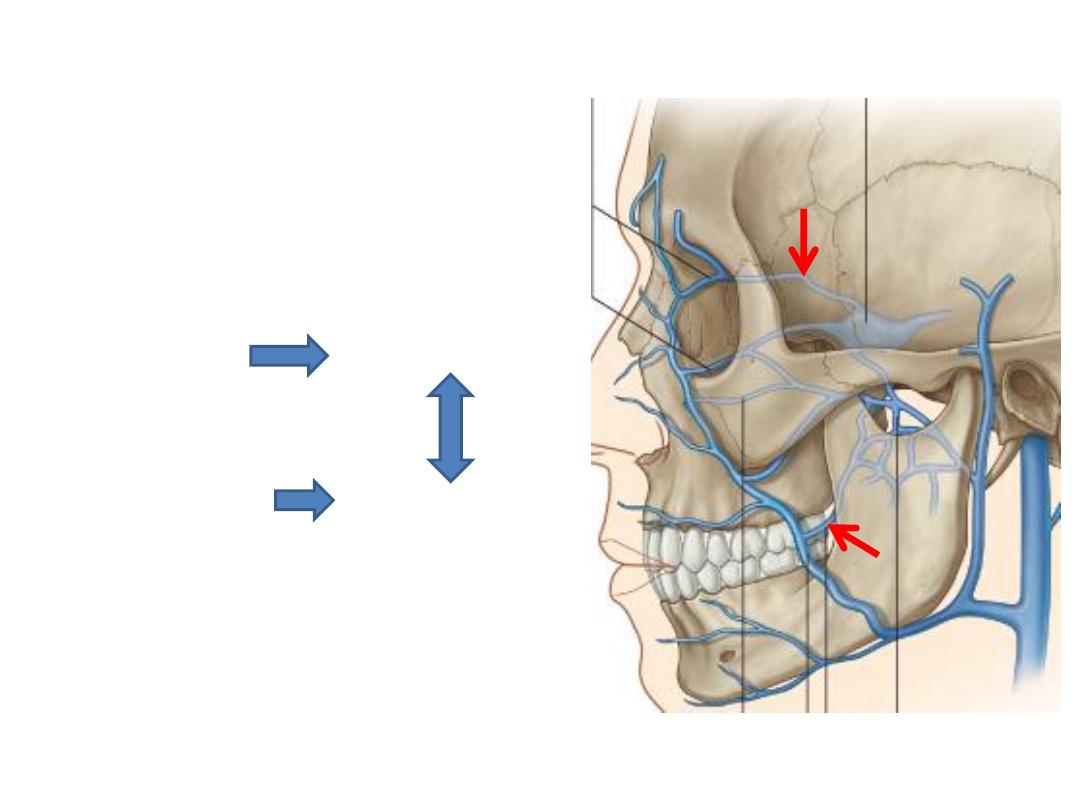
Connections of anterior facial v.:
-
Orbital veins Cavernous sinus
-
Deep facial vein Pterygoid plexus
F. ovale
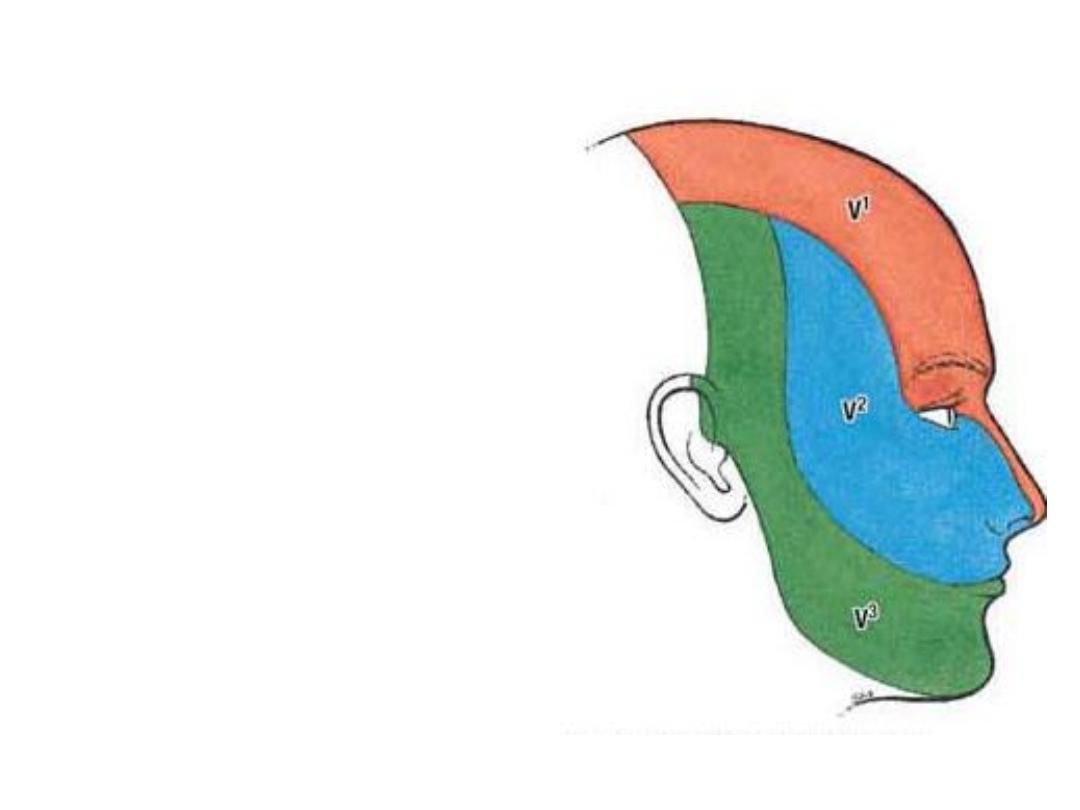
Sensory innervation:
1- Great auricular nerve
2- Trigeminal nerve (CN V):
Terminal branches of the three divisions
of trigeminal nerve supply the face as
follows:
