NEOPLASIA
Dr Mustafa Salah Fadhil MSc, FIBMS pathMolecular basis of cancer
• Nonlethal genetic damage, the initial damage (or mutation) may be :A) Acquired by environmental factors such as:
- Radiation
- Chemical substances
- Viruses
B) Inherited in the germ line cells; e.g. Familial adenomatous polyps (APC gene) autosomal dominant disorder.
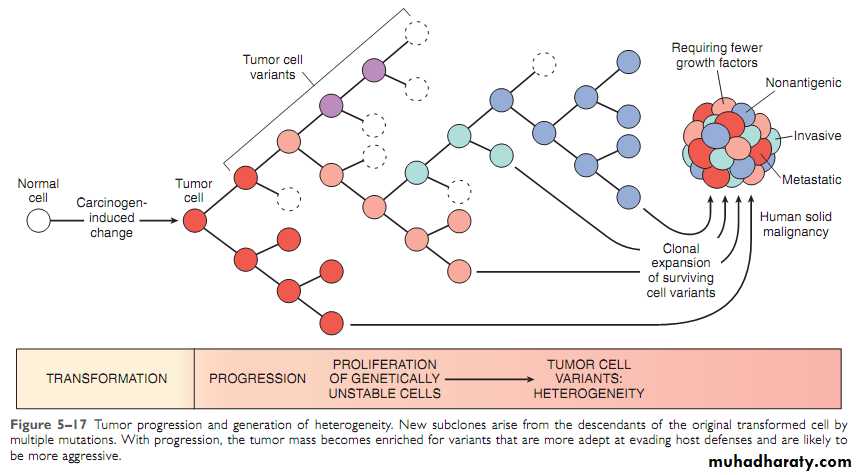
• A tumor is formed by the clonal expansion of a single precursor (progenitor) cell that has incurred genetic damage (i.e., tumors are clonal).
• Involvement of normal regulatory genes. Four classes of normal regulatory genes are involved in carcinogenesis:
• Proto-oncogenes.
• Tumor Suppressor Genes.
• Programmed cell death genes.
• DNA repair genes.
1-Proto-oncogenes:
Proto-oncogenes: normal cellular genes whose products promote cell proliferation.Oncogenes: are genes that created by mutations in proto-oncogenes and encode proteins called oncoproteins that have the ability to promote cell growth in the absence of normal growth-promoting signals.
The numerous proto-oncogenes fall into at least four main categories:
-Genes which produce growth factors.
-Genes which produce growth factor receptors.
-Genes which encode ‘signal transducers’, i.e. proteins which transmit the growth signal to the nucleus.
