Schistosoma spp.
S. japonicum
S. haematobiumS. mansoni
Lateral spine
Terminal spine
Rounded spine
Schistosoma spp.
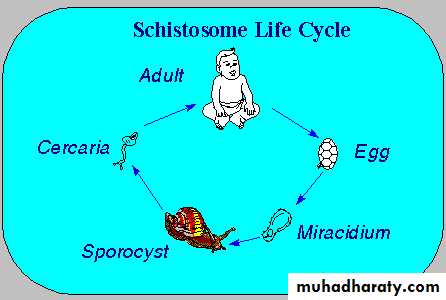
Also known as bilharzia, cause schistosomiasis or bilhariziasis.Schistosoma spp. have 4 stages:
Eggs, miracidia, cercaria, and adult stage.
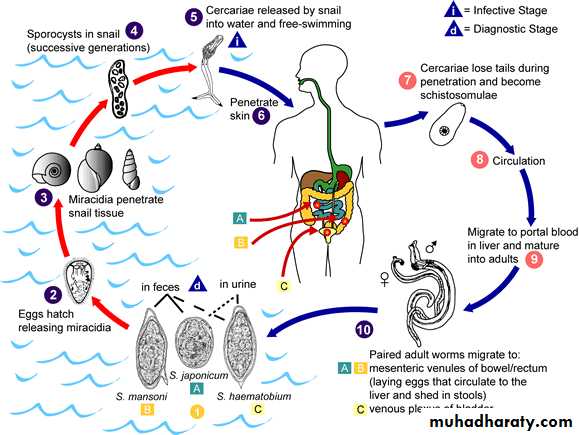
Eggs are passed through urine or feces to fresh water, where larvae stage can infect a new host by penetrating the skin.
Schistosoma spp.
There are three medically important species:
Schistosoma mansoni, lives in the mesenteric venules of large intestine, and cause intestinal bilharziasis.
Schistosoma japonicum, lives in the mesenteric venules of small intestine.
Schistosoma haematobium, lives in the venous plexus of the urinary bladder and cause schistosomal hematuria or urinary bilhariziasis.
S. mansoni and S. japonicum are produce their eggs in stool, but S. haematobium produce eggs in urine.
Schistosoma spp.
Intermediate host: snail.Definitive host: human.
infective stage: Cercaria
diagnostic stage: eggs
Morphology
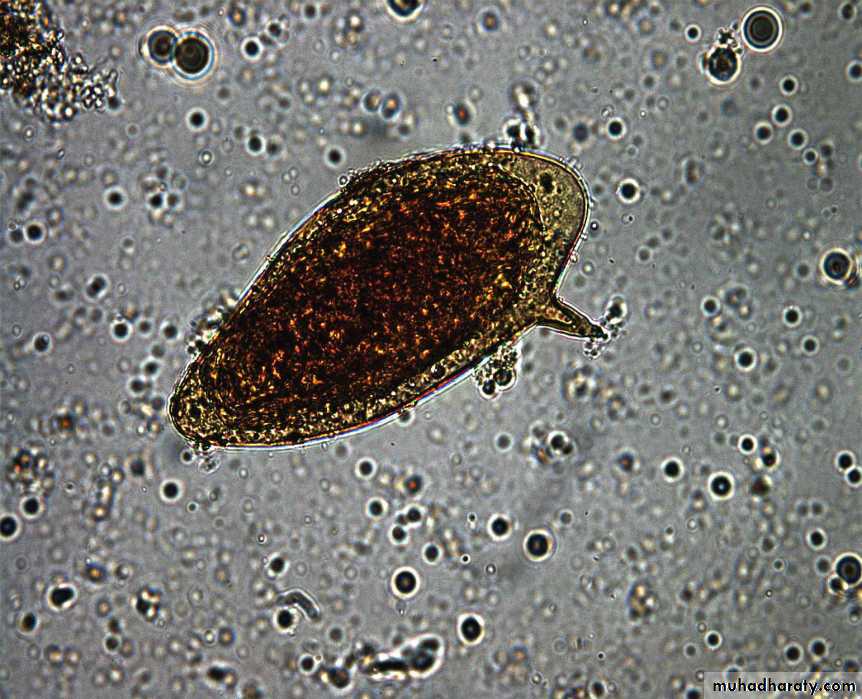
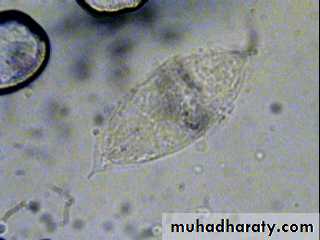
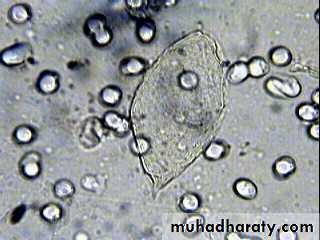
• Schistosoma spp. EggsDepends on finding the characteristic ova in feces or urine.
