
PRELEMINARY
MEDICAL, DENTAL
HISTORY AND CLINICAL
EXAMINATION

Before making a diagnosis and developing a
treatment plan,
the dentist must collect and evaluate the
facts associated with the
patient’s or
parents’ chief concern
and any other
identified problems that may be unknown
to the patient or parents.

Some pathological signs may lead to an almost
immediate diagnosis.
For example
, obvious
gingival swelling
and
drainage may be associated with a single,
badly carious primary molar.
Although the
collection and evaluation of these
associated facts are performed rapidly
, they
provide a diagnosis only for a single problem
area.

On the other hand,
a comprehensive
diagnosis
of all of the patient’s problems or
potential problems may sometimes
need to
be postponed until more urgent conditions
are resolved.
For example, a patient with
necrotizing
ulcerative gingivitis
or a
newly fractured
crown
needs immediate treatment, but the
treatment will likely be only palliative
, and
further diagnostic and treatment procedures
will be required later.

1
. Medical and
dental history.
2. Inspection.
3. Palpation.
4. Auscultation
5. Exploration.
6. Radiographs.
.
7. Percussion.
8. Transillumination.
9. Vitality test.
10. Study cast.
11. Laboratory test.
12. Photography

Medical history
It helps to alter or modify the
treatment plan in accordance
to the child’s systemic
condition
.
It’s started from pregnancy

1. during pregnancy
2. during birth
3. during infancy

type and duration of feeding
habits, nutritional disturbances.
Trauma
childhood diseases
History of immunization.

The history briefly includes:
recent
hospitalization or medication
:
Drug
Allergy
: Children normally tend to be
more allergic to
drugs, food items
,
etc. and it suppresses as they grow.

When there is an
acute or
chronic systemic disease or
anomaly:
dentist should
consult the
child’s physician
to learn the
status of the condition, long
range prognosis and the
current drug therapy.

recording the
frequency,
intensity,
duration
of
the
habits
such
as
finger/thumb
sucking,
nail
biting/lip
biting,
tongue
thrusting,
bruxism,
mouth
breathing, etc.

This will help us during
management
of
the
child's behavior
during
the procedure.

Brushing:
Number of times
and
method of brushing
.
History regarding’ brushing the
teeth is very important especially
in
children less than 5 years.

Brush
:
Type of brush and how
often it is changed.
Other oral hygiene aids used like
flossing, rinses
, etc.
Ideal method would be to record a
full diet
history in a week

It is possible to determine
whether an
individual’s growth
is
progressing
normally
or
abnormally by comparing his/hers
height and weight
with the
standard height and weight chart.

History
of
rhinitis,
repeated cold,
adenoidectomy,
and
tonsillectomy
persisting nasal
obstruction
before
undertaking
orthodontic
treatment with
appliance.
should be
carefully
examined for
evidence of

Dentist should be alert to
identify
Potential communicable
infections
conditions that
threaten the health of the
patient and others as well.
Then it is advisable to
postpone nonemergency
dental care.

Infectious diseases in the
family
such
as
tuberculosis
should be
carefully dealt with.

• Patients with
cardiac defects
should be
referred to a
pediatrician.
Antibiotic prophylaxis must be
given prior to any treatment to
minimize
the
risk
of
development
of
subacute
bacterial endocarditis (SABE).

During
anticoagulant therapy,
adjustment
of anticoagulant
dosage may be required.

