Male Genital
System
Third Year Class
By Dr.Riyadh A. Ali
Department of Pathology
TUCOM

Titles
• Normal prostate
• Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
• Adenocarcinoma of prostate
• Normal testis
• Atrophic (gross)
• Seminoma
Normal Prostate
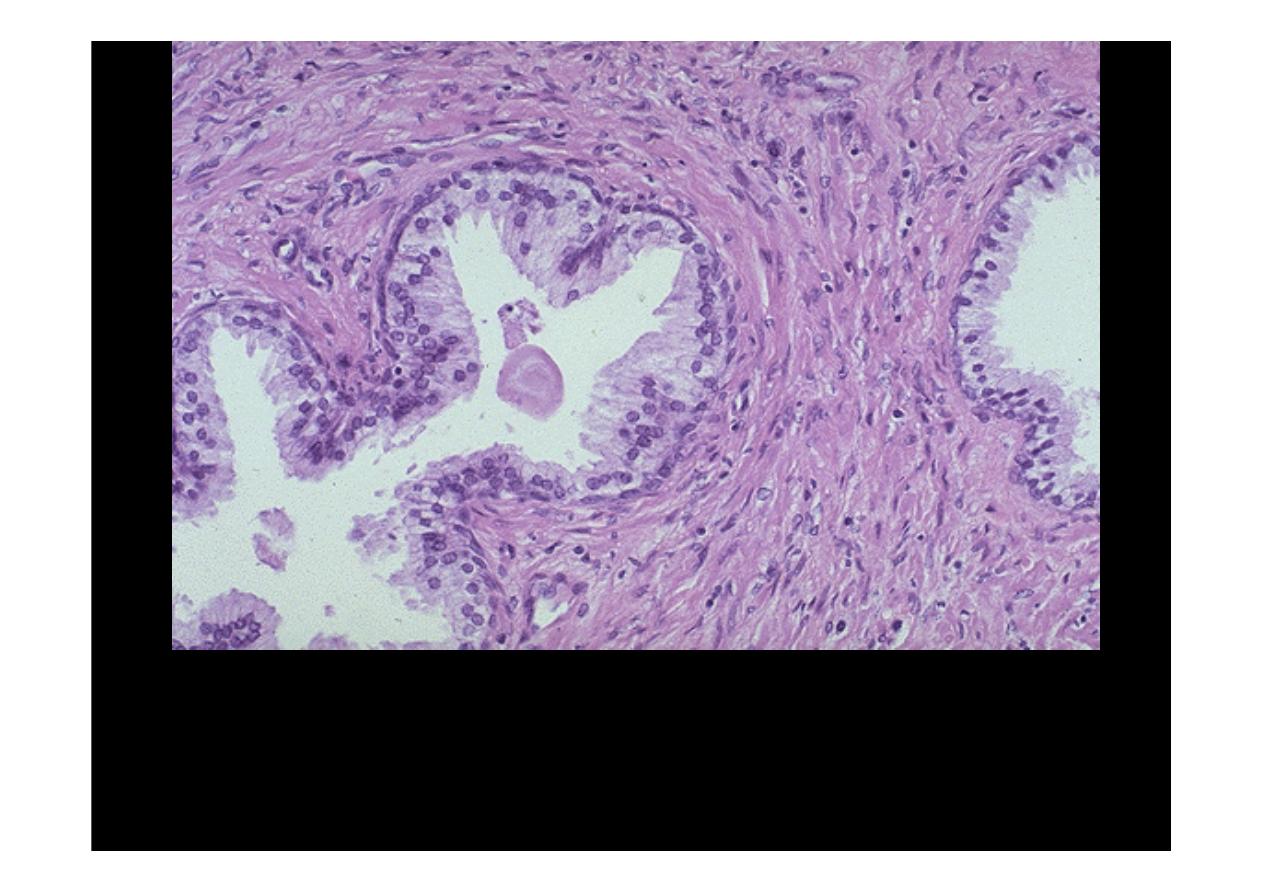
The
normal
histologic
appearance
of
prostate
glands
and
surrounding
fibromuscular stroma is shown here at high magnification. A small pink concretion
(typical of the corpora amylacea seen in benign prostatic glands) appears in the
gland just to the left of center. Note the well-differentiated glands with tall columnar
epithelial lining cells. These cells do not have prominent nucleoli.
Benign Prostatic
Hyperplasia (BPH)
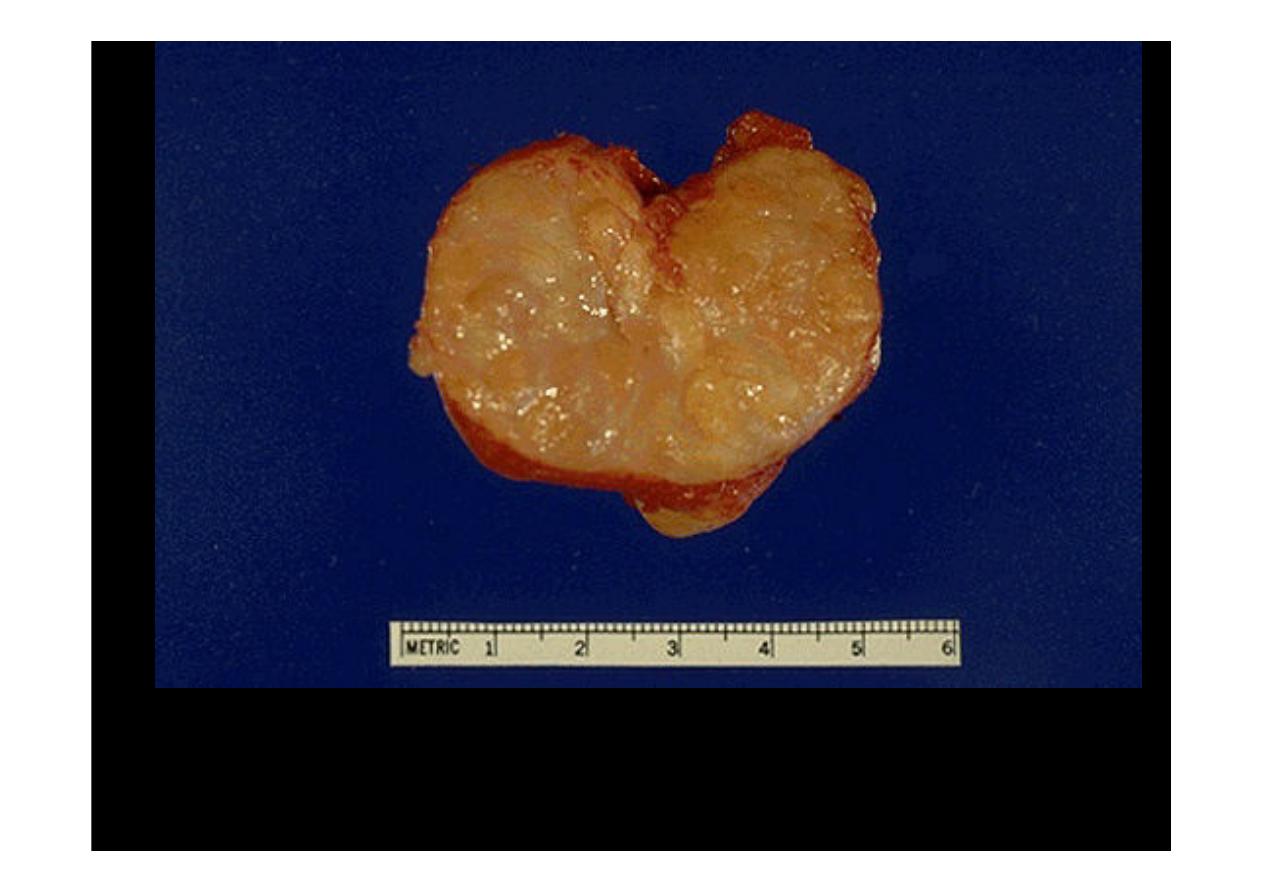
A normal prostate gland is about 3 to 4 cm in diameter. This prostate is enlarged due
to
prostatic hyperplasia
, which appears nodular. Thus, this condition is termed
either BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia) or nodular prostatic hyperplasia.