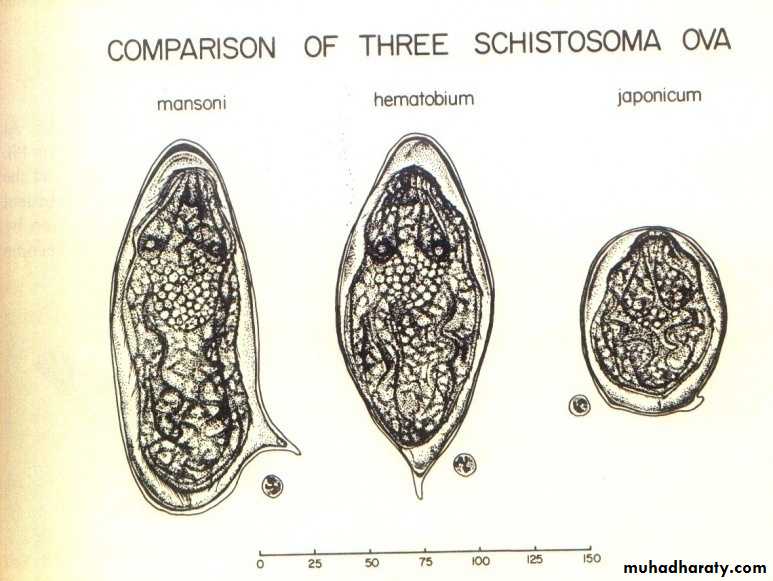
Three species can be distinguished by the appearance of their eggs under microscope:
