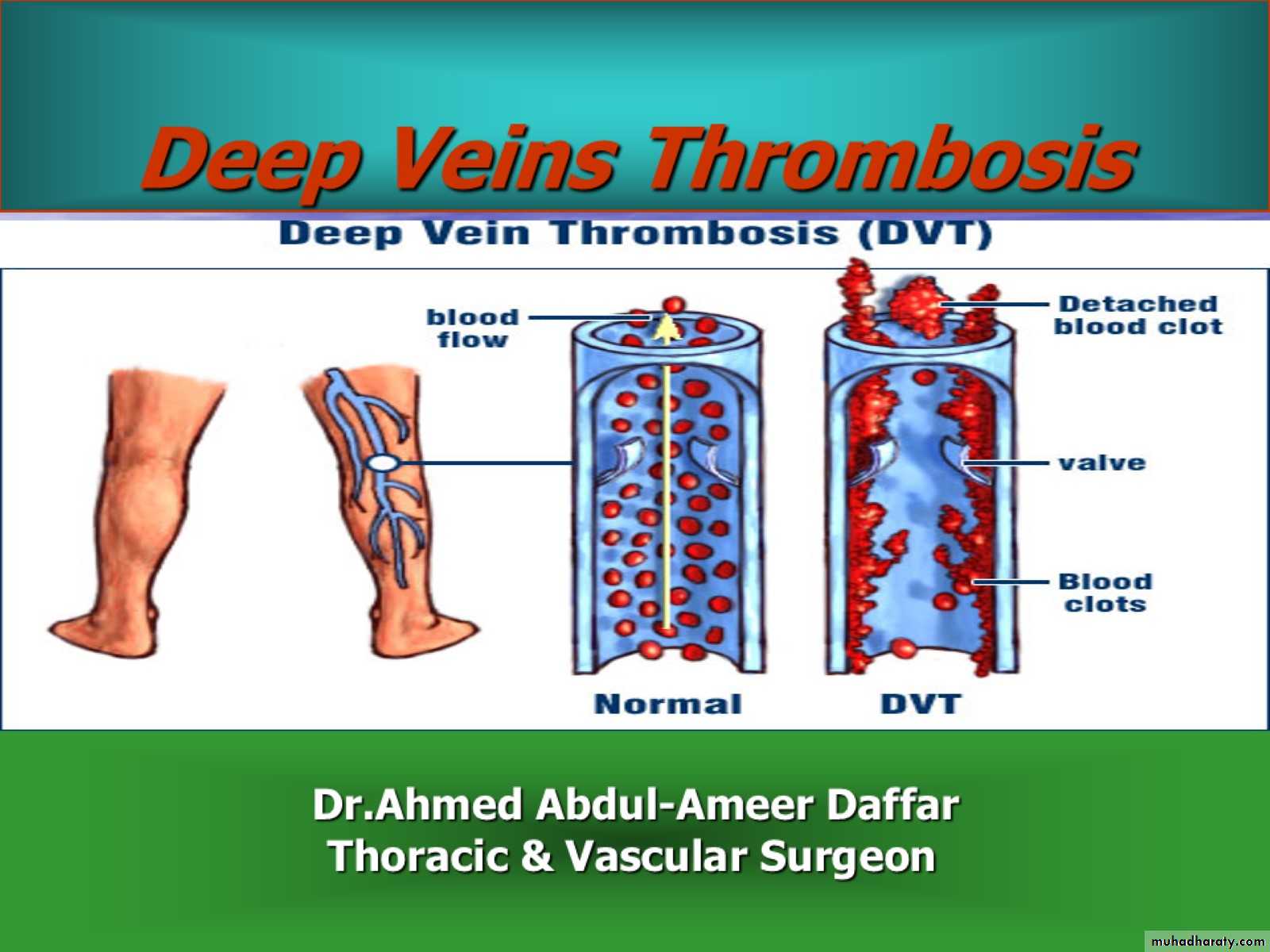
Deep Veins Thrombosis
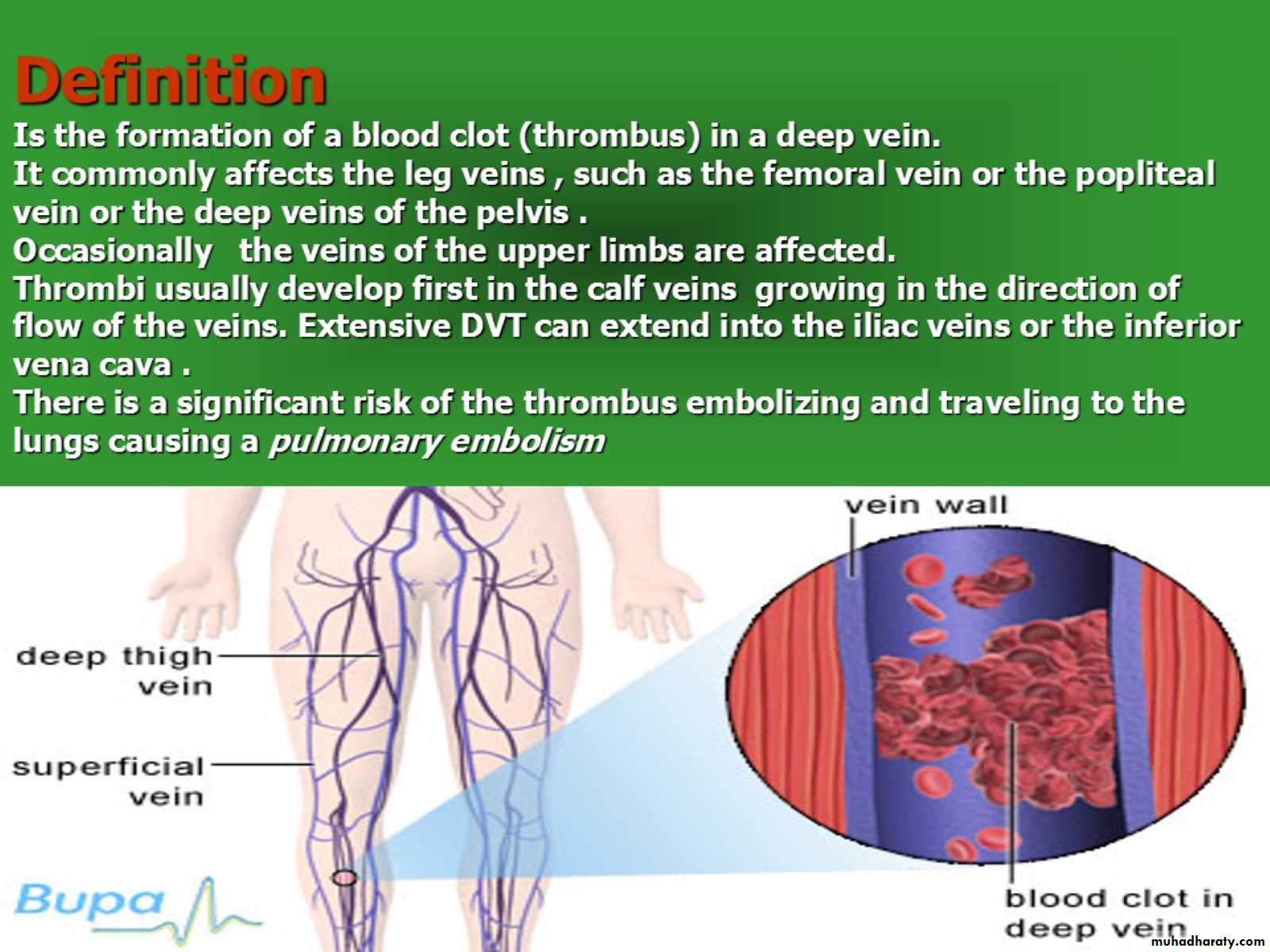
Definition Is the formation of a blood clot (thrombus) in a deep vein.It commonly affects the leg veins , such as the femoral vein or the popliteal vein or the deep veins of the pelvis .Occasionally the veins