OCULAR ANATOMY
* THE ORBITAL CAVITY* Def. : - pair of large pear-shaped bony sockets.
- contain the eyeballs , extra ocular muscles , nerves , vessels , fat , and most of the Lacrimal apparatus.
* Bones Forming The Orbit : ( 7 Bones )
1. Sphenoid B. 2. Maxillae.
3. Palatine B. 4. Frontal B.
5. Zygomatic B. 6. Ethmoid B.
7. Lacrimal B.
* PARTS :
1- Orbital apex. 2- orbital roof.3- Orbital floor. 4- lateral wall.
5- Medial wall.
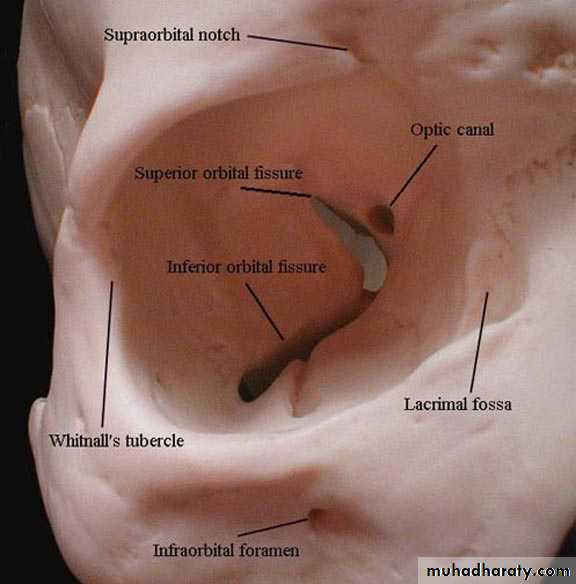
* Main Orbital Openings :
a. Optic canal---- optic nerve, meningies , sympathetic plexus.
b. Superior orbital fissure---lacrimal, frontal, trochlaer,nasociliary, abducent nerves & superior ophthalmic vein.
c. Inferior Orbital Fissure.
d. Foramina .
* RELATIONS :
a. Superior--- meningies , frontal lobe of C.H.
b. Inferior --- maxillary air sinus.
c. lateral --- temporal fossa , temporal lobe of C.H.
d. Medial --- nasal cavity , ethmoidal&sphenoidalsinuses.
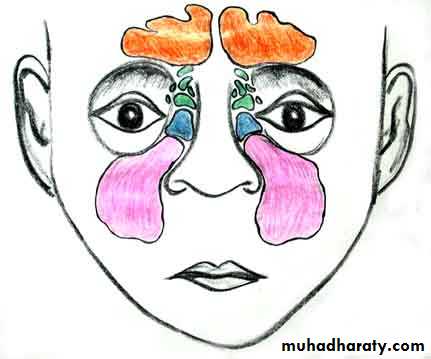
* THE PARANASAL SINUSES :
- Def.---- bony cavities within the interior of the maxilla , sphenoid, frontal , and Ethmoid bones.
- Types :
