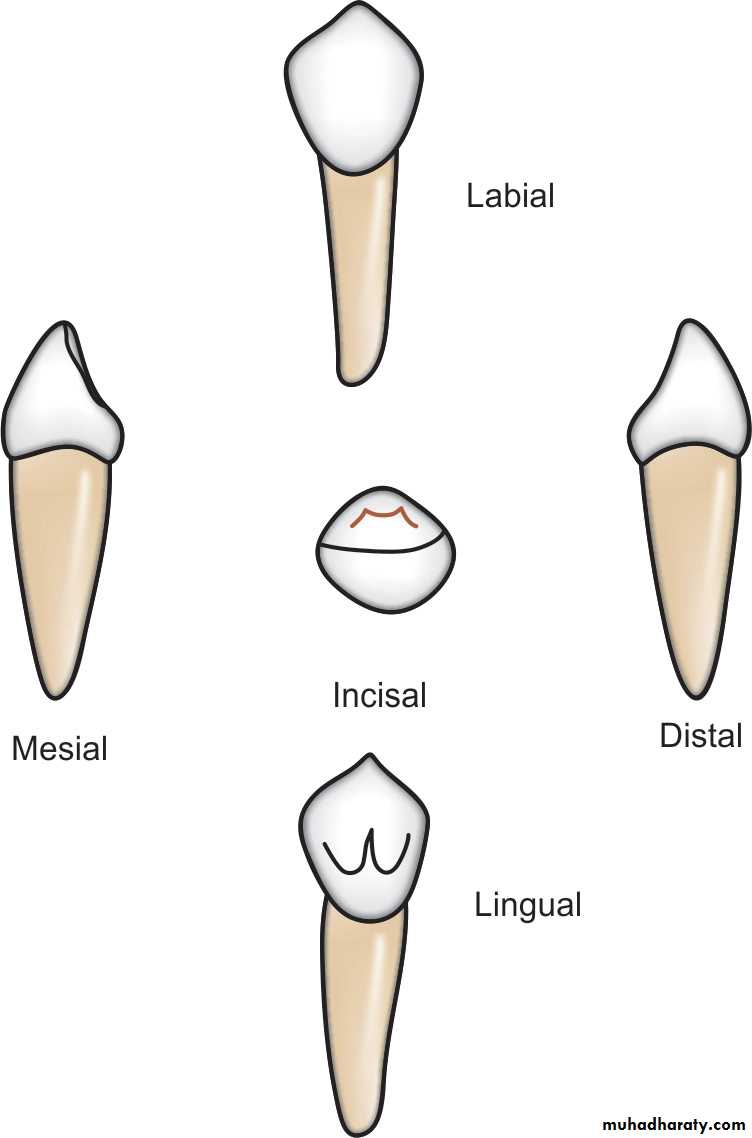
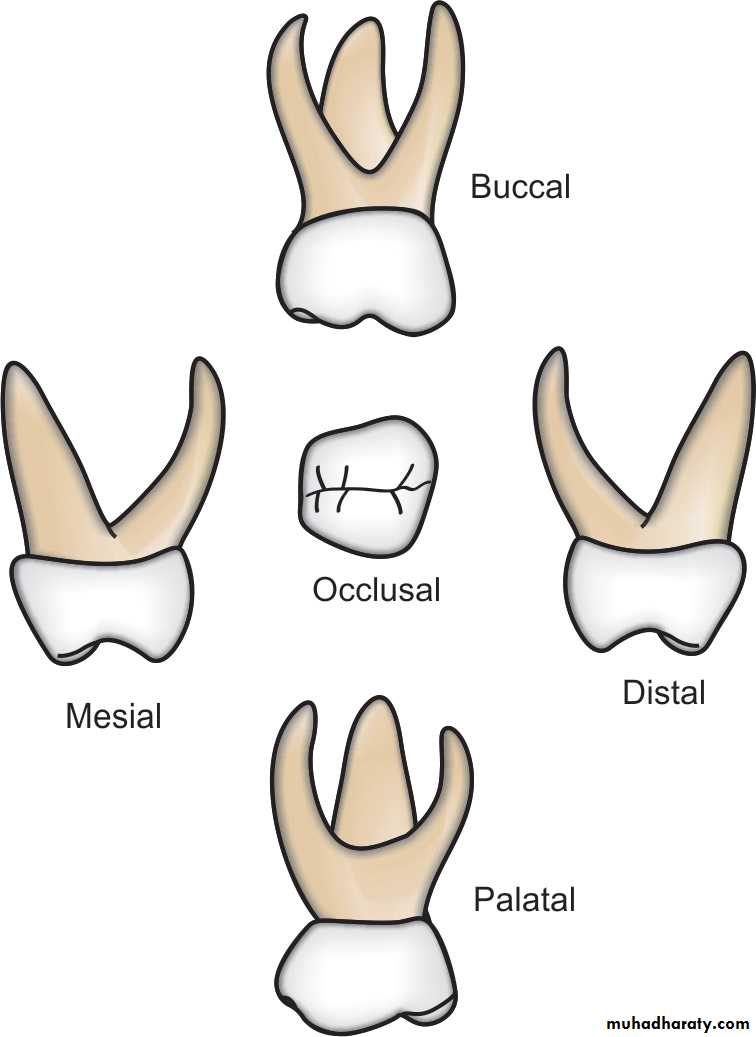
MORPHOLOGY OF INDIVIDUAL
DECIDUOUS TEETH• The morphology of the crown of each primary tooth
• The numbers and shape of the root of the primary teeth• Differences in morphology between primary and permanent teeth
objectives