of the upper limbs are affected.Thrombi usually develop first in the calf veins growing in the direction of flow of the veins. Extensive DVT can extend into the iliac veins or the inferior vena cava .There is a significant risk of the thrombus embolizing and traveling to the lungs causing a pulmonary embolism
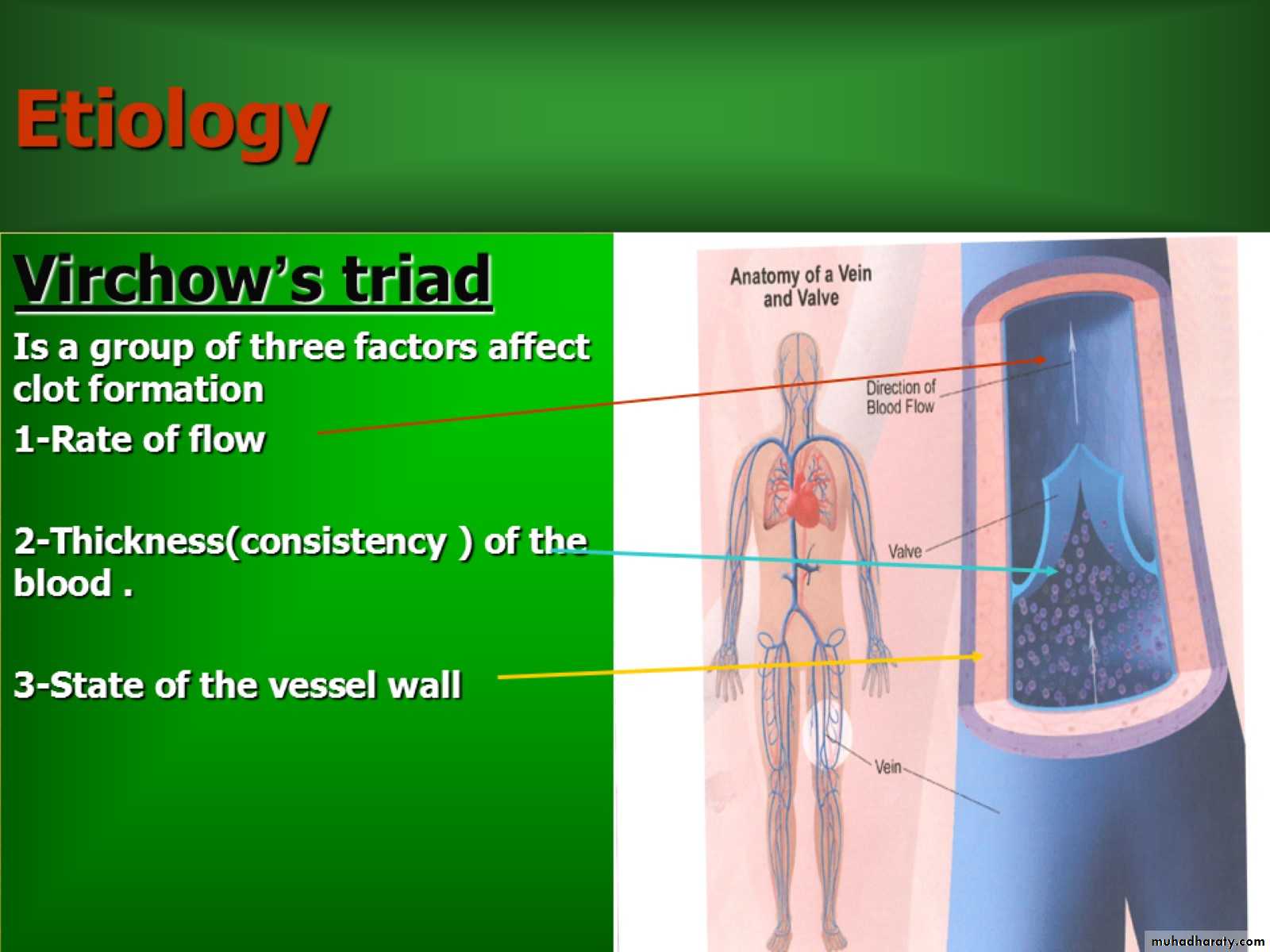
Etiology
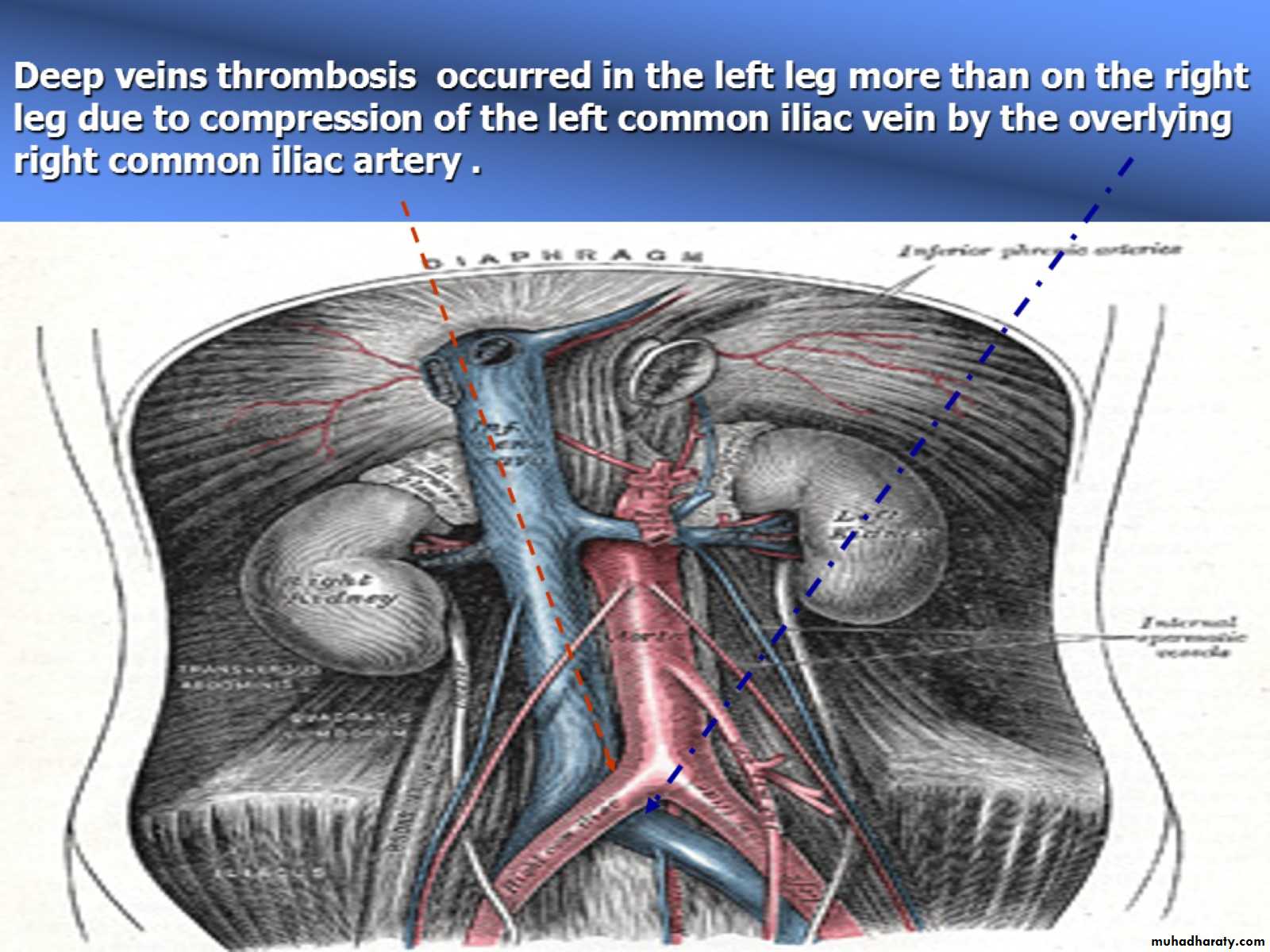
Deep veins thrombosis occurred in the left leg more than on the right leg due to compression of the left common iliac vein by the overlying right common iliac artery .
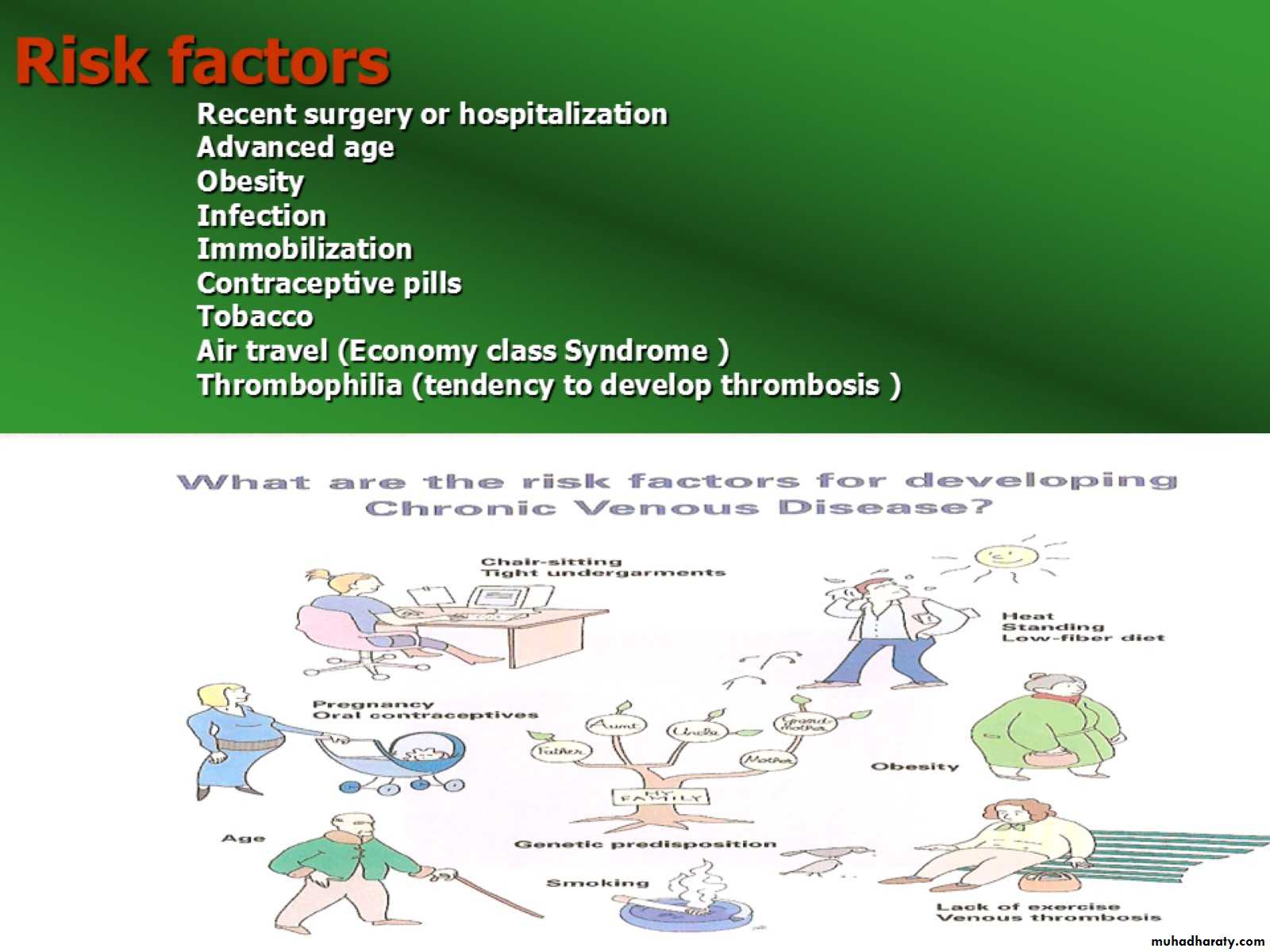