1. Maxillary S.
2. Frontal S.
3. Sphenoidal S.
4. Ethmoidal S.
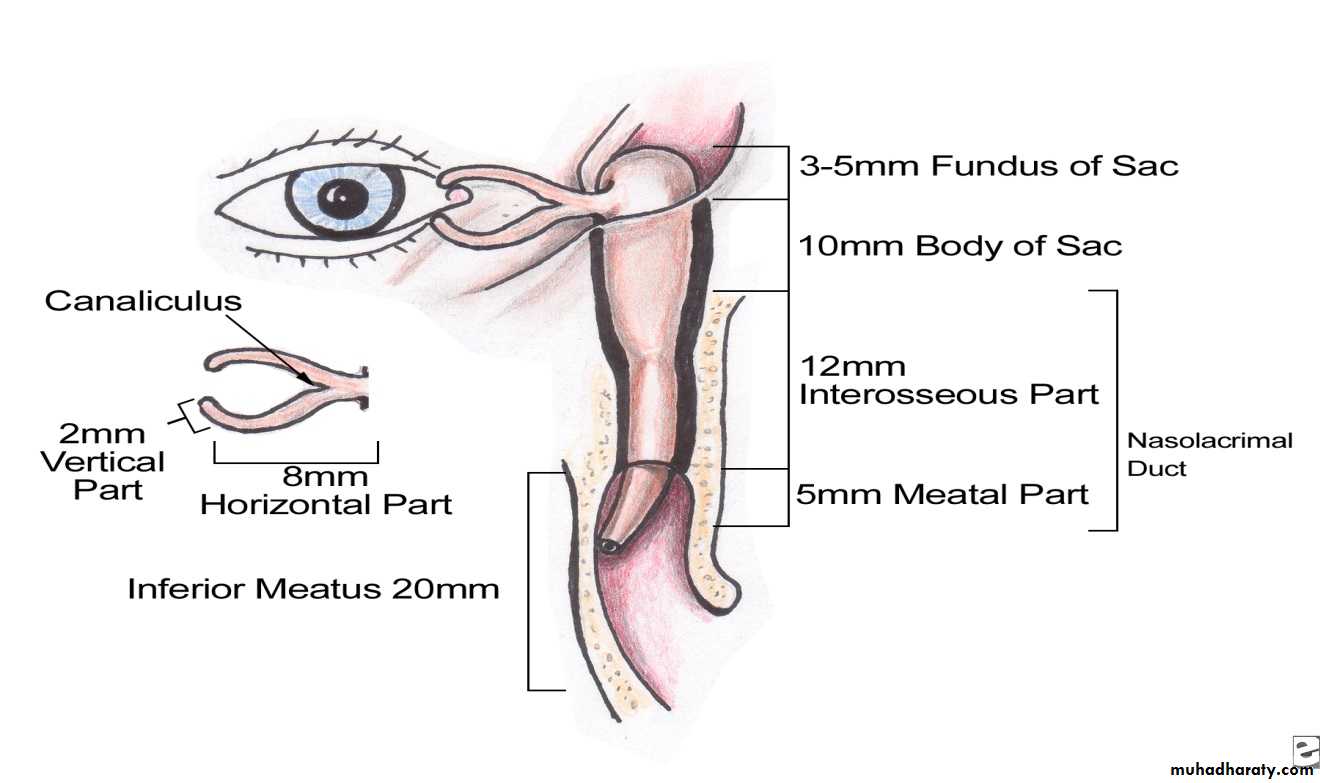
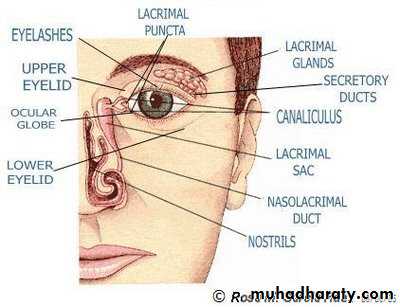
* THE LACRIMAL SYSTEM:
* Def. : - that system which is responsible for tear secretion and excretion.* PARTS:
-A- The secretory portion: main and accessory lacrimal glands.
-B- The collecting portion:
- the puncti. - lacrimal canaliculi.
- lacrimal sac. - nasolacrimal duct.
- inferior nasal meatus--- nasal cavity.
* PRECORNEAL TEAR FILM:
( layers ) (functions )1. outer lipid L. .reduce evaporization.
2. middle aqueous L .antimicrobial.
3. inner mucinous L. .lubrication.
