regional orthopedic .
THE ElbowAss.Prof.
Dr. Zaid Al- Shahwanii
Consultant orthopedic surgeon
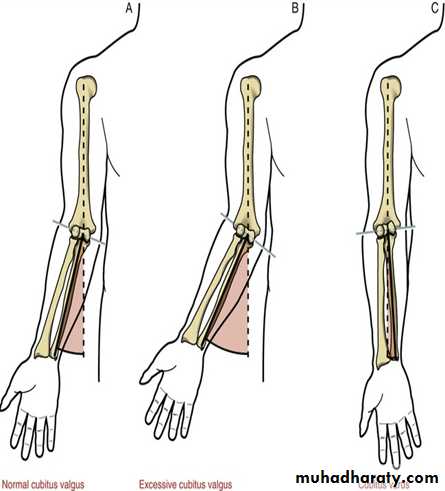
Valgus versus Varus
… In orthopedics, a varus deformity is a term for the inward angulation of the distal segment of a bone or joint.The opposite of varus is called valgus
((Which is a term for the outward angulation of the distal segment of a bone or joint.))
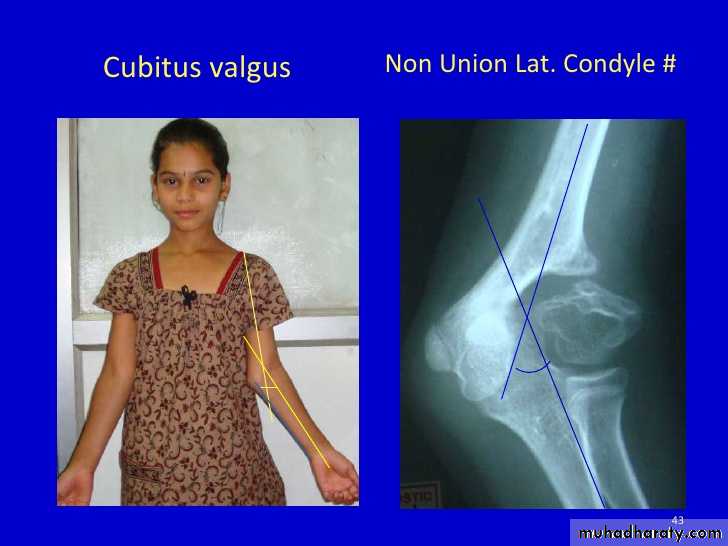
Cubitus valguscubitus is the Latin word for elbow and valgus means angled outward
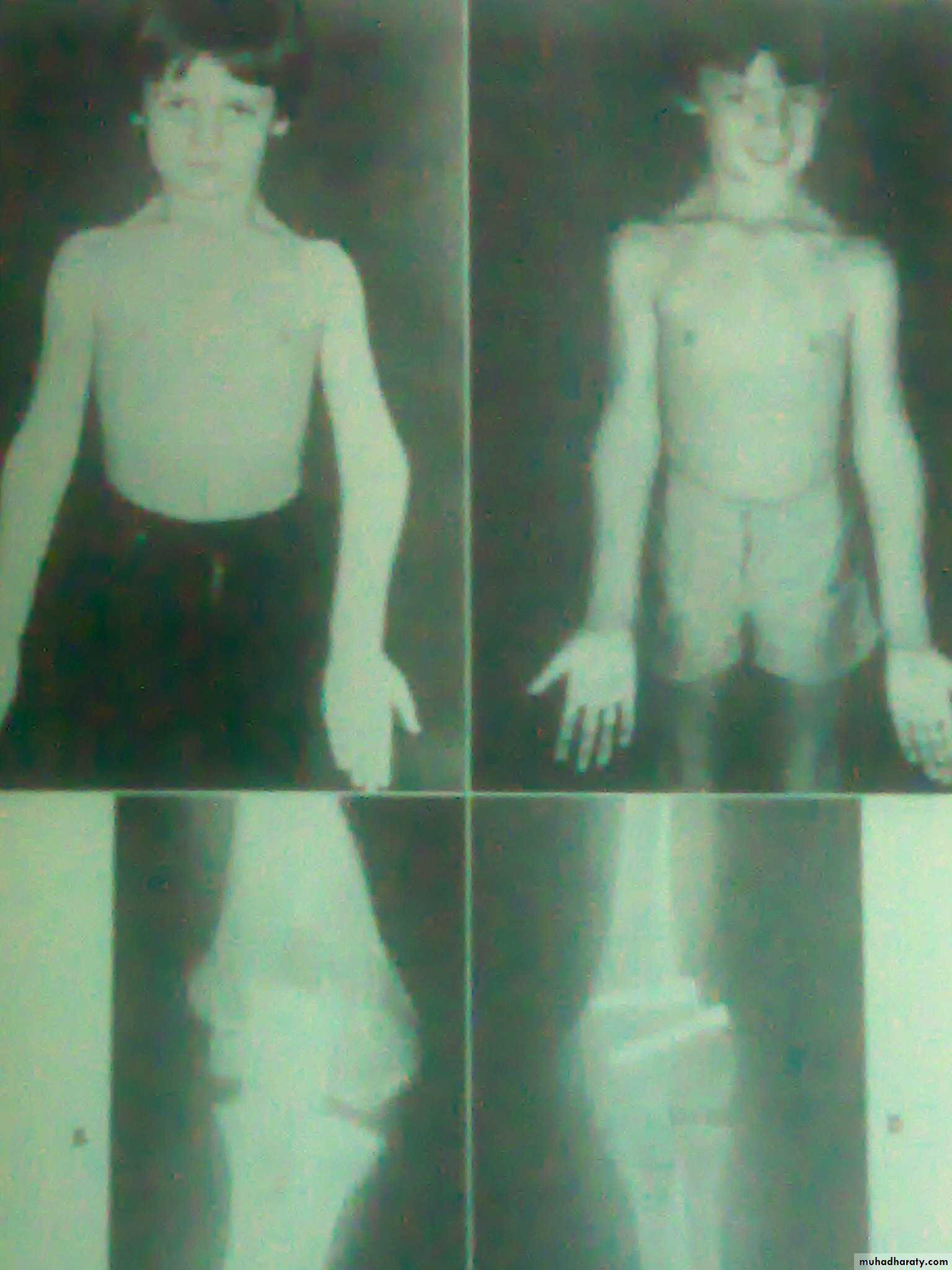
DefinitionA deformity of the elbow that resulting in an increased carrying angle. (so that, with the arm extended at the side and the palm facing forward, the forearm and hand are held at greater than 15 degrees).
Cubitus valgus can be due to
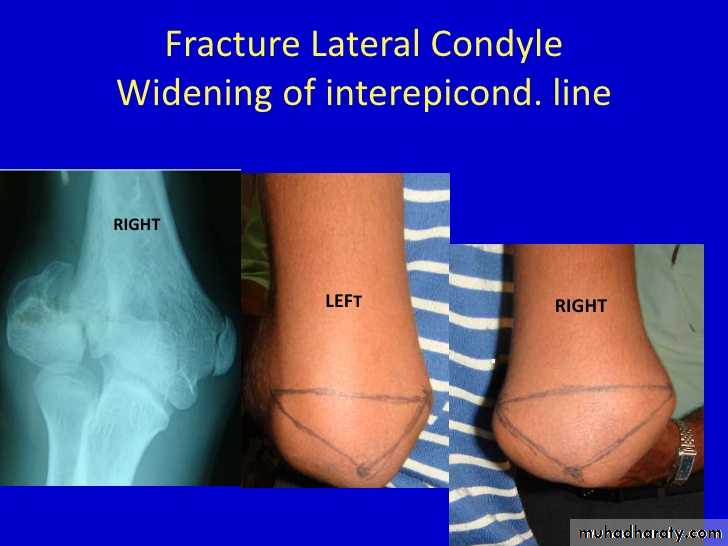
1) congenital malformation, as in Turn syndrome and Noonan syndrome,2)Fracture ( non united fr. of the lateral humeral condyle )
