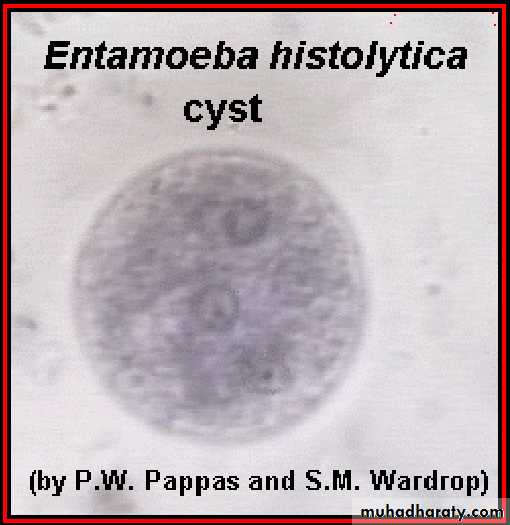
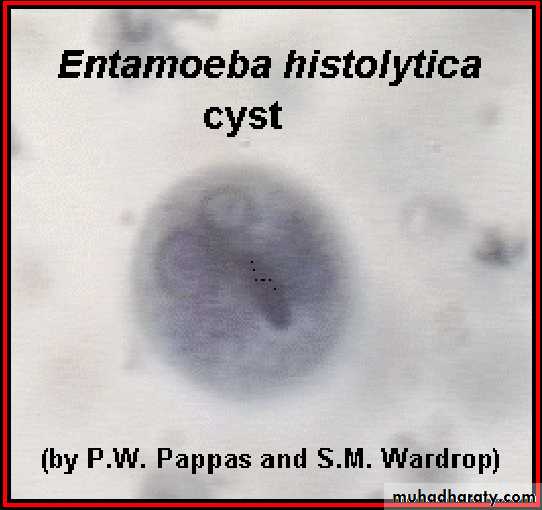
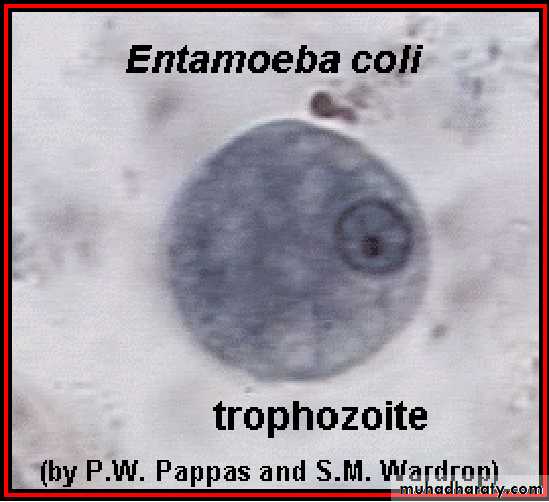
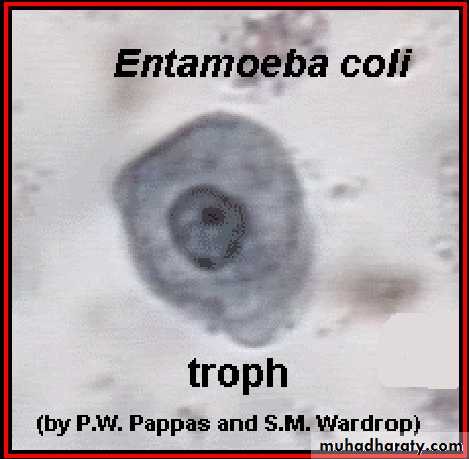
Entamoeba histolytica
Morphology
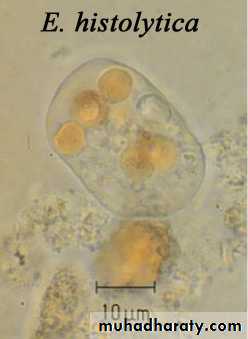
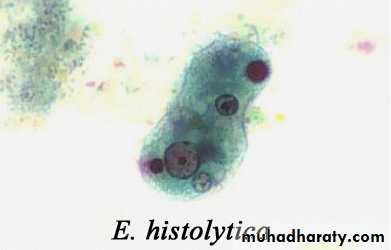
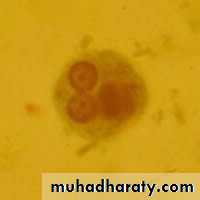
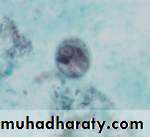
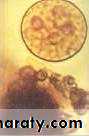
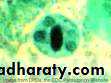
