Larva Migrans
CLM & VLMLarva Migrans
1-Cutaneous Larva Migrans (CLM)2-Visceral Larva Migrans (VLM) (Toxocaraiasis)
Toxocariasis is caused by larvae of Toxocara canis
(dog roundworm) and less frequently of T. cati(cat roundworm), two nematode parasites of animals.
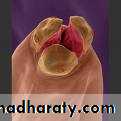
Morphology Toxocara canis
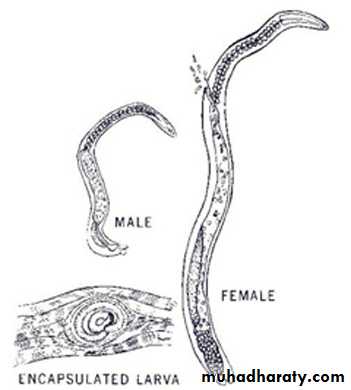
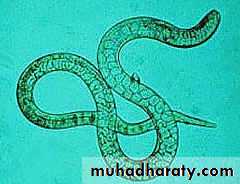
Adult Parasite:The adult worms measure between 10 cm (males) and 18 cm (females) long.
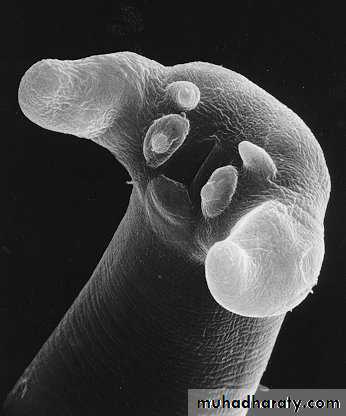
it have spiky cranial and caudal parts, covered by yellow cuticula. The cranial part of the body contains two lateral alae.
Toxocara canis
Toxocara canis
Morphology Toxocara canis
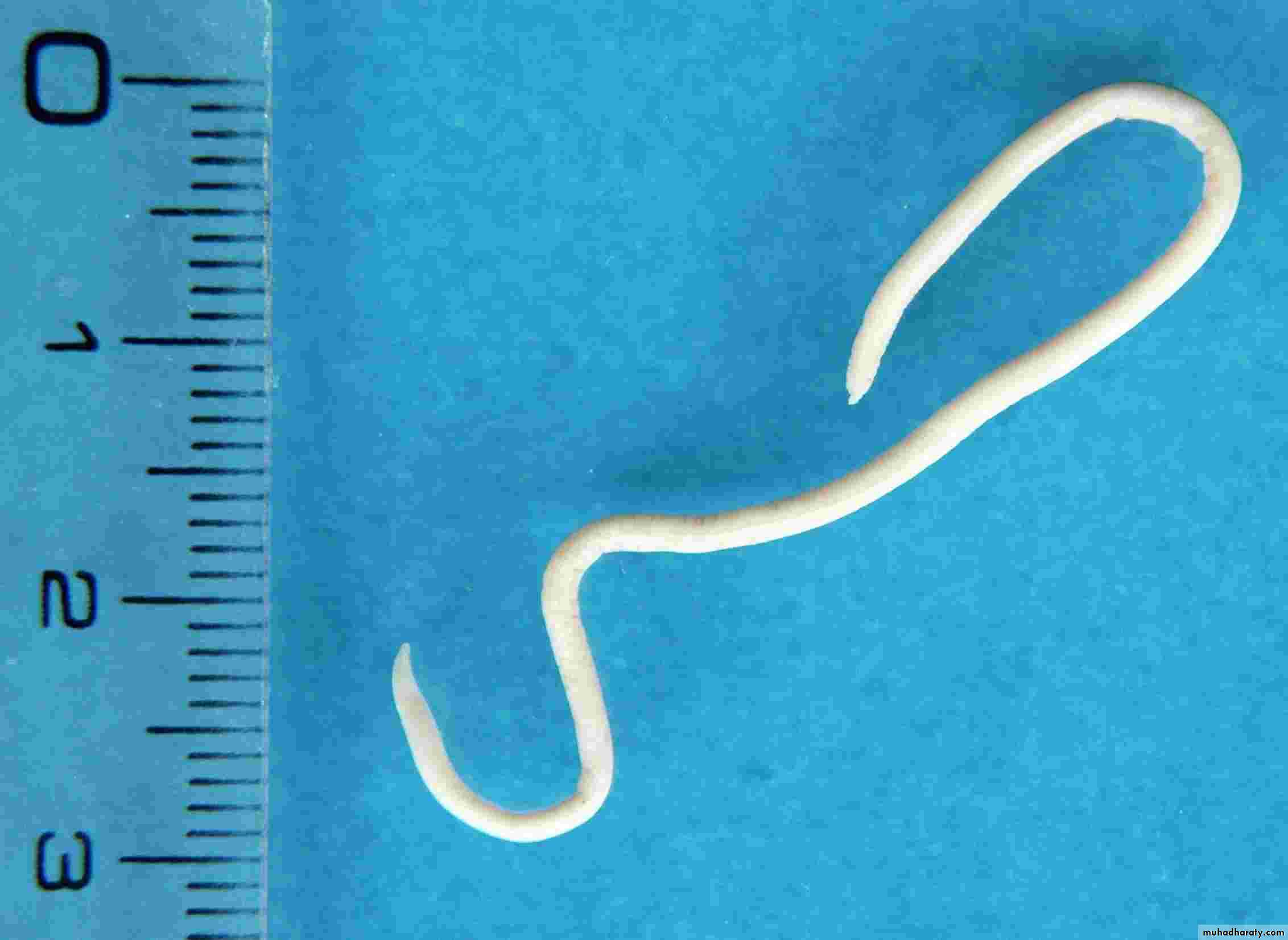
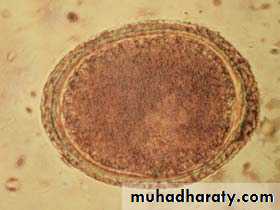
Egg:Eggs are light brown with a thick protein coat that is pitted.
