Abdominal wall, Hernia, and
umbilicus
Dr. Ali K. Shaaeli
MBChB, FACS
Feb. 2019

Learning objectives
To know and understand;
• Basic anatomy of abdominal wall
• Causes of abdominal hernia
• Types of hernia and classifications
• Complications of abdominal hernia
• Non surgical and surgical management of hernia
• To know that femoral hernias are especially
susceptible to strangulation
• To know the common surgical approaches to
hernias

Hernia
• It is protrusion of viscus or part of viscus
through an abnormal opening in the wall of its
containing cavity

Hernia
•
1-External ; inguinal, femoral ,umbilical
,incisional, epigastric, spigelian, obturator,
gluteal and divarication of recti.
•
2-Internal; hiatal hernia, diaphragmatic hernia

Causes
• Weakness due to structures entering and
leaving the
abdomen
• Developmental failures
• Genetic weakness of collagen
• Weakness due to ageing and pregnancy
• Primary neurological and muscle diseases
• ? Excessive intra-abdominal pressure

Composition of hernia
•
sac ; usually parietal peritoneum
•
covering ; wall layers covering the sac
•
content; omentum, small & large bowel
,ovary, bladder
Femoral hernia

classification of hernia
• 1-reducible ; content can be reduced inside the
abdomen
• 2-irreducible ; content cannot be reduced (but no
complication )
• 3-obstructed ; it is irreducible plus obstruction of
bowel
• 4-strangulated ; obstructed bowel plus obstructed
blood supply

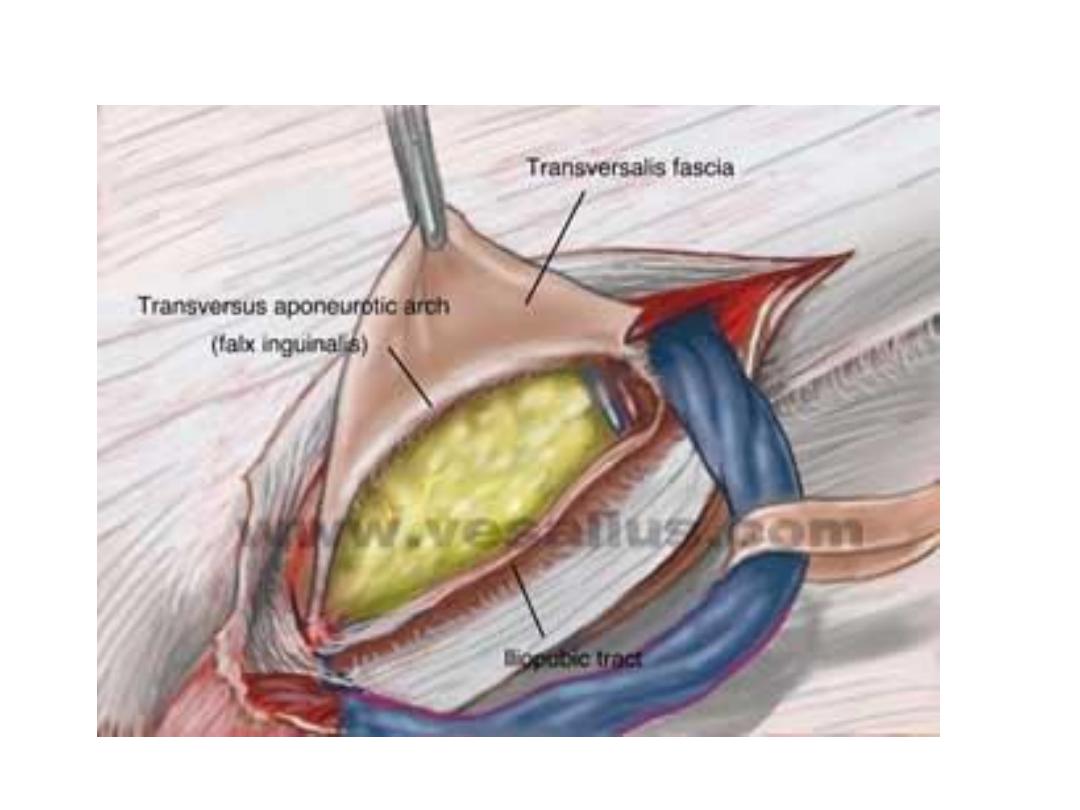
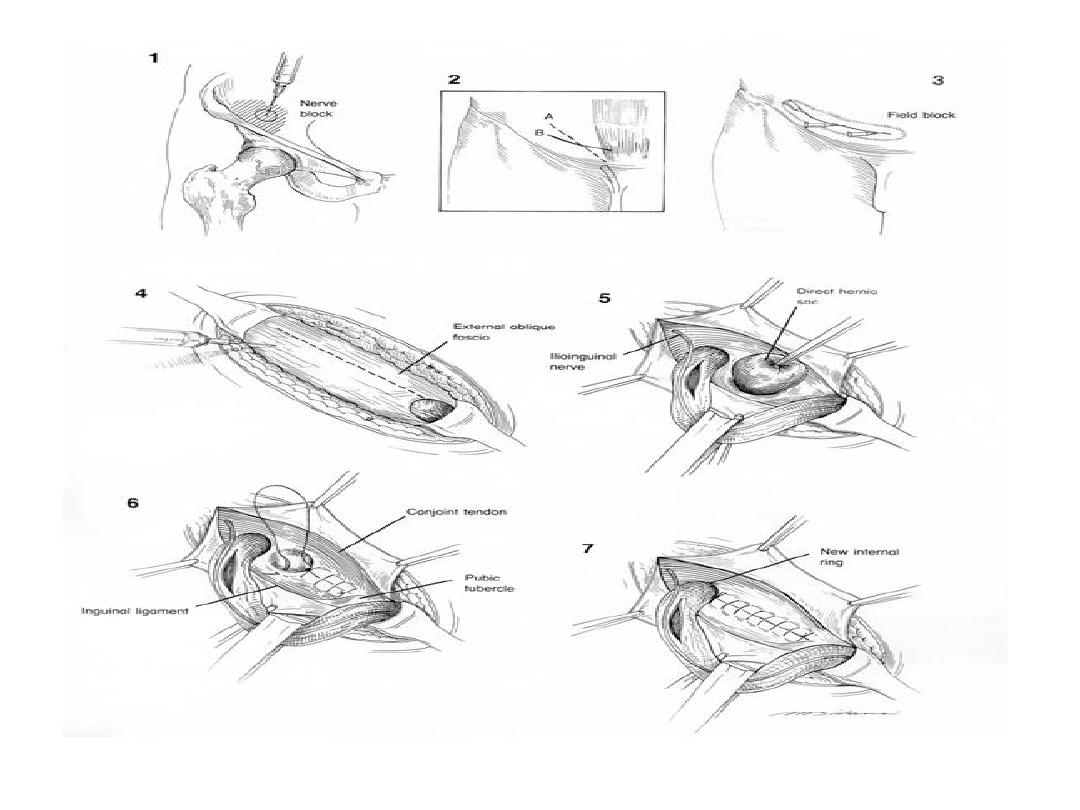
Inguinal hernia, Anatomy
• superficial inguinal ring; it is an opening in the
external oblique aponeurosis, 1.25 cm above
pubic tubercle
• pubic tubercle ; is the upper most lateral most
part of pubic bone
• deep inguinal ring ; it is 2-3 cm above mid
inguinal lig. point it is an opening in the
transversalis fascia

Inguinal hernia,
Anatomy
• inguinal canal; it is about 4cm in length
,directed downward &medially for the
passage of spermatic cord, ilioinguinal N
,genital branch of genitofemoral Nerve.
• in female the round ligament replace
spermatic cord

inguinal hernia,
anatomy
• anteriorly ; external oblique aponeurosis plus
conjoined muscle laterally
• posteriorly ;fascia transversalis and conjoined
tendon
• superiorly ; conjoined muscle (internal oblique
&transversalis )
• inferiorly ; inguinal ligament
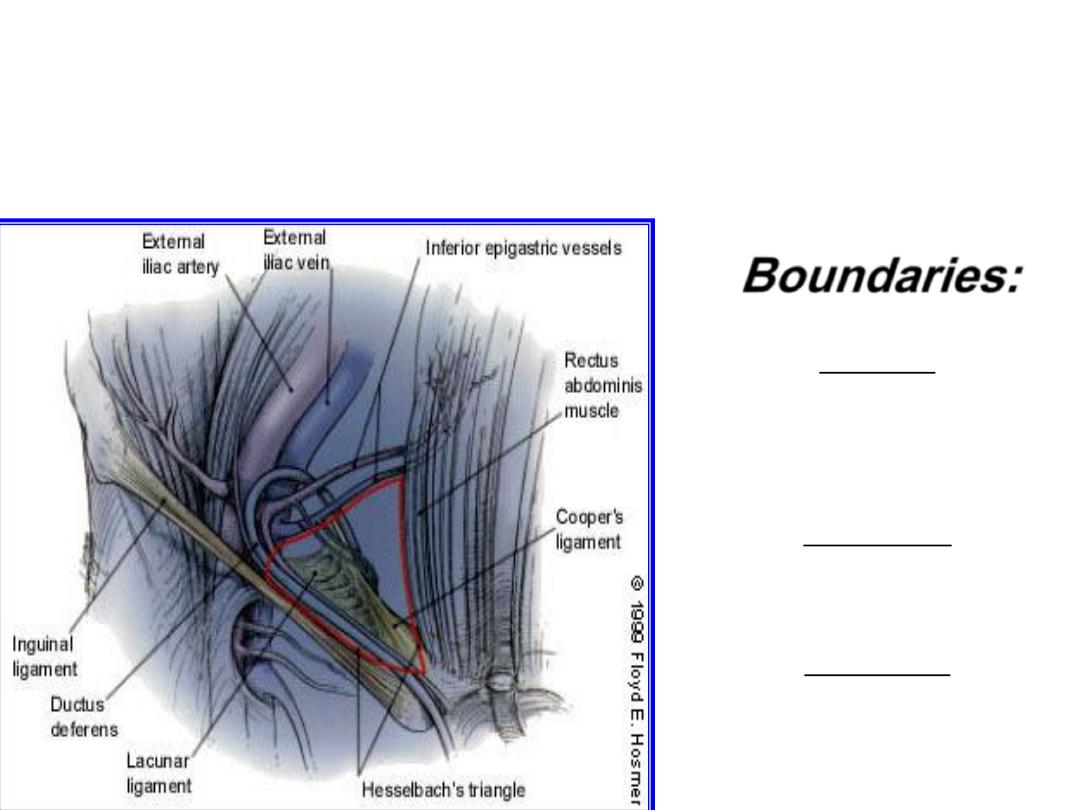
Hesselbach's triangle
Boundaries:
Hesselbach's triangle
Medial:
Rectus abdominis
muscle medially,
Inferiorly:
Inguinal ligament
Laterally:
Inf. Epigastrics
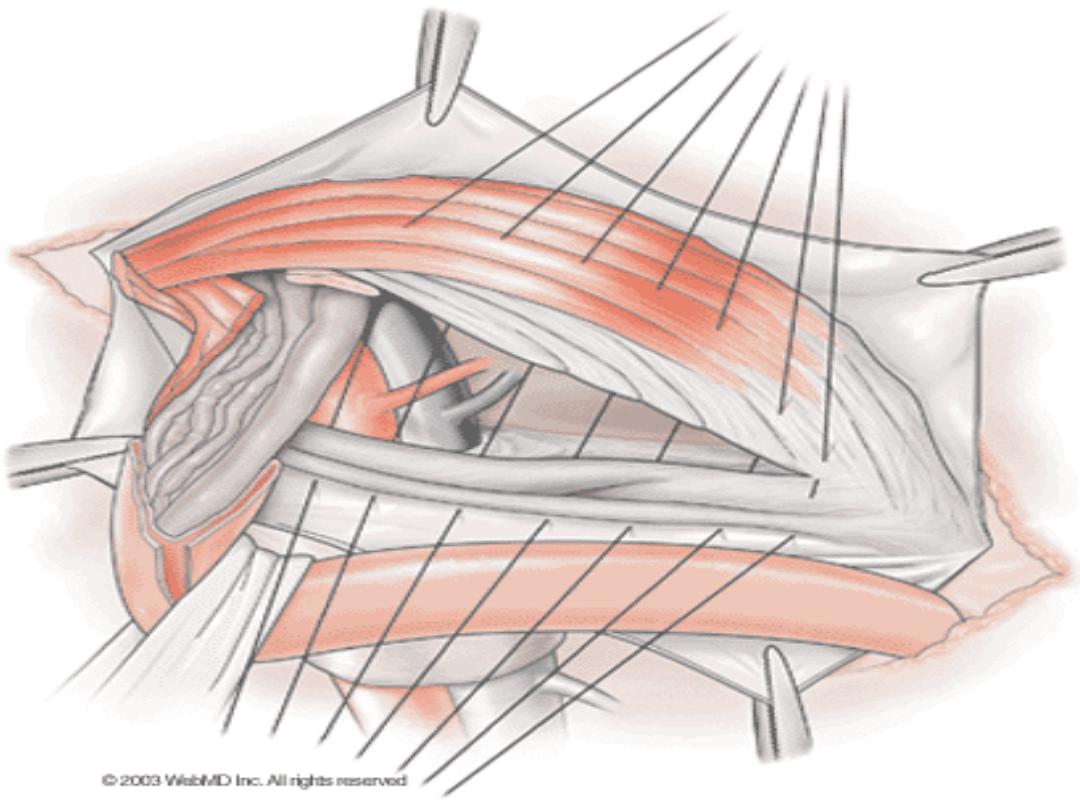

