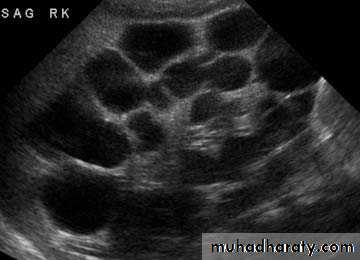
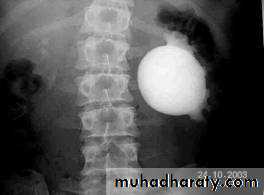
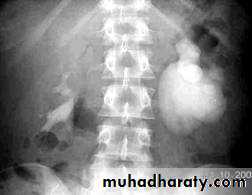
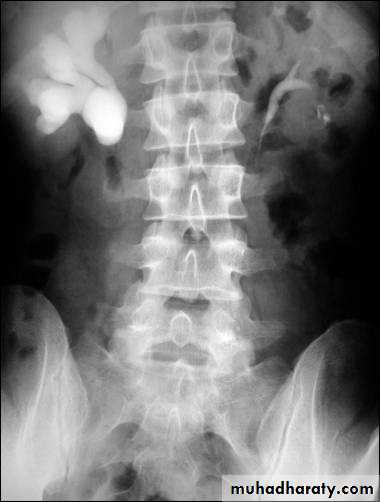
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction (UPJO)
مرحلة رابعة\107 د.محمد فوزي23\10\2017 العدد8
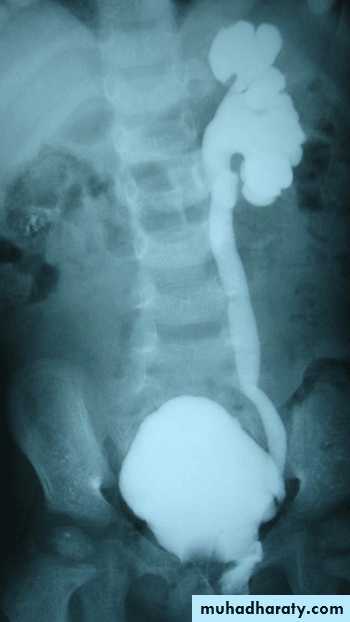
Most common cause of fetal hydronephrosis.
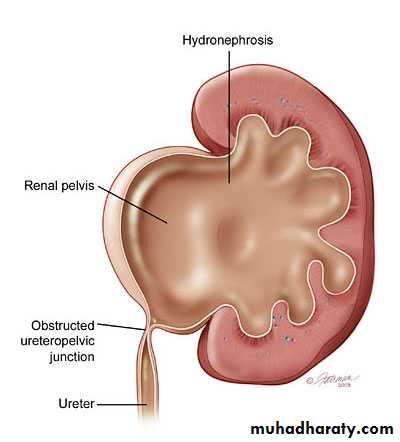
Obstruction at the junction between renal pelvis and ureter.Incidence: 1:1000
Boys:Girls = 2:1
Left:Right = 2:1
Bilateral in 10%.
Overview
Aetiology
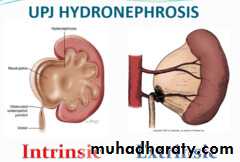
Congenital:Intrinsic
Aperistaltic segment
Fibrous stricture
Extrinsic:Crossing vessels (Aberrant vessel).
Acquired:
Stone disease
Iatrogenic post-operative stricture.
Chronic inflammatory process
Malignancy
VUR (Vesico-ureteral Reflux disease)
Idiopathic.
Clinical Presentation
Antenatal US Detection.Abdominal mass
Recurrent UTI
Hematuria
In older children:
flank or abdominal pain,
UTI,
hematuria following minor trauma
Dietl’s crisis.