Eggs are found in fecal flotation.
The egg measures 90 um X 75 um.
Toxocara canis Egg - note the pitted appearance of the surface
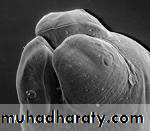
Morphology Toxocara cati
Adult Parasite:
Males measure 3 to 6 cm and females 4 to 10 cm. There are large cervical alae which end abruptly, giving the anterior end an arrow-head shape .
Toxocara cati
Toxocara cati
Morphology Toxocara cati
Egg :Egg - 65 µm by 75 µm in diameter with a pitted shell.
Toxocara cati egg
Toxocara spp
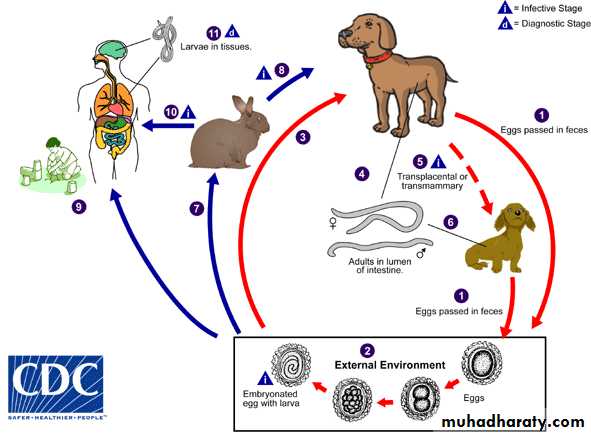
Definitive (Toxocara canis) : Dogs and foxes.
Definitive (Toxocara cati): Cats and wild felids.
Site adult parasite : Small intestine lumen.
Diagnostic Stage: egg and larva in tissue.
Infective stage : embryonated egg with larva.
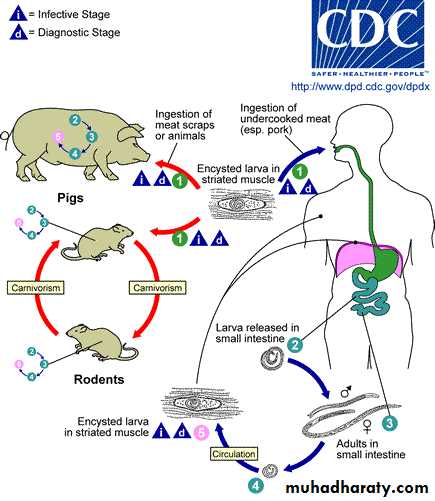
Life cycle
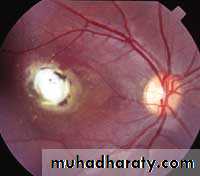
OLM
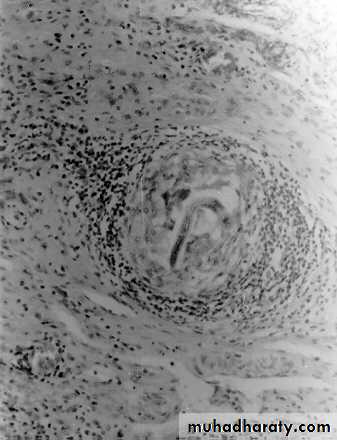
Pulmonary granuloma
Laboratory Diagnosis
Fecal floatation or stool examination detect any Toxocara eggs.Identification of the adult worm recovered from the feces or vomitus.
For both VLM and OLM, a presumptive diagnosis rests on clinical signs, laboratory findings (including eosinophilia), and the detection of antibodies to Toxocara.
Causal Agents:Trichinellosis (trichinosis) is caused by nematodes (roundworms) of the genus Trichinella.
In addition to the classical agent T. spiralis found worldwide in many carnivorous and omnivorous animals, several other species of Trichinella are now recognized.