Extra-oral
examinations
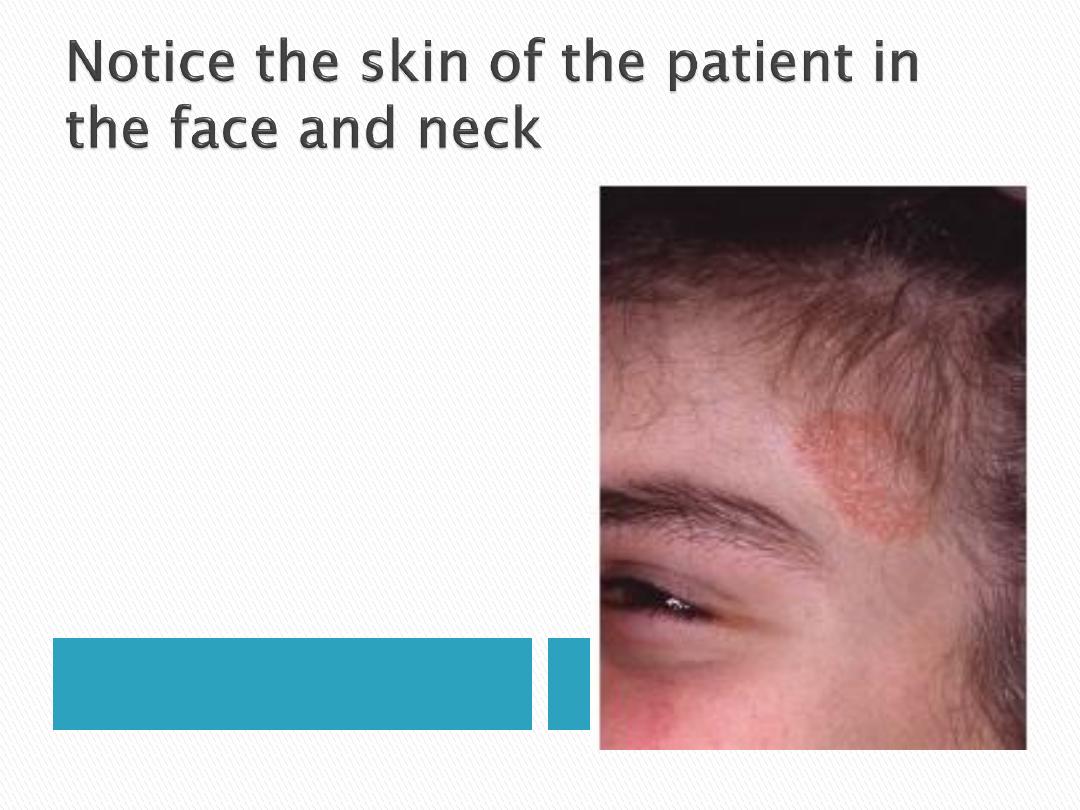
Figure shows a Lesion
on forehead above left
eyebrow is caused by
ringworm infection
.
Several fungal species
may cause the lesions
on various areas of the
body.
The dentist may
identify
lesions on the
head, face, or neck of a
patient during a
routine clinical
examination.
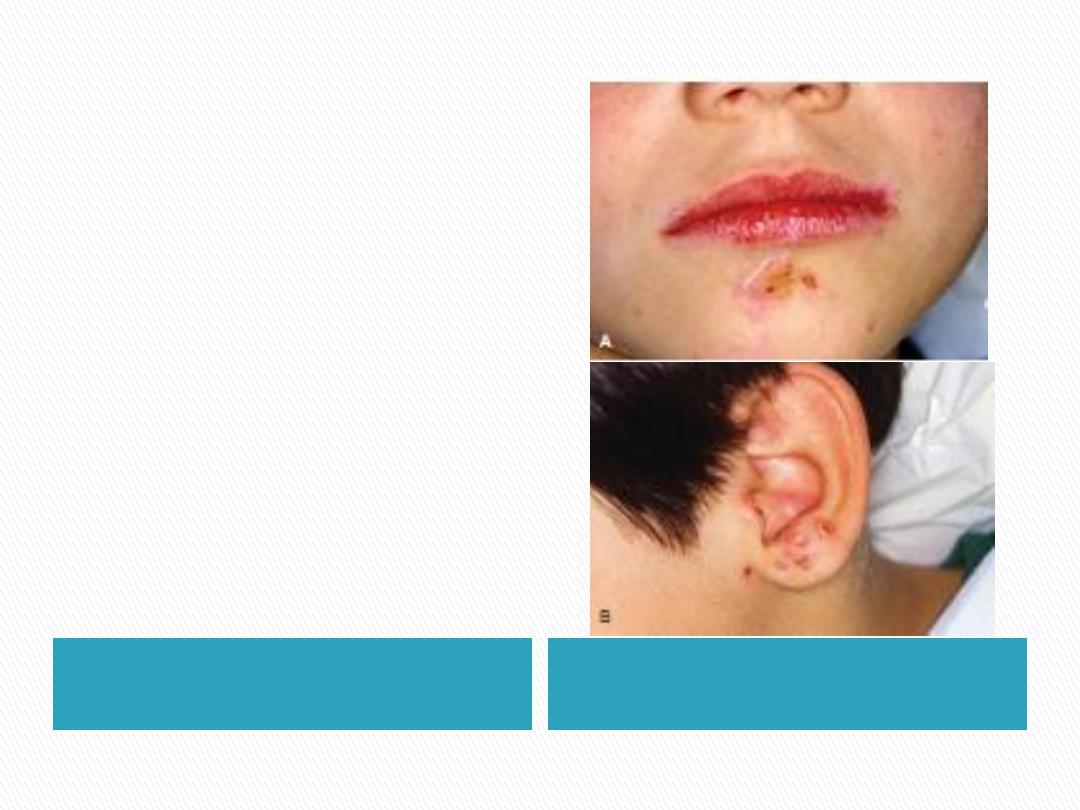
Figure shows: Characteristic
lesions of
impetigo
(A) on the lower face
(B) on the right ear
These lesions occur on
various skin surfaces
, but
the dentist is most likely to
encounter them on upper