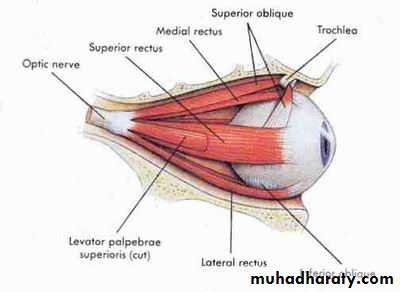
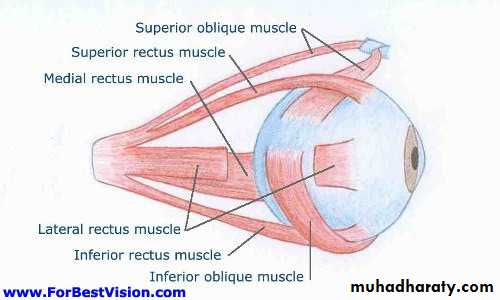
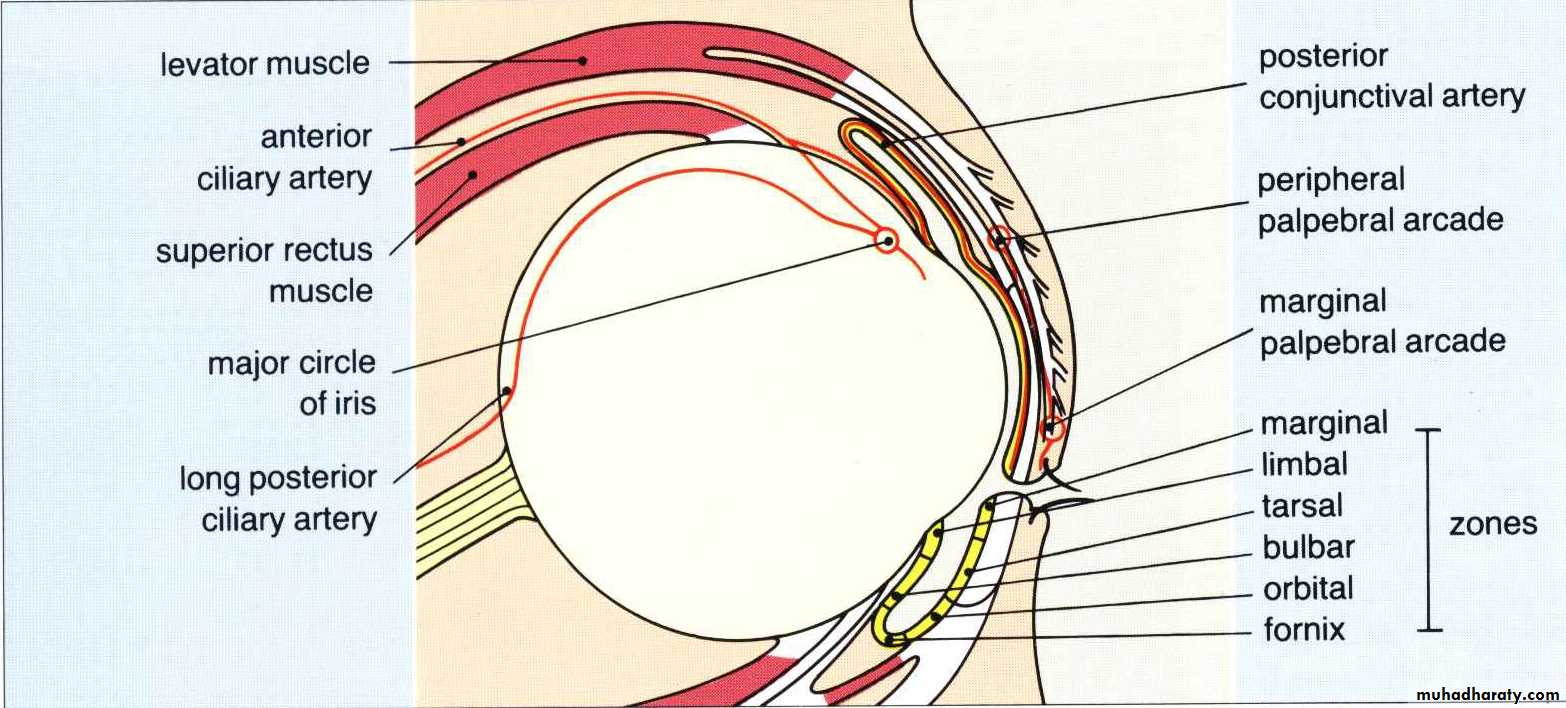
*EXTRA OCULAR MUSCLES:
(A) RECTI MUSCLES :
MUSCLE NERVE SUPLLY ACTION
1. superior rectus oculomotor n.(3) Elevation
2. Inferior r. Oculomotor n. Depression
3. Medial r. Oculomotor n. Adduction
4. Lateral r. Abducent n.(6) Abduction
(B) Oblique Muscles:
1. Superior O. Trochlaer n.(4) Depression
2. Inferior O. Oculomotor n. Elevation
(C) Lid Muscles:
1. Levator P.S. Oculomotor n. Lid elevation
2. Muller muscle sympathetic n. Partial lid elevation
* OCULAR APPENDAGES:
* PARTS :a. Eyebrows. b. Eyelids.
c. Lacrimal apparatus. d. Lacrimal glands.
e. tears f. conjunctiva.