Trichinella spp.
1- T. pseudospiralis (mammals and birds) worldwide.2- T. nativa
3- T. nelsoni
4- T. britovi
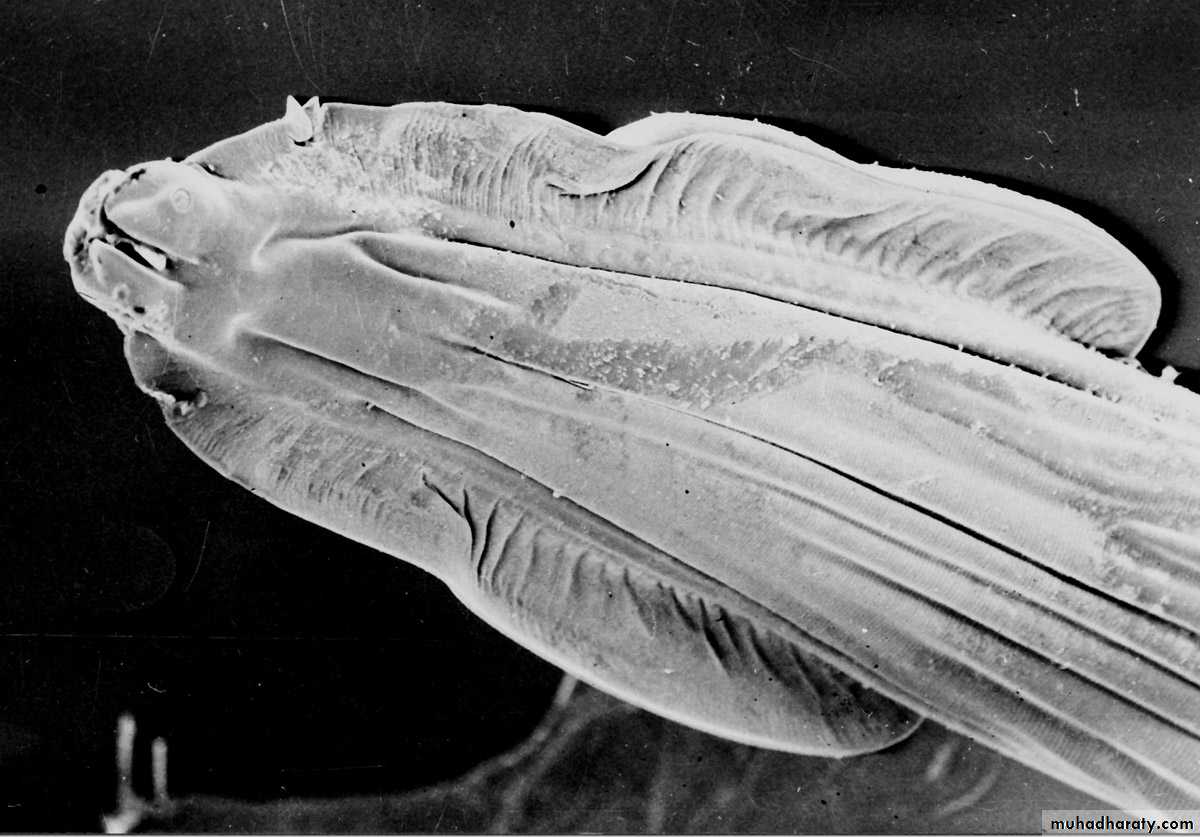
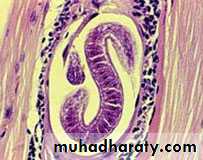
Morphology Trichinella spp
The posterior portion of a gravid female contains the uterus full of eggs.
Both males and females taper at the anterior end. Males are 1.4 to 1.6 mm long and females are about twice that length.
The males anus can be found in the terminal end, and they have a large copulatory pseudobursa on each side.
The vulva in female is located near the esophagus.
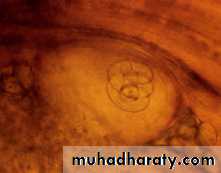
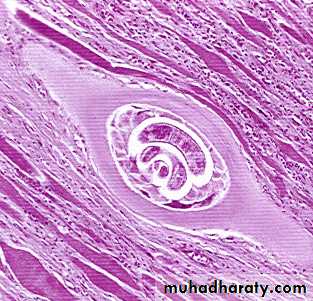
Infective larvae are coiled into a spiral. T. pseudospiralis (a species a Trichinella) does not form as distinct of a coil as the other Trichinella species.
Trichinella
adult-Trichinella
Trichinella nativa
Life cycle
A, B: Encysted larvae of Trichinella in pressed muscle tissue sample. The coiled larvae can be seen inside the cysts
ش
A B
Trichinella spiralis encysted larva
C, D: Larvae of Trichinella, freed from their cysts, typically coiled; length: 0.8 to 1 mm.
A
C D