body areas.
The infections are of
bacterial (usually
streptococcal)
origin and
generally
require antibiotic
therapy for control.
The child often
spreads
the infection by
scratching
the lesions
.
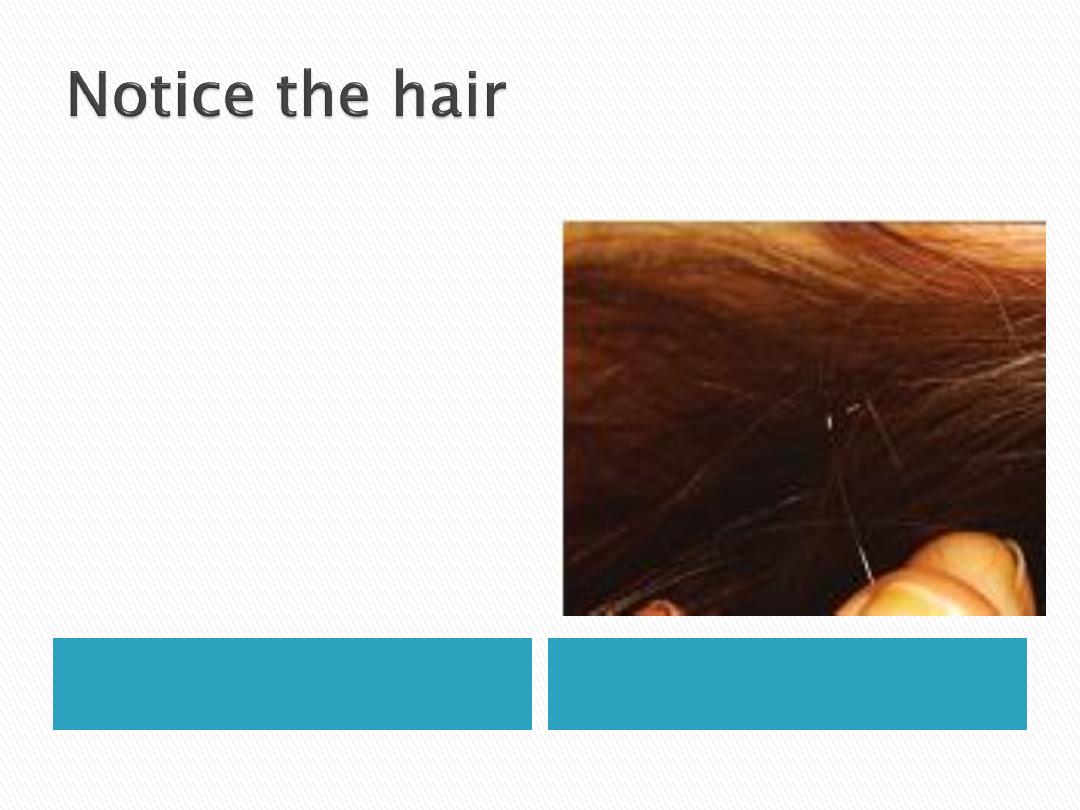
Figure shows:
Evidence of head lice
infestation.
Usually the insects are
not seen, but their
eggs, or nits, cling to
hair filaments until
they hatch.
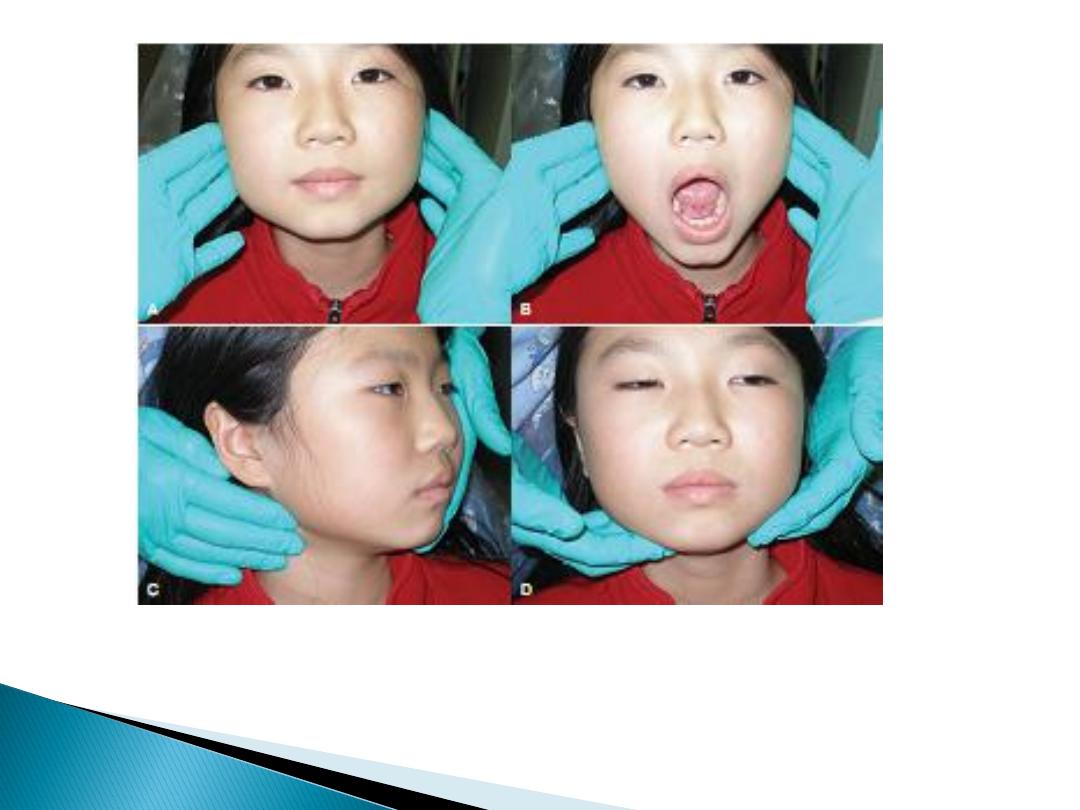
Figure A and B, Observation and palpation of temporomandibular joint
function. C and D, Palpation of the neck and submandibular areas.