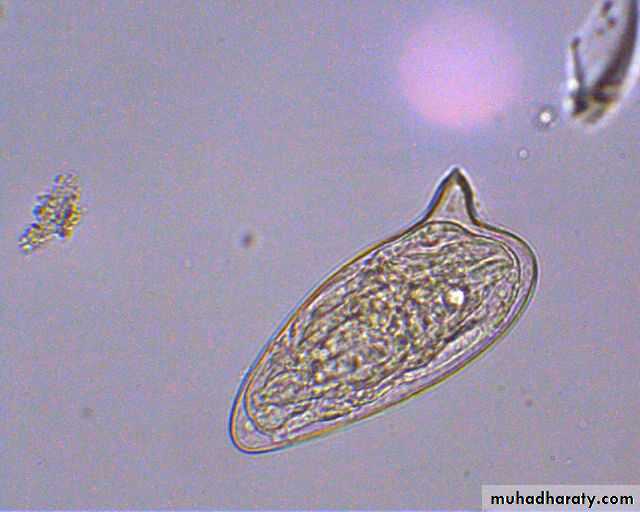
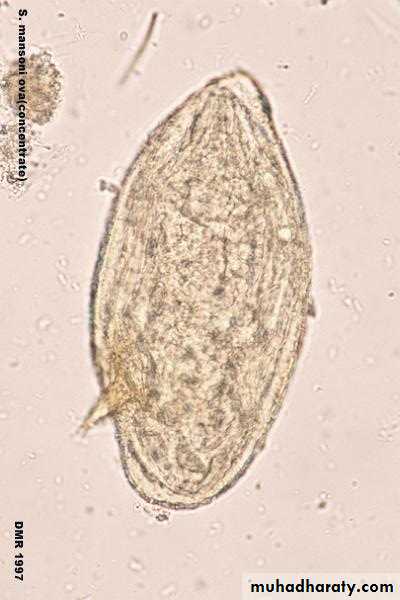
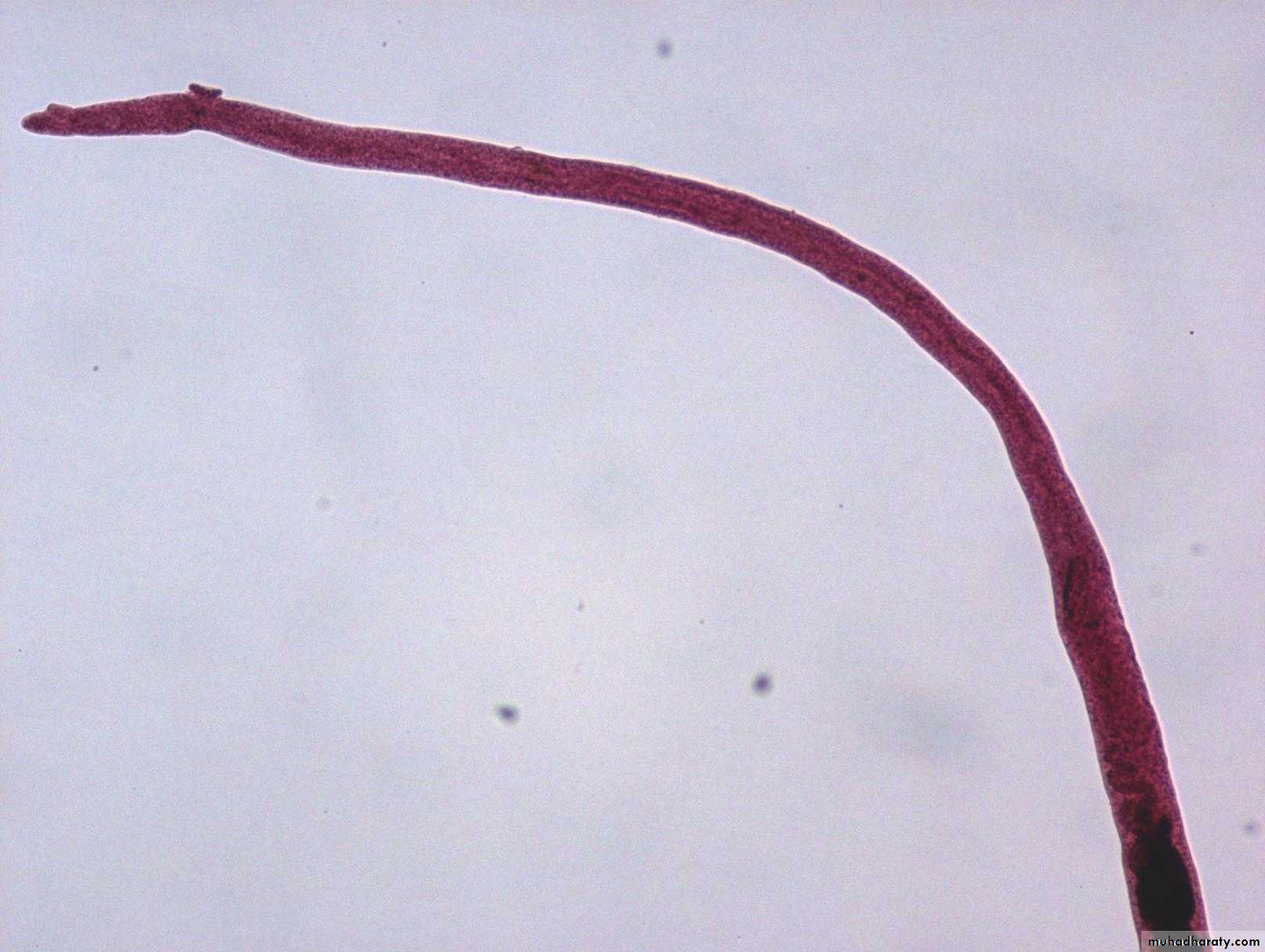
S. mansoni eggs have prominent lateral spine.
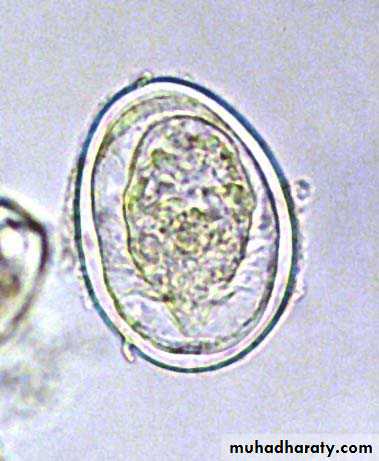
S. japonicum eggs have a very small round lateral spine.