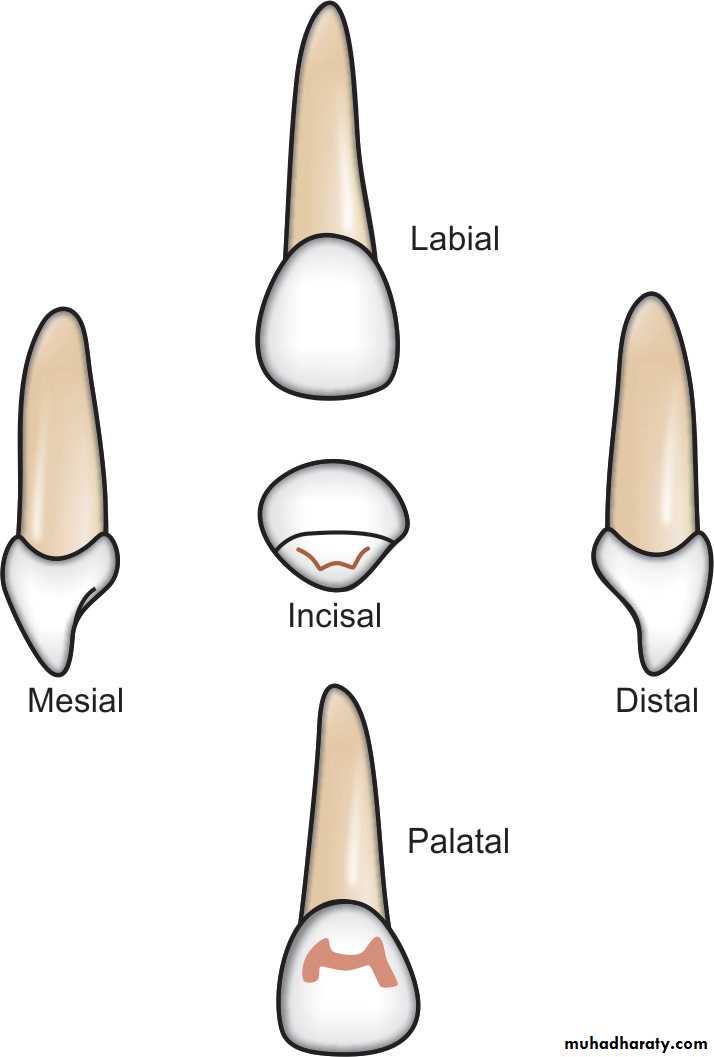
The deciduous maxillary central incisor
is unique in that it is the only tooth in the human dentition that has a greater mesiodistal dimension than crown height.The contact points with adjacent teeth are broad,
extending from the incisal one-third to the gingivalone-third.