indirect inguinal hernia
• it is the most common of all form of hernia
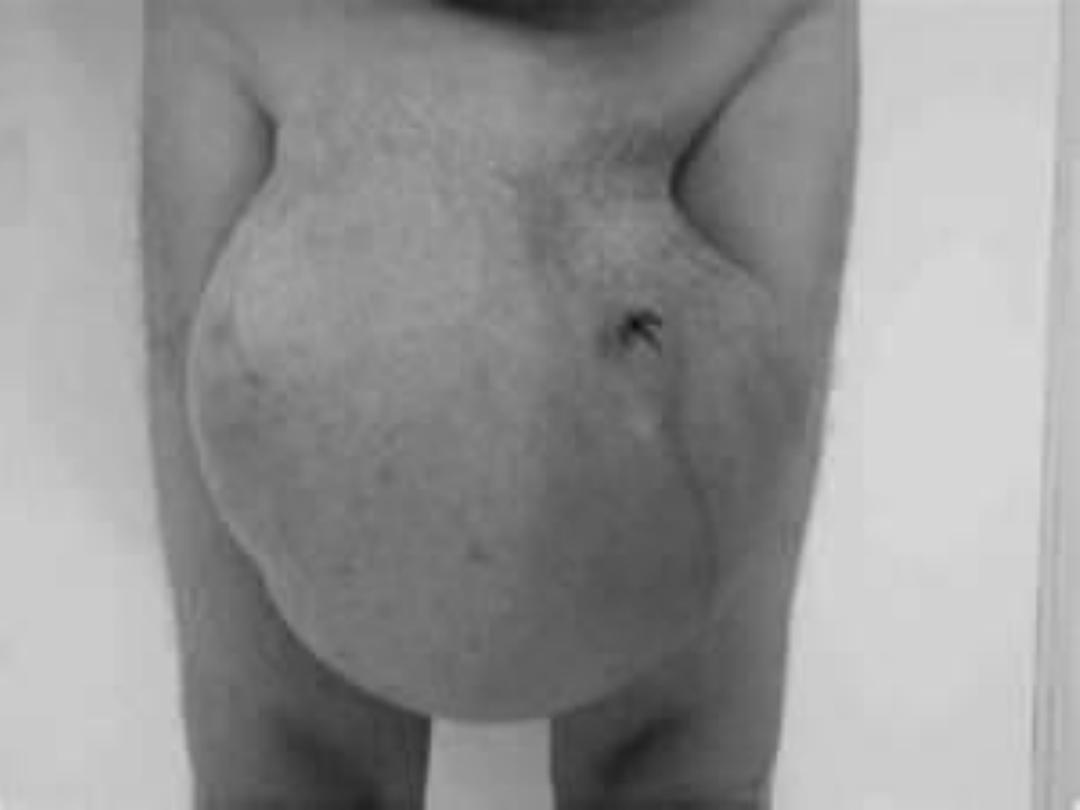

clinical feature
symptom
• occur at all age
• male > female
• pain at groin, at walking & exercise
• swelling on cough, standing in the groin
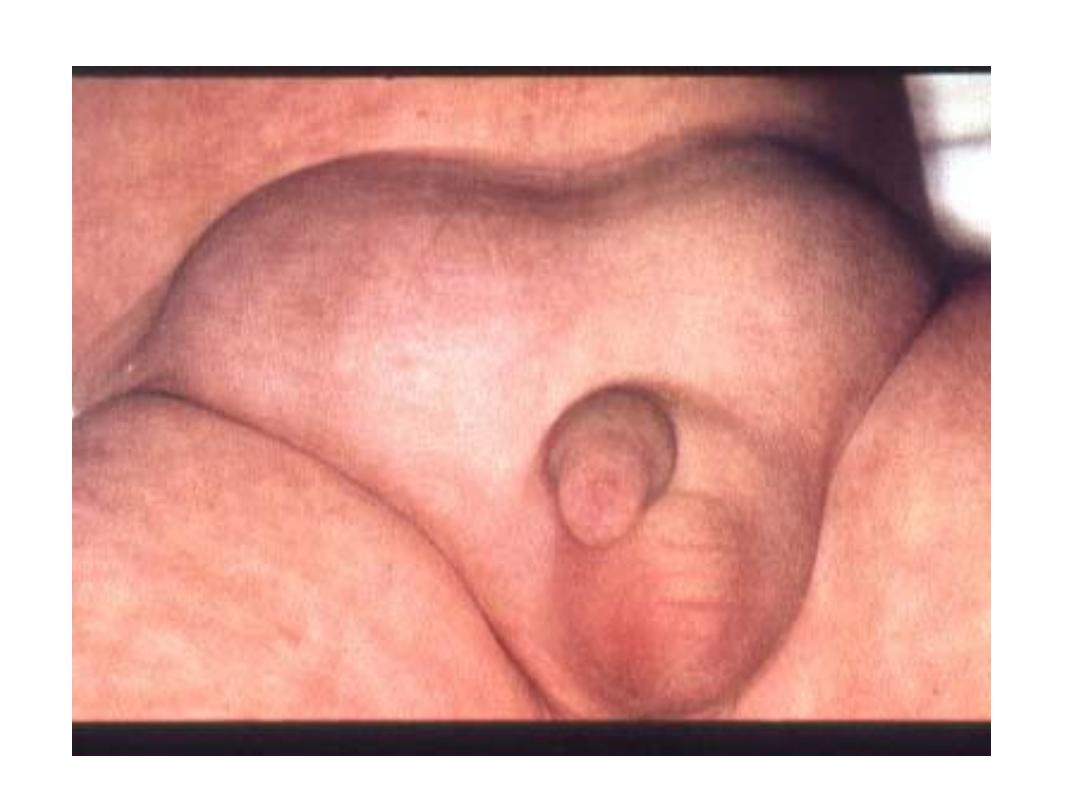
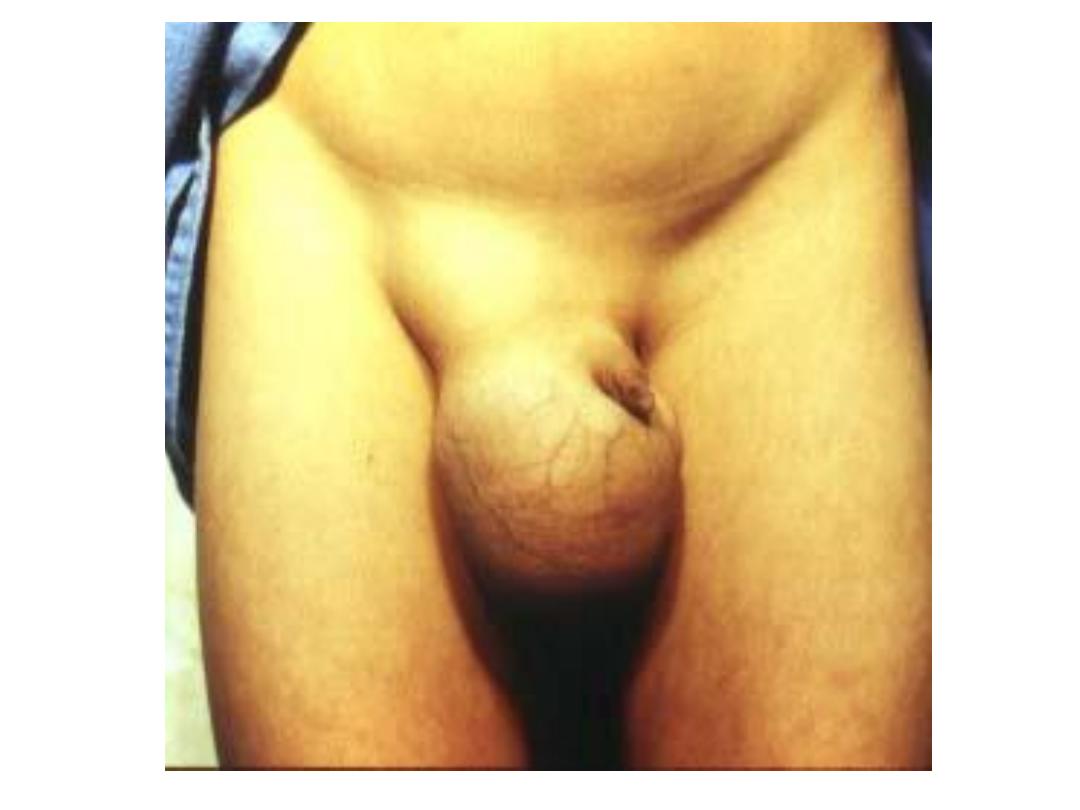

sign
• On standing; ask patient to cough, you will see
expansible impulse, and you can feel it
• In supine position; you can confirm the
reducibility of hernia
• Also we can feel the content

Differential diagnosis
• Vaginal hydrocoele
• Encysted hydrocoel
• Spermatocoel
• Femoral hernia
In female
• Hydrocoel of canal of nuck
• Femoral hernia

Treatment
The treatment of choice is operation
The principles of operation are;
•
1-infant, children & young adults
herniotomy ; this mean excision of the sac, after
reduction of content and transfixation of the
neck .

2-adults hernia
•
1-herniotomy ;
•
2-herniorrhaphy ; this achieved by
– A-repair of stretched internal inguinal ring and
transversalis fascia
– B-reinforcement of post wall of inguinal canal