*DEFINITIONS:
- Eyebrows--- transverse skin elevation, studded with hair, located between forehead and upper lid.
- Eyelids --- thin , mobile, skin folds covering the eyeballs.
- canthi --- the area at which both lids meet--- medial and lateral.
- puncti --- small openings at medio-posterior aspect of lids.
-palpebralfissure --- the fissure that formed by the two lids.
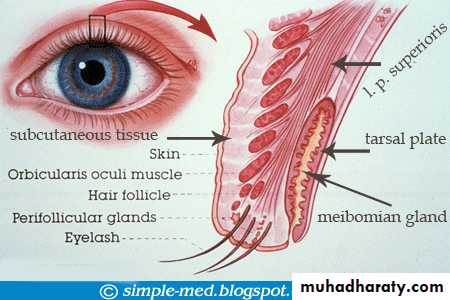
* THE STRUCTURE OF THE EYELIDS : ( HISTOLOGY)
1. skin.
2. subcutaneous tissue.
3. striated muscles--- orbicularis muscle.
4. orbital septum.
5. tarsal plate.
6. palpebral ligaments.
7. palpebral glands.
8. smooth muscles.
9. Levator muscle.
10. conjunctiva (palpebral).
* THE CONJUNCTIVA
* Def.
- thin , transparent, mucous membrane.
- lines the inner surface of eyelids and anterior part of the sclera.
* Parts :
a. palpebral– between skin and conjunctivalfornex.
b. conj. Fornex – between palpebral and bulbar conj.
c. bulbar conj. – thin , translucent , covering the sclera.
d. lacrimal caruncle – small, ovoid, pinkish body at lacus lacrimalis.
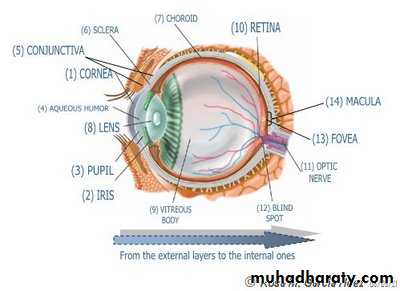
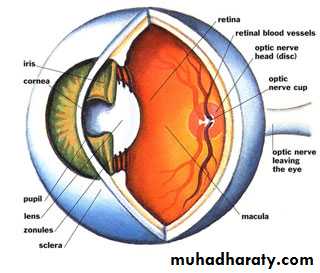
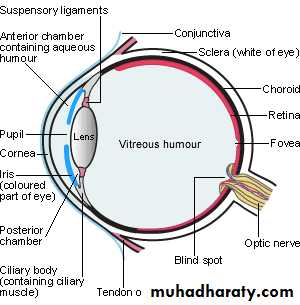
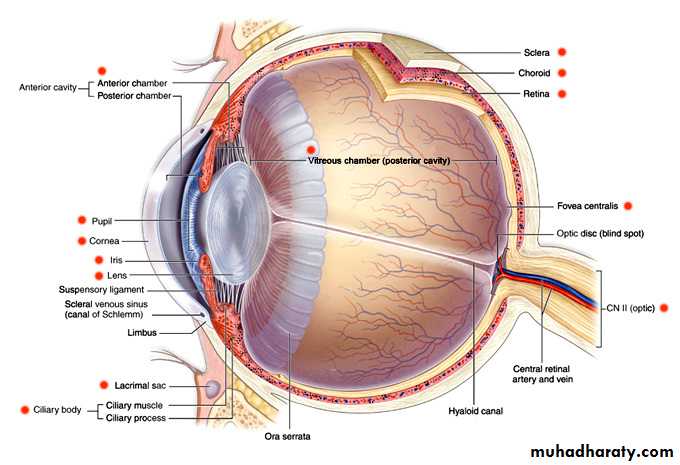
* THE EYEBALL ( THE GLOBE ):
* PARTS :
(A) Outer Coat [ anterior]:
- sclera and episclera.