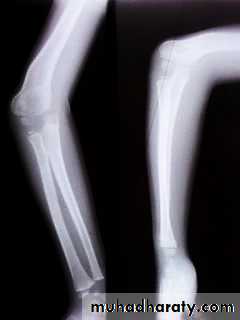
Cubitus Varus
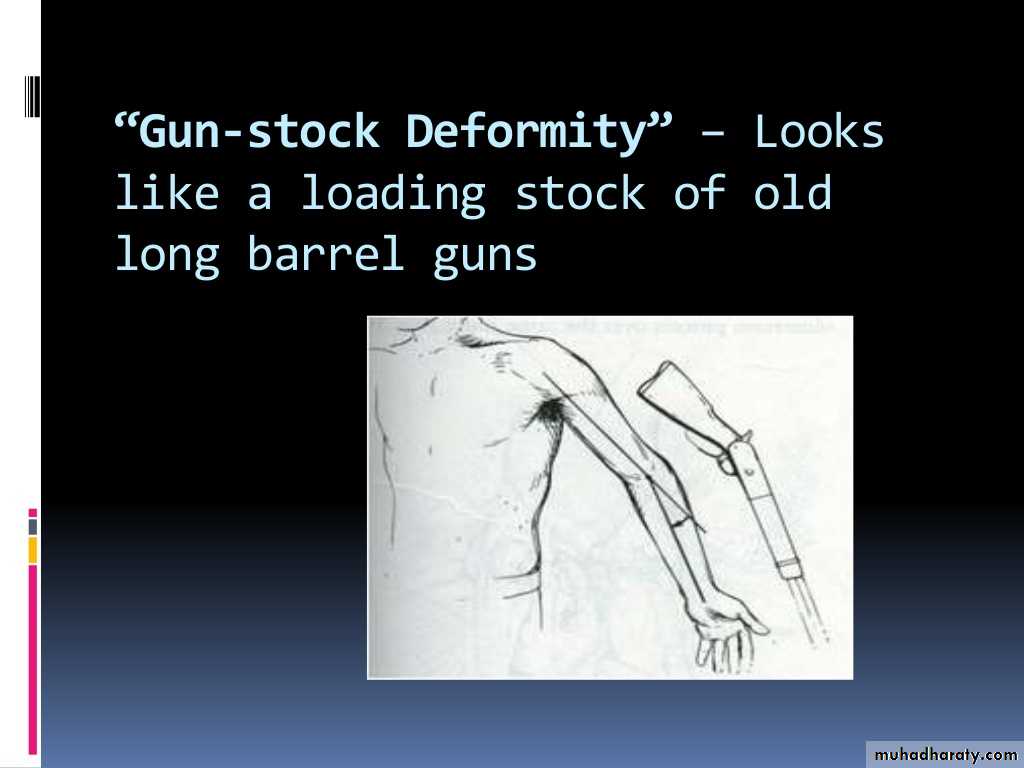
common deformity means a deformity of a limb in which its distal part is deviated towards the midline of the body . ( extended forearm is deviated towards midline of the body).Cubitus varus is often referred to as 'Gunstock deformity', due to the crooked nature of the healing
The "opposite" condition is cubitus valgus
Causes
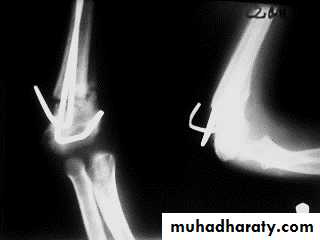
A common cause is the supracondylar fracture of humerus. It can be corrected via an osteotomy of the lower humerus fixed eithert externally or internally until bone heal.
QUIZ
1)What do we call this deformity?2)What is the main causes for such a deformity ?
;
;
DiagnosisCubitus varus is not able to be diagnosed until healing of the prior fracture, as the arm must be in full extension, not in flexion, for the deformity to be noticed
.
Complications
1)A cubitus varus deformity is more cosmetic than limiting of any function.
how ever there will be some limitation in radius internal rotation over the ulna due to over growth of the lower end of the humerus this can be noticed in some activity as using the mouse computer
2)The Medial condyle of the of the distal humerus is malformed due to the inital fracture at the humeral endplate which may result in subluxation (snapping) of the ulnar nerve over the medial epicondyle with active flexion and extension of the elbow
. In such instances, conductance of the ulnar nerve may be compromised due to chronic irritation, potentially resulting in irreversible ulnar neuropatrhy
.
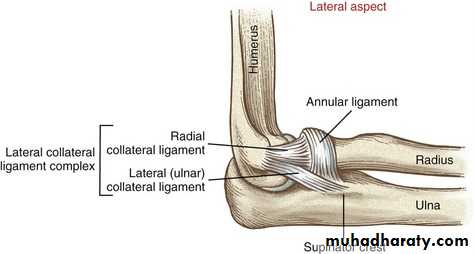
Tennis elbow lateral epicondylitis
is the most common injury in patients seeking medical attention for elbow pain. Exactly what causes tennis elbow is unknown, but it is thought to be due to small tears of the tendons that attach forearm muscles to the arm bone at the elbow joint.
