INDICES USED FORDENTAL FLUOROSIS
DENTAL FLUOROSIS
is a hypoplasia or hypo mineralisation of tooth enamel or dentine produced by the chronic ingestion of excessive amounts of fluoride during the period when teeth are developing.HISTORY
1888 : “KUHNS” described teeth of persons inareas of Mexico that were opaque, discolored and
disfigured. (Kuhns1888; Moller 1982).
1901 Dr. Fredrick Mckay of Colorado USA discovered permanent stains on teeth of his patients which were referred as Colorado stains.
Mckay named then “mottled enamel”.
An Assitant surgeon of U.S marine hospital service reported similar condition in Italians emigrating from USA to Naples named it denti di chiaie. ( Eager 1901).
1916 Mckay and Black published a series of articles in dental cosmos.
HISTORY
In 1931 this condition of teeth was found to be
correlated to fluoride content of drinking water.(Churchill 1931; Smith et al 1931)
1931 shoe leather survey by Trendley H. Dean
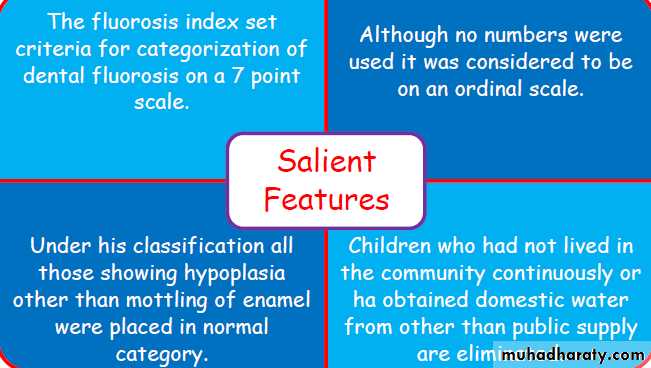
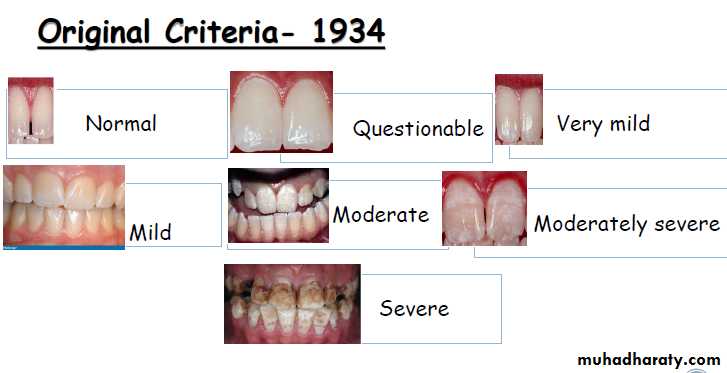
1934 DEAN‟S FLUOROSIS INDEX was given
by Trendley H. Dean
CLASSIFICATION OFFLUOROSIS MEASURINGINDICES
DEAN’S FLUOROSIS INDEX1934; TRENDLEY H.DEAN
devised an index for
assessing the presence and
severity of mottled enamel.
METHOD ( as implied by DEAN)
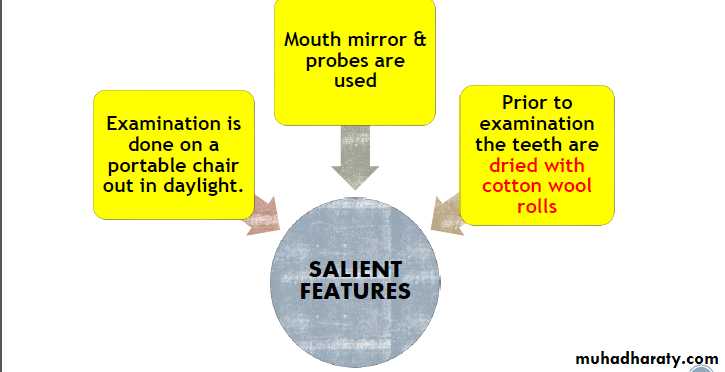
Each individual recieves a score corresponding to clinical appearance of two most affected teeth.• Examinations are made in good natural light with the subject sitting facing the window
No specific information as to whether the teeth were cleaned or dried before examination is given
• Mouth mirror and probes were utilised for examination.