Intra-oral
examination
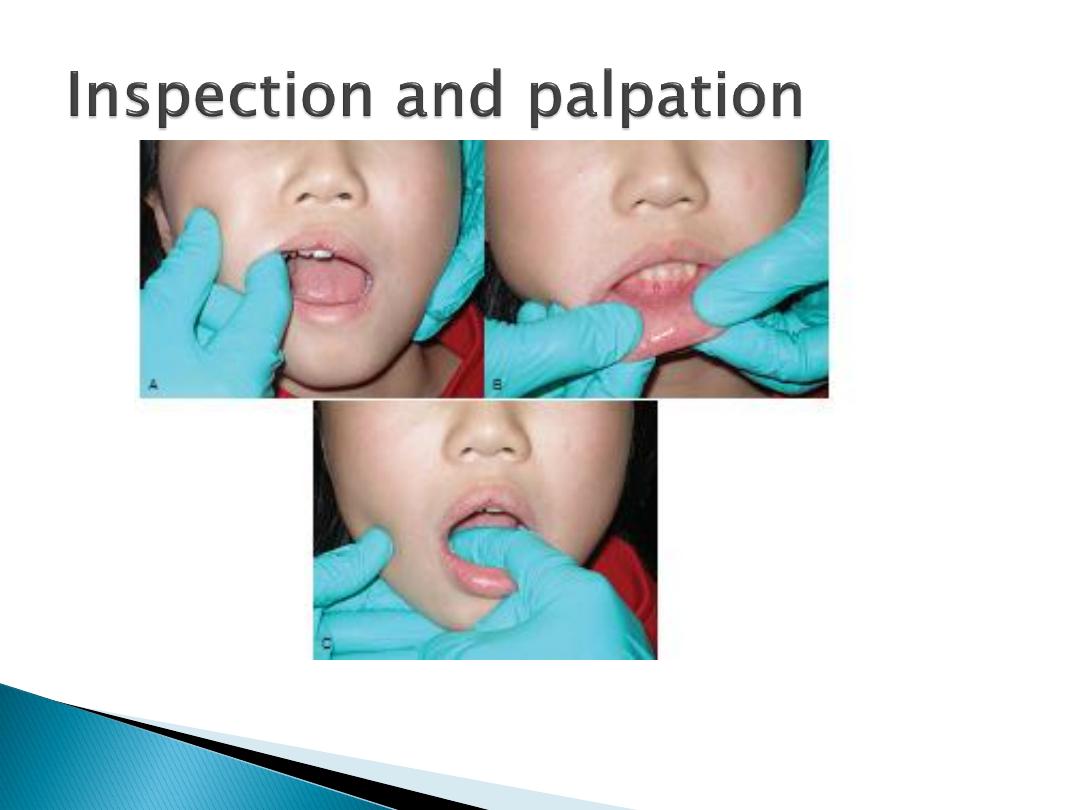
Figure : Inspection and palpation of (A), the buccal tissues (B), the lips
and (C) the floor of the mouth

