Fifth Stage
E.N.T
Dr. Mushtaq – Lecture 1
1
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing
Introduction
The ears are paired sensory organs comprising the auditory system, involved in
the detection of sound, and the vestibular system, involved with maintaining body
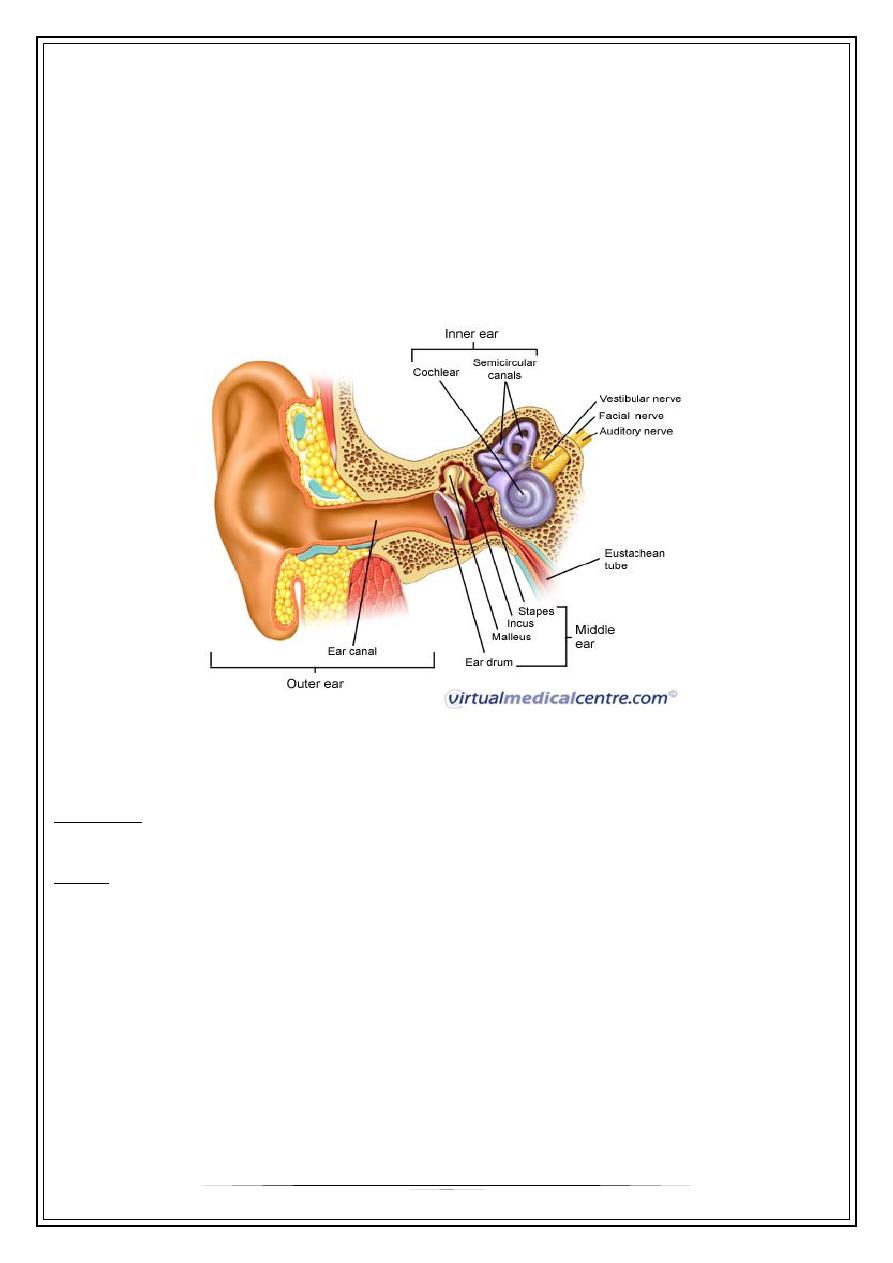
balance/ equilibrium. The ear divides anatomically and functionally into three regions:
the external ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. All three regions are involved in
hearing. Only the inner ear functions in the vestibular system
OUTER EAR
AURICLE-/ framework of cartilaginous fibers except lobule
-capture sound & funnel it
E.A.M.
2.5cm.
Direction
Histology : - cart.2/3 X bone 1/3
- hair /skin
- seb.&cerumucinous gl.
Isthmus
Channel , tubal resonator, amplifying sound pr.