-Genes which activate other genes to promote growth.
Transformation of proto-oncogenes to oncogenes:
- Point mutation
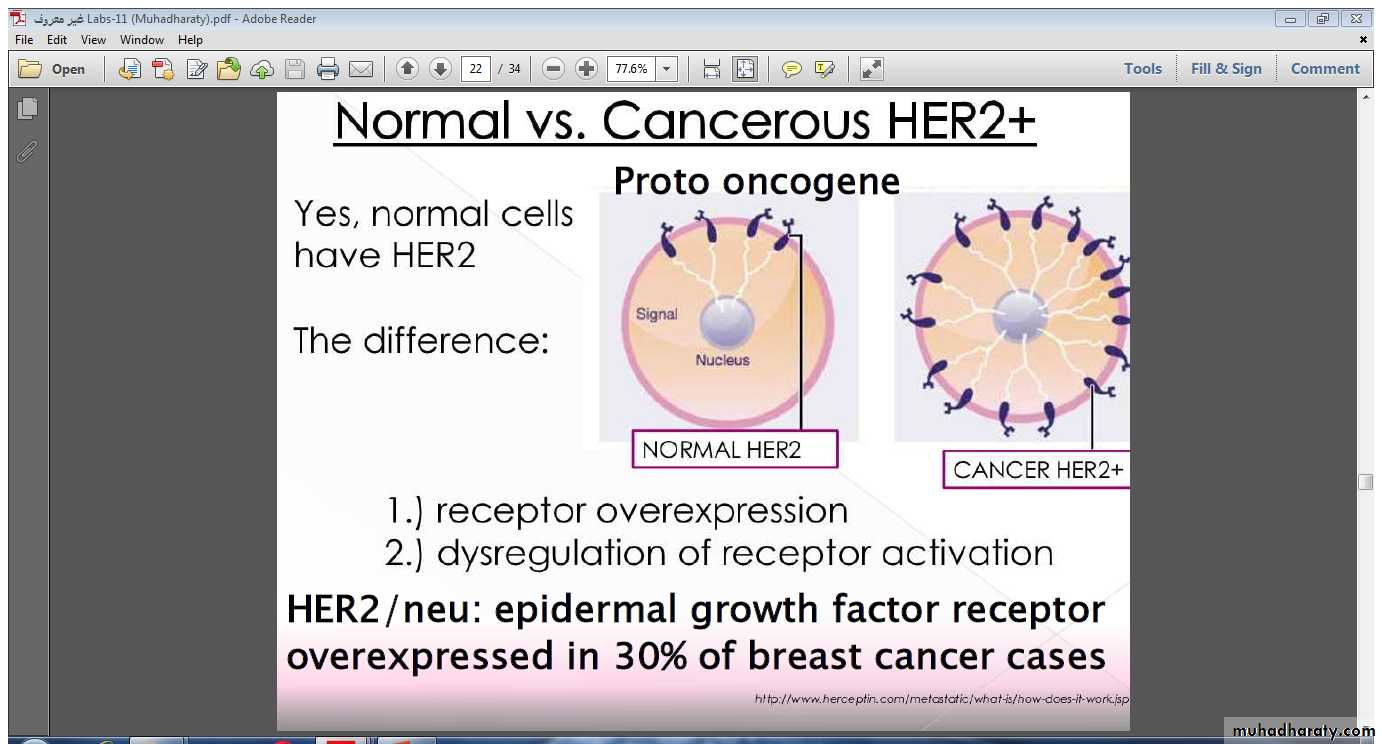
- Chromosomal translocation- Amplification e.g.
ERBB2 (HER-2) overexpression in Breast carcinoma
N-myc gene overexpression in neuroblastoma
2- Tumor Suppressor Genes
These are genes whose products normally stop a cell growing, or trigger checkpoints that cause cell cycle arrest if DNA damage occurs.Tumor suppressor genes are cell cycle arrest genes or DNA repair genes, e.g.:
Mutant P53 gene (found in more than 50% of cancers).
Mutant APC gene →Familial adenomatous polyps
Mutant Rb gene → retinoblastoma.
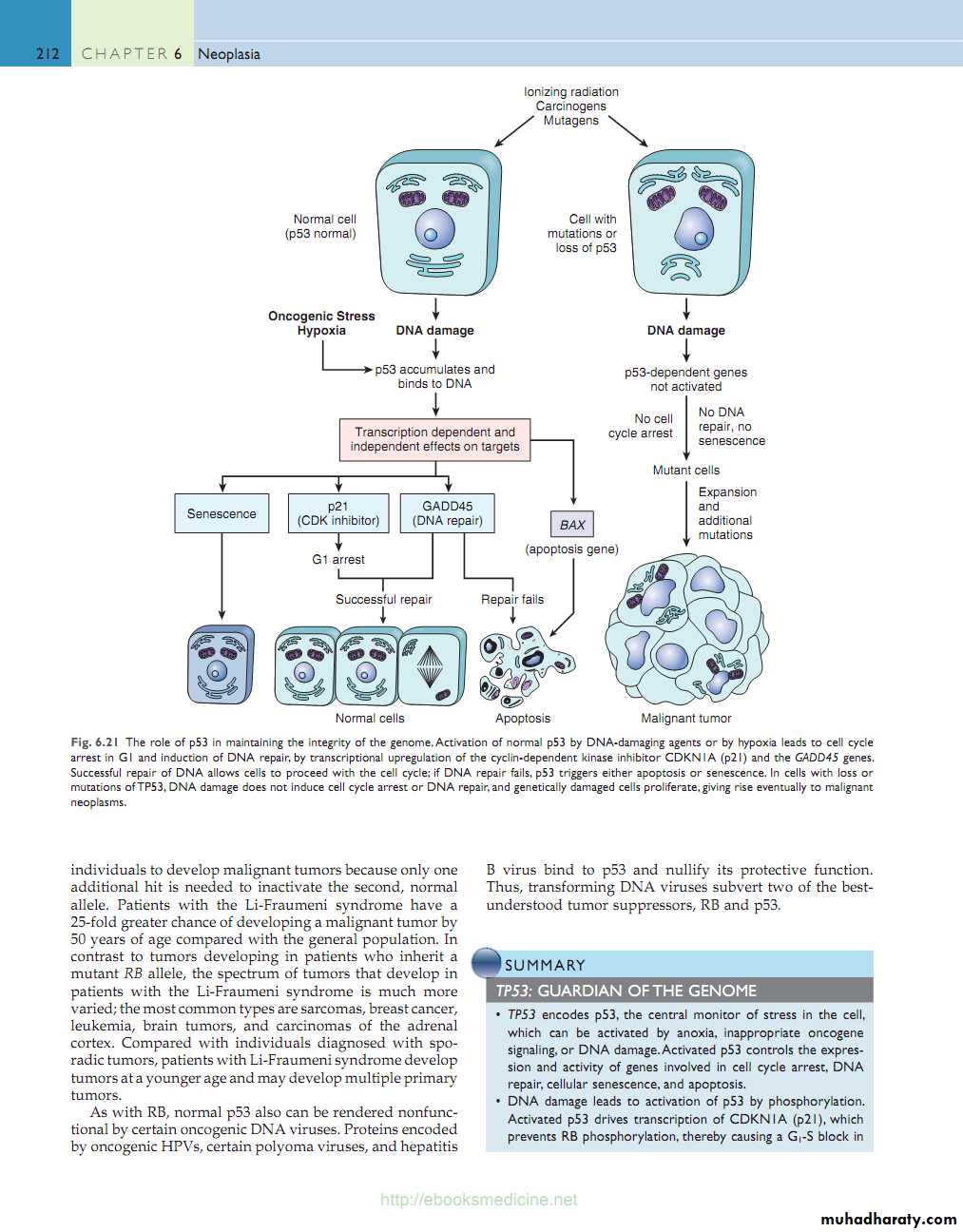
P53 “Guardian of the Genome”
A very important gene (17p13); it is the molecular policeman (P53 prevents replication of damaged DNA)
P53 prevents neoplastic transformation by three interlocking mechanisms:
- Activation of temporary cell cycle arrest (quiescence)
- Induction of permanent cell cycle arrest (senescence)
- Triggering of programmed cell death (apoptosis).
• More than 70% of human cancers have a defect in this gene
• Inherited mutation TP53 allele; results in disorder called the Li-Fraumeni syndrome. 25x
3- Programmed cell death genes: (apoptosis)