Risk factors Recent surgery or hospitalization Advanced age Obesity Infection Immobilization Contraceptive pills Tobacco Air travel (Economy class Syndrome ) Thrombophilia (tendency to develop thrombosis )
Signs & Symptoms
Physical examination
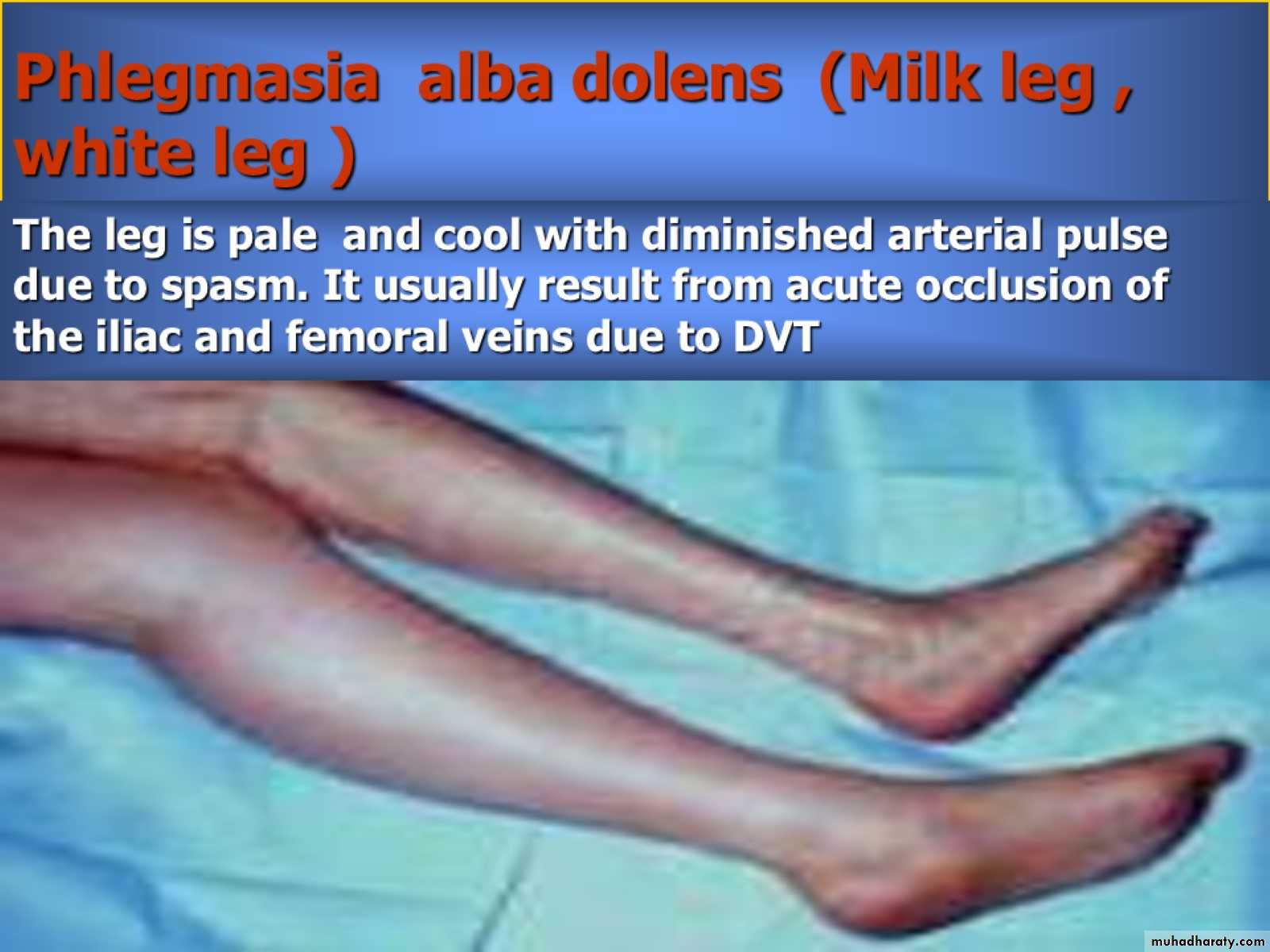
Phlegmasia alba dolens (Milk leg , white leg )
