Movement disorders
Parkinson disease: is a disease with certain clinical features (idiopathic).Parkinson Syndrome (Parkinson plus):
a term includes a list of DDX contains many other diseases that have parkinsonian picture.
Multiple systems atrophy (MSA)
Progressive supranuclear palsy
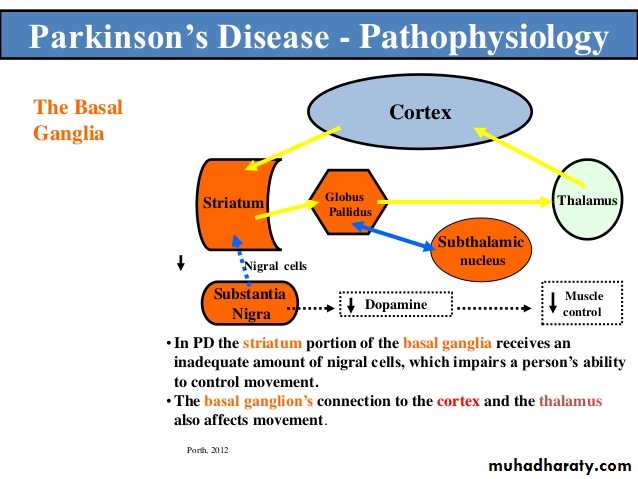
Parkinson disease
The disease was discovered by Dr. James ParkinsonClinical features
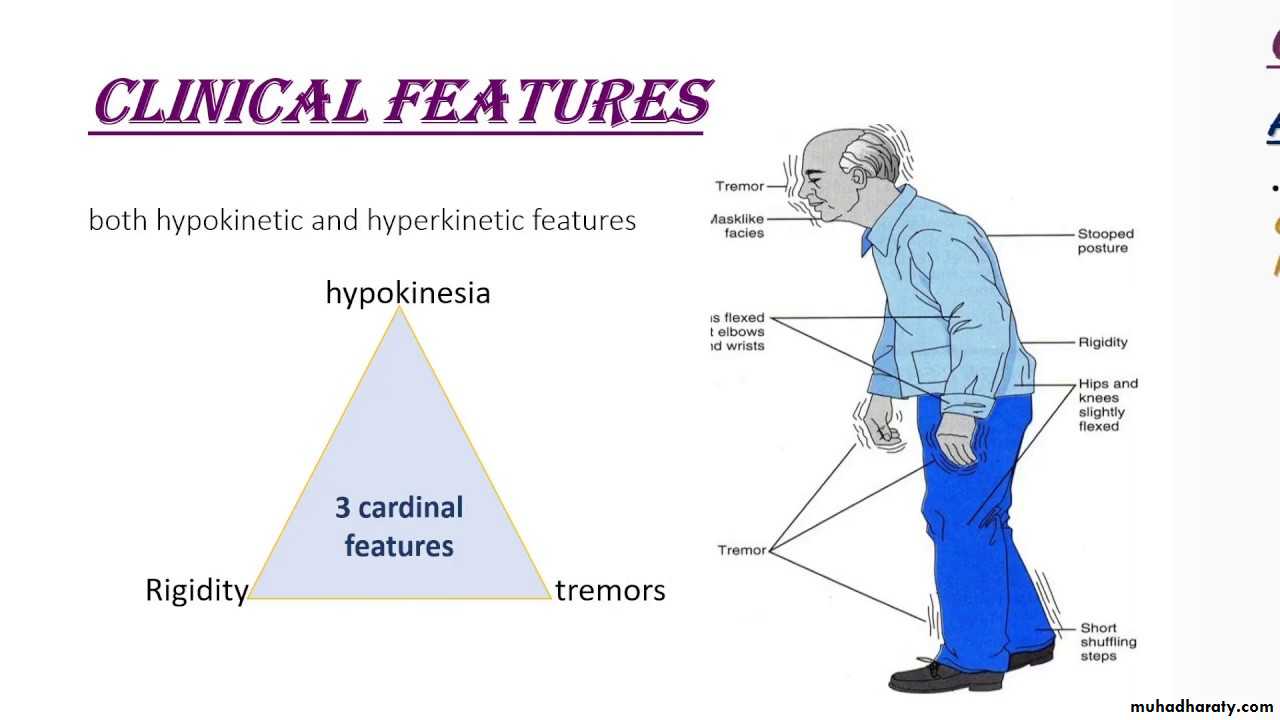
1 - Tremors occurring in the limbs, jaws and face2 -Bradykinesia (slow movement)
3 -Impaired balance and coordination
4-Stiffness of the limbs and trunk
The presentation is almost always unilateral, a resting tremor in an upper limb being a common presenting feature.