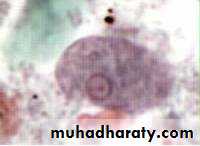
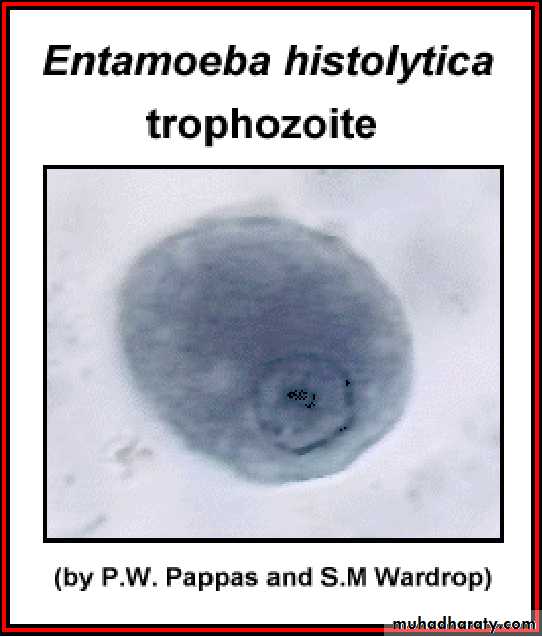
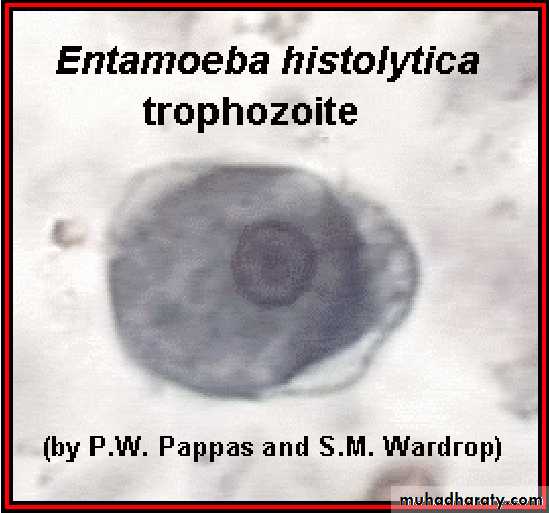
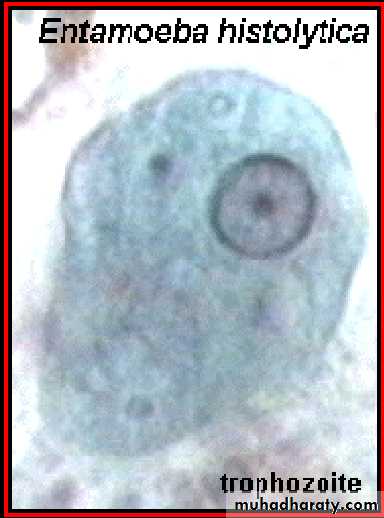
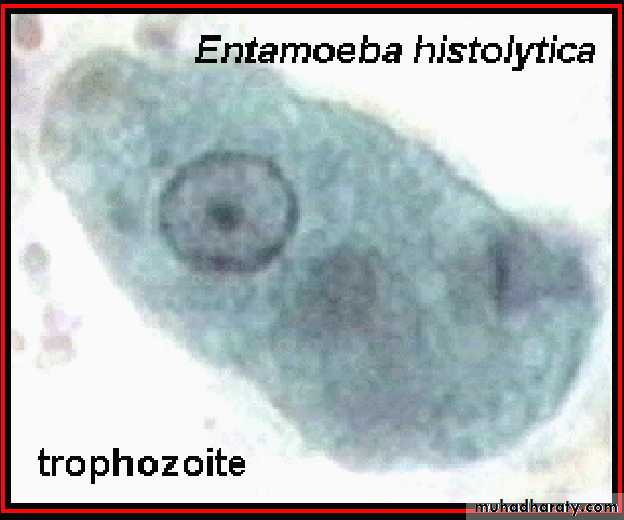
Different form of E. histolytica;1- trophozoite
2- precyst
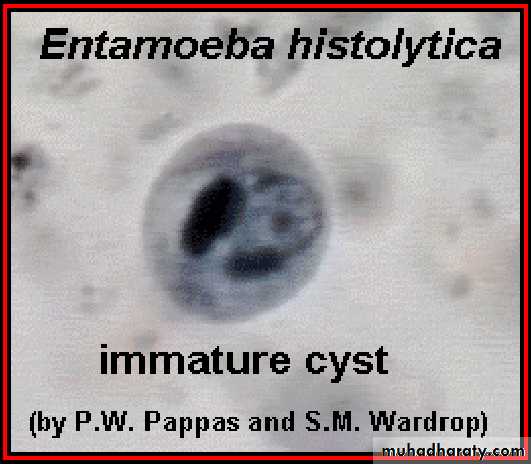
3- cyst(1, 2, 4 nuclei)
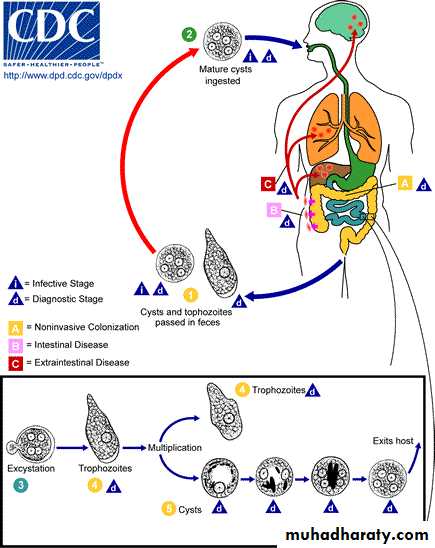
Life cycle
Life cycle
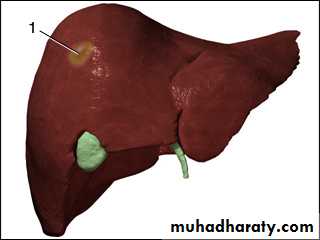
Pyogenic- Liver Abscess
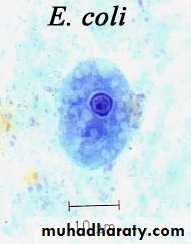
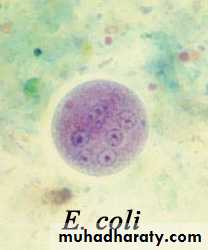
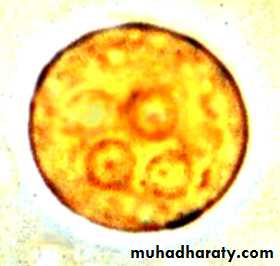
Laboratory diagnosis. An iodine-stained cyst of the pathogen Entamoeba hystolytica with 4 nuclei is illustrated. The harmless commensal Entamoeba coli has larger cyts with 8 nuclei. Furthermore, recall that E. histolytica has a lookalike E. dispars that is harmless.
