
RESTORATION OF
ENDODONTICALLY TREATED
TEETH

indicated for the endodontic restoration of severely
damaged molars.
The endocrown is described as a
monolithic (one-piece) ceramic bonded construction
objective
is to dispense with metal and achieve an
all-ceramic bonded reconstruction that is minimally
invasive of root canals, as the use of root canals for
anchoring has been cited as an important factor in
weakening the tooth
Endocrown

characterized by a supra-cervical finishing lines, butt joint,
retaining maximum enamel to improve adhesion.
The endocrown invades the pulpal chamber, but not the root
canals
milled using computer-aided technique
s
The specific preparation and bonding result in a particularly
favourable reconstruction in terms of biomechanics.
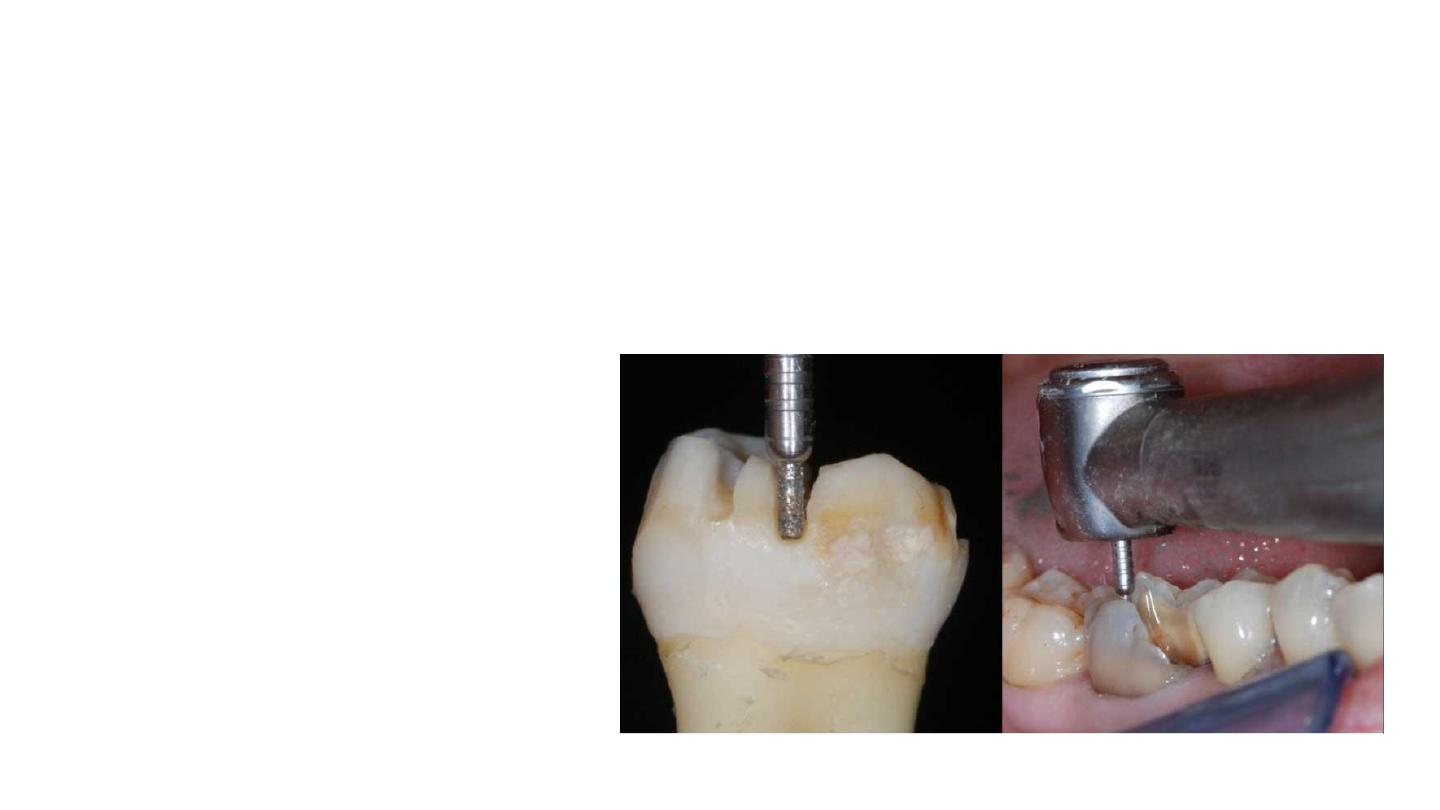
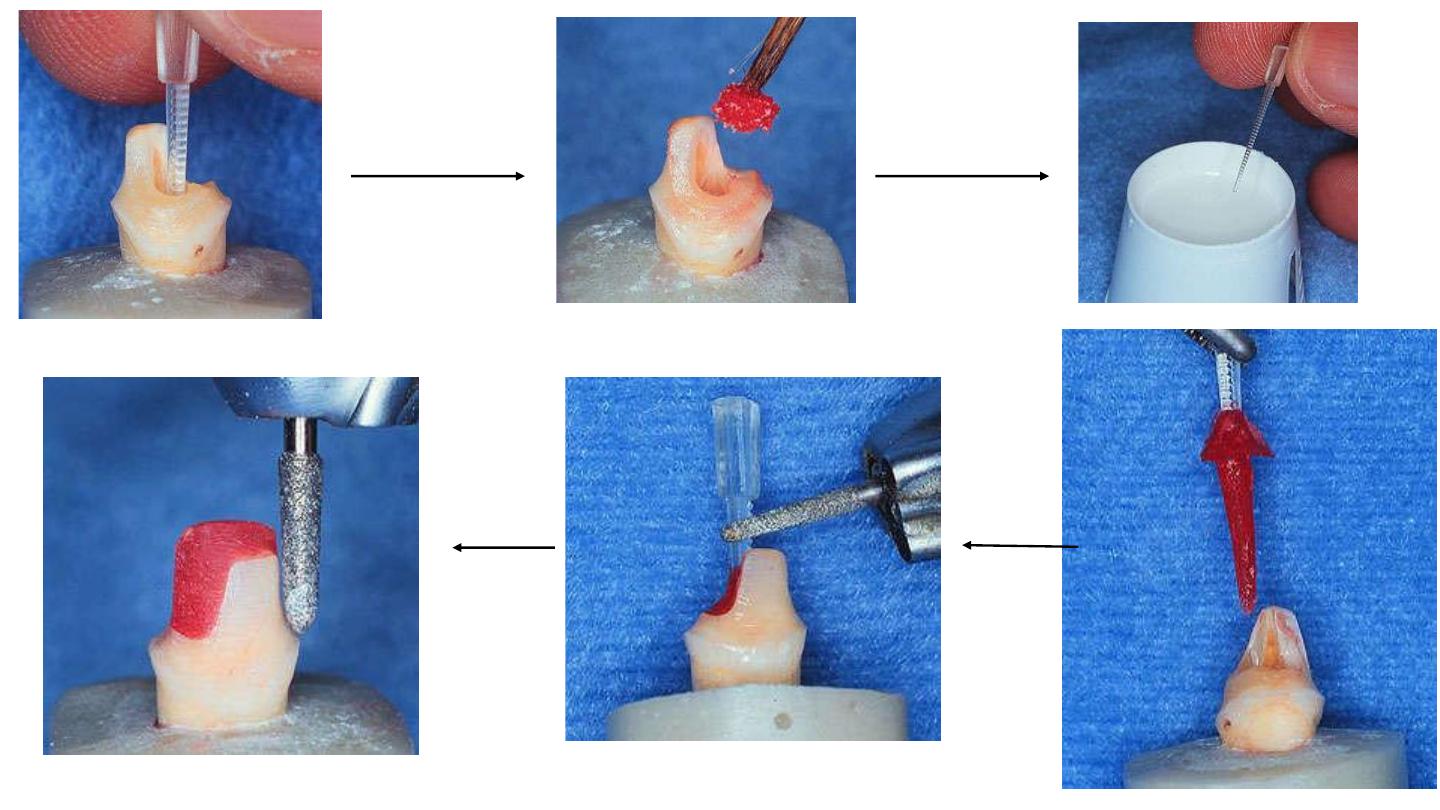
Occlusal Preparation
The goal in preparation is to achieve an overall reduction in the height of
the occlusal surface of at least 2 mm in the axial direction.
This reduction can be
achieved by drilling 2-mm-
deep grooves as guides
then using a green diamond
wheel bur to reduce the
occlusal surface.
the margin can follow the gingival margin.
Differences in level between
the various parts of the cervical
margin must be linked by a
slope of no more than 60° to
avoid a staircase effect.
