
1
Urinary incontinence
Definition
Involuntary loss of urine which is a social or hyogenic problem and
is objectively demonstrable
Types
1.retention overflow
2.stress incontinence (urodynemic stress incontinence)
3.detrusor instability
4.urinary fistulae (true incontinence)
Retention overflow
Gradual failure of bladder emptying may lead to chronic retention and
finally when normal voiding is ineffective, to overflow incontinence

2
Causes
. Haematocolpas: retention of blood into vagina and pressure effect on
the urethra
. Retroverted gravid uterus: when the fundus is directed back word
(toward the sacrum )and the cervix is directed forewords (to word the
anterior fornix) usually it is found in 20-30% of female if it is mobile ,it
has no effect and sometimes, it is fixed (due to disease process like
endometriosis and adhesion )and causes some problem
. Impacted tumor in the pelvis eg fibroid
. Prolong labour and episiotomy
. Difficult vaginal delivery cause inhibition of bladder function lead to
urine retention
. Sever vaginal prolapse cause angulation of the urethra
. Post-operative specially vaginal surgery
. Others Lower mote neuron lesion
Drugs
Urodynemic stress incontinence
Is define as the involuntary leakage of urine during increase intra-
abdominal pressure, in the absence of detrusor contraction .it is a
urodynamic diagnosis
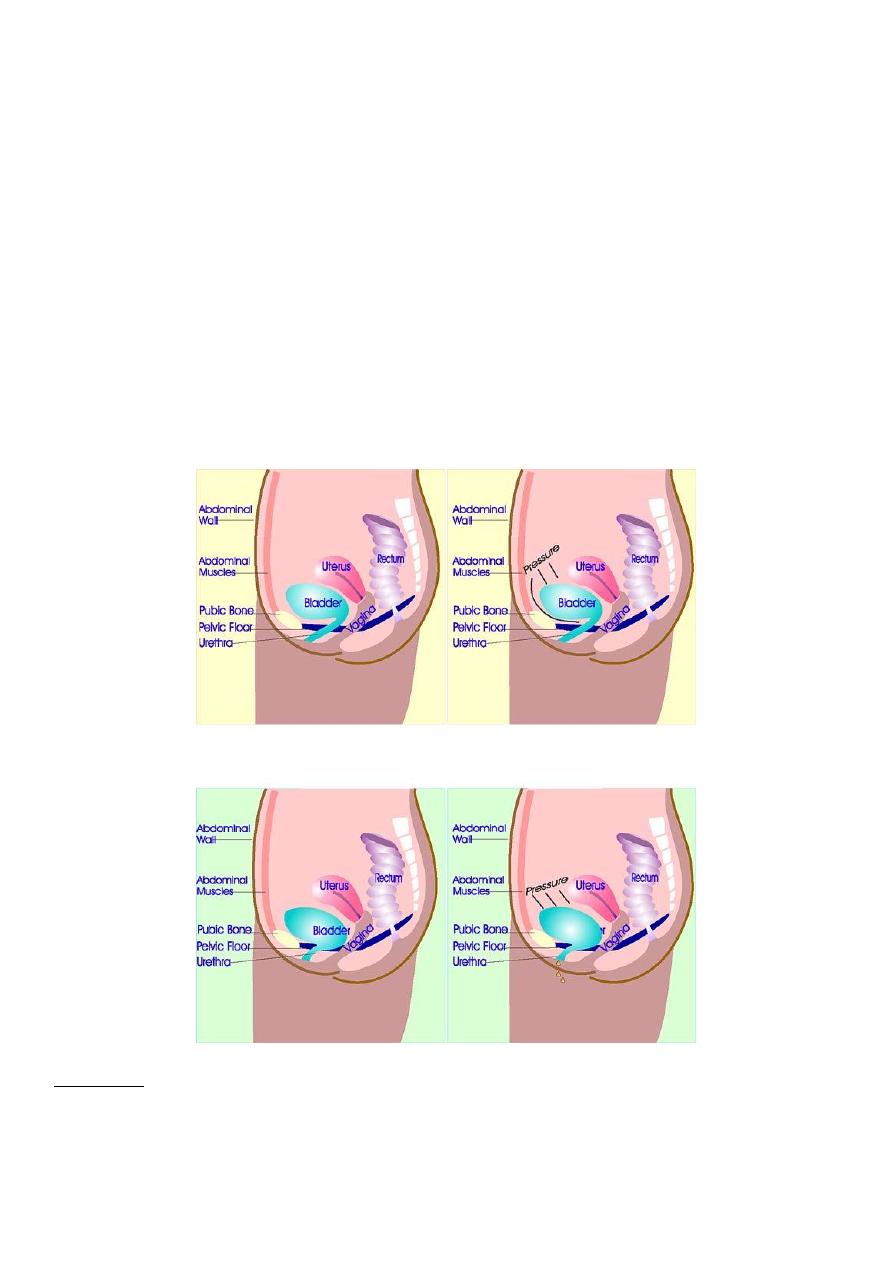
3
This condition related to weakness at vesicourethral junction defect in
one or more supporting mechanism of the urethra. Its common
symptoms 50% associated with some degree of anterior vaginal wall
prolapse .
The bladder neck and proximal urethra are normally situated in an
intra-abdominal position above the pelvic floor and are supported by
the pubourethral ligaments. Damage to either the pelvic floor
musculature (levator ani) or pub urethral ligament may result in
descend of the proximal urethra such that it is no longer an intra-
abdominal organ and this results in leakage of urine per urethra during
stress
Causes :
. Damage to nerve supply of pelvic floor and urethral sphincter (difficult
labor ,instrumental delivery ,direct trauma )

