بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
PRURITUS
د. رزانObjectives:1. to define pruritus.2. to classify its causes.
PRURITUS
Definition:PRURITUS : Itching= Unpleasant sensation that provokes the desire for scratching.
Scratching: Is the action taken in response to itching.
Itching= sensation.
Scratching=action.
P. is the commonest dermatologic complaint.
It is not a diagnosis.P. is a symptom that may be caused by many conditions.
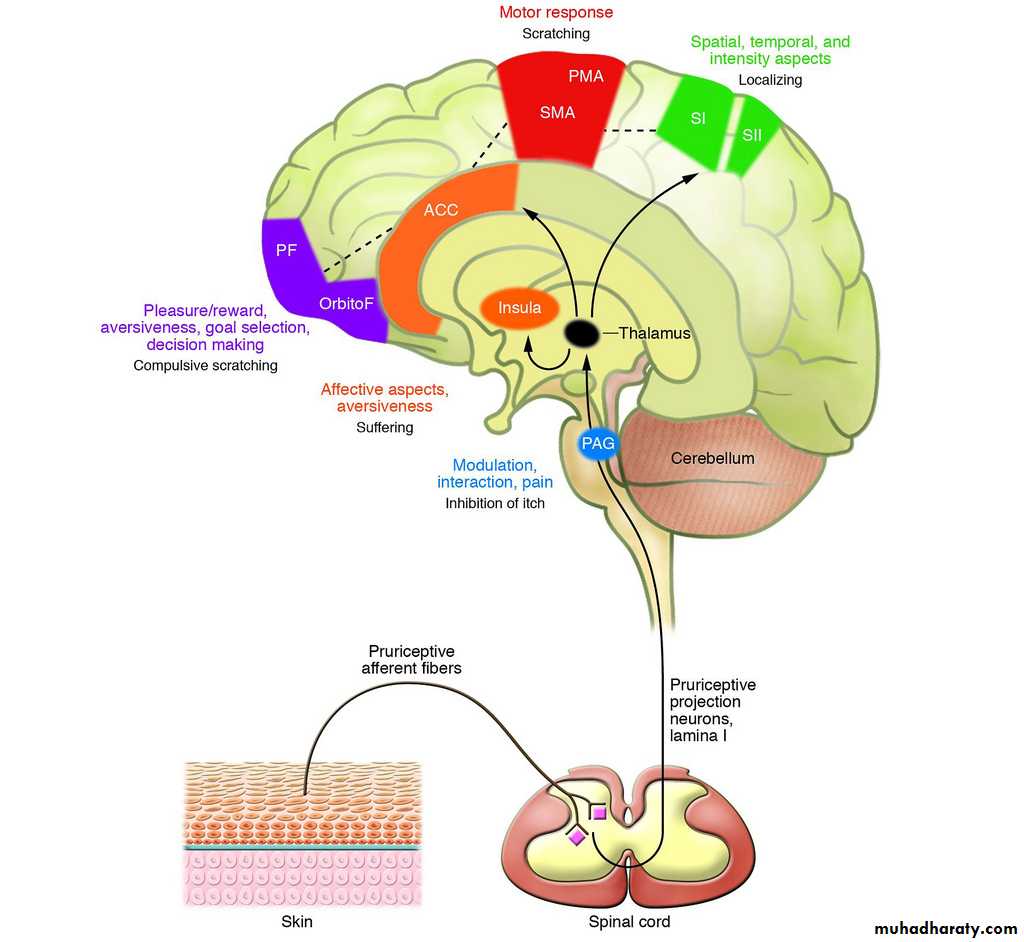
Itch pathway
Mediatedors: mainly ;histamine from mast cell.
other mediatedors: vasoactive chemicals like serotonin, bradykinin.
Itch nerve ending are lie very close to dermo-epidermal junction.
Itching sensation is transmitted via C fibers(slow conduction speed) through spino-thalamic tract to the thalamus & on to a cortical representation
How to analyze itching?
• Site• Duration
• Onset
• Diurnal variation.
• Severity.
• Precipitating factors.
• Aggravating factors.
• Alleviating factors.
• Associated features.
*Classification:
Generalized Pruritus:-
Acute Generalized pruritus:• Wide spread urticaria.
• Scabies.
• Acute allergic contact dermatitis.
• Drug eruption.
• Pediculosis corporis.
• Acute erupted lichen planus.
A) Pure cutaneous causes of chronich generalized itching;
• Atopic dermatitis.• Seborhoic dermatitis.
• Senile pruritus.
• Dry skin.
• Dermatitis herpitiformis.
• Cutaneous T cell lymphoma(Mycosis fungoides).
B) Systemic causes:
• Neuro-psychogenic pruritus.• Endocrine disease;
• a-Hyper thyroidism & Hypothyroidism;
• b-D.M.
• c-Pregnancy; (Obstetric Cholestasis.).
• Liver disease;a- Cholestatic jaundice; b-Primary Biliary Cirrhosis.c-Chronic active hepatitis(HBV & HCV).
• Renal disease;-Chronic renal failure;
• Blood disease;a-Polycythaemia rubra vera.
b-Iron deficiency anaemia; c-Leukaemia; lymphoma, Myeloma.
6. Malignancy;
a-Hodgkin's disease;
b-Carcinoma; Ca. breast, bronchus, stomach & pancreas.
7. HIV .
Localized chronic itching:
• Lichen planus.
• Chronic contact dermatitis.
• Nurodermatitis
• Pomphylax
• Discoid eczema
• Varicose dermatitis.
• Asteatotic eczema.
• Lichen sclerosus it atrophicus.
• Paget disease.
Localized –acute itching:
• Insect bite• Acute contact dermatitis.
• Photodermatitis
• Fixed drug eruption.
• Pediculosis pubis& capitis.
• Worm infestation (Oxyuriasis).
Diagnosis:
Mainly clinicalSimple Investigations.
Sophisticated Investigations.
According to the suspected cause.
Treatment:
A-General measures:
• Reassure.
• Explain the condition.
• Treat the primary underlying cause.
• Avoid aggravating factors(scratching).
• Gentle skin care.
B-Topical measures:
• Topical Emollients agent on skin.• Topical antihistamine.
• Topical CS (have potent anti-pruritic effect).
• Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus.
• Other therapies to decrease itching include:
• Topical menthol 1%, camphor.
C-Systemic therapies
Systemic H1 blocking anti histamines (either sedative or not).-Systemic CS (short course small dose).
D-Others:
Phototherapy: UVB & PUVA.