procedure
•
Basini repair
•
Shouldice repair
•
Mesh repair by Lichtenstein tension free
hernioplasty
•
Plug & mesh repair
•
Laparoscopic herniorrhaphy
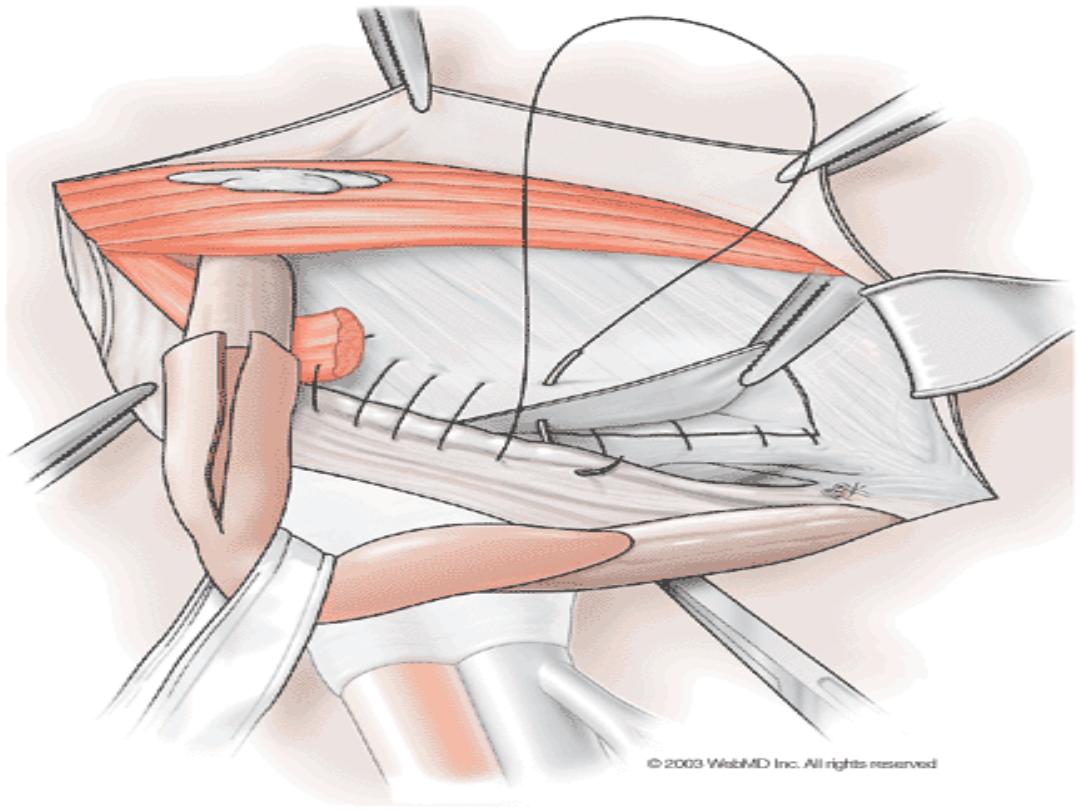
Shouldice repair
2
nd
layer
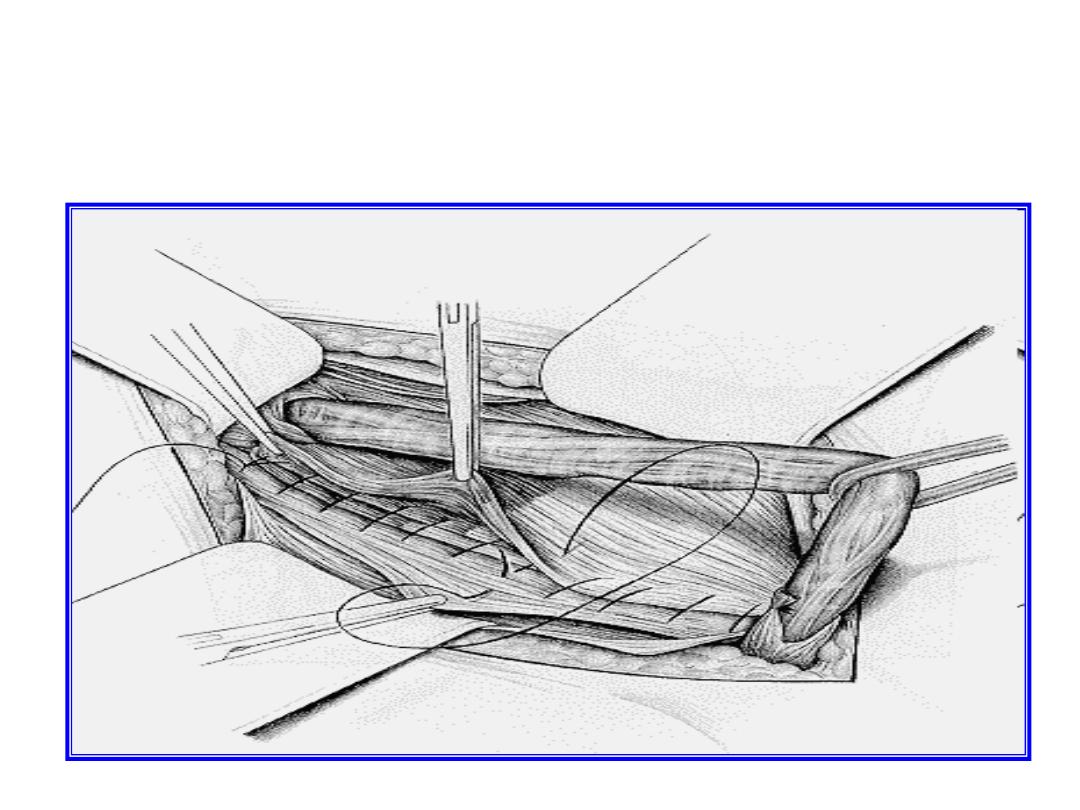
Shouldice repair
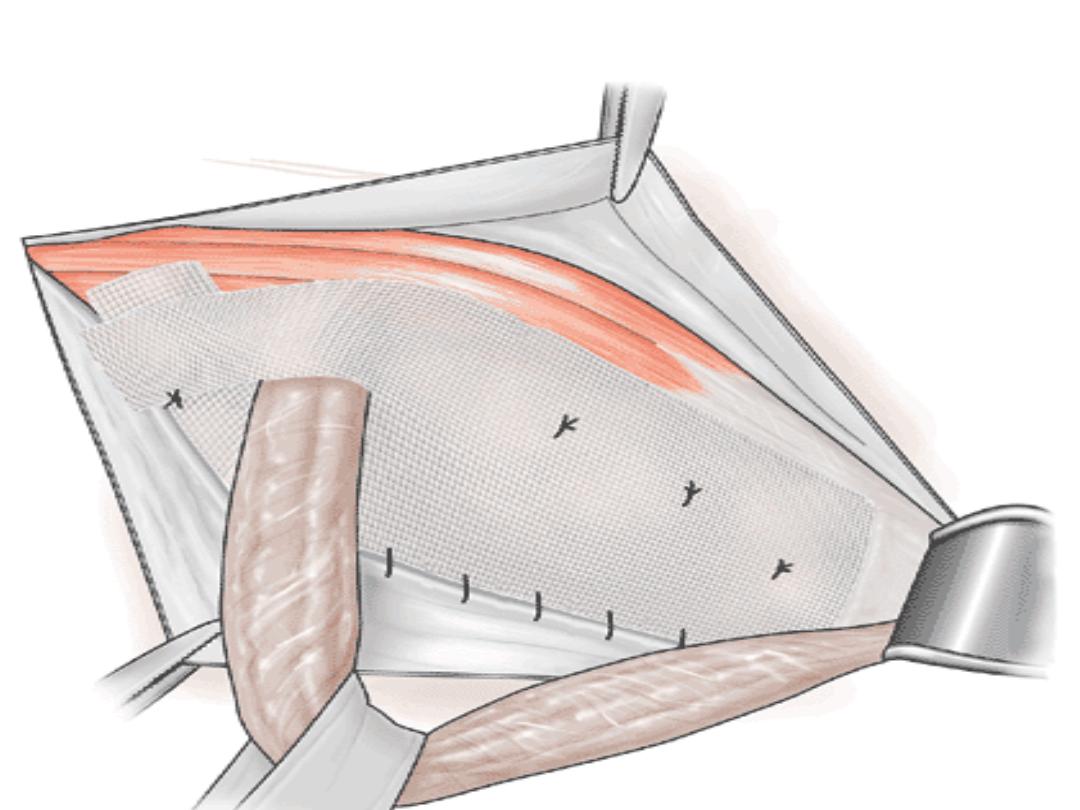
Lichtenstein repair
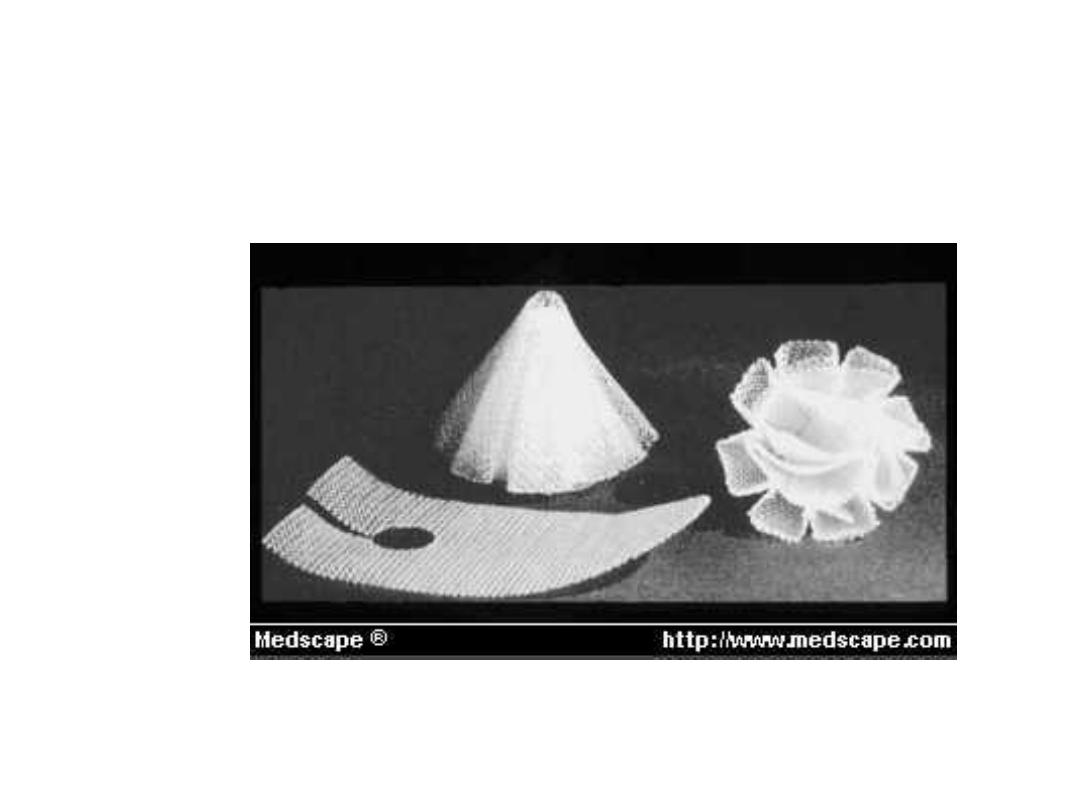

Polypropylen Mesh for plug and onlay patch

Direct inguinal hernia
It is an adult male hernia
The sac arise from posterior wall, medial to the
inferior epigastric vessels
• To differentiate direct from indirect hernia by
obliteration test
• Which mean obliteration of deep ring by
thumb ask patient to cough after reduction it
should not appear

Treatment;
• The same principle herniorraphy of
indirect inguinal hernia, with sac
invaginated to inside instead of excision

Sliding hernia
It is acquired indirect inguinal hernia
with sliding part of large bowel or
urinary bladder

Strangulated hernia

Clinical features,
symptom
•
Pain; sever pain, at site of hernia, then
become generalized colicky, central abdominal
pain
•
Nausea ,vomiting
•
Absolute constipation (no feces nor flatus )
•
If this not relieved followed by generalized
peritonitis and paralytic ileus ( stop colicky
pain )

