صناعة
Lec 3Rests & Rest Seats
A Rest: is any rigid part of an RPD framework which contacts a properly prepared surface of a tooth.
A Rest Preparation or Rest Seat: is any portion of a tooth or restoration properly prepared to receive a rest.
Functions:
The functions of rests and their rest preparations are to:
1. Transmit forces from the prosthetic teeth to the abutment teeth.
2. Provide positive vertical support for the RPD and thus prevent the impingement of the RPD on the gingival tissues adjacent to the abutment tooth.
3. Maintain the clasp in the correct position on the abutment tooth.
4. Serve as a reference point for evaluating the fit of the framework to the teeth.
5. Help prevent extrusion, tipping, or migration of the abutment teeth.
6. Act, along with its minor connector, as an indirect retainer for a tooth-tissue supported RPD.
Types of rests:
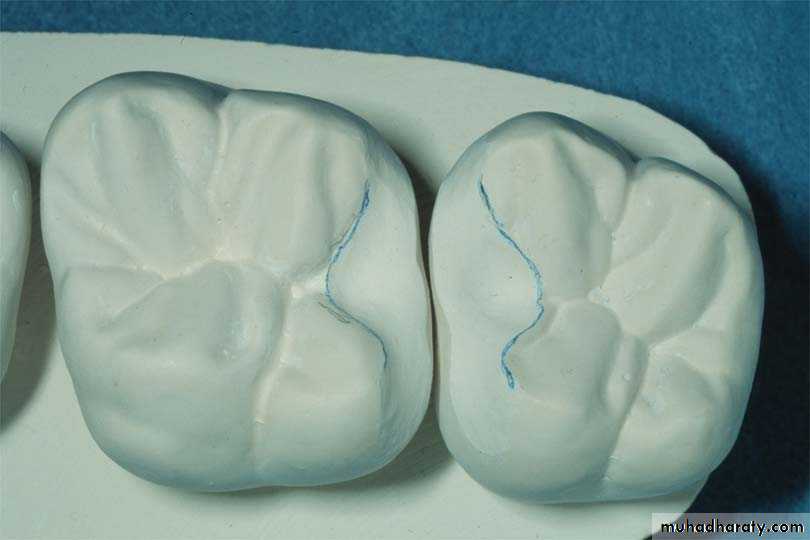
Occlusal rest : Occlusal rests are located in occlusal fossae of molars and premolars. There are three types of occlusal rests based on their location and extent: (1) proximal occlusal rest, (2) Double embrasure (interproximal occlusal rest ) , and (3) transocclusal ( extended occlusal rest)
Requirements of occlusal rest:
1. Rounded triangular shaped with apex nearest the center.
2. It must fit the tooth accurately with beveled margin????? To prevent food stagnation.
3. The floor inclined toward center of tooth so that the angle formed by the rest and minor connector must be less than right angle to the long axis of the tooth?????? To prevent force tooth away from the saddle by direct the vertical load with long axis of the tooth.
4. The Length, width and thickness of the rest 2.5,2.5, and 1.5 respectivly.
5. It should cover 1/3 of the width of the marginal ridge
6. The internal angle of the rest should be rounded ????? To allow a considerable thickness of metal so increase its strength.
The preparation is at least 1.0 mm deep with a slightly deeper portion (0.5 mm) called the POSITIVE SEAT located toward the center of the preparation.
Double Embrasure Occlusal Rest(Interproximal occlusal rest): is located in a fossa of two adjacent teeth, it is used to prevent interproximal wedging by the framework. Its size, shape and dimensions are similar to the proximal occlusal rest preparation EXCEPT that the flare of the facial margin is limited by the proximal contact with the adjacent tooth, and extended lingually to provide strong contact with minor connector. In this way the adjacent embrasure occlusal rests eliminate the occlusal embrasure making the area more "self cleansing" and splint the two teeth together .
Transocclusal rest (Extended occlusal Rest):
It is indicated in most posterior abutment, mesially tipped molar ??? to minimize further tipping of the abutment and to direct the force down the long axis of abutment.This rest should extend more than 1\2 mesiodistal width of the tooth, 1\\3 buccolingal width, and 1mm thickness.
