Lec.2
HISTOLOGYGlandular Epithelium
Glandular Epithelium
• A gland is one or more cells that produce and secrete a specific product.• The product is always a water-based fluid and usually contains proteins (the product is a secretion).
• Glandular cells obtain substances needed from blood and transform them (chemically) into a product
• Glands include two types:
1. Endocrine Glands2. Exocrine Glands
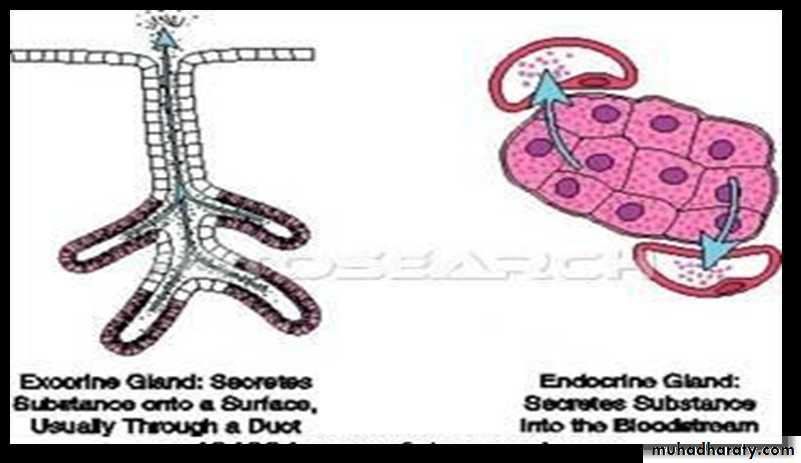
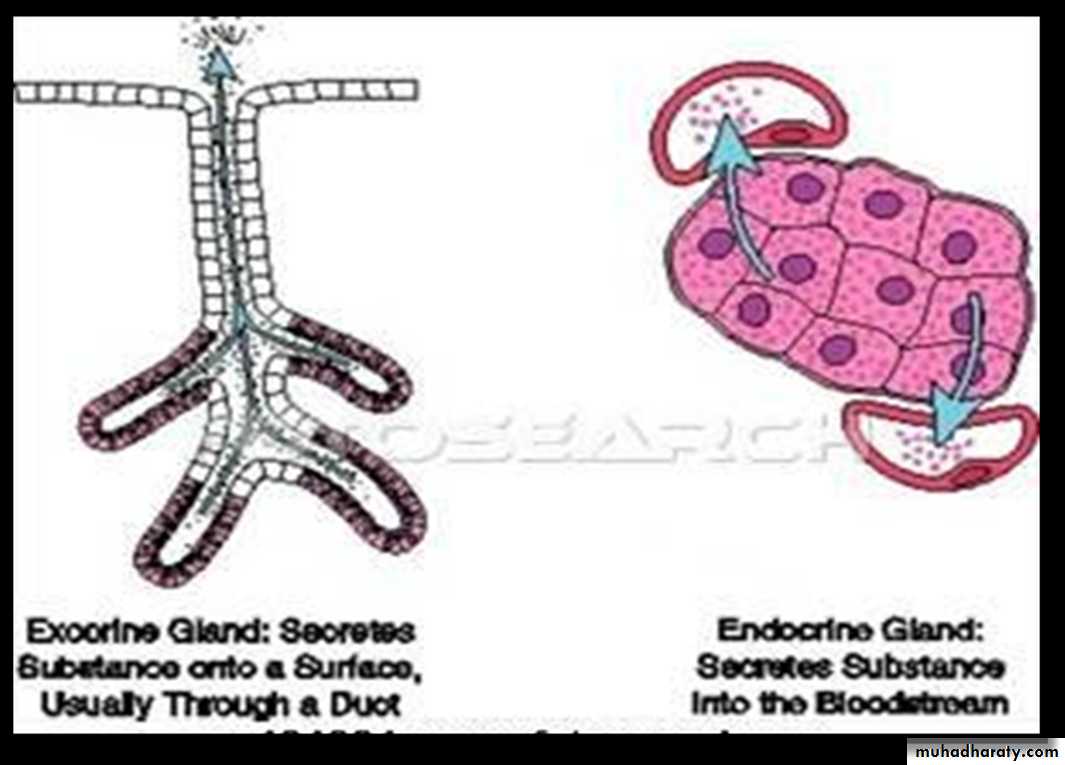
Endocrine Glands
• Endocrine glands are also called ductless glands because, they lose their ducts.• They produce hormones and secrete them by exocytosis into the extracellular space . then, they enter the blood or lymphatic fluid and travel to specific organs.
