TOOTHBRUSHING METHODS
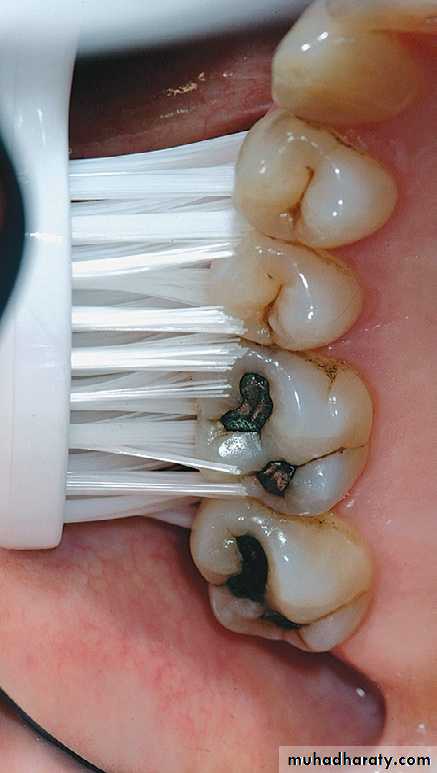
Place the toothbrush so that the bristles are angled approximately 45 degrees from the tooth surfaces.Start at the most distal tooth in the arch, and use a vibrating, back-and-forth motion to brush.
BASS METHOD
Patients with periodontal disease are most frequently taught a sulcular brushing technique using a vibratory motion to improve access in the gingival areas. This is referred to as “target hygiene.”The method most often recommended is the Bass technique because it emphasizes sulcular placement of bristles, adapting the bristle tips to the gingival margin to reach the supragingival plaque and accessing subgingival plaque to the extent possible
Brushing with Powered Toothbrushes
The various mechanical motions built into powered toothbrushes do not require special techniques. The patient needs only place the brush head next to the teeth at the gingival margin, using a targeted hygiene approach, and proceed systematically around the dentition.Round-head placement
Straight-head placement
Recommendations
• Targeted hygiene focuses brushing efforts on the cervical and interproximal portions of the teeth, where microbial plaque accumulates first.• Brushing with either a manual or a powered toothbrush requires a systematic routine to clean all the accessible areas.
• Patients will modify any technique to their needs but must achieve the goal of brushing until the teeth are free of plaque.
INTERDENTAL CLEANING AIDS
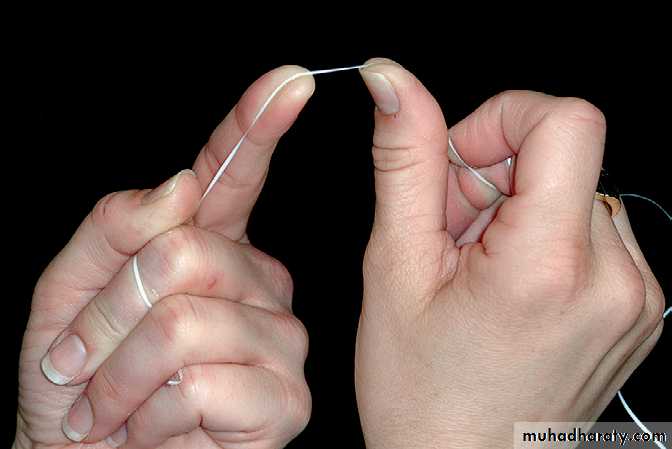
Dental FlossDental floss is the most widely recommended tool for removing plaque from proximal tooth surfaces. Floss is made from nylon filaments or plastic monofilaments, and can be waxed, unwaxed, thick, thin, and even flavored.
Clinical research has demonstrated no significant differences in the ability of the various types of floss to remove dental plaque; they all work equally well.
Factors influencing the choice of dental floss include the tightness of tooth contacts, roughness of proximal surfaces, and the patient’s manual dexterity, not the superiority of any one product. Therefore recommendations about type of floss should be based on ease of use and personal preference.
Technique
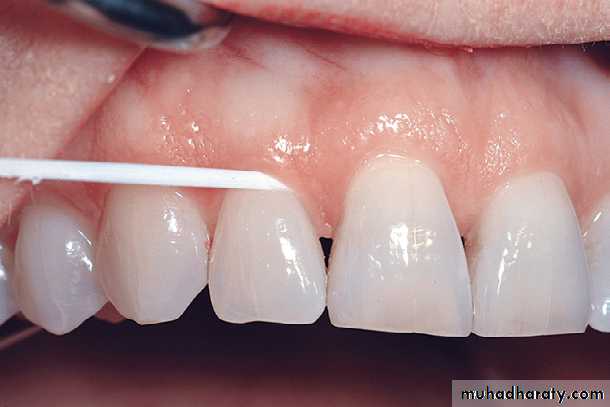
)) Stretch the floss tightly between the thumb and forefinger, or between both forefingers, and pass it gently through each contact area with a firm back-and-forth motion.)) Once the floss is apical to the contact area between the teeth, wrap the floss around the proximal surface of one tooth, and slip it under the marginal gingiva. Move the floss firmly along the tooth up to the contact area and gently down into the sulcus again, repeating this up-and-down stroke two or three times. Then, move the floss across the interdental gingiva, and repeat the procedure on the proximal surface of the adjacent tooth.
