Liver pathology
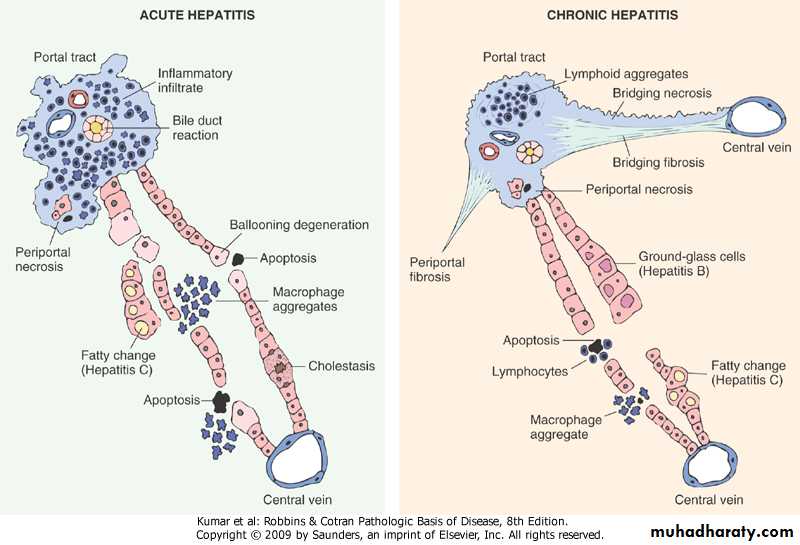
A diagram illustrating the difference between acute & chronic viral hepatitisViral hepatitis: A large pink cell undergoing ballooning degeneration is seen below the right arrow. At a later stage a dying hepatocyte is seen shrinking down to form an eosinophilic “councilman body” below the arrow on the left.
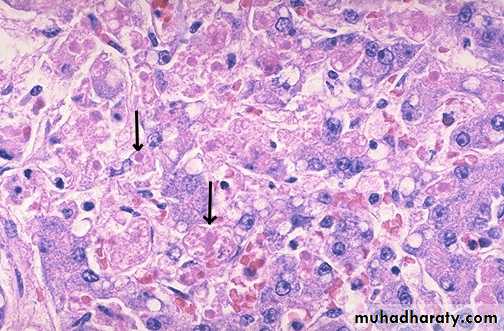
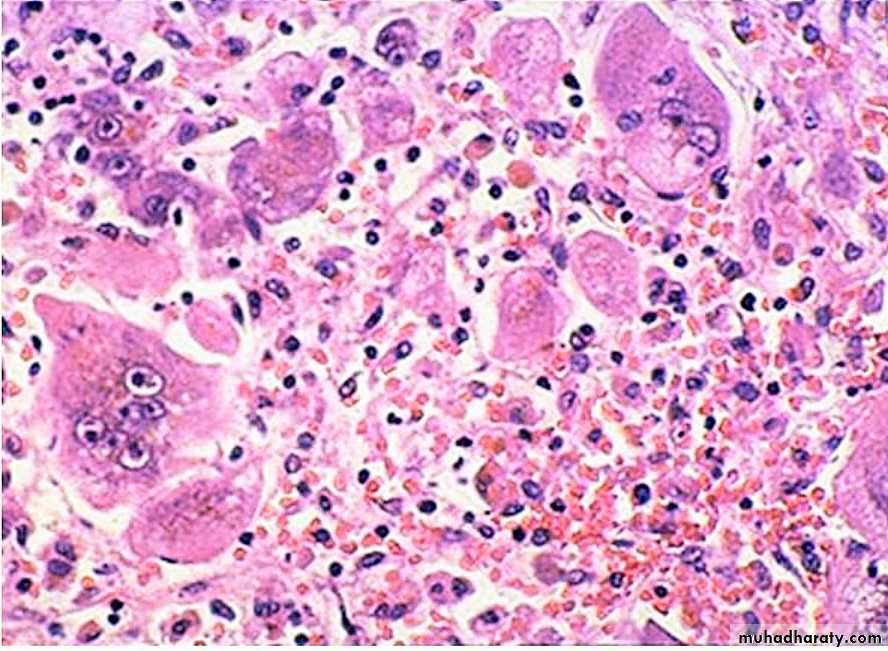
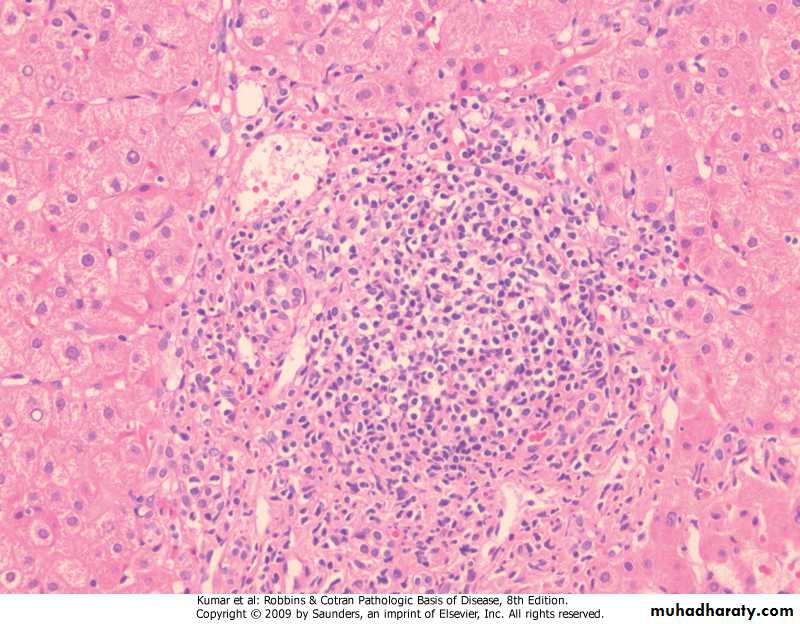