1- Ophthalmic division.
2- Maxillary division.
3- Mandibular division.
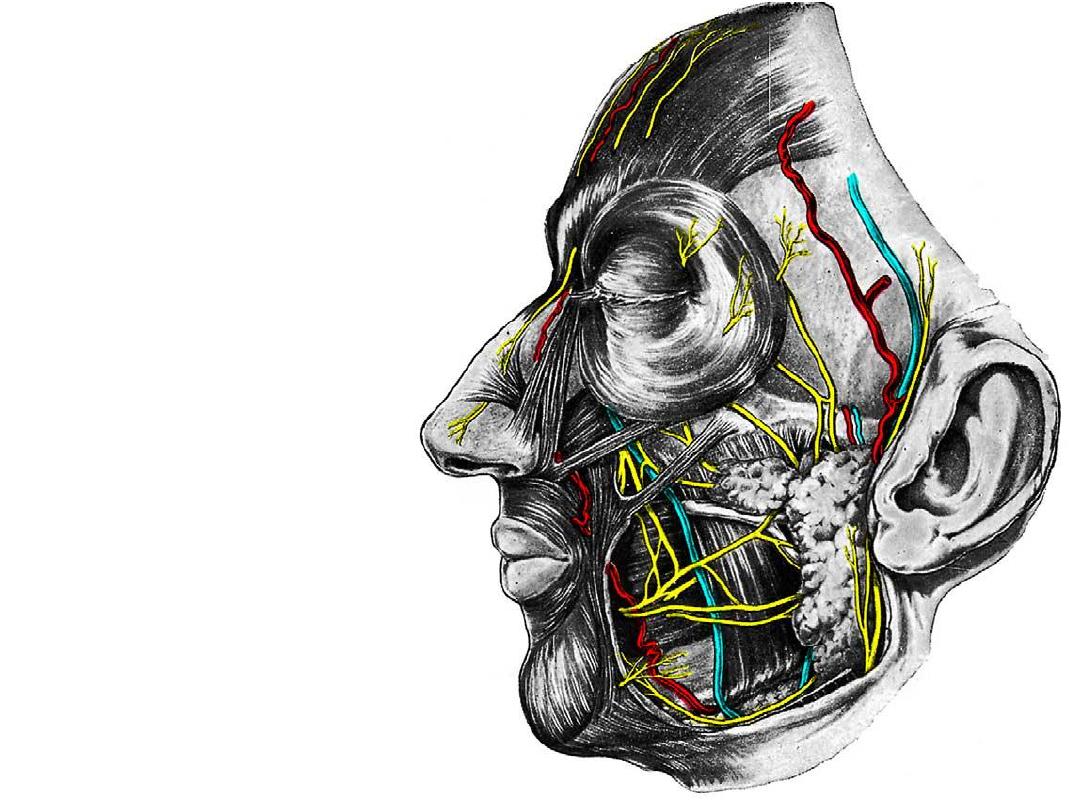
I: Ophthalmic division (orbit):
-
Enters the orbit via SOF as
3 branches
-
Supplies orbit, some PNS
&
nasal
cavity
before
reaching the face
Supraorbital nerve
Supratrochlear nerve
Infratrochlear nerve
Lacrimal nerve
External nasal nerve
