E.coliCommensal, Pathogen,& Genetic tool
Dr.T.V.Rao MDDr.T.V.Rao MD
Classification of Bacteria
Dr.T.V.Rao MD2
Enterobacteriaceae
Commonly present in large intestineNon sporing , Non Acid fast, Gram – bacilli.
A complex family of organisms,
Some are non pathogenic
A few are highly Pathogenic,
Some commensals turn out to be pathogenic. as in UTI after catheterization.
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
3
Characters of Enterobacteriaceae
All Enterobacteriaceae
Gram-negative rods
Ferment glucose with acid production
Reduce nitrates into nitrites
Oxidase negative
Facultative anaerobic
Motile except Shigella and Klebsiella
Non-capsulated except Klebsiella
Non-fastidious
Grow on bile containing media (MacConkey agar)
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
4Classification of Enterobacteriaceae
There are several selective and differential media used toisolate distinguishes between LF & LNF
The most important media are:
MacConkey agar
Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) agar
Salmonella Shigella (SS) agar
In addition to Triple Sugar Iron (TSI) agar
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
5
Escherichia coli
Named by Escherichia
Wide group of bacteria on basis of
Bio typing and Serotyping
Produce infections in Humans and Animals
Detection of E.coli in water indicates pollution and contamination.
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
6Classification
Domain: BacteriaKingdom: Bacteria
Phylum: Proteobacteria
Class: Gamma Proteobacteria
Order: Enterobacteriales
Family: Enterobacteriaceae
Genus: Escherichia
Species: Escherichia coli (E. coli)
E.coli
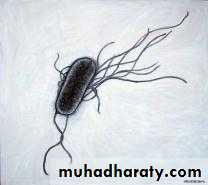
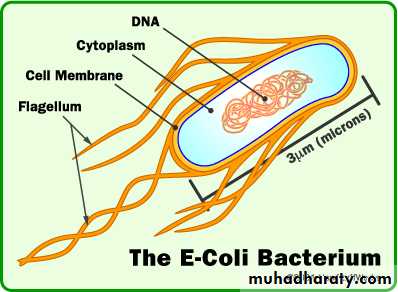
Morphology Gram - ve Straight rods,1-3 X 0.4 -0.7 microns,
Appear in singles or in pairs,
Motile by peritrichate flagella.
Very few strains non motile
Not spore forming, Non acid fast.
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
8Enterobacteriaceae: Genetic Properties
Chromosomal DNA has 39-59% guanine-plus-cytosine (G+C) contentEscherichia coli is the type genus and species of the Enterobacteriaceae
Species of Enterobacteriaceae more closely related by evolutionary distance to Escherichia coli than to organisms of other families (Pseudomonadaceae, Aeromonadaceae)
E.coliCultural characters
Aerobic / Facultative AnaerobicGrows between 10 – 40 c optimal at 37 c
Grown in simple medium
Produce Large grayish ,Thick white , moist smooth opaque colonies
May contain capsule.
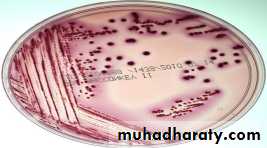
On MacConkey medium Produce Bright pink Lactose fermenters.
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
10
E.coli
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
11Identification of EnterobacteriaceaeBiochemical reactions
Oxidase testAll members of Enterobacteriaceae are oxidase negative
Pseudomonas is oxidase positive
O/F test
All members of Enterobacteriaceae are O+/F+
Pseudomonas is O+/F-
Nitrate reductase
All members of Enterobacteriaceae are nitrate reductase positive
Pseudomonas is nitrate reductase negative
E.coliBiochemical Characters,
Glucose,Lactose,Mannitol,Maltosefermented. with A/G
I,M,Vi,C tests.
Indole +
Methyl Red +
Voges Proskauer – ve I,M,Vi,C tests.
Citrate –ve
Urease not produced.