USES
• Most widely used index to measure dental fluorosis.• Helped to indicate prevalence of moderate to severe fluorosis in many communities as
1.Sweden by Forsman in 1974
2. Austria by Binder in 1973
3.England by Murray et al(1956), Forrest (1965), Goward (1976)
4. USA by Galagan and Lamson (1953)
5. India by Nanda et al (1974)
. The National Survey of Children’s Dental Health in Ireland in 1984 measured fluorosis using Dean’s index to provide baseline data for future reference.
( Whelton HP;Ketley CE;Mcsweeny F;O’Mullane DM;2004)
• National Fluorosis Survey in USA in 1986-87 to note baseline values was done using Dean’s index.
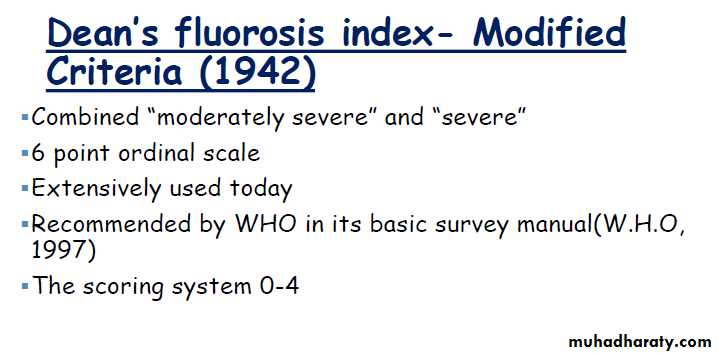
Deans revised index (1942)
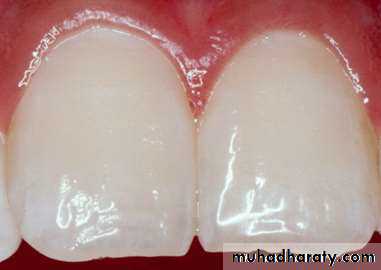
NORMAL (0) Theenamel represents the
usual translucent
Semi vitriform type of
structure. The surface is
smooth , glossy and
usually of a pale, creamy
QUESTIONABLE(0.5) The enamel
discloses slight aberrations from thetranslucency of normal enamel,
ranging from a few white fleck to
occasional white spots. This
classification is used in those
instances where a definite diagnosis
of the mildest form of fluorosis is not
warranted and a classification of
“normal” not justified.
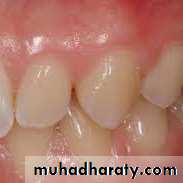
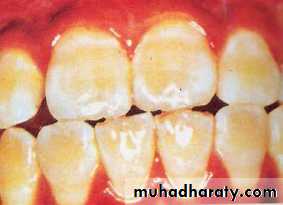
VERY MILD (1) Small, opaque, paper
white areas scattered irregularly overthe tooth , but not involving as much as
approximately 25% of tooth surface.
Frequently included in this
classification are teeth showing no
more than about 1-2 mm of white
opacity at the tip of the summit of the
cusps of bicuspids or second molars.
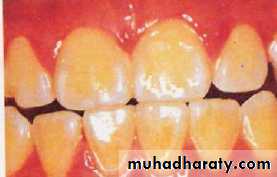
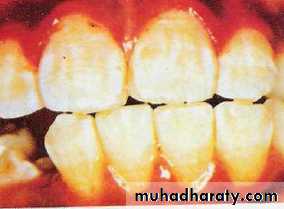
MILD (2)The white opaque
areas in the enamel ofteeth are more extensive
but do not involves as
much as 50% of tooth
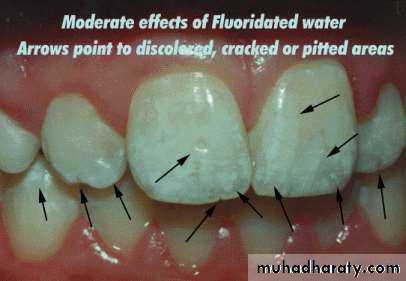
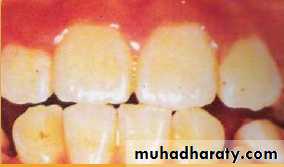
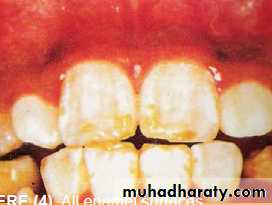
. MODERATE (3) All enamel
surfaces of the teeth are
affected and surfaces subject
to attrition show wear. Brown
stain is frequently a disfiguring
feature.