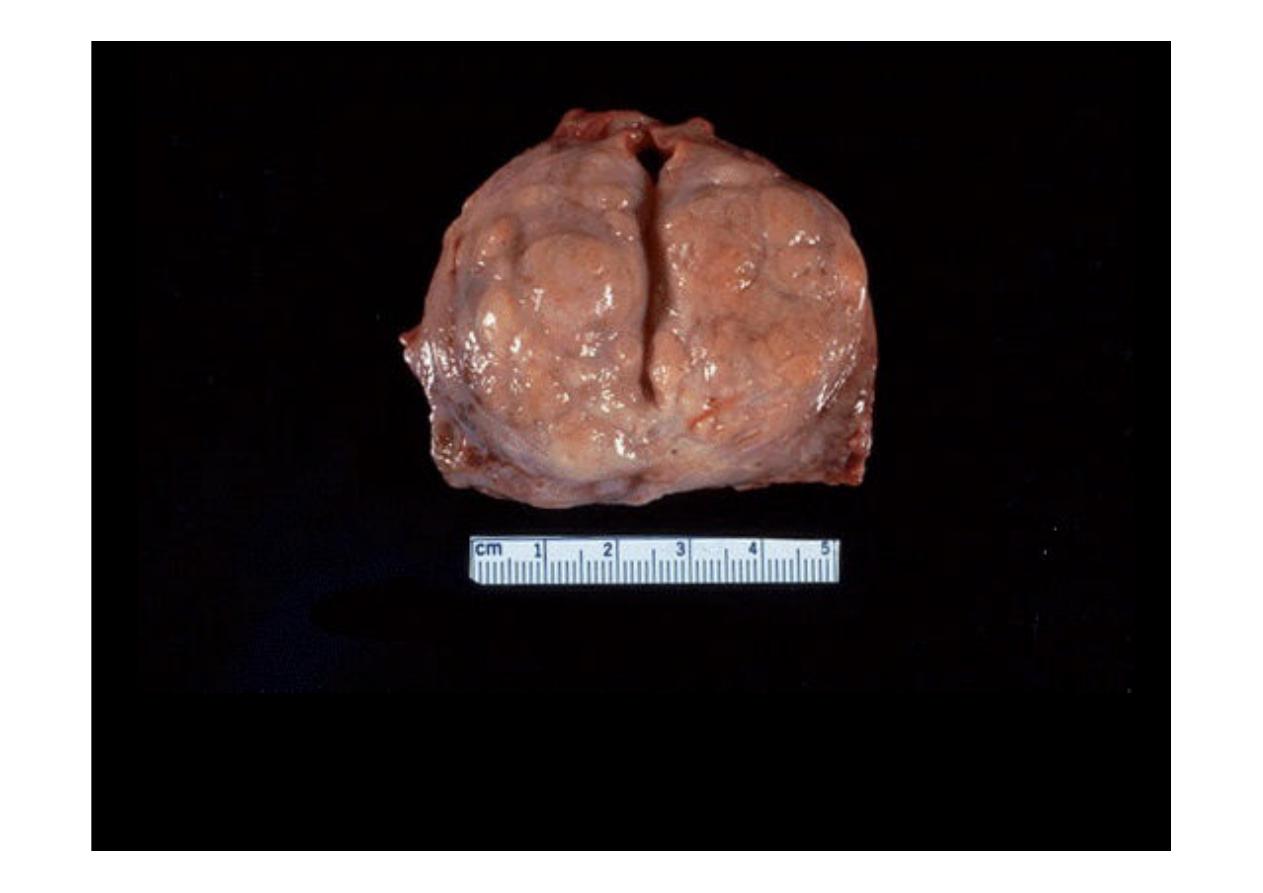
Here is another example of
benign prostatic hyperplasia
. Nodules appear
mainly in the lateral lobes. Such an enlarged prostate can obstruct urinary outflow
from the bladder and lead to an obstructive uropathy.
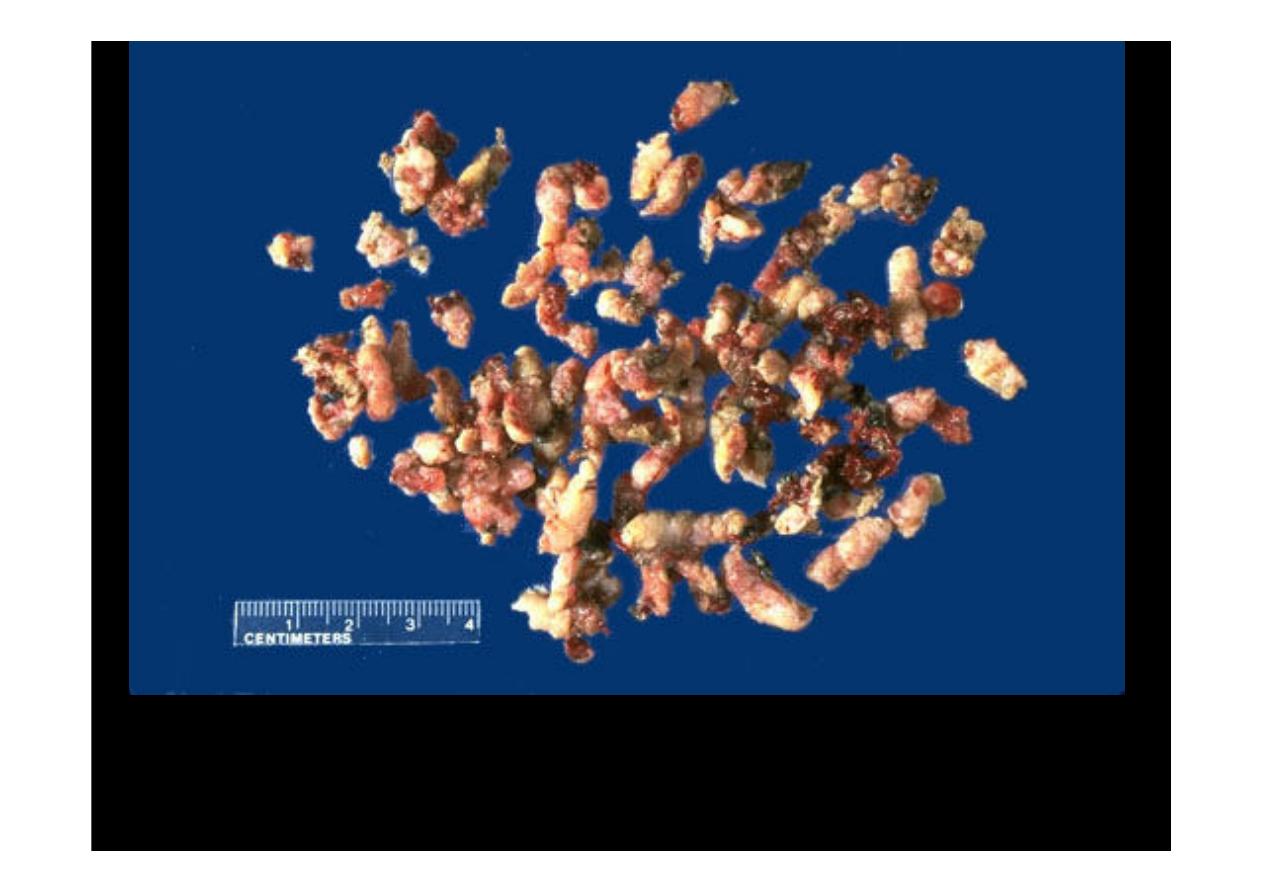
A frequently performed operation for symptomatic nodular
prostatic hyperplasia
is a transurethral resection
(transurethral resection of prostate (TURP))
, which
yields the small "chips" of rubbery prostatic tissue seen here