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
13
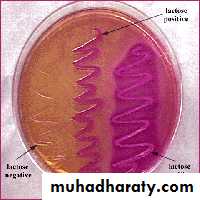
Identification of EnterobacteriaceaeDifferentiation between LF & NLF by Growth on MacConkey agar
Method:
MacConkey agar is inoculated with tested organism using streak plate technique
Incubate the plate in incubator at 37 C/24 hrs
Results:
LF organism appears as pink colonies (e.g. E. coli)
NLF organism appears as colorless colonies (e.g. Shigella)
Flame & Cool
Flame & CoolFlame & Cool
1
2
3
4
5
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
14
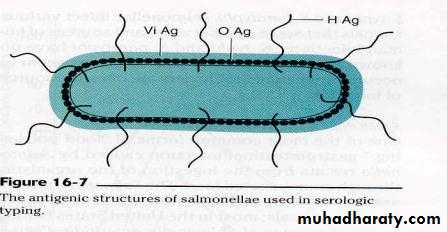
E.coliAntigenic Structure
Somatic 0 170Capsular K 100
Flagella H 75
Virulence factors
Surface Antigens Toxins
O Endotoxic activity
K protects against the phagocytosis
Fimbriae promote virulence ( important in UTI )
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
15Toxins and E.coli
E.coli produce ExotoxinsHemolysins, Enterotoxins causes Diarrheas,
Important toxins produces.
Heat labile HL Heat stable HS
Vero toxins VT Like Shigella toxins
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
16
Toxins
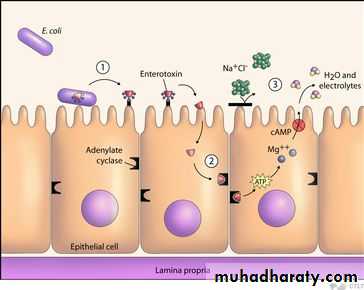
Enterotoxins – produced by enterotoxigenic strains of E. coli (ETEC). Causes a movement of water and ions from the tissues to the bowel resulting in watery diarrhea. There are two types of enterotoxin:
LT – is heat labile and binds to specific Gm1 gangliosides on the epithelial cells of the small intestine where it ADP-ribosylates Gs which stimulates adenylate cyclase to increase production of cAMP
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
17
Mechanism of action of Toxins
Increased cAMP alters the activity of sodium and chloride transporters producing an ion imbalance that results in fluid transport into the bowelDr.T.V.Rao MD
18Toxins in E.coli
Produce Enterotoxin L T and S TLabile toxin 1956 De experiments in Rabbit illeal loop causes outpouring of fluids
E.coli Labile toxin like Cholera toxin
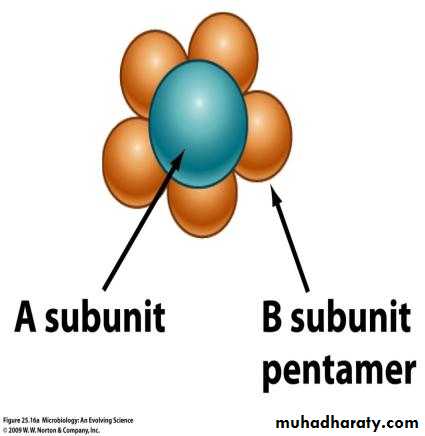
L T contains component A and B
A = Active B= Binding
B causes Binding with Gm I Ganglioside receptor on Intestinal epithelial cells
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
19
E. coli toxins
• Both enterotoxins are composed of five beta subunits (for binding) and 1 alpha subunit (has the toxic enzymatic activity).Dr.T.V.Rao MD
20Toxins E.coliLabile toxin
Component A Activated to A1 and A2A1 Activates adenyl cyclase in the enterocytes to form cyclic adenosine 5 monophosphate
Causes to increase outflow of water and electrolytes in the gut lumen causes Diarrhea
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
21
Toxins of E.coliStable Toxin
ST A and ST BST A Acts by activation of Cyclic guano sine monophosphate.( C GMP )
Causes fluid accumulation in Intestine.
E.coli ( Some ) produce Verocytotoxin causes cytotoxicity to Vero cells.