- cornea.
- anterior champer and drainage angle.
- lens.
(B) Intermediate Coat [ middle]: uveal tract
- iris.
- ciliary body.
- the choroid.
- pupils.
(C) Inner Coat [ posterior]:
- retina.
- vitreous.
*THE SCLERA & EPISCLERA:
*Def. : - dense , fibrous, opaque , collagenous posterior 5/6th of the eyeball outer coat.- divided into episclera , scleral stroma and lamina fusca.
* Functions:
1. mechanical protection.
2. maintain I.O.P.
3. prevent globe deformity.
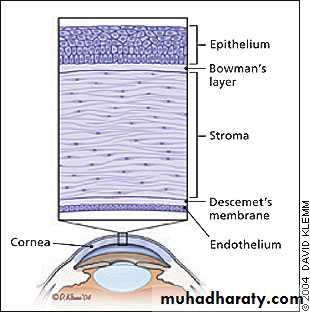
* THE CORNEA:
* Def. : - transparent , a vascular, anterior 1/6th of the eyeball outer coat.
- represent the most refractive power.(75%).
- maintain IOP.
* Histology : ( 5 Layers );
1. Epithelium. 2. Bowman’s layer.
3. The stroma. 4. Descement membrane.
5. Endothelium.
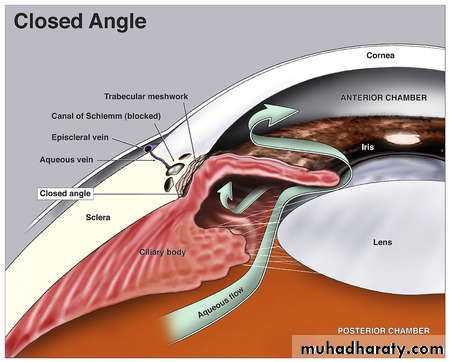
*ANTERIOR CHAMBER & DRAINAGE ANGLE:
* Def. - the chamber which is bounded anteriorly by the cornea and posteriorly by the iris, lens and anterior surface of ciliary body.
- LIMBUS--- the transitional zone between thecornea and sclera.
- Drainage Angle --- the angle which drains the aqueous.
- Anterior chamber contains Aqueous which is secreted posteriorly and moves to AC. through the pupil.
* THE UVEAL TRACT :
( A ) THE IRIS :- thin , pigmented anterior part of the uveal tract .
- located between AC. & PC.
- continuous peripherally with ciliary body.
( B ) THE PUPIL :
- small , opening within the iris regulates
the lightentering to the eye.
- normal diameter is 5-8 mm.
- sphincter pupillae constrict the pupil
under parasym. control of oculomotor nerve.
- Dilator pupillae dilate the pupil
under sympatheticcontrol.
* THE CILIARY BODY & CHOROID
* ( THE CILIARY BODY ):- a ring of tissue about 6mm wide , extends from scleral spur to oraserrata.
- anterior part --- pars plicata.
- posterior part --- pars plana.
- represents the peripheral extension of the iris.
* ( THE CHOROID ):
- soft , brown coat, lining the scleral inner surface , and represent the posterior portion of uveal tract.
- extends from optic disc to oraserrata.
- highly vascularised.
- parts : 1. stroma. 2. choriocapillaries.
3. Bruch’s membrane.
-Functions:
a. retinal nourishment. B. regulate IOP.
c. retinal heat exchange.
* THE LENS :
* Def. :- a transparent , biconvex , a vascular body , with crystalline appearance.
- located between the iris and vitreous.
- lateral part attached to the ciliary body by the zonules.
* PARTS :
a - lens capsule. b - lens nucleolus.
c - lens epithelium. d – lens cells & fibers.
