
Lecture 2
Thorax
د.رندعبداللطيف
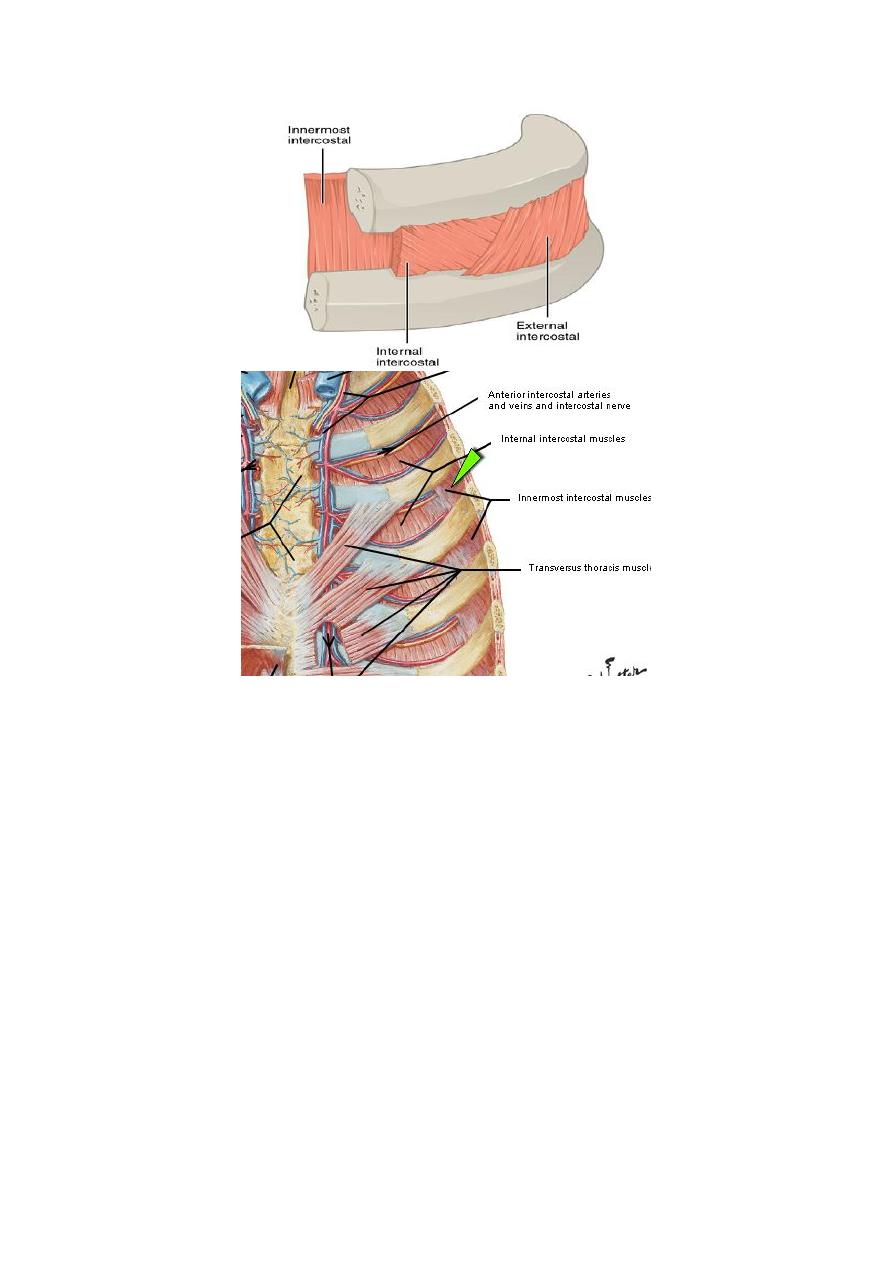
Intercostal Spaces
The spaces between the ribs contain three muscles of respiration:
1. The external intercostal m.
2. The internal intercostal m.
3. The innermost intercostal m. This muscle is lined internally by the
endothoracic fascia, which is lined internally by the parietal pleura. The
intercostal nerves and blood vessels run between the intermediate and
deepest layers of muscles (Fig. 2.8). They are arranged in the following
order from above downward: intercostal vein, intercostal artery, and
intercostal nerve (i.e., VAN).