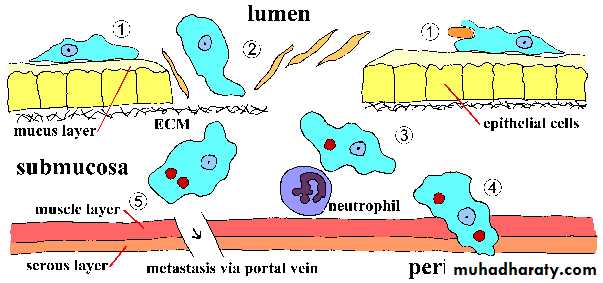
Transmission
1-driect contact of person to person( fecal-oral)2- Veneral transmission among homosexual males( oral-anal
3- Food or drink contaminated with feces containing the E.his. cyst
4- Use of human feces (night soil) for soil fertilizer
5- contamination of foodstuffs by flies, and possibly cockroaches
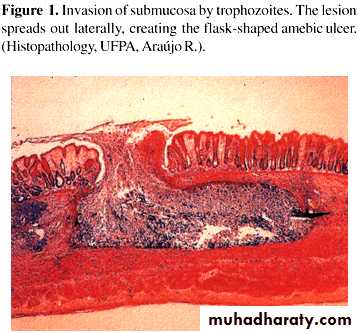
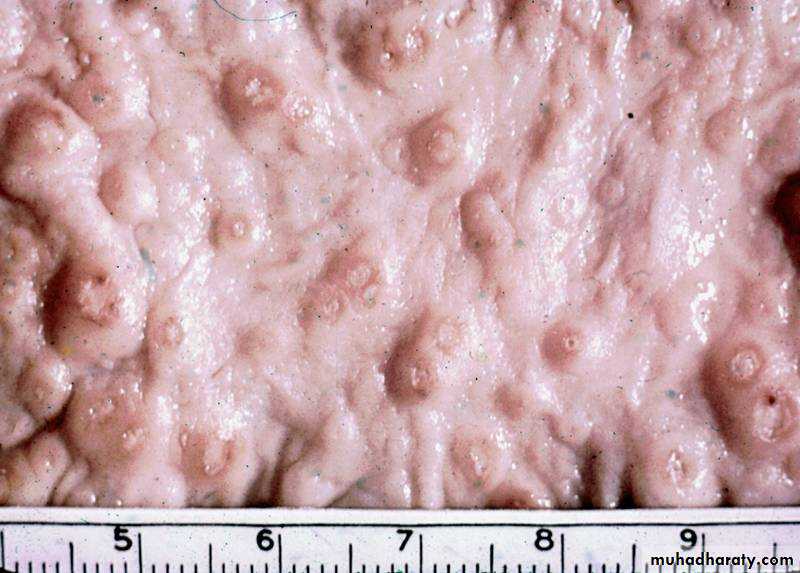
• ulcers with raised borders
• little inflammation between lesionsDiagnosis
Paraclinical Diagnosis:Sigmoidoscopic examination:
precence of a grossly normal mucosa between the ulcers serves to differentiate amebic from bacillary dysentery,( the entire mucosa being involvoed in bacillary dysentery).
Hepatomegally
C.B.C. : leukocytosis in Amebic dys. rises above 12000 per microliter, but counts may reach 16000 to 20000 per microliter.
Treatment
Intestinal Amebiasis:*Asymptomatic amebiasis(cyst passer): Diloxanide furoate ( furamide)
500 mg 3 times daily / 10 days
*Symptomatic amebiasis ( troph. & cyst): - Iodoquinol , 650 mg 3 times daily/ 20 days or Metronidazole (Flagyl) , 750 mg 3 times daily/ 10 days
*Amebic colitis: Chloroquine, 250 mg 2 times daily
* Acute amebic dysentery: Emetine hydrochloride, 1mg/kg daily IM or SC
Treatment
Extraintestinal Amebiasis:*Amebic liver abscess, ameboma:
Metronidazole, as above plus dehydroemetine / 10 days or Metronidazole or dehydroemetine as above plus Chloroquine , 500 mg 2 times daily / 2 days,…..