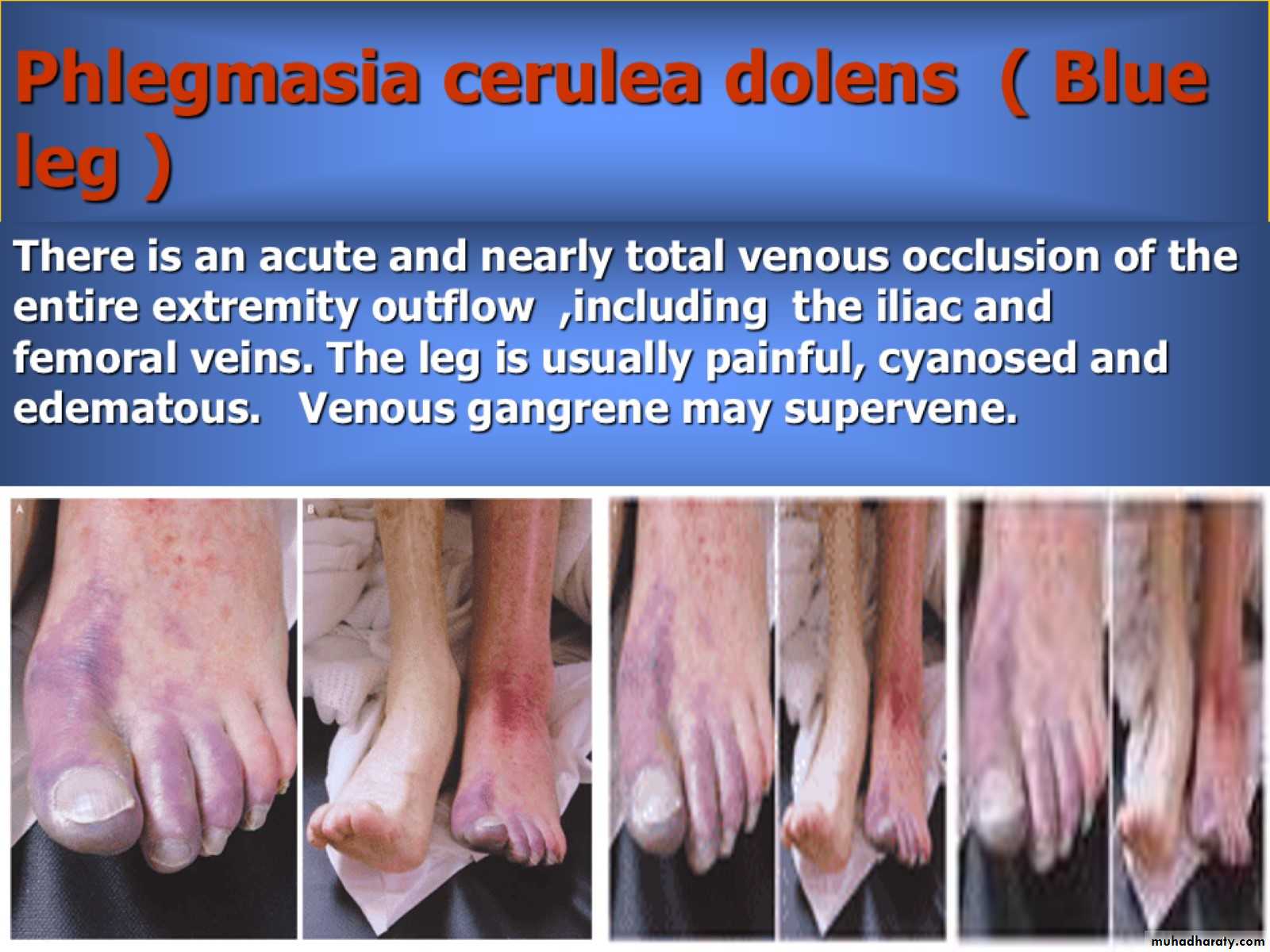
Phlegmasia cerulea dolens ( Blue leg )
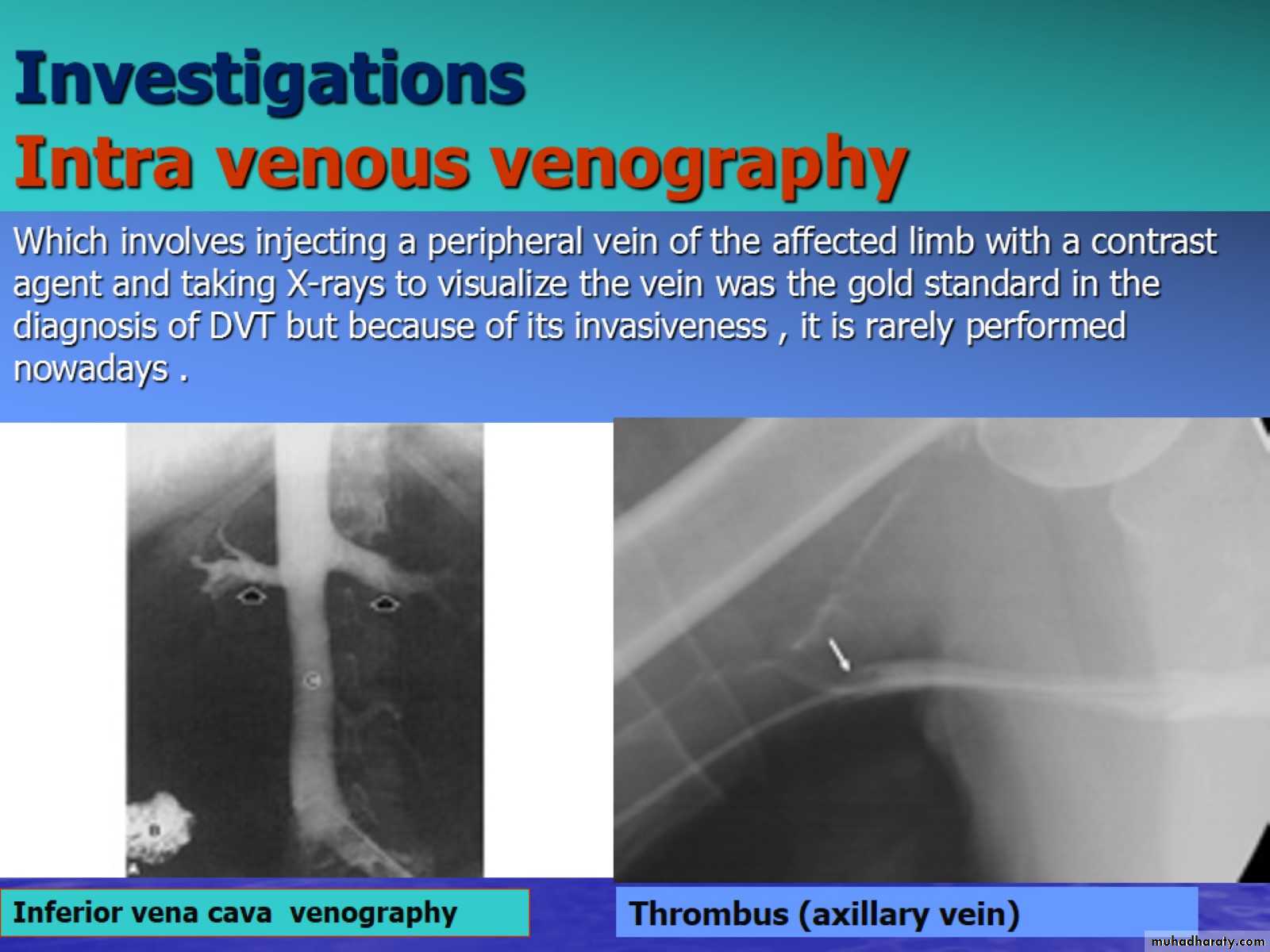
InvestigationsIntra venous venography
Blood Tests
PlethysmographyIt’s a device used to measure changes in blood flow or air volume in different parts of the body. It may be done to