The external intercostal muscle
1. It forms the most superficial layer.
2. Its fibers are directed downward and forward from the inferior border of
the rib above to the superior border of the rib below.
3. The muscle extends forward to the costal cartilage where it is replaced by
an aponeurosis, which is named as the anterior (external) intercostal
membrane
The internal intercostal muscle
1. It forms the intermediate layer.
2. Its fibers are directed downward and backward from the subcostal groove
of the rib above to the upper border of the rib below.
3. The muscle extends backward from the sternum in front to the angles of
the ribs behind, where the muscle is replaced by an aponeurosis, which is
named as the posterior (internal) intercostal membrane
The innermost intercostal muscle
1. It forms the deepest layer. It is an incomplete muscle layer and crosses
more than one intercostal space within the ribs.
2. It is related internally to endothoracic fascia and parietal pleura and
externally to the intercostal nerves and vessels. The innermost intercostal
muscle can be divided into three portions, which are more or less separate
from one another.
Lecture 2
Thorax
د.رندعبداللطيف
Nerve Supply of I.C.M
The intercostal muscles are supplied by the corresponding intercostal nerves.
The intercostal nerves and blood vessels (the neurovascular
bundle) run between the middle and innermost layers of muscles . They are
arranged from above downward: intercostal vein, intercostal artery, and
intercostal nerve (i.e., VAN).
The intercostal nerves:
The upper 6 thoracic nerves will be distributed to the thorax
supplying the thoracic wall and intercostal muscles, while T7, T8,
T9 leave their intercostal spaces anteriorly (after innervating the
structures within) and pass to the anterior abdominal wall. T10 and
T11ribs pass directly into the abdominal wall because of the fact
that the corresponding ribs are floating.will pass deep and inter to
the abdomen.

Lecture 2
Thorax
د.رندعبداللطيف
1. They give branches:
Collateral branches; each nerve gives a collateral branch which
passes below & parallel to the main nerve, these branches contain
most of the motor fibers & they are the nerves which supply the
intercostal muscles.
Lateral cutaneous branches; arise at the midaxillary line from
the remaining part of the nerve, each divides into anterior &
posterior branches which meet the lateral branches of the anterior
& posterior cutaneous nerves.
Anterior cutaneous branches; are the remaining part of the spinal
nerve, pierce the muscles lateral to the sternum & ends into lateral
(large) & medial (small) branches.
Intercostal Arteries
Each intercostal space contains a large single posterior intercostal artery and
two small anterior intercostal arteries.
The anterior intercostal arteries of the first six spaces are branches of the
internal thoracic artery, which arises from the first part of the subclavian artery.
The anterior intercostal arteries of the lower spaces are branches of the
musculophrenic artery, one of the terminal branches of the internal thoracic
artery.
Each intercostal artery gives off branches to the muscles, skin, and parietal
pleura. Those of the 2nd, 3rd & 4th spaces supply the mammary gland in
female.
The posterior intercostal arteries of the first two spaces are branches from the
superior intercostal artery, a branch of the costocervical trunk of the subclavian
artery. The posterior intercostal arteries of the lower
nine spaces are branches of the descending thoracic aorta.
