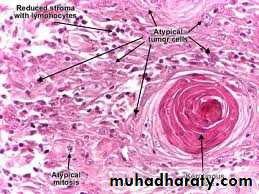
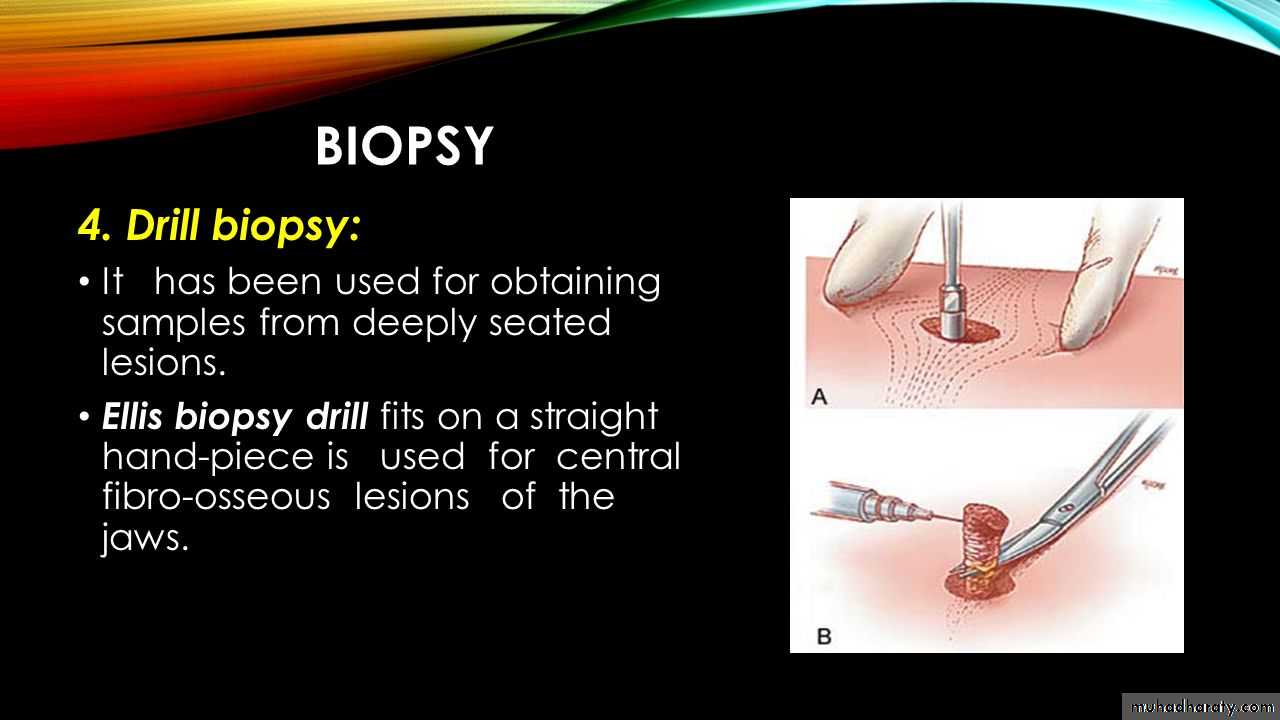
Biopsy in oral surgery
Biopcy: it’s a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist or an interventional cardiologist. involving removal of sample cells or tissues for examination under microscope to determine the presence or extent of disease.different techniques are used in clinical practice to obtaia specimen of tissue for biopsy purposes which are :
• Incisional biopsy :
when this technique is employed only part of the lesion is removed for biopsy purposes and it is usually used to obtain specimens of lesions which might be difficult to excise completely owing to either their extent or situation in the mouth.
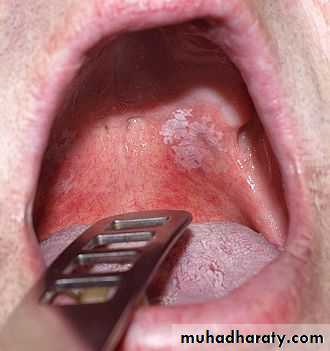
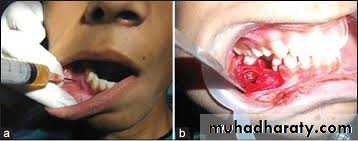
commonest lesions of this type are the white hyperkeratotic lesions which effect the oral mucosa, in such cases bleeding ulcerated ,painful or indurated areas should always be removed for biopsy We must ensure that local anesthetic solution is deposited well away from the site from which the tissue is to be removed.