• Hormones secreted by endocrine glands vary, one gland might secrete an amino acid while another secretes glycoproteins or steroids.
• The major endocrine glands of the body include pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, and as well as the ovaries and testes.
Exocrine Glands
Exocrine glands are glands that produce substances and then secrete these substances by a duct.• Products secreted by exocrine glands include sweat, oil, mucous, bile….
• Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, sebaceous, and mucous glands.
• Classification of Exocrine Glands:
According to number of cells
According to structure
According to method of secretion
According to product secreted
1- According to number of cells
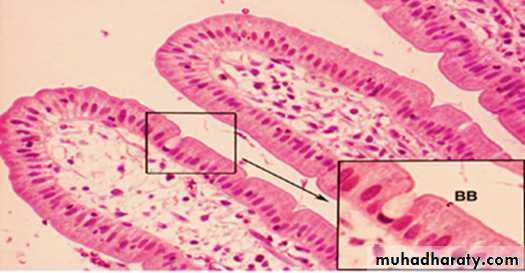
A. Unicellular Exocrine Glands:• Represent the simplest form of exocrine gland, in which a single cell forms a gland.
• Important example of unicellular glands include goblet cells (looks like a goblet).
• Unicellular glands can be found within the epithelial linings of the intestinal and respiratory tracts.
• In humans, unicellular exocrine glands produce mucin, a complex glycoprotein that dissolves in water. When the mucin is dissolved, it forms mucous (which protects and lubricates surfaces).
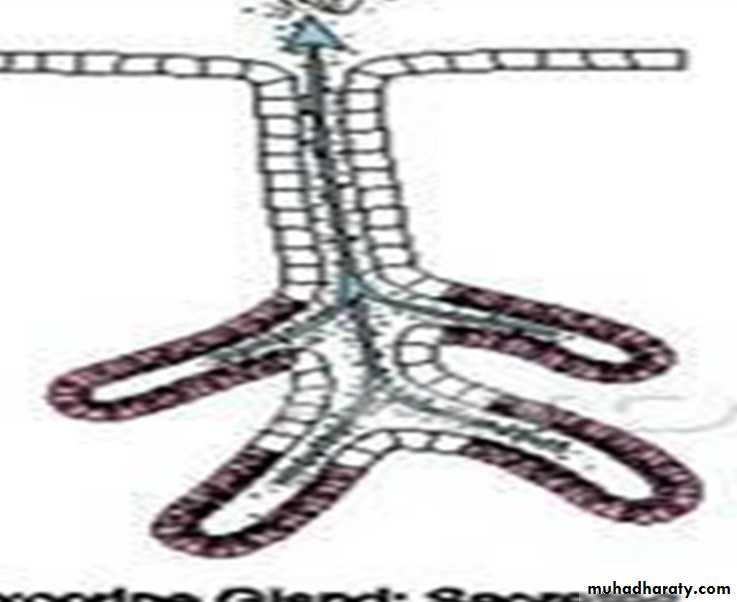
B. Multicellular Exocrine Glands:
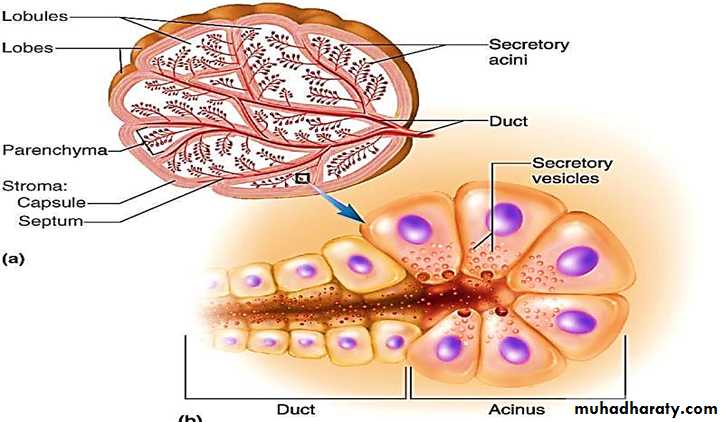
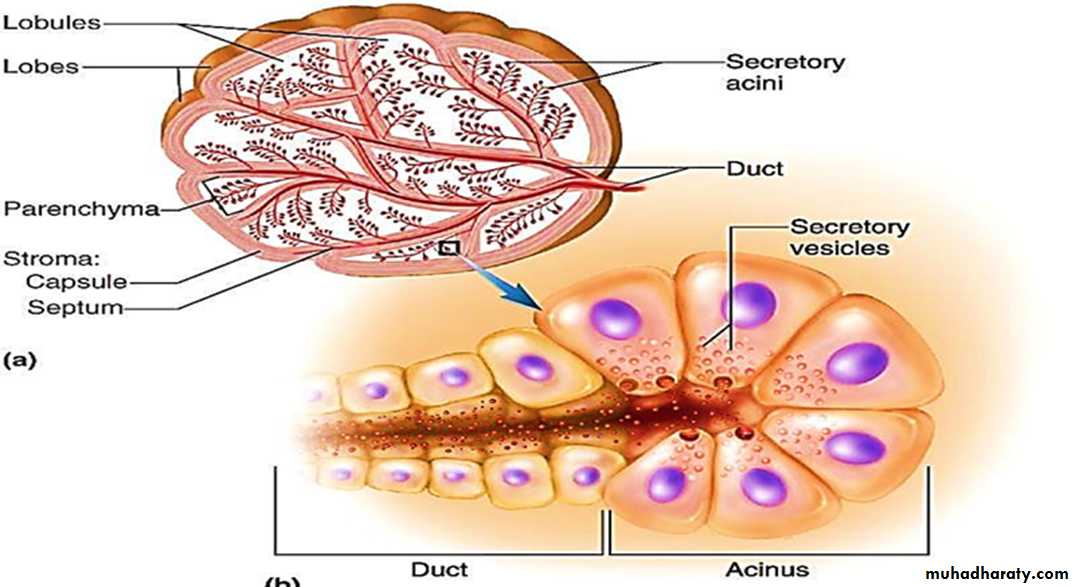
• multicellular exocrine glands are more complex than unicellular glands.• They have two main parts: a duct and a secretory unit (made of secretory cells).
•
