د.منى زهير
Lec.3Third, fourth to eighth week of development (or the embryonic period)
During this period:
Each of the three germ layers gives rise to a number of specific tissues and organs.
By the end of this period the main organ systems have been established.
Therefore, this period is also called period of organogenesis, and it is the most critical period of development because any developmental disturbance during this period gives rise to many congenital malformations .
Derivatives of Ectodermal Germ layer :
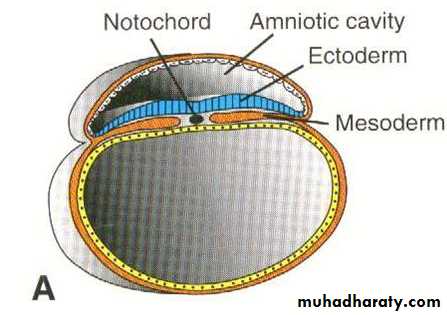
This layer gives rise to those structures and organs that maintain contact with the outside :Central nervous system (CNS). ( CNS comes from the neural tube which is an inward invagination of ectoderm overlying the notochord)
Peripheral nervous system.
Subcutaneous glands, mammary, and pituitary glands.
Sensory epithelium of ear , nose and eye.
Epidermis including the hair and nails.
Enamel of teeth.
Mucous membrane of the mouth , nasal cavity , para nasal sinuses and lower part of the anal canal.
Medulla of adrenals.
Derivatives of mesodermal germ layer :
The mesoderm on each side of the midline form a thickened plate called paraxial mesoderm, more laterally the mesoderm remains thin and is known as the lateral plate. The region between the paraxial mesoderm and the lateral plate is called the intermediate mesoderm. By the end of the 3rd week the paraxial mesoderm breaks up or divides into segmented blocks ( cuboidal bodies ) of tissue , called the somites.
The somites: are a series of mesodermal tissue blocks found on each side of the neural tube. The first pair of somites appear at about the twentieth (20th) day in the cephalic region , then new somites appear in craniocaudal direction , until at the end of the 5th week when about 42-44 pairs are formed.The first and last 5-7 somites disappeared. During this period the age of embryo is expressed in the number of somites .
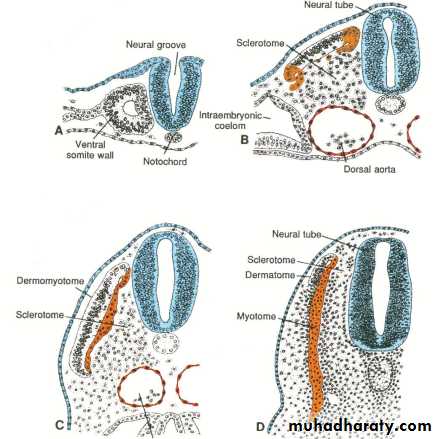
Differentiation of the somite :
The cells forming the ventral and medial walls of somites migrate toward the notochord surrounding it . these cells are called sclerotome, they form loose tissue called mesenchyme that will surround the notochord and spinal cord ( spinal cord known as neural tube ) forming the vertebral column.
The remaining dorsal wall of somites which are called dermomyotome will give rise to the muscles , dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin.
Each somite forms its own sclerotome (bone and cartilage component) and its own myotome (muscle component) and its own dermatome (skin component).
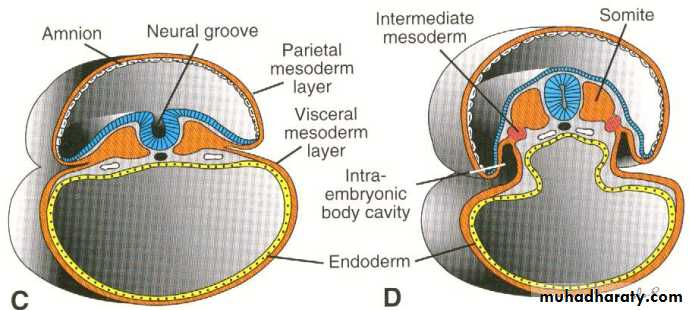
The intermediate mesoderm : will form the excretory units of the urinary system and share in the formation of genital system .
Differentiation of the lateral Plate :
Due to the formation and fusion of the intercellular cavities ,the lateral Plate divided into two layers :
A layer continuous with the mesoderm covering the amnion , known as the somatic or parietal mesoderm.
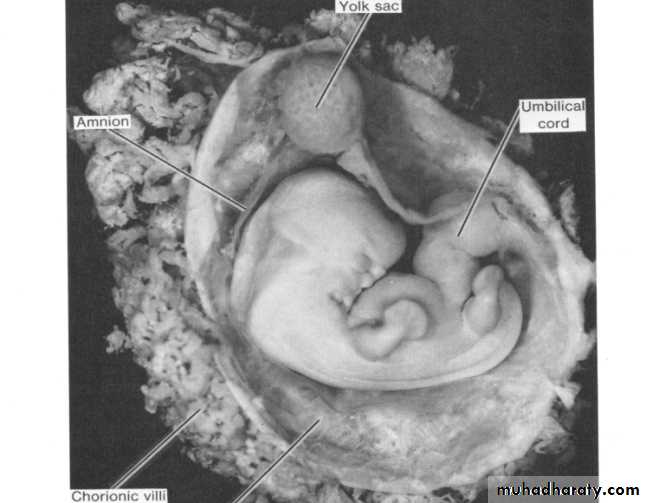
A layer continuous with the mesoderm covering the yolk sac , known as the splanchnic or visceral mesoderm layer.