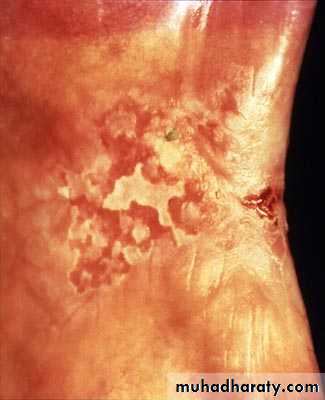
Incisional biopsy should not be performed on either pigmented or vascular lesions melanomas are highly metastatic and so pigmented lesions should be excised with a generous margin of macroscopically normal tissue around and beneath them, a clinical diagnosis of hemangioma can often be confirmed by the aspiration of blood from the lesion into a glass syringe via a wide- bore needle
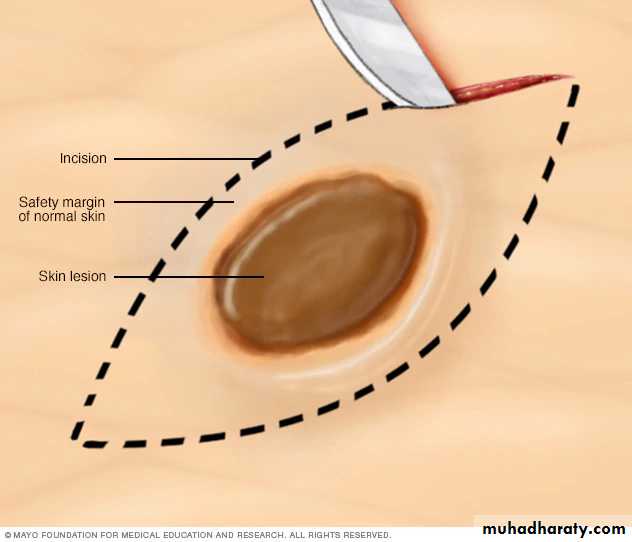
• Excisional biopsy:
During an excisional biopsy, you most remove an entire lump or an entire area of abnormal mucosa or skin , including a portion of normal skin or oral mucosa . You'll likely receive stitches to close the biopsy site after this procedure.3-Aspiration biopsy:
aspiration biopsy is a most valuble investigation and should be carried out on all cystic and fluctuant lesions.it is simple examination and causes the patient minimal inconvenience local anesthesia is injecte over the lesion after which a wide-bore needle attached to a 10-ml syringe is Inserted.
• inability to aspirate usually indicates that the lesion is solid.
• aspiration of air in the maxillary molars indicates that the needle is in the maxillary sinus and it is best method of differentiating the sinus from a suspected cystic.
• Aspiration of air from a cystic lesion in the lower jaw usually indicates a solitary bone cyst (traumatic, hemorrhagic)