• The secretory unit is surrounded by connective tissue. The connective tissue supplies the secretory unit with blood vessels and nerve fibers . It also forms a fibrous capsule that extends into the gland and divides it into lobes .
2-According to structure:
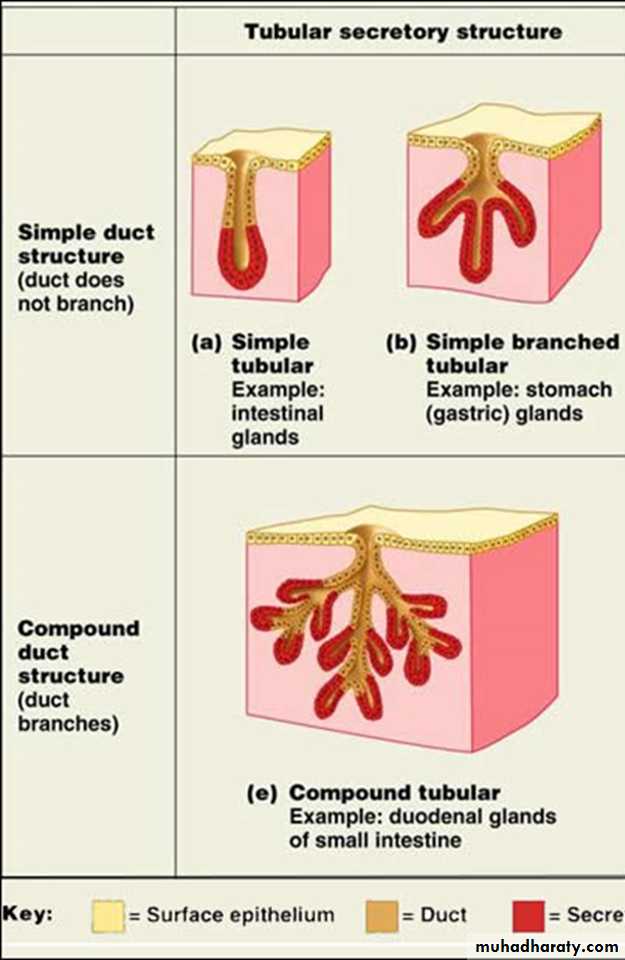
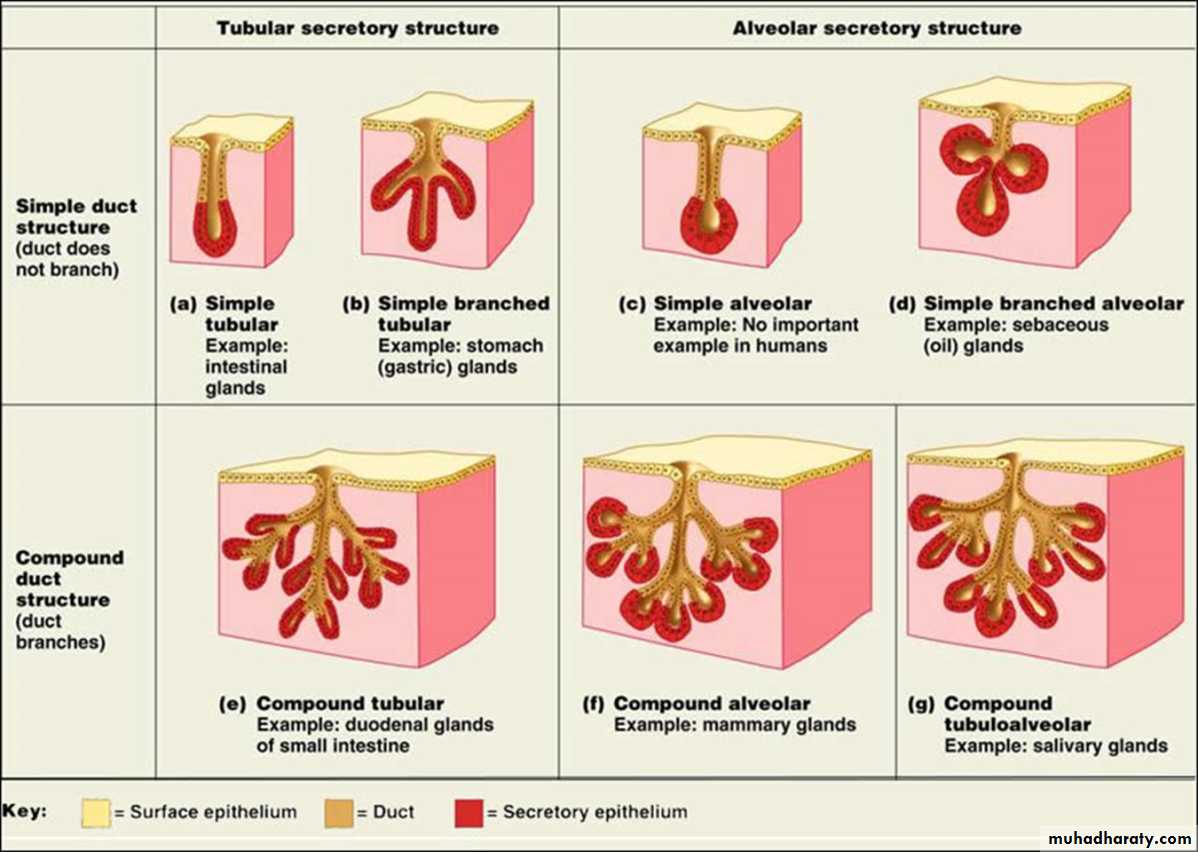
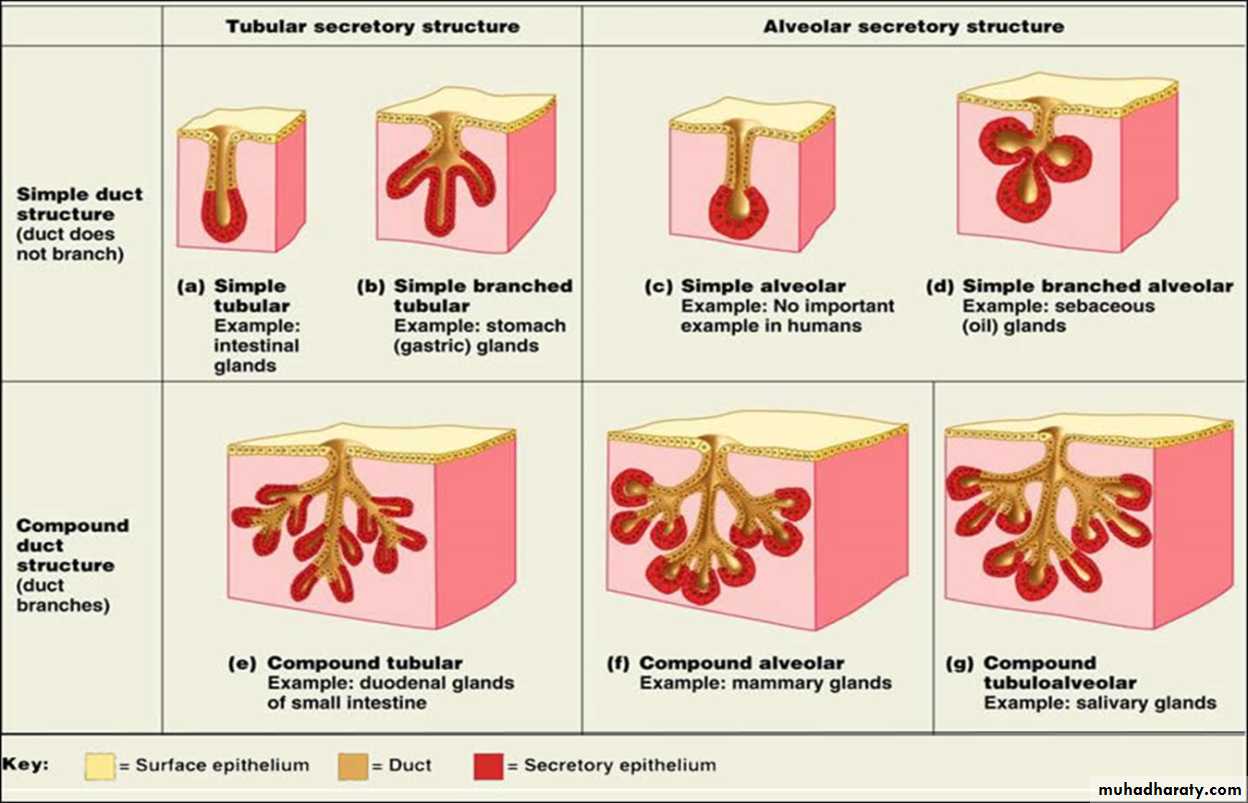
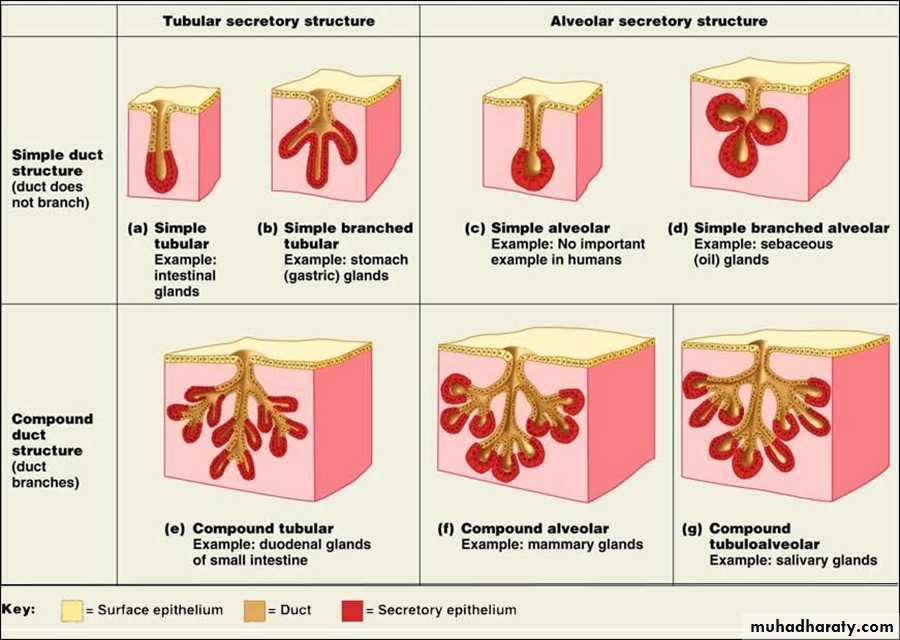
Multicellular exocrine glands are structurally classified depending on the structure of their duct in to:• Simple multicellular exocrine glands: Simple glands have one unbranched duct.