Enamel walls less than 2 mm thick should be removed

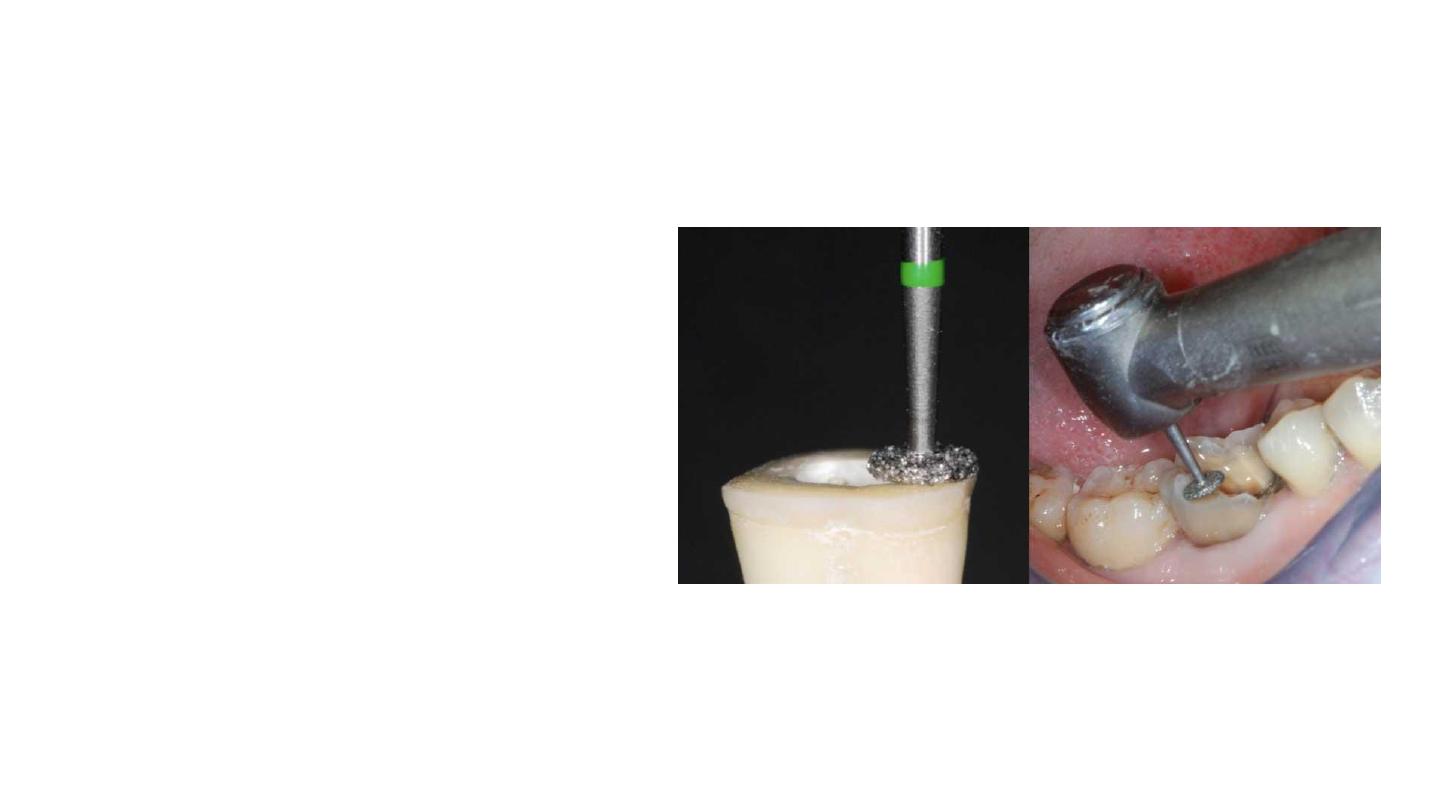
Axial Preparation
eliminating undercuts in the access cavity
A cylindrical-conical green diamond bur with a total occlusal convergence of 7°
is used to make the coronal pulp chamber and endodontic access cavity
continuous
With the bur orientated along the long axis of the tooth, the preparation is carried
out without excessive pressure and without touching the pulpal floor.
Removing too much tissue from the pulp chamber walls will reduce their
thickness and the width strip of enamel.
The depth of the cavity should be at least 3 mm.
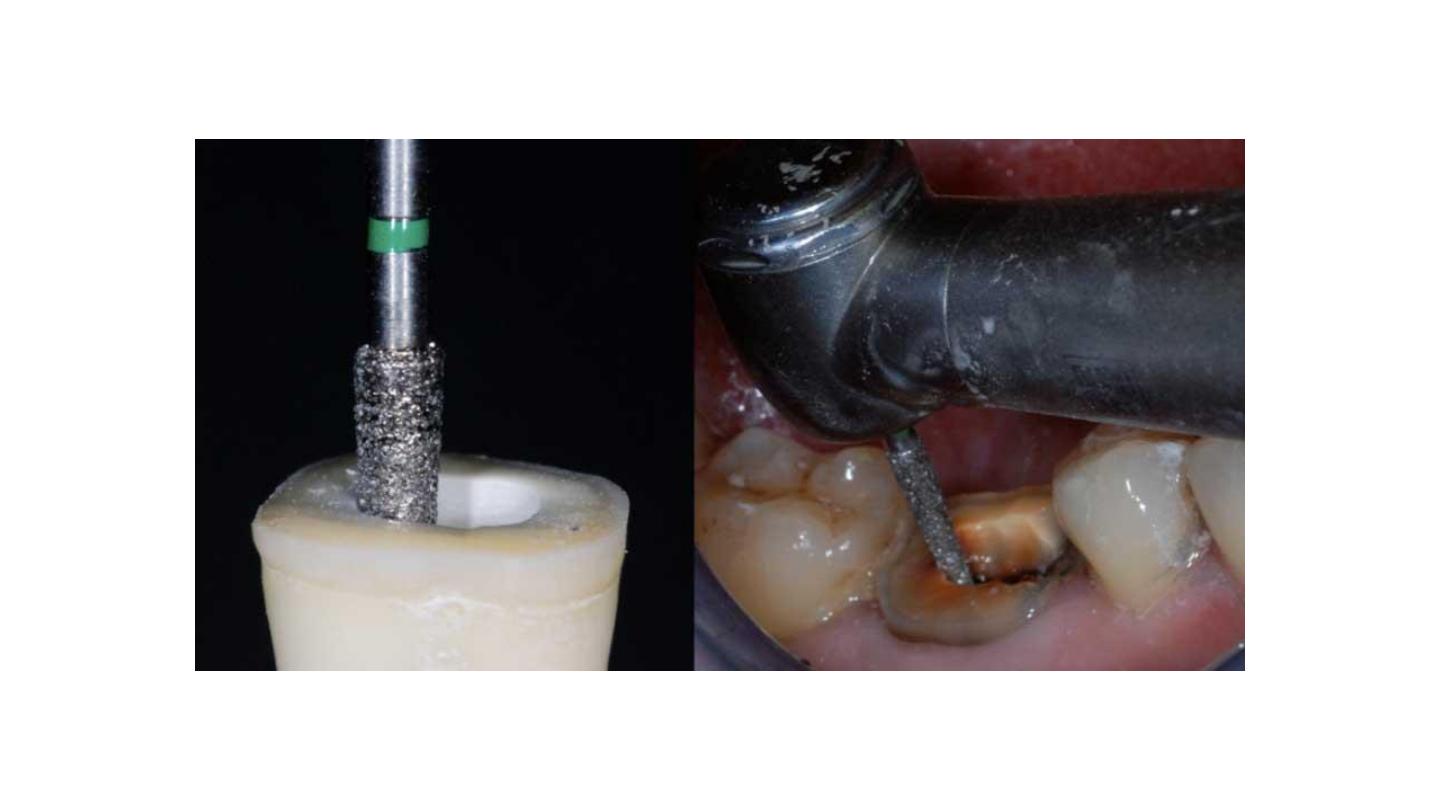
Polishing the Cervical Band
The bur used in this step has the same taper as the one
used in axial preparation, but a larger diameter and a finer
particle size.
