The Orbit
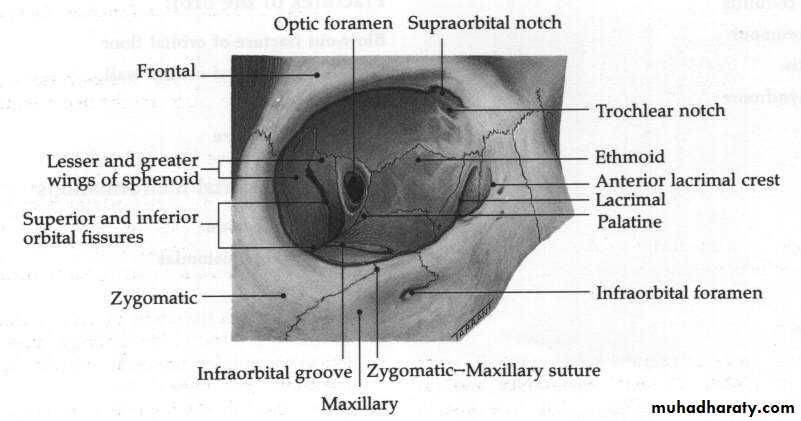
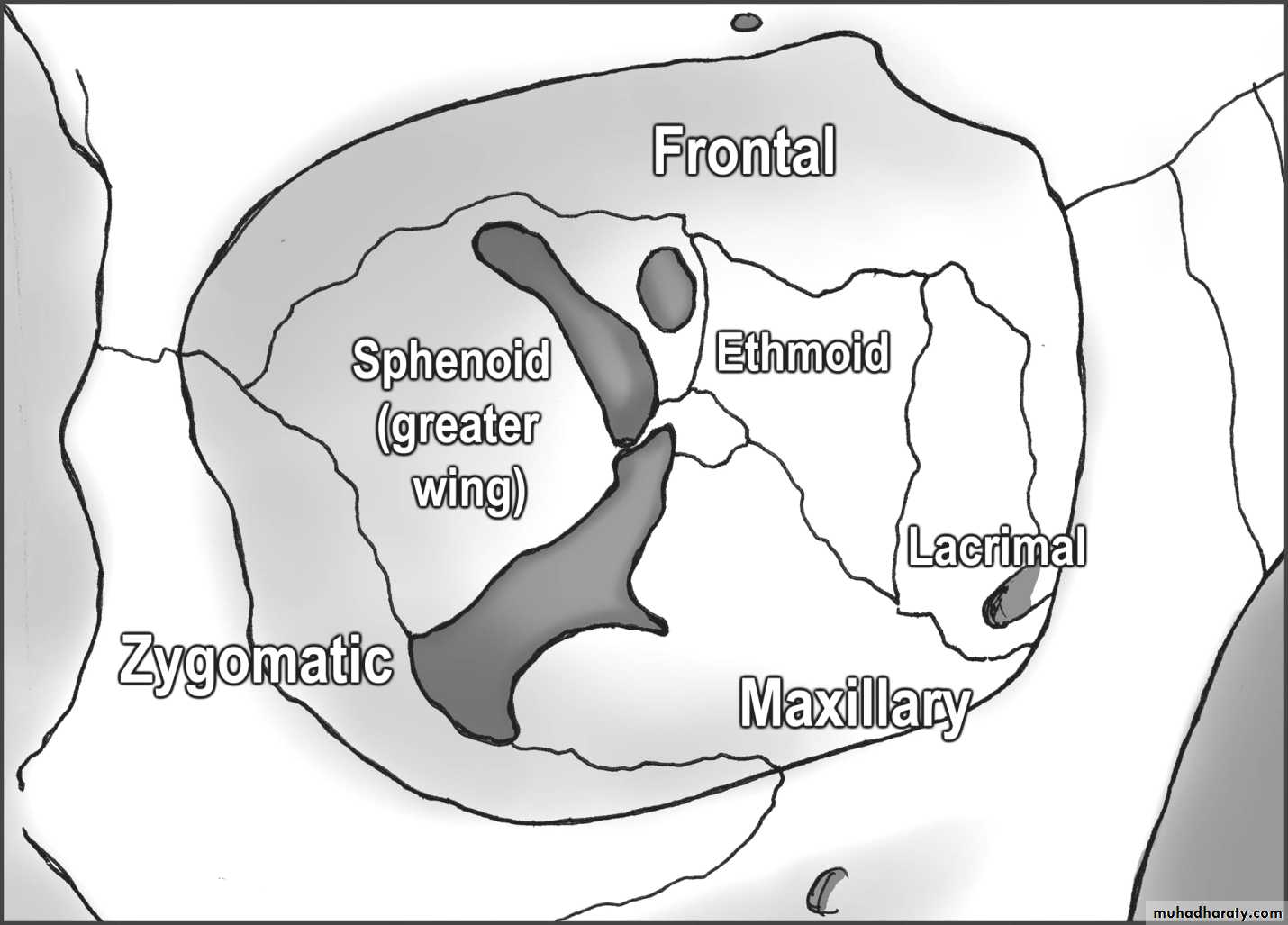
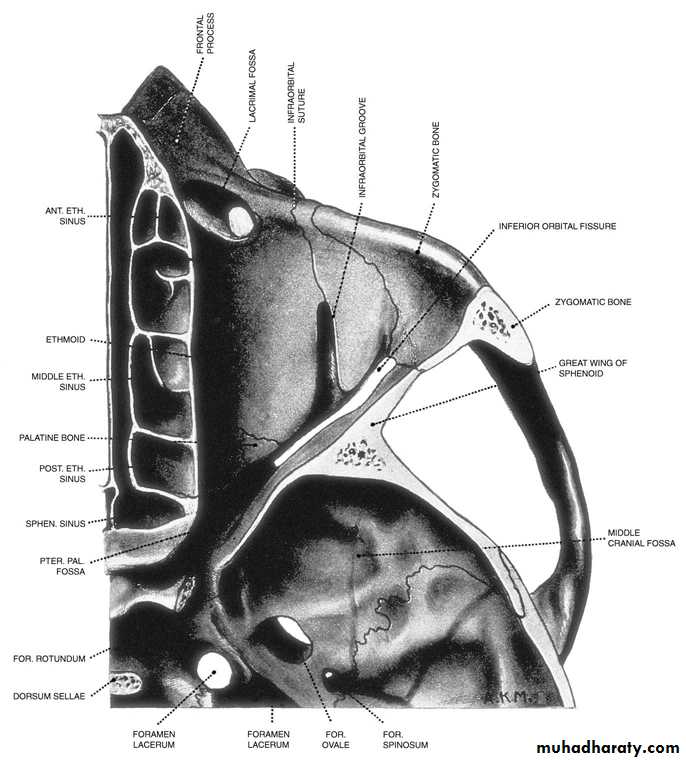
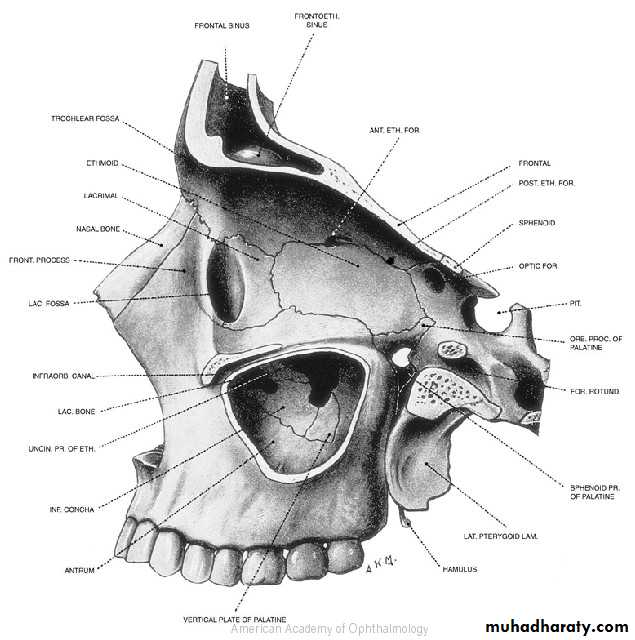
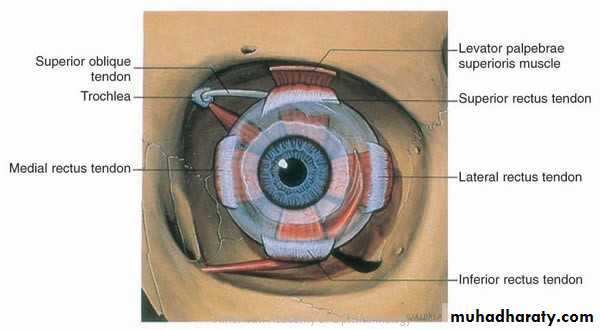
AnatomyThe Roof : Frontal bone, Lesser wing of sphenoid
The Lateral wall : Greater wing of sphenoid, Zygomatic
The floor : Maxillary, Zygomatic , Palatine
The medial wall : Maxillary, Lacrimal , Ethmoid , Sphenoid.