Specific skin areas of these
nerves should be studied
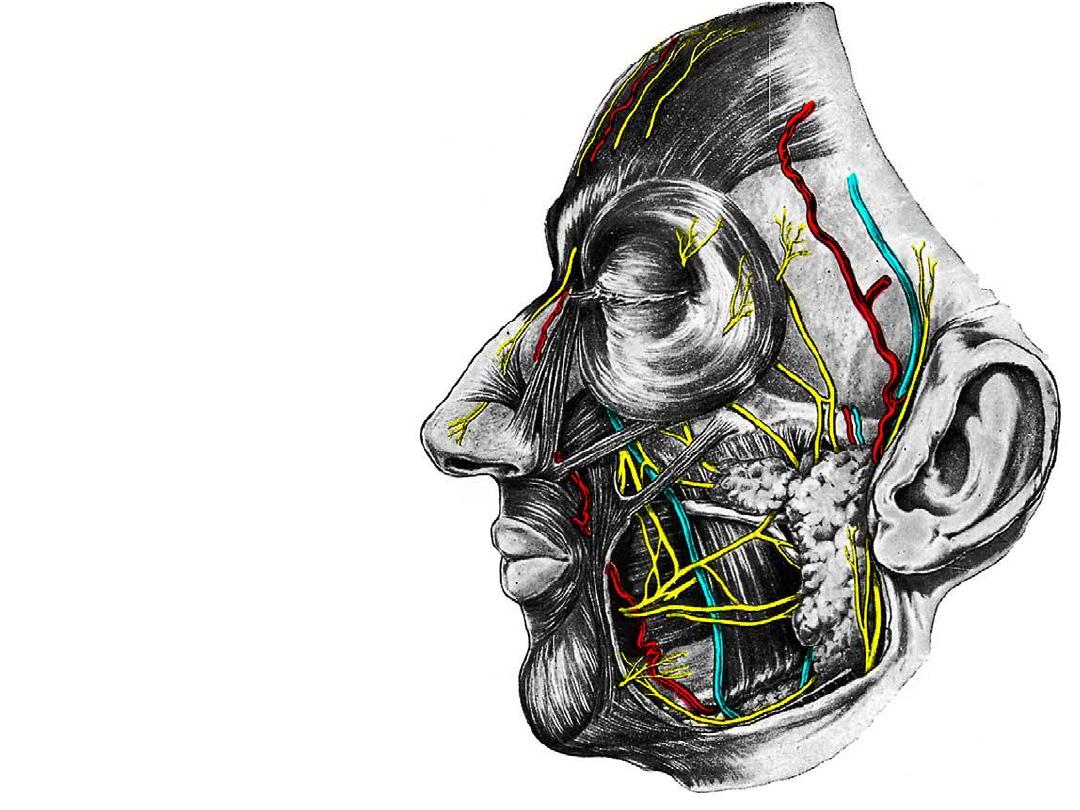
II: Maxillary division (PPF):
- After supplying some PNS,
nasopharynx, nasal cavity &
upper teeth it reaches the
face
Zygomaticofacial nerve
Zygomaticotemporal nerve
Infraorbital nerve
Specific skin areas of these
nerves should be studied
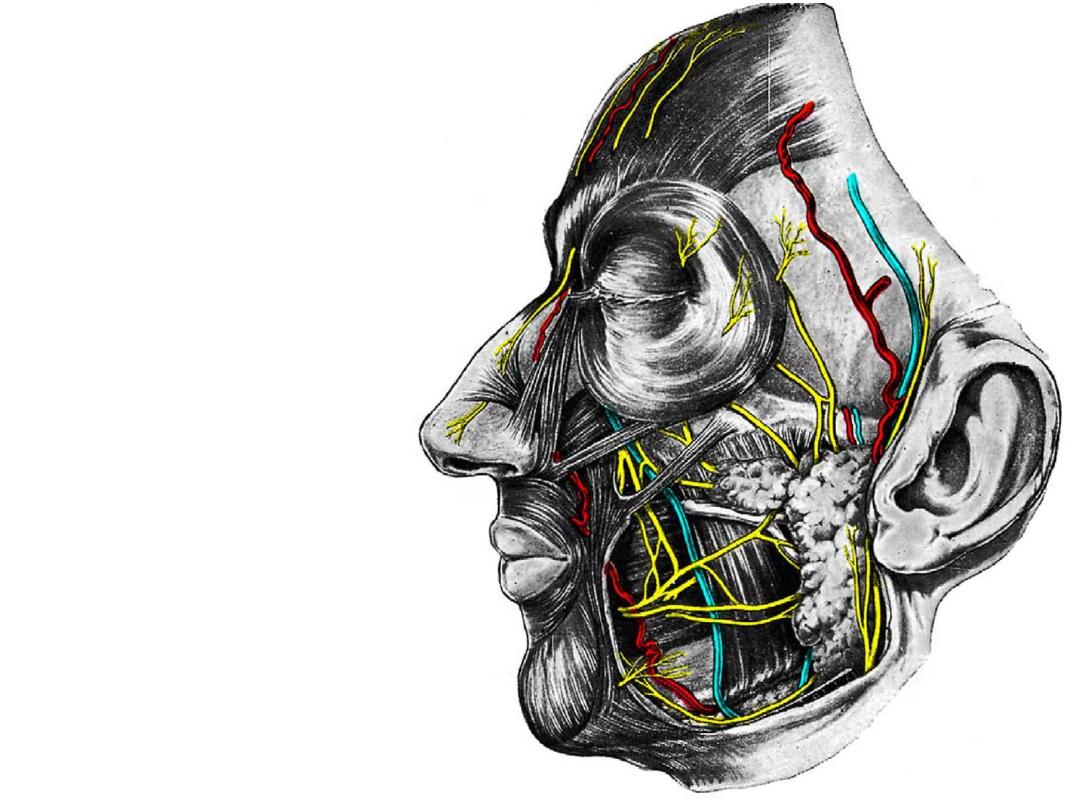