Labial surface is flat.
There is a prominent lingual cingulum.The root is conical and roughly 2.5 times as long as the crown height.
The maxillary lateral incisor is smaller than the maxillary
central incisor.The root is more conical.
Maxillary lateral incisors
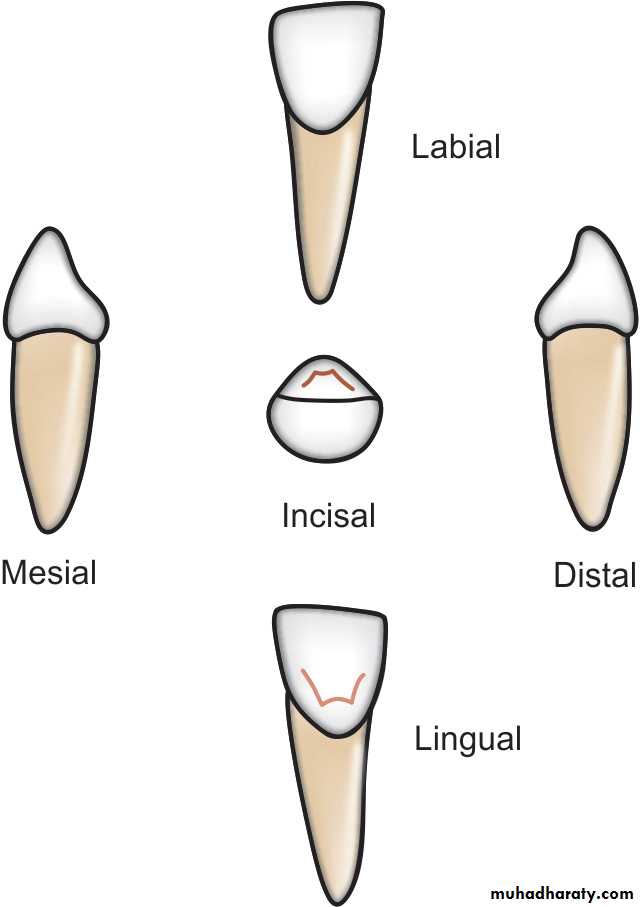
Mandibular central Incisors
• • is almost flat when• viewed from the labial aspect.
The crown is one-third the length of the root with a cingulum on the lingual surface.
by the distoincisal angle, which is more rounded.
In overall dimensions, theprimary lateral incisor is
somewhat
longer but narrower than the primary central incisor.
The primary mandibular lateral incisor is distinguished from the mandibular central incisor
L
C
M
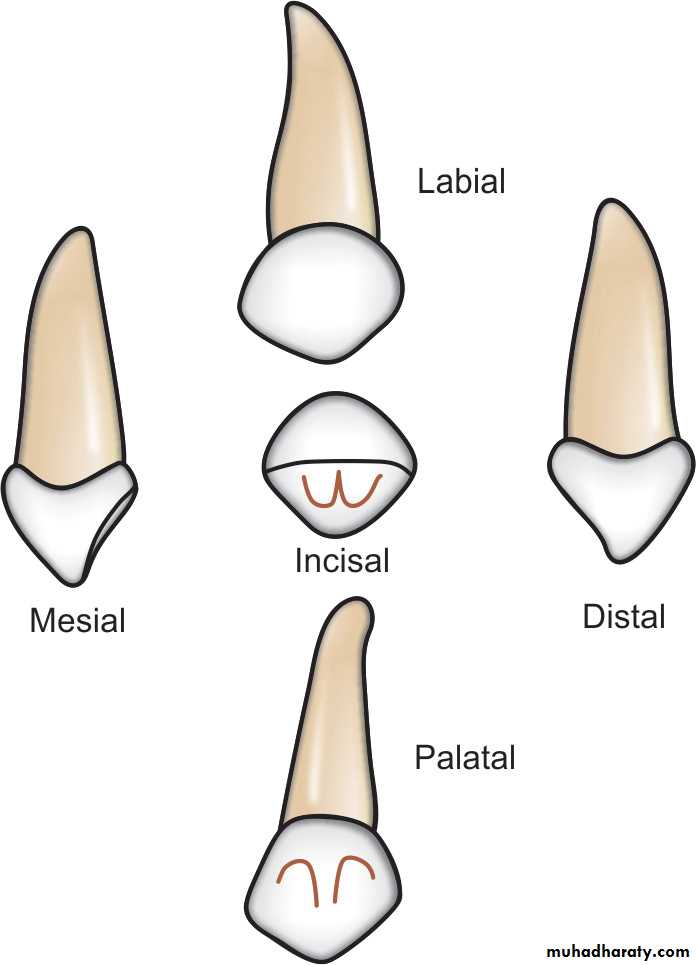
Maxillary Canines
1. long and sharp.
