Pharmaceutical preparations
Dr. Fayhaa Azher2017
1
Pharmaceutical preparations for internal use
21- solid preparations
A- TabletsB- Capsule
C- Pill
3
Types of tablets
4
Tablets
Ordinary tabletsprepared by forcing the powdered drug into solid mass
the powdered contain the drug alone or the drug with a suitable diluent into a solid mass using a mechanical machine with optimal degree of compression.
e.g. paracetamol tab.
5
Ordinary tablets
6
Diluent: it is an inert substance (pharmacologically inactive) used to increase the size of the powder in order to make compression of tablet easier.
Some very common diluents in tablets include starch, cellulose derivatives, and magnesium stearate
7
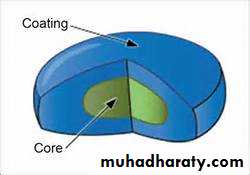
Coated tablet
A solid disc of one or more pharmaceutic agents that is coated with sugar or a flavoring to mask the taste .
Enteric-coated, meaning that it is coated with a substance that resists dissolution in the stomach but allows release of the medication in the intestine.
• It has the following advantages :
• 1- to avoid the bitter taste of the drug
• oxidation of the drug 2-to prevent air
• 3- to facilitate swallowing in some patients
• e.g. flu out tablet
8
Coated tablet
9
Enteric coated table
ordinary compressed tablet covered with acid resistant covering (salol) to allow the tablet to pass the stomach unchanged but is dissolved in the alkaline medium of the intestinee.g. aspirin
10
Enteric coated tablet
advantages:
1- avoid irritation
2- prevent drug destruction
3-to get local action
11
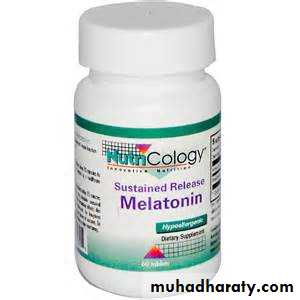
Sustain release tablet(SR)
an ordinary tab. Coated by many coats each with different disintegration and dissolution ratesAdvantages:
1- prolong the duration of action
2-decrease the frequency of administration
e.g. glucophage retard tab.
12
Sustain release tablet
13
Sublingual tablet
.It is uncoated tab. especially manufactured to be suitable for absorption from sublingual mucosa
Advantages
1-rapid action
2-avoid destruction by 1st pass metabolism
e.g. glyceride trinitrates
14
Sublingual tablet
15
Effervescent tablet
Effervescent or carbon tablets are tablets which are designed to dissolve in water, and release carbon dioxide.
Large tab. Contain large dose ,manufactured by mixing the drug with citric acid and sodium bicarbonate to get granules.
The action of drug appears more rapid because the disintegration and dissolution takes place inside water and become ready for absorption .
16
Effervescent tablet
17
Chewable tablet
Ordinary uncoated tab. specially manufactured to be sucked or chewed
This tab. usually with good taste
To bite and grind with the teeth; masticate.
18Chewable tablet
19
Lozenges
Sugar flavored tab with different shapes and attractive colors.It is sucked to treat tonsillitis and relief cough
It contains volatile oils , antiseptic , antibiotics
e.g. Riabas
20
Lozenges
21
Capsules
Ordinary capsulesSmall cylindrical , oval , or rounded receptacles made of gelatin,,,,,, typers:
Hard gelatin cap.
Soft gelatin cap.
Sustain release cap.
Enteric coated cap.
Cap . Shell which dissolve in the stomach is used for the following purposes
1- to mask the bad taste of the drug
2- to prevent air and moisture oxidation
3- to get accurate amount of the drug
22
Ordinary capsules
23Spancule capsule
Ordinary cap. Contains different granules each with different disintegration and dissolution ratesAdvantages :
1- prolong the duration of action
2- decrease the frequency of administration
24
Spancule capsule
25
Pill
It is solid spherical body containing a drug in solid or liquid form given by mouth usually apill should not weight more than 0.3 g , it is sometime coated with sugar coat when the drug is liable to change during exposure to aim or when the drug has bitter tastee.g. contraceptive
26pill
27
Liquid preparation
SyrupWater soluble drug dissloved in already prepared simple syrup to get good taste particularly for children
28
Syrup
29
Syrup of antibiotics supplied as powder form in which the antibiotic is mixed with specified quantity of sugar to be prepared as syrup by adding certain quantity of water ,this is because antibiotics may hydrolyzed in aqueous solution to other component which either has no antibacterial activity or a substance causes allergic reactions ,therefore all syrups of antibiotics must be discarded (7) days after adding water.