Sign
• Tender hernial site
• Irreducible
• No expansile cough impulse
• Patient looks pale, tachycardia,
• Bowel sound exaggerated, and absent in
advanced condition
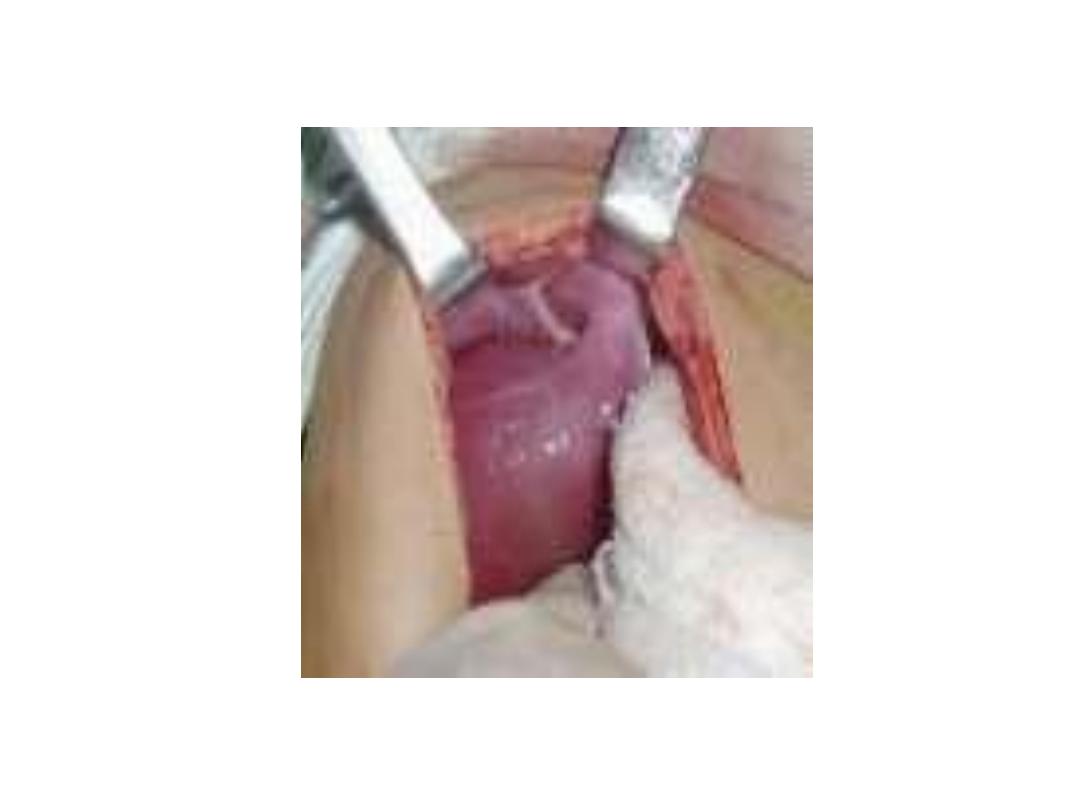
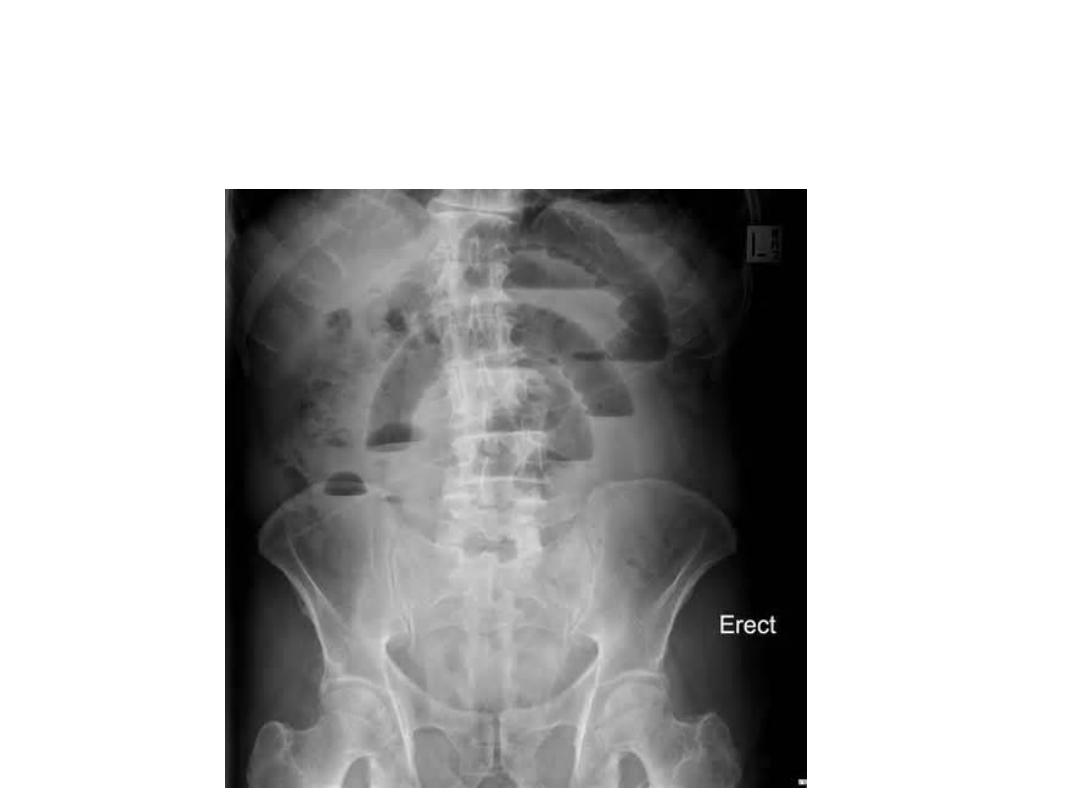
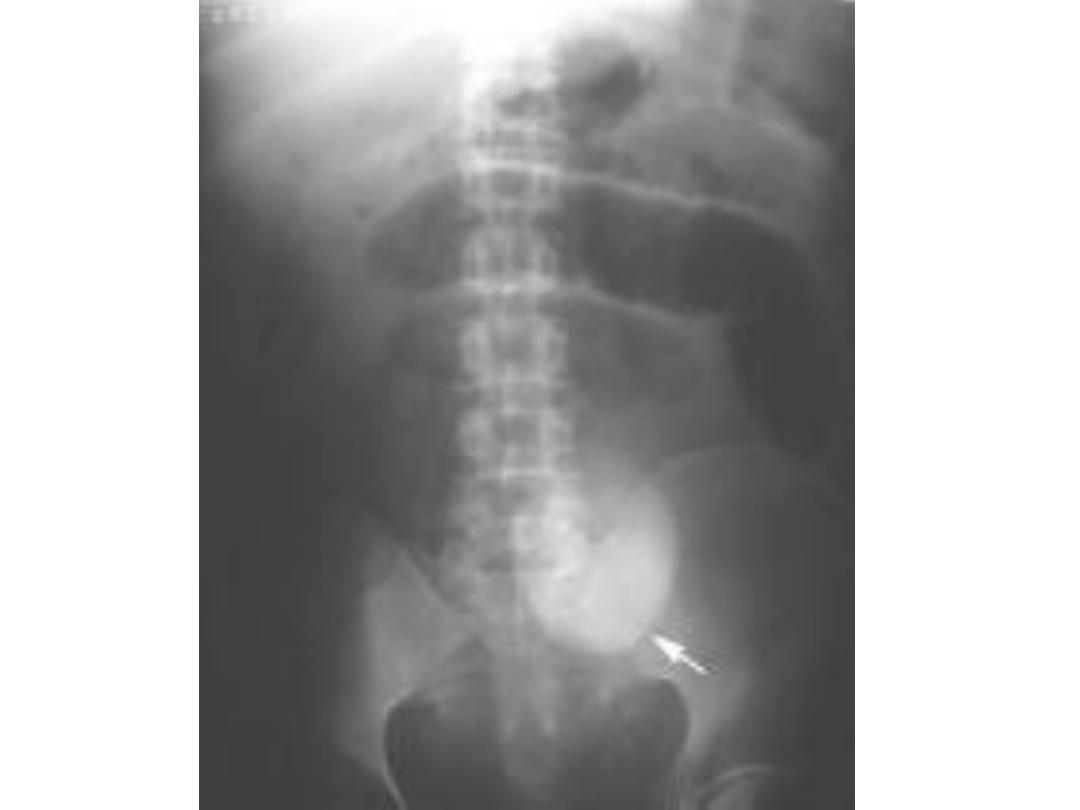
Plain X-ray abdomen erect
position
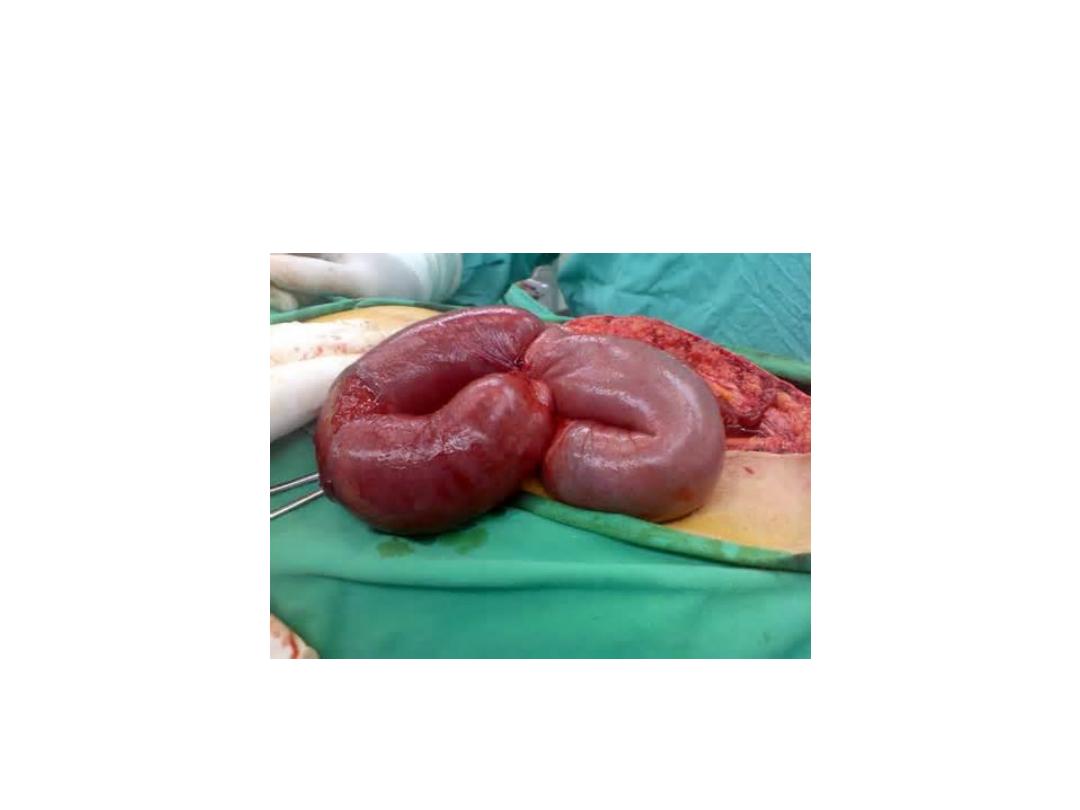
Strangulated hernia

Treatment
• Fluid replacement
• Antibiotic
• Emergency operation
• Repair of hernia according to site and age

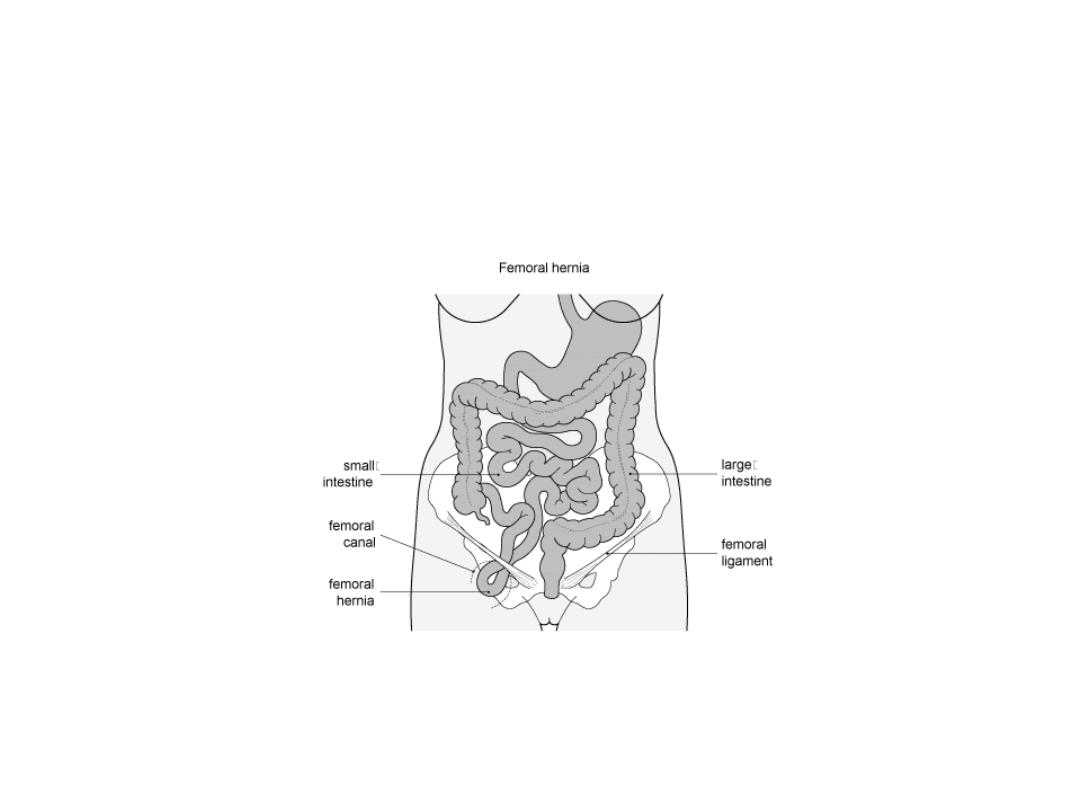
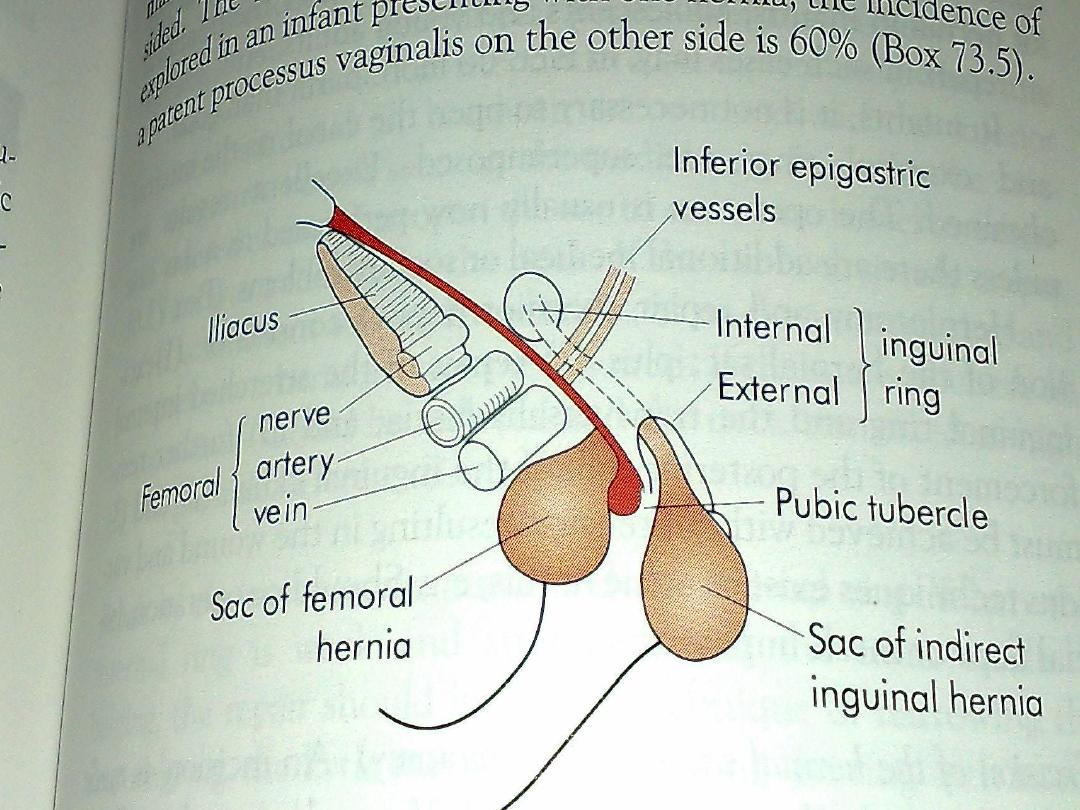
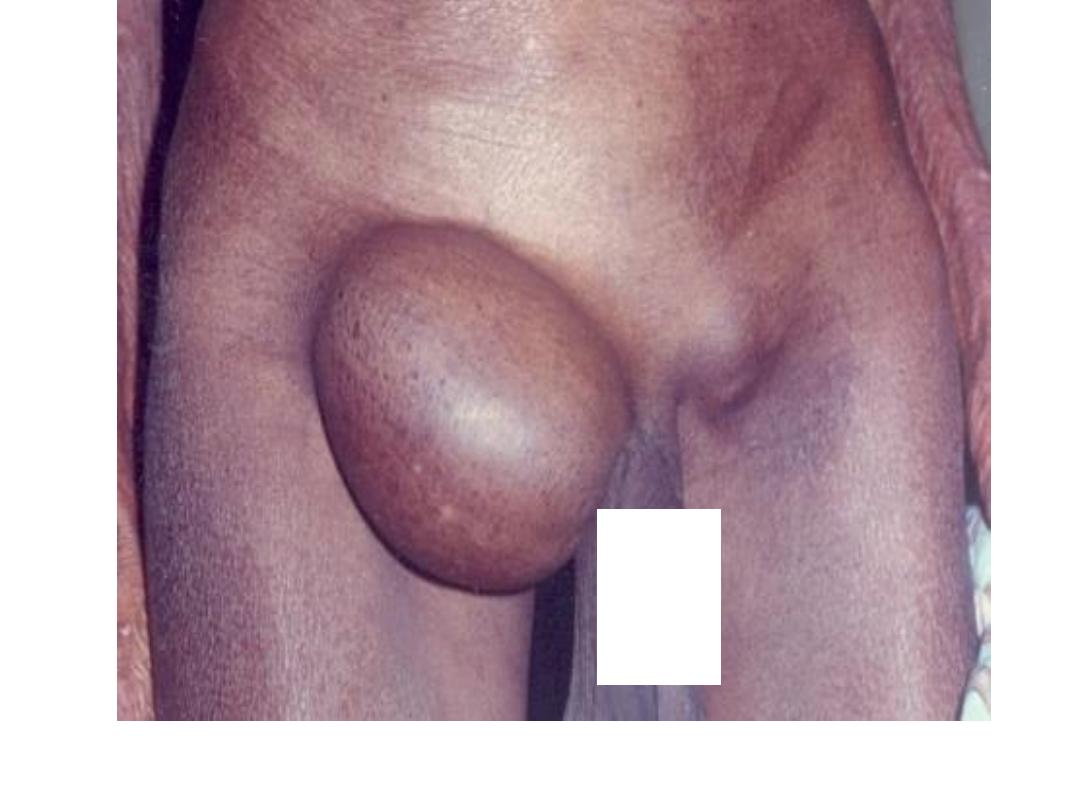
Femoral hernia
• It is a herniation through femoral canal
• It is more in female ,
• It is liable for strangulation