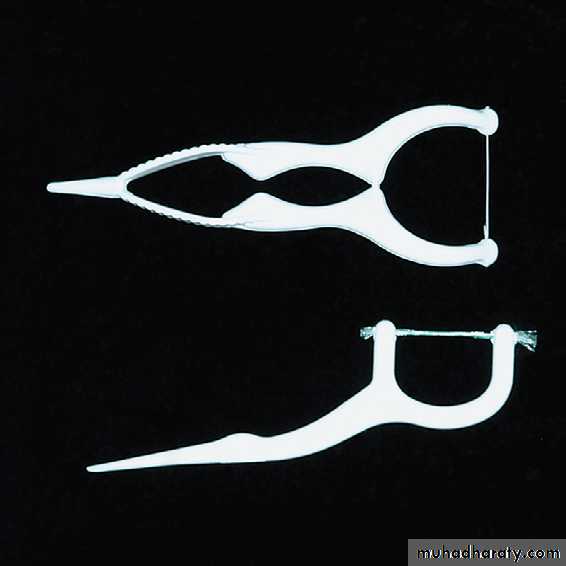
Flossing can be facilitated by using a floss holder. Floss holders are helpful for patients lacking manual dexterity and for caregivers assisting patients in cleaning their teeth. A floss holder should be rigid enough to keep the floss taut when penetrating into tight contact areas, and it should be simple to string with floss. The disadvantage is that floss tools are time-consuming because they must be rethreaded frequently when the floss shreds.
Powered flossing devices are also available. The devices have been shown to be safe and effective, but no better at plaque removal than holding the floss in the fingers.
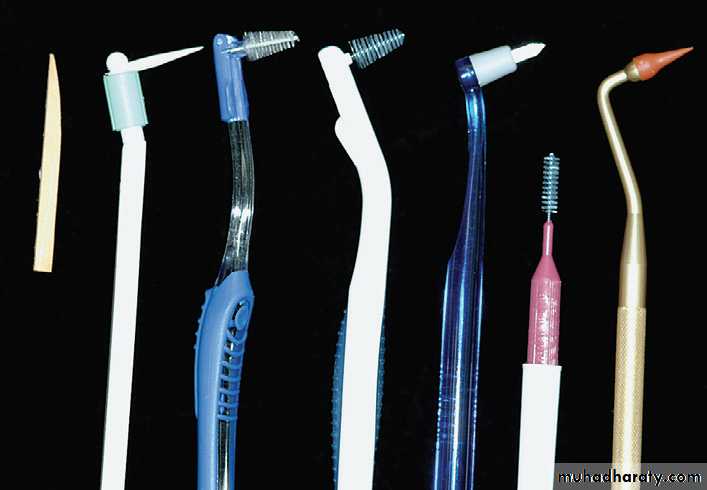