Chronic Hepatitis, A mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltrate within the portal areas & hepatocytes which are undergoing necrosis,
Alcoholic hepatitis (acute alcoholic hepatitis): Mallory's hyaline is seen with neutrophils, necrosis of hepatocytes, collagen deposition and fatty changes
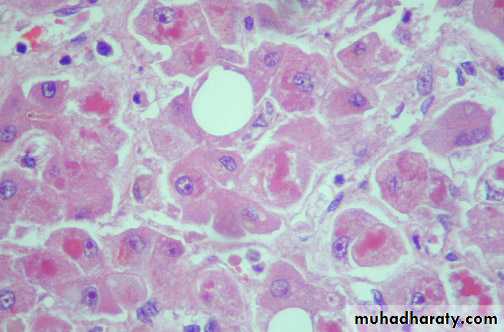
Globular red hyaline material within hepatocytes. This is Mallory's hyaline, also known as "alcoholic" hyaline because it is most often seen in conjunction with chronic alcoholism.
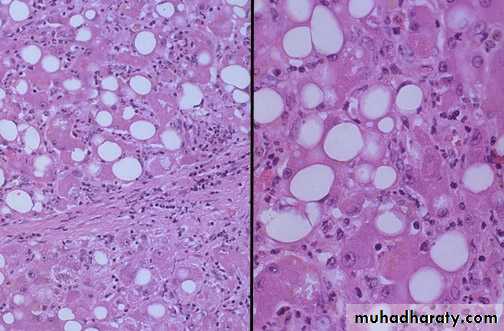
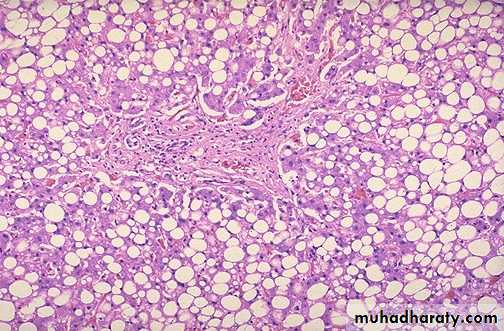
Fatty change (steatosis), liver is large yellow & greezy. Histology; lipid accumulates within the cytoplasm of hepatocytes, creating large clear vacuoles within cells. The nuclei in such cells are pushed to the periphery of the cell
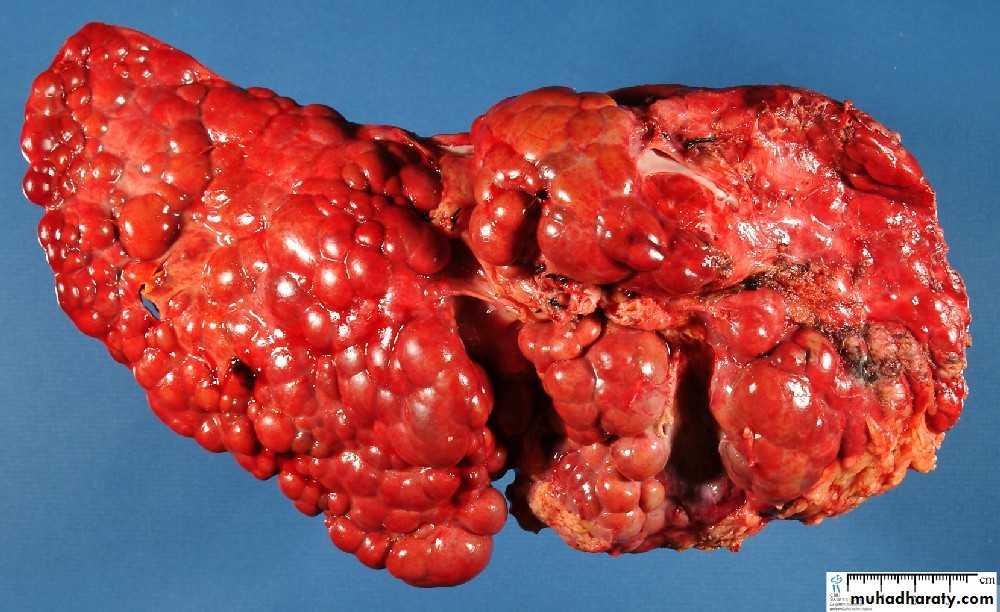
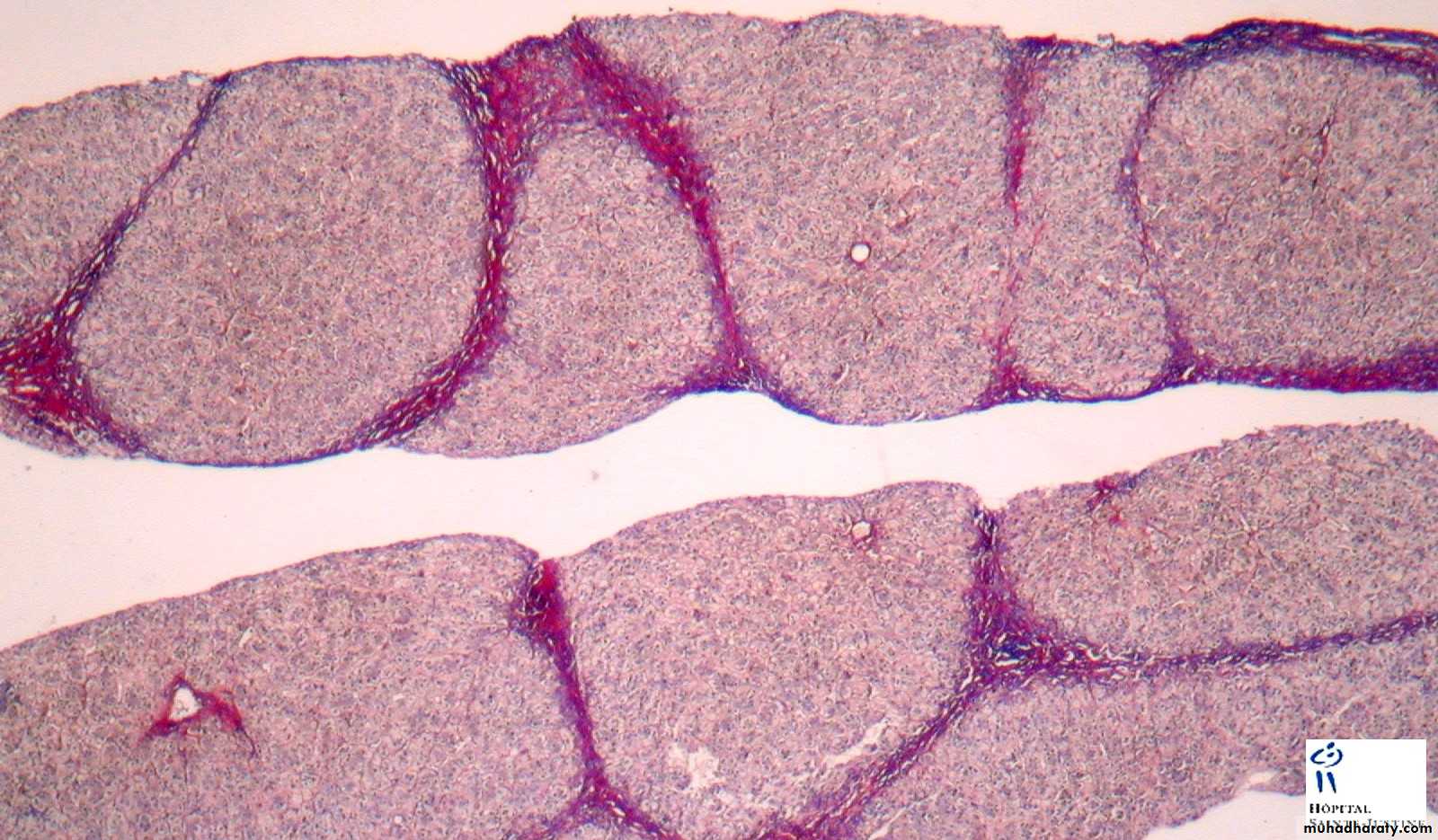
Maconodular cirrhosis the liver is enlarged, firm & nodular. The size of nodule>3mm .