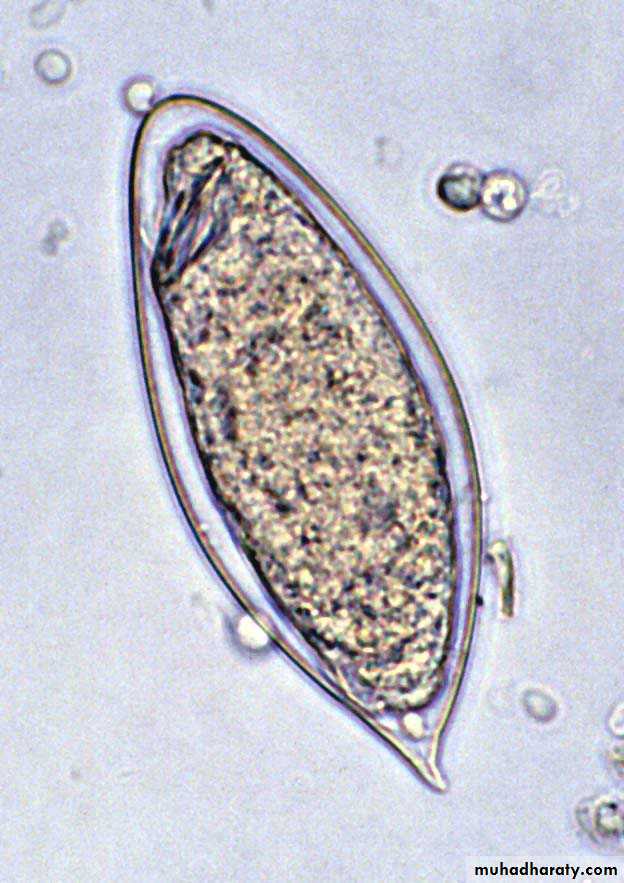
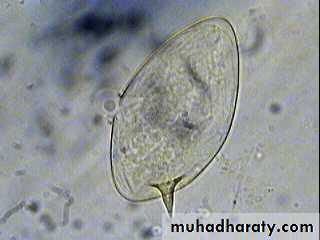
S. haematobium eggs have a terminal spine.
Schistosoma spp. Eggs
S. japonicum
S. haematobiumS. mansoni
Lateral spine
Terminal spine
Rounded spine
Schistosoma haematobium Egg
Schistosoma mansoni Egg
Schistosoma japonicum Egg
