د. منى زهير
Lec.5Umbilical Cord
Development of the umbilical cord:
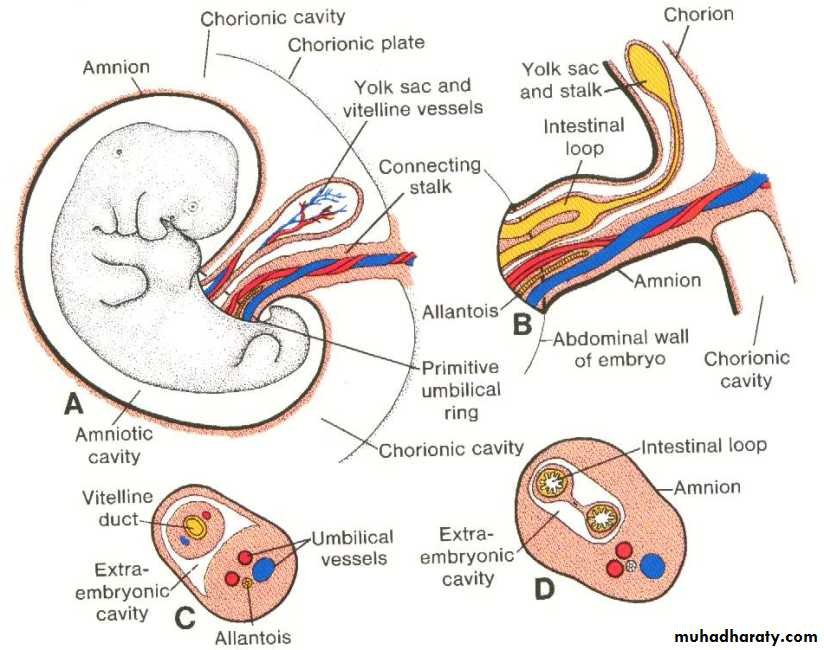
The junction between the ectoderm and amnion (the amino-ectodermal junction) is oval shaped, it is known as the primitive umbilical ring. During the 5th week of development, the following structures pass through this ring are :The connecting stalk, contain the allantois and the umbilical vessels (2 arteries + 1 vein).
Vitelline duct ( yolk sac stalk) with the vitelline vessels.
The canal connecting the intra and extra embryonic coelomic cavities.
During further development:
the amniotic cavity expands and the amnion begins to envelop the connecting stalk and yolk sac stalk forming the primitive umbilical cord, which contains:Proximally: the remnant of allantois and some intestinal loops in addition to the umbilical vessels.
Distally the cord contains the yolk sac and the umbilical vessels, (in addition to the canal connecting the intra and extra embryonic coelomic cavities).
At the end of the 3rd month:
The amniotic cavity expands more and more and comes in contact with the chorion, thereby obliterating the chorionic cavity.The yolk sac shrinks and gradually obliterated.
The intestinal loops are withdrawn into the body of the embryo.
The coelomic canal in the cord is obliterated.
Then the allantois and vitelline ducts, and vessels are obliterated.
So all that remains in the cord are the umbilical vessels surrounded by the jelly of Wharton. This tissue is rich in mucopolysaccharides and functions as a protective layer for the blood vessels.
At birth the umbilical cord is about 2 cm in diameter and 50-60 cm in length. It is tortuous, causing false knots.
Amniotic fluid (Liquer amnii):
It is a clear, watery fluid that fills the amniotic cavity.
It is produced partly by amniotic cells and derived primarily from maternal blood.
The amount of fluid increases gradually reaching 1000 ml at 37 weeks of pregnancy and the volume of amniotic fluid is replaced every 3 hours.
From the beginning of the 5th month, the fetus swallows about 400 ml/day of its own amniotic fluid. Fetal urine is added daily to the amniotic fluid in the 5th month but this urine is mostly water, since the placenta is functioning as on exchange of metabolic wastes.
The main functions of the amniotic fluid are :
Serves as a protective cushion and absorbing jolts since the embryo is suspended by its umbilical cord in this fluid.
Prevents adherence of the embryo to the amnion.
Serves as a medium allowing the fetus to move freely.
Keeps the fetus at an even temperature.
If the amount of amniotic fluid is more than 1500 ml the condition is known as polyhydramnios.
If the amount of amniotic fluid is less than 400 ml the condition is known as oligohydramnios.