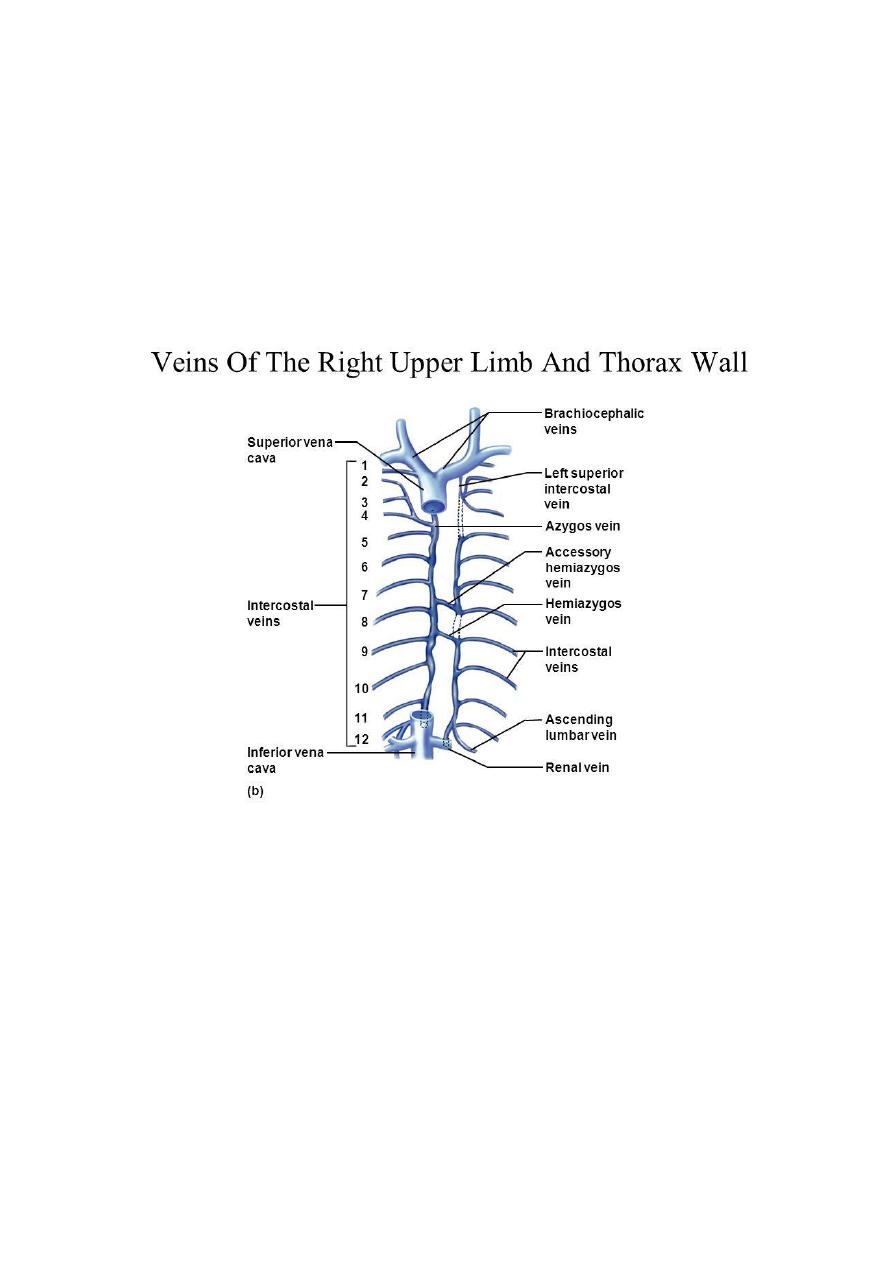
Intercostal veins:
- They accompany the arteries & have the same course, with some variations:
• The anterior intercostal veins drain into the internal thoracic and the
musculophrenic veins. The internal thoracic veins end in the corresponding
brachiocephalic veins
• The highest intercostal vein (1st posterior intercostal) drains on each side to
the brachiocephalic or vertebral veins after passing over the pleura of the lung
apex
• The 2nd & 3rd and sometimes the 4 th posterior intercostal veins unite to form
the superior intercostal vein which drains on the left in the brachiocephalic vein
Lecture 2
Thorax
د.رندعبداللطيف
& on the right in the azygos arch. The eight lower right intercostal veins drain
to azygos vein.
The fourth to the eighth left intercostal veins will unite to form
the Accessory Hemiazygos Vein which joins the azygos vein at the level of the
seventh thoracic vertebra
The 9
th
to 11 th post. left intercostal veins drain into the Hemiazygos Vein
which join the azygos vein that empty to superior vena cava.