III: Mandibular division (ITF):
Supplies
widespread
area
including the temporal &
infratemporal fossae with the
tongue
Buccal nerve
Mental nerve
Auriculotemporal nerve
Specific skin areas of these
nerves should be studied
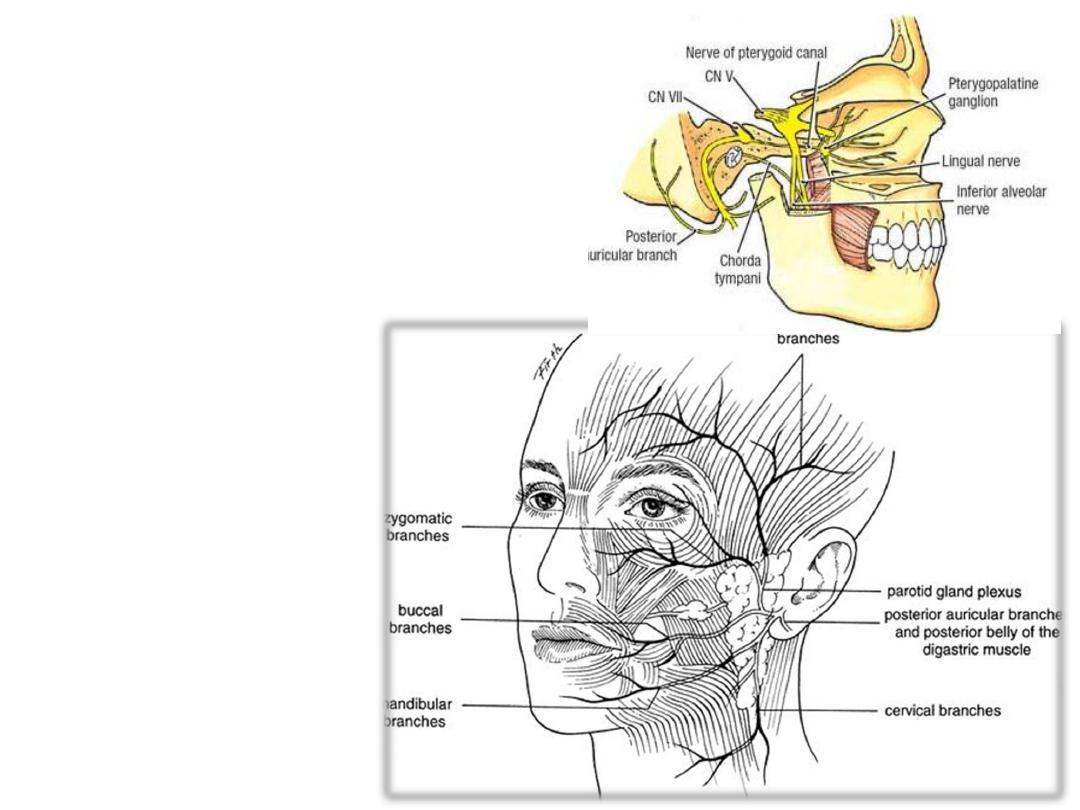
Motor innervation:
Facial nerve (CN VII):
- Leaves the stylomastoid foramen