Examine all the soft tissue including
All oral mucosa
Palate
Floor of the mouth
Cheeks
Tongue
Gingivae around all teeth

All the surfaces of the teeth should be
examined
Record all lesions you can see
Caries
Anomalies
Traumatized teeth
Defective fillings
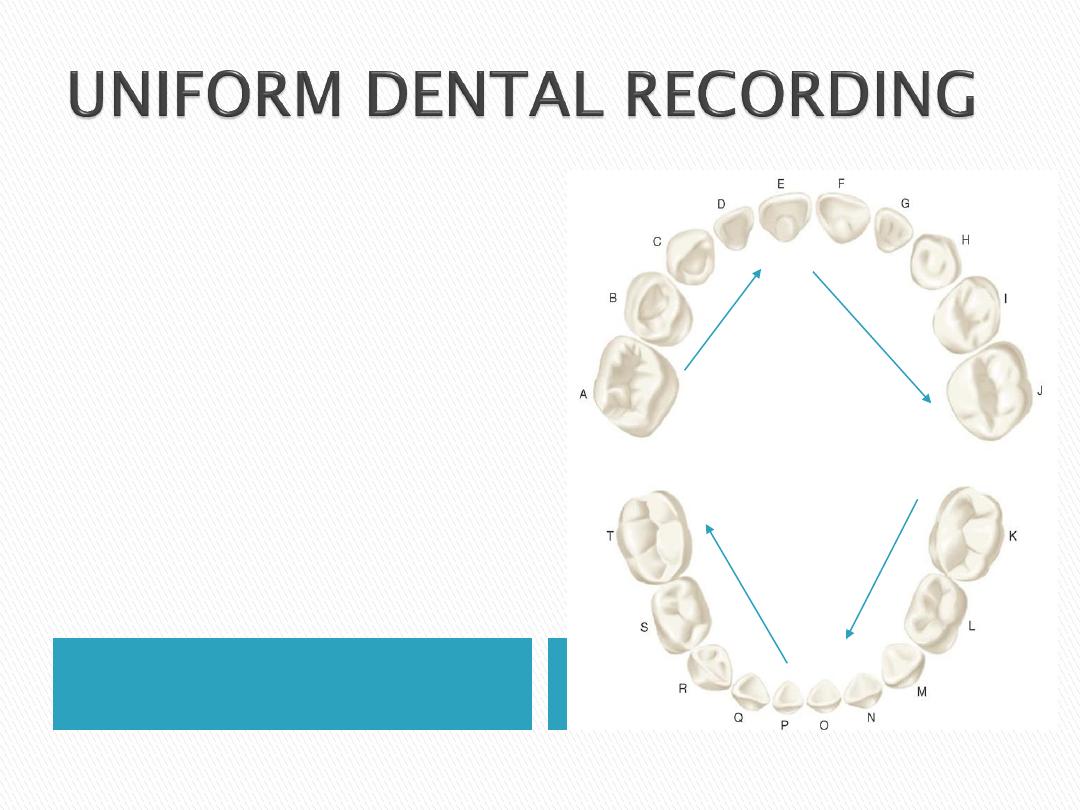
The upper right
quadrant
The upper left
quadrant
The lower left quadrant
The lower right
quadrant

When indicated, radiographic examination
for children must be completed
before the
comprehensive oral health care plan
can be
developed,
(before treatment planning)

trauma,
toothache,
suspected developmental disturbances,
proximal caries.
Deep caries
note: Carious lesions appear smaller on
radiographs than they actually are

dental care for children has been designed
primarily to
1. prevent oral pain and infection,
2. the occurrence and progress of dental
caries,
3. the premature loss of primary teeth,
4. the loss of arch length,
5. prevent the development of an association
between fear and dental care

Dentistry guidelines on infant oral health care
include the following recommendations:
1. All primary health care professionals who
serve mothers and infants should provide
parent/caregiver education
on the etiology
and prevention of early childhood caries
(ECC).