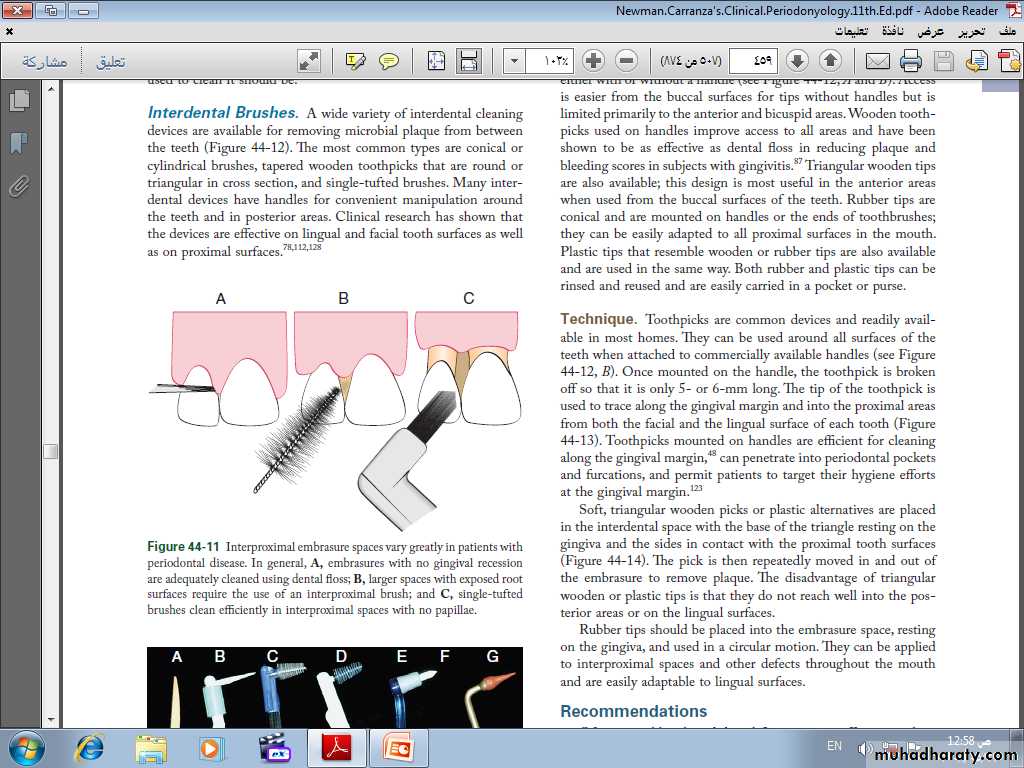
Interdental Cleaning Devices
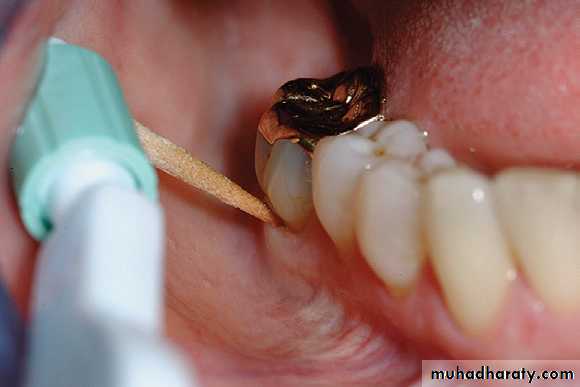
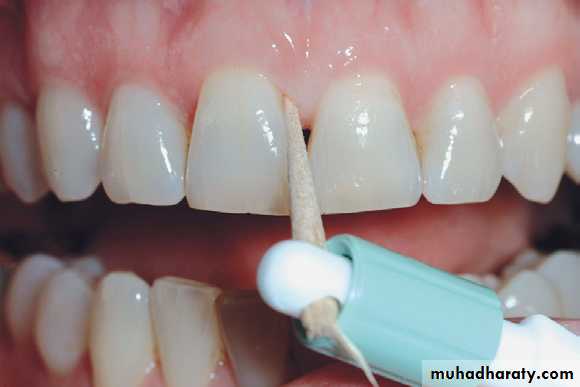
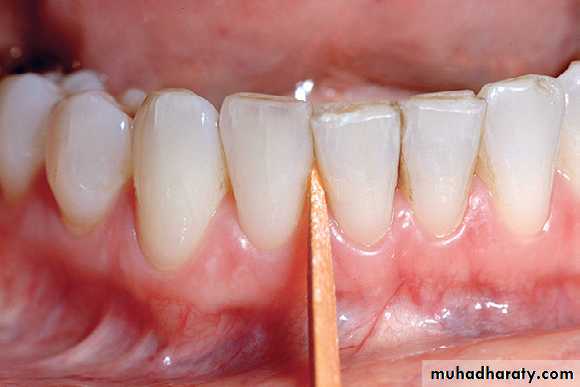
wooden tips
interproximal brushesrubber tip
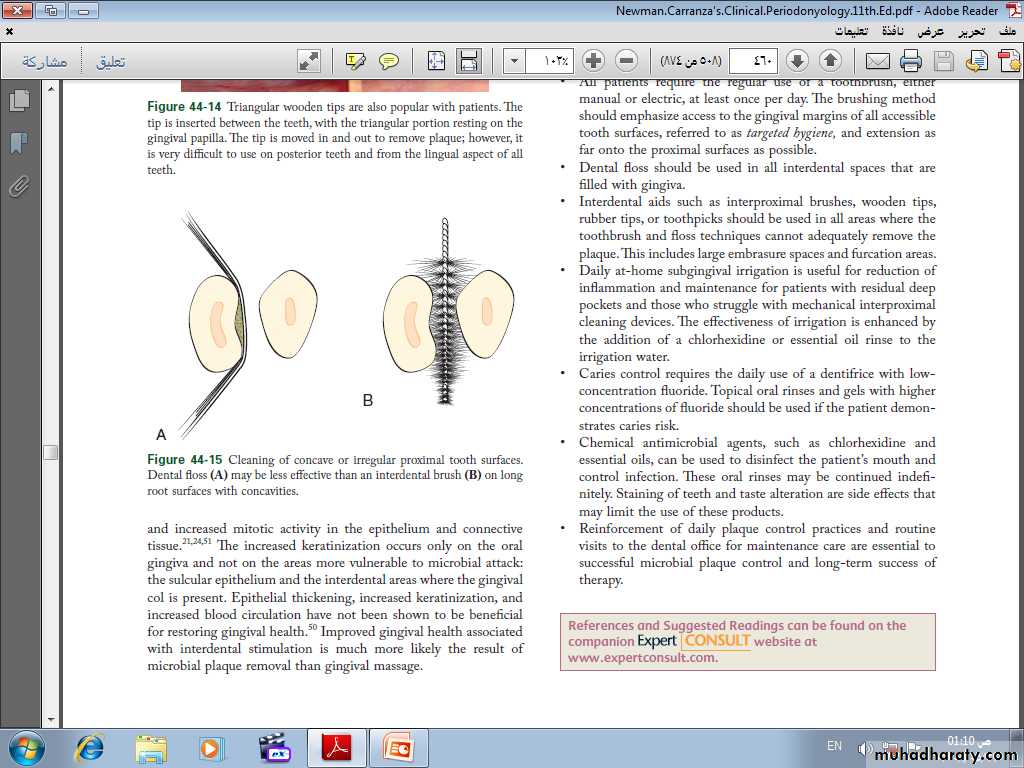
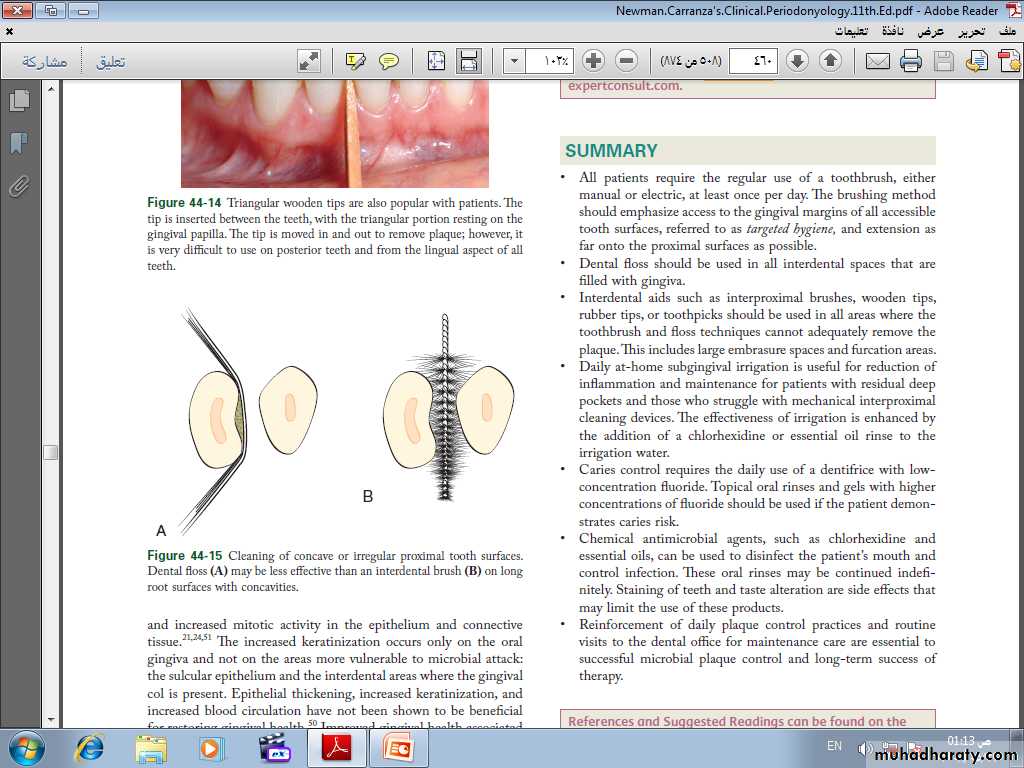
Wooden toothpicks
Recommendations
• Often a toothbrush and dental floss are not sufficient to clean interdental spaces adequately, so it is extremely important to find an interdental device that the patient likes and will use.• Many interdental cleaning aids are available for patients. The patient might need to try several devices before finding one that is acceptable and cleans adequately.