4
. Mnopause associated with tissue atrophy
. Congenital
. Chronic cause like obesity , chronic cough ,obstructive air way disease
Investigation :
1.midstream urine specimen
2.urinary diary :is a simple record of the patient fluid intake and
output, episode of urgency and leakage ,and precipitating factors
and events are also recording .
3.pad test :used to verify and quantify urine loss
The patient wears pre weight sanitary towel ,drink 500 ml of
water and rest for 15 min .after a series of define maneuver ,the
pad is re weight ,urine loss of more than 1 gm is considered
significant
4.uroflowmatry :is measurement of urine flow rate
5.cystomatry its measurement of the pressure volume
relationship of the bladder with known volume of water and
observe pressure changes in the bladder during filling
The fallowing are parameters of normal bladder function:
. Residual urine of 50 ml
. First desire to void between 150-200 ml
. Capacity between 400- 600 ml
. Detrusor pressure rise of less than 15 H
2
O during filling and
in standing
. Absence of detrusor contractions
. No leak during coughing
. Voiding detrusor pressure rise of less 70 cm H
2
O with apeak
flow rate of more than 15 ml/ s for volume more 150 ml
6. Videocystourethrography :
7.intravenous urography

5
8.ultrasound
9.cystourthroscopy
10. Urethral pressure profilometry
11. Ambulatory monitoring
Treatment
Surgery is the most commonly employed treatment for stress
urinary incontinence
The aim of all the surgical procedures is to correct the pelvic
relaxation defect and to stabilize and restore the normal intra
abdominal position of the proximal urethra
The aim of the surgery are
. To provide suburethral support
. Restoration of proximal urethra and bladder neck to the zone of
intra abdominal pressure transmission
. To increase urethral resistance
. Combination of both
Either vaginal or abdominal approach
Type of surgery
. Anterior colporraphy :it is usually the best operation for
cystourethrocel, the cure rates for stress incontinence are poor
compared with other operations
. Marshall-marchetti-krantz procedure is suprapubic operation in
which the para urethral tissue at the level of bladder neck is
sutured to the periostium and perichondrium of the posterior
aspect of the pubis symphysis

6
. Burch colposuspension : the fascia lateral to bladder neck and
proximal urethra is sutured to ipsilateral iliopectineal ligament
. Laparoscopic colposuspension
. Tvt (transvaginal tape )
. Sling operation
