The predisposing factors for periodental diseases
Factors that predispose periodental diseasesFaulty dentistry
1-Margins of restoration:
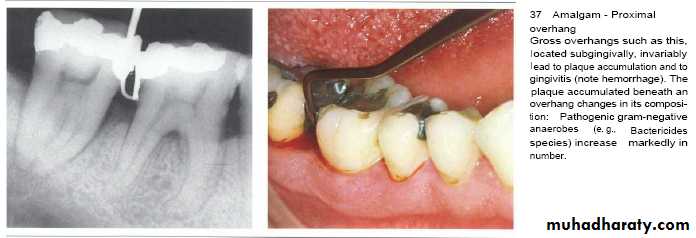
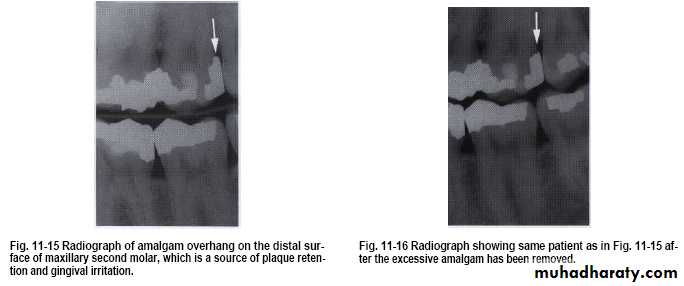
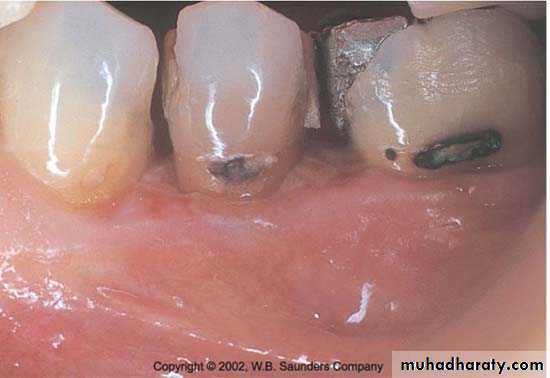
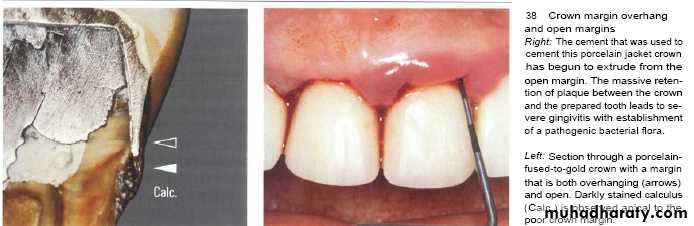
• Overhanging margins induce plaque accumulation & change
• the environment that allows growth of pathogenic bacteria &
• inhibit patient access to remove plaque.
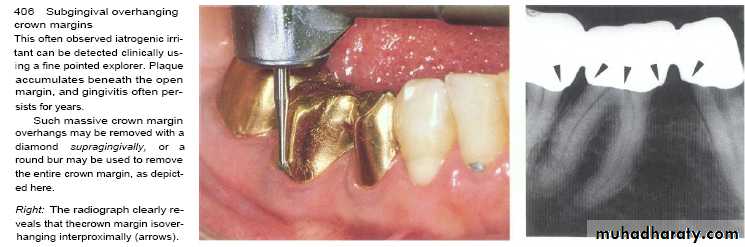
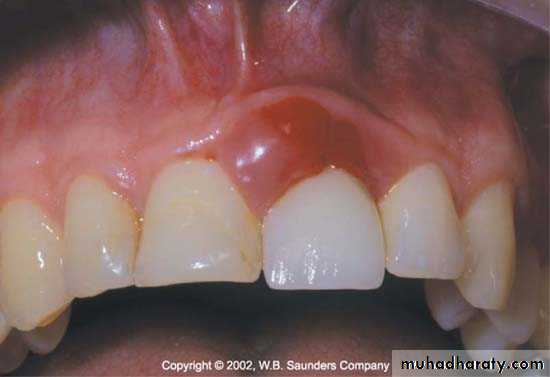
• Subgingival placed restorations
Plaque accumulated are detected even with high quality subgingivally restoration, whereas supragingival restorations are similar to unrestored teeth.
Contour of restoration
• Over contoured restoration:• accumulate plaque& prevent self-cleaning by tongue, lips & cheek .
• Improperly located proximal contact that is located more apically with inadequate gingival embrasure spaces associated with papillary inflammation.
