Frozen shoulder( adhesive capsulitis)
Dr. Ihsan AlshamyF.I.B.M.S
definition
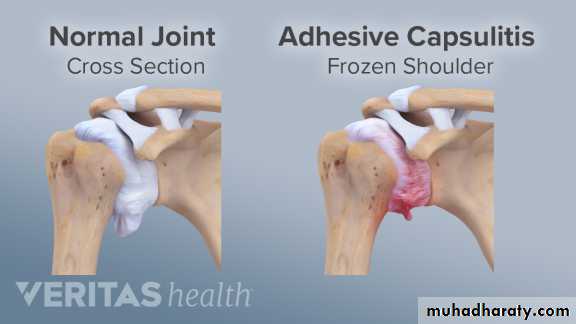
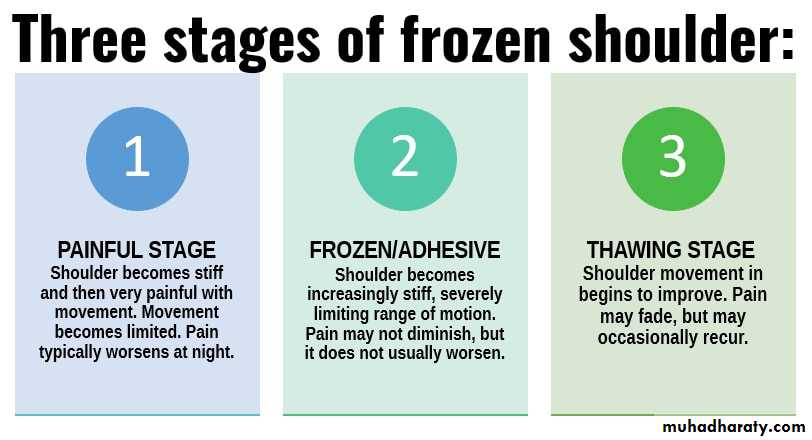
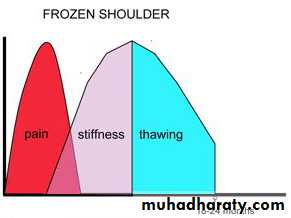
Frozen shoulder is :characterized by progressive pain and stiffness of the shoulder which usually resolves spontaneously after about 18 months.Clinical features
pathology
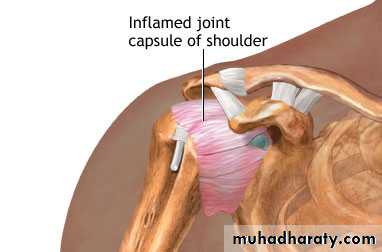
active fibroblastic and myofibroblastic proliferation in the rotator interval, anterior capsule and coracohumeral ligament.diagnosis
Usually clinical ; typical successive phases of pain, stiffness , thawing phase in presence of normal x-ray.
