Group B Streptococcus (GBS) (Sterptococcus agalactiae)
Pathogenesis:Approximately 30% of women are vaginal or rectal carriers of group B Streptococcus. Hence, the infection is common in neonates and in pregnancy. It is a major cause of:
• Neonatal sepsis and meningitis: Neonatal sepsis can be of two types-early onset and late onset type.
• Puerperal sepsis and peripartum fever
• Infections in elderly people with underlying illness, such as diabetes mellitus or malignancy: Cellulitis and soft tissue infections, UTI, pneumonia, and endocarditis.
Pathogenesis & Clinical Infection:
Pathogen of neonate: associated with in utero or perinatal organism acquisitionduring birthing process
Early onset – within 7 days.
Late 7 – 28 days from birth process.
Pregnant women carry organism in the cervix and/or rectal area. All should be tested at 35 – 37 weeks of pregnancy.
Pathogenesis & Clinical Infection:
Distinguishing Featuresβ hemolytic
Bacitracin resistant
Hydrolyze hippurate
It has a capsular polysaccharide, which can be typed into nine serotypes.
Pathogenesis & Clinical Infection:
CAMP test positive (Christie, Atkins, and Munch-Petersen) (CAMP test),
(CAMP factor is a polypeptide which “complements” the sphingomyelinase of Staphylococcus aureus to create an enhanced hemolytic pattern in shape of an arrowhead)
Streptococcus agalactiae
Staphylococcus aureusCAMP Test +
Pathogenesis & Clinical Infection:
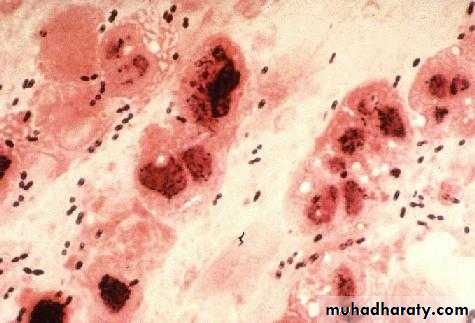
Early-onset infection often manifests as pneumonia and sepsis, and late-onset infection manifests as meningitis and sepsis. The mortality rate is high, and death usually occurs if treatment is not started quickly.*Neonatal meningitis / septicemia
Cystitis and pyelonephritisPostpartum endometritis
Postpartum septicemia
Laboratory Diagnosis
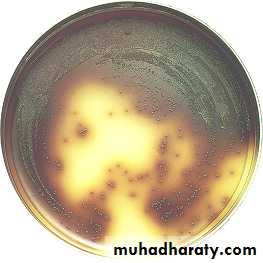
Streptococcus agalactiae colony growing on sheep blood agar (GBS).Identification
Schematic diagram for differentiation of group A streptococci (GAS) from group B streptococci (GBS).
Treatment:
Ampicillin with an Aminoglycoside (Gentamicin, Amikacin, Kanamycin, Tobramycin) or a Cephalosporin.Prevention:
Prophylaxis during delivery in women with positive vaginal/rectal culture of GBS, history of recent infection with GBS.Ampicillin or Penicillin drugs of choice,
Clindamycin or Erythromycin for Penicillin allergies.
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococci)Pneumococci are gram-positive diplococci, often lancet shaped or arranged in chains, possessing a capsule of polysaccharide that permits typing with specific antisera.
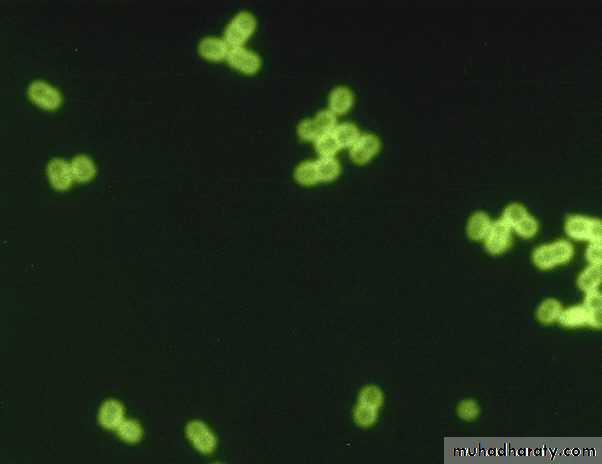
Streptococcus pneumonia
(diplococcus). Fluorescent stainSchematic diagram for differentiation of
α-hemolytic streptococci from Enterococcus.
Streptococcus pneumonia
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Virulence Factors and PathogenesisCapsular polysaccharide: It protects the cocci from phagocytosis:
It is type specific (> 90 capsular serotypes are recognized).
Quellung reaction: Capsular swelling occurs when colonies are added with type specific antiserum and methylene blue dye.
It diffuses (soluble) into culture media, tissue and exudates, hence also called soluble specific substance.
C-carbohydrate antigen (C-polysaccharide or C-substance): It is species specific. CRP (C-reactive protein) present in sera of patients with acute inflammation. It is so named because; it precipitates with pneumococcal C-antigen.
Pneumolysin: It is a membrane damaging toxin, inhibits neutrophil chemotaxis (amoeboid movement, which allows them to migrate toward sites of infection or inflammation).
Autolysin: It is an amidase enzyme that cleaves peptidoglycan leading to autolysis of cells. This property is responsible for bile solubility and draughtsman appearance of pneumococcal colonies.