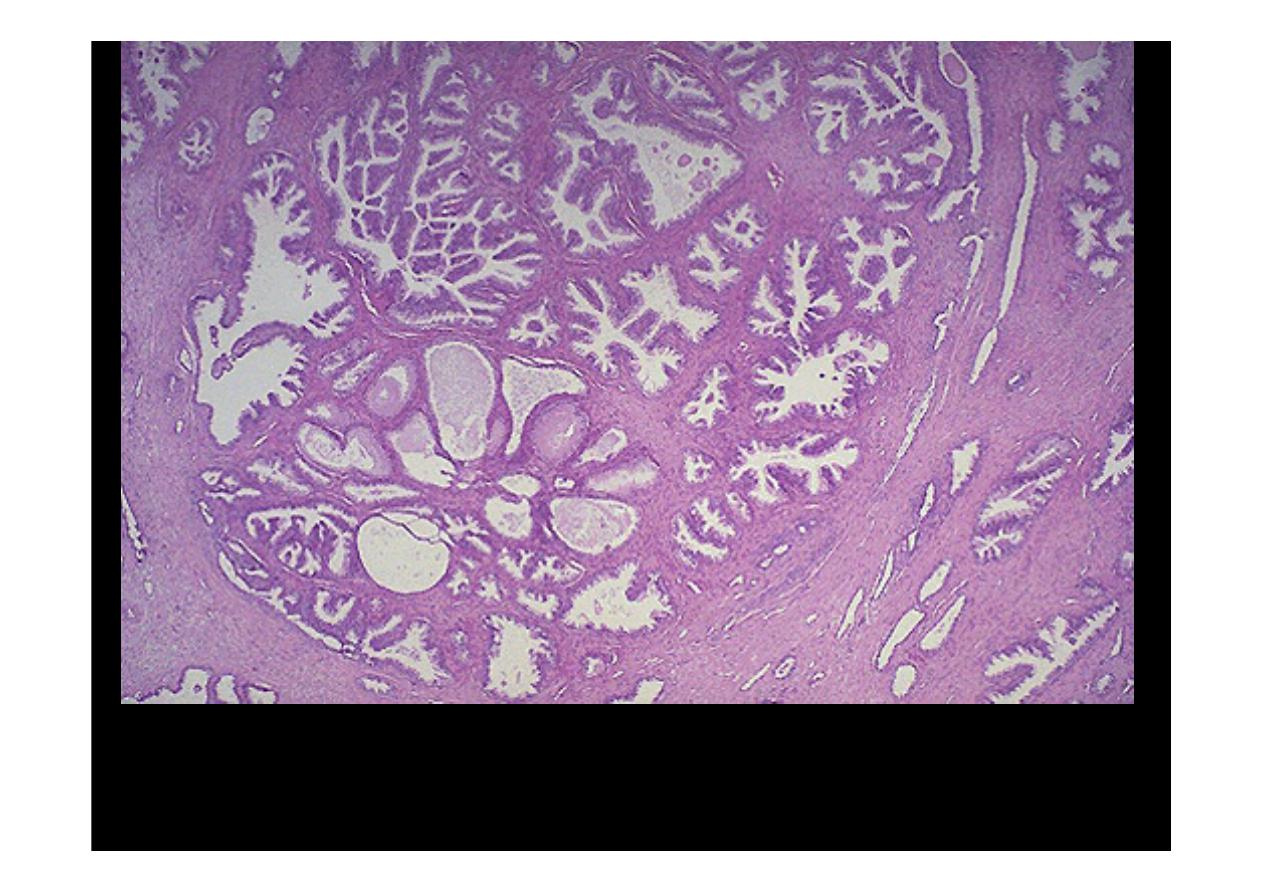
Microscopically,
benign prostatic hyperplasia
can involve both glands and
stroma, though the former is usually more prominent. Here, a large
hyperplastic nodule of glands is seen.
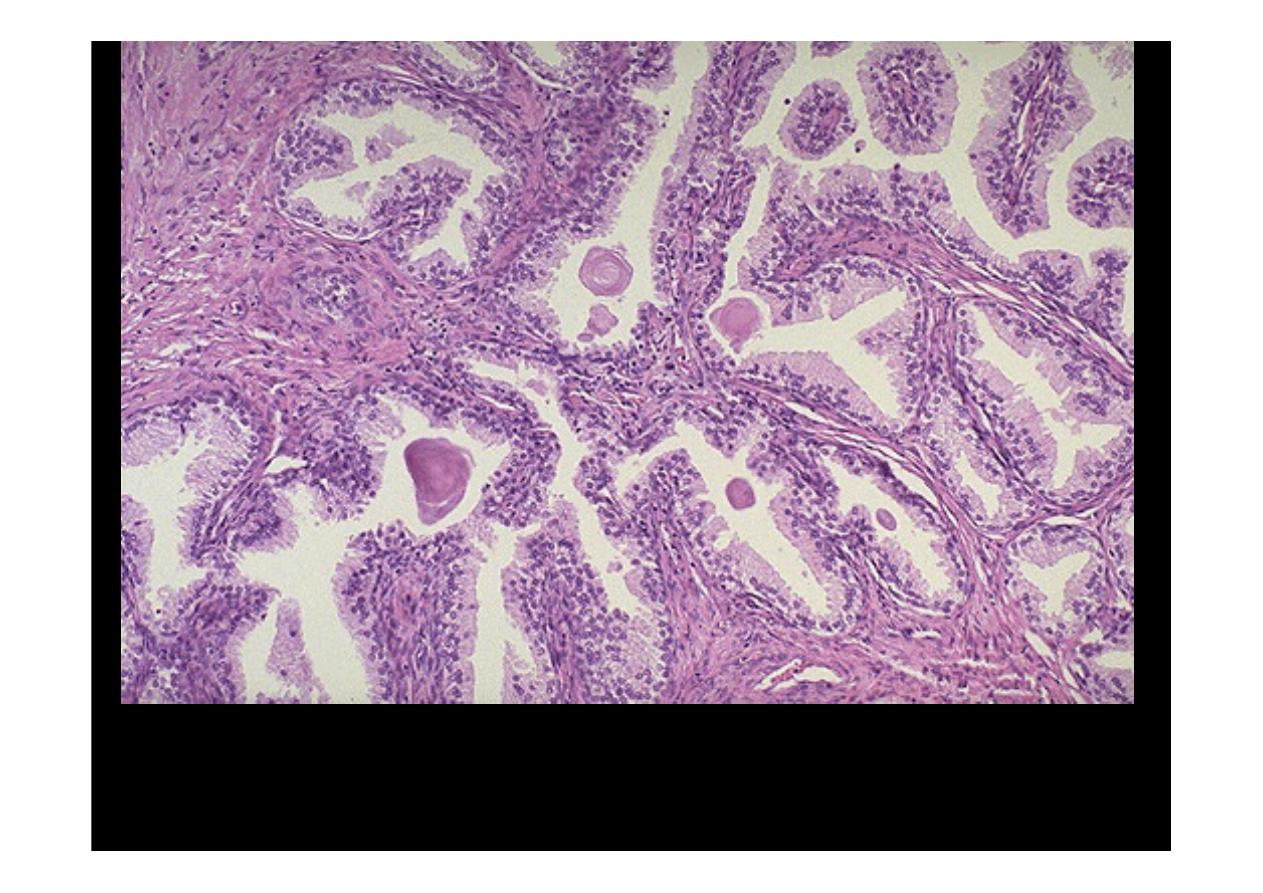
At higher magnification, the enlarged prostate has glandular hyperplasia. The
glands are well-differentiated and still have some intervening stroma. The small
laminated pink concretions within the glandular lumens are known as corpora
amylacea.