Treatment
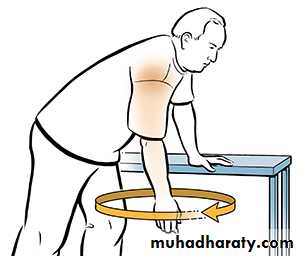
* NSAI* Physiotherapy ( pendulum exercises)
* Intraarticular injection of steroid
1- Conservative treatment
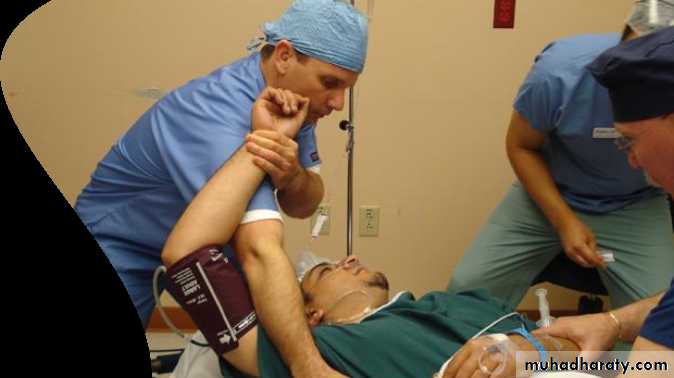
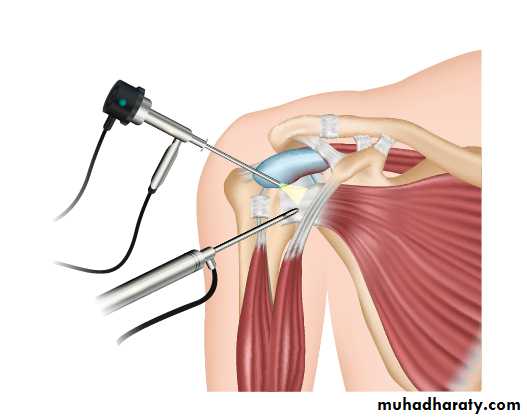
2- MAU ( Manipulation under anesthesia)external rotation --abduction -- flexion3- surgery ( open or arthroscopic capsular release)
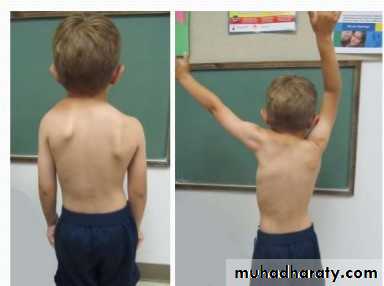
Congenital elevation of the scapula
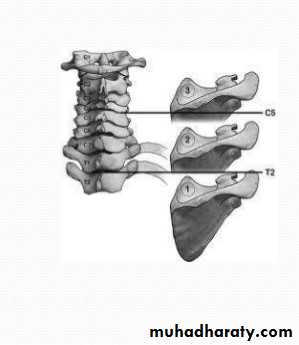
The scapulae normally complete their descent from the neck by the third month of fetal life; occasionally one or both scapulae remain incompletely descended, 2 recognized syndromes ; sprengle deformity and klippel-feil syndrome.Sprengel’s deformity
Usually unilateral, may associated with cervical spine anomalies, the scapula on affected side looks high and prominent, the shoulder movement is limitedKlippel–Feil syndrome
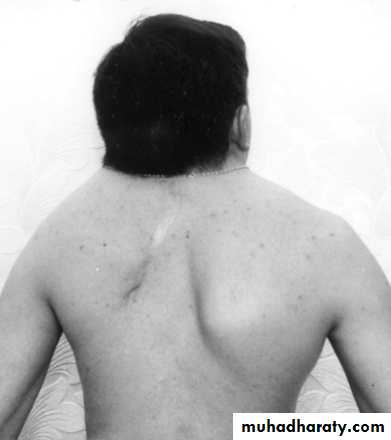
Usually bilateral ,associated with marked anomalies of the cervical spine, short neck, low hair lineGRATING (SNAPPING) SCAPULA
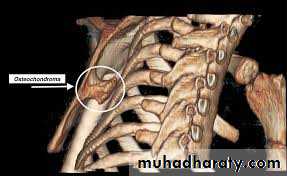
grating sensation or clicking on moving the arm; the condition is often painless, Usually no cause is found.X-rays and CT scan of the scapula should be obtained to exclude an osteochondroma on the undersurface of the scapula. If so; excision of the osteochondroma, if not, just conservative treatment.
Problems of elbow joint
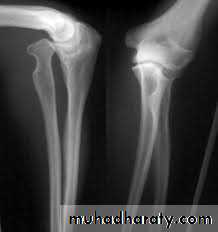
CONGENITAL DISLOCATION OF THE RADIAL HEAusually dorsal dislocations, the radial head present as a lump on the lateral side of the elbow. It become dome shaped dueto unrestrained growth.
Treatment: excision of radial head.