2. The infectious and transmissible
nature of
bacteria that cause ECC.
3. Every infant should receive an
oral health
risk assessment
from his or her primary
health care provider or qualified health care
professional
by 6 months of age
.

4. Parents or caregivers should establish a
dental home care for infants by 12 months of
age
.
5.
Health care professionals and all who
participated
in children’s health should
support the identification of a dental home
for all infants at 12 months of age.

Thus it is appropriate for a dentist to
perform an
oral examination for an
infant of any age, even a newborn
,
and an examination is recommended
anytime
the parent or physician calls
with questions concerning the
appearance of an infant’s oral tissues.
Even when there are no complain

It is not always necessary to conduct the infant
oral examination in the dental operatory, but it
should take place where there is adequate
light for a visual examination.
The dentist may find it convenient to conduct
the examination
in the private consultation
room
during the initial meeting with the child
and the parents.
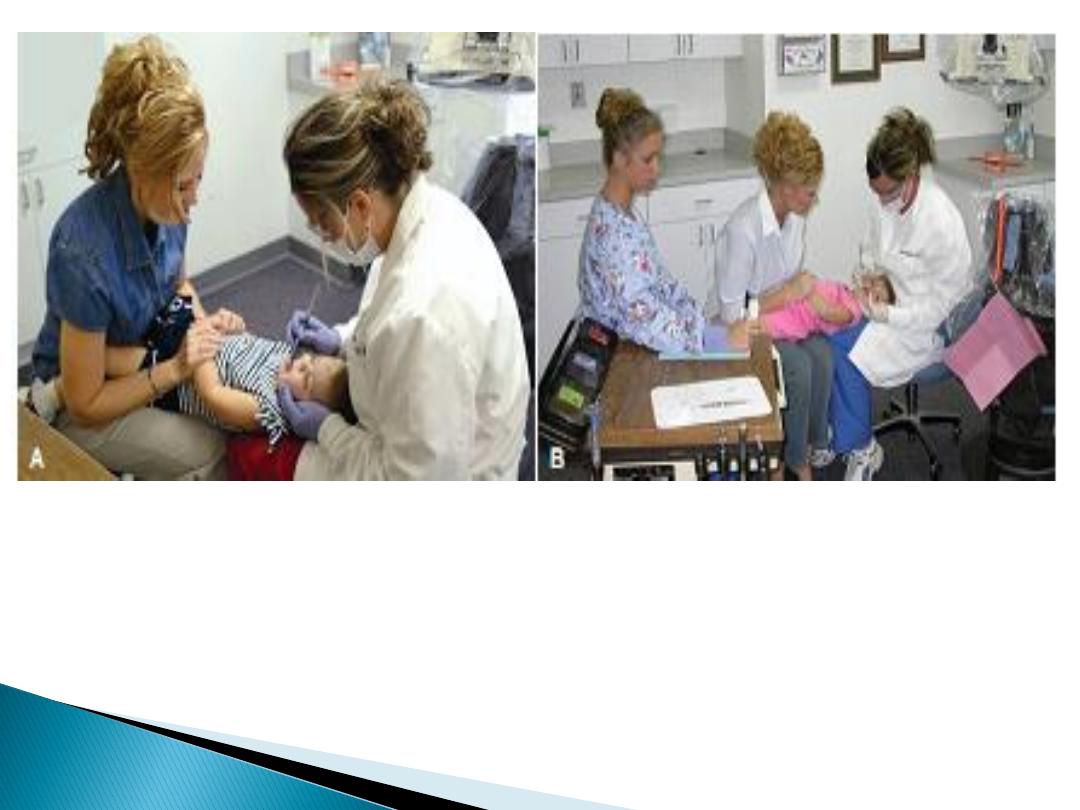
Figure A, One method of positioning a child for an oral examination in a
small, private consultation area. The dental assistant is nearby to record
findings
B, If space allows three people to sit in a row, this method may be used to
make it easier for the dental assistant to hear the findings dictated by the
dentist. The dental assistant also helps restrain the child’s legs.

too often a patient’s initial dental appointment is
prompted by an emergency situation.
the emergency appointment tends to focus on
and resolve
a single problem or a single set of related
problems
Once the emergency problem is under control,
the dentist should offer comprehensive services
to the patient or parents.