2
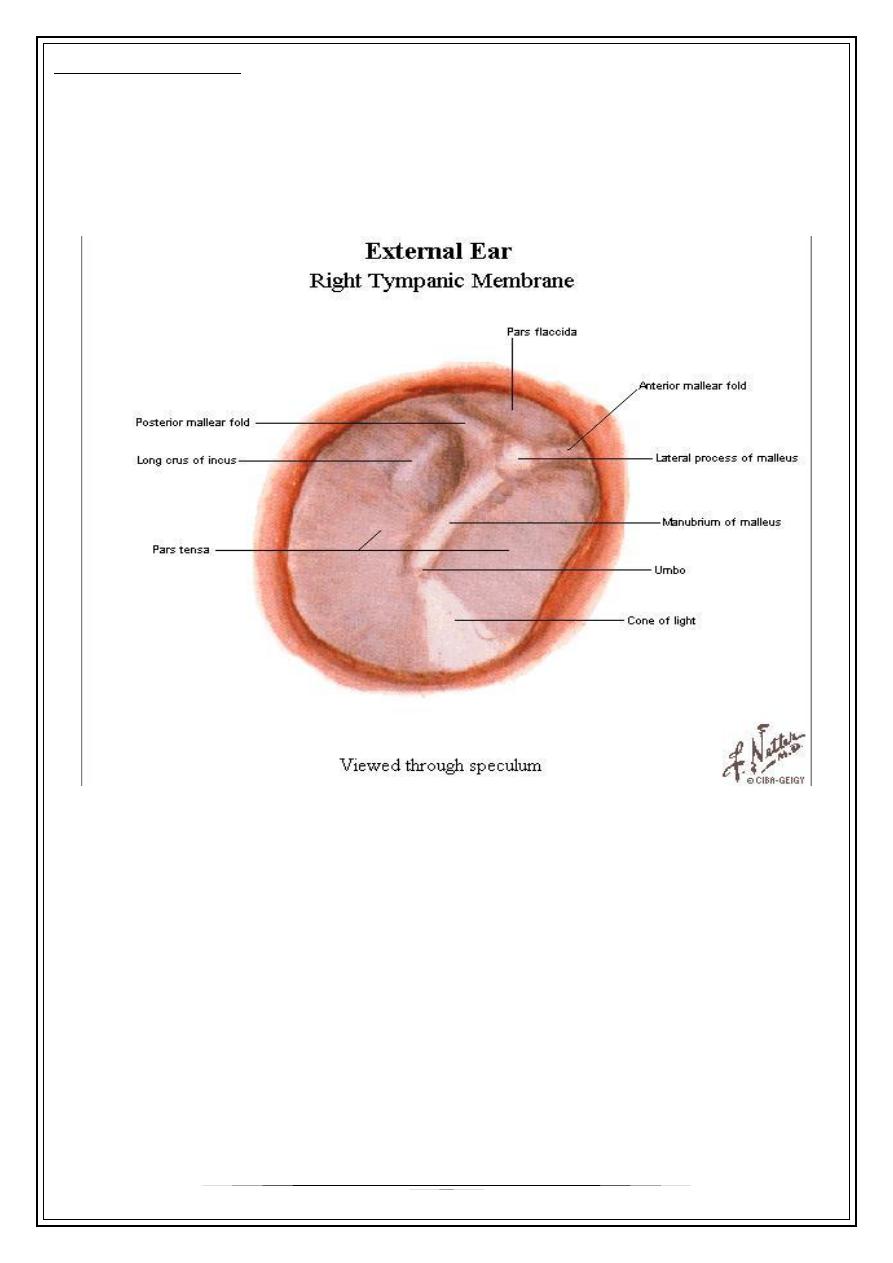
Tympanic membrane
Three layers : - ecto .