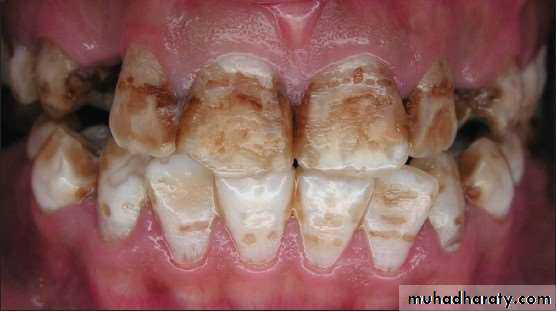
SEVERE (4) All enamel surfaces
of the tooth are affected andhypoplasia is so marked that the
general form of the tooth may be
affected. The major diagnostic
sign of this classification is
discrete or confluent pitting.
Brown stains are widespread
and teeth often present a
corroded-like appearance.
Limitations
1. Does not give sufficient information ondistribution of fluorosis within the
dentition.
2. Isolated defects are not recorded.
3. The distinction amongst the categories is
unclear, indistinct and lacking sensitivity.
4. Even though Dean’s scale is ordinal , it
involves averaging of the scores which is
inappropriate.
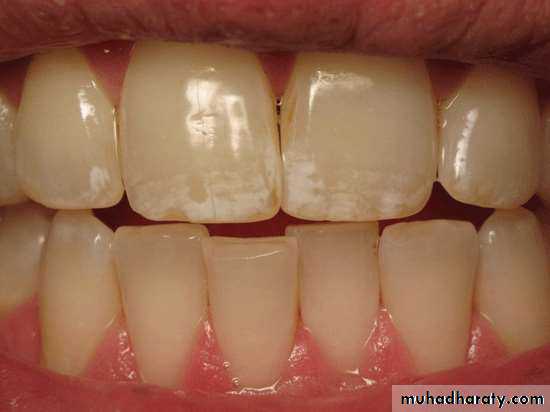
Mottled enamel
Mottled enamel is a condition indicates the fluorosischaracterized by minute white flecks, or yellow or brown