Polyhydramnios occur when the fetus has esophageal atresia that prevent the fetus from swallowing the fluid.
Oligohydramnios is rare and may result from fetal renal agensis.
Twins (Multiple pregnancy) :
The multiple pregnancy is uncommon in human it ranges from 2-8% but it is extremely rare to have more than four twins.
Types of Twins:
Essentially two types of twins are common :
Dizygotic (fraternal) twins :
Occur in 70-75% of cases.
Results from the shedding of two oocytes at the same time from one ovarian cycle that will be fertilized by two different sperms.
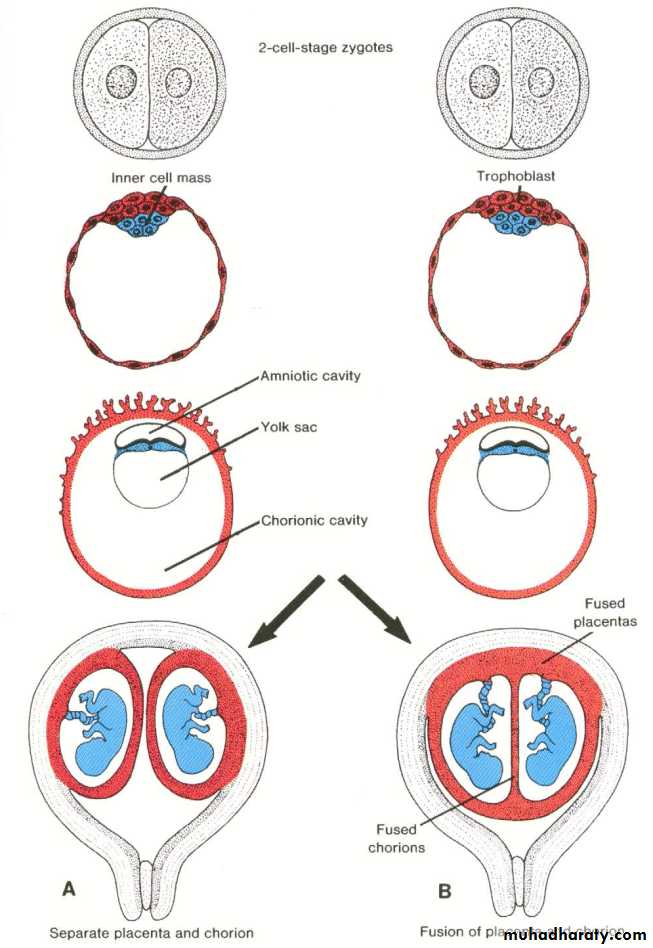
Each zygote will implant separately and develops its own placenta, its own amnion, and its own chorionic sac.
The two placenta may be located so close together that fusion occurs, similarly the walls of the chorionic sacs may also came into close apposition and fuse.
The individual members, have different genetic constitution, may or may not be of the same sex.
Monozygotic (identical) twins :
Occur in 25-30% of cases.They develop from a single fertilized oocyte .
Result from the splitting of the zygote at various stages of development.
So the identical members have the same genetic constitution, the same sex, the same blood group, the same finger prints and external features.