Acts like Shigella dysentery toxin
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
22
E.coli a Complex Microbe
More than 700 serotypes of E. coli have been identified. The different E. coli serotypes are distinguished by their “O” and “H” antigens on their bodies and flagella, respectively.
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
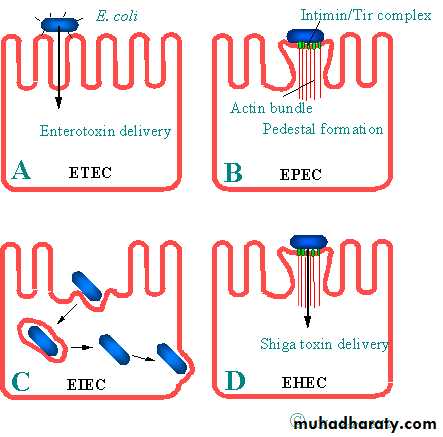
23Classification of E.coli
1.Enteropathogenic EPEC2.Enterotoxigenic ETEC
3.Enteroinvasive EIEC
4.Enterohemorrhagic EHEC
5.Enteroaggresive EAEC
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
24
Enteropathogenic E.coli
Causes diarrheal disease in children,EPEC O26/O11
Produce Verocytotoxin
Infantile enteritis, Involves upper part of Intestine
Brush border of the intestine is lost
Intimacin – EPEC adhesion factor.
Frequent in summer months
Poor hygiene predisposes.
Out breaks in Institutions
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
25
26
• Enteropathogenic E. coli
destruction of surface microvilli
feverdiarrhea
vomiting
nausea
non-bloody stools (not generally seen as dysentery)
Gut lumen
Laboratory Diagnosis EPECConfirm with Polyvalent sera
Test Sero groups with polyvalent and monovalent sera.
HEp2 – adherence.
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
27Enterotoxigenic E.coli
Produce Heat stable /Heat labile toxinsAdheres to epithelium of small intestine.
Present with Nausea, Vomiting and Lose stool
H L like cholera toxin
Causes accumulation of fluids
Adhesive factors
Fimbriae specific receptor in the intestinal epithelium CFA
Mortality in children < 5 years
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
28
29
Enterotoxigenic E. coli
Heat labile toxin
like choleragenAdenyl cyclase activated
cyclic AMP
secretion water/ions
Heat stable toxin
Guanylate cyclase activated
cyclic GMP
uptake water/ions
Enterotoxigenic E.coli
Causes travelers diarrheaWater contaminated with Human and Animal feces predisposes.
Laboratory Diagnosis
Demonstration of Enterotoxin LT and ST
Tissue culture tests,
ELISA
Passive agglutination tests.
Animal experiments in Rabbit ileal loop test.
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
30
Treatment and Prophylaxis in Travelers diarrhea
Doxycycline,Trimethoprim,
Norfloxacillin
Fluroquinolones
Avoid contaminated food,
Safe protected water ,prefer bottled water,
Hot foods, Hot Drinks,
Boiled milk
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
31
Entero invasive E.coli
Some are non motile strains,Atypical resembles like Shigella.
Clinically mild diarrhea
Sereny test positive animal Rabbit.