• Under contoured restoration:induced no effect
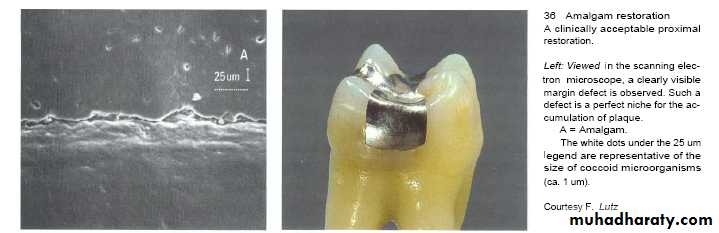
Roughness of restorations is the main cause of plaque accumulation and subsequent inflammation which is caused by:-
1- Scratches of highly polished surfaces.
2- Exposed rough surface of prepared tooth between crown margin & finishing line (luting agent).
3- Disintegration of luting agent lead to crater formation.
4- Inadequate marginal fitness of restoration.
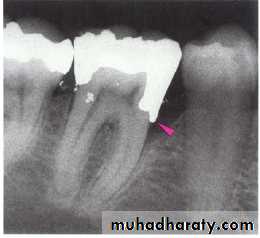
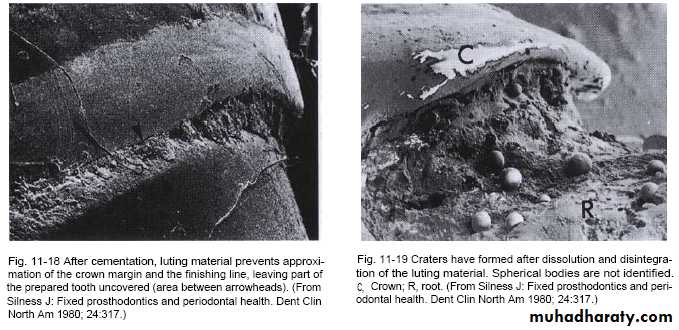
The subgingival zone is composed of the margin of the restoration, the luting material, and the prepared as well as the unprepared tooth surface.
Subgingival margins typically have a gap of 20 to 40 microns between the margin of the restoration and the unprepared tooth.
Marginal Fit
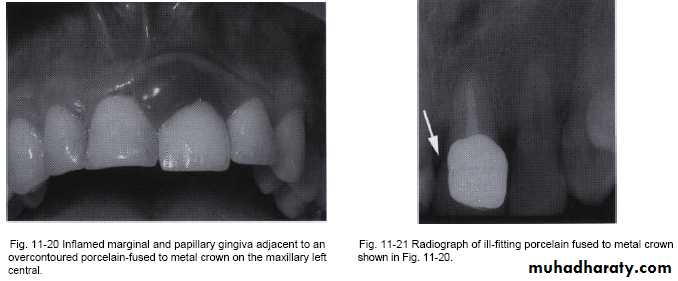
Marginal fit has close relation with an inflammatory response in the periodontium.
It has been shown that the level of gingival inflammation can increase with increasing level of marginal opening.
Margins that are significantly open are capable of harboring large numbers of bacteria and may be responsible for the inflammatory response .
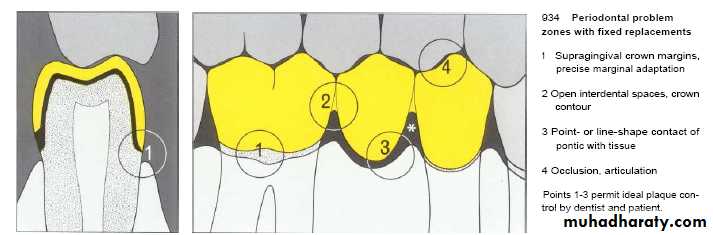
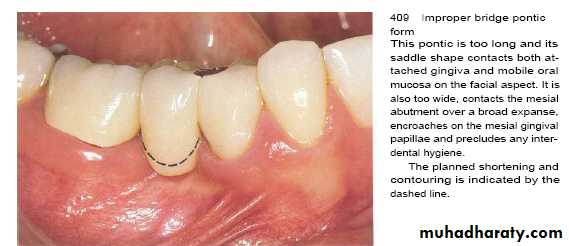
The undersurface of pontics in fixed bridges should barely touch the mucosa.
Access for oral hygiene is inhibited with excessive pontic contact to tissue which can leads to plaque accumulation and pseudpocket.Crown Contour
• Restorations contour is extremely important to the maintain periodontal health.• Ideal contour provides
• Access for hygiene
• The fullness to create the desired gingival form
• Pleasing