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Clinical ManifestationStreptococcus pneumoniae is the most common cause of:
Lobar pneumonia
Pyogenic meningitis in all ages (except in neonates)
Non-invasive manifestations such as otitis media and sinusitis.
Other invasive manifestations: S. pneumoniae can cause osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, endocarditis, pericarditis, primary peritonitis, rarely, brain abscess and hemolytic-uremic syndrome.
Cytolytic toxins produced by
Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Epidemiology
Source of infection in humans is upper respiratory tract of carriers (less often patients).
Because 40–70% of humans are at some time carriers of virulent pneumococci but normal respiratory mucosa must possess great natural resistance to the pneumococcus.
Mode of transmission is by inhalation of contaminated droplet.
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Risk factors:Children (< 2years)
Splenectomy, As spleen is the site of destruction of capsulated bacteria, the conditions where the opsonization and clearance of circulating bacteria by the spleen is hampered, there is increase risk of pneumococcal infection.
Chronic lung, heart, kidney and liver disease, diabetes mellitus and immunosuppression (e.g. HIV).
Underlying viral upper respiratory tract infections (e.g. Influenza).
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Pathogenesis:Thick Polysaccharide capsule is the major virulence factor, decreasing phagocytic uptake; there are more than 90 different capsular polysaccharide types.
Colonizes with the help of protein adhesins and an IgA protease.
Hemolyzes cells through pneumolysis and partially reduces hemoglobin to green pigment (alpha-hemolysis).
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Diagnostic Laboratory TestsA Gram-stained film of rusty-red sputum shows typical organisms,
many polymorphonuclear neutrophils.
Quellung reaction: positive
(swelling of the capsule with the addition of type-specific antiserum)
Culture
Alpha-hemolytic, lysed by bile, and inhibited by optochin.
Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests.
Schematic diagram for differentiation of α-hemolytic streptococci from Enterococcus.
Optochin Test
-
+
Optochin
Sensitive
Optochin
Resistance
Streptococcus pneumoniae
TreatmentPenicillin G, but penicillin resistance due to decreased binding to penicillin-binding proteins (PBP).
Ceftriaxone or Cefotaxime for adult meningitis (add Vancomycin if penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae has been reported).
Amoxicillin for otitis media and sinusitis in children (Erythromycin in cases of allergy)
Streptococcus pneumoniae
PreventionVaccine
Vaccines can probably provide 90% protection against bacteremic pneumonia.
Pediatric (Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine PCV 13): 13 of most common serotypes; conjugated to diphtheria toxoid
PPV23 (Polysaccharide Pneumococca Vaccine) includes capsular polysaccharide of 23 serotypes of pneumococci. It gives protection for about 5 years.
Adults 19 years of age or older with immunocompromising conditions should receive both PPSV23 and PCV13.
Indication: It is recommended for people with
Genus: Enterococcus
Enterococci: Contain a C-substance that reacts with group D anti sera.Therefore, in the past, they were considered group D streptococci.
Today, DNA analysis and other properties have placed them in their own genus, Enterococcus.
The clinically most important species are Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium.
Genus: Enterococcus
Various Clinical Manifestations IncludeUrinary tract infections (cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis and prostatitis).
Bacteremia and mitral valve endocarditis (in IV drug abusers).
Intra-abdominal, pelvic, and soft tissue Infection.
Late-onset neonatal sepsis and meningitis.
Infection on burn surface.
Genus: Enterococcus
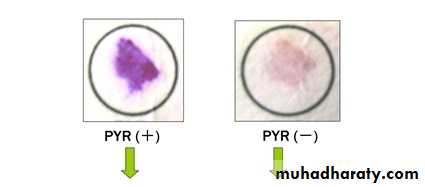
Distinguishing FeaturesPYR Pyrrolidonyl Arylamidase test Positive.
Catalase-negative.
Varied hemolysis.
Hydrolyze esculin in 40% bile and 6.5% NaCl (bile esculin agar turns black).
Enterococcus spp.
Bile- esculin test +
Genus: Enterococcus
Pathogenesis:Bile/salt tolerance allows survival in bowel and gall bladder.
During medical procedures on GIT or GUS Genitourinary system : Enterococcus faecalis → bloodstream → previously damaged heart valves → endocarditis.
Diseases:
Urinary and biliary tract infection; infective (subacute) endocarditis in persons (often elderly) with damaged heart valves.
Genus: Enterococcus
Diagnosis:Culture on blood agar.
Genus: Enterococcus
Treatment: all strains carry some drug resistance.Vancomycin resistance in Enterococci has been increasingly reported nowadays.
VRE is mediated by Van gene, which codes for altered target site for vancomycin in the cell wall.
Van gene has 9 genotypes. Important ones are: VanA to VanE.
Strains with Van-A gene show high level resistance to both Glycopeptides- Vancomycin and Teicoplanin.
Strains with Van-B gene show low level resistance to Vancomycin, but sensitive to Teicoplanin.
Some Vancomycin-Resistant (VRE) Strains of Enterococcus faecium or Enterococcus faecalis have no reliably effective treatment; or low-level resistance use Ampicillin, Gentamicin, or Streptomycin.
Screening of patients for VRE is carried out by: Rectal swab culturing on Bile esculin azide agar with 6 μg/ml vancomycin
Genus: Enterococcus
Treatment:
Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole Resistance
Enterococci often show susceptibility to SXT by in vitro testing,
• but the drugs are not effective in treating infections.
Prevention:
prophylactic use of penicillin and gentamicin for patients with
• damaged heart valves prior to intestinal or urinary tract
• manipulation