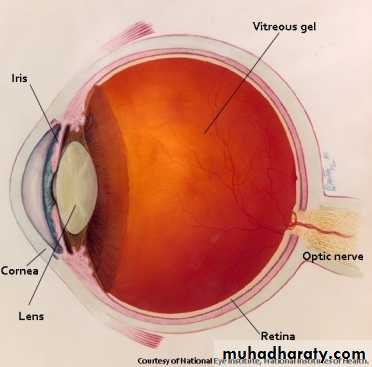
* THE POSTERIOR CHAMBER & VITEROUS :
* DEF. :
- that chamber which is bounded anteriorly by the lens & posteriorly by the retina.
- this chamber filled with gel – like fluid called VITEREOUS.
- the vitreous:
. Transparent gel, formed by 99% water , some salts, soluble proteins and Hyaluronic acid.
. Filled posterior 4/5th of the globe.
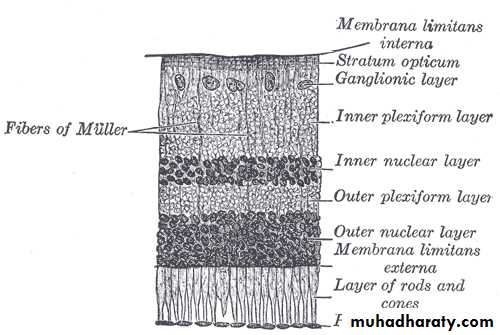
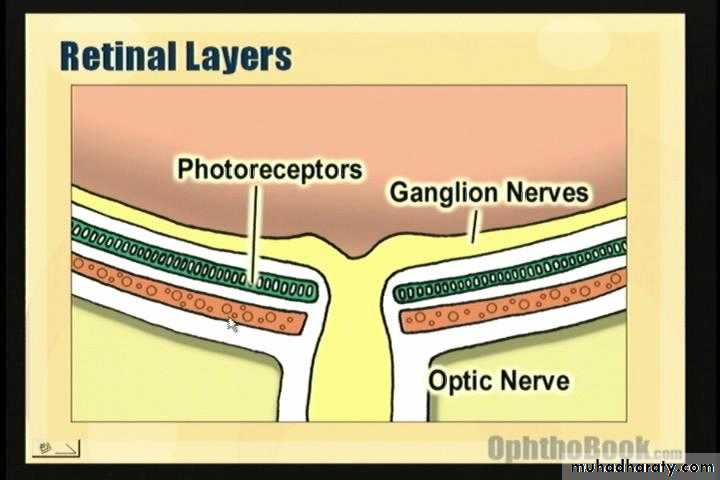
* THE RETINA :
* DEF. :- thin , transparent , membrane.
- red colour ( purple ).
- continuous anteriorly with the iris and ciliary
body, whileposteriorly as an optic nerve.
* PARTS:
1. optic disc– small, oval structure,
1.5 mm diameter &devoid cones and rods.
2. macula – yellow oval zone, within central retina.
3. Fovea– central part of the macula.
4. Foveola – central part of the fovea.
* Layers :
*10 layers starting by retinal pigmented epithelium
internally.
* most important layers:
-retinal pigmented epithelium.
-retinal cells.
-Photoreceptors :
- RODS---- dark vision.
- CONES ----- bright light and coloured vision.
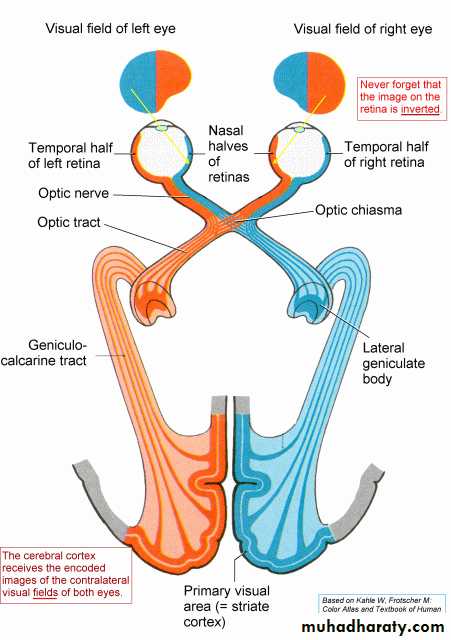
* THE VISUAL PATHWAY:
* PARTS :
1. optic nerve. 2. optic chiasma.