2. The crown is constricted at the cemento-enamel junction (CEJ)
there is often
a prominentcingulum.
ROOT:
long slender is more than twice the crown length.
Mandibular Canines
• The mandibular canines• It is a long narrow tooth, much smaller than the primary maxillary canine.
• The distal marginal ridge is much lower than the mesial marginal ridge.
The point of contact is very close to the cervical third of the tooth.
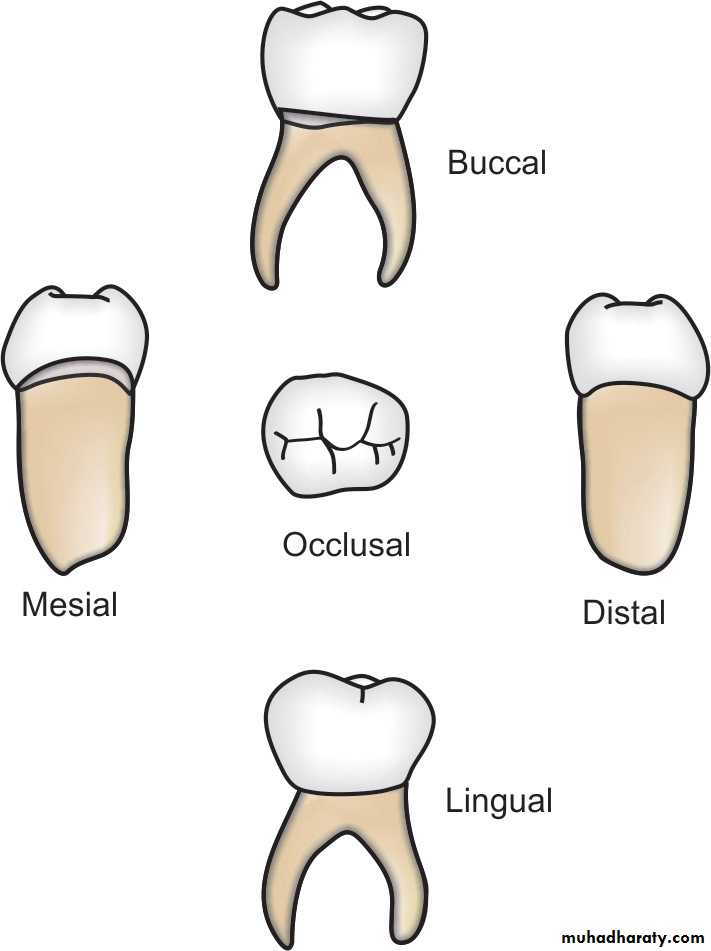
The root is long and slender and is about twice the crown length.Maxillary First Molars
• The primary maxillary first molar resembles a molarand a premolar
The occlusal surface consists of four cusps, mesiobuccal and distobuccal cusps
and mesiolingual and small distolingual on the lingual surface.This gives the tooth a square look.