should be guided around the entire surface of the cervical
band to remove micro-irregularities and produce a flat,
polished surface
The margin line should appear as a regular line with a
sharp edge
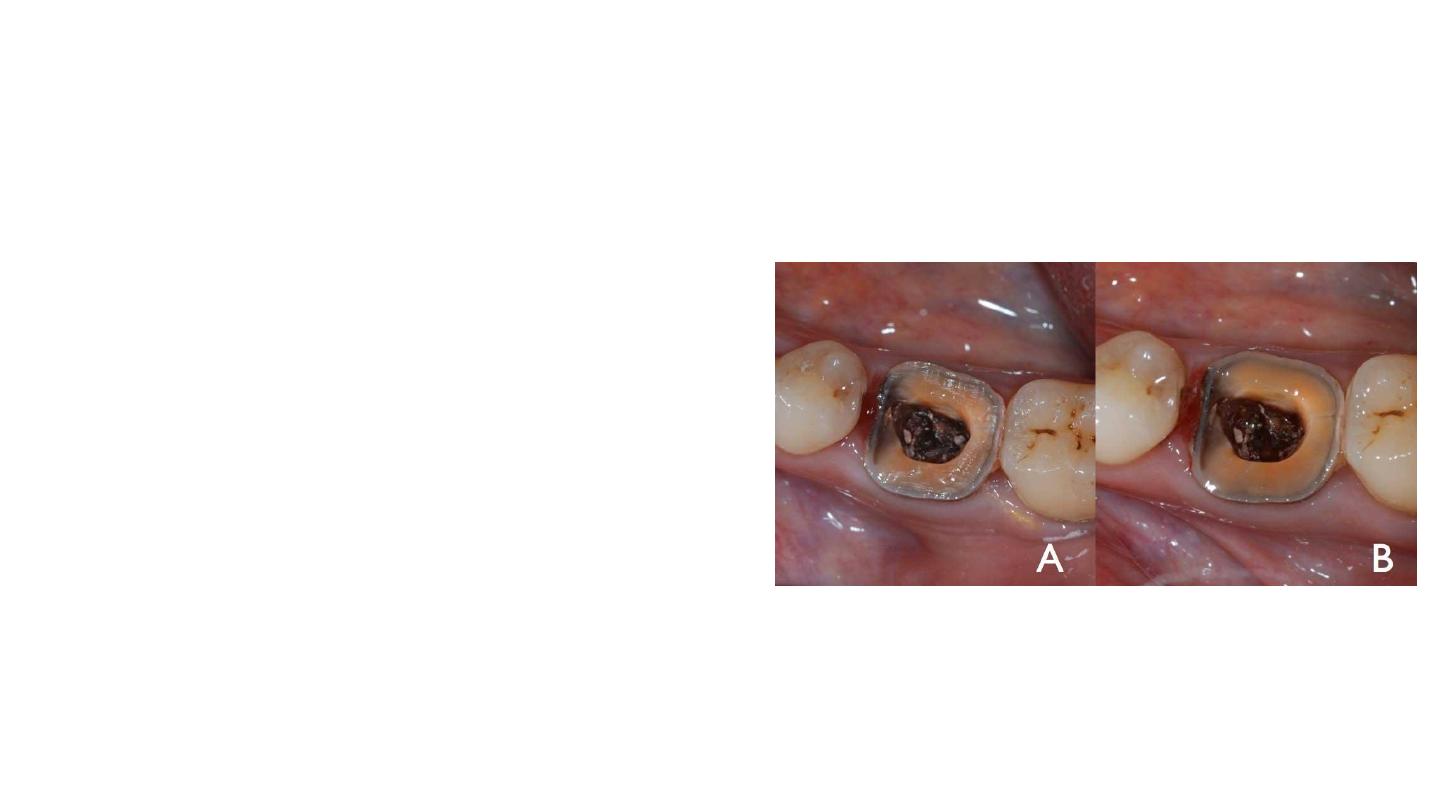
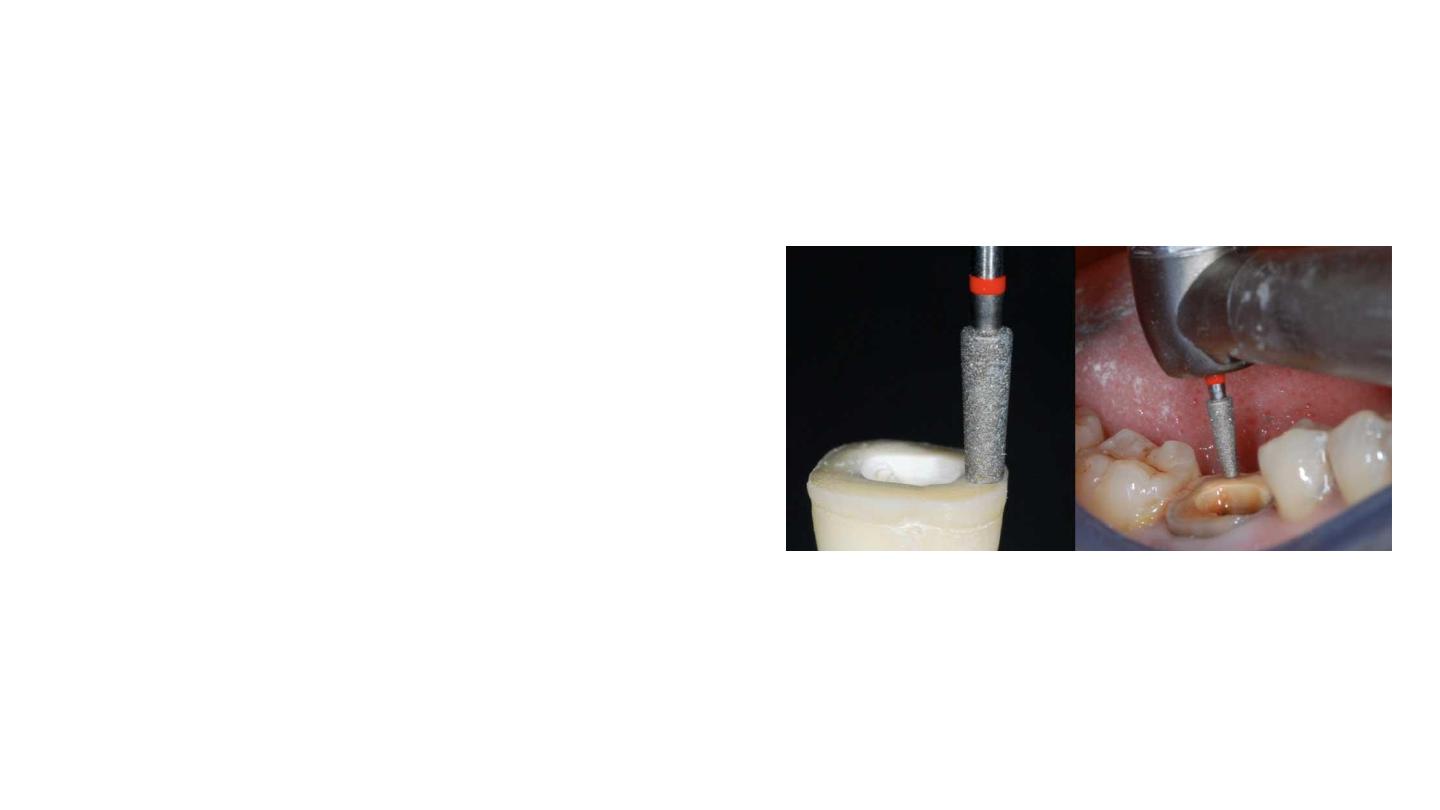
Preparation of the Cavity Floor
The entrance to the pulpal canal is opened
Gutta percha is removed to a depth not exceeding 2 mm
to take advantage of the saddle-like anatomy of the cavity
floor
This should be done with a nonabrasive instrument to
maintain the integrity of the canals entrance. No drilling of
dentin is carried out.
Ultrasound is recommended to clean the pulp chamber and its floor thoroughly. Abrasion is not indicated
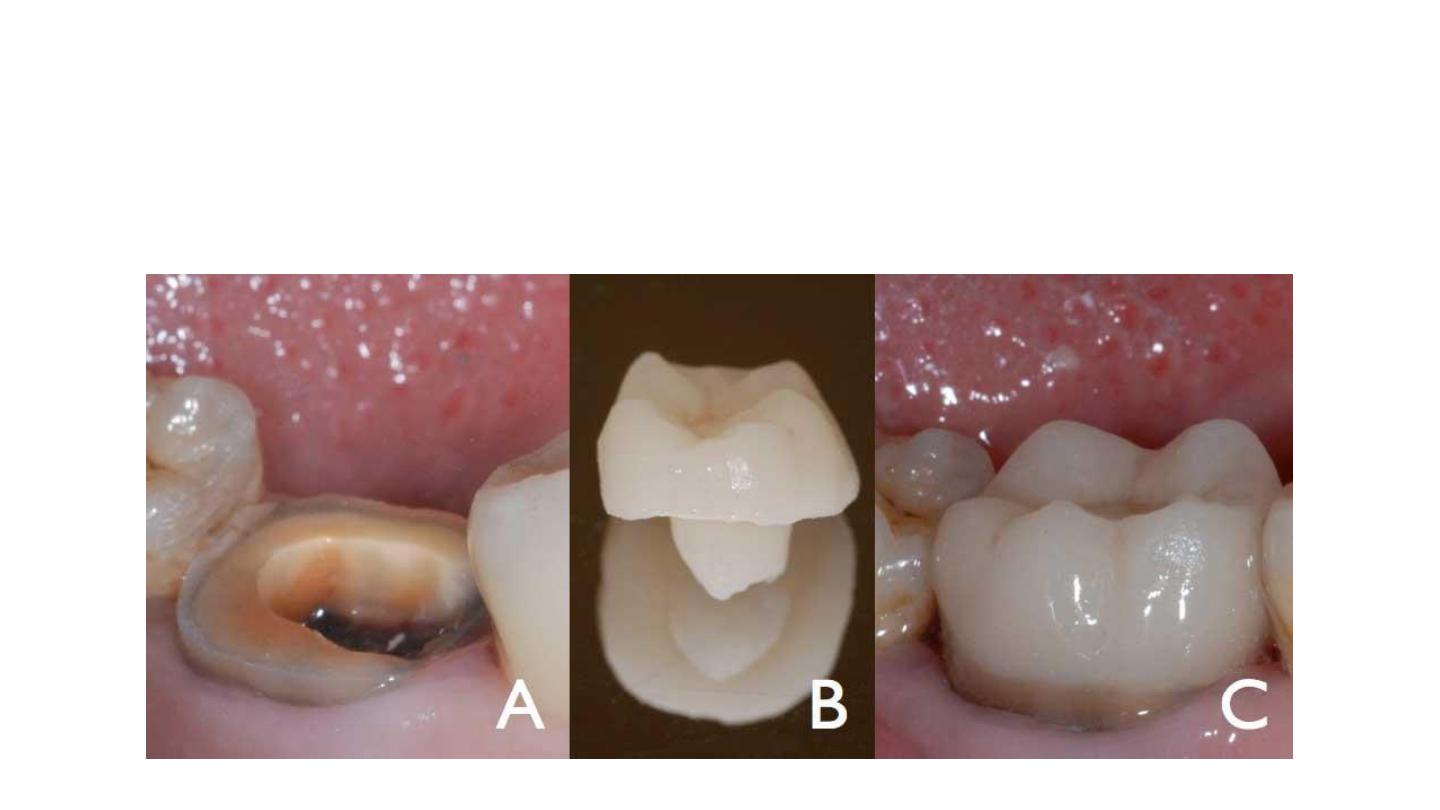
Bonding
Adhesives such as self-adhesive RelyX Unicem /
composites //

The endocrown is suitable for all molars, particularly those
with clinically low crowns, calcified root canals or very
slender roots.
Contraindication
if adhesion cannot be assured.
if the pulpal chamber is less than 3 mm deep
if the cervical margin is less than 2 mm wide for most of
its circumference.