-Supplies occipitalis, digastric, stylohyoid
-Enters the parotid gland where it divides,
then leaves its anterior border as five
branches:
- Temporal branch
- Zygomatic branch
- Buccal branch
- Mandibular branch
- Cervical branch
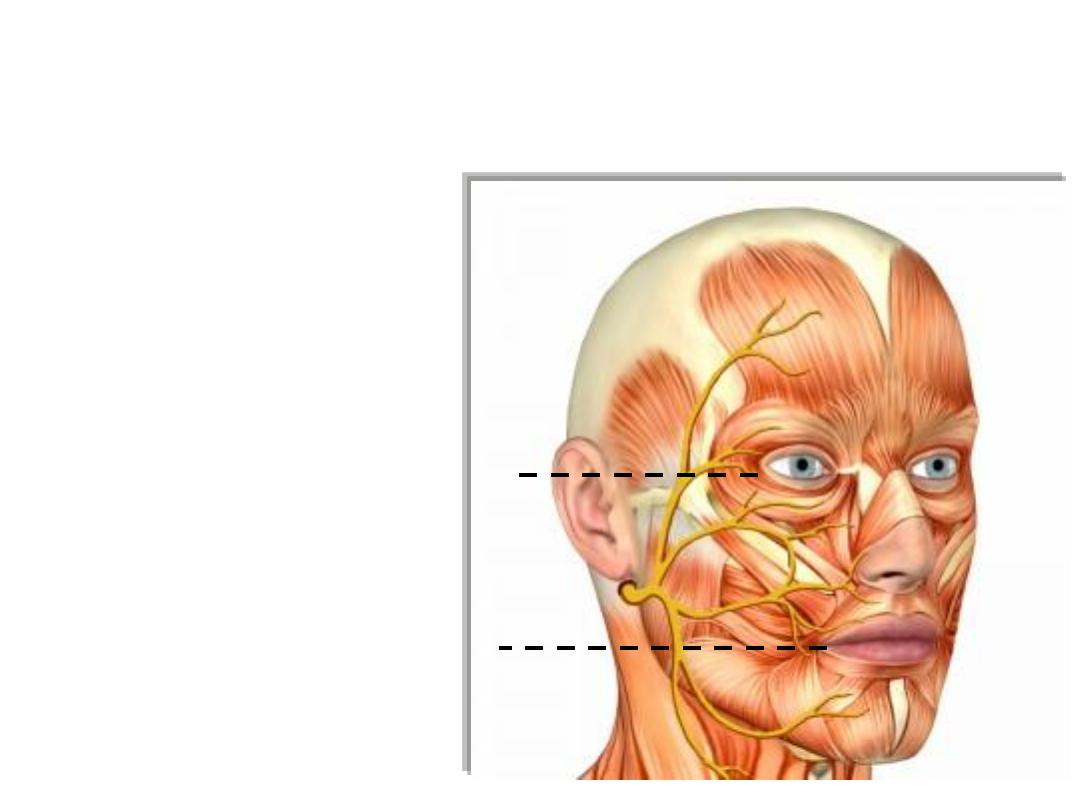
-Temporal:
Muscles above the palpebral fissure
-Zygomatic:
Muscles between the palpebral & oral fissures