Figure : Ova of Schistosoma spp.
( in urine )( in stool )
( in stool )
Iodine s.Saline s.
Fig. 5: Schistosoma mansoni Egg
R. B. C
In Saline
Iodine stain
Eggs
R. B. CFig. 12 : S. haematobium eggs
Iodine s.
Saline s.
Saline s.
Morphology
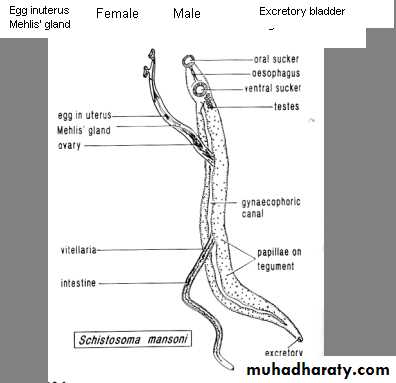
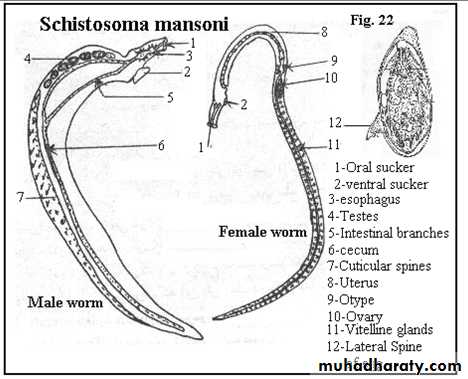
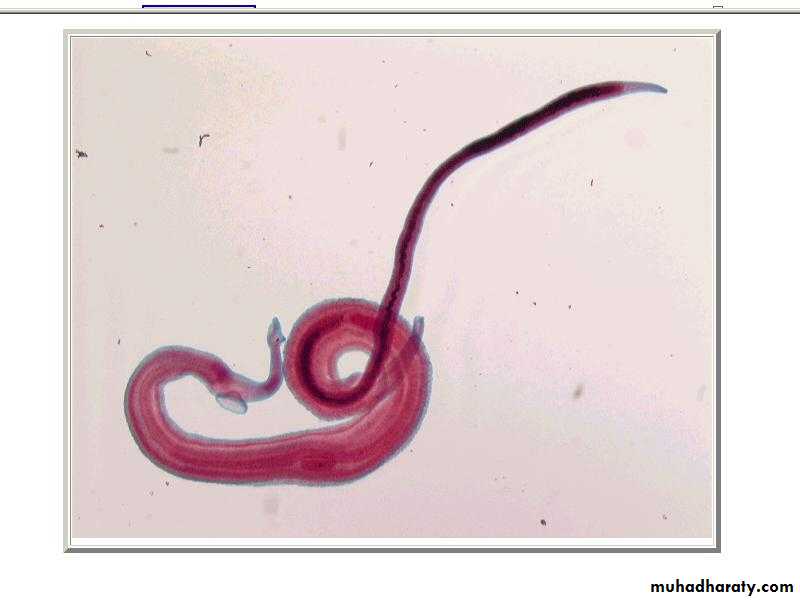
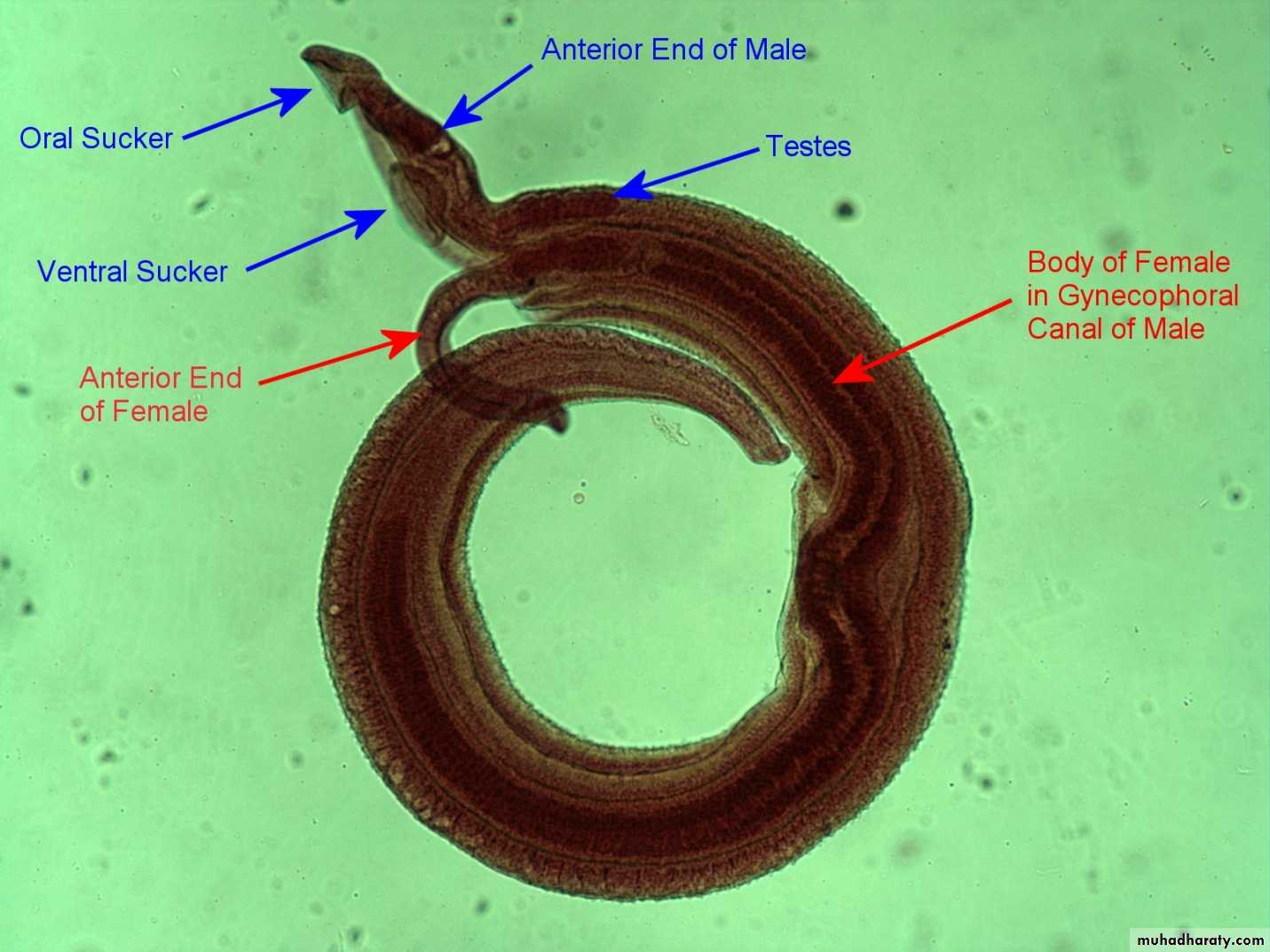
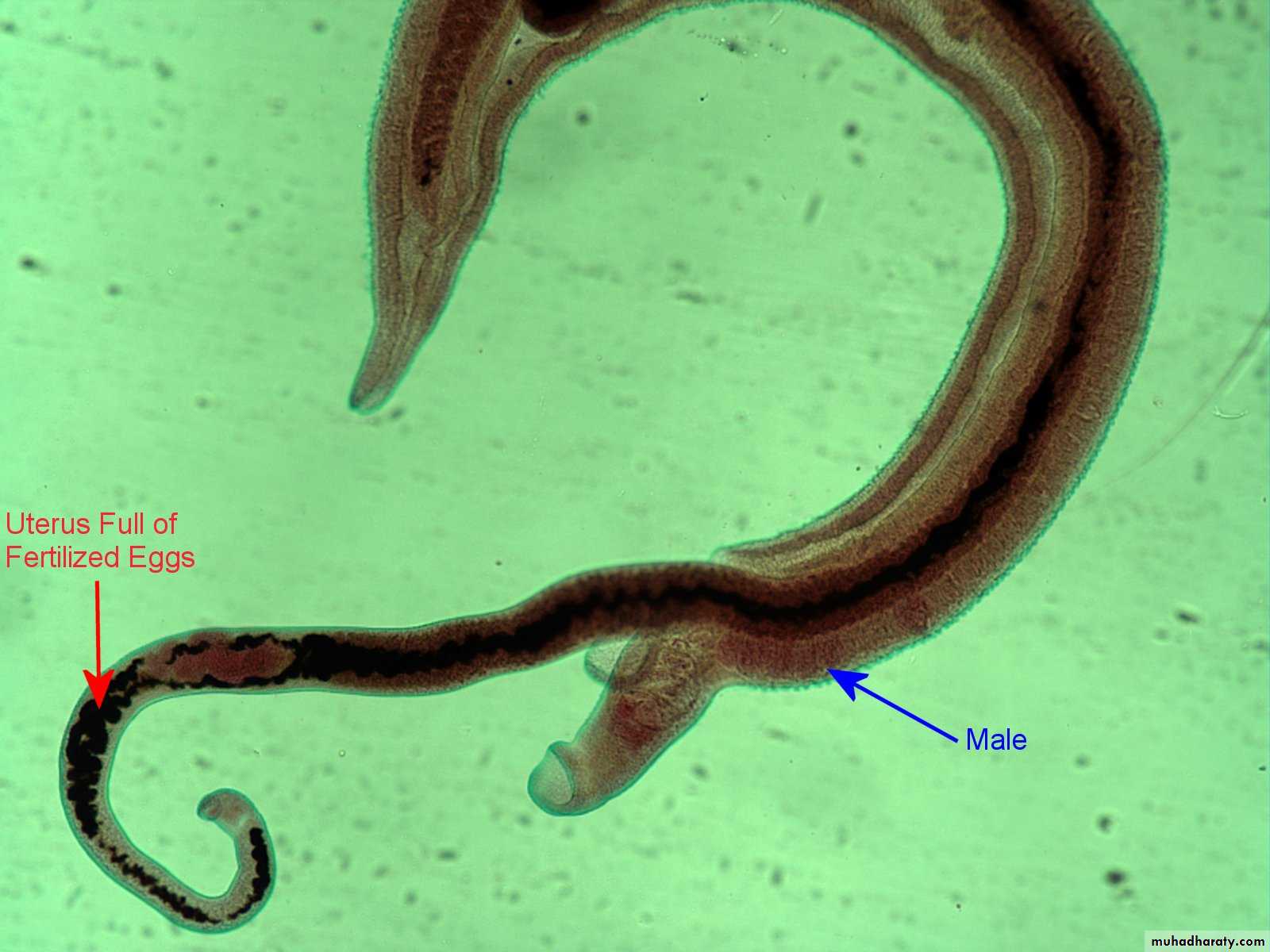
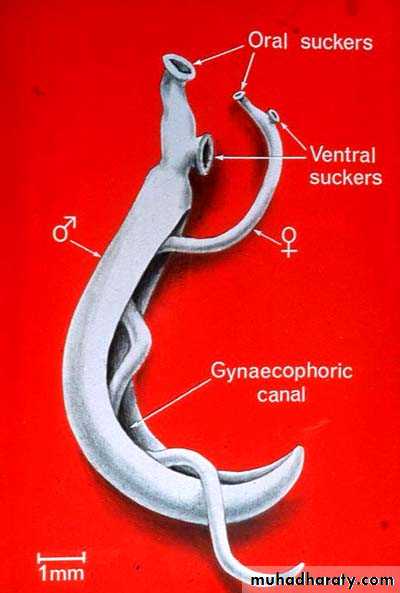
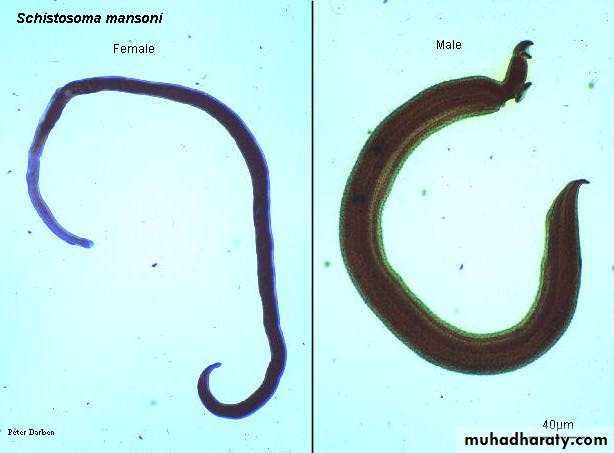
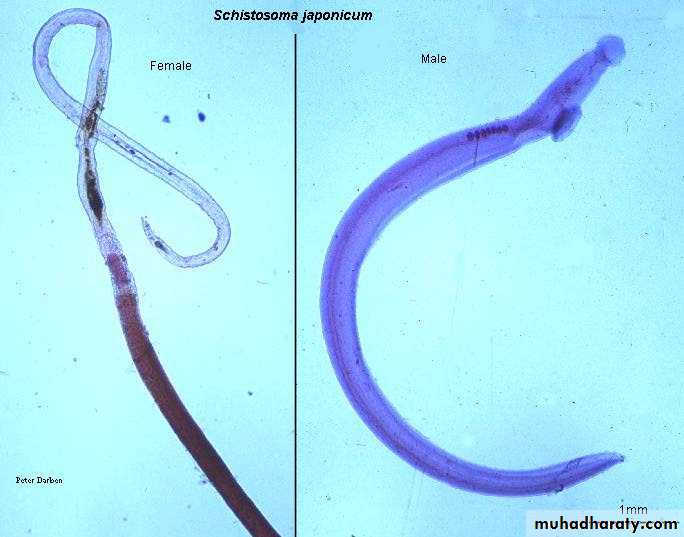