Indications
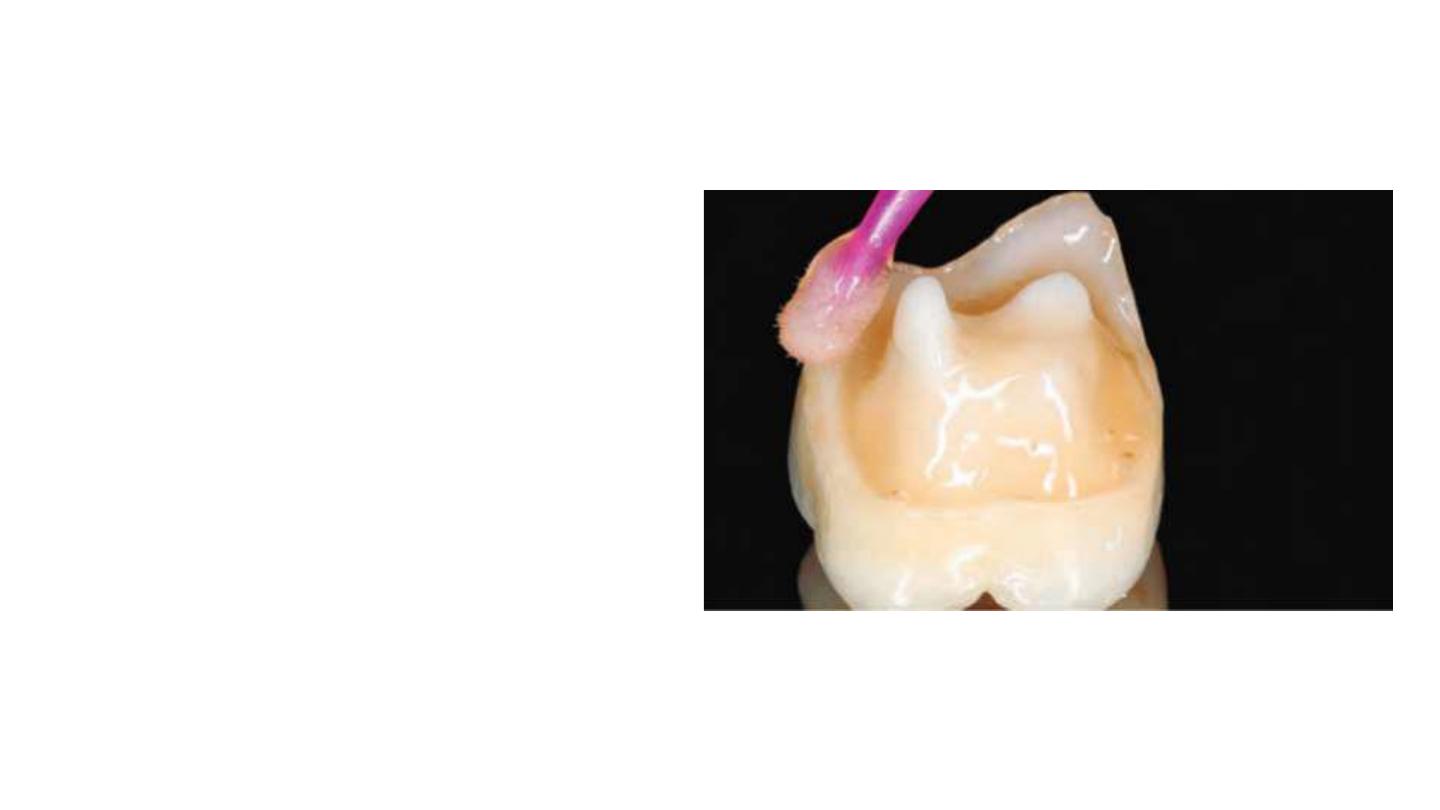
Choice of Materials
Glass-ceramic: Glass-ceramic has the advantages of
biocompatibility and biomimicry
wear coefficient is close to that of the natural tooth
the single interface of a 1-piece restoration enhances
cohesion
You add????
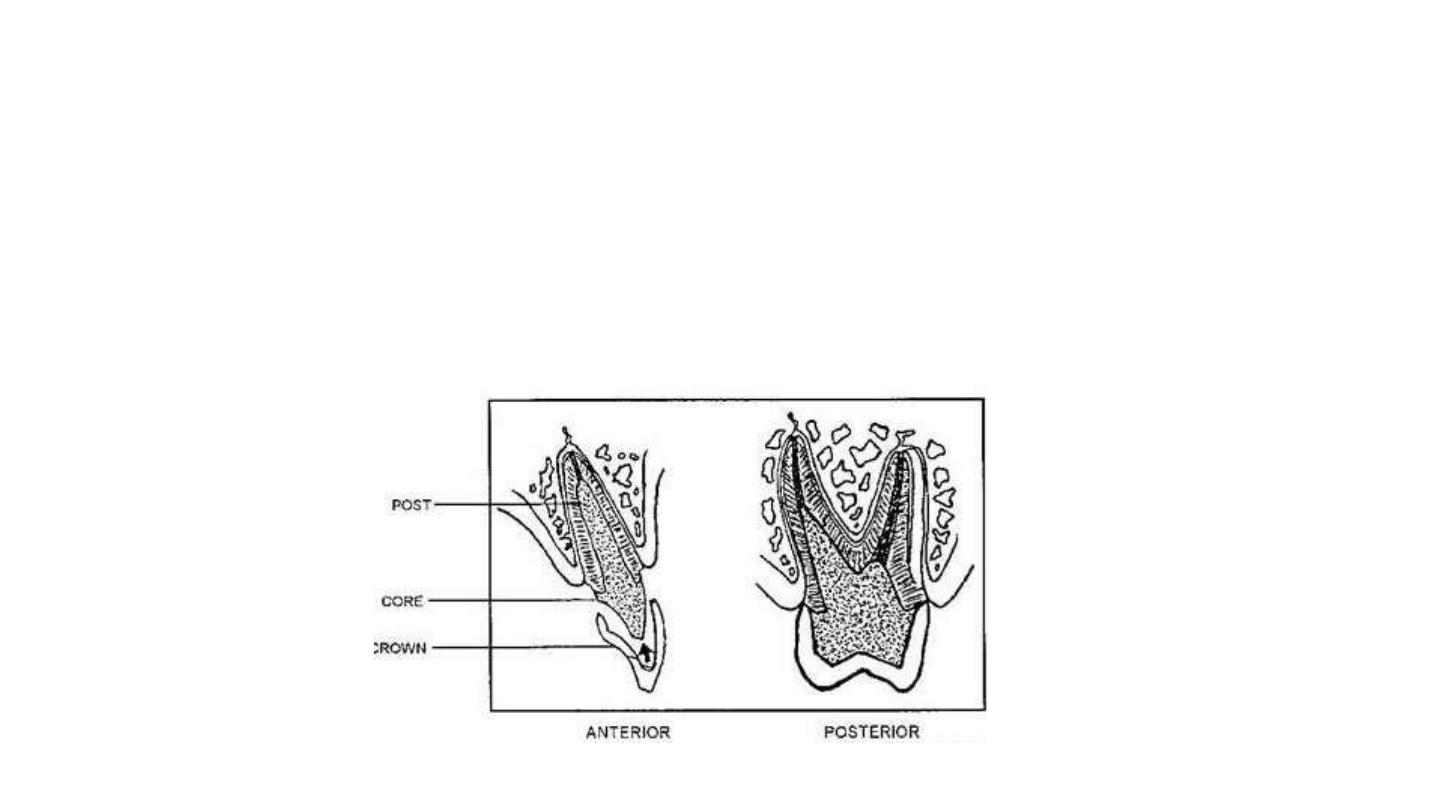
Post and core
A post and core is a dental restoration used to sufficiently build-up tooth structure for future
restoration i.e crown when there is not enough tooth structure to properly retain the crown.
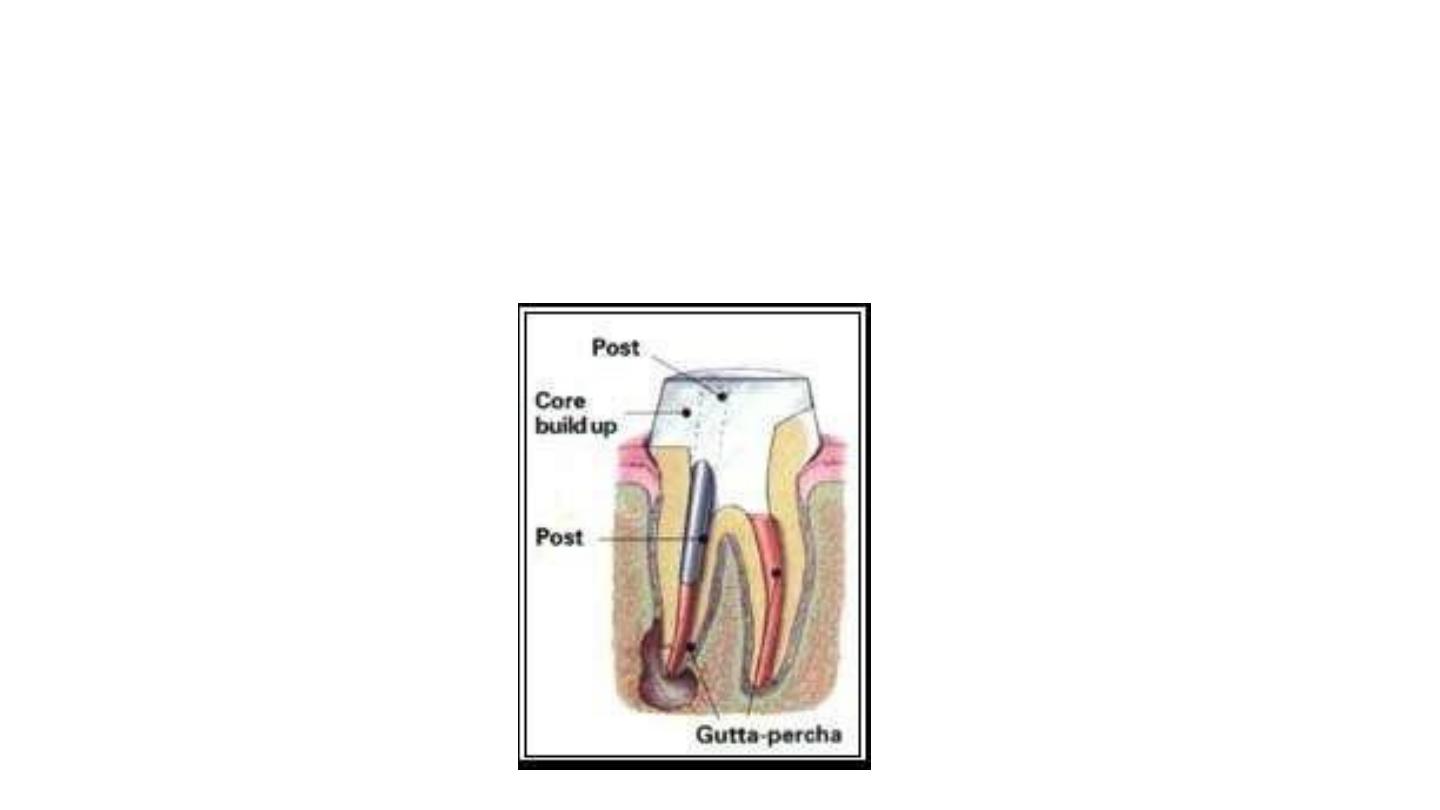
post
is placed within the body of the root of a tooth that has already treated with root canal
treatment.