The femoral canal
• is the most medial part of femoral sheath
• it contain fat, lymphatic vessels & LN
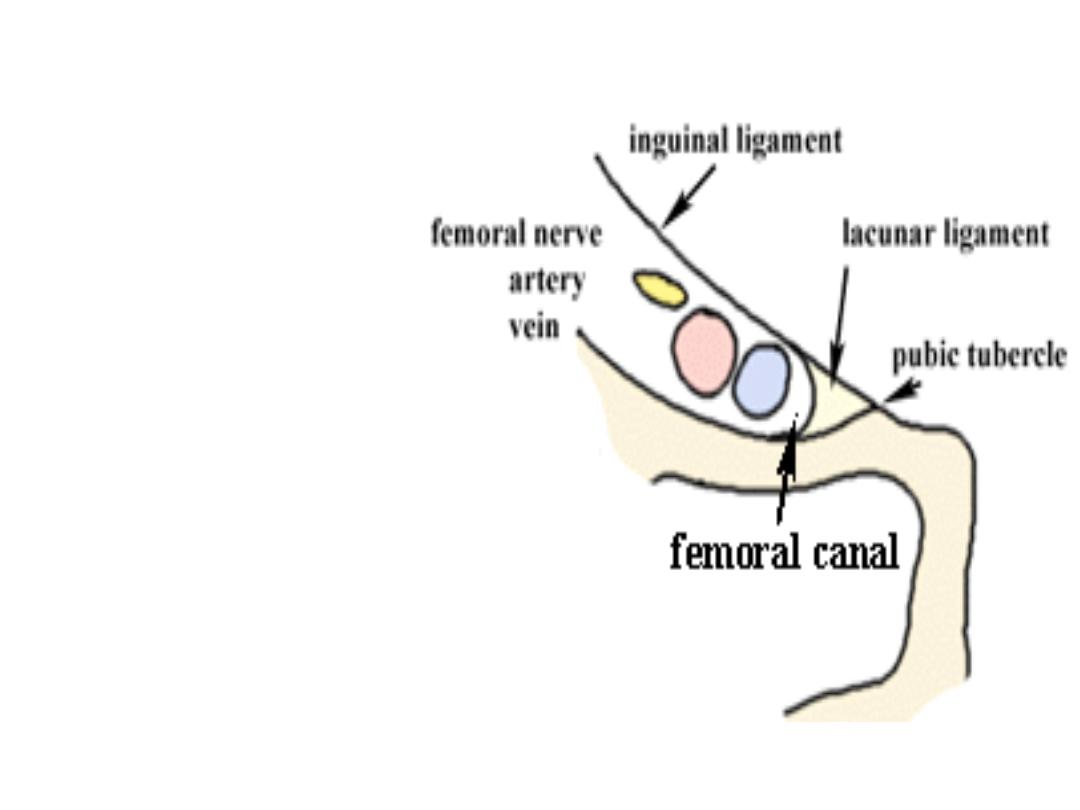

Femoral ring boundaries
Ant. Inguinal ligament
•
Post ;iliopectineal lig. Pubic bone& fascia over
pectineus muscle
•
Med; lacunar lig.
•
Lat ; thin septa separate it from femoral vein
--------
-----
---

Clinical features
• It is rare below 20 years
• It is rarely cause symptom ,it may present for
years without complaint till present with
strangulation
• Patient may notice a lump
• Patient may complain of mild pain

Diferential diagnosis
• Inguinal hernia
• Saphena varix
• Enlarged femoral LN
• Lipoma
• Psoas abscess
• Psoas bursa

Treatment
• Surgical repair as early as possible, because it
is very liable for strangulation
• Lockwood operation; (low approach )
• Mc Evedy operation (high approach )
• Lotheissen’s operation (inguinal approach )

Qwestion
•
A 35 year old male presented with a red and
swollen lump in the left groin . An inguinal hernia
suspected and, at the time of operation ,the lump
is found to contain small loop of necrotic bowel.
This type of hernia is best described as :
•
A- Irreducible
•
B-strangulated
•
C-obstructed
•
D-sliding
•
E-Richter’s

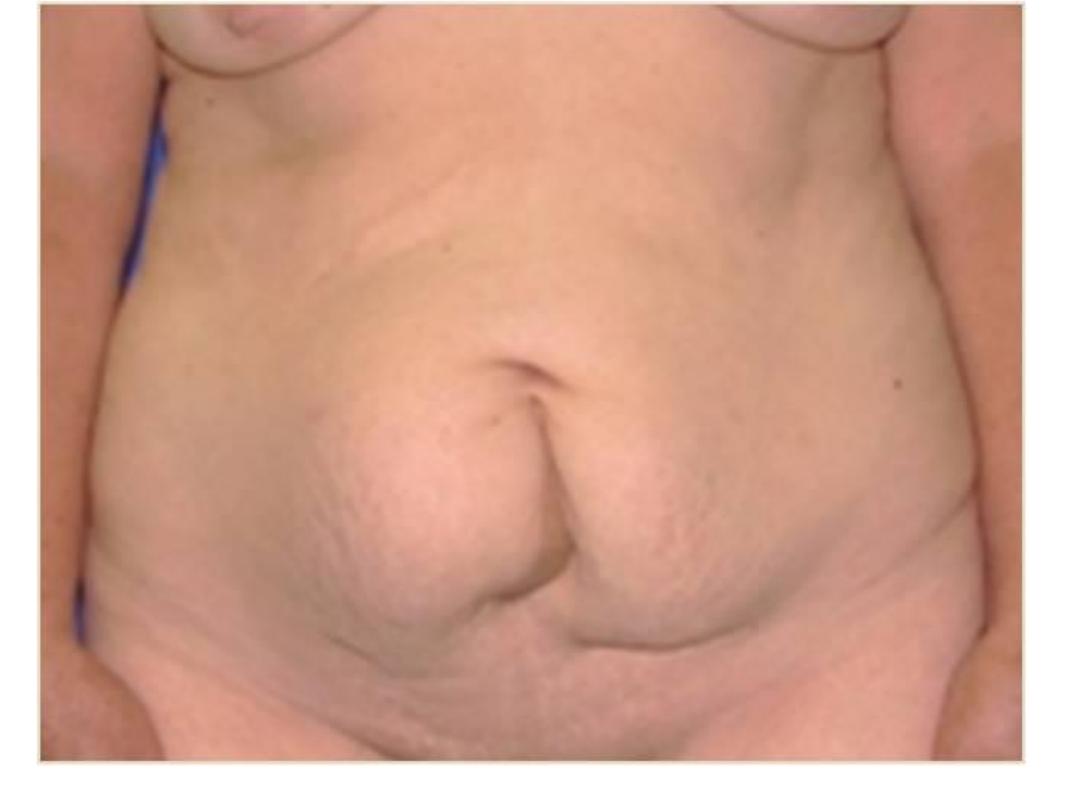
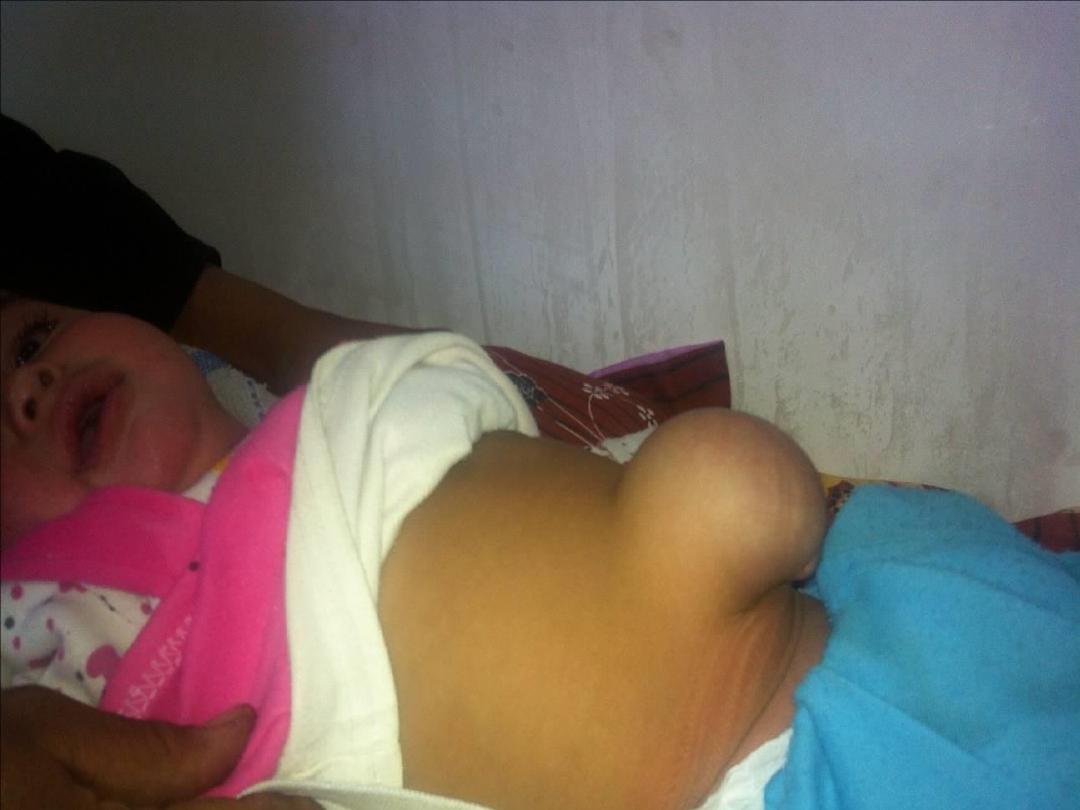
Umbilical hernia
• This hernia through a weak umbilicus ,it is
rarely get obstructed ,it is often not painful