30
Elixir
It is a clear sweat – flavored liquid (usually contain alcohol)It contains at least one active ingredient dissolved in a solution contains 15 – 50 % by volume of ethyl alcohol and is designed to be taken orally .
31
spirit
Volatile oil in alcohol32
Tinicture
Alcoholic extract33
Decoction
By boiling raw material in water.
34
Emulsion
It is amixture containg 2 immiscible liqiuds (such as oil and water )One of which is broken up into minute globules.
Each globule is surrounded by a film of emulsifying agent and dispersed through out the other liquid .
35
Emulsion
36
Suspension
A solution containing indiffusable solids which do not remain the vehicle evenly distributed long enough to give uniform measured dose ,therefore it is suspended in water using certain suspending agent to be shacked before use to get temporarly uniform doseShake well before use
37Suspension
38
Powdered preparations
1- ordinary powder : drug for internal use in form of fine powder mixed with water before administration2- effervescent powder active drug manufactured in form of effervescent granules by complexing the drug with sodium bicarbonate , citric acid , to be dissolved in water before ingestion.
39
effervescent powder
40
Drops for internal use
This preparation is mostly convenient for infants , it is prepared by concentrating the drug in few drops to decrease volume of dose in order to facilitate swallowing of this small dose and minimize loss of the dose .41
Parental preparation
Ampoule
It’s a thin glass container for a single injectable dose the solution of ampoule is usually sterile indented to be use IM , SC , IV
42
Ampoule for IV injection usually contains very purified pyrogen free solution and most of IV ampoule contain large volume in comparison with ampoule for IM injection
In some instances the active ingredient is putted in separated ampoule in form of powder and the solvent is putted in another separated ampoule to be mixed immediately before injection to avoid hydrolysis of the active ingredient
43
Ampoule
44
Vials
It is a thick glass container with rubber cap containing either solution or powdered drugs either for a single or multiple dose45
Vials
46
47
Pharmaceutical preparations
Pharmaceutical preparations for external use48
Suppository
It is a drug delivery system that is inserted into the rectum (rectal suppository ) , vaginal (vaginal supp) or urethra (urethral supp) where it dissolve .It can be defined as a small piece of medicated substance , usually conical , ovoid , or cylindrical introduced into a body passage as the rectum or vagina where body heat causes it to melt .
49
Suppository
50
Reasons of manufacturing the drug in the form of a suppository :
1- to avoid irritation of stomach2-to get sustain action during the night
3-to get full dose in uncooperative patients such as children
4- to get local action in the intestine
5- in patients who can not taken oral therapy
51
Rectocaps
Supp . Shaped soft shell cap. With a lubricating film layer for rectal delivery of drugAdvantages
1- they are coated so easy to apply
2- they offer the logical alternative when a drug cannot be swallowed because of nausea , vomiting and swallowing difficulties or because high dose has to be used
3-it is ideal dosage form for babies and children
4- they are stable in tropics ,so they retain their shape and action even at high temperatures .
52
Rectocaps
53
Ointment
Is semisolid homogenous , viscous preparation consist of a fatty substance mixed with an active drug . The base may be either soft paraffin, wax,olive oit or vasaline .The drug ,if insoluble in the base ,it should be in the finest possible state and be evenly distributed through out the base
The base of the oit is immiscible with water ,therefore is mostly suitable applied on dry surface such as arms , legs and trunk , the potency of oit is charged with its base
54
ointment
55
Eye oitment
The contents are sterile and contains less concentration of the active ingredient, eye oit , also could be applied to the ear and nose56
cream
It is semisolid preparation in which the drugs are mixed with a fatty base which is miscible with water , therefore it is suitable to be applied on wet surfaces57
cream
58
liniment
Is semisolid or liquid preparation for external use only indented to be applied to the skin by friction, it must contains irritant substances such as camphor, friction of camphor at the site of the spasm or pain will cause irritation leading to local vasodilatation i.e. increase blood supply and relief spasm or pain.59
liniment
60
Lotion
Is liquid preparation intended to be applied to the skin without friction , lotion differ from liniment in that it contains a cooling substances such as mentholLotion sometimes contain drug such as antiseptic or steroid.