• There are three slender roots,
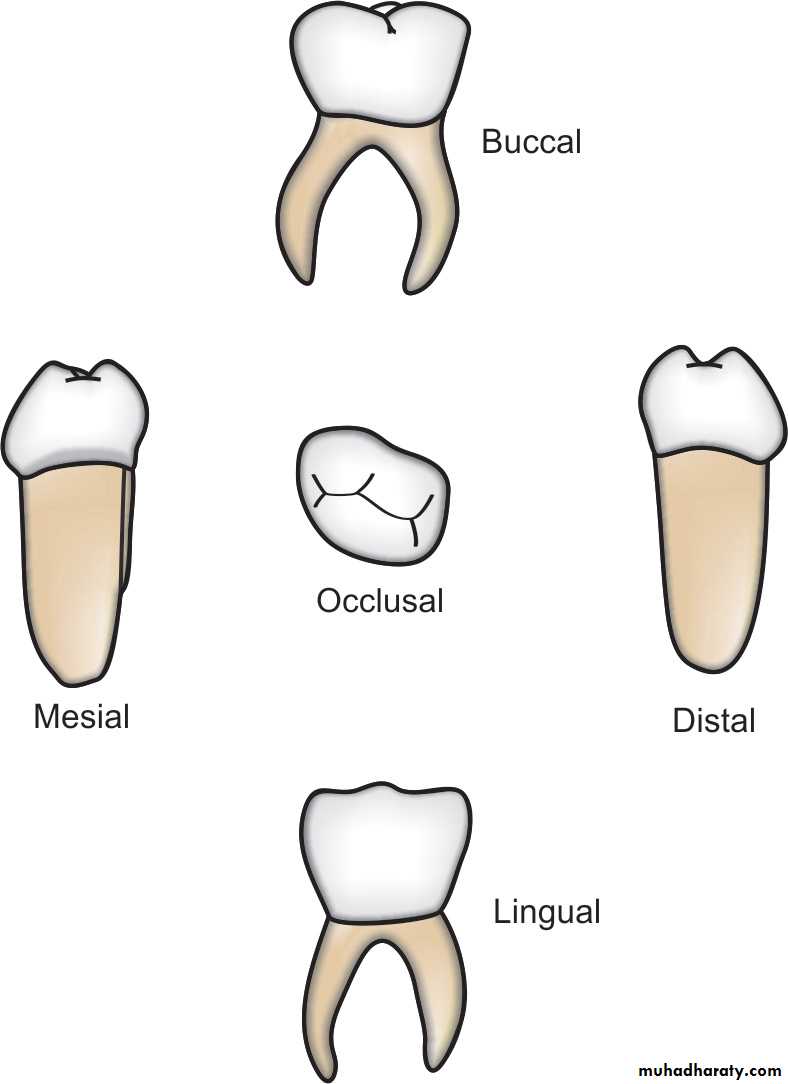
Mandibular First Molars
It has four cusps, two buccal and two lingual.The occlusal surface is narrow due to the convergence of the mesiobuccal and mesiolingual cusps.
• Transverse ridge is very prominent and divides the occlusal surface
• The enamel of this tooth is uniformly thick.• There are two broad but thin mesial and distal roots,
one on the mesial aspect and one on the distal aspect.
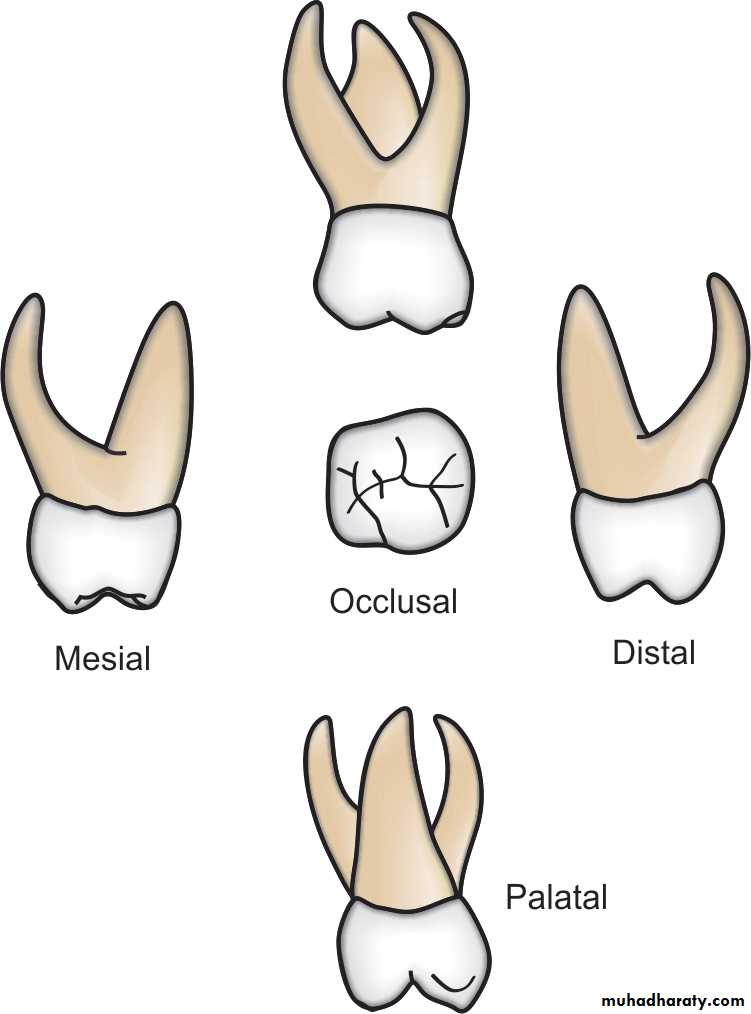
Maxillary Second Molars
The primary second molars are the last primary teeth to erupt.The primary maxillary second molar resembles the permanent maxillary first molar in appearance but is smaller.
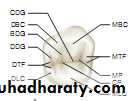
BDG, Buccal developmental groove; CDG, central developmental groove; CP, central pit;
DBC, distobuccal cusp; DBDG, distobuccal developmental groove; DC, distal cusp; DDG, distal developmental groove; DLC, distolingual cusp;DP, distal pit; FC, fifth cusp; LDG, lingual developmental groove;
MBC, mesio-buccal cusp; MBDG, mesiobuccal developmental groove; MLC, mesiolingual cusp; MP, mesial pit; MTF, mesial triangular fossa; OR, oblique ridge.
There are four cusps, two on the buccal and two on the lingual aspects. The largest one is the mesiopalatal.
• Often there is a fifth cusp prominence, called as the tubercle of Carabelli on the palatal surface of the mesiopalatal cusp
