Indices for Root surface caries
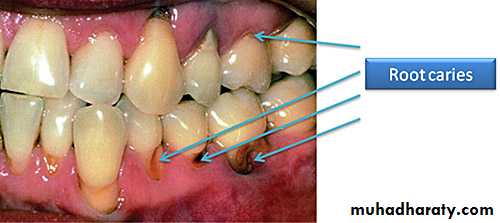
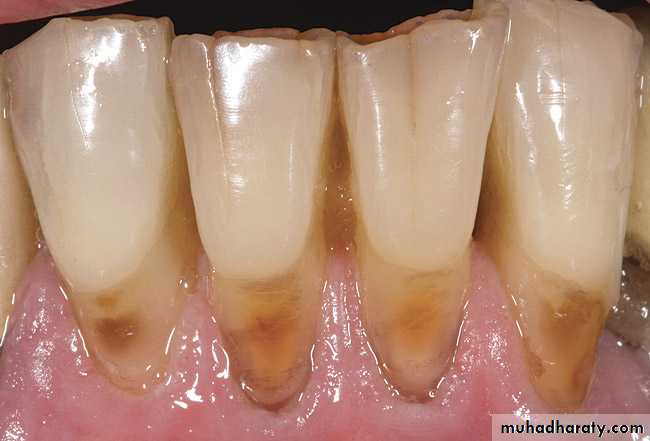
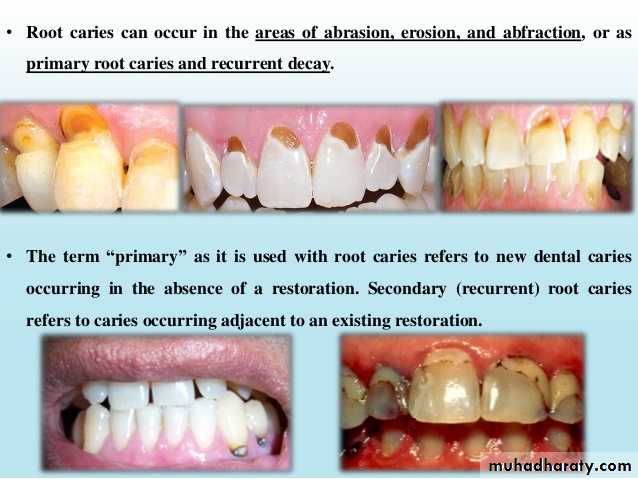
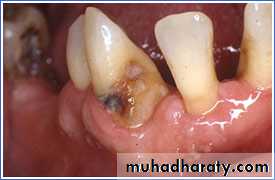
Root caries is a common problem among the elderly. Root caries, by definition, occurs on the root of the tooth. It is initiated on a root surface exposed to the oral environment.
Root caries can be defined as a soft irregularly shaped lesion either totally confined to the root surface or involved the enamel at the cemento- enamel junction but clinically indicating that the lesion is initiated on the root surface.
The most commonly used clinical signs to describe root caries utilized visual (color, contour, surface cavitation) ,
and tactile (surface texture) specifications. There are no reported clinical symptoms of root caries although pain may be present in advanced lesions.
The criteria for diagnosis of root caries:
Banting et al (1980) identified root caries as:1. A discrete well defined and discolored soft area.
2. An explorer enters easily and displays some resistance.
3. the lesion is located either in the cemento-enamel - junction or wholly on the root.
Risk factors for Root surface caries(RSC)
Intra- Oral Factors:Diminished salivary flow.
Diminished salivary buffer capacity.
High plaque score.
Periodontal pocketing.
Sever attachment loss.
Gingival recession.
Calculus.
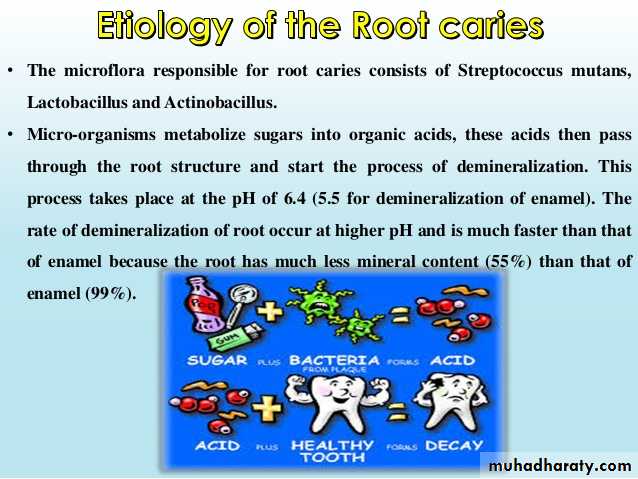
Elevated salivary S. mutans.
Elevated salivary Lactobacillus counts.
Elevated salivary Candida albicans counts.
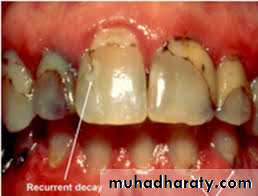
Unrestored and restored coronal caries.Unrestored and restored root caries.
Over denture abutments.
Retained root tips.
Eight or more missing teeth.
Reduced masticatory ability.
Removable partial denture.
Clenching, grinding, compressive and disclusive forces.
Extra- oral factors:
Advanced age.Infrequent use dental services.
Lower educational level.
Gender .
Race.
Smoking.
Physical debility.
Lack of a social support network.
Use of medications that decrease salivary flow.
Limited exposure to fluoridated water.
Frequent ingestion of sucrose containing food.
Limited ingestion of milk product (particularly cheese).
The root caries index (RCI) was developed by Ralph V Katz in 1979 intended to make the simple prevalence measures for root caries more specific by including the concept of teeth at risk for root caries . The RCI is specifically designed for analytical epidemiological studies in which risk factors and causes of disease are being studied ; it is also appropriate for basic descriptive epidemiology.
A tooth was considered “ at risk ” if enough gingival recession had occurred to expose part of the cemental surface to the oral environment.
Root Caries Index (RCL)
The root caries index was calculated for each subject ( Only root surfaces exposed to the oral environment are at risk ; the data are recorded) as follow:
(R-D)+(R-F)
RCI = -------------------------------- x 100
(R-D)+(R-F)+(R-N)
R-D: recession with decay root surface.
R-F: recession with filled root surface.
R-N: recession with a sound root surface.
Root Caries Index (RCI)
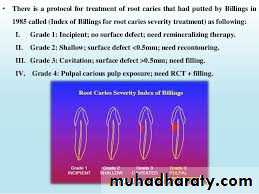
Root surface caries severity IndexBilling et al 1985
According to severity it is classified in to:Grade 1: is characterized by an incipient lesion , the surface texture is soft and irregular and can be penetrated with a dental explorer, there is no surface defect and pigmentation variable light tan to brown.
Root surface caries severity IndexBilling et al 1985
Grade 2: is characterized by a shallow lesion, the surface texture is soft, irregular and rough and can be penetrated with a dental explorer, there is surface defect (less than 0.5 mm in depth) and pigmentation variable from light tan to dark brown.Root surface caries severity IndexBilling et al 1985
Grade3:is characterized by cavitation of the surface texture which is soft and can be penetrated with a dental explorer. There is a penetrating lesion and cavitation is present (greater than 0.5 mm in depth) however there is no pulp involvement, pigmentation is variable ranging from light brown to dark brown.
Root surface caries severity IndexBilling et al 1985
Grade4:is characterized by pulpal involvement, there is a deeply penetrating lesion pulpal or root canal involvement, pigmentation is variable ranging from brown to dark brown.