Treatment
• Reassurance of family ,most of them closed
spontaneously before two year
• Hernia remain after two years should be
closed surgically

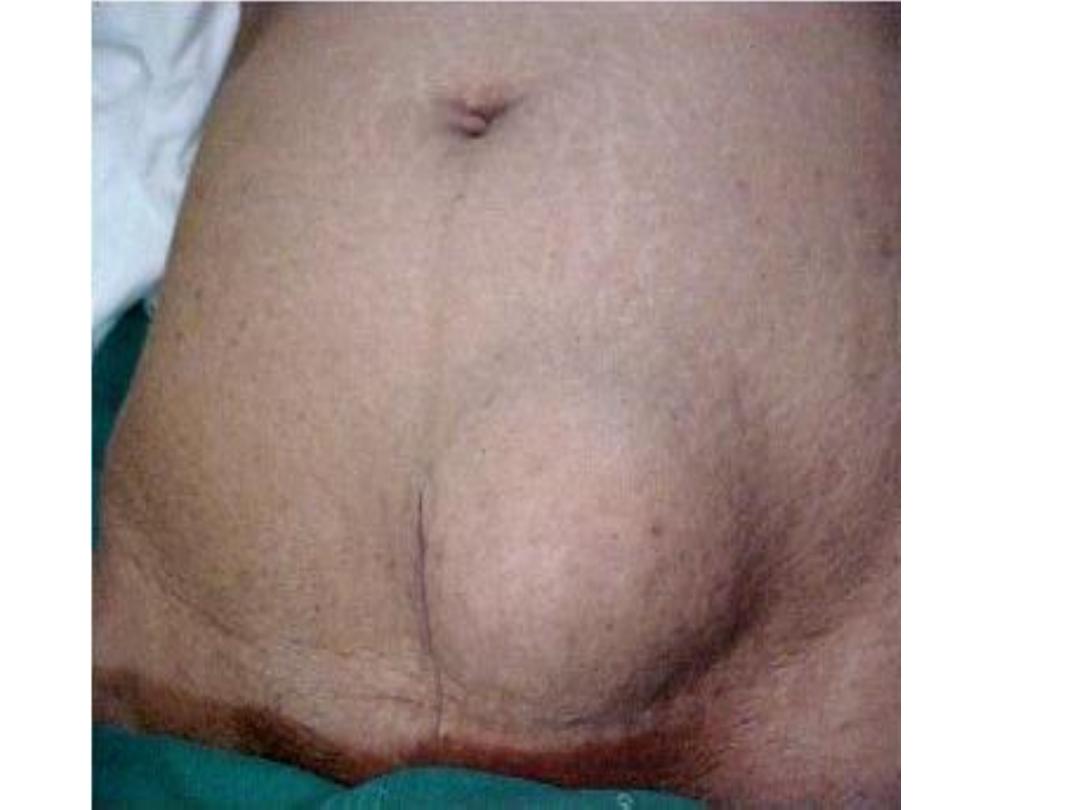
Paraumblical hernia
• It is a defect in the linea elba above or below
umbilicus
• The content of the sac is usually omentum
or/and bowel
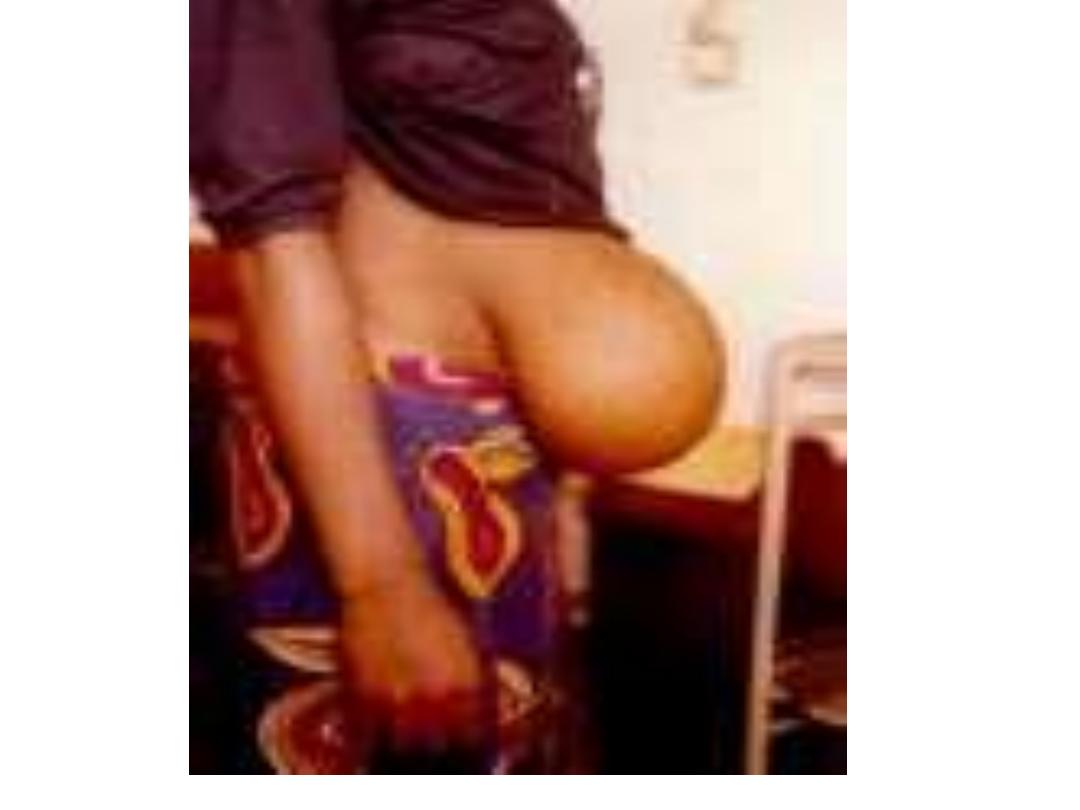
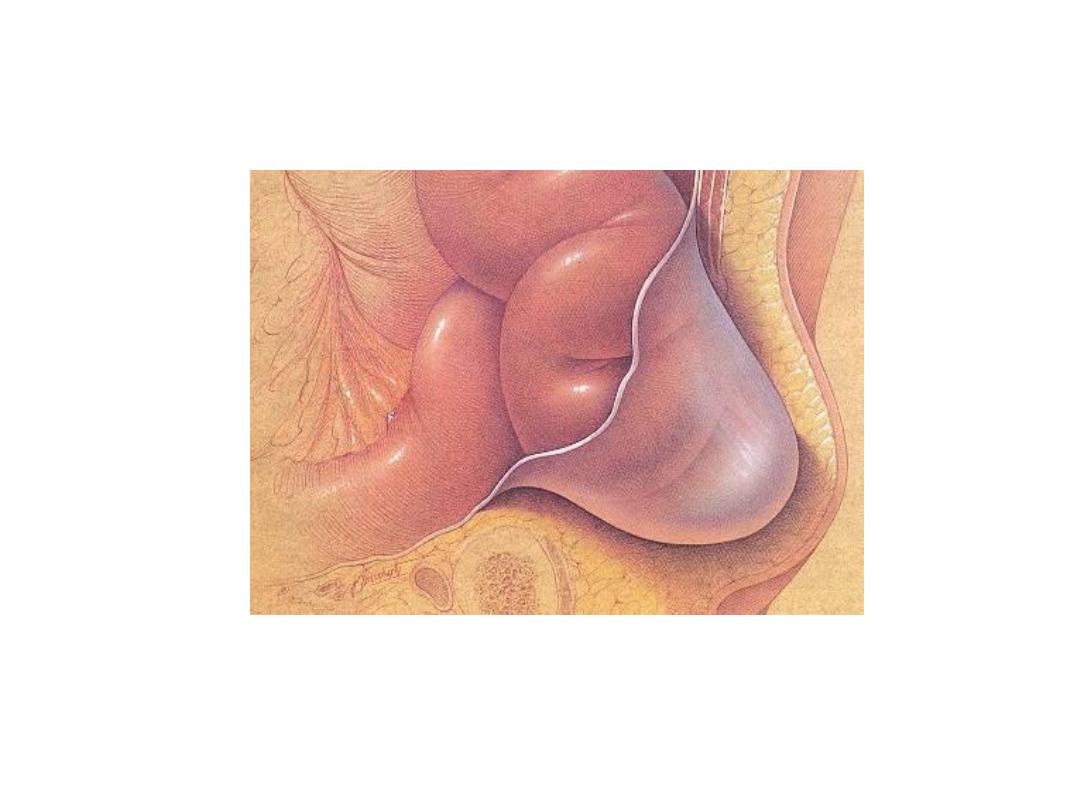

Clinical feature
• Female >male by five time
• Adult, above 30 years
• These patient usually multiparus and over
weight
• Patient may complain of attack of colicky pain,
due to partial obstruction
• It might be irreducible due to adhesion of
omentum to the sac
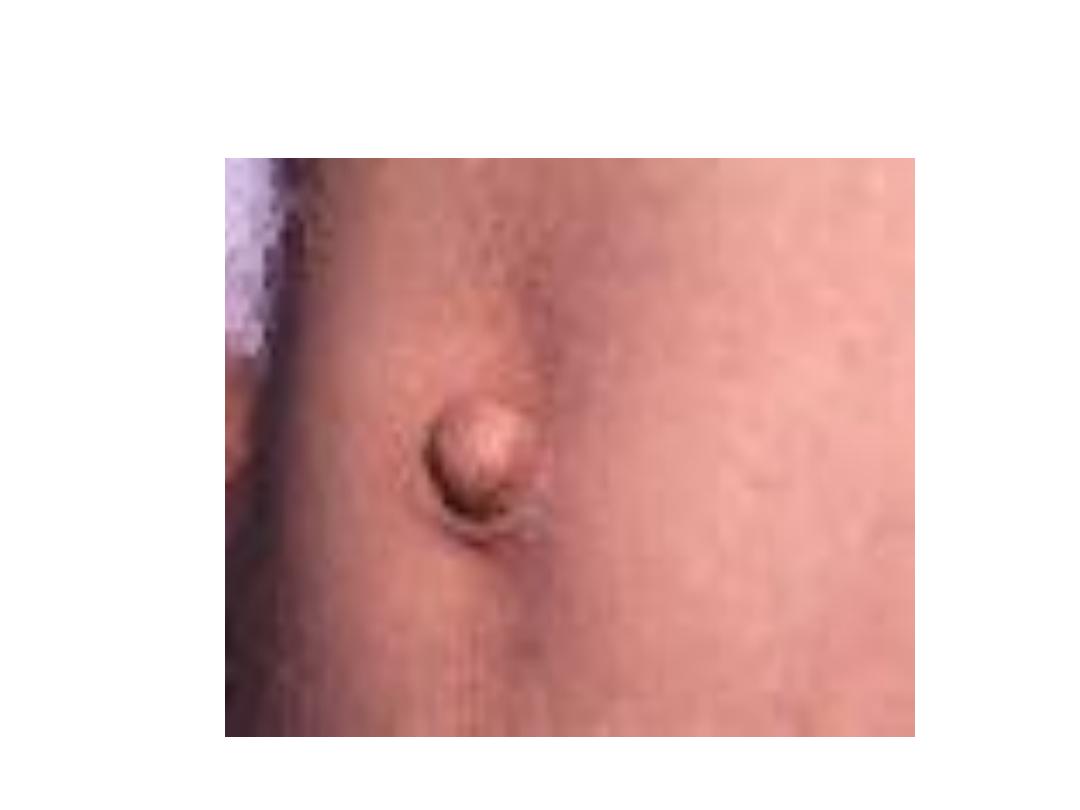
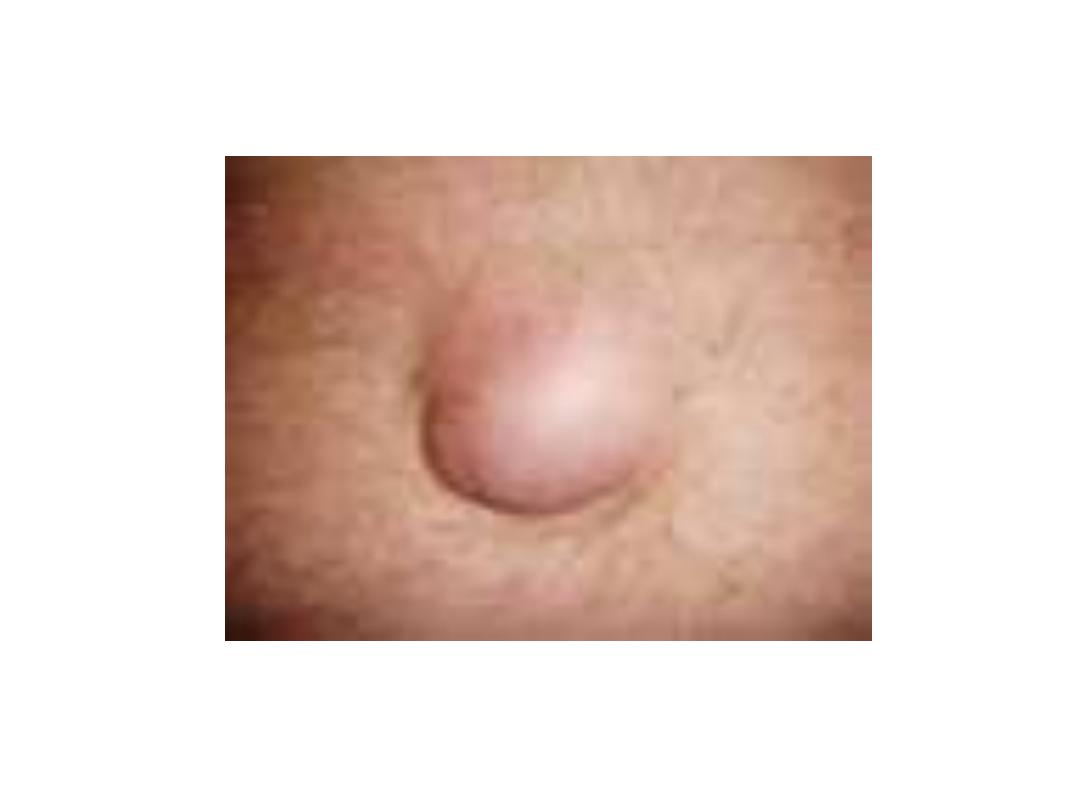