- fibrous
- mucosal
Cone-shaped /tension by T.T.M for better reception of vibrations of high frequency
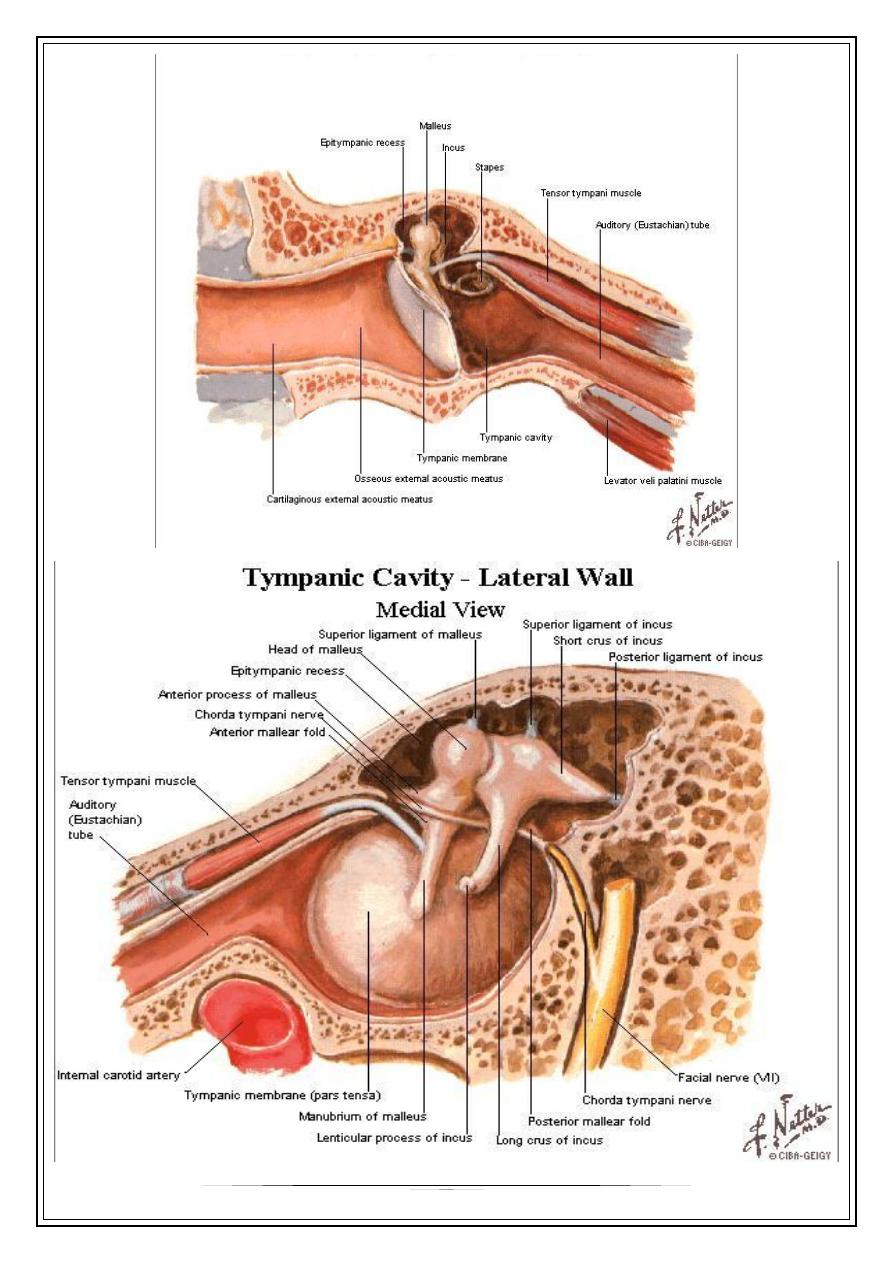
Middle ear
Walls
15x13x2mm.
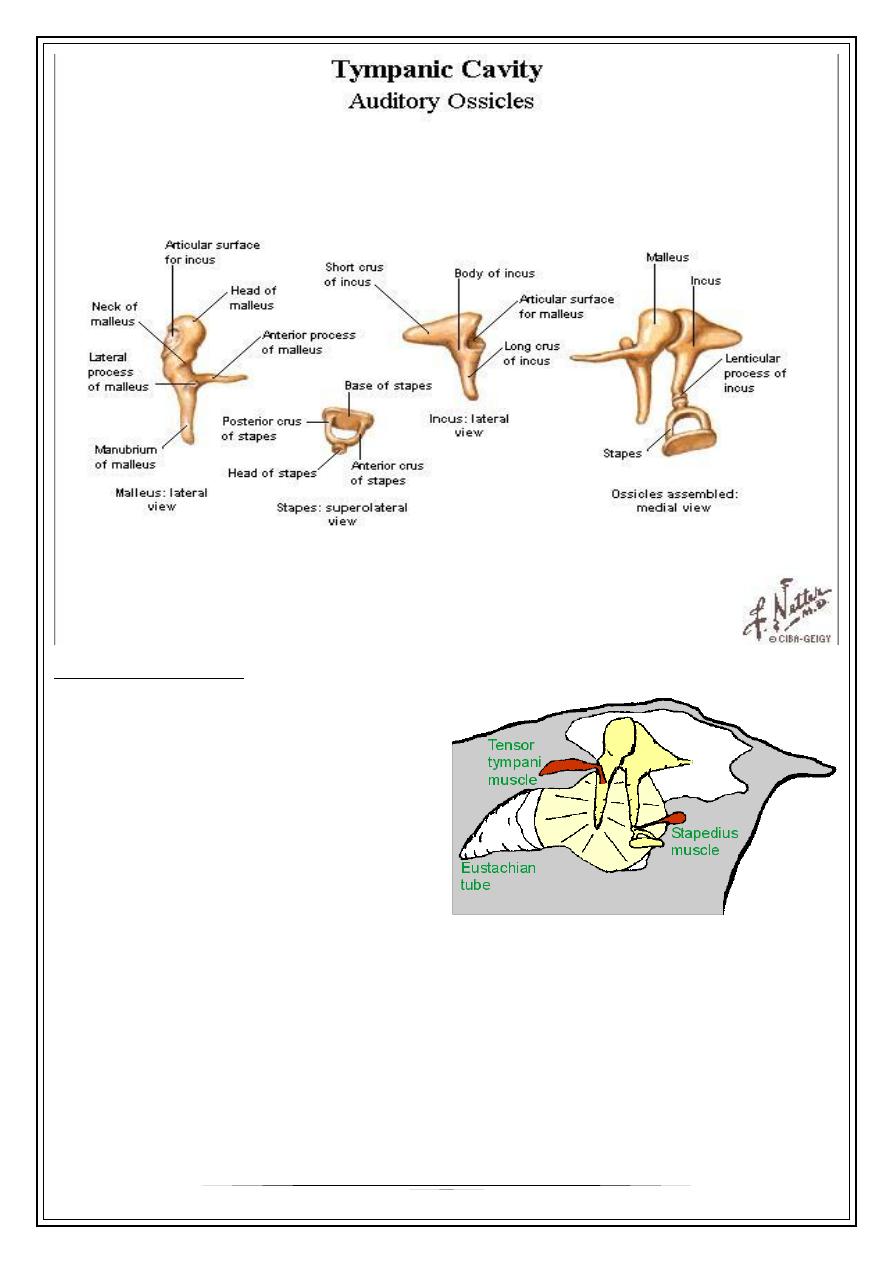
Ossicles : -malleus
-incus
-stapes
Muscles : - tensor tympani m.
- stapedius m.
3
4
Middle Ear Muscles
Tensor tympani
Attached to malleus
Innervated by V, trigeminal
nerve
Stapedius
Attached to stapes
Innervated by VII, facial nerve
Middle Ear Muscle Function:
Help maintain ossicles in proper position
Protect inner ear from excessive sound levels
When ear exposed to sound levels above 70 dB, the muscles contract,
decreasing amount of energy transferred to inner ear
This protective reflex termed "acoustic reflex"

5
Function of Middle Ear
1-Conduction
Conduct sound from the outer ear to the inner ea-
2 ) Protection
Creates a barrier that protects the middle and inner areas from foreign objects
Middle ear muscles may provide protection from loud sounds
3) Transducer
Converts acoustic energy to mechanical energy
Converts mechanical energy to hydraulic energy
4) Amplifier
Transformer action of the middle ear (traveling wave )
Eustachian Tube
The eustachian tube connects the front wall
of the middle ear with the nasopharynx
The eustachian tube also operates like a
valve, which opens during swallowing and
yawning
This equalizes the pressure on either side of the eardrum, which is necessary for
optimal hearing.Without this function, a difference between the static pressure in
the middle ear and the outside pressure may develop, causing the eardrum to
displace inward or outward and this reduces the efficiency of the middle ear and
less acoustic energy will be transmitted to the inner ear.
Inner ear
Bony labyrinth ___ perilymph
Membranous labyrinth ___endolymph
Cochlea
Vestibule(utricle ,saccule ,s.c.c.)