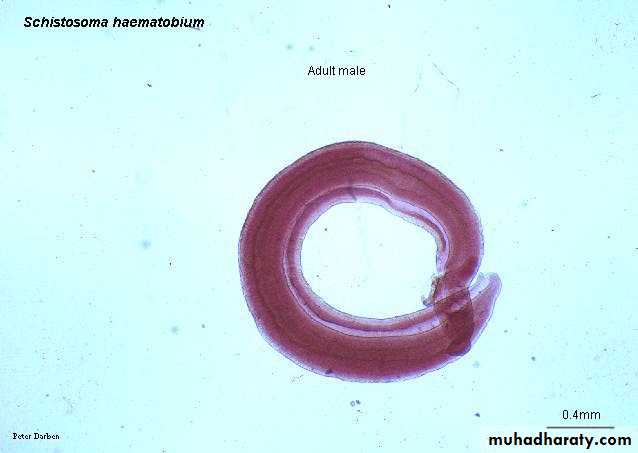
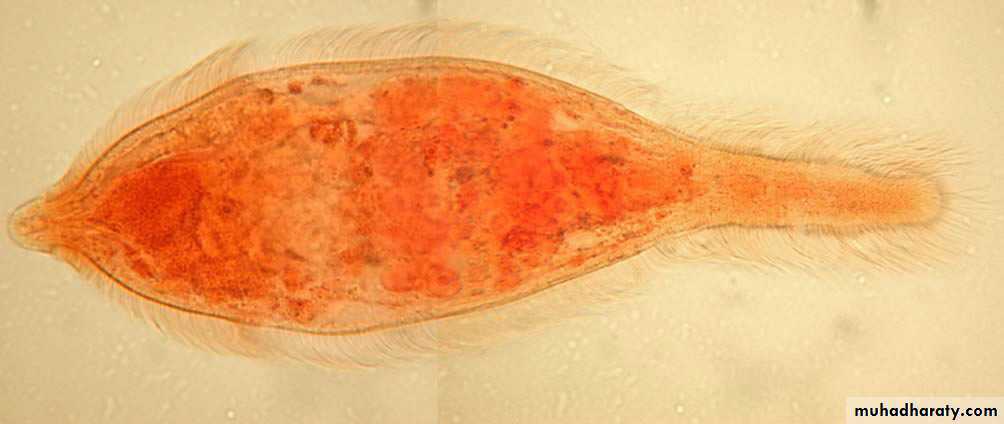
Schistosoma adult male:Adult male short from female.
thick than adult female .
have gyanchophoric canal.
Morphology
Schistosoma adult femaleAdult female longer from male.
thinner than adult male.