-Buccal:
Buccinator
-Marginal mandibular:
Muscles of the lower lip
-Cervical:
Platysma
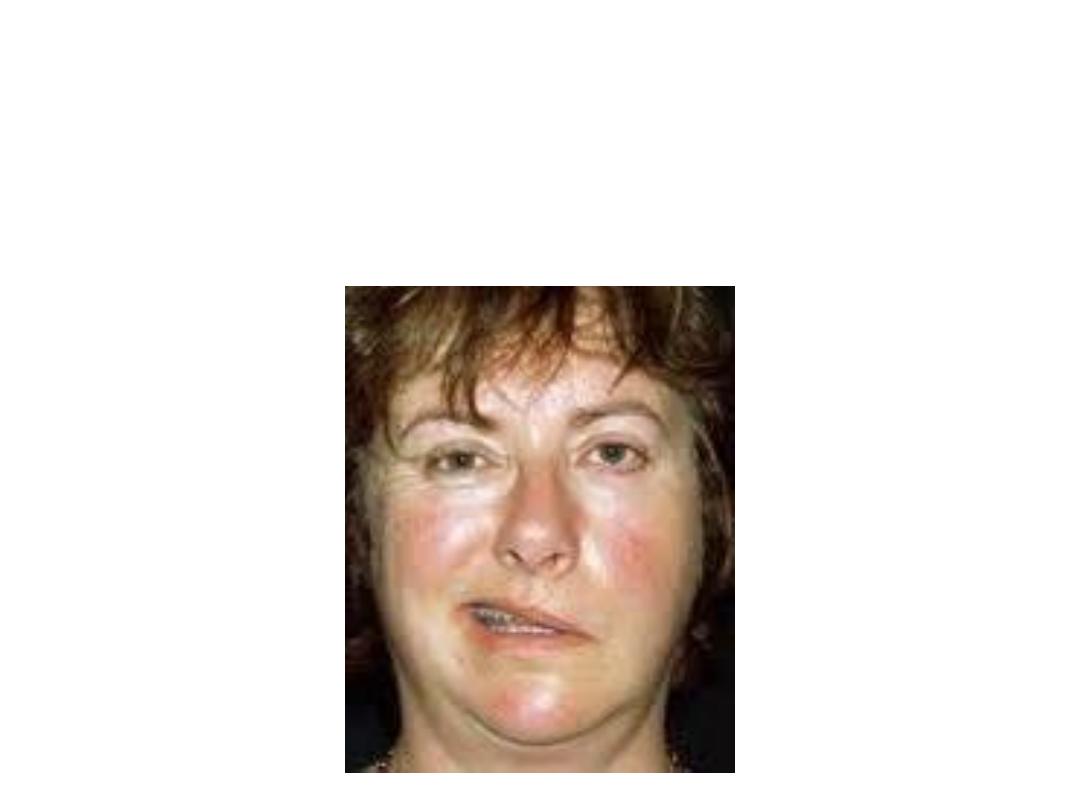

Case
A 40 years old lady consulted you of
severe weakness in her left
face
with inability to blink & lip drop with inability to keep the food
in her mouth during mastication. She gave
history of acute otitis
media
3 weeks ago.