These two layers will line a newly formed cavity between them called intra embryonic coelomic cavity.
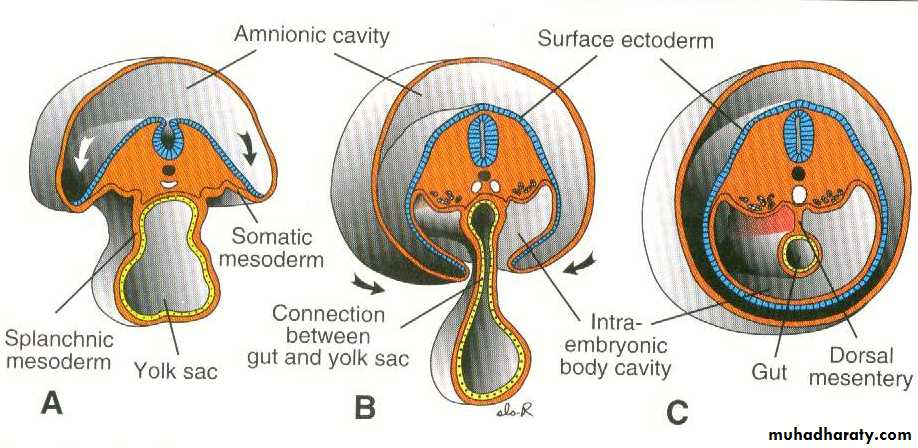
The parietal mesoderm with the overlying ectoderm will form the lateral and ventral body wall ( skin and muscle )
The visceral mesoderm with the embryonic endoderm will form the wall of the gut ( the muscles and epithelial lining ) .
The intra embryonic coelomic cavity will divided into pleural , pericardial and peritoneal cavities , the cells of mesoderm facing these cavities will form a thin membrane called serous or mesothelial membranes.
So the main derivatives of the mesoderm are :
Supporting tissue such as: connective tissue , cartilage and bone.Striated , smooth and cardiac ( so mesoderm layer will form the muscular wall of gut , heart , blood and lymphatic vessels ).
Synovial membrane of joints and serous membrane lining the pericardial , pleural and peritoneal cavities.
Blood and lymphatic cells.
Dermis and subcutaneous tissue of skin.
Gonads and kidneys and their ducts ( except the bladder ).
Spleen.
Cortex of suprarenal gland.
Derivatives of endodermal germ layer :
The (GIT) is the main organ system derived from the endoderm. It is formation depend on the cephalocaudal and lateral folding of the embryo.
The cephalocaudal folding is caused by the rapid longitudinal growth of the CNS.
whereas the lateral folding is produced by the formation of the rapidly growing somites.
As a result of these foldings: the initial wide communication between the embryo and the yolk sac become constricted until only a narrow , long duct is left. this duct is called vitelline duct.
So the endoderm gives rise to the following structures :
Epithelial lining of the GIT.
Epithelial lining of the respiratory tract.
Epithelial lining of urinary bladder and urethra.
Epithelial lining of the eustachian tube and tympanic cavity.
Parenchyma of the tonsil , thyroid , para thyroids , thymus , liver and pancreas.
Period of morphogenesis (shape formation):
External appearance during the second month :
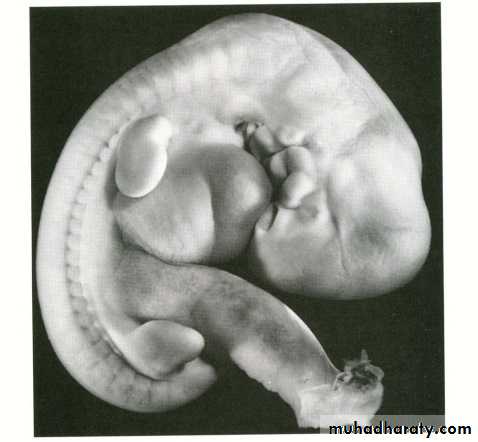
As a result of organ formation and due to craniocaudal and lateral folding, the shape of the embryo changes greatly and the major features of the external body form will be recognized by the end of the 2nd month. so this period is also known as the period of morphogenesis.
By the end of the 4th week when the embryo has about 28 somites the main external features are the somites and pharyngeal arches , and the age of the embryo is expressed in the number of somites.
During the 2nd month , due to craniocaudal and lateral folding the germ disc ( embryo ) bends and become tubular , and there will be the formation of head and tail folds. the age of embryo is indicated as the crown-rump (C.R.) length and expressed in millimeters. the C.R. length is the measurement from the vertex of the skull to the midpoint between the apices of the buttocks (the sitting height).
By the end of the 2nd month the following external appearance of the embryo are formed :
Very large head.
Face , ears , nose and eyes.
Limbs.
The limbs appear as a puddle – shaped buds. (the upper limb appear before the lower) , the distal part of the bud will flatten and becomes separated from the proximal part by a circular constriction . then four radial grooves appear on the distal part of the bud , called rays or hich leads to the formation of digits , then another circular constriction appears in the proximal part , thus leading to the formation of the three main parts of the limb (hand , forearm and arm).