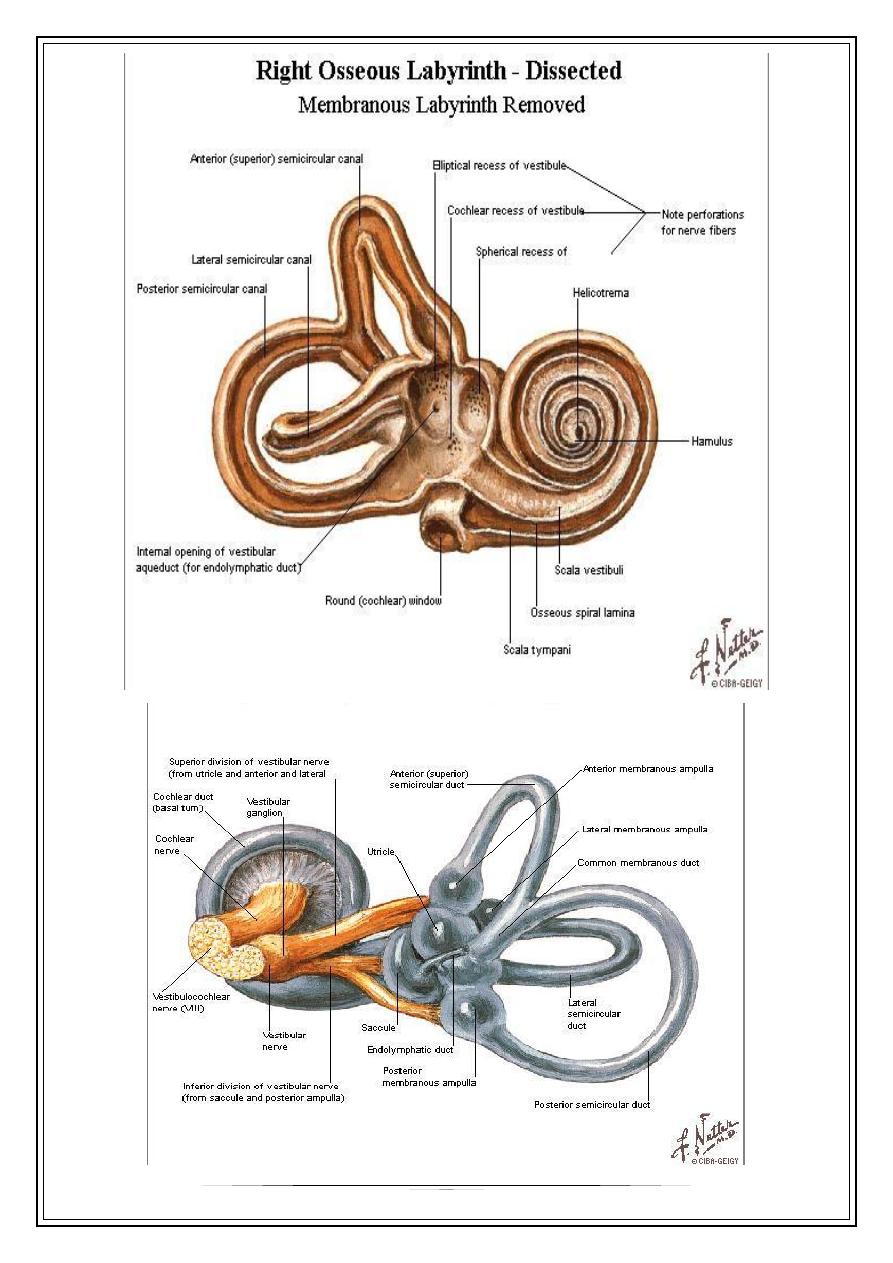
6
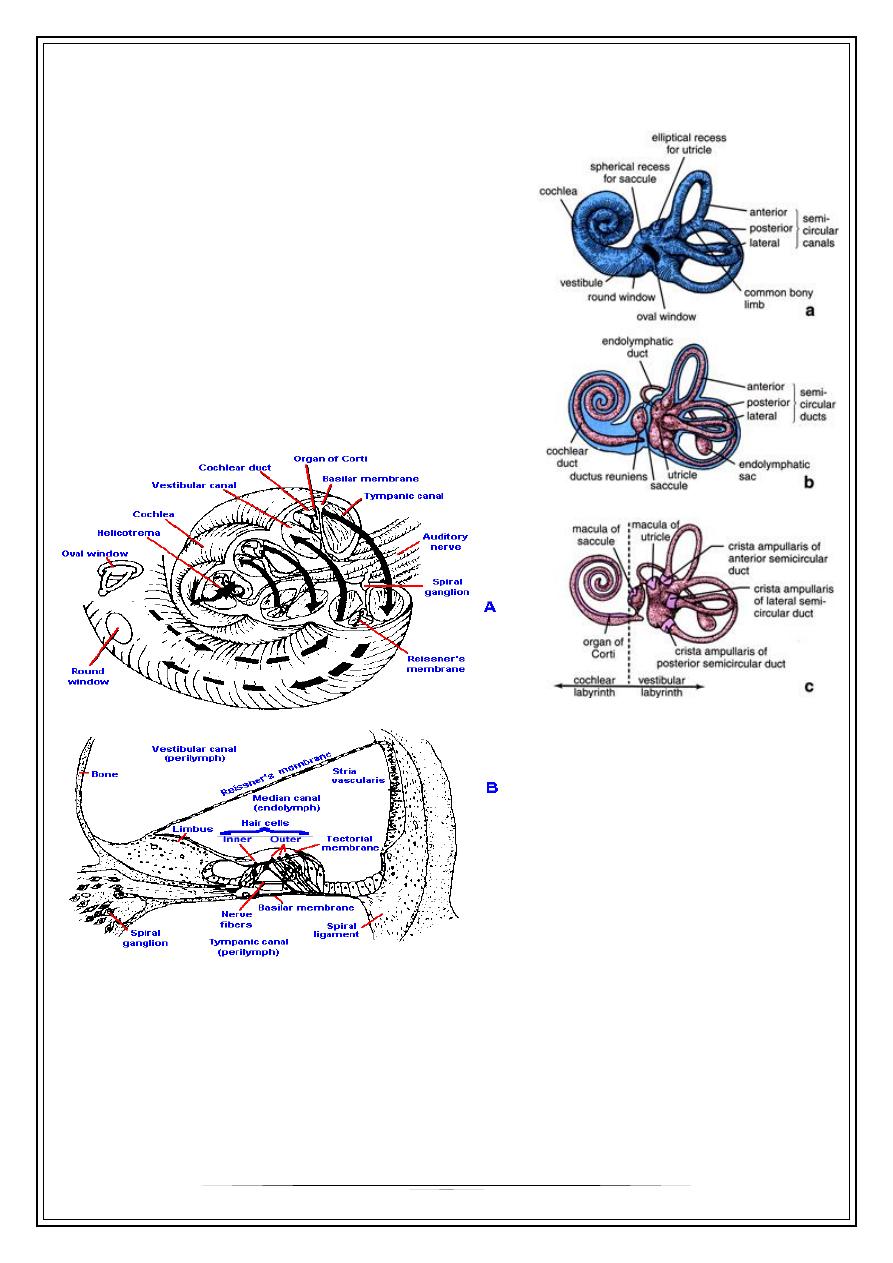
7
Function of Inner Ear
Convert mechanical sound waves to neural impulses that can be recognized by
the brain for:
Hearing
Balance
Cochlea
The cochlea is a spiral structure, like a snail
shell containing two and one half turns from its base
at the oval window to its apex taken along the
central pillar or modiolus,
*Small opening Scala v.&scala t. communicate
through, at apex called helicotrema
Organ of corti
•
Located on the basilar membrane
•
Contains the hair cells covered by tectorial membrane
-Outer h. c.
-Inner h. c.

8
OHC vs. IHC Function
Sound conduction pathways
I. Through Ossicular chain to oval window
II. Directly cross middle ear to round window (large perforation)
III. Bone conduction (vibration of skull bones)
Traveling waves
The impedance of the fluid in the cochlea is about 30 times greater than that of
air, and if the sound were applied directly to the oval window, most of it (~97%) would
be reflected, leaving only 3% transmission.
Transformer/Amplifier
•
The middle ear enhances the transfer of acoustical energy in two ways:
–
The area of the eardrum is about 17 times larger than the oval window
•
The effective pressure (force per unit area) is increased by this
amount.
–
The ossicles produce a lever action that further amplifies the pressure
–
Without the transformer action of middle ear energy in air transmitted to
(about 30 dB loss).