Stage of splitting :
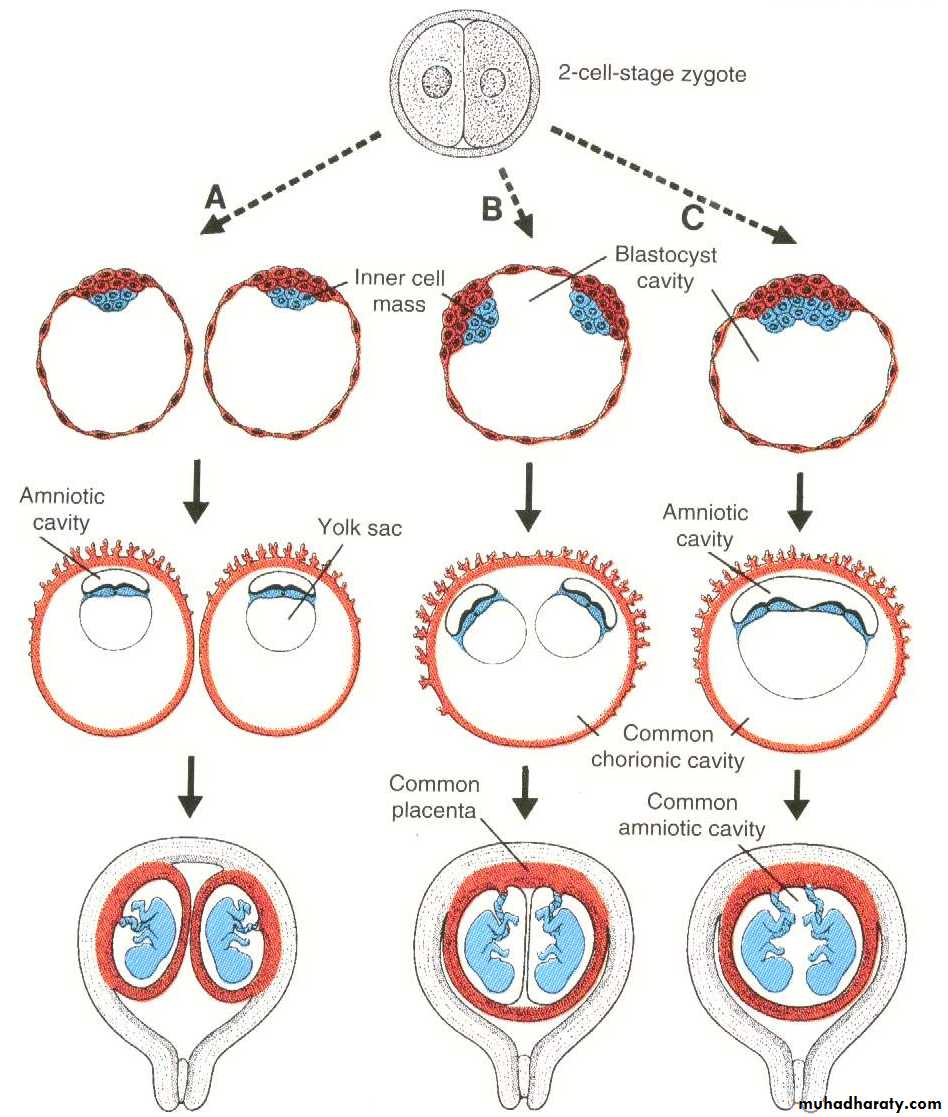
At the two cell stage : two separate zygotes develop. Both implant separately, each embryo has its own placenta, chorion and amnion. (Similar to Dizygotic twin).
At early blastocyst stage : the inner cell mass divided into two groups of cells within the same blastocyts cavity. The embryos have a common placenta and chorionic sac but a separate amniotic cavity.
At the stage of bilaminar germ disc just before the appearance of the primitive streak. The two embryos will share a common placenta, chorionic sac and amniotic sac.
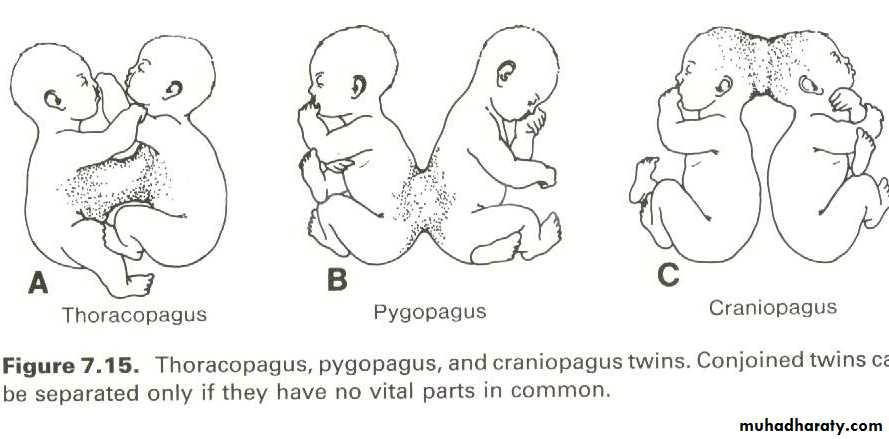
In the later stages of development this will result in an incomplete separation of the axial area of the germ disc leading to the formation of the conjoined twins (also called Siamese twins or double monsters). According to the nature and degree of union they are classified as: thoracopagus, pyopagus, and craniopagus.. The separation of these twins can be done by surgical operation only if they not share a vital organs.