Epidemiology
Average age of onset 62.5.Men and women affected equally.
Genetic Link.
Caffeine and smoking shows some protective effects.
Trauma (boxing)
General physical abnormality
Expressionless faceGreasy skin
Soft, rapid, indistinct speech
Flexed posture
Impaired postural reflexes
• Tremor
Resting 4-6 Hz
Usually first in fingers/thumb
Coarse, complex movements, flexion/extension fingers .
Abduction/adduction of thumb
Supination/pronation of forearm pill rolling
Diminished on action
Rigidity
Cogwheel type, mostly upper limbs .Plastic (lead pipe) type, mostly legs .
Bradykinesia
Slowness in initiating or repeating movements
Impaired fine movements, especially of fingers
gait abnormality
Slow to start walking .Rapid, small steps, tendency to run (festination) .
Reduced arm swing.
Impaired balance on turning .
Diagnosis
There is no specific diagnostic test , it is mainly clinical diagnosis
Bradykinesia must be present with at least two of the following:
limb muscle rigidity
resting tremor (abolished with movement)
postural instability.
Management
Drug therapyLevodopa combined with a peripheral-acting dopa-decarboxylase inhibitor provides the mainstay of treatment in Parkinson's disease
TWO decarboxylate inhibitor (Carbidopa;beneserazide) are combined with the
L-dopa to prevent peripheral decarboxylation (reduce side effects) and increase the amount supplied to the CNS.
it is contraindicated in cases of MYLOMA ,PEPTIC ULCER and myocardial infarction
There are two important phenomena in using L-dopa:
END-of-Dose deterioration: means loss of efficacy of the dose at the end of the course of treatment or end of the day, this is treated by small more frequent dose or using other drugsON-off- : more serious, means sudden loss of efficacy following taking the L-dopa (sudden freezing) .treated by SC injection of apomorphine (dopamine agonist) or use other drugs
Dopamine receptor agonists
BromocriptinePergolide
Ropinerole
Pramipexole
Cabergoline
Apomorphine (SC)
Could be Added-on to L-dopa or used as monotherapy , initiated with low dose and increase gradually , sudden-onset sleep is serious especially with Pramipexole
Anticholinergic drug
Dopamine depletion lead to hypercholinergic state.
Trihexyphenidyl (artane), benztropine .
Use early in the course, mainly affect tremor predominates with lesser effect in bradykinesia.
Start with small dose and increase gradually.
It has three serious side effects: acute glaucoma, prostate enlargement and confusion and hallucination.
Amantadine
particularly useful in controlling the dyskinesias produced by dopaminergic treatment later in the disease.Selegiline
Evidence that it slows the progression of the disease is highly controversial
Dystonia
is a movement disorder that causes involuntary contractions of muscles. These contractions result in twisting and repetitive movements. Sometimes they are painful.Drug Induced Dystonia.
A large number of drugs are capable of causing dystonia, In most cases, people develop an acute dystonic reaction resulting after a one-time exposure.
The most common drugs leading to dystonia are:
Antipsychotics – haloperidol and fluphenazine (more potent); chlorpromazineAtypical antipsychotics – quetiapine, olanzapine, risperidone, etc. (low incidence)
Anti-emetics – prochlorperazine, promethazine
Essential Familial Tremor
The most important feature is bilateral (symmetrical) and affection to upper limb more than lower limb .
Essential tremor (ET) is the most common involuntary movement disorder, affecting ~5–10 million individuals in the United States alone.
Worse slowly over many years
10% lave family history (AD)
Disability due to mainly social embarrassment
Normal neurological exam (except for tremor)
Propranolol is the drug of choice, small amount of alcohol can, subside the tremor.
Pimidone is also effective if introduce slowly
Chorea
a state of excessive, spontaneous movements, irregularly timed, non-repetitive, randomly distributed and abrupt in character.HUNTINGTON'S DISEASE
This is an inherited disorder with autosomal dominant transmission, affecting both males and females, and usually starting in adult lifeClinical features
Symptoms usually begin in middle adult life with the development of chorea, which gradually worsens.
This is accompanied by cognitive impairment which often manifests initially as psychiatric symptoms, but later becomes frank dementia.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is made clinically but is supported by the finding of atrophy of the caudate nucleus on CT or MRI. DNA analysis can be used to confirm the diagnosis and provide pre-symptomatic testing for other family membersManagement
At present this is symptomatic only. The chorea may respond to tetrabenazine or dopamine antagonists such as sulpiride.