check for blood clots in the arms and legs, or other extremities to determine circulatory capacity
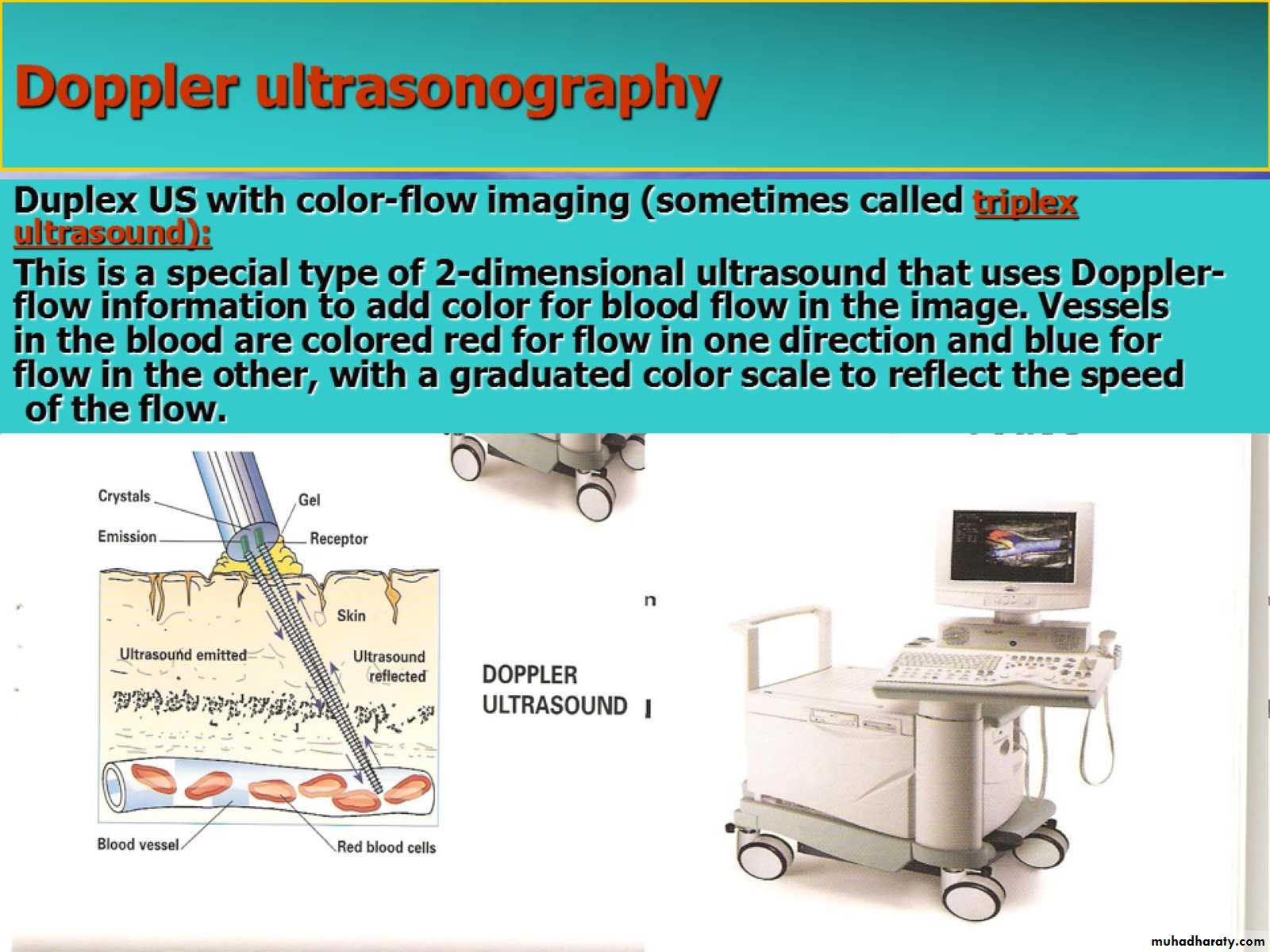
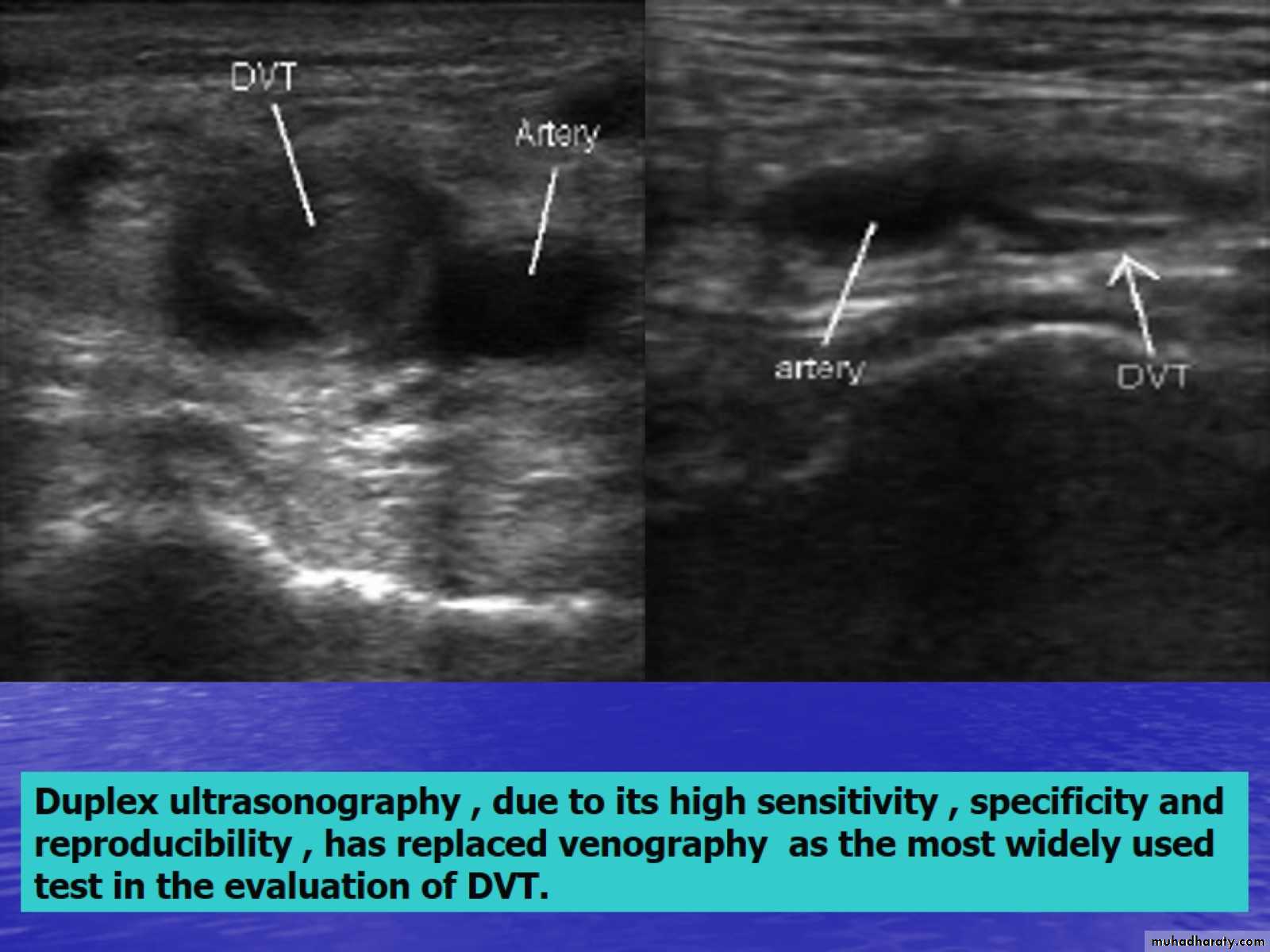
Doppler ultrasonography
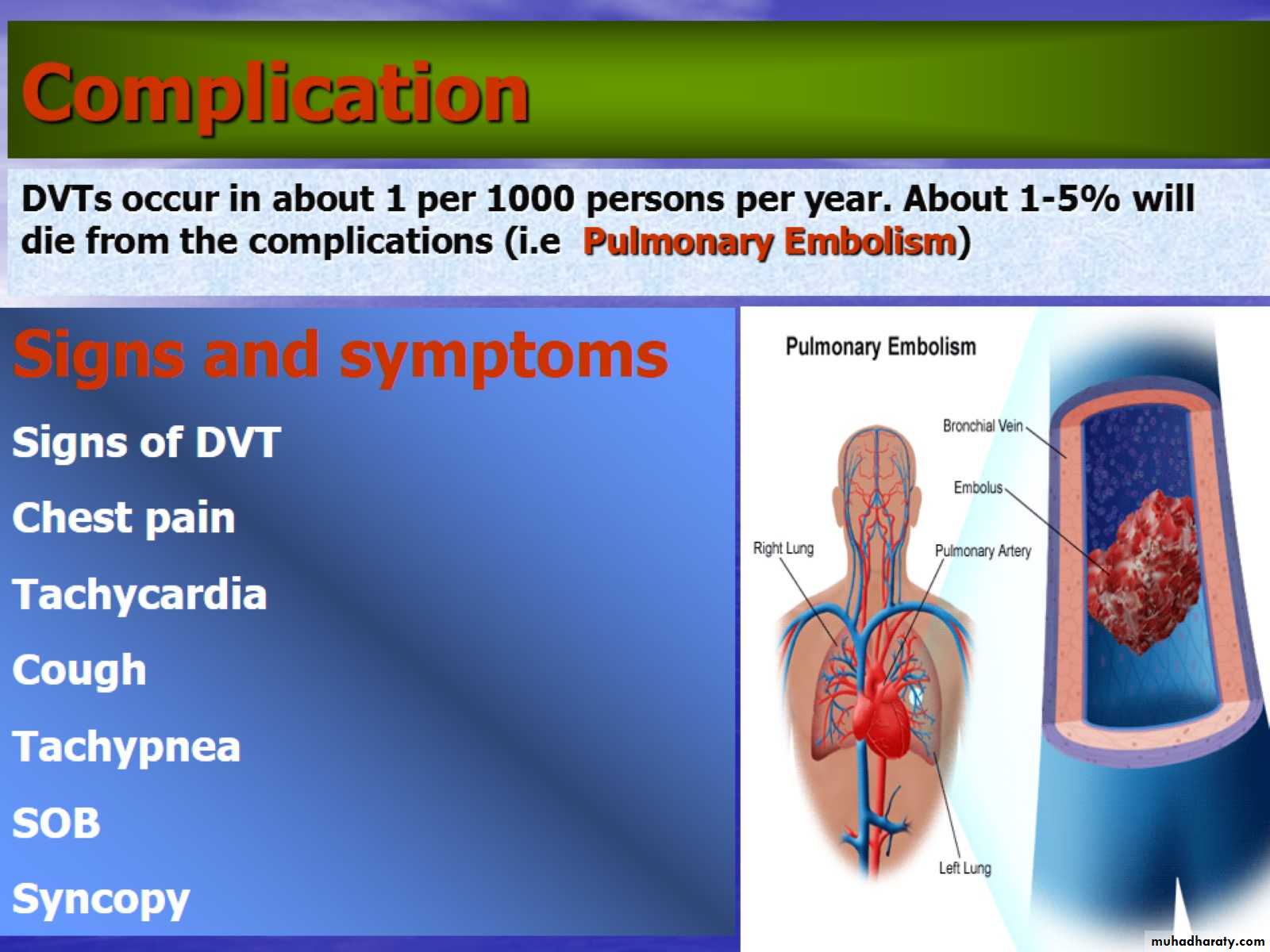
Complication
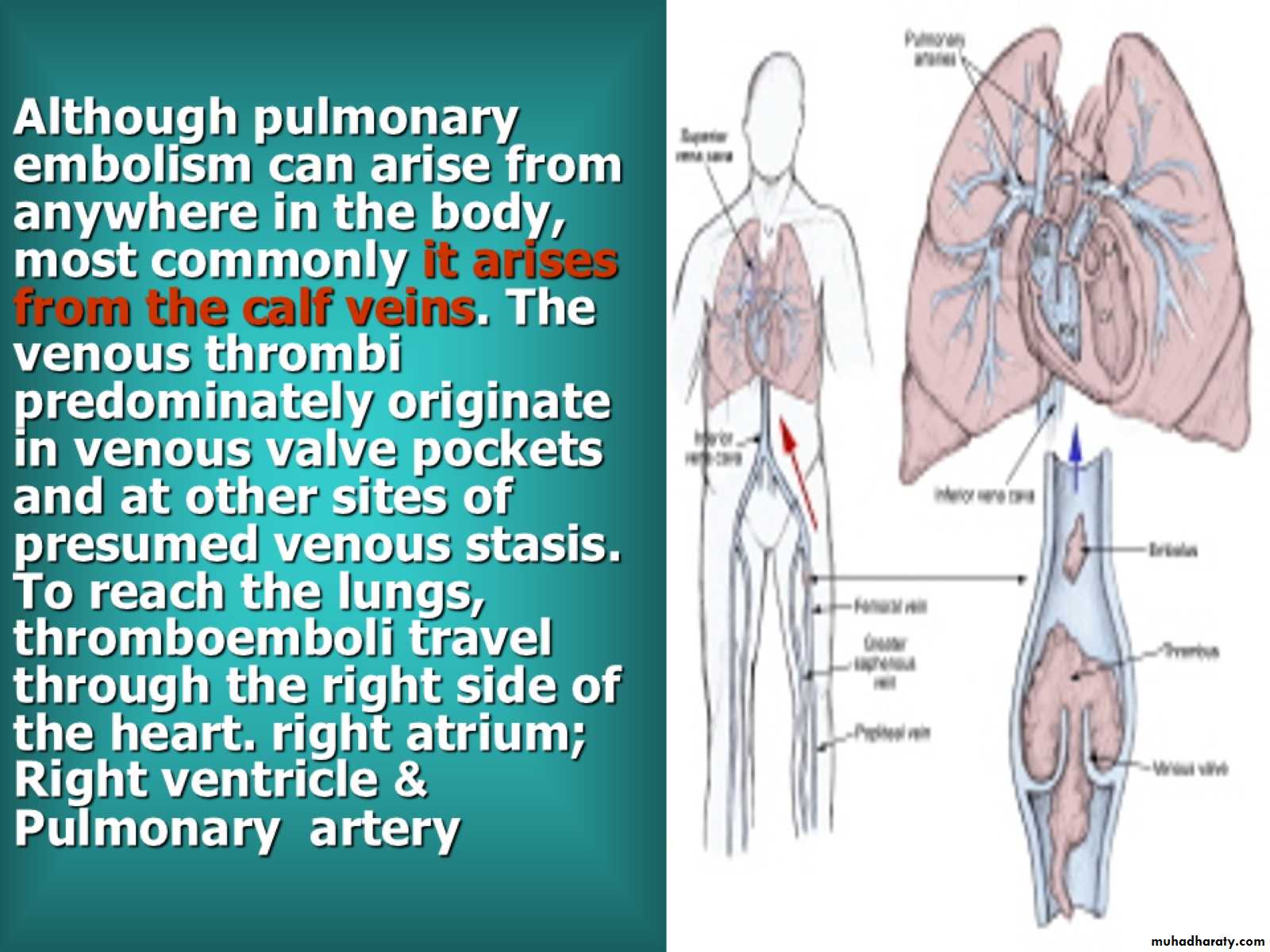