• In general, the largest brush or device that fits into a space will clean most efficiently.
Scaling and Root Planing
CLASSIFICATION OF PERIODONTAL INSTRUMENTSPeriodontal Probes
ExplorersScaling and Curettage Instruments
Cleansing and Polishing Instruments
Periodontal probes are used to locate, measure, and mark pockets, as well as determine their course on individual tooth surfaces.
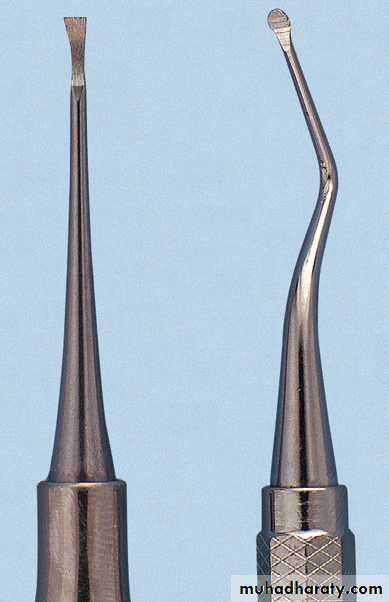
Explorers
Explorers are used to locate subgingival deposits and carious areas and to check the smoothness of the root surfaces after root planing. Explorers are designed with different shapes and angles, with various uses.