The
core
is the part of the restoration that shows out in the mouth that help anchor a cap or
crown
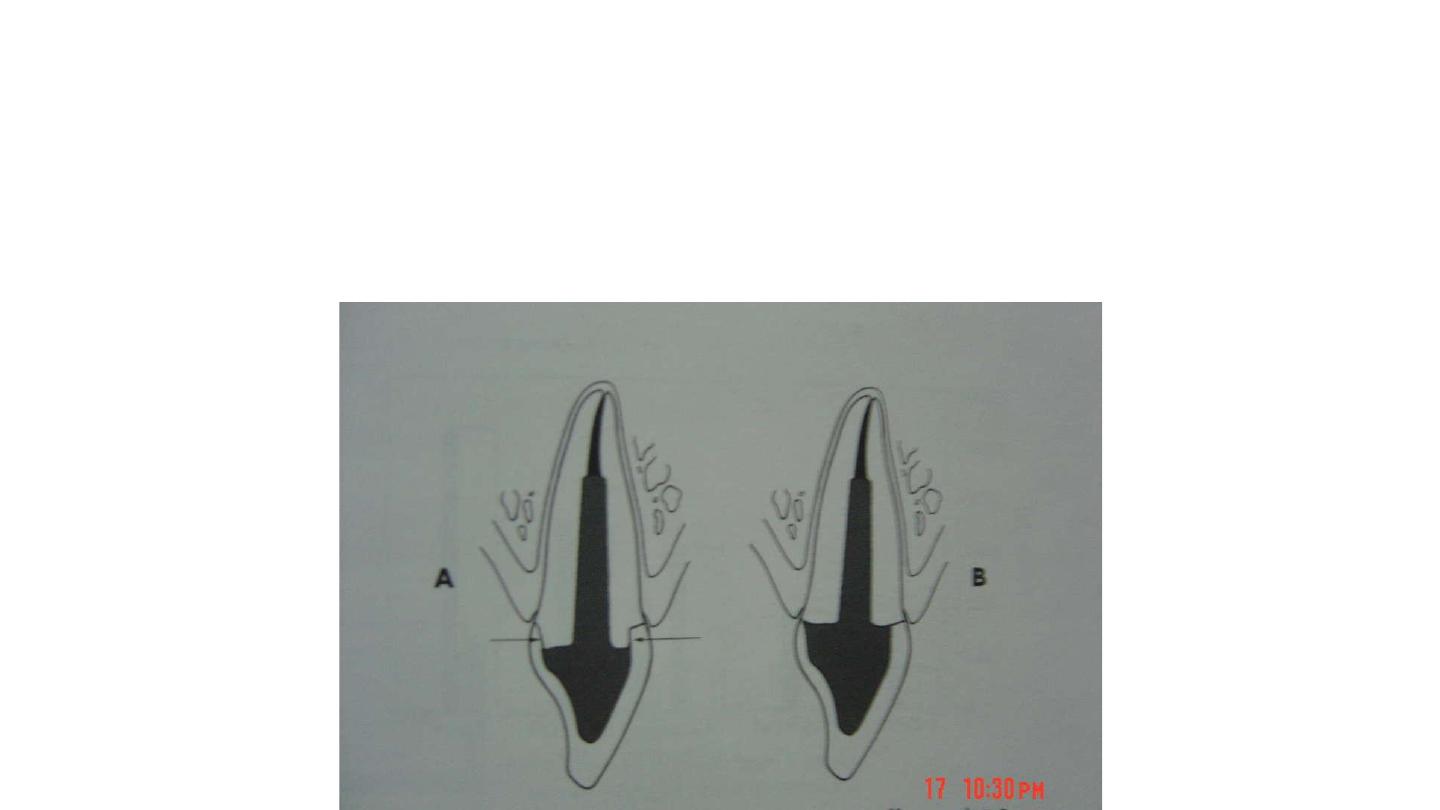
Canal preparation
: enlargement of canal should exceed about 1-2 additional file sizes
beyond the largest size used.
Coronal part
:
preparation removal of undercuts and ferrule (extension of axial wall of the
crown apical to the missing tooth structure)
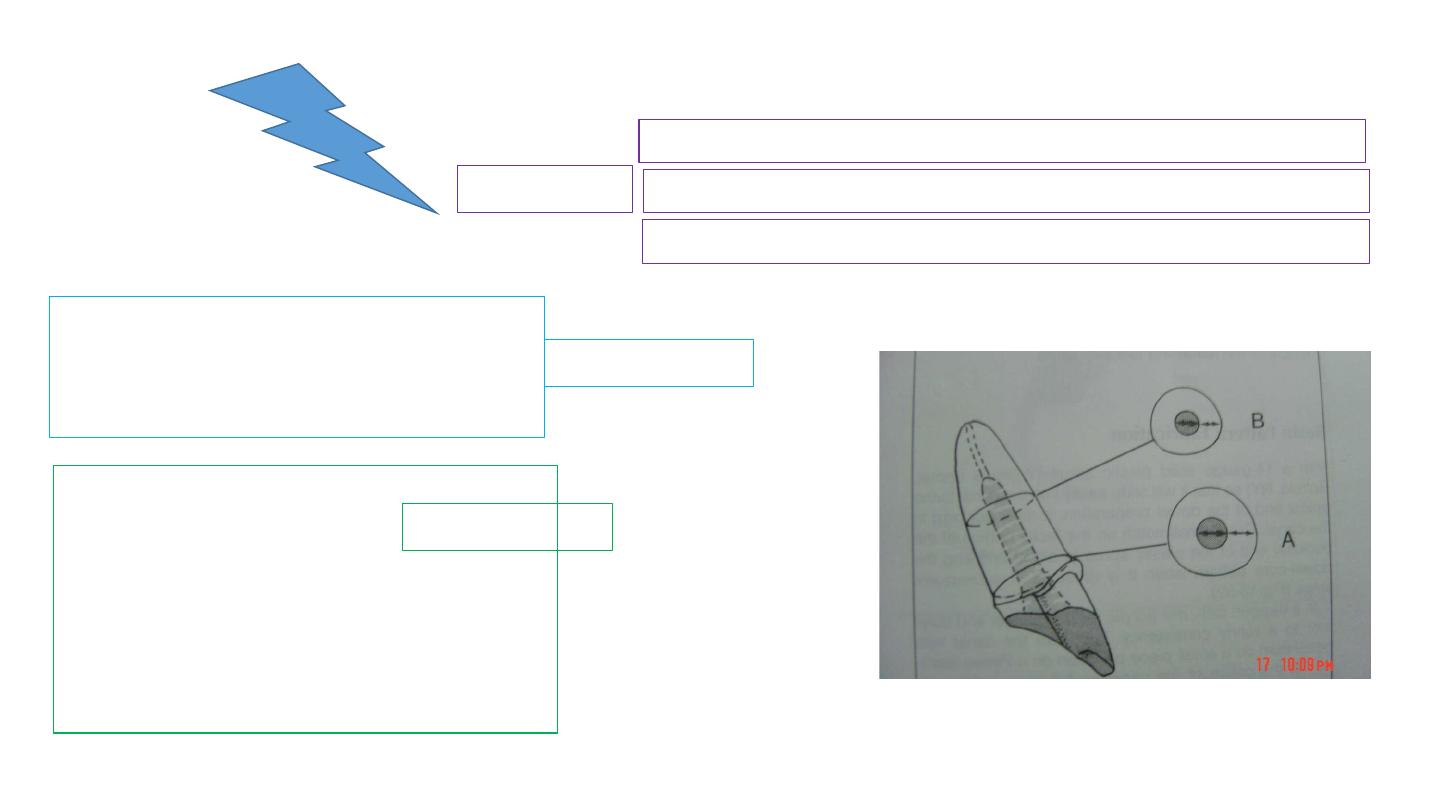
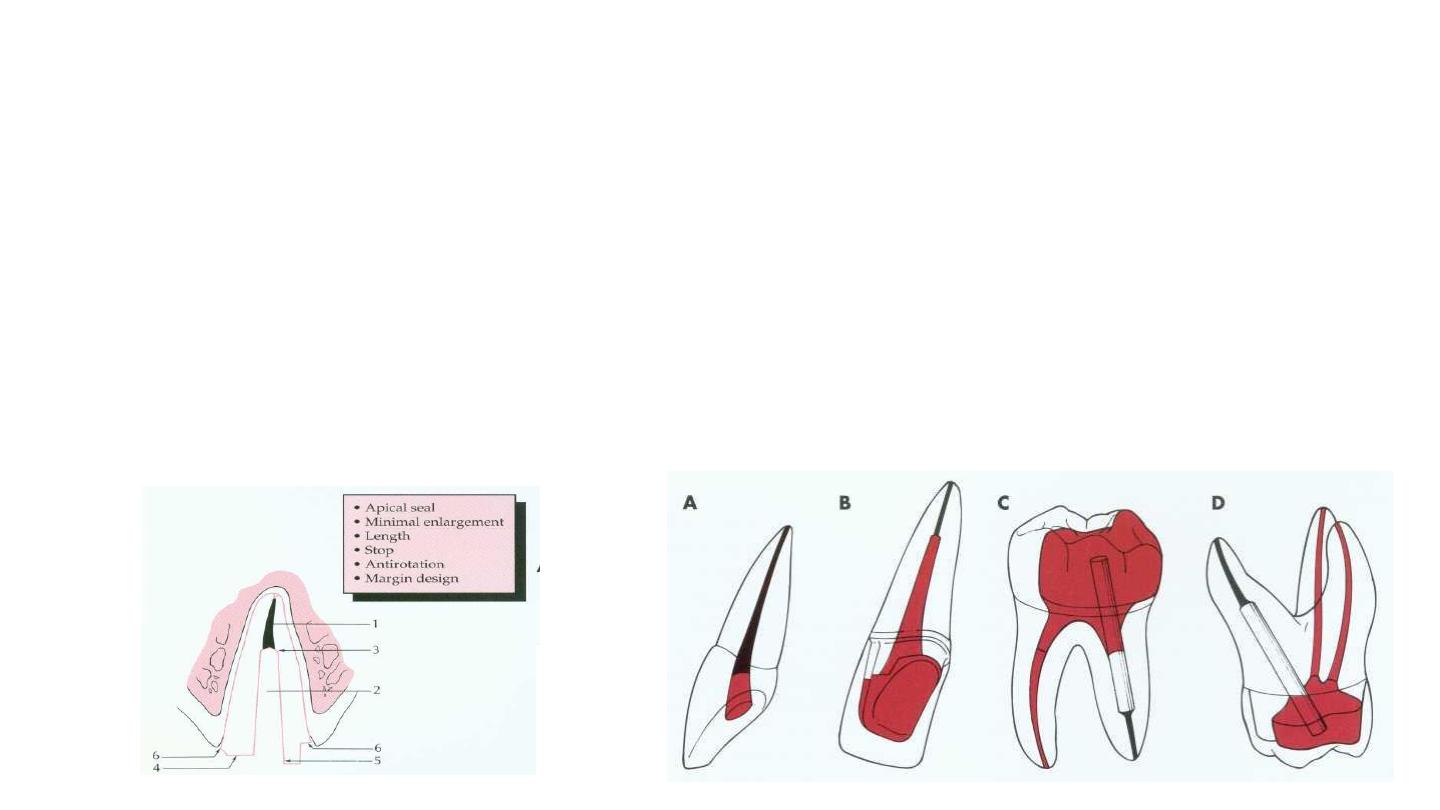
Retention form
Luting agent
Post length
Greater post length=greater retention
2/3 length of root / post length should equal crown length
Maintain 3
– 5mm apical seal
Post diameter
Shouldn't exceed 1/3 diameter of the
root
A minimum of 1 mm of sound dentin
should be maintained circumferentially
Surface txture