Functions
Protection to the eye ballProvide attachments to the ligaments which stabilize the eye ball
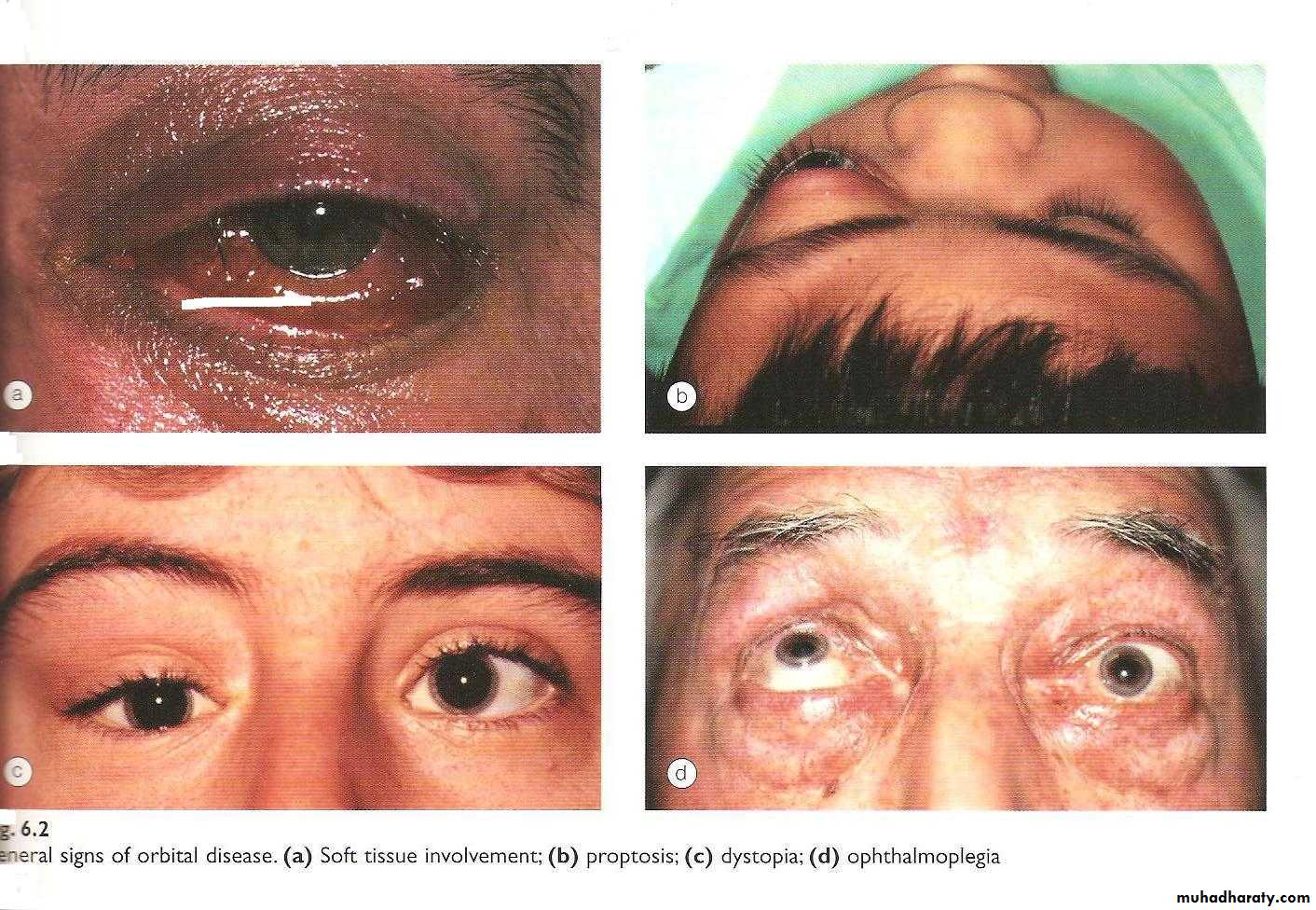
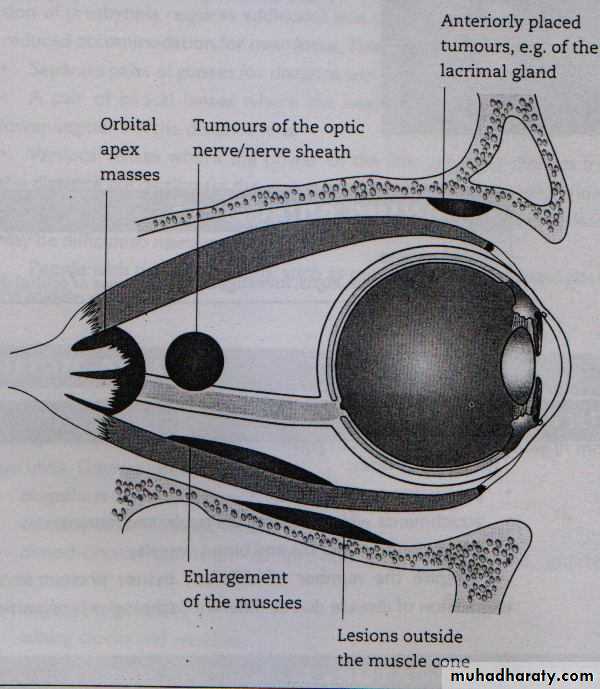
Clinical features of orbital lesions
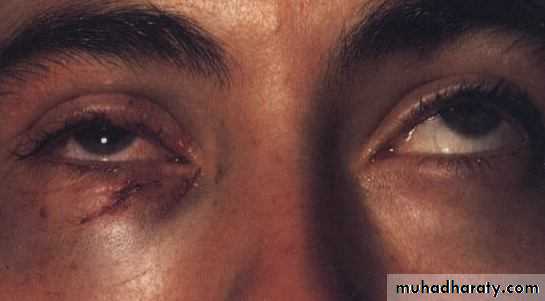
Abnormal Displacement of The Eye BallProptosis
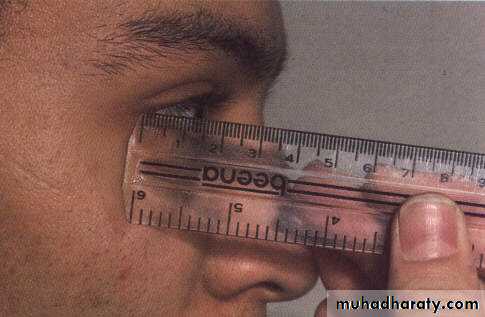
Abnormal protrusion of the eye ballDistance between lateral orbital rim and the apex of the cornea is more than 20mm, or difference of 2mm between the two eyes is suspicious.
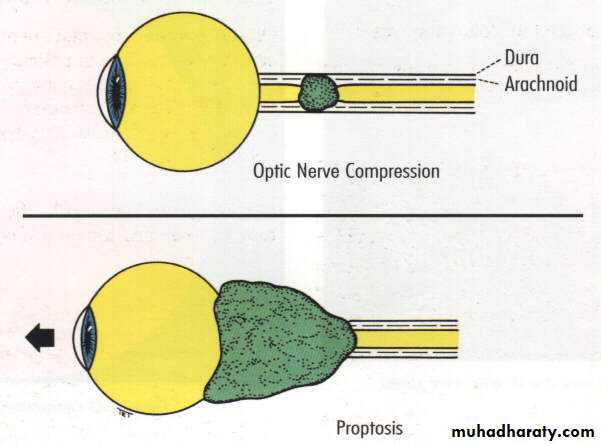
Axial proptosis :
axial displacement of the eyeball