spots or areas, scattered irregularly or streaked over the
surface of a tooth
• It is scored according to a method described by Al alousi’
et al as follow:
• Type A:white areas less than 2mm
• Type B:white areas more than 2mm
• Type C:brown areas less than 2mm
• Type D:brown areas more than 2mm
• Type E:horizontal white lines
• Type F:horizontal brown lines
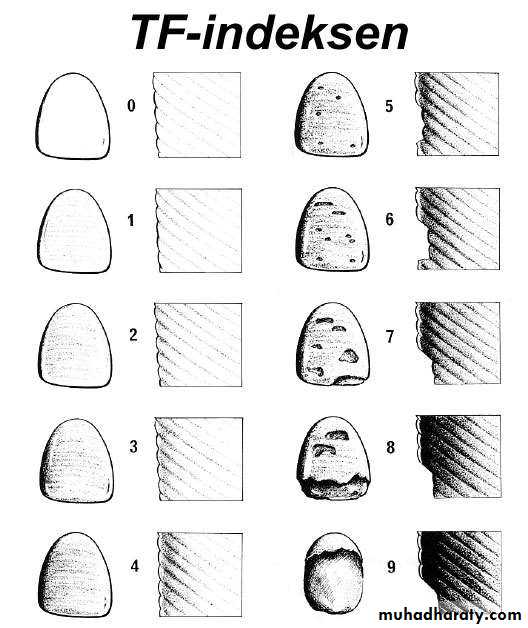
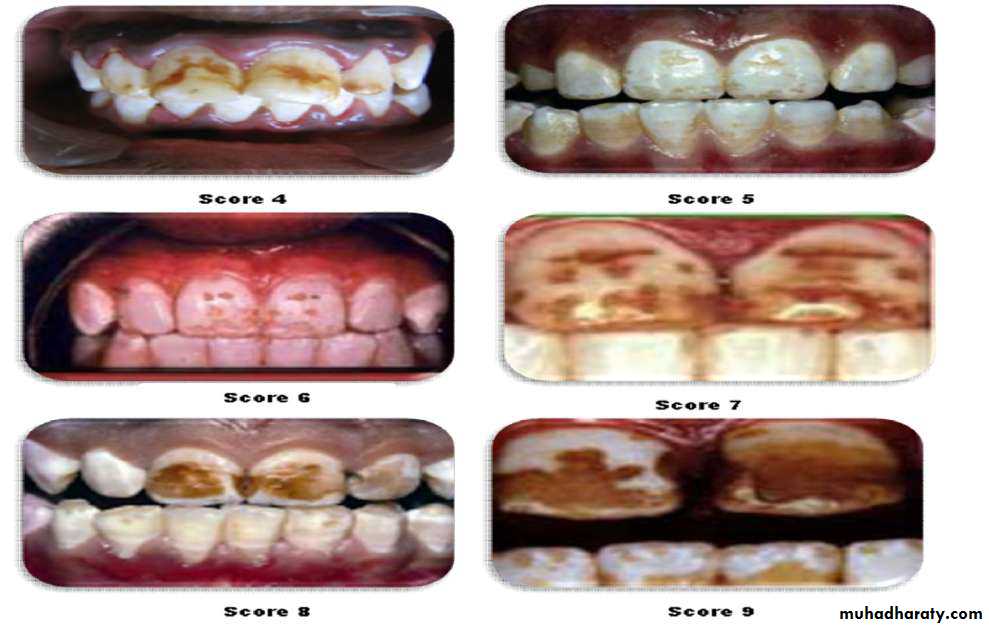
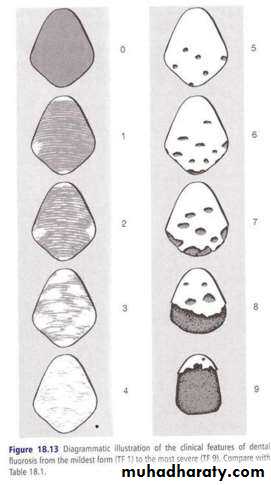
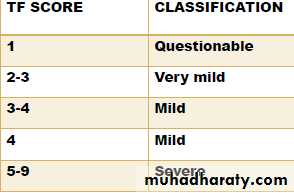
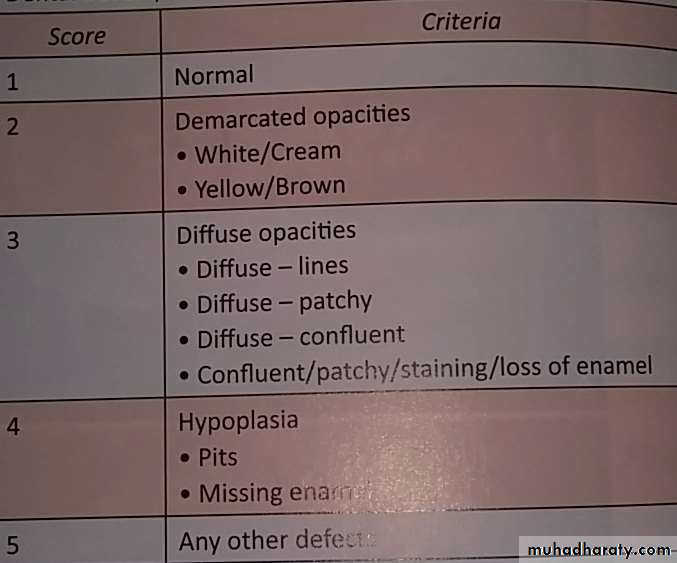
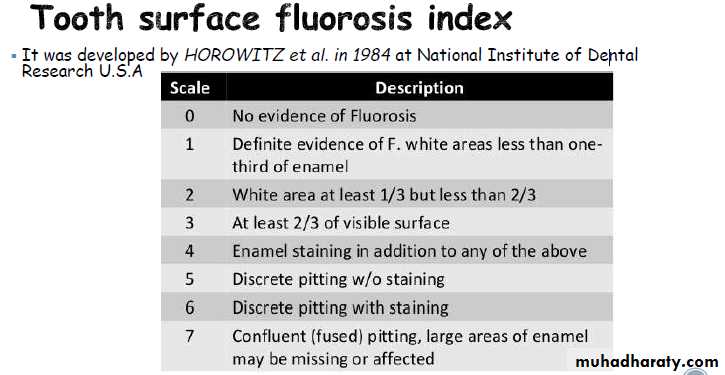
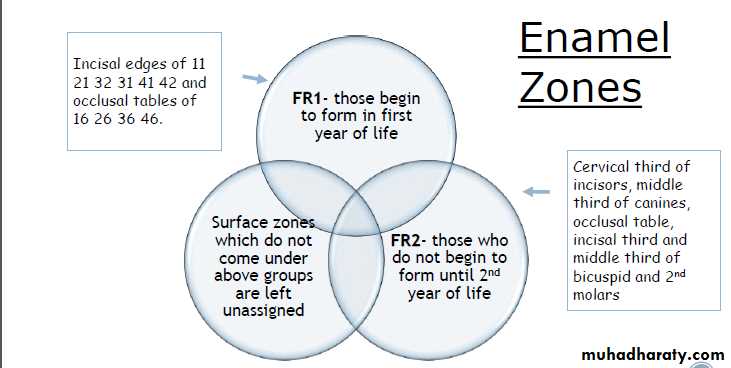
Thylstrup and Fejerskov Index for Fluorosis
1978TFI given By Thylstrup A. and Fejerskov O.