Your diagnosis was left sided facial palsy!
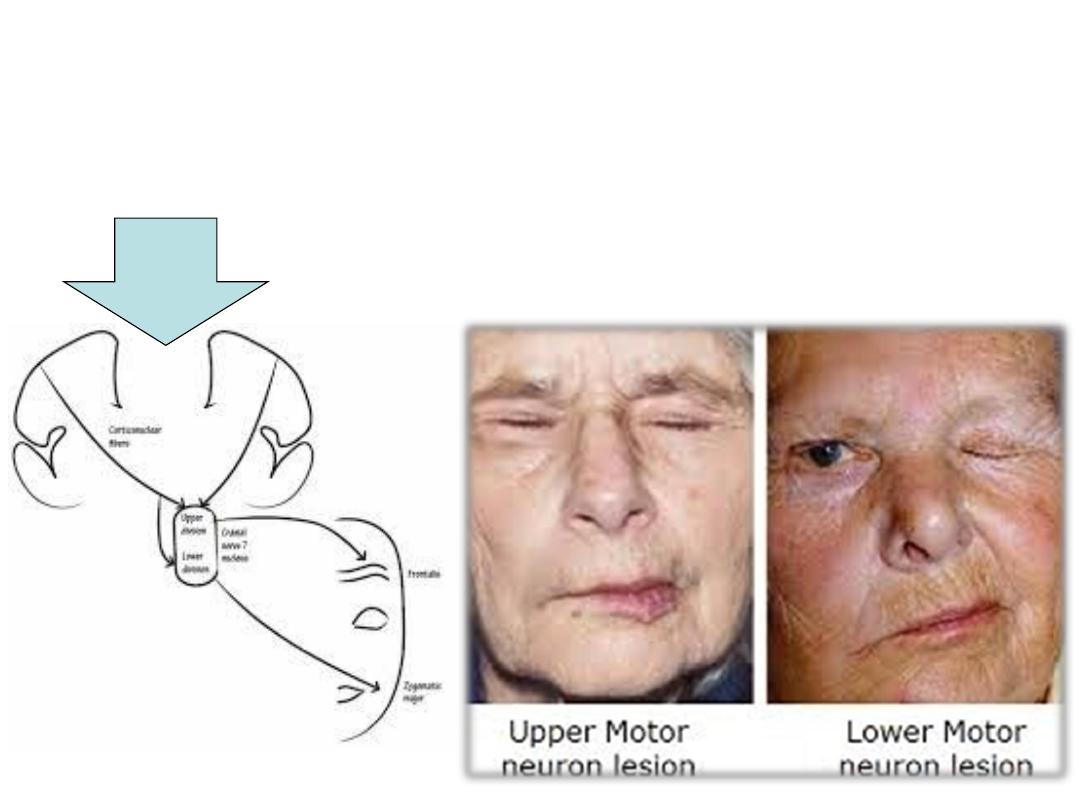
Facial palsy:
a) Upper motor neuron; especially evident in the lower facial muscles
b) Lower motor neuron; Complete ipsilateral paralysis of all facial
muscles