Space occupying lesion inside the muscle cone
Optic nerve glioma
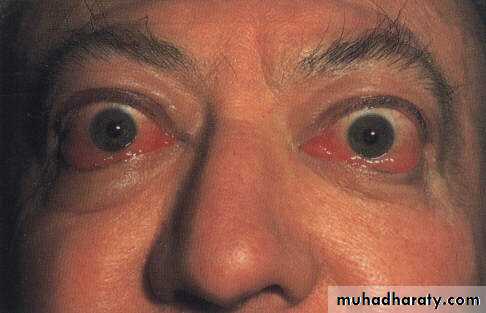
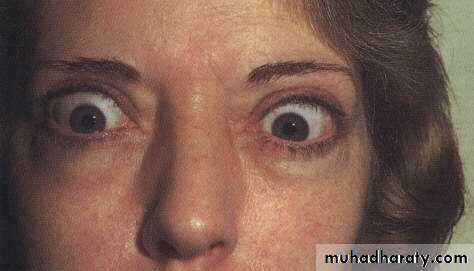
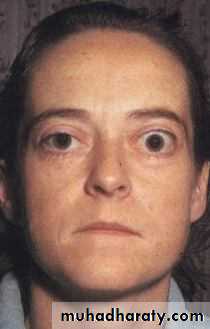
Thyroid dysfunction:Exophthalmus
Eccentric proptosis:
non-axial displacement of the eye ballspace occupying lesion outside the muscle cone
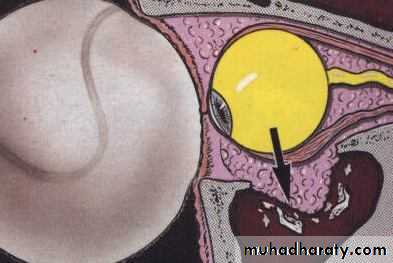
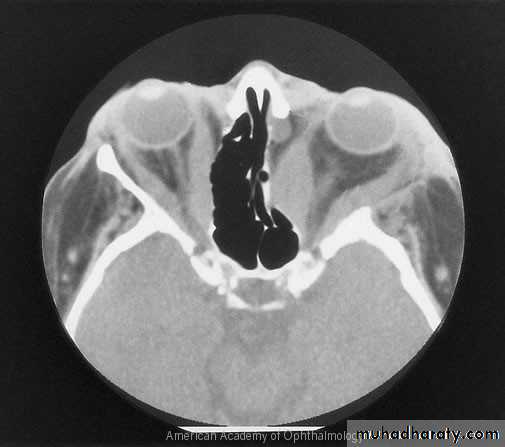
Tumors of the lacrimal gland
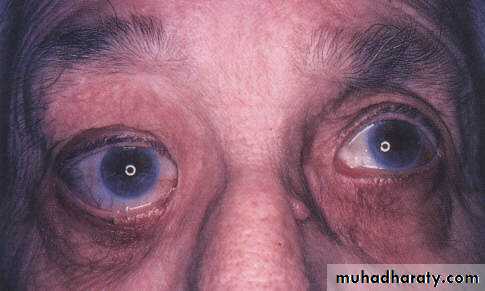
Enophthalmos:
Backward displacement of the eye ballOrbital fracture with herniation of the orbital contents .