3. optic tract . 4. lateral geniculate body.
5. optic radiation. 6. visual cortex.
* THE OPTIC NERVE :
- a long tract of white matter , 5 cm long , formed by fibers of the ganglionic cells.
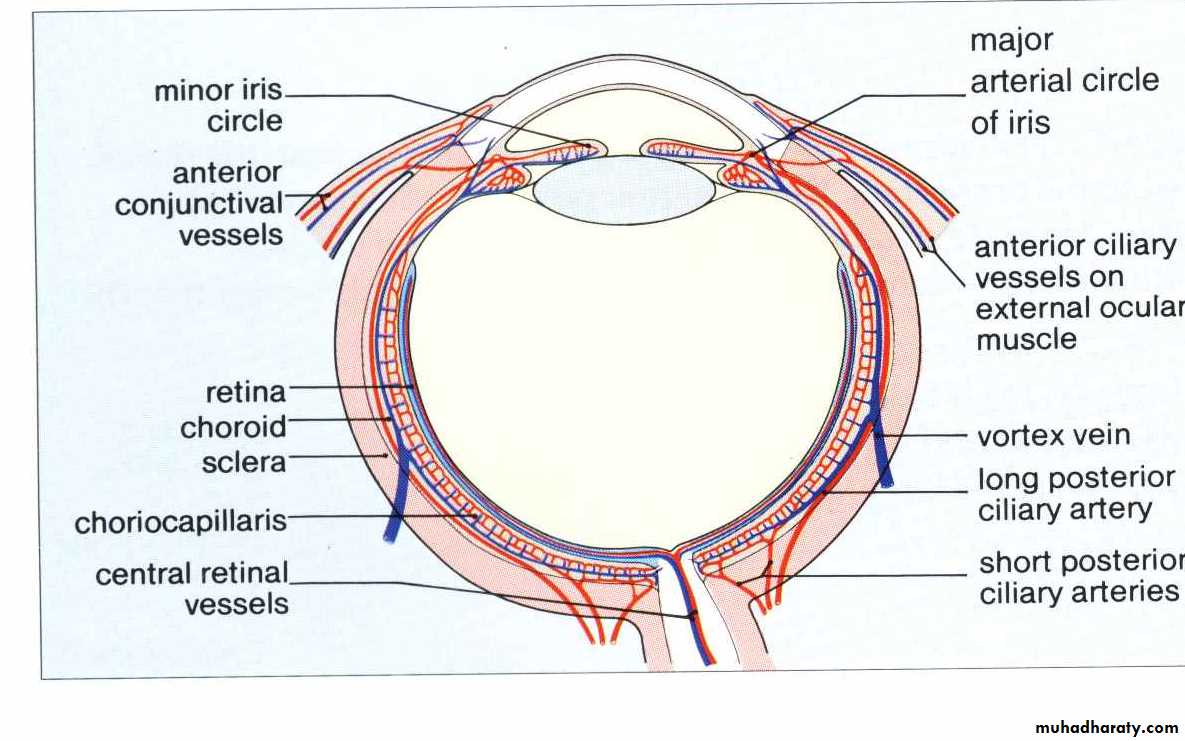
* BLOOD & NERVE SUPPLY :
* BLOOD SUPPLY :1. mainly via ophthalmic artery from internal carotid artery.
2. partially via infraorbital artery from external CA.
3. venous drainage through vortex veins to facial vein and to cavernous sinus.
* NERVE SUPPLY:
( A ) MOTOR NERVES :
1- OCULOMOTOR N.– muscular , Levator ,sphincter p.
2- TROCHLEAR N. – superior oblique.
3- Abducent N. – lateral rectus.
( B ) SENSORY NERVES :
- ophthalmic and maxillary divisions of trigeminal nerves.
( C ) AUTONOMIC NERVES :
- sympathetic and parasympathetic supply for glands , smooth muscles and blood vessels.
written by omar abid ALsammer
WITH BEST WISHES…..