Post design influences
the stress distribution and
in turn resistance
-post length
-parallel posts
-threaded posts produce
stress conc.
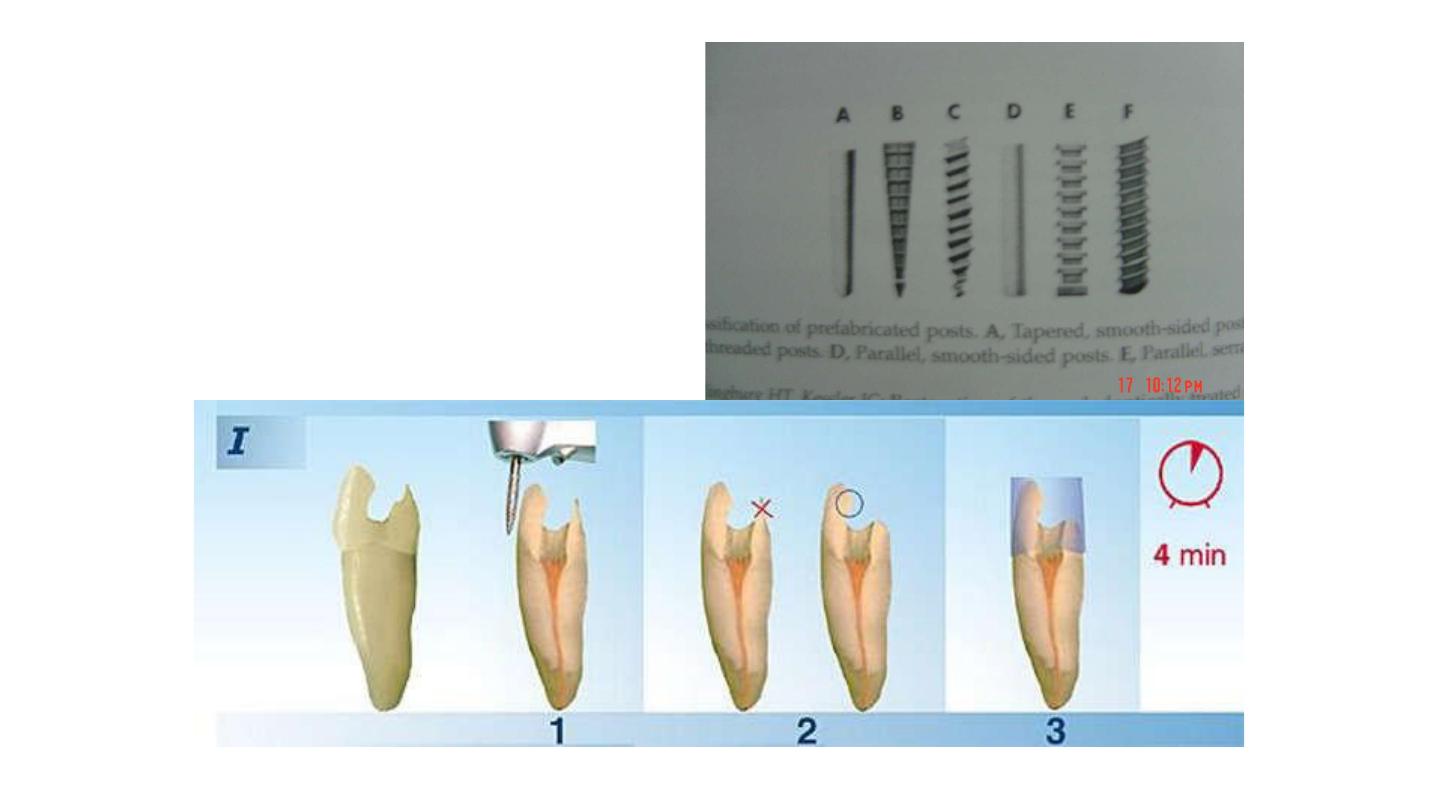
Steps in tooth preparation
Removal of RC filling material
Enlargement of the canal
Preparation of coronal tooth structure
Prefabricated post and core system
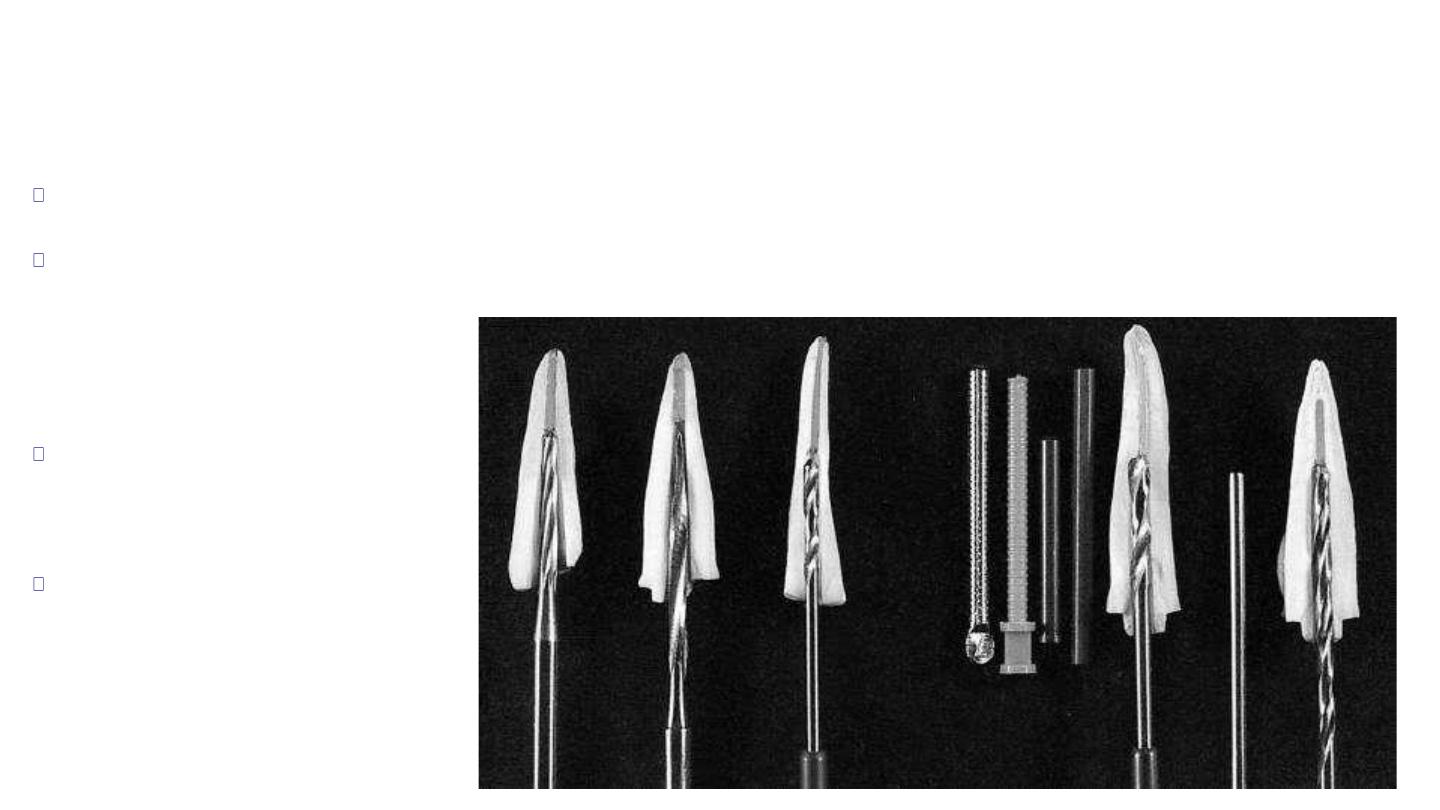

Preparing teeth for dowel
crowns
The shoulder or other margin is prepared
The post hole is prepared by post drill
removing the root canal filling (thermal method with heat
plugers safer)
shaping the post hole
finishing the preparation
Any remaining tissue
between the two is reduced
as necessary
A post, sized for the particular
diameter of the root canal, is
placed as far down as possible
into the post space.