Causes
• a- Small globe, congenital anomaly e.g. microphthalmos or nanophthalmos• b- Structural bony abnormalities
• c- Atrophy of orbital contents
• d- Cicatrizing orbital lesions
Clinical features of orbital lesions
PainInflammatory or infective conditions
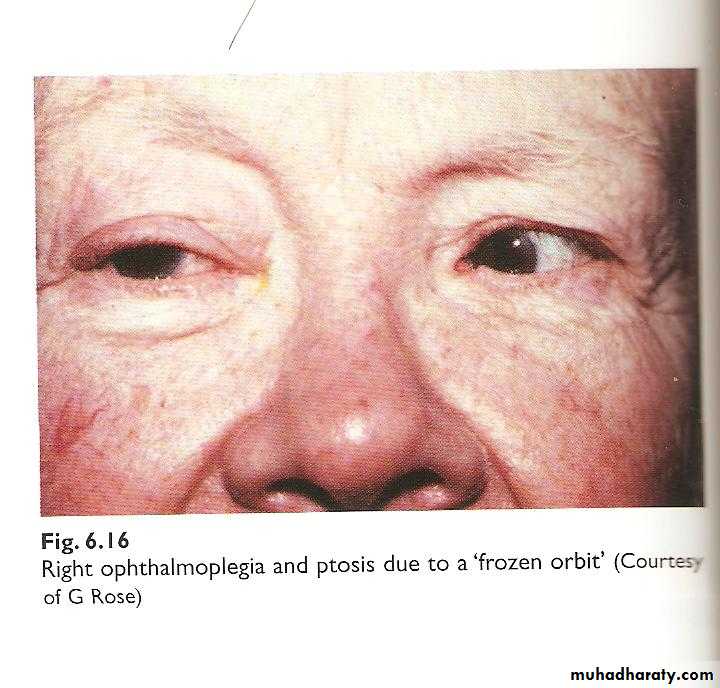
Ophthalmoplegia:
Impairment of extraocular movementCauses
Inflammation (myositis)
Fibrosis (thyroid dysfunction)
Tethering of the muscles (blow out fractures)
Paralysis (ocular motor nerves lesions).