Treatment
• Surgical repair by Mayo’s repair for small
hernia less than 2cm in diameter; It is double
layer unabsorbable interrupted suture
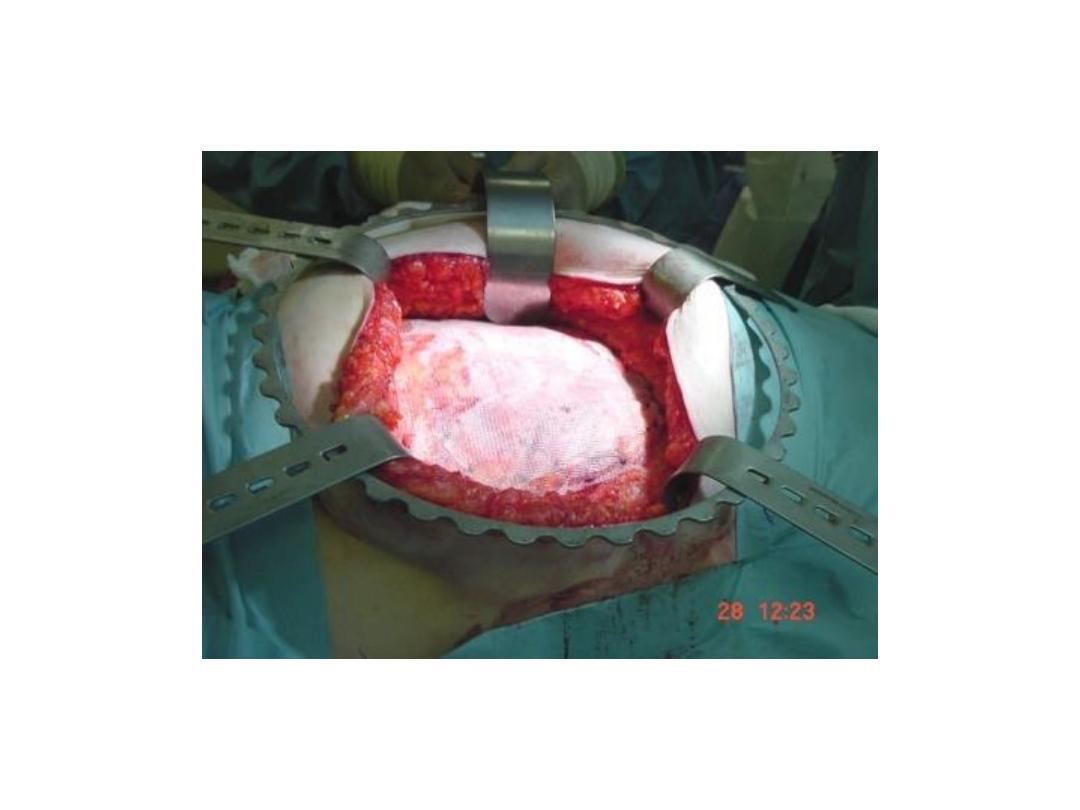
• Mesh repair(by open or laparoscopic
procedure ) in different position (onlay, or
sublay, subperitoneal)
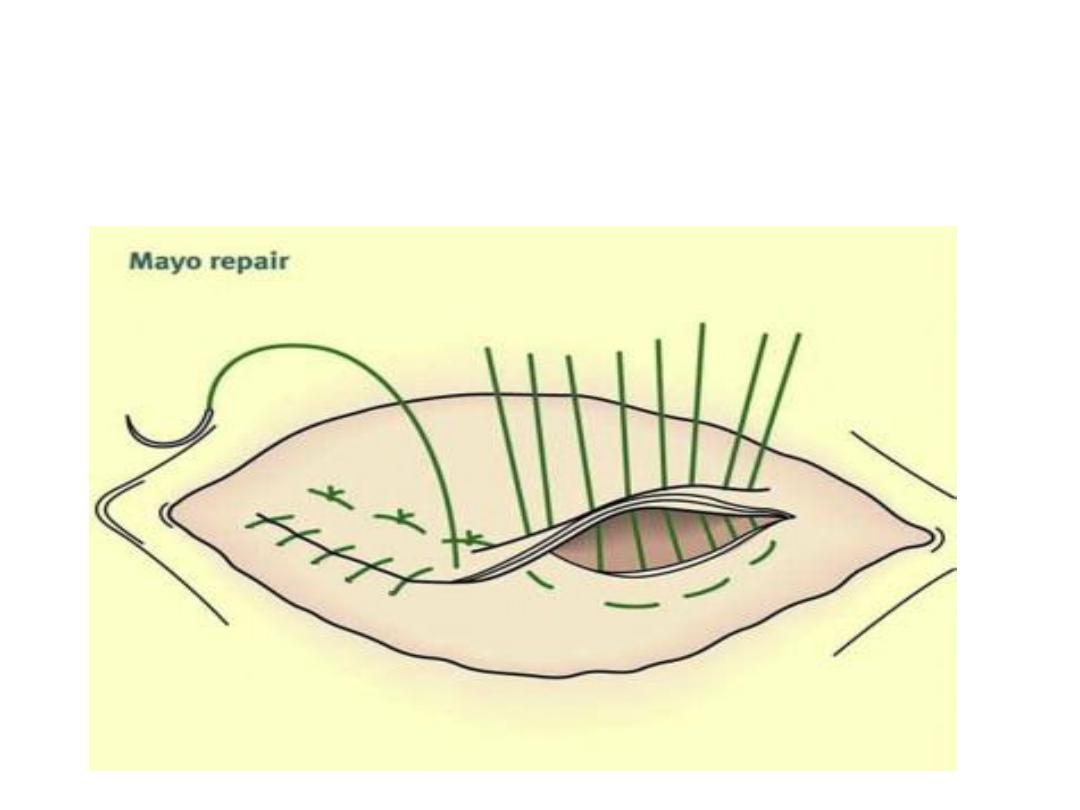
Mayo’s repair
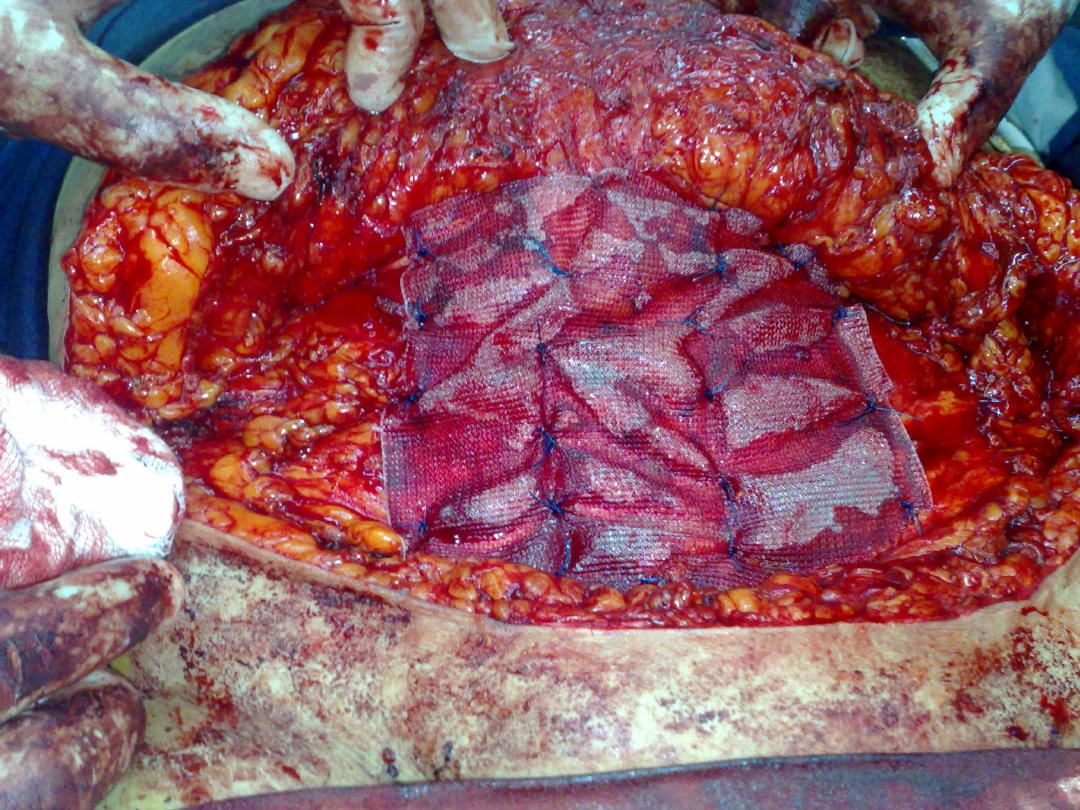
On lay mesh repair

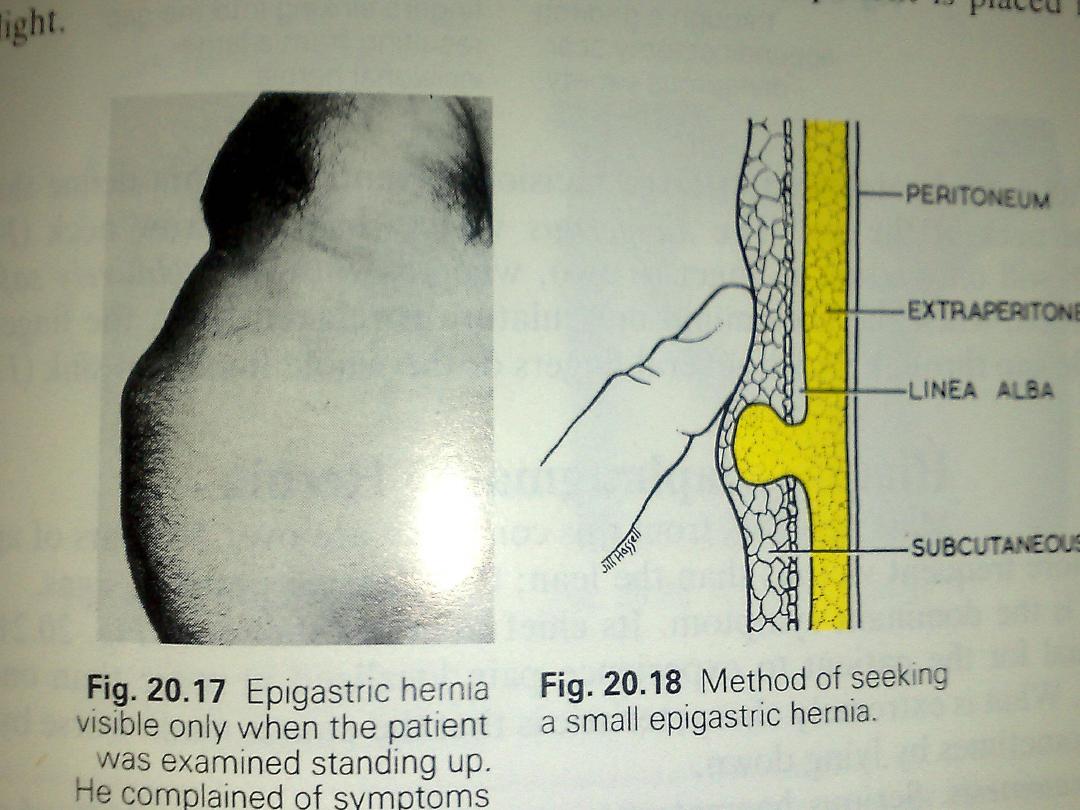
Epigastric hernia
• Hernial defect in the linea alba from
xiphisternum to the umblicus
• Felt as swelling
• My be associate with pain
• Epigastric pain like that of DU
• Treatment ;operative repair for painful and big
one