•
Malleus and incus vibrate together, transmitting the sound waves from the
eardrum to the footplate of the stapes (this pushes the oval window in and
out)(mechanical energy)
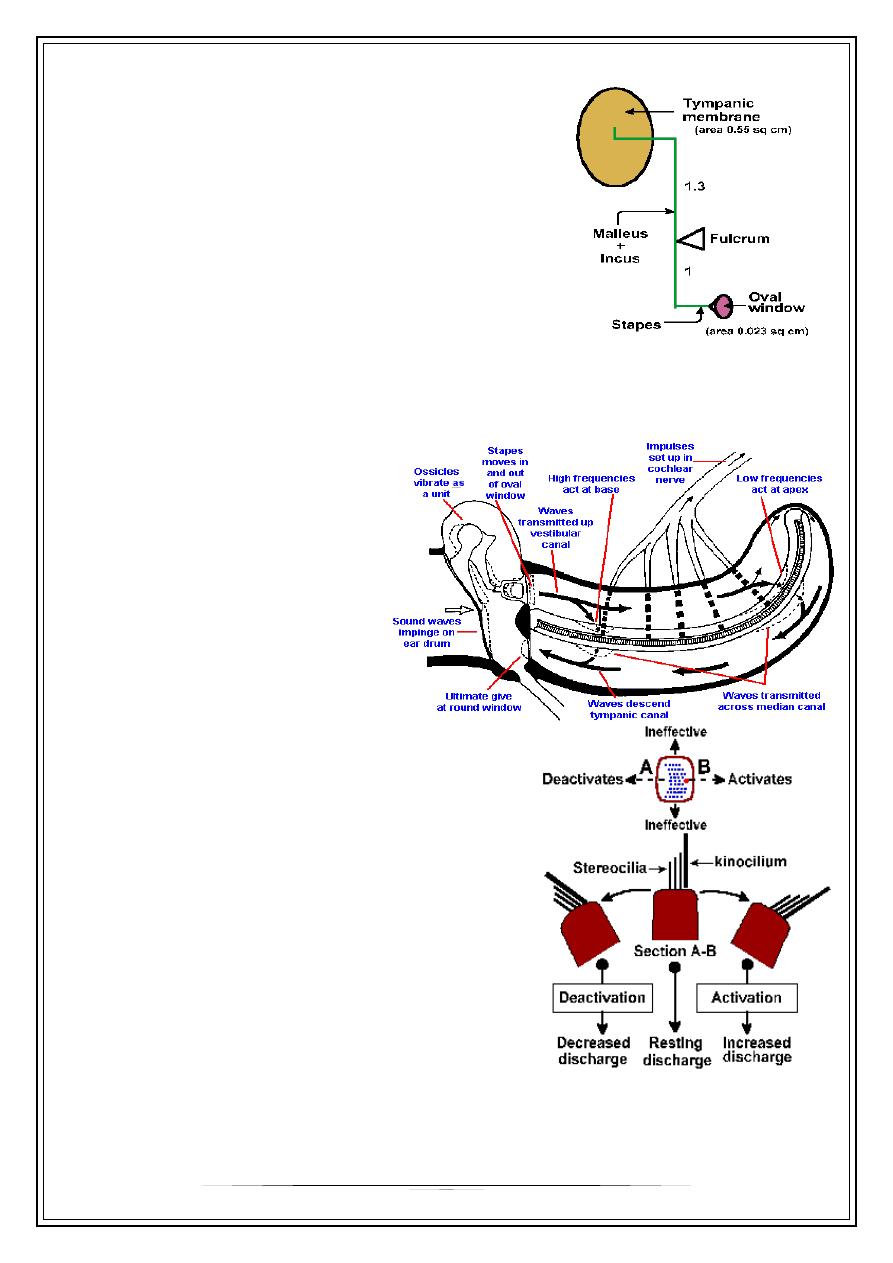
9
Lever system
Areal ratio =18:1
Lever ratio=1.3:1
Transformer ratio=21:1
Fig. 8-5. Schematic drawing of ossicle system to
illustrate the lever arms and the position of the
fulcrum. Relative areas of the tympanic membrane
and the membrane of the oval window are shown
.
When the stapes moves inward at the oval window pressure waves are transmitted
to the perilymph of the scala vestibuli and thence through Reissner's membrane and the
basilar membrane to the scala
tympani. In the scala tympani, the
vibrations pass again through
perilymph to the round window at
the base of the cochlea. The
membranous covering of the round
window bulges into the middle ear
and forms the ultimate "give".The
"give" at the round window is
necessary to prevent pressure-wave
reflections within the cochlea.