61
Lotion
62
Enema
It is liquid preparation intened to be injected to rectum either to get local action e.g. watery solution of soap to cause laxation or for systemic action63
Enema
64
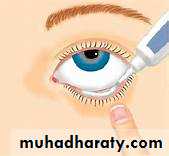
Eye drop
It is watery isotonic sterile solution intended to be instilled into the eye by a dropperit contains one or more of the following ingredients :
1-antiseptic
2-antibiotic
3-antihistamine
4-mydriatic or miotic drugs
5- decongestant drugs
Note: Ocusert pilocarpine system
65
Nasal drop
Watery solution intended to be instilled into the nose by a dropper which is usually contains one or more of the following ingredients66
Ear drop
Watery or oily solution indented to be instilled into the ear and it is usually contains one or more of the following ingredients :Substance which solubilize the wax , antibiotic , steroid , alcohol and antifungal
67
pastes
Oit like preparation contains medication with adhesive materials contain high preparation of powder , so it is more absorpable and more sterngth than oit
68
pastes
69
Plaster
Solid adhesive preparation applied to skin to protect , sooth and lesser pain , and divided to 2 types :1- with medicament
2- without medicament70
Plaster
71
Gargles and mouth wash
Are liquid solution pleasant taste and odour to runs and remove the debris from the mouth72
Gargles and mouth wash
73
Inhalants and aerosols
A substance consisting of very fine particles of a liquid or solid suspended in gasMist : consists of very fine droplets of water in air (aerosols )
Inhalants : are drugs or combination of drugs under vapor pressure carried to nasal passages for inhalation74
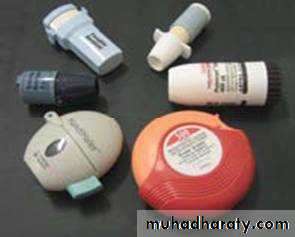
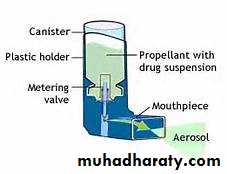
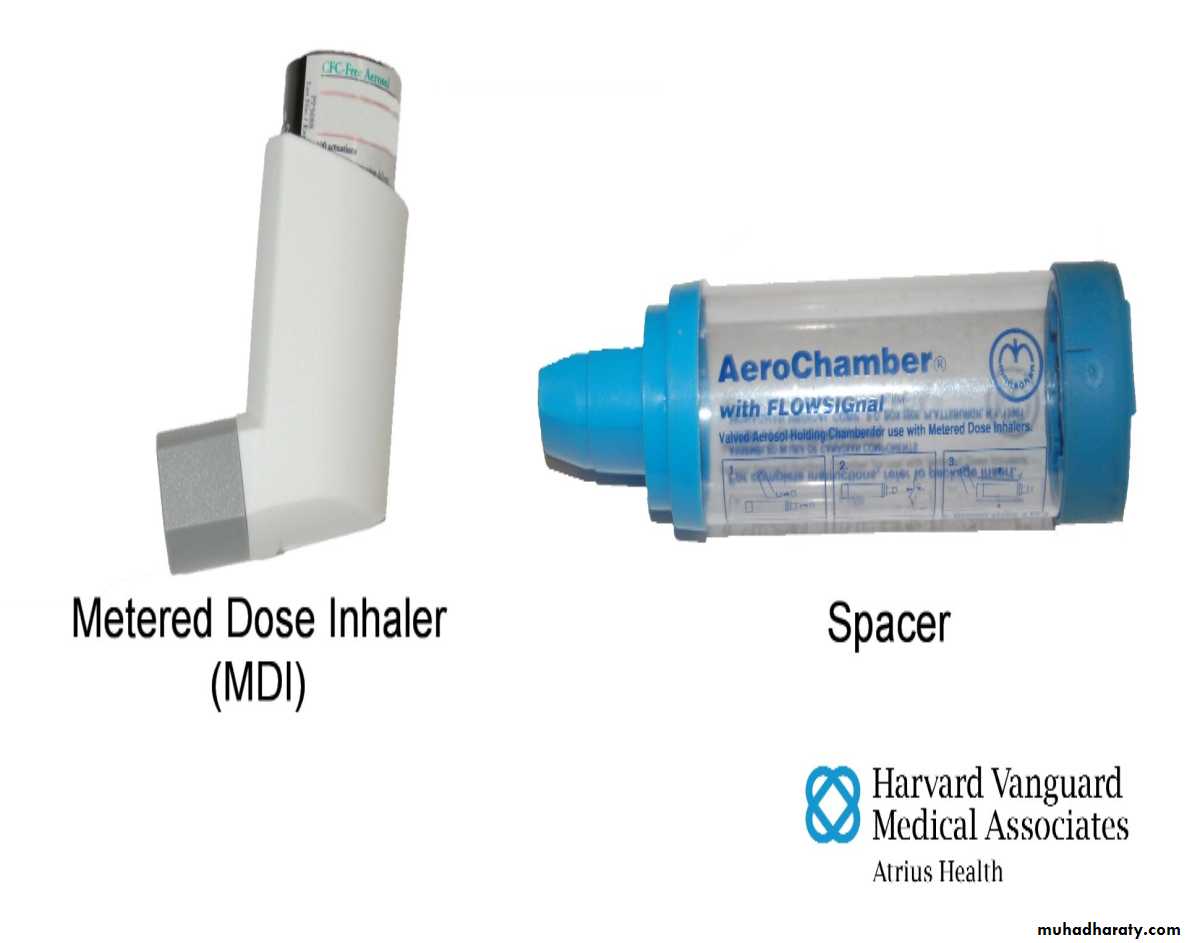
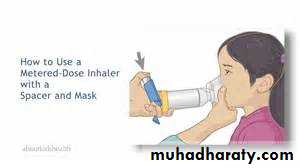
Metered – dose inhaler
A device that delivers
A device that delivers a measured amount of medication as a mist that patient can inhale