Impairment of Vision
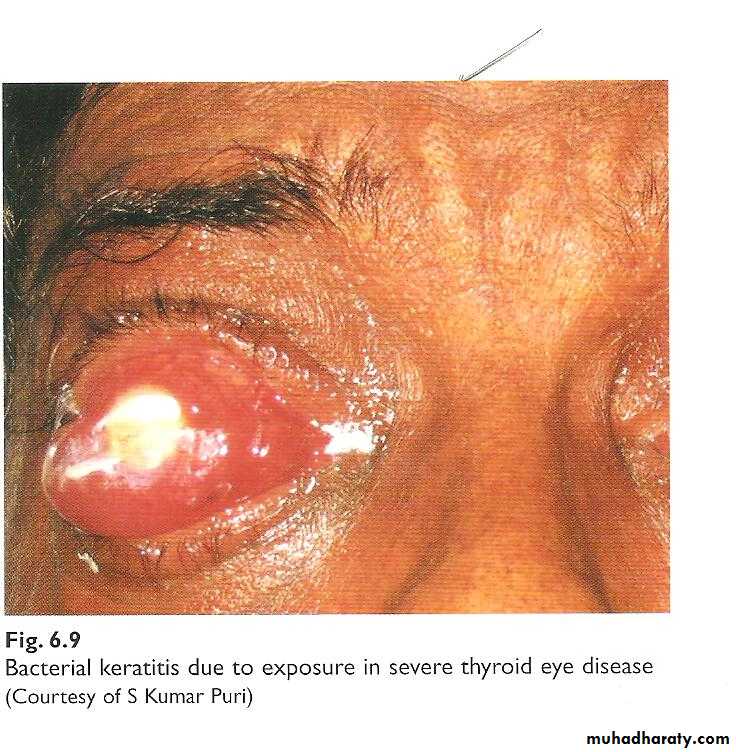
• Exposure keratopathy secondary to proptosis• Optic nerve dysfunction
diminished pupillary light reflex
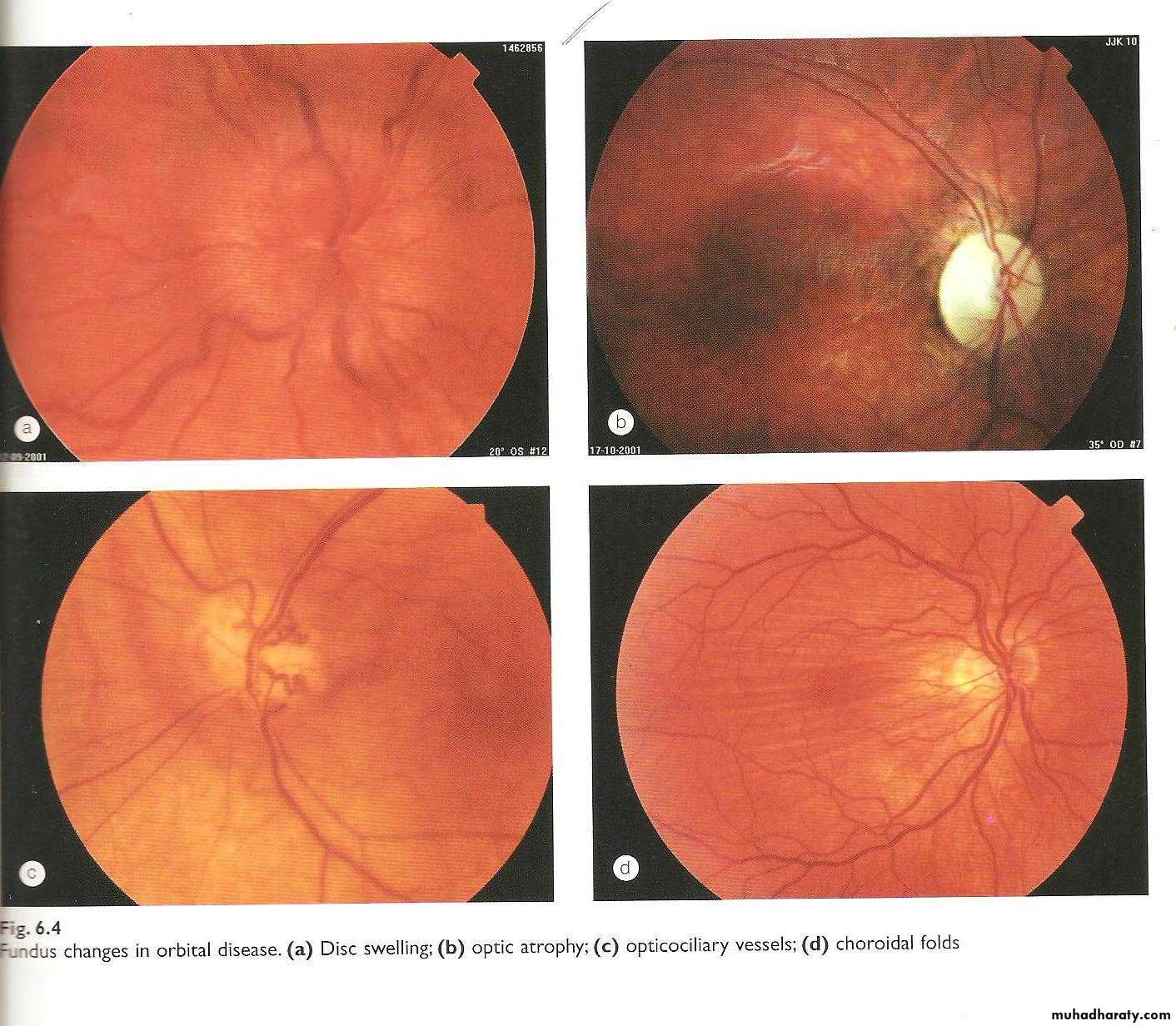
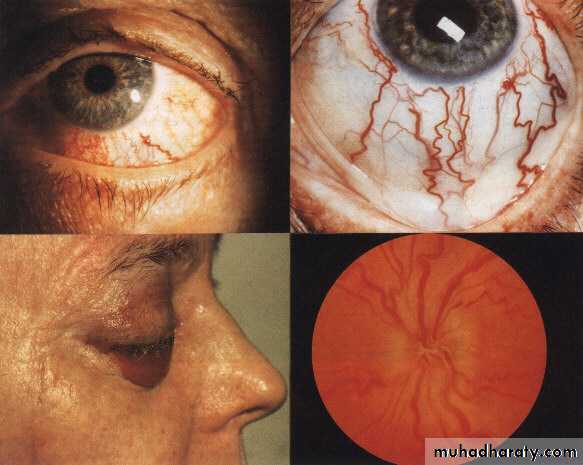
acute stage; optic nerve congestion, swollen
chronic stage; secondary optic disc atrophy
Investigations
X-rayC.T. scan
MRI
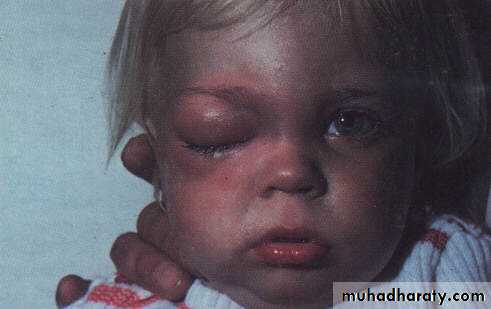
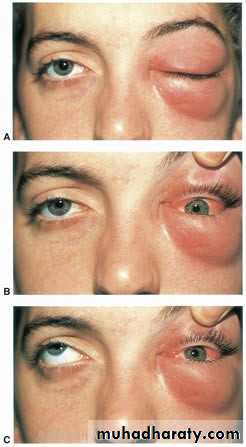
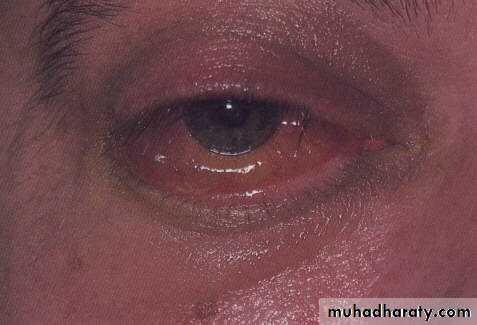
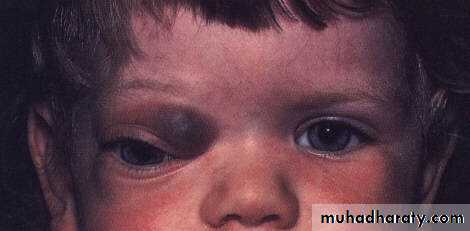
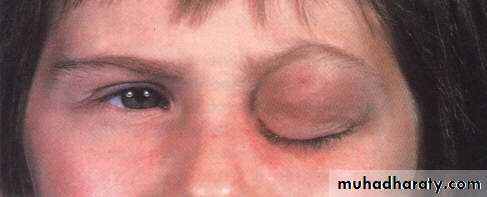
Orbital Cellulitis
Vision threatening and can be life threatening condition
Infection of the soft tissue of the orbit
mostly by bacteria
Strep. pneumoniae, Staph. aureus, H. influenzae.
Causes; 1-spread of microorganisms from the
adjacent structures, paranasal sinuses2-Post traumatic
Clinical features:
SymptomsRapid onset
Fever , malaise
Pain
Impairment of vision
Signs
Lid swelling,
Conjunctival congestion
Proptosis
Ophthalmoplegia
Optic nerve dysfunction
Complications;