Movement of the cilia to kinocillium side results
in a depolarization of the hair cell`s receptor that in
turn releases a transmitter substance that finally
depolarizes the afferent fibers that contact it.resulting
in generation of action potential & transmission of the
impulses
10
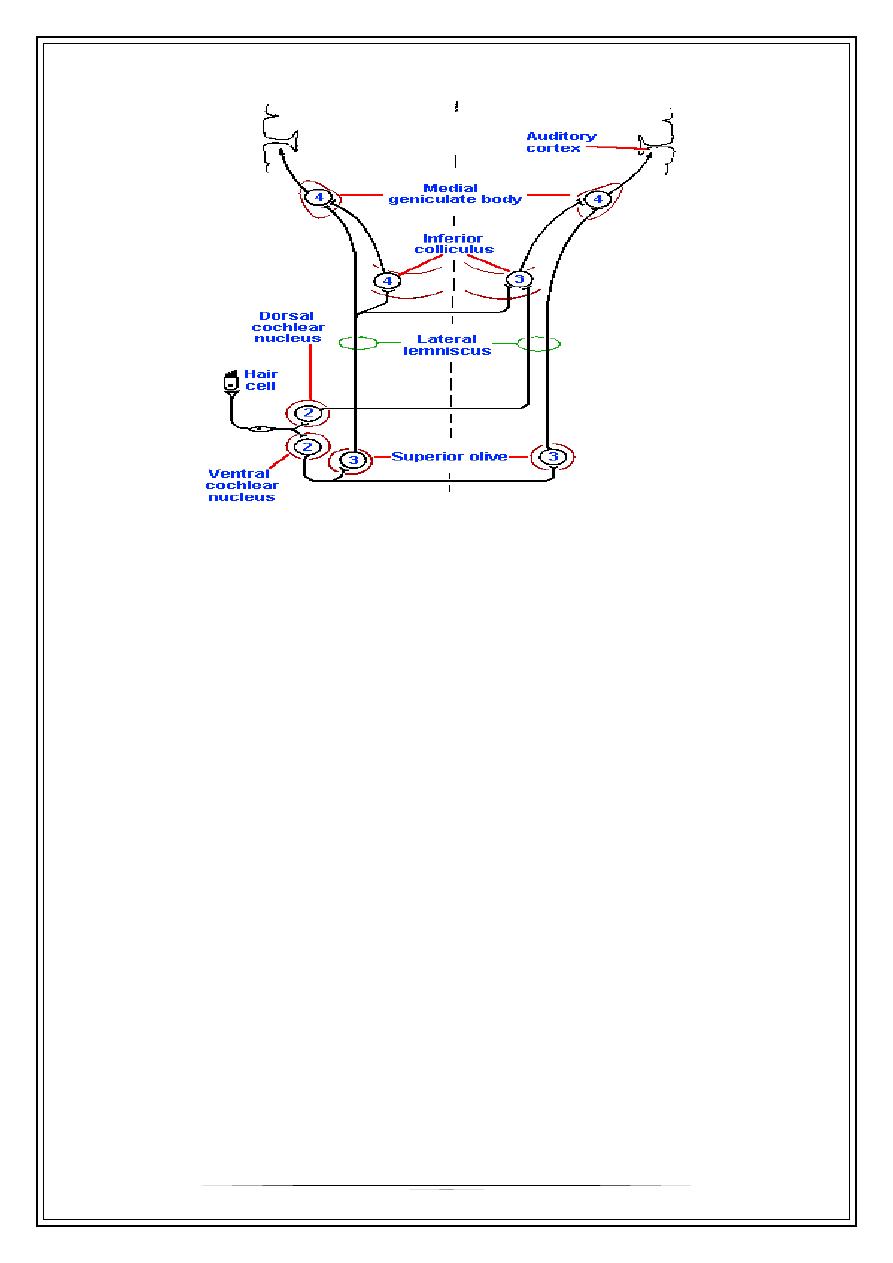
Central auditory pathways
Sound localization
1. Differences in the phase of the signals at each ear help in localization the source
of low-frequency sound.
2. Differences in intensity are used to localize the source of high-frequency sound.
3. The difference in time of arrival of a sound at the two ears
4. Central system function .
- - - - - - - - - -
Question 1/ What is the purpose of the pinna?
A. Cosmetics
B. Sound collector
C. Same side localization
D. A and B
E. A, B and C
Question :2 / The pars tensa portion of the TM:
A. Consists of 2 layers of tissue
B. Consists of 4 layers of tissue
C. Consists of 1 layer of tissue
D. Consists of 3 layers of tissue
E. Consists of 5 layers of tissue
11
Question
:
3/ The Eustachian tube:
A. Opens when one yawns
B. Opens when one smiles
C. Opens when one blinks
D. It is always open
E. Never opens
Question :4/ The middle ear:
A. Converts acoustic energy to hydraulic
B. Converts hydraulic energy to mechanical
C. Converts acoustic energy to mechanical
D. Converts acoustic energy to electrical
E. Converts mechanical to electrical
Question
:
5/ The middle ear amplifies sound:
A. About 15 dB
B. About 25 dB
C. About 35 dB
D. About 20 dB
E. About 30 dB
Question 6
:
/ The function of the inner ear:
A. Balance
B. Hearing
C. Touch
D. All the above
E. A and B
Question : 7/ The channel that houses the organ of Corti:
A. Scala tympani
B. Scala media
C. Scala vestibuli
D. Semicircular canals
E. B and D
Thank you,,,