Benign Prostatic Hyperpalsia (BPH)

Adenocarcinoma
of Prostate
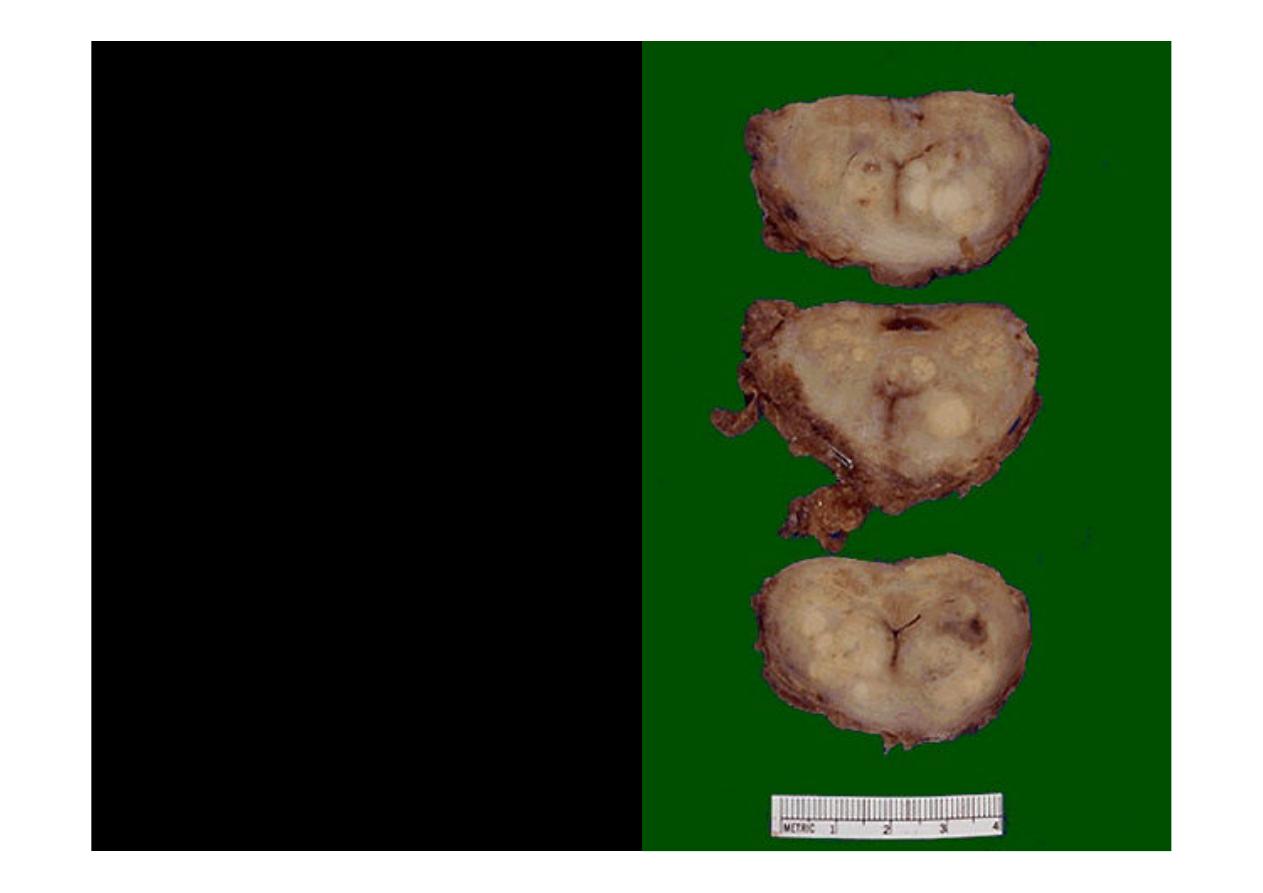
These sections through a
prostate removed via
radical prostatectomy
reveal irregular yellowish
nodules, mostly in the
posterior portion (seen
here superiorly). This
proved to be
prostatic
adenocarcinoma.
Prostate glands containing
adenocarcinoma are not
necessarily enlarged
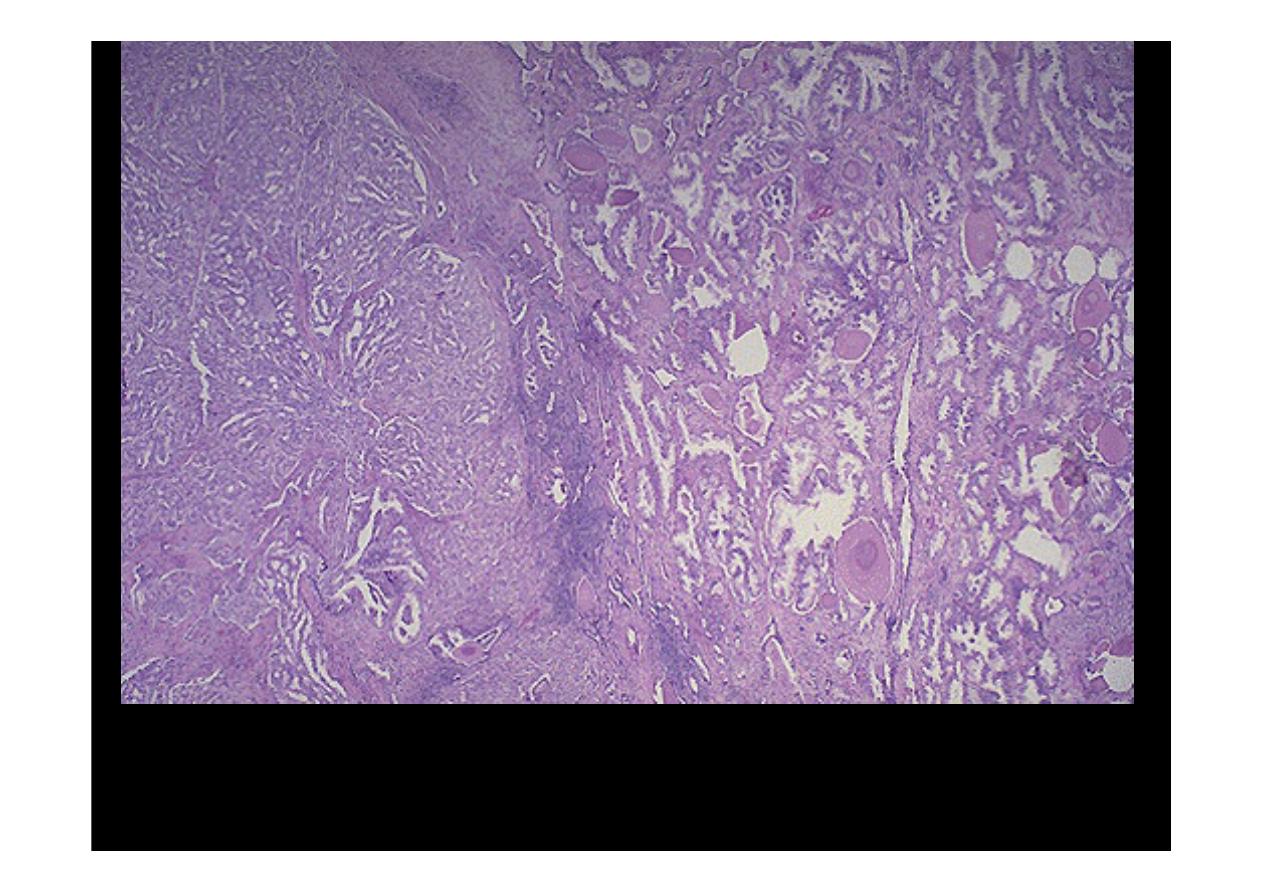
At the right are normal prostatic glands containing scattered corpora amylacea. At
the left is prostatic adenocarcinoma. Note how the glands of the carcinoma are
small and crowded.