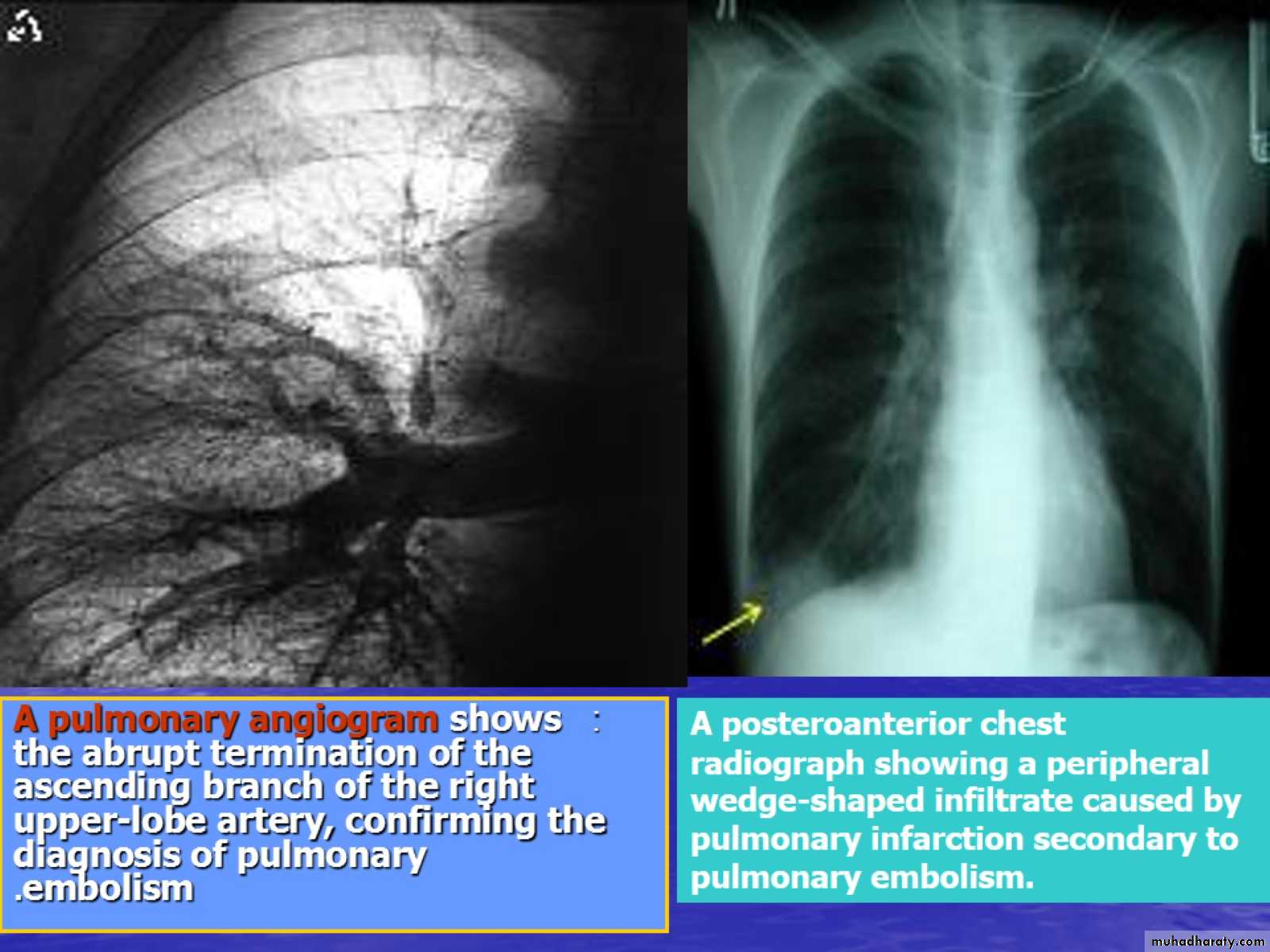
Although pulmonary embolism can arise from anywhere in the body, most commonly it arises from the calf veins. The venous thrombi predominately originate in venous valve pockets and at other sites of presumed venous stasis. To reach the lungs, thromboemboli travel through the right side