Tumor mass may result not only from activation of growth-promoting oncogenes or inactivation of growth-suppressing tumor suppressor genes, but also from mutations in the genes that regulate apoptosis.e.g. overexpression of BCL2 ( anti-apoptotic gene) in follicular B cell lymphomas
4- DNA repair genes:
• e.g. Xeroderma Pigmentosum.
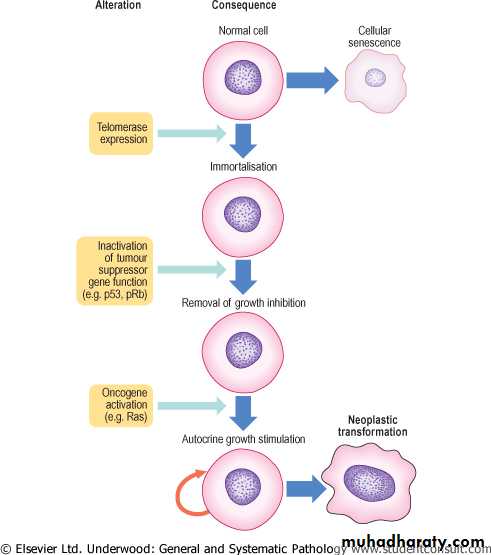
• Autosomal recessive disorder, individuals with inherited disorder of DNA repair, are at increased risk for the development of skin cancer at early age particularly following exposure to the UV light contained in sun rays.Essential steps in neoplastic transformation. Three key genetic events are the minimum needed to convert a normal human cell into a neoplastic cell. Telomerase expression prevents telomeric shortening with each cell division and thus thwarts cellular senescence. Inactivation of tumour suppressor gene function in the immortalised cells removes inhibition of growth control. Oncogene activation sets up autocrine growth stimulation; the cell now produces a growth factor for which it already has a receptor or expresses a receptor for a growth factor it normally produces. The cell is now fully transformed
Host Defense against tumors(Antitumor Effector Mechanisms)
-Tumor cells can be recognized by the immune system as non-self and destroyed.-Cell-mediated immunity is the dominant antitumor mechanism.
Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CD8+ T-Cells).
NK cells.
Macrophages.
-Although sera from cancer patients may contain antibodies that recognize tumors, there is limited evidence that they play a protective role under physiologic conditions.
-Tumor antigens are presented on the cell surface by MHC class I molecules and are recognized by CD8+ cytotoxic T-lymphocytes.
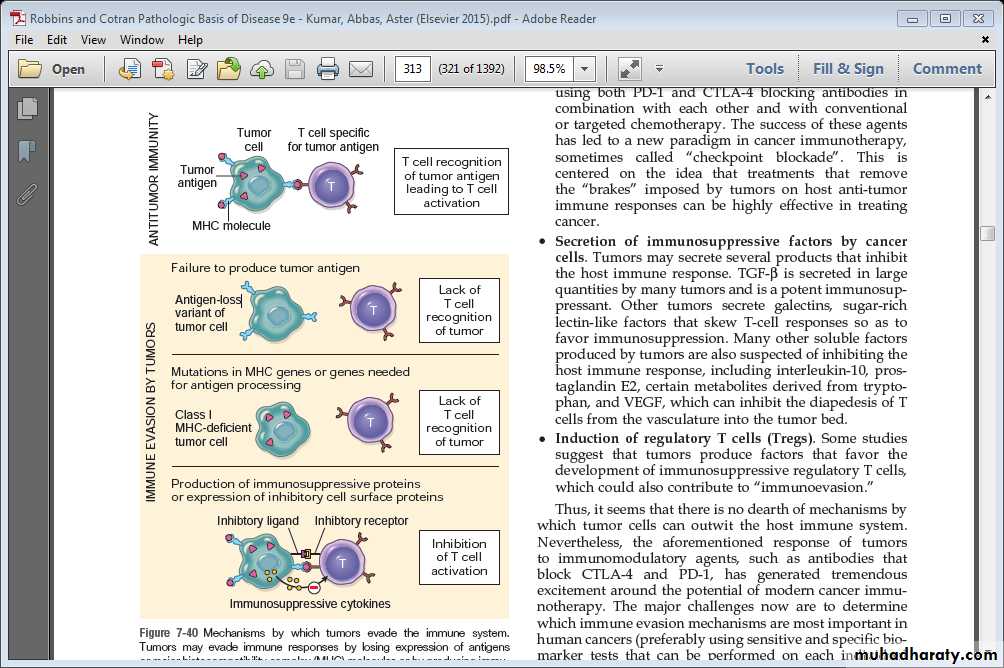
1-Selective outgrowth of antigen-negative variants: elimination of strongly immunogenic variants.
2-Loss/reduced expression of MHC molecules(class I): escaping attack by cytotoxic T cells.
• Mechanisms developed by tumor cells to escape or evade immune system:3. Lack of costimulation:
- T-cells requires two signals to be sensitizeda) MHC molecules b) Co-stimulatory molecules;
• failure to express costimulatory molecules → Prevents T-cell sensitization.
4. Secretion of immunosuppressive factors by cancer
Cells: e.g. TGF-β is secreted in large quantities by many tumors and is a potent immunosuppressant.
5. Expression of inhibitory cell surface proteins→ inhibition of T cell activation.
Mechanismby which tumors evade the immune system.
Cellular and Molecular Hallmarks of Cancer
All cancers display eight fundamental changes in cell physiology
• Self-sufficiency in growth signals: Tumors have the capacity to proliferate without external stimuli.• Insensitivity to growth-inhibitory signals: Tumors may not respond to molecules that inhibit the proliferation of normal cells.
• Altered cellular metabolism: cancer cells demonstrate a distinctive form of cellular metabolism characterized by high levels of glucose uptake and increased conversion of glucose to lactose (fermentation) via the glycolytic pathway. This phenomenon, called the Warburg effect which enables the synthesis of the macromolecules and organelles that are needed for rapid cell growth.
• Evasion of apoptosis: Tumors are resistant to programmed cell death.
• Limitless replicative potential: immortality.• Sustained angiogenesis.
• Ability to invade and metastasize.
• Ability to evade the host immune response.