ELISA
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
3233
Dysentery
- resembles shigellosis
Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC )
Gut lumen
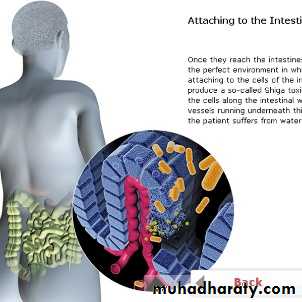
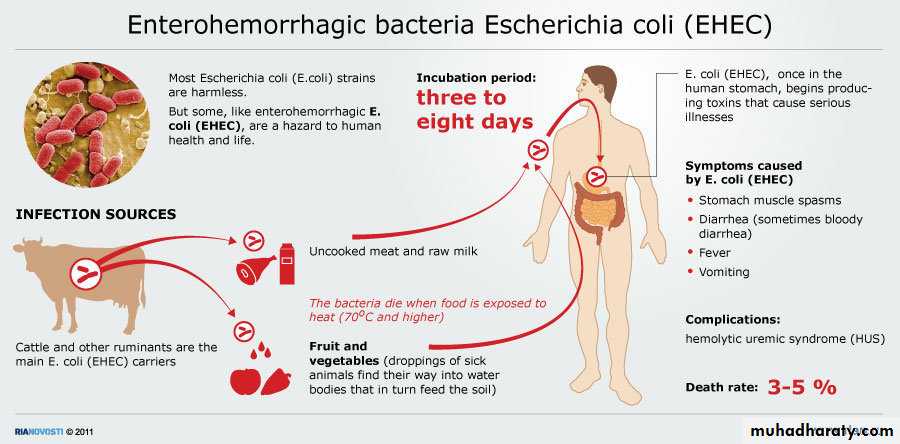
Enterohemorrhagic E.coli
Produce VerocytotoxinMild diarrhea - can be fatal hemorrhagic colitis. and uremic syndrome.
Present in Human and Animal feces.
Hemorrhagic complication with O157 in Japan and USA.
Salads vegetables, Radish Proper cooking
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
34EHEC ( contd )
CultureDNA detection methods.
Cytotoxic effects on Vero cells.
Detection with monovalent sera O157/H7
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
35Dr.T.V.Rao MD
36Enterohemorrhagic E.coli can cause HUS
HUS develops when the toxin from E. coli bacteria, known as Shiga-like toxin (SLT) , enters the circulation by binding to special receptors. These Shiga-toxin receptors, known as Gb3 receptors , are probably heterogeneously distributed in the major body organs allowing disparate thrombotic (blood clotting) impacts in different HUS victims, although the greatest receptor concentration appears to be in the kidneys, especially in children.Dr.T.V.Rao MD
37
Mechanism of HUS
As the inflammatory reaction process accelerates, red blood cells are destroyed and cellular debris aggregates within the microvasculature while the body’s inherent clot breaking mechanisms are disrupted. The result is formation of micro thrombi within particularly susceptible organs such as the kidneys and brain. Because there exists no way to halt the progression of HUS,The patients are supported with medical care
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
38
Enteroaggresive E.coliEAEC
Can cause Diarrhea Detect by Culture methodsBrick-like aggregates on cell surfaces
Mucus biofilm inhibits fluid absorption
Diarrhea
Detection of Enterotoxin
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
39
E.coli resembles Shigella spp
The E. coli serotypes that are responsible for the reports of contaminated foods and beverages are those that produce Shiga toxin, because the toxin is identical to that produced by another bacteria known as Shigella dysenteryDr.T.V.Rao MD
4041
Treatment – E.coli Gastrointestinal disease
Fluid replacement
Antibiotics
not used usually unless systemic infections prevails
e.g. hemolytic-uremia syndrome
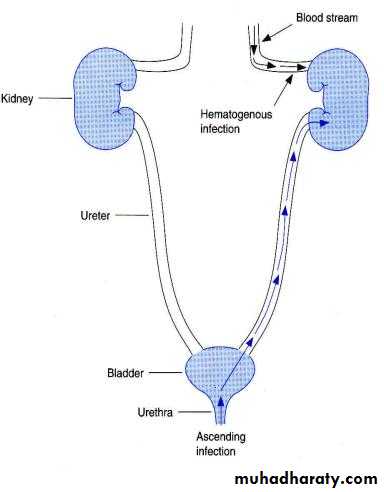
E. Coli leading cause of UTI
Clinical significanceIs the leading cause of urinary tract infections which can lead to acute cystitis (bladder infection) and pyelonephritis (kidney infection).
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
42Urinary Tract Infections
E.coli produce urinary tract infection.Majority of UTI s are produce by E.coli.