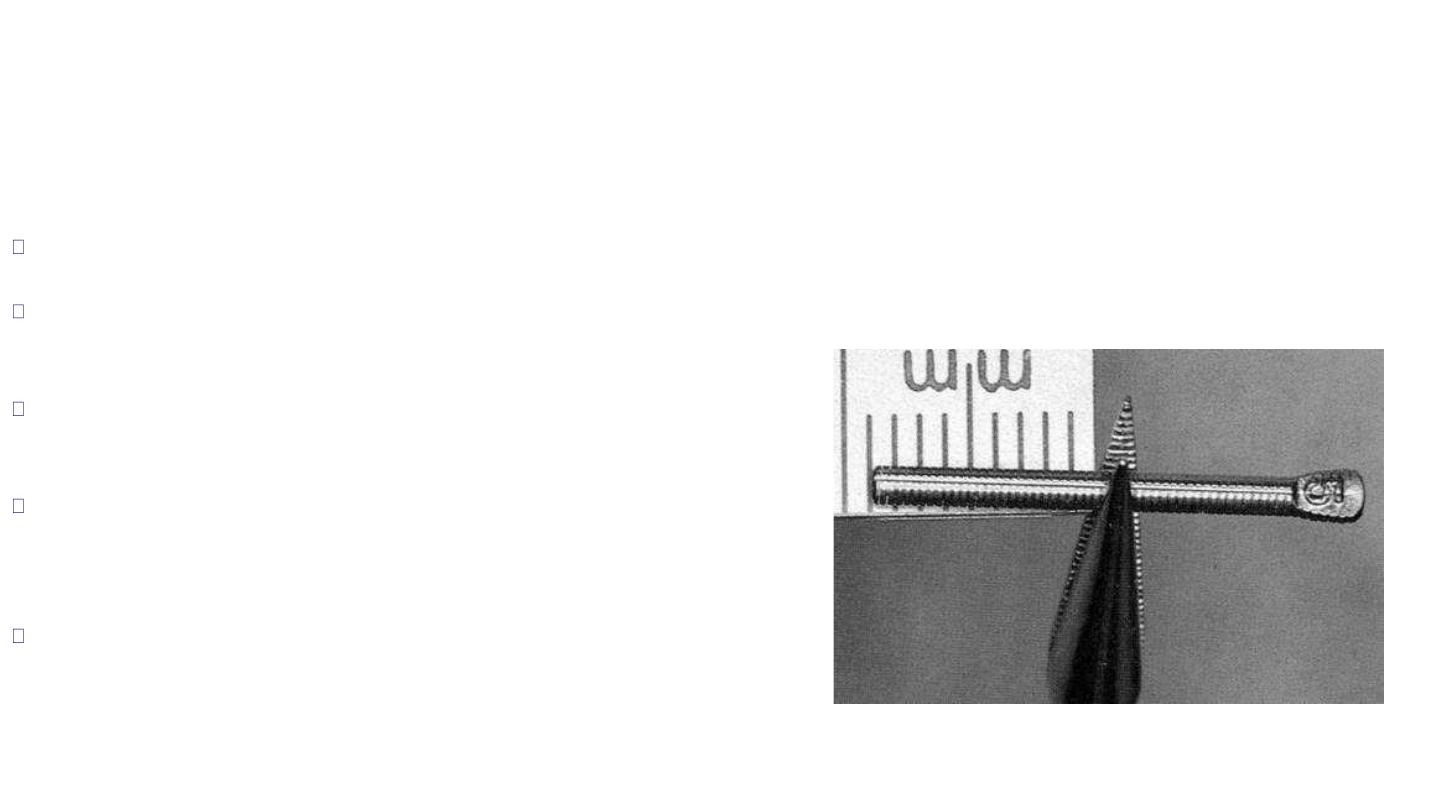

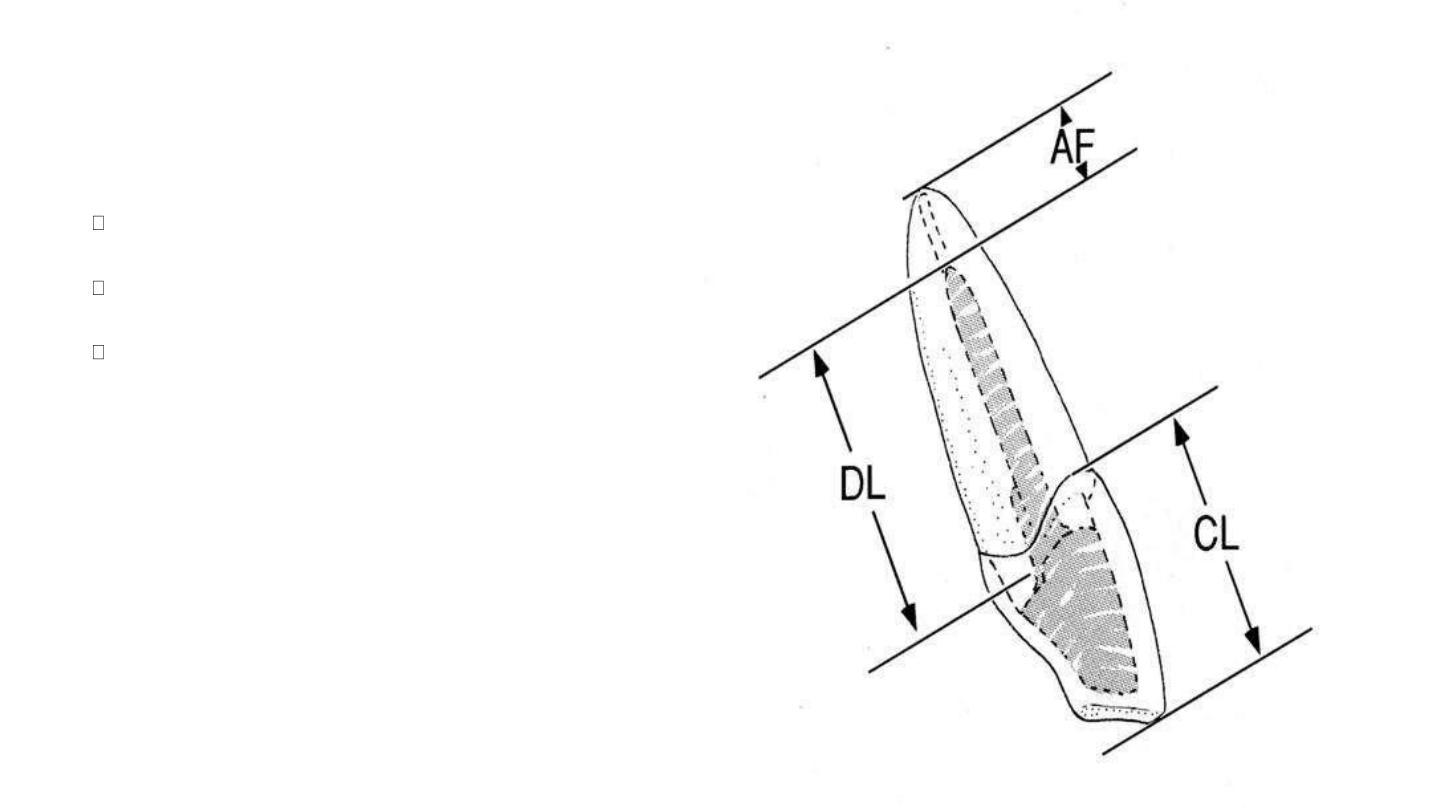
Acceptable guidelines for determining the
post length and width include the following:
post length should be equal to the clinical crown length
post length should be equal to one-half to two-thirds of the length of
the remaining root
post should extend to one-half the length of the root that is
supported by bone
post width should not exceed one-third of the root width at its
narrowest dimension, bear in mind that most roots are not perfectly
rounded.