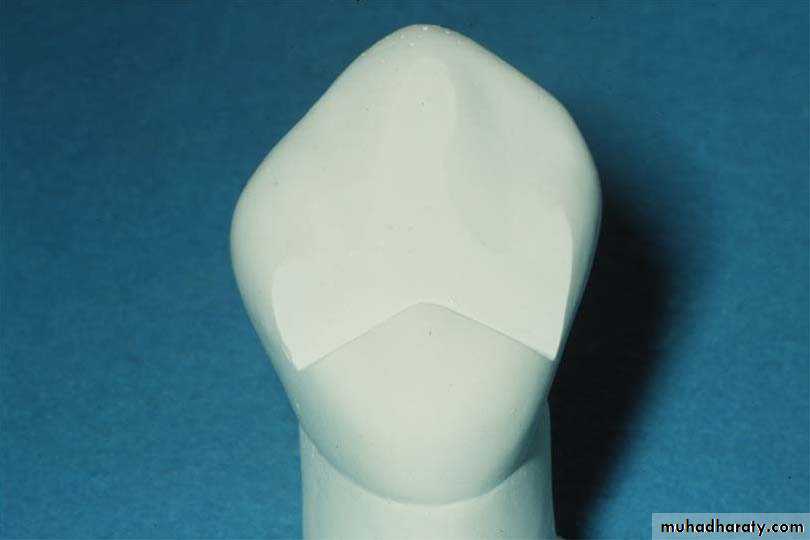
Cingulum or lingual rest and rest preparation:
Lingual rests are placed on the lingual surface of canines and incisors.
They are routinely placed on maxillary canines and incisors.
Lingual rests are rarely use on natural mandibular incisors and canines because there is usually insufficient enamel thickness for an adequate lingual rest preparation.
The floor of the rest preparation is inverted V- shaped, deepest toward the center of the tooth
The preparation extends more cervically on the mesial and distal thus forming a positive mesiodistal seat.
The cingulum shaped rest preparation is approximately 1.0 mm deep pulpally and cervically.
Lingual rests are preferred to incisal rests because:
(1) they do not show metal when viewed from the facial and are, therefore, more esthetic,(2) they are more cervical on the tooth and, therefore, closer to the fulcrum point and have a shorter lever arm and lower mechanical advantage in torquing the tooth and
(3) for mandibular teeth they are not involved in the occlusion
Ledged shape rest:
can be made in any tooth when the enamel thickness is greater than 1mm. They are used where the tooth does not have a prominent cingulum or where a finger-type rest is to be used The preparation extends through the mesial and distal marginal ridges. The faciolingual width of the lingual ledge-shaped rest preparation is approximately 1.0 mm.
Round lingual rest seat:
Lingual dimple-shaped rest preparation is employed when there is limited surface on anterior teeth due to occlusal contacts.
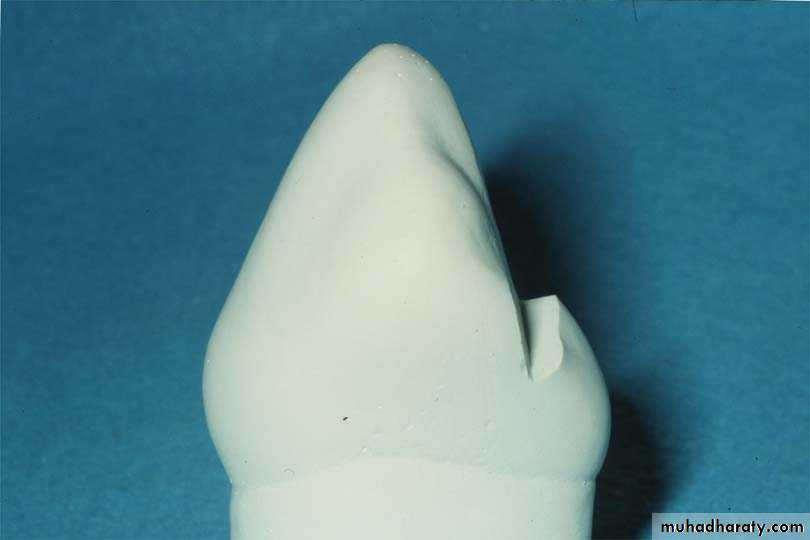
Incisal rest and rest preparation:
Incisal rests are placed on the incisal edges of mandibular canines and incisors. They are not placed on maxillary canines or incisors because the minor connector of the rest would interfere with occlusion and the facial portion of the rest would be very visible and unaesthetic.Requirements of incisal rest:
The rest should also be located so that it will direct forces parallel to the long axis of the tooth.
. Incisal rest preparations are Ushaped when viewed from the facial or lingual and inverted U-shaped when viewed from the proximal .
The mesiodistal dimension of the rest preparation should be 1½-2 mm and the depth at least 1 mm to provide adequate space for a bulk of metal for the rest.
Desirable materials for rest preparation:
Enamel and cast metal are ideal materials for rest preparations.
Porcelain is less desirable because of its propensity to fracture.
Rest preparations may be prepared as an economic necessity in amalgam but the flow and low yield strength of amalgam and the possibility of recurrent caries and fracture of the tooth and/or restoration make amalgam an undesirable material for a rest preparation.
Dentin is an undesirable material for a rest preparation because of its low abrasion resistance and propensity for caries. Unfortunately, dentin is frequently exposed when placing rest preparations in natural teeth. In these situations the tooth does not need to be restored unless it is sensitive or caries is anticipated.
Conventional and resin composite are unacceptable materials for rest
preparations because of their low yield strength and low abrasion resistance.