The muscle group involved, the wrist extensors,
function to extend the wrist up wards . Specifically, the extensor carpi radialis brevis has been implicated in causing the symptoms of tennis elbow.
lateral epicondylitis
symptoms of tennis elbowPatients with tennis elbow syndrome experience pain on the outside of the elbow that is worsened by grasping objects and cocking back the wrist. The most common symptoms of tennis elbow are:
1) Pain over the outside of the elbow
2) Pain when lifting objects
3)Pain at rest radiating down the forearm
The pain associated with tennis elbow usually has a gradual onset, but it may also come on suddenly. Most patients with tennis elbow are between the ages of ((35 and 65 years old)), and it affects about an equal number of men and women. Tennis elbow occurs in the dominant arm in about 75 percent of patients. Anyone can be affected, but tennis elbow is most commonly seen in two groups of people
a-Manual LaborersPeople who work with their hands are at greater risk of developing tennis elbow. Jobs that may lead to tennis elbow include plumbers, painters, gardeners, and carpenters.
b-Sports ParticipantsSports participants, especially racquet sport players, are prone to developing tennis elbow. About a third of regular tennis players experience tennis elbow at some point in their careers.
• Tennis Elbow Treatment 1) Ice application on the injured elbow The recommended sports therapy medical treatment for a sprained elbow is to use cold (ice wraps) and compression to stop elbow pain and stop elbow swelling 2) non steroidal Anti –infl.drugs 3) Cortico sterpoid long acting or recently PRP ( platlet rich plasma) injection 4) using of sling or splint for injured elbow
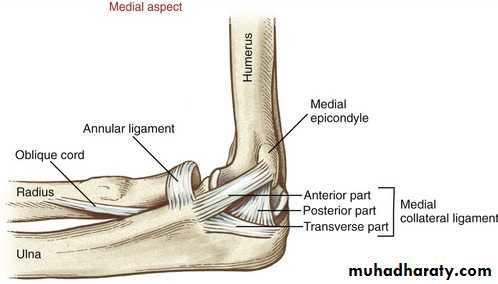
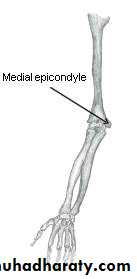
Golfers Elbow ( Throwers Elbow) Medial Epicondylitis
•• Golfer elbow is a similar injury to tennis elbow only it affects the inside of the elbow instead. origin of the flexor muscles common tendon
• Golfer elbow is more common in throwers and golfers hence the 'nicknames'. Also known as flexor / pronator tendinopathy this elbow pain is seen in tennis players who use a lot of top spin on their forehand shots.
• Symptoms of golfer elbow include:
Pain on the bony bit on the inside of the elbow.,,,Weakness in the wrist. Pain on the inside of the elbow when you grip something hard,, ,,Pain when wrist flexion (bending the wrist palm downwards) is resisted,,,Pain on resisted wrist pronation - rotating inwards (thumb downwards).
•
Treatment…
primary measuresIce the injury for two days (20 min's on up to six times a day)
Rest Rest is a very important.
Heat After 2 days apply heat and use a heat retainer..
Definitive measures
1)Apply ultrasound or laser treatment.
2)Prescribe anti-inflammatory medication.
3)Use sports massage techniques.
4)Give a steroid injection.or PRP injection
5) Use a forearm brace or heat retainer if you have a weak wrist or elbow
6)Correct technique - especially if you are a thrower. See a good coach if you are not sure how.
.