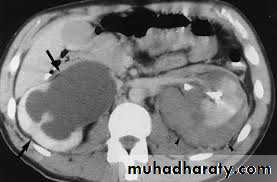
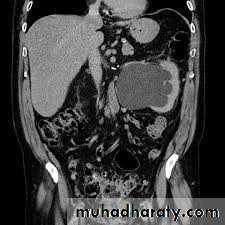
Investigations
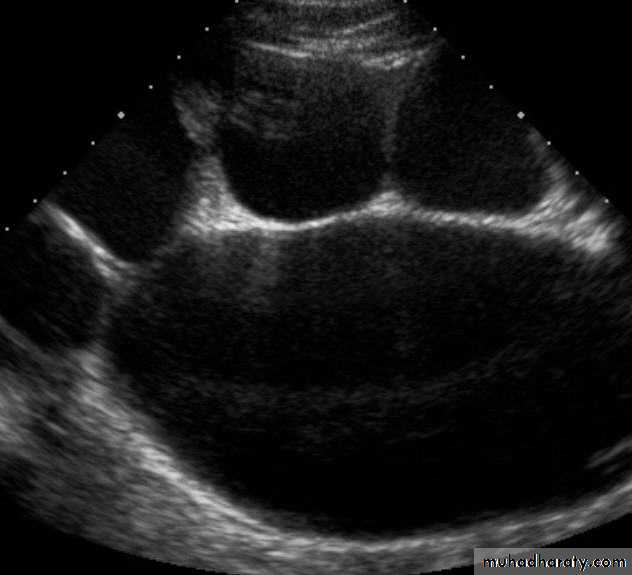
US: pre- and post-natal.IV Urography
Isotope renal scan.
CT & MRI
Pressure-Flow Study (Whitaker Test)
Management
Conservative:Prophylactic antibiotics.
Serial follow-up and observation for complications.
Indications of Surgery
Symptomatic UPJOComplications
Progressing hydronephrosis
Impaired function of the affected kidney
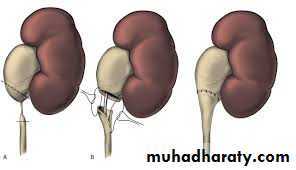
Options include open or laparoscopic pyeloplasty. (Anderson-Hynes)
Renal impairment eg. bilateral disease may necessate nephrostomy.
A sac-like non-functioning kidney needs removal.Vesico-ureteric Reflux Disease (VUR)
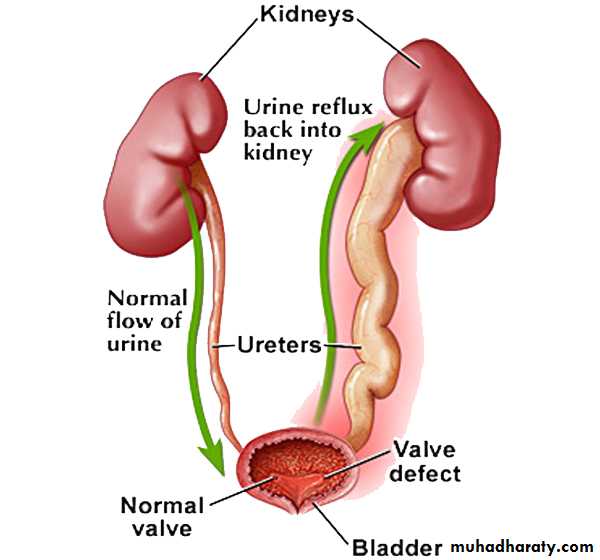
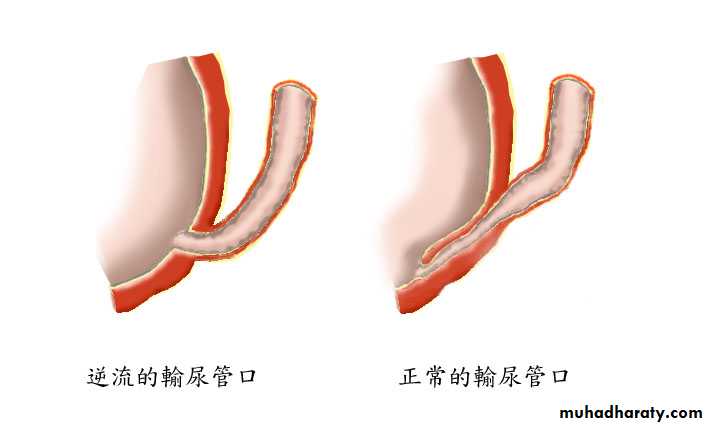
An abnormal retrograde flow of urine from the bladder into the upper urinary tract.