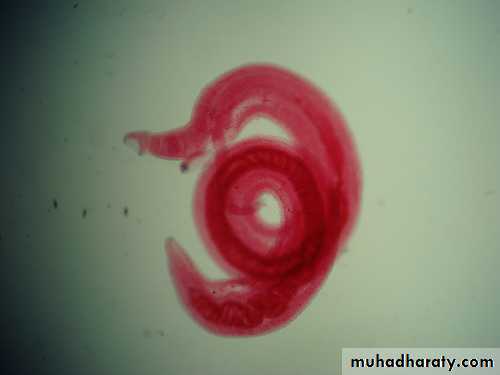
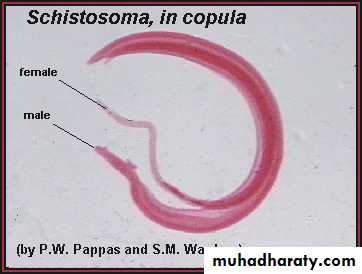
Schistosoma mansoni Male-Female Copula
MaleFemale
Oral suckerVentral sucker
2/25/201816
Figure : Schistosoma mansoni male and female in copula
Figure 3: Schistosoma mansoni male and female in copula
Fig. 4 : S. mansoni, female and male
Fig. 8: Schistosoma japonicum female and male
Methylene blue s.Fig. 11 : Schistosoma haematobium female and male
Eosin s.Morphology
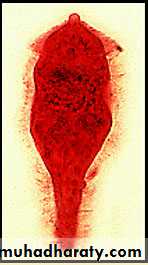
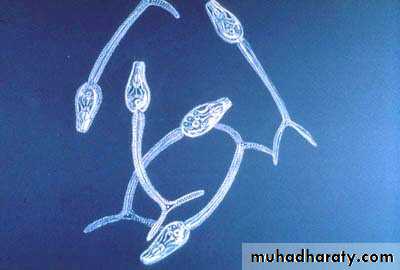
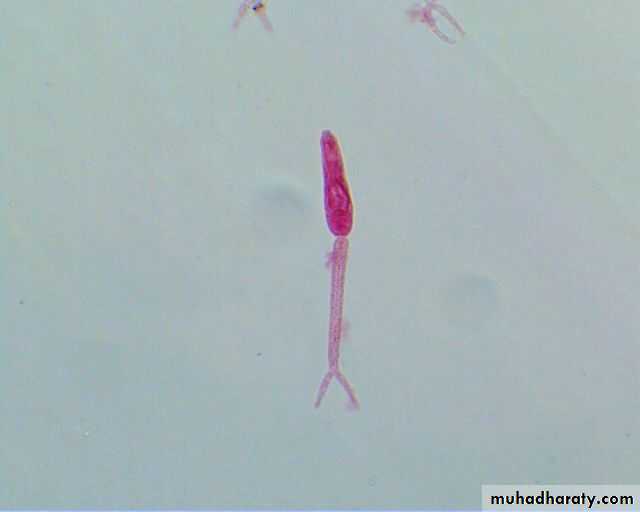
Miracidium• A ciliated, swimming larva
• Size about 99×35µm• The germinal cells will become sporocysts
• Tropism – toward limpidity ; phototrophic .
Schistosoma miracidium
(Intermediate host (Snail
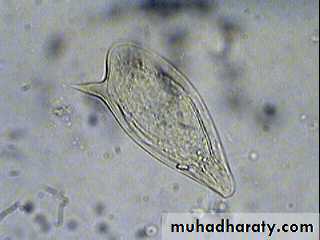
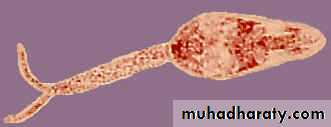
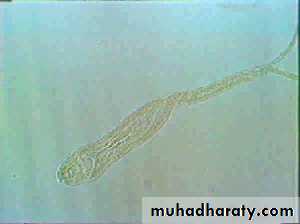
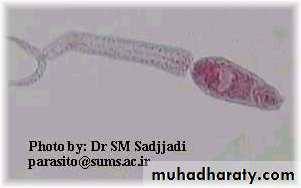
• Cercaria
Free- swimminga forked tail
penetrating glands
Schistosoma cercaria
Bifid tail
Oval head
Life Cycle
Laboratory Diagnosis
Microscopic identification of eggs in stool or urine is the most practical method for diagnosis.Stool examination should be performed when infection with S. mansoni or S. japonicum is suspected,
and urine examination should be performed if S. haematobium is suspected
Tissue biopsy (rectal biopsy for all species and biopsy of the bladder for S. haematobium) may demonstrate eggs when stool or urine examinations are negative