• aspiration of pus indicates an abscess or an infected cyst.
• Keratin aspiration which has the clinical appearance of pus without its unpleasant smell denotes the presence of keratocyst
• while periodent and dentigerous cyst contain straw -coloured fluid containing cholesterol crystals.
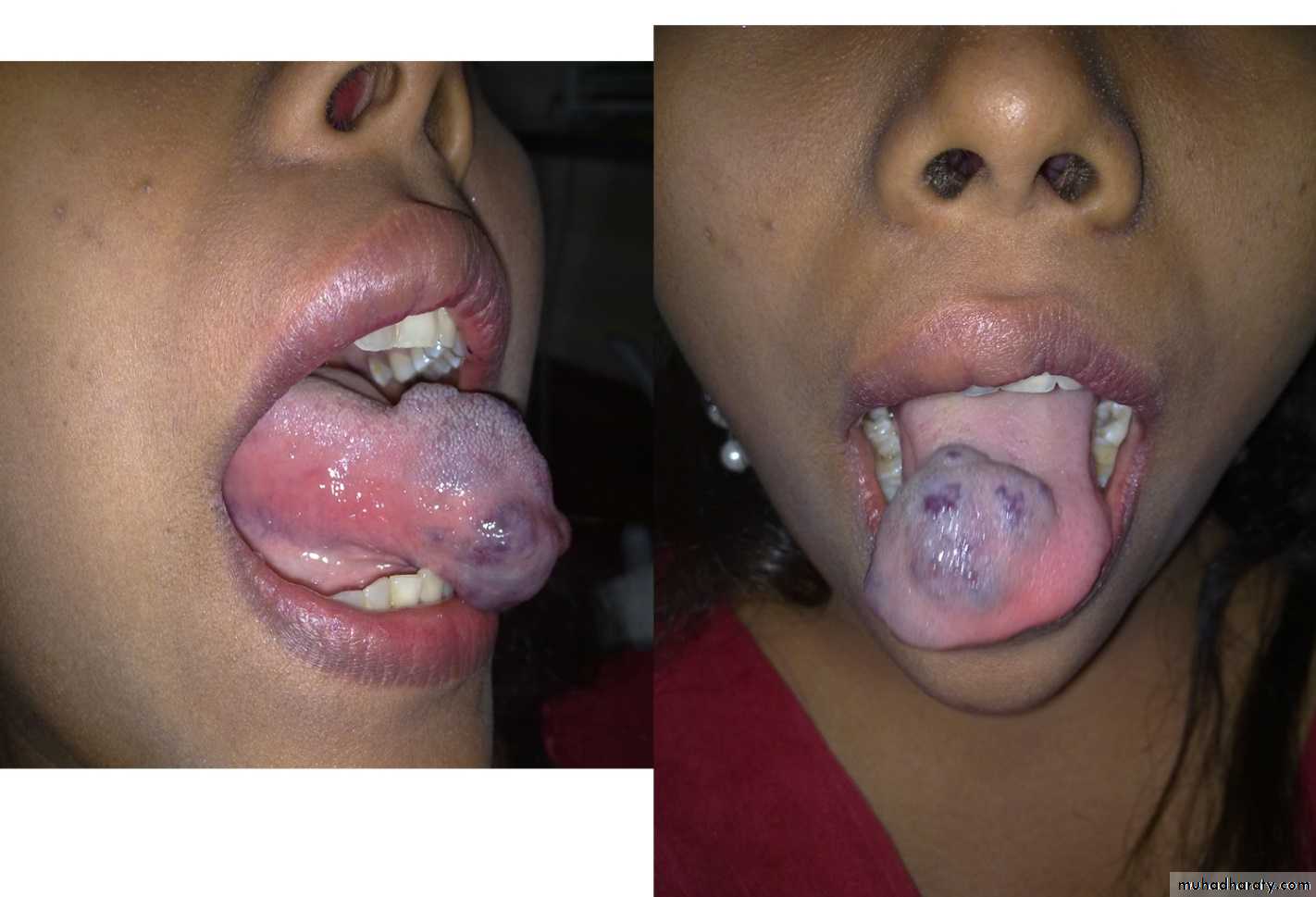
• aspiration of blood denotesa hemorrhagic tumor or a blood vessel
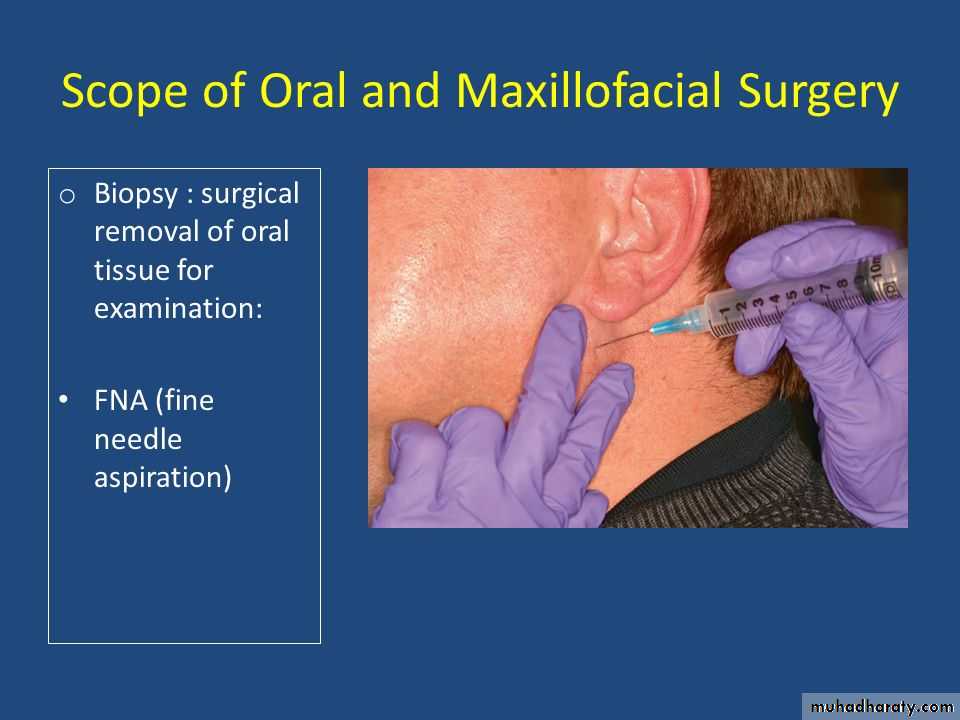
4. Fine-needle aspiration (FNA):
is a diagnostic procedure used to investigate lumps or masses. In this technique, a thin (23-25 gauge), hollow needle is inserted into the mass for sampling of cells that, after being stained, will be examined under a microscope called fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) (the latter to emphasize that any aspiration biopsy involves cytopathology not histopathology). Fine-needle aspiration biopsies are very safe, minor surgical procedures. Often, a major surgical (excisional or open) biopsy can be avoided by performing a needle aspiration biopsy.Today, this procedure is widely used in the diagnosis of cancer and inflammatory conditions.
A needle aspiration biopsy is safer and less traumatic than an open surgical biopsy
Common complications include bruising and soreness.
The biopsy is very small (only a few cells), that the problematic cells will be missed, resulting in a false negative result.
The cells taken will not enable a definitive diagnosis.