Prostatic adenocarcinomas
are given a histologic grade
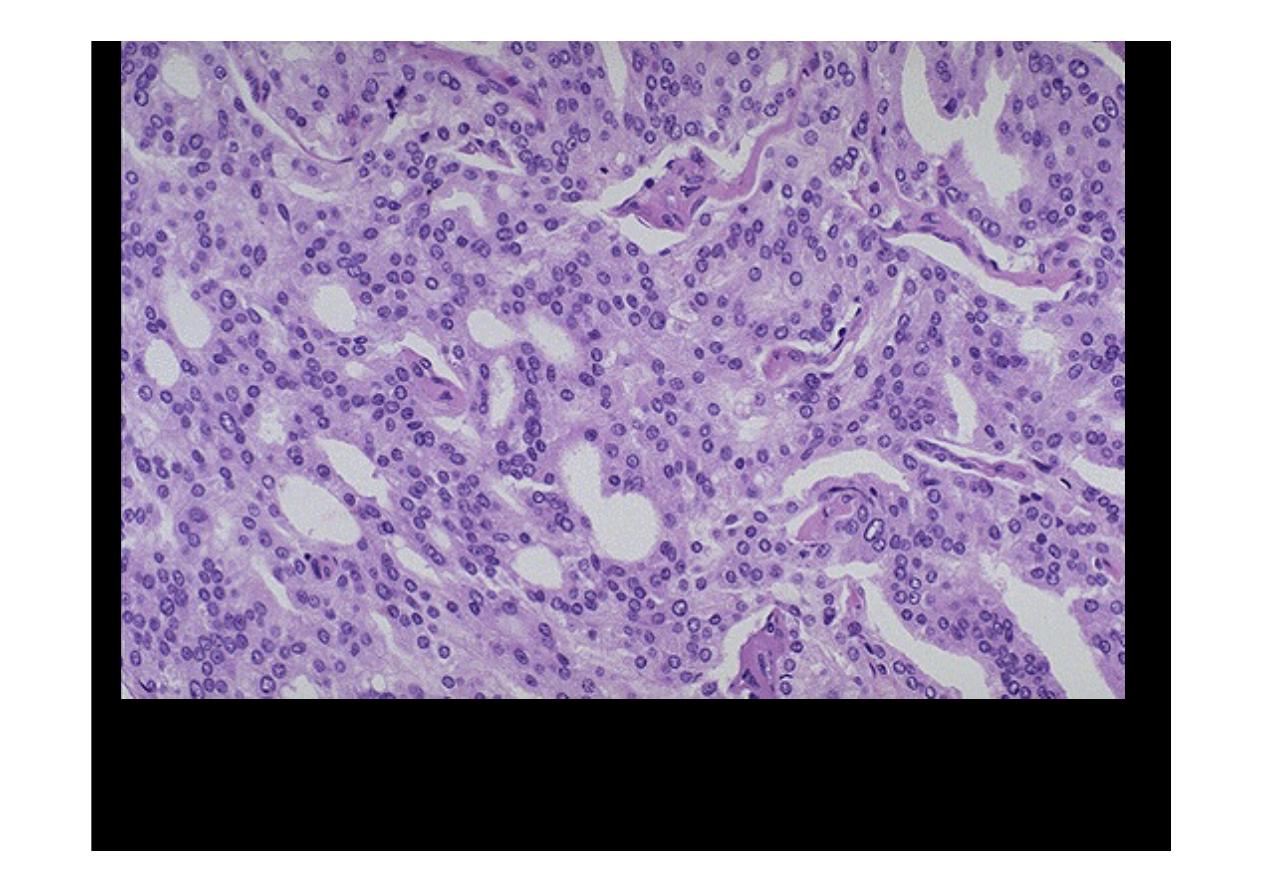
At high magnification, the neoplastic glands of
prostatic adenocarcinoma
are
still recognizable as glands, but there is no intervening stroma and the nuclei
are hyperchromatic.
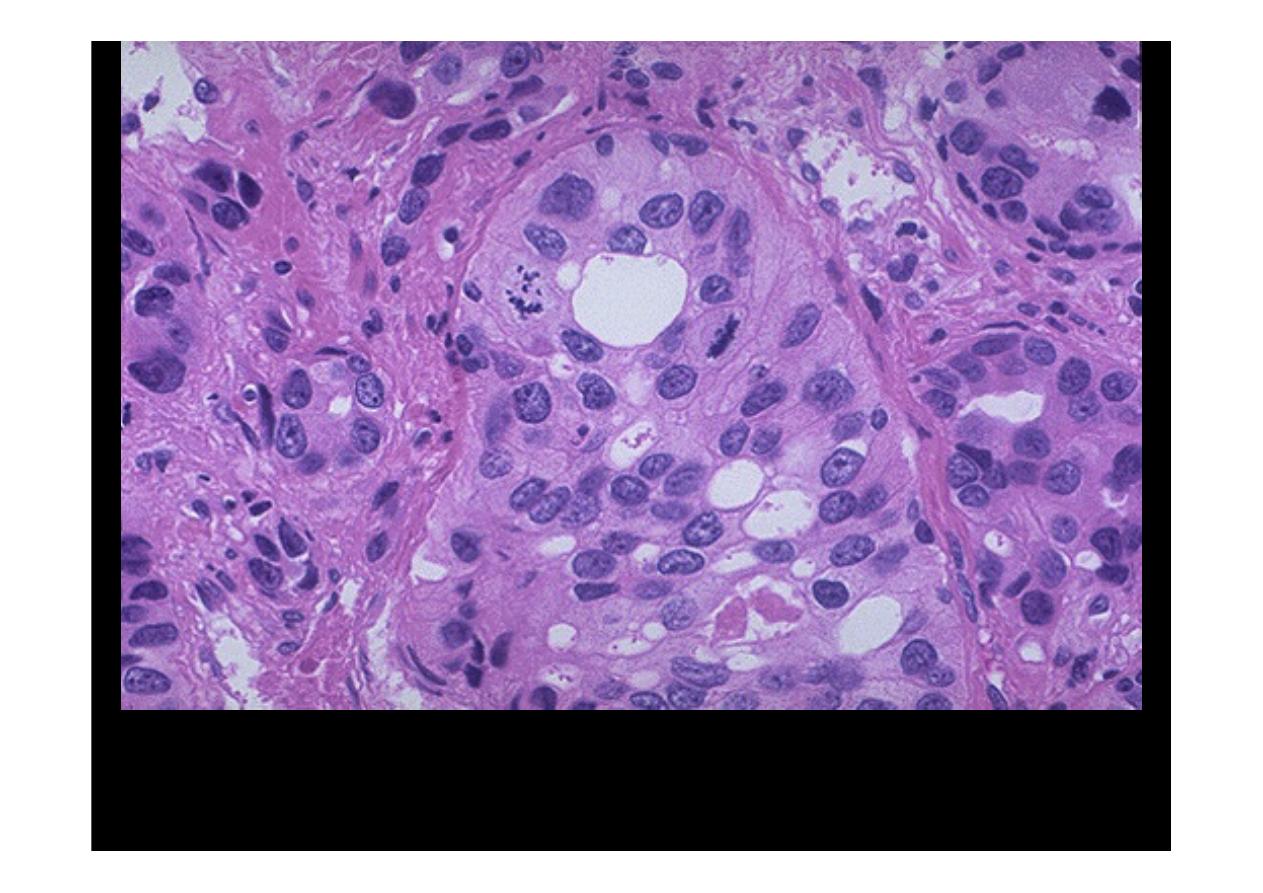
At high magnification, this poorly differentiated
prostatic
adenocarcinoma
demonstrates cells with nucleoli and mitotic figures