Purpose-to refine modify and extend the Dean’s Index.
10 point classification system designed to characterize the macroscopic appearance of teeth in relation to the
underlying histological condition of enamel.
In 1988 TFI was modified by Fejerskov - 0nly one surface examined
It is possible to produce exact and comparable estimates of severity of dental fluorosis in various populations by
1. Frequency distribution of TF score of individual teeth.
2. Cumulative distribution of severity of the TF scores.
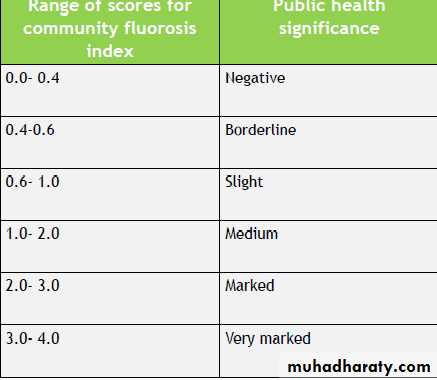
INTERPRETATION (based on Dean’s Index
Advantages
• It attempts to validate the visual appearance against the histological defect.• Most sensitive of all fluorosis measuring indices.
• Granath et al. (1985), comparing the DEAN and T-F indexes, concluded that the latter was more detailed and sensitive because it was based on biological aspects where there is an increase in hypo mineralization with a simultaneous increase in the depth of the enamel surface in direction of the amelo-dentin junction.
They concluded that the T-F index is the most indicated for work where detailed information about the problem is required.
DISADVANTAGES :
Clarkson (1989) reported that in TF index drying of teeth creates an unnatural situation due to which changes in score 1 and 2 are very minor.
The aesthetic significance of these changes are questionable
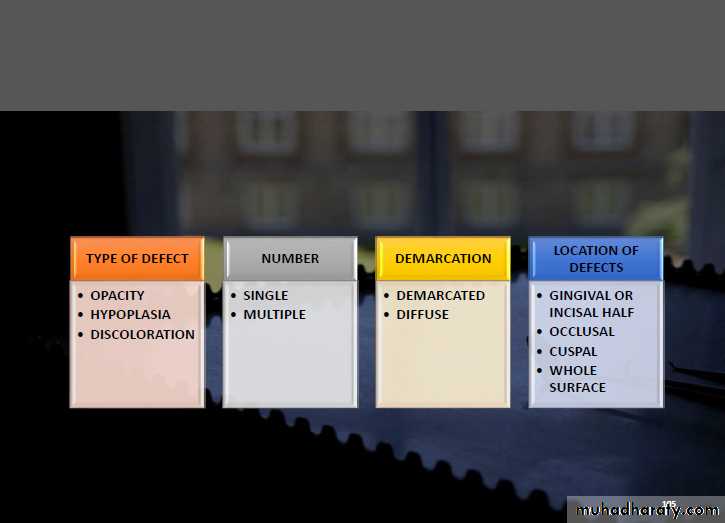
DEVELOPMENTAL DEFECTS OF INDEX
• The developmental defects of enamel was developed by “ FDI –Commission on Oral Health, Research and Epidemiology” in 1982 to avoid need for diagnosing fluorosis before recording enamel opacities.MODIFICATIONS
• Clarkson J.J and O’Mullane D.M in 1985 modified the DDE to be usedin one of the two manners
1. General purpose epidemiology studies
2. Screening surveys
Dental Developmental Index modified in 1989
What are the Selected Teeth and Scoring for Oral Hygiene Index (OHI) by Green and Vermillion(1960)?
What are the Selected teeth and the scoring for Ramfjord periodontal disease index ( pocket depth ) and what are the Criteria ?