Incidence: 1%Male:Female = 1:5
Family history.
Pathophysiology
The distal ureter passes through the bladder wall creating anti-reflux valve.Reflux may cause renal scarring.
Remote changes may include hypertension and ESRD.
Classification
• Primary• Secondary
• BOO
• Neurogenic bladder dysfunction.
Presentation
VUR by itself is asymptomatic
Symptoms and signs are due to associated UTI.
Febrile UTI in infants:
Irritability
Persistent high fever
Respiratory distress
FTT
Renal impairment
Older children may more clearly reveal symptoms and signs of UTI
Urgency,Frequency,
Dysuria,
Incontinence.
Investigations
Baseline measurementsUrine analysis
Urine culture
Ultrasound scan.
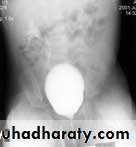
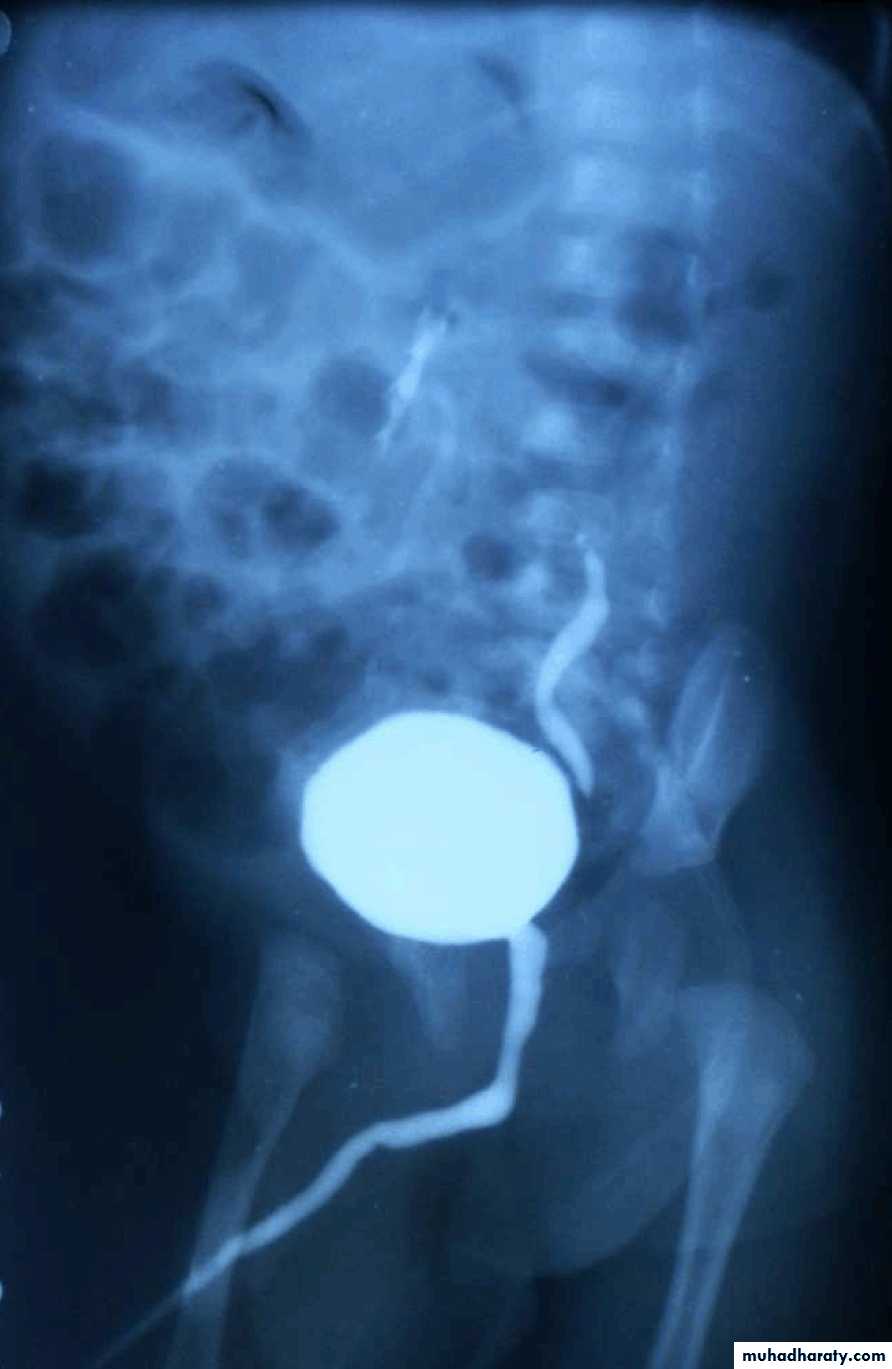
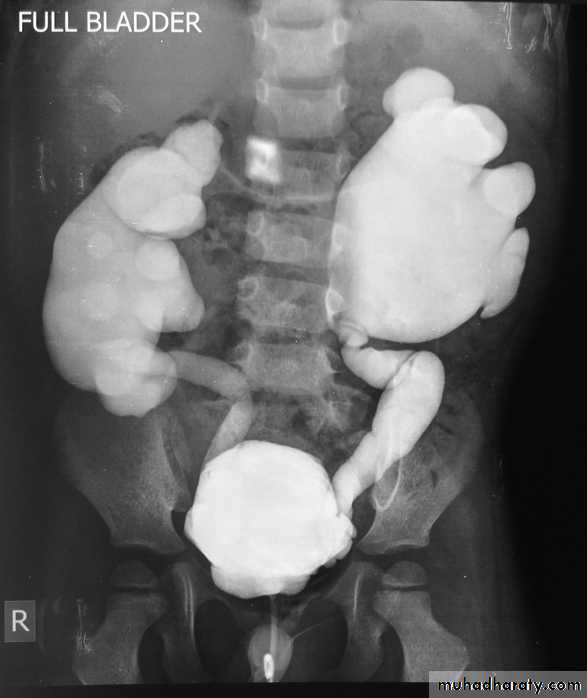
Micturating Cystourethrography (MCUG)
Isotope renal
Video-urodynamics.
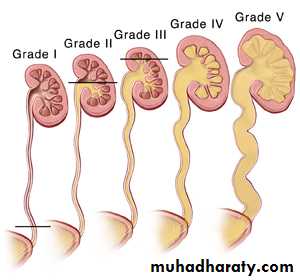
VUR is classified into 5 grades depending on the severity of reflux and the associated dilatation of the renal system.
Treatment
Depends on the severityGrades 1 & 2 resolve spontaneously.
Reflux improves by age.
General Advices:
Adequate fluid intake.
Regular voiding.
Good genital hygiene
Medical attention required in cases of:
Unexplained fever
Features of UTI
Medical Treatment
Low-dose antibiotics.
Regular monitoring of growth and blood pressure.
Serial follow-up US
Indications of Surgery
High grade reflux.Febrile UTI in spite of prophylactic antibiotics
Surgical options include:
Endoscopic minimally invasive techniques
Reimplantation of the ureter into the bladder