Normal Testis + atrophic
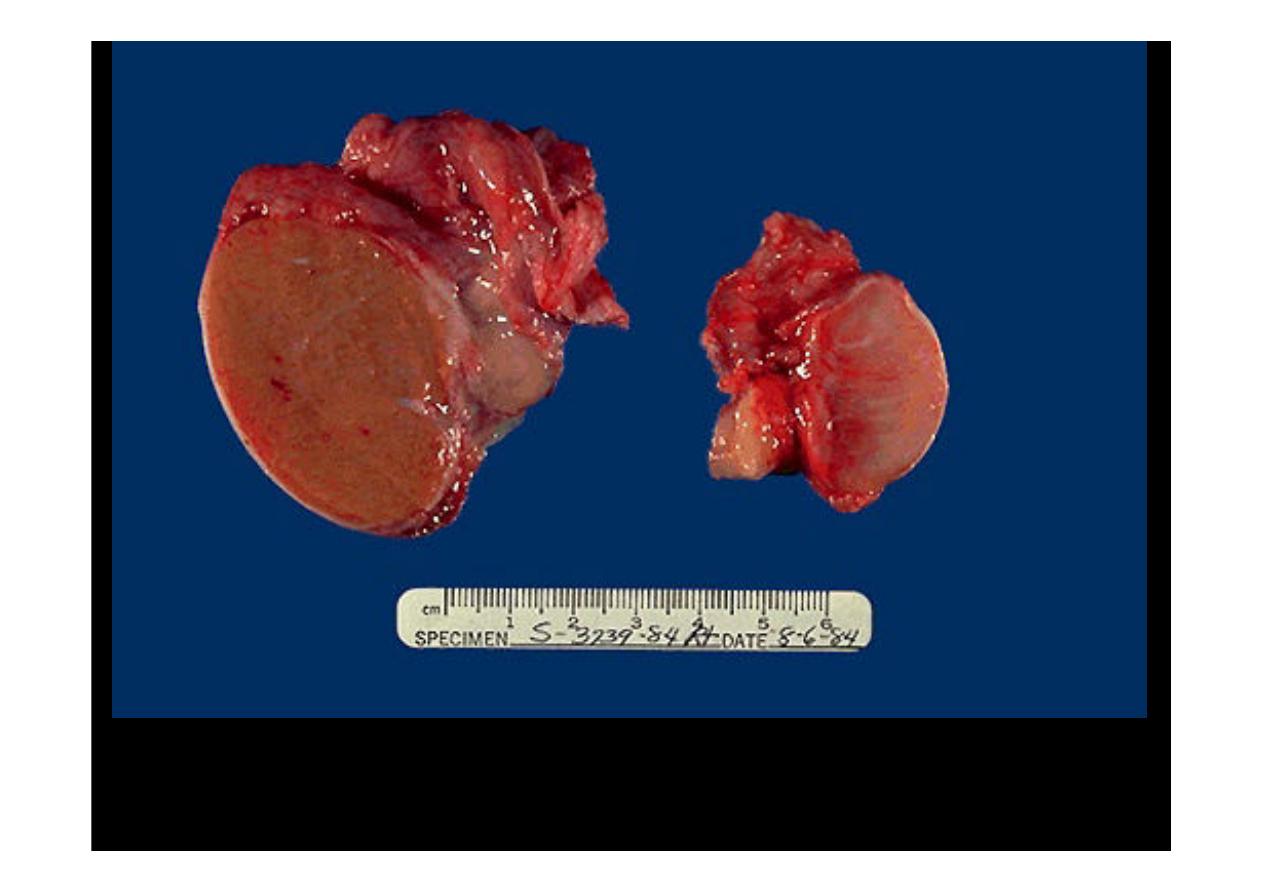
On the left is a
normal testis
. On the right is a testis that has
undergone atrophy
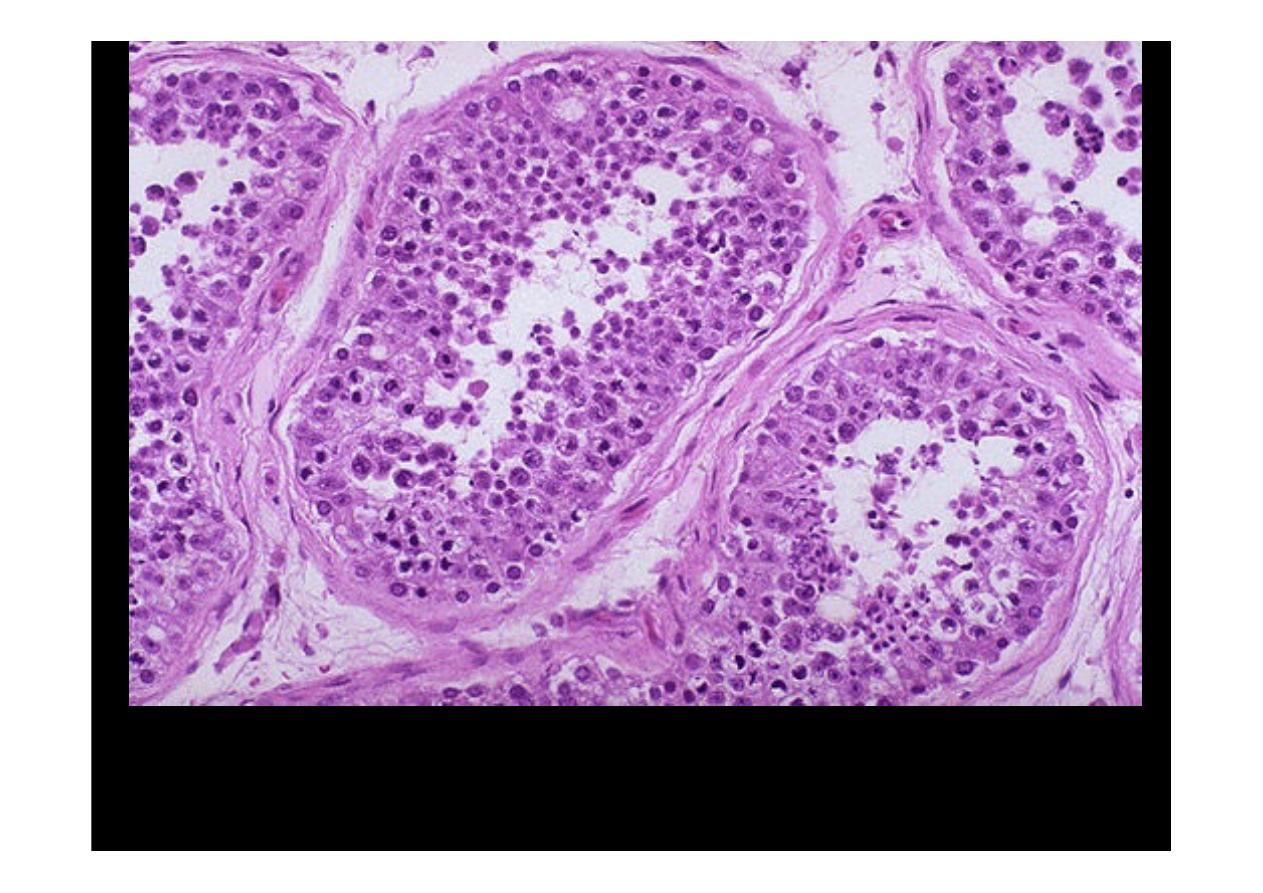
This is the microscopic appearance of
normal testis
. The seminiferous tubules
have numerous germ cells. Sertoli cells are inconspicuous. Small dark oblong
spermatozoa are seen in the center of the tubules.