Cavernous sinus thrombosisOrbital abscess
Brain abscess
Management
Hospital admissionAntibiotic therapy; started immediately with broad spectrum antibiotics
Third generation Cephalosporins+ metronidazole
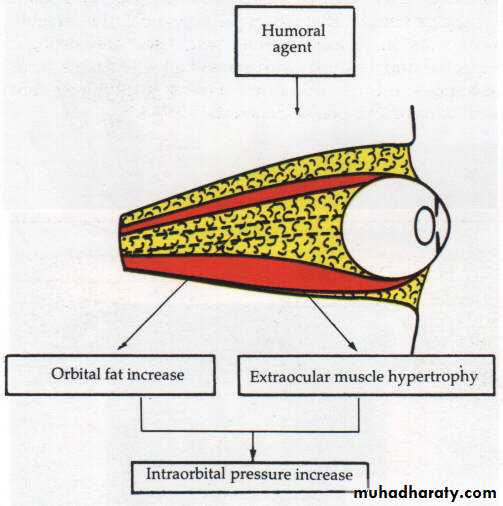
Dysthyroid Ophthalmopathy
Autoimmune disorder usually associated with abnormal thyroid functionPathogenesis;
Hypertrophy of extraocular muscles
Deposition of glycosaminoglycans
Infiltration with mononuclear cells, macrophage
Clinical features
1-Exophthalmus; most common cause of unilateral and bilateral
proptosis
2-Conjunctival hyperemia and edema
3-Lid retraction
4-Lid lag
5-Ophthalmoplegia
6-Optic nerve neuropathy
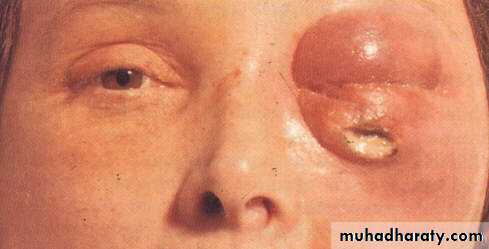
Orbital TumorsDermoid
Benign cystic teratoma,Growth of displaced ectodermal tissue at subcutaneous location
Presentation: during infancy
Painless nodule at the upper temporal or upper nasal angle of the orbit
Firm non tender, smooth surface, freely mobile under the skin
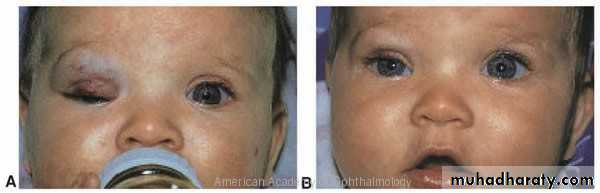
Orbital Tumors Capillary haemangioma