Scaling and Curettage Instruments
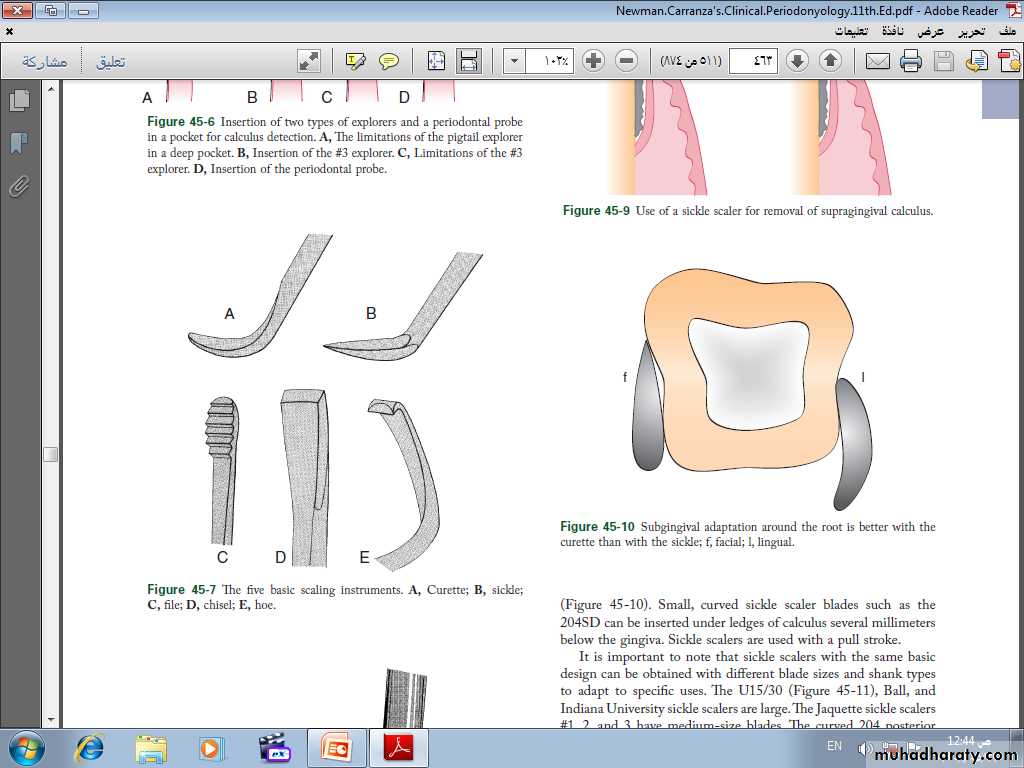
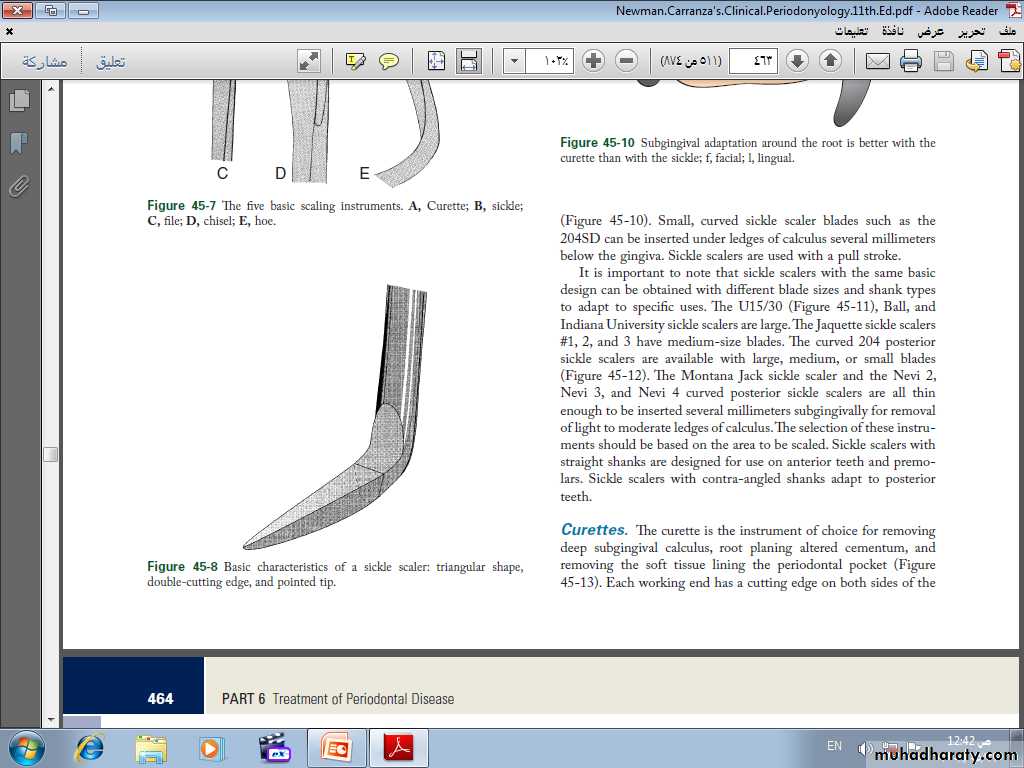
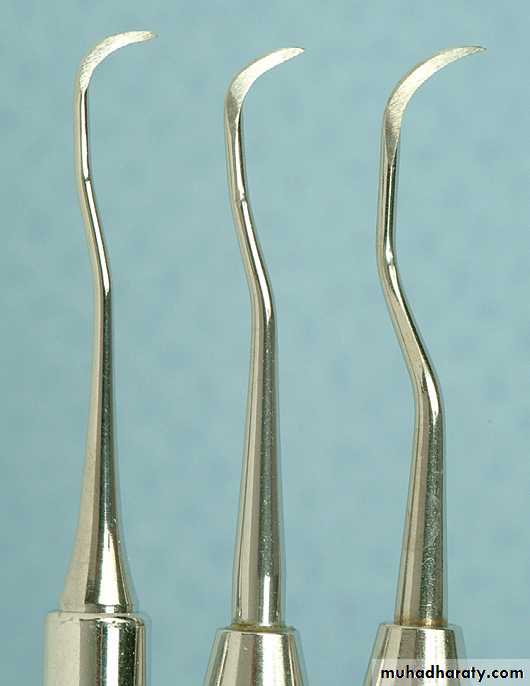
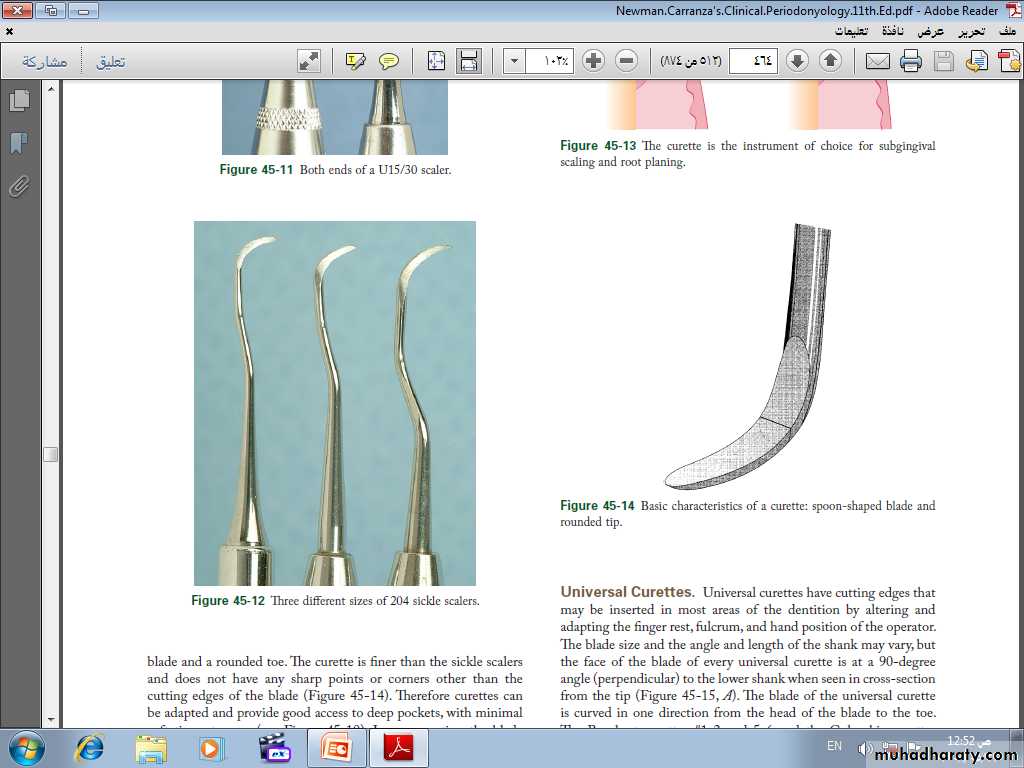
Sickle Scalers. Sickle scalers have a flat surface and two cutting edges that converge in a sharply pointed tip. The shape of the instrument makes the tip strong so that it will not break off during use. The sickle scaler is used primarily to remove supragingival calculus. Sickle scalers are used with a pull stroke.