Seminoma
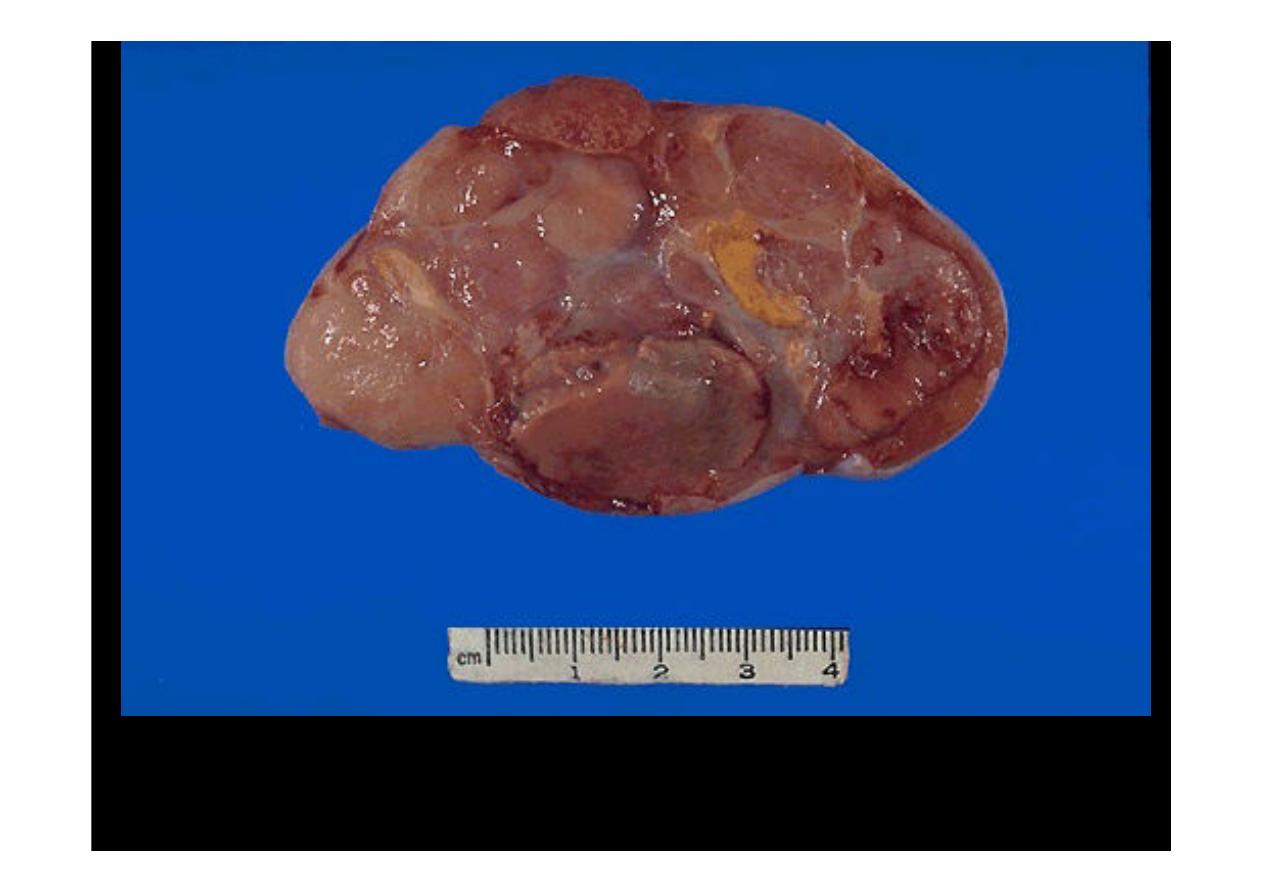
This is
seminoma of
the testis. A small rim of remaining normal testis appears at
the far right. The tumor is composed of lobulated soft tan to brown tissue
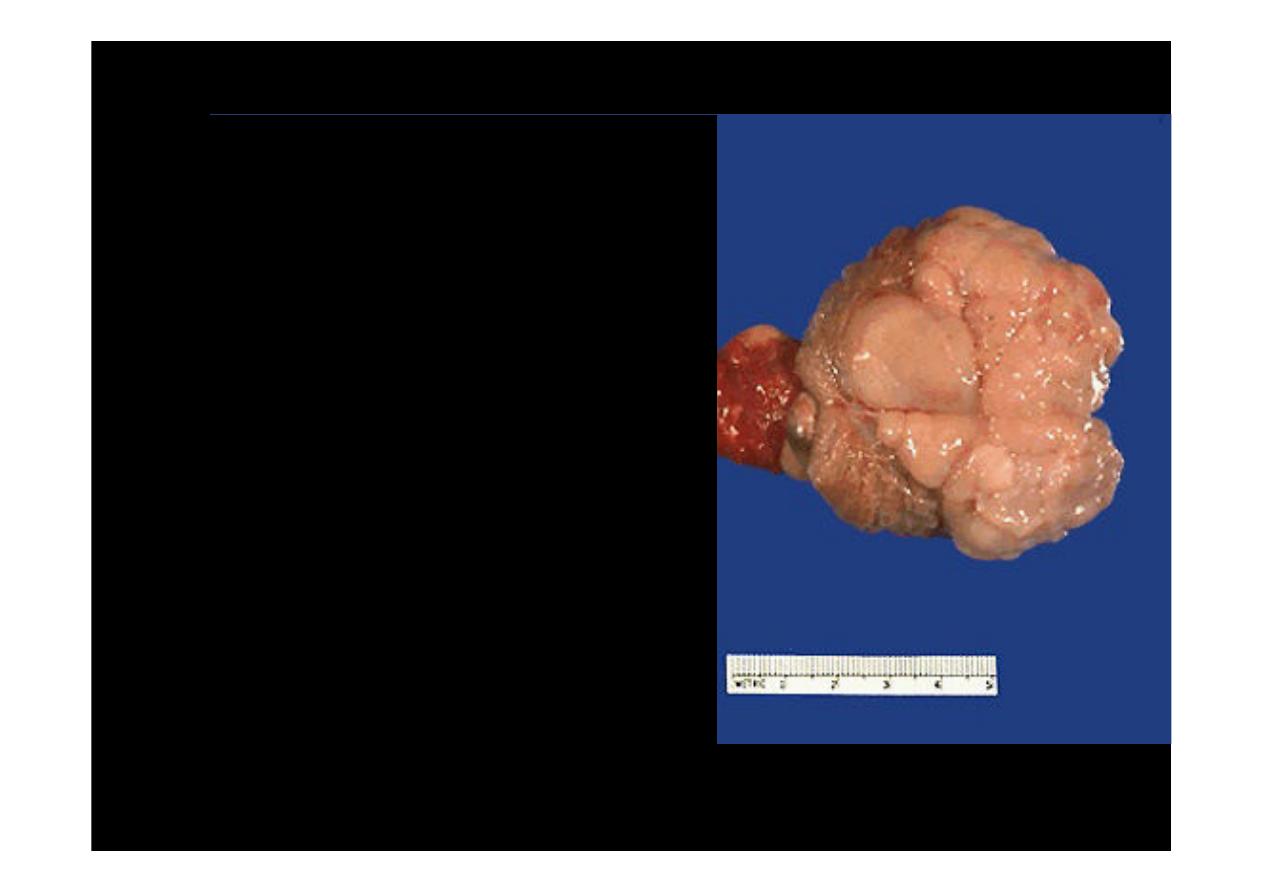
Seminoma
tumor is
composed of lobulated
soft tan white tissue.