Instrumentation, Prostatic enlargement, Urinary caliculi ,Pregnancy, increase the predisposition
Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in pregnant women,
Pyelonephritis,
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
43Facts on UTI
Women suffer more than males Short urethra Pregnancy, Sexual intercourse /Honey moon cystitis.Other factors
Urethral obstruction,
Urinary stones
Congenital malformation's
Neurological disorders,
Catheterization , Cystoscopy
Usually cystitis is produced from fecal strains entering urethra
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
44
Culturing for E.coli
Mid stream sample/semi quantitative culturing (Kass et al ) >_ 1.00,000/ml of urine. ( significant Bacteriuria )Urine should not be kept in wards for > 2 hours and to be preserved at 4 c
Culture by standard loop method.
Fixed volume cultured on MacConkey agar Lactose fermenters I M Vi C
Antibiotic sensitivity tested.
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
45
Other infection withE.coli
Pyogenic infections.Intraabdominal infections
Peritonitis. Abscess.
Septicemias
Produce Drug resistant infections.
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
46
Other Important E. coli Infections
Neonatal meningitis – is the leading cause of neonatal meningitis and septicemia with a high mortality rate.
Usually caused by strains with the K1 capsular antigen.
Gastroenteritis – there are several distinct types of E. coli that are involved in different types of gastroenteritis:
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
47
E.coli
Antimicrobial therapy- E. coli is usually susceptible to a variety of chemotherapeutic agents, though drug resistant strains are increasingly prevalent.It is essential to do susceptibility testing.
Treatment of patients with EHEC infections is not recommended because it can increase the release of shiga-like toxins and actually trigger HUS
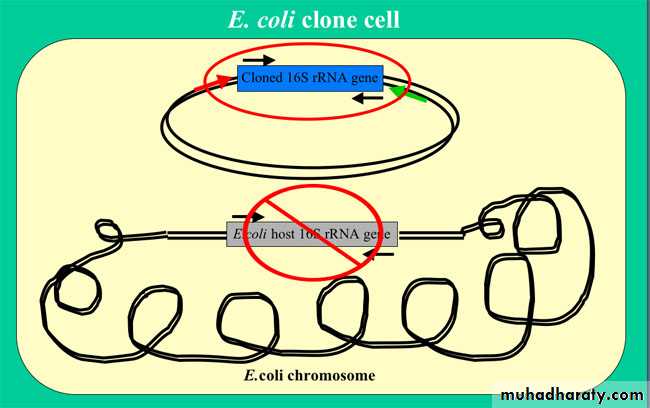
Escherichia coli as a Genetic tool.
The study of Escherichia coli and its plasmids and bacteriophages has provided a vast body of genetical information, much of it relevant to the whole of biology. This was true even before the development of the new techniques, for cloning and analysing DNA, that have revolutionized biological research during the past decade.. Much of the background of knowledge necessary for the cloning and expression of genetically engineered information, as well as the techniques themselves, came from work with this organism.Dr.T.V.Rao MD
49
Why E.coli is preferred
E. coli cells only have about 4,400 genes whereas the human genome project has determined that humans contain approximately 30,000 genes. Also, bacteria, including E. coli, live their entire lifetime in a haploid state, with no second allele to mask the effects of mutations during protein engineering experiments.Dr.T.V.Rao MD
50
How Does Molecular Cloning Work?
Cloning of any DNA sequence involves the introduction of a foreign piece of DNA into an extra chromosomal element (cloning vector) of an organism which then produces copies of the vector as it replicates itself, thereby amplifying the DNA of interest. The whole process can be summarized in the following steps: fragmentation, ligation, transfection, screening/selection, and conformation of insert.
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
51
E.coli Preferred in Genetic Engineering
It is a favorite organism for genetic engineering as cultures of it can be made to produce unlimited quantities of the product of an introduced gene. Several important drugs (insulin, for example) are now manufactured in E. coli. However, E. coli cannot attach sugars to proteins so proteins requiring such sugars have to be made in the cells of eukaryotes such as yeast cells and mammalian cells grown in cell culture.Dr.T.V.Rao MD
52Programme Created by Dr.T.V.Rao MD for Microbiologists, Medical and Paramedical Students in the Developing World
Email.com
doctortvrao@gmail.com
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
53
Reference
www.slideshare.comDr.T.V.Rao MD
54