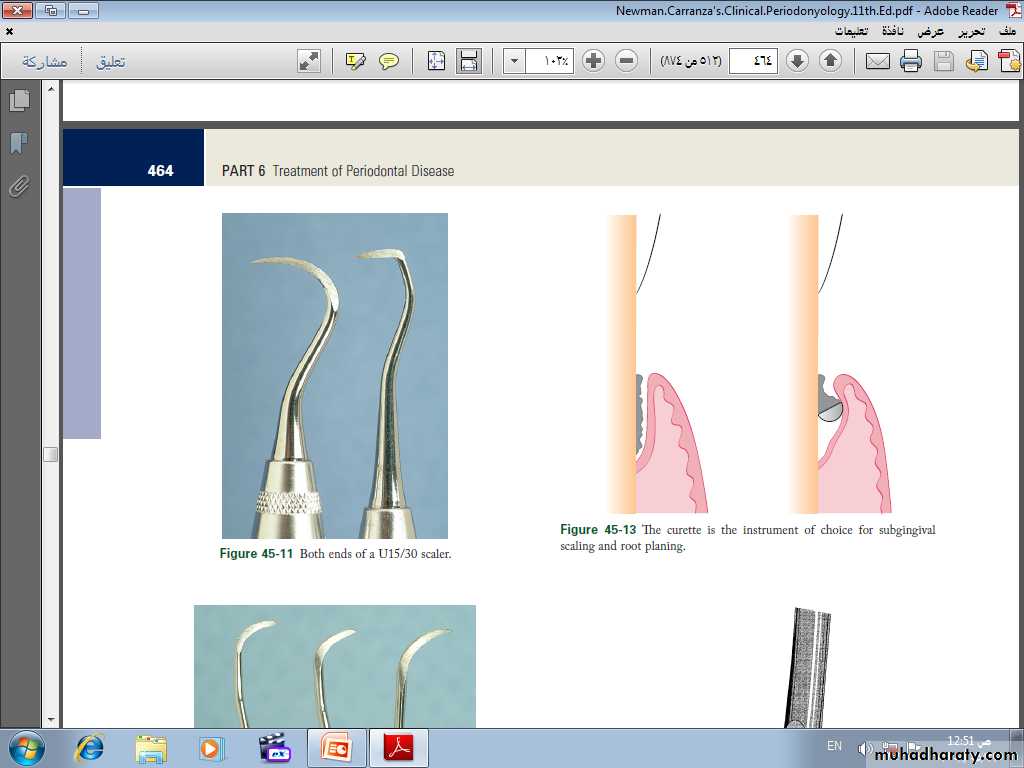
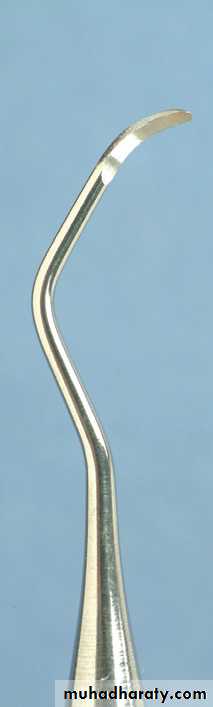
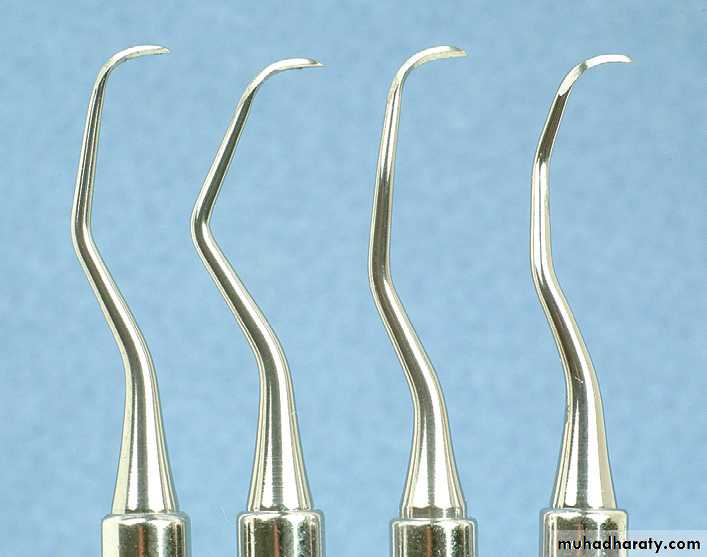
Curettes. The curette is the instrument of choice for removing deep subgingival calculus, root planing altered cementum, and removing the soft tissue lining the periodontal pocket
The curette is finer than the sickle scalers and does not have any sharp points or corners other than the cutting edges of the blade Therefore curettes can be adapted and provide good access to deep pockets, with minimal soft tissue trauma.
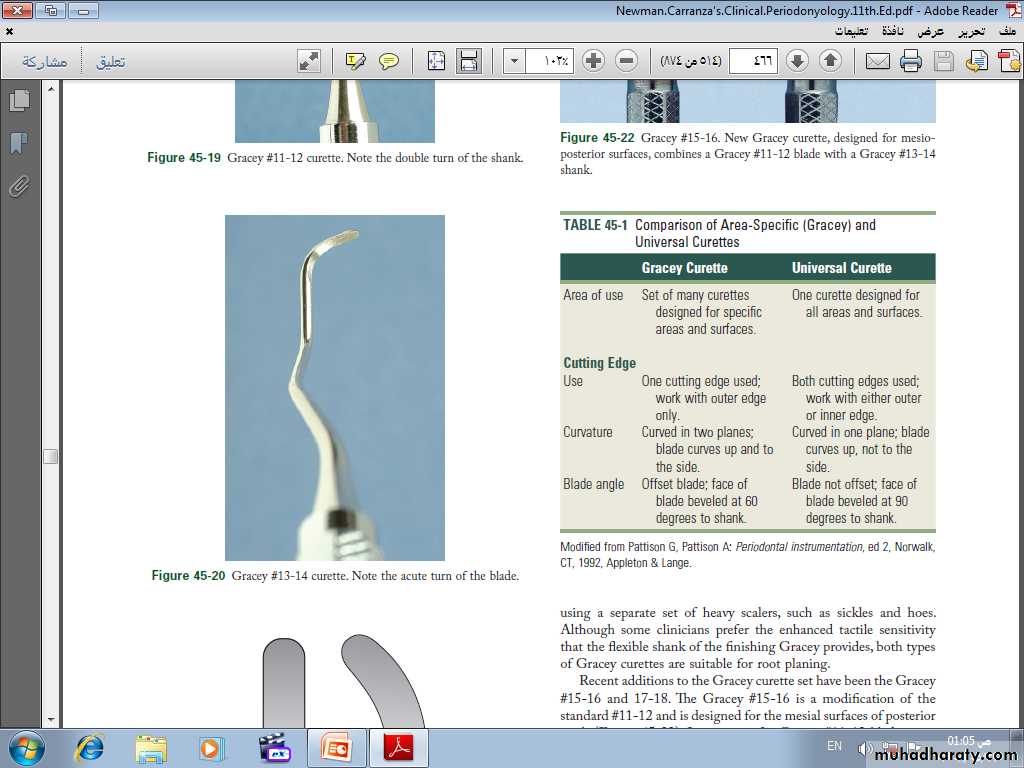
Universal Curettes. Universal curettes have cutting edges that may be inserted in most areas of the dentition by altering and adapting the finger rest, fulcrum, and hand position of the operator.