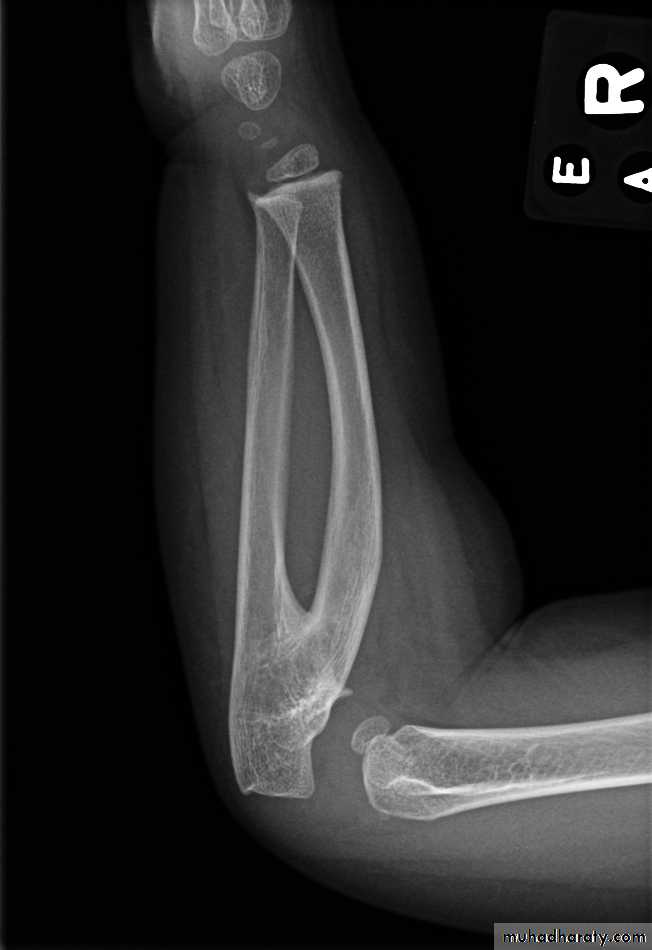
Radioulnar synostosis
Fusion of proximal ulna to the radius, results in sever limitation of forearm pronation and supination. Excision of synostosis is unsuccessful, rotation osteotomy in functional position is the only treatment.CUBITUS VALGUS
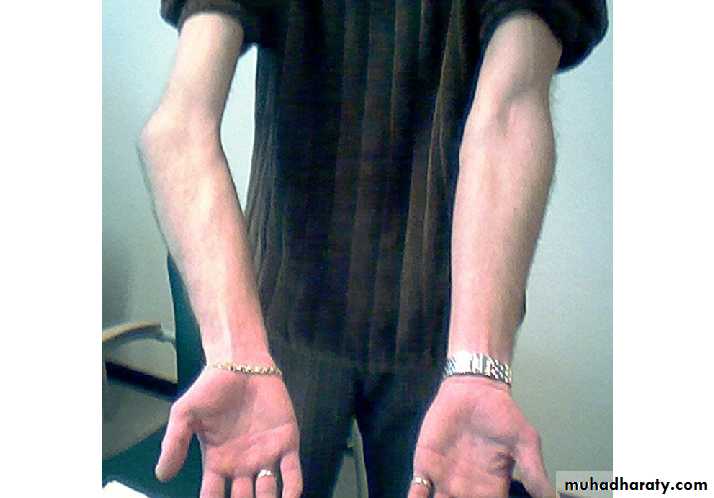
The most common cause is long-standing non-union of a fractured lateral condyle, there is an increased risk of a delayed or tardy ulnar nerve palsy, The deformity itself requires no treatment but the ulnar nerve should be transposed anterior to the medial epicondyle.CUBITUS VARUS (‘GUNSTOCK’ DEFORMITY)
The most common cause is malunion of a supracondylar fracture in childhood. The deformity corrected at skeletal maturity, the surgery called wedge osteotomy of distal humerus