It consists of a pressurized canister of medications in a case with a mouthpiece , they are portable, efficient and convenient
75
Metered – dose inhaler
76
Metered – dose inhaler
77
Metered – dose inhaler
78
Gel
A colloid in which the solid disperse phase forms a network in combination with fluid continuous phase ,resulting in a viscous semi rigid solution
It is thicker than solution, often a semisolid emulsion in an alcohol base tend to be drying
There is high risk of hypersensitivity ,it is useful for the scalp and body folds ,but fissures and erosions should be avoided because of drying and stinging of alcohol base
79
80
81
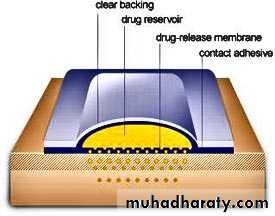
Patch
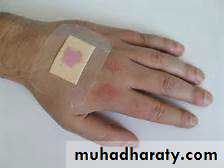
A very precise time release method of delivering a drugCutting a path can affect the dose delivered
The release of the active component from a transdermal delivery systems can be controlled by diffusion through the adhesive which covers the whole patch by diffusion through a membrane
There is also transmucosal patch like fentanyl patch , lidocaine patch
82
Transdermal patch
83
The administration of drug by transmucosal routes offers the advantage of being a relatively painless administration and has the potential for greater flexibility in a variety of clinical situations.
The transmucosal route includes oral, nasal, vaginal, and urethral and presents a challenge in the field of novel drug delivery technology.
84
The oral transmucosal delivery, especially the buccal and sublingual routes have been explored successfully for a number of drugs in the last few decades with novel approaches emerging continuously.
The transmucosal membranes are relatively permeable, have a rich blood flow and hence allow the rapid uptake of a drug into systemic circulation to avoid first pass metabolism.
This route of drug delivery offers a number of benefits over other drug delivery approaches and allows drugs to circumvent some of the body’s natural defense mechanisms like first pass metabolism,
85
86
87