•
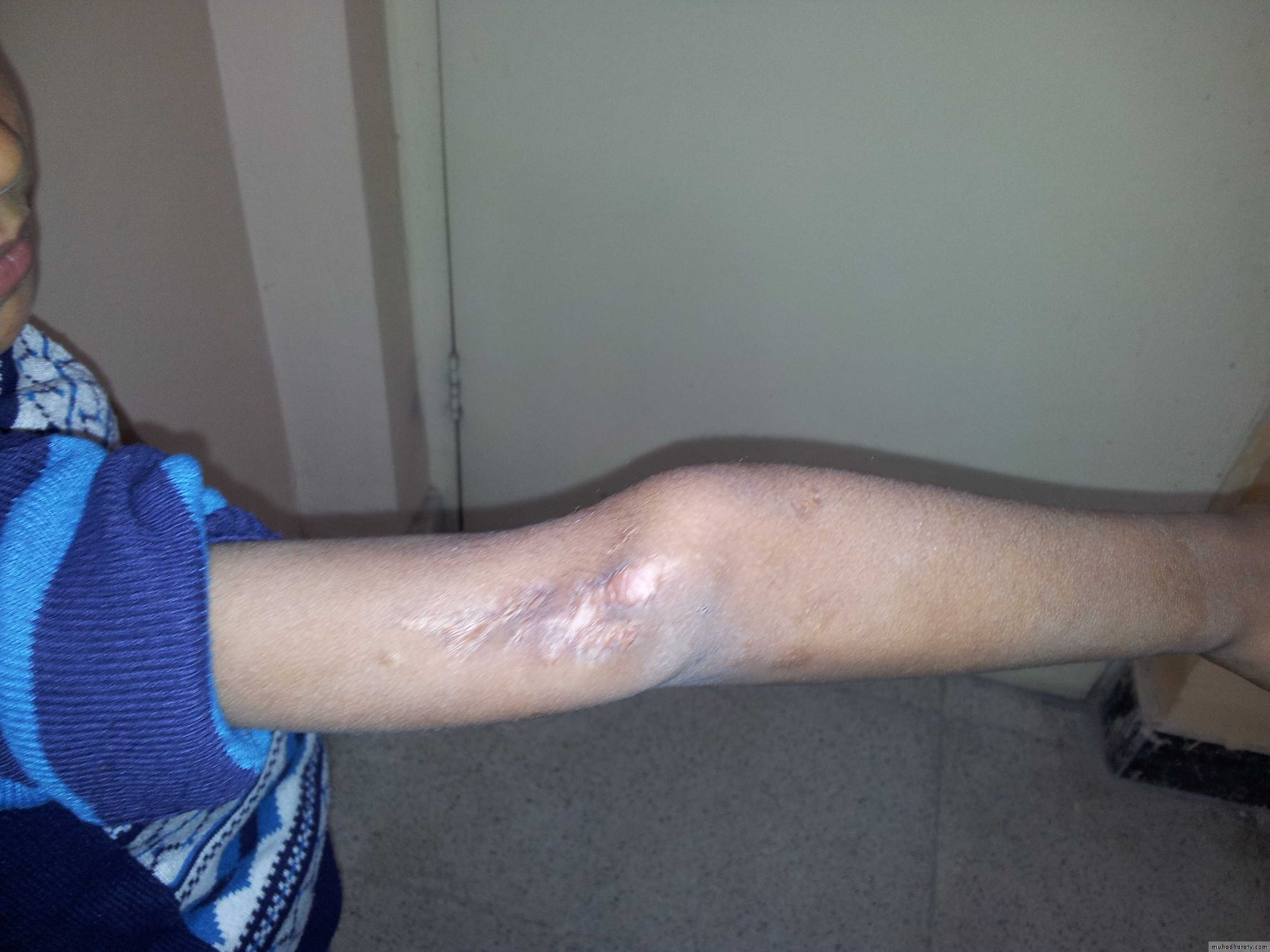
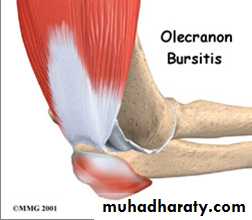
Olecranon bursitis student elbow
neighbours elbow.The bursa behind the olecranon process sometimes becomes enlarged as a result of pressure or friction,When it becomes painful; it is likely to be infection, gout or rheumatoid arthritis.
Causes A. Traumatic bursitis (students elbow).
The bursa is distended with clean fluid. Treatment: first by aspiration followed by injection of hydrocortisone into the bursa, if the swelling reoccur then the bursa should be excised.
B. Septic bursitis ;-With sign & symptom of inflammation: treatment by course of antibiotics but if it becomes an abscess with pus, then treatment is incision for adequate drainage.
C. Gouty bursitis
There is usually a history of previous gouty attack. Could be bilateral.
There is whitish deposite of sodium biurate (tophi), and it maybe visible through the walls of the bursa.
In acute attack it is difficult to distinguish it from septic bursitis (unless pus is aspirated) definitive treatment is by : excision of the bursa.
D. Rheumatoid arthritis:
Causes both swelling and nodularity foermation over the olecranon.In almost all the cases it is associated with typical symmetrical polyarthritis.