The blade size and the angle and length of the shank may vary, but the face of the blade of every universal curette is at a 90-degree angle (perpendicular) to the lower shank when seen in cross-section from the tip
Area-Specific Curettes
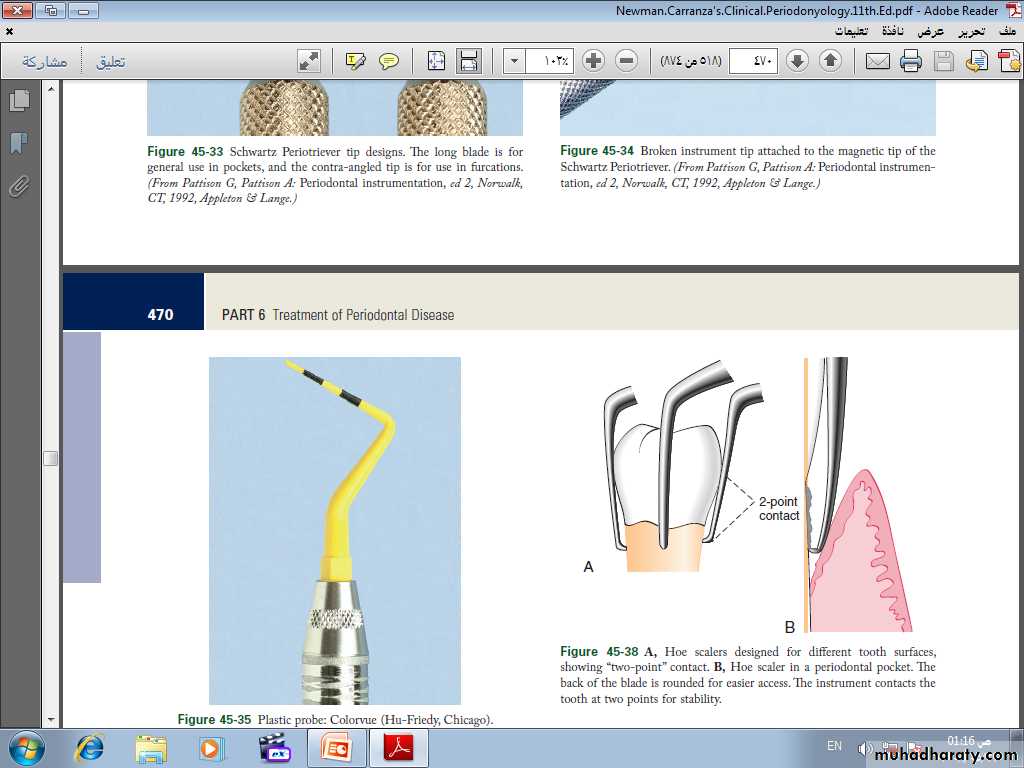
Gracey Curettes. Gracey curettes are representative of the area specific curettes, a set of several instruments designed and angled to adapt to specific anatomic areas of the dentitionHoe Scalers. Hoe scalers are used for scaling of ledges or rings of calculus. The blade is bent at a 99-degree angle; the cutting edge is formed by the junction of the flattened terminal surface with the inner aspect of the blade. The cutting edge is beveled at 45 degrees.
The blade is slightly bowed so that it can maintain contact at two points on a convex surface. Hoe scalers are used in the following manner:
1. The blade is inserted to the base of the periodontal pocket so that it makes two-point contact with the tooth. This stabilizes the instrument and prevents nicking of the root.
2. The instrument is activated with a firm pull stroke toward the crown, with every effort being made to preserve the twopoint contact with the tooth.
Chisel Scalers. The chisel scaler, designed for the proximal surfaces of teeth too closely spaced to permit the use of other scalers, is usually used in the anterior part of the mouth. It is a double-ended instrument with a curved shank at one end and a straight shank at the other; the blades are slightly curved and have a straight cutting edge beveled at 45 degrees.
Files. Files have a series of blades on a base. Their primary function is to fracture or crush large deposits of tenacious calculus or burnished sheets of calculus. Files can easily gouge and roughen root surfaces when used improperly. Therefore they are not suitable for fine scaling and root planing
To be continued…