Normal testis appears
to the left of the mass,
and the spermatic cord
extends to the left of
that
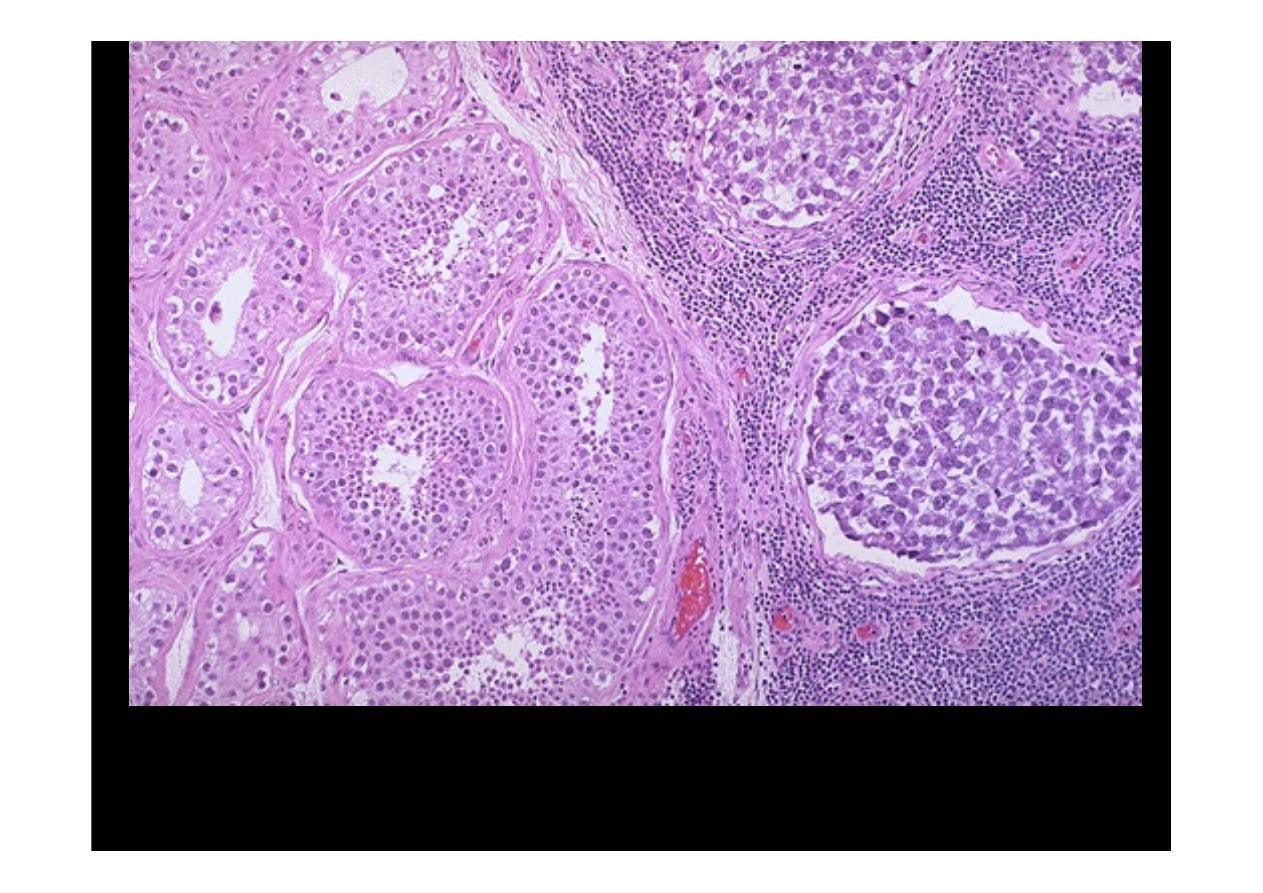
Normal testis appears at the left, and
seminoma
is present at the right. Note the
difference in size and staining quality of the neoplastic nests of cells compared to
normal germ cells. Note the lymphoid stroma between the nests of seminoma.
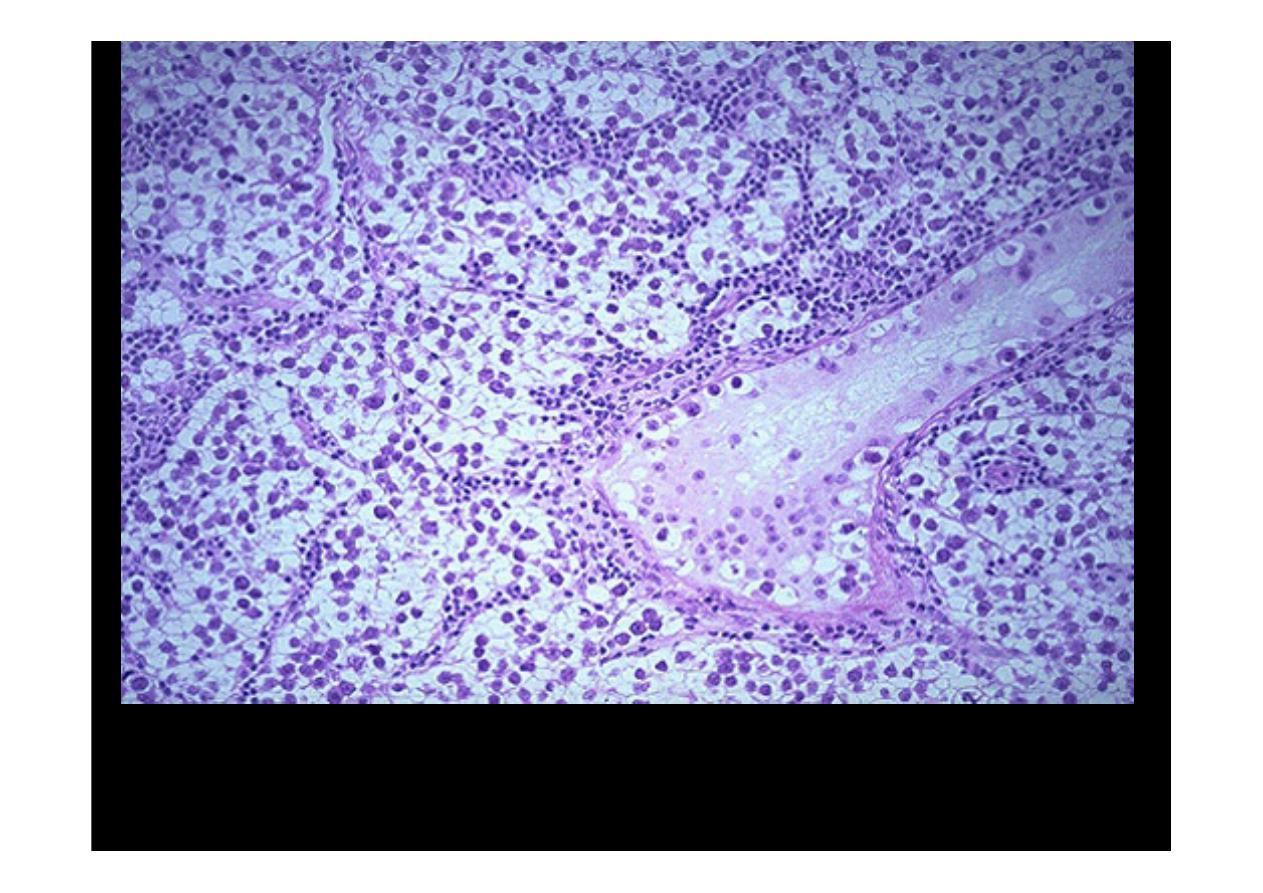
This is the histologic pattern of the typical
seminoma
. Lobules of neoplasitic
cells have an intervening stroma with characteristic lymphoid infiltrates. The
seminoma cells are large with vesicular nuclei, and pale watery cytoplasm.