of the heart. right atrium; &Right ventricle Pulmonary artery
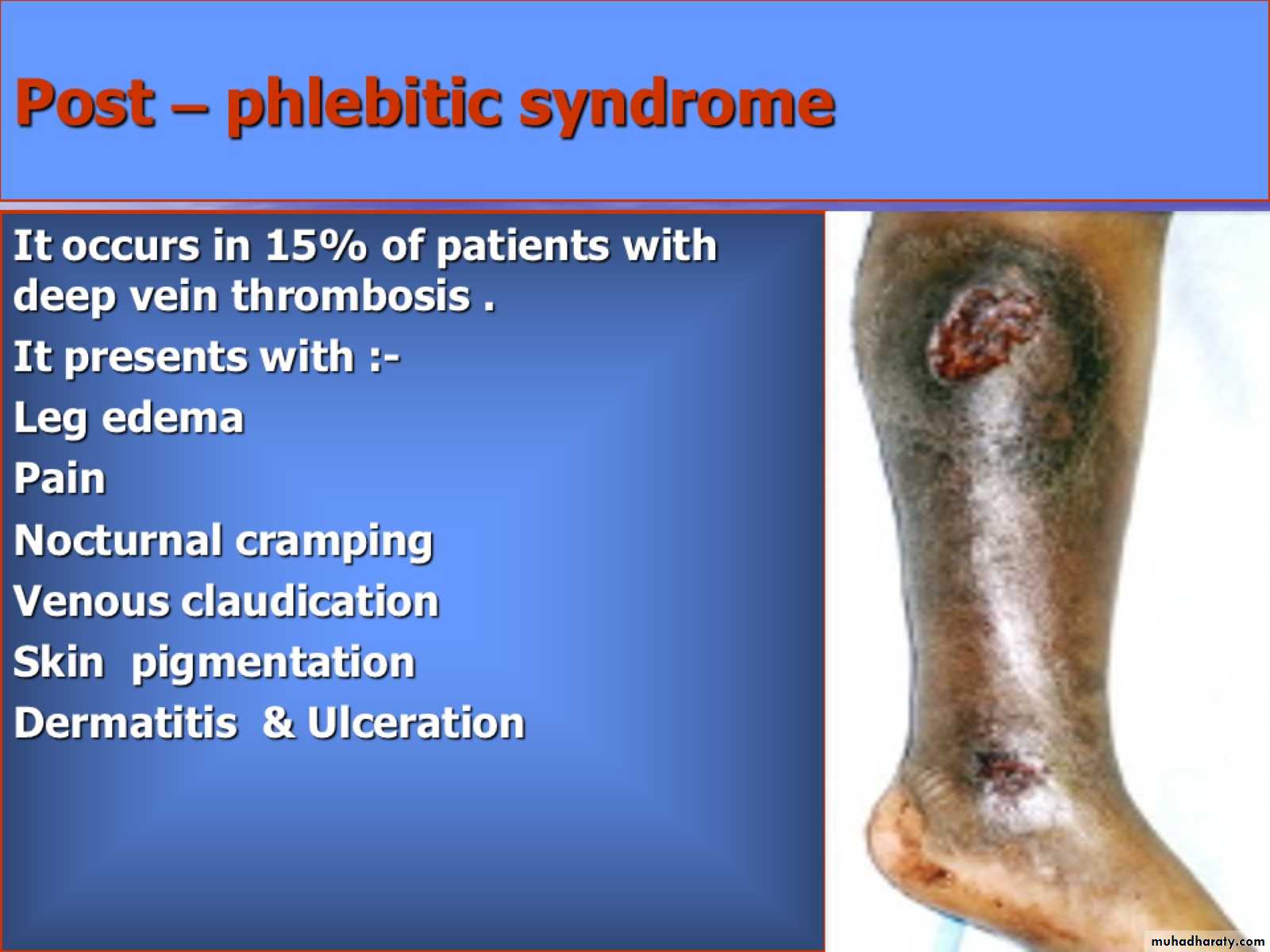
Post – phlebitic syndrome
Treatment
2-Anti coagulant
Heparin increases the activity of anti thrombin III , prevent conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin monitored by P.T.T
3-Thrombolysis