2. Compound multicellular exocrine glands: Compound glands have ducts that branch repeatedly.They are further classified according to the morphology of their secretory units as:
1.Tubular – secretory portion is shaped like a tube .2.Acinar– secretory portion is saclike or shaped like a flask.
3.Tubuloacinar – has both tubular and acinar secretory unit.
2- According to method of secretion
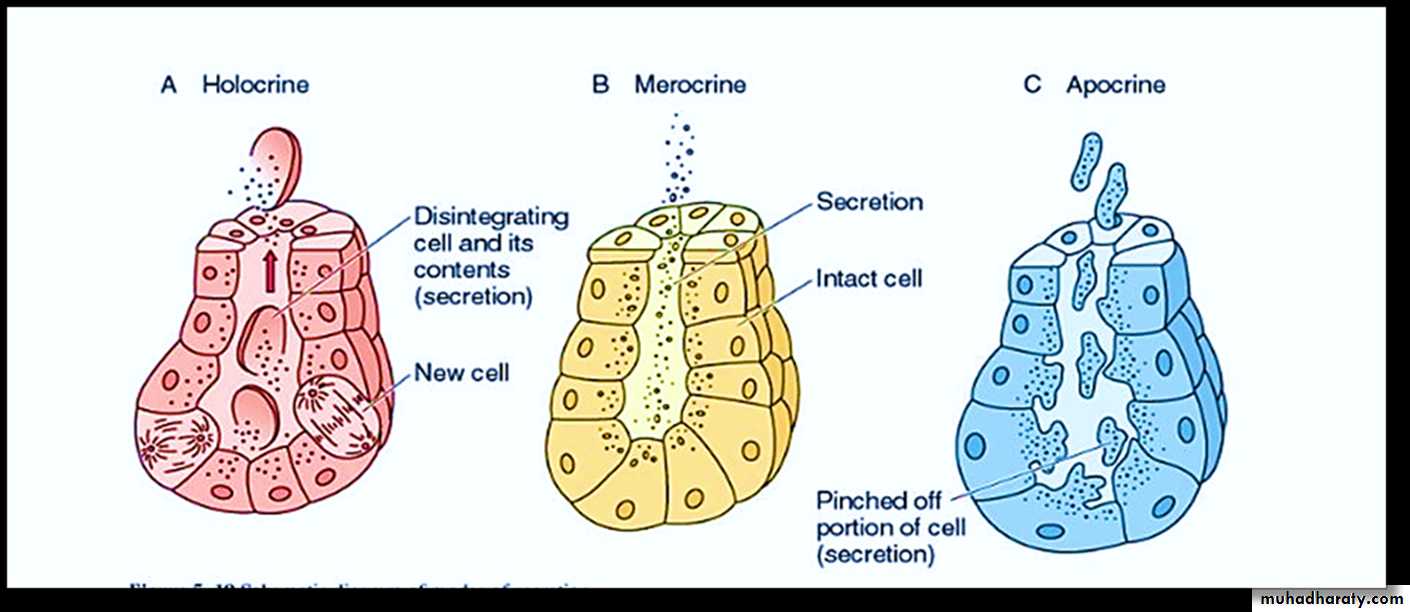
Exocrine glands are classified according to the mode or way in which the secretory products leave the cell, into:• Holocrine glands
B. Merocrine glands
C. Apocrine glands
• Holocrine glands: The product of secretion is shed with the whole cell, and the cell division in such gland must be rapid to replace cells lost in secretion (e.g. sebaceous glands ).
•
B. Merocrine glands: In merocrine glands, the secretory granules leave the cells by exocytosis with no loss of other cellular material, (e.g. pancreas and salivary glands).
C. Apocrine glands: the secretory product is discharge together with parts of the apical cytoplasm. The cell then passes through another secretory cycle after a short recovery period (e.g. the mammary glands).
3- According to product secreted Exocrine glands are classified according to the nature of their secretion , into :
• Serous glands : Secretes proteins , enzymes e.g : cells of stomach
B) Mucus Glands : Secretes mucus e.g:esophageal glands ,pyloric glands
C) Mixed Glands : Secretes both proteins and mucous e.g : Salivary glands
D) Sebaceous Glands : Secretes oil / lipids