A minimum of 1 mm of sound dentin should be maintained
circumferentially, especially in the apical area where the root surface
usually becomes narrower and functional stresses are concentrated
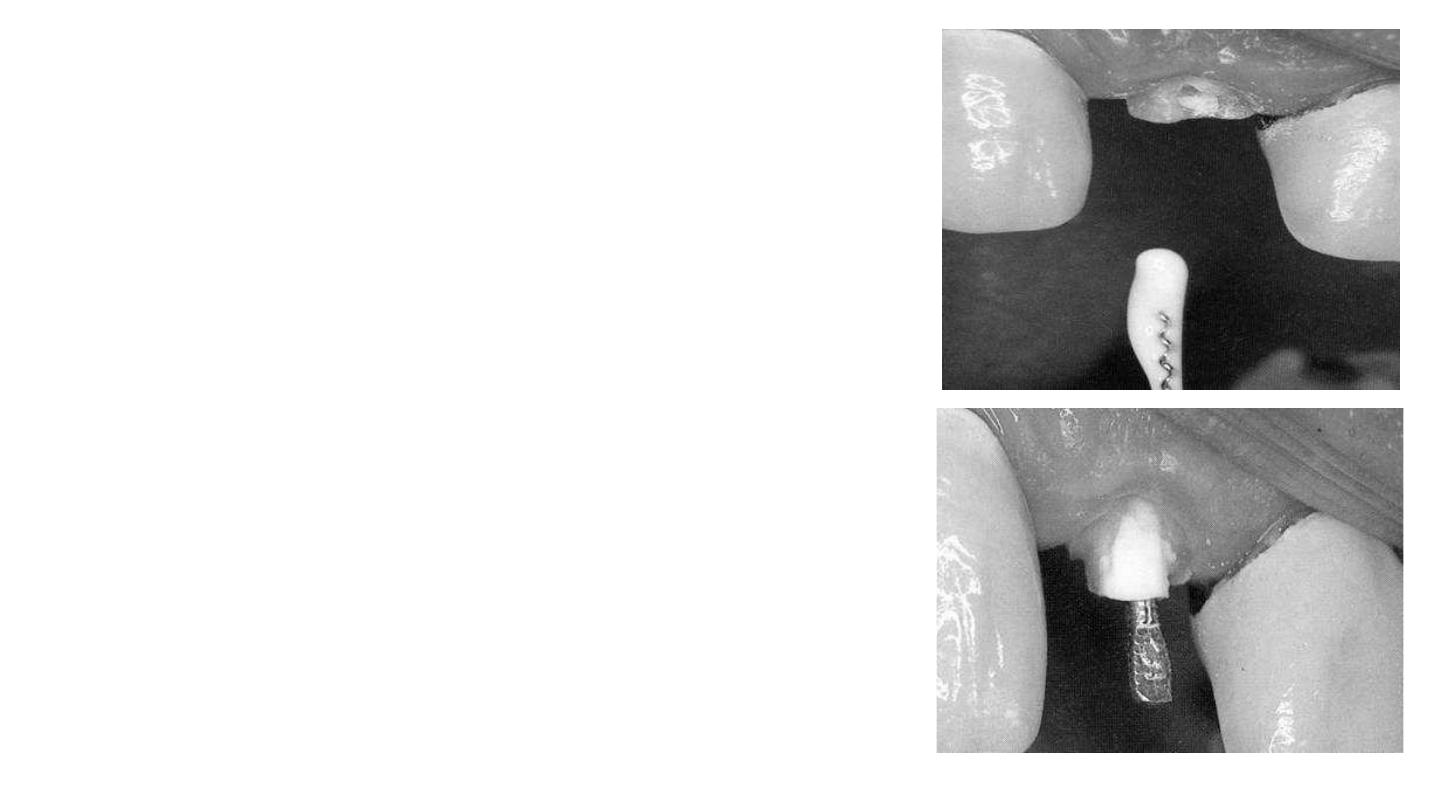
cementing with a permanent cement, such
as zinc-oxide phosphate (ZOP) or
glass ionomer luting cement. The ZOP should
be mixed to a slightly more fluid consistency
than when it is being used to cement a
prosthetic crown, and can be more evenly
distributed along the length of the post space if
placed with a Lentulo spiral The post cemented

Casted(custem) Post and Core
Types of post crown
1. One unit post-crown: It is the poorest design and can be used with full metal or full metal
with facing and porcelain fused to metal crown.
2. Two units post-crown: the post and core are in one peace and the veneer crown is the
another peace, it is the most preferred design, can be used with full metal, full metal with
facing, porcelain fused to metal and finally with jacket crown.
3. Three units post-crown: The post or the dowel in one peace, the core is the second peace
and inserted in the post part, the third segment is the veneer restoration, can be used with the
same types o restorations mentioned in two units post-crown.
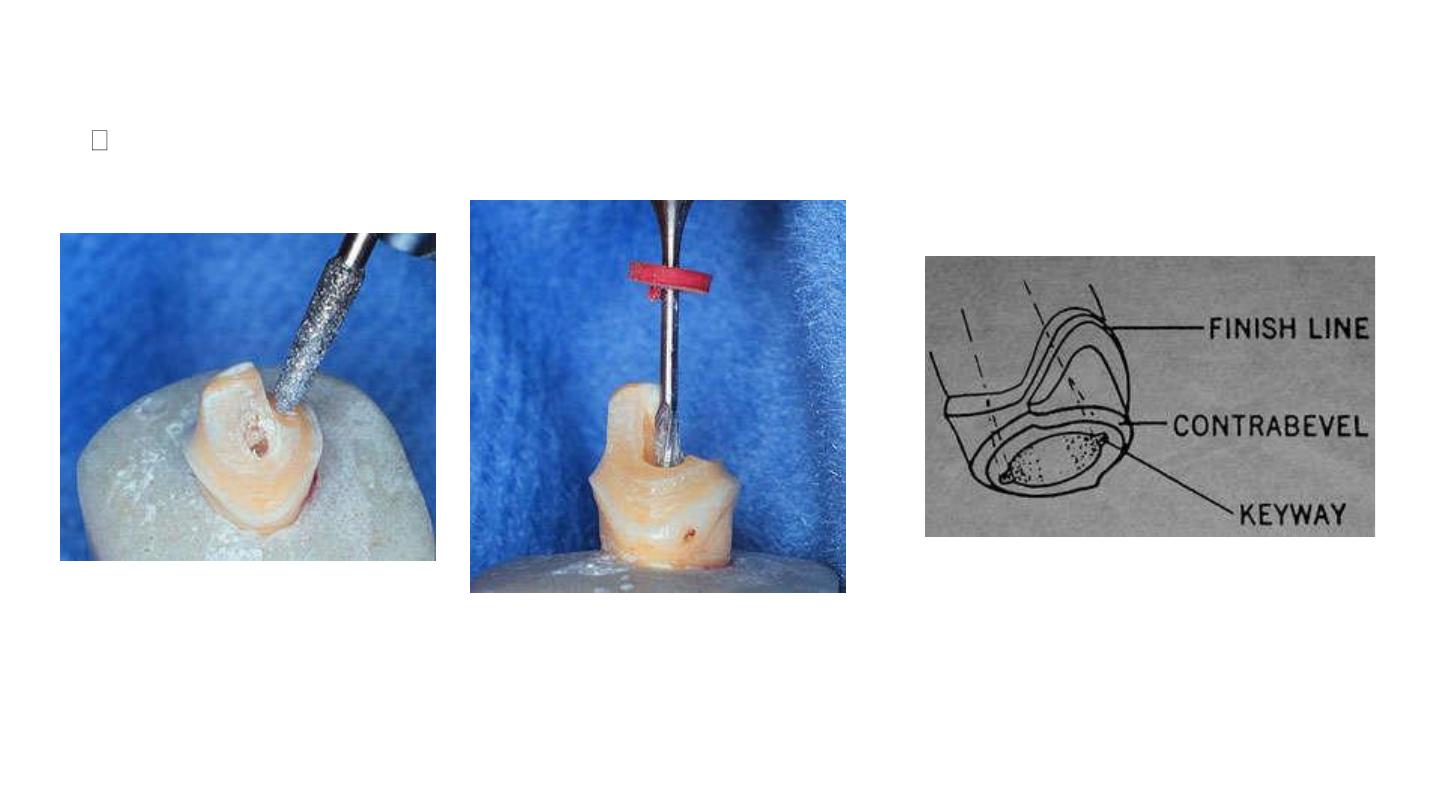
Contra bevel:
It is the bevel placed around the occlusal external surface of the periphery of the preparation;
this will provide a good collar around the occlusal surface periphery of the preparation which
will help in holding the tooth structure together and preventing the fracture of the remaining
tooth structure.
For the multirooted posterior teeth we should place the post in the largest canal which is the
palatal canal in the upper molar teeth and the distal canal of the lower molar teeth for the
maxillary premolar we place the post in the buccal canal. Multipost sometimes avoided in
order not to weaken the tooth and also it will not be parallel to each other.
Custom cast post system
Direct technique

Anti-rotation devices:
1. Key way.
2. Triangular shape for incisors and elliptical
shape for upper canine
3. Pins.
4. Post surface texture: Post with rough surface
is more retentive than post with smooth
surface.

Indirect technique