Umblical pilonidal sinus
• Is sinus contain hair
• Discharging pus
• Treatment; excision
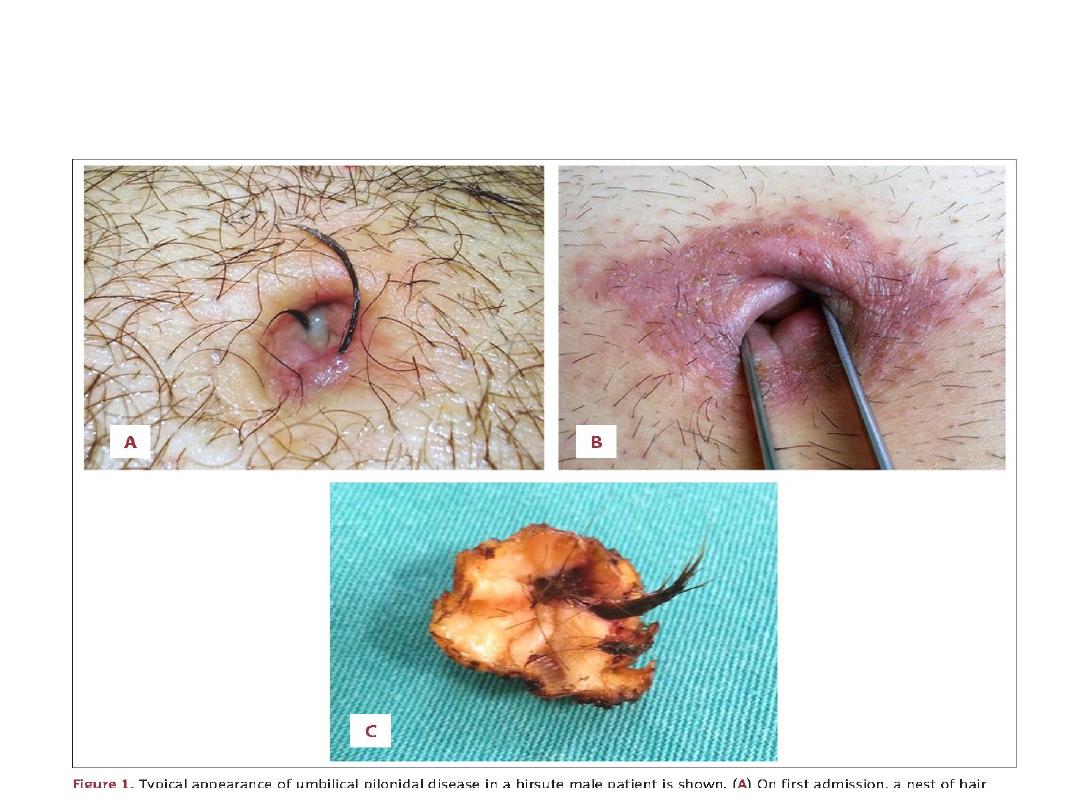
Umbilical Pinlonidal sinus

Umblical fistulae
• Patent vitelointestinal duct
• Patent Urachus
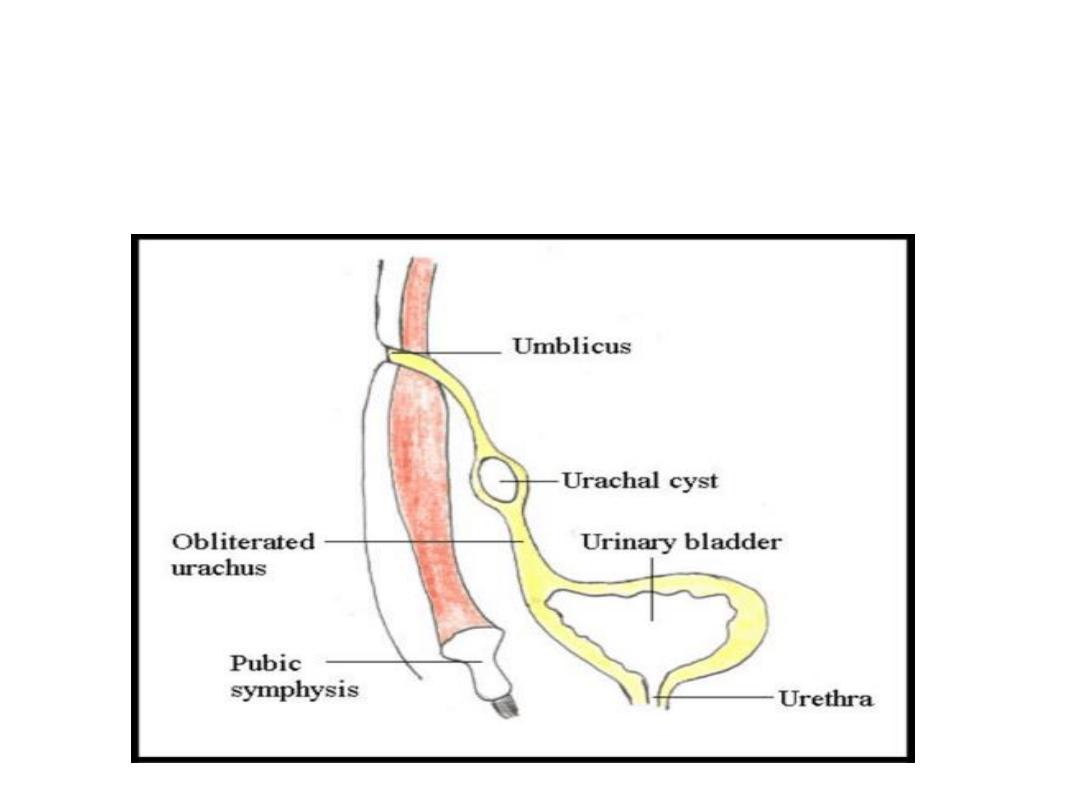
Urachal cyst

Burst abdomen
• Burst abdomen ( abdominal dehiscence ) the
viscera extruded to out side due to burst of
abdominal wall suturing
• Incisional hernia; partial disruption of deeper
layer the skin remain intact

causes
• Technique of wound closure
• Factors related to incisions
• Reasons for initial operation
• Coughing, vomiting , distension
• General condition (obesity, jaundice,
malignant disease, hypoprotinemia, and
anemia, steroid, pregnancy, ascites )
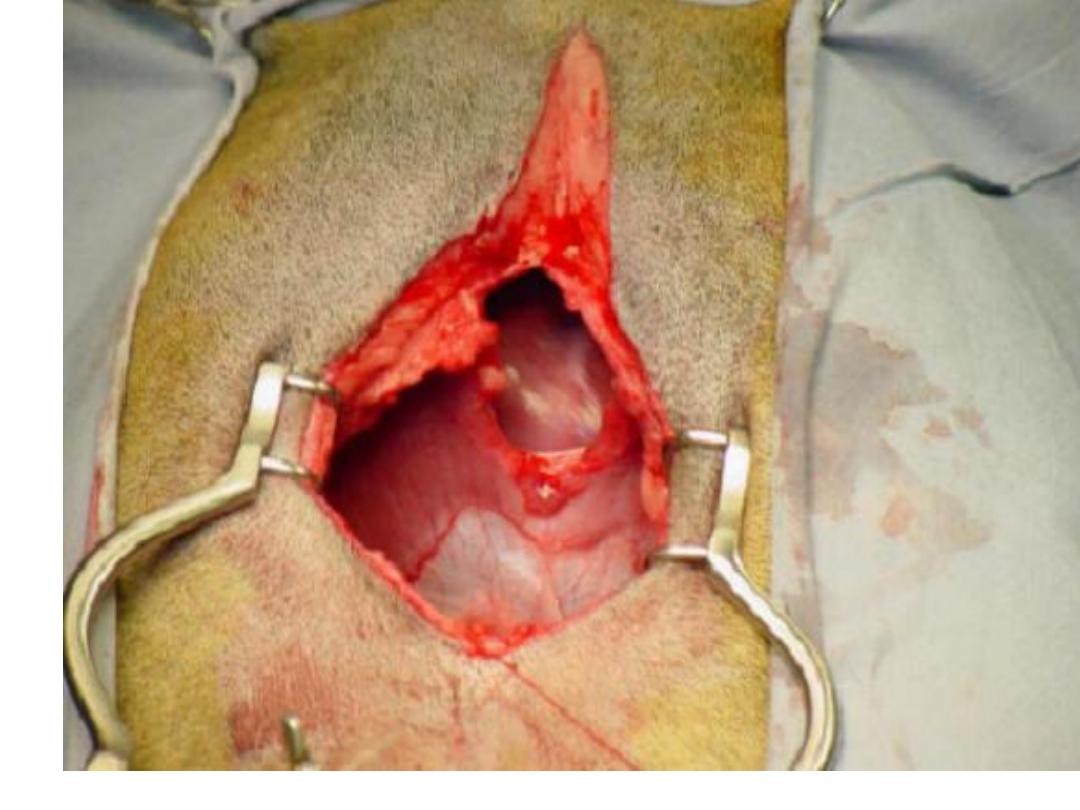

Burst abdomen
• Serosanguinous discharge, the
pathognomonic feature
• Some time patient fell some thing giveaway
• Emergency operation

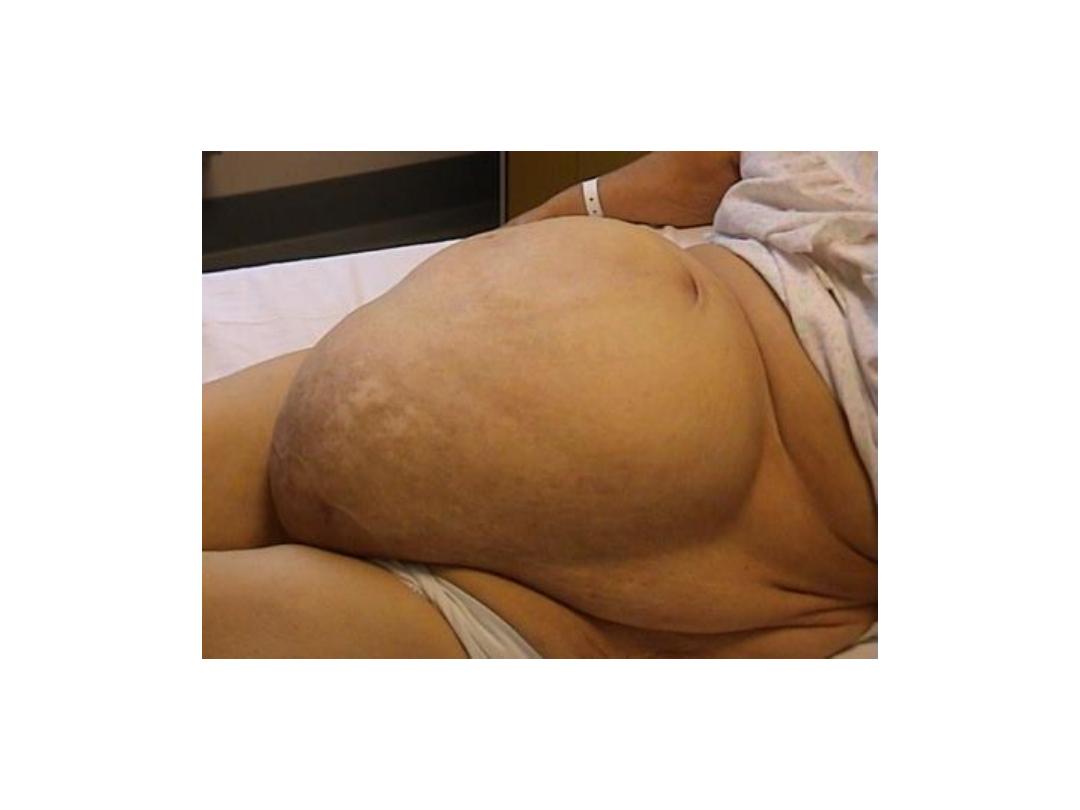
Incisional hernia
• Aetiology
• Clinical features
• Treatment