Most common benign tumor of the orbit. Vascular hamartomaPresentation: during perinatal period
Location:
Skin, Strawberry swelling on the eyelid
Subcutaneous
fornix conjunctiva
deep in the orbit causing proptosis
Course; 70% spontaneous resolution at age 7 years.
Treatment; for large lesions,beta blocker, local injection of steroids
Orbital Tumors
Optic nerve glioma
MeningiomaLacrimal gland tumors
Rhabdomyosarcoma; commonest orbital tumor in children
Carotid-cavernous fistula:
Abnormal communication between internal carotid artery and cavernous sinusCauses; rupture congenital aneurysm or post traumatic
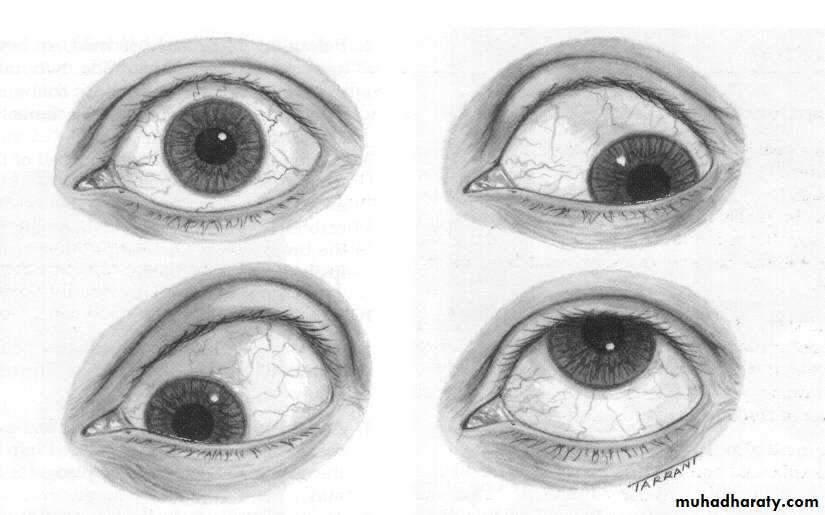
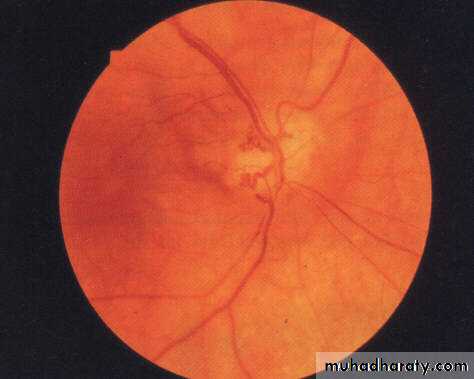
Clinical features;Congested vessels,
Chemosis,
Hyperemic disc,
Pulsating exophthalmus
Examination for proptosis
InspectionExophthalmus
Thyroidectomy scar
Palpation
Orbital margin
Retropulsion
Measurement
Amount of proptosis
Margin reflex distance
Observe eye movement
Lid lag
Restrictive eye movement
Additional test
Check RAPDCheck colour vision
Check V.F
Perform fundoscopy
Listen with the bell if CCF is suspected