Cirrhosis: loss of architecture of the liver, regeneration nodules which are separated by fibrous tissues septa.
Secondary in the Liver, multiple irregular variable size nodules with central cavitations & necrosis
Bone Pathology
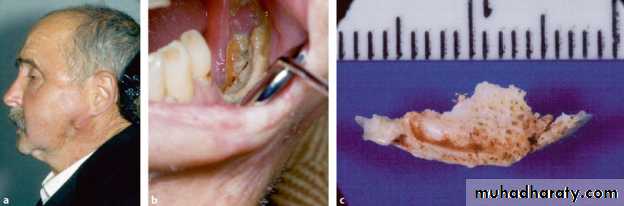
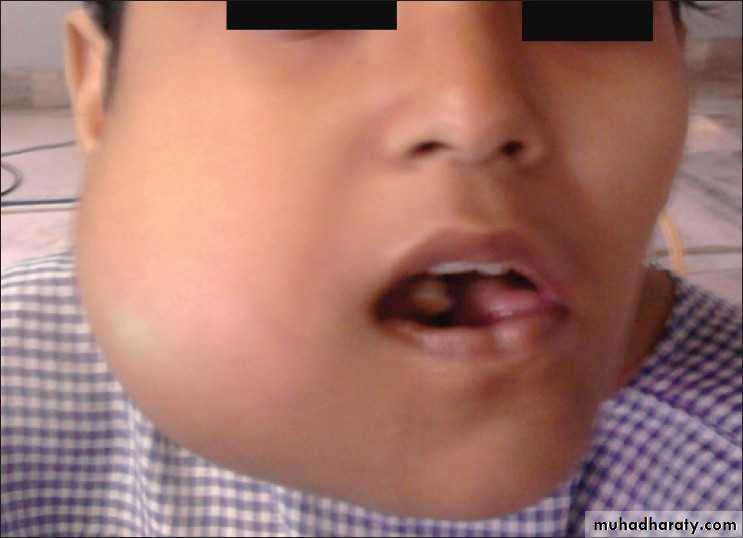
• Old case with advanced chronic osteomyelitis of the left mandible.
• (a) The massive affection of the left mandible demonstrates extraoral fistula• and scar formation.