A prominent transverse or oblique ridge connects the
Disto-buccal cusp with the mesiopalatal cusp.
There are three roots
The enamel is usually 1.2 mm thick uniformly on the tooth.Mandibular Second Molars
The primary mandibular second molar resembles apermanent mandibular first molar.
• There are five cusps, three on the buccal surface and
two on the lingual.
• The enamel is uniformly 1.2 mm thick.
There are two roots which are narrow mesiodistally
but very broad buccolingually.
A characteristic of all primary molars is
that1. the furcation of the roots begins at the CEJ.
This is not apparent in permanent molars.
2. There is a very prominent buccal cervical ridge.
3. The roots are diverged and curved to accommodate the developing permanent tooth bud beneathMorphological differences between permanent and Deciduous Teeth
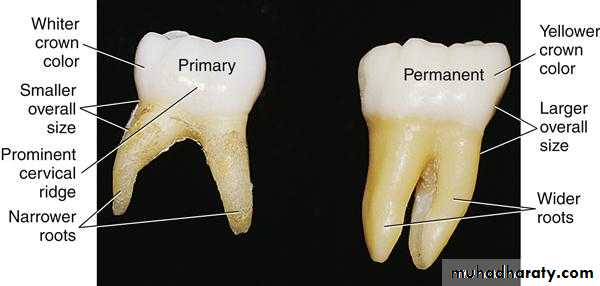
Dr. Bushra Rashid Noman1. The crown of
the deciduoustooth is shorter
than the
permanent
tooth.
Features of a Deciduous Crown
• 2. The occlusal
• table of a• deciduous tooth
• is narrower
• Labiolingually
• than is the
• permanent tooth.
3. The deciduous tooth
is constricted inthe cervical
portion of the
crown.
4. The enamel
and dentinlayers are
thinner in the
deciduous tooth.
5. The enamel rods in the gingival third extend in a slightly
occlusal direction
from the dentinoenamel
junction in deciduous
teeth but extend slightly
apically in the permanent
dentition.