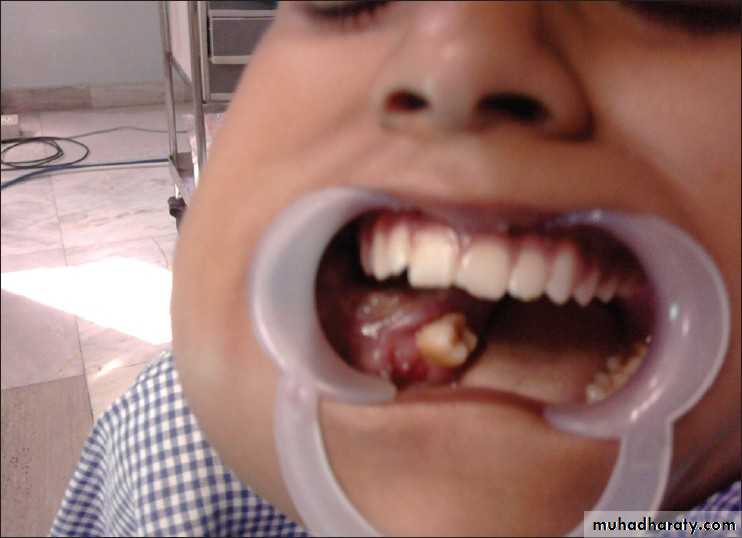
• (b) Intraoral view of the same patient with large exposure of infected bone and sequestra.
• (c) Large sequester collected from surgery
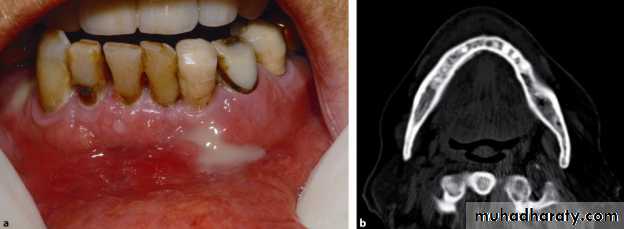
A patient with a clinically extensive chronic osteomyelitis of the frontal region with multiple fistula and abscess formations.
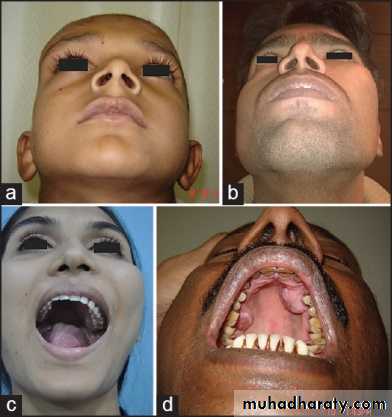
Common presentation of fibrous dysplasia (FD) as asymptomatic swellings of peri-orbital area (a), zygoma (b), maxilla (c) and palatal surface of maxilla (d)
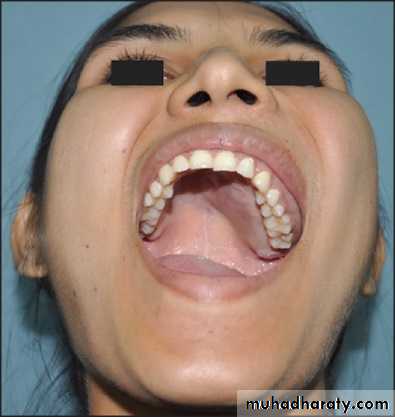
Fibrous dysplasia of left maxilla with involvement of both labial as well as palatal surface with visible left palatal bulge
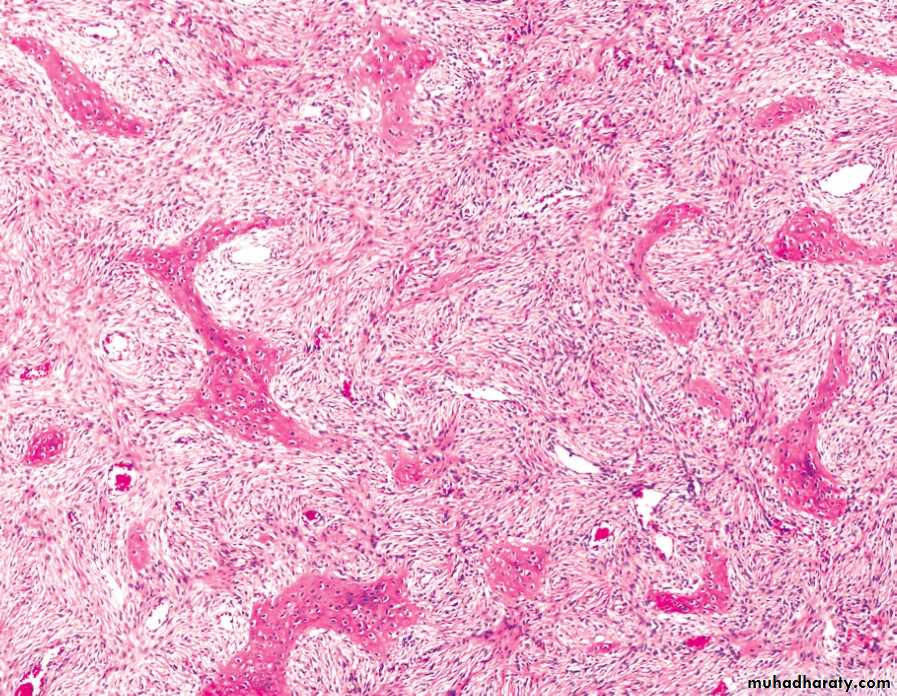
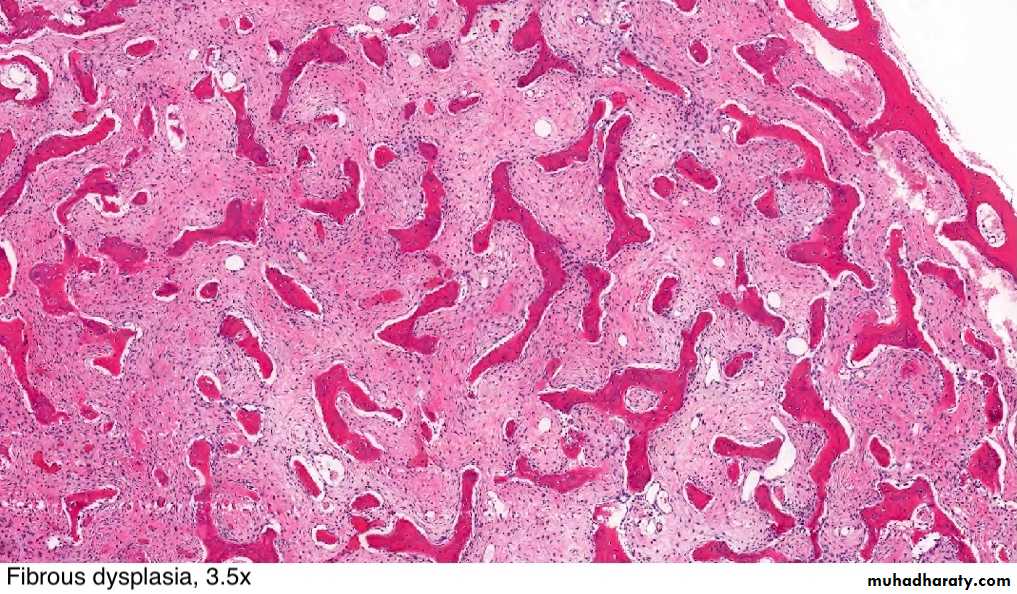
FD showing irregular trabecullae (C-shaped or Chinese characters shaped trabaculae, (described as "Chinese letters“) which are usually coarse woven bone, are seen instead of well-organized lamellar bone. with compact stroma of interlacing collagen fibers
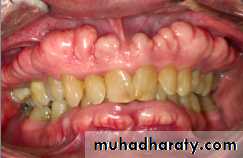
Buccal exostoses: Multiple bony nodular excrescences (growth) in the buccal aspect of .the maxilla
Facial asymmetry with apparent massive swelling involving the right side of the lower jaw measuring approx. 6.8 * 7.2 cm. The swelling was firm and non tender
Huge soft tissue mass obliterating the buccal, as well as the lingual sulcus pushing the tongue to the contra lateral side. The superior surface of the mass was ulcerated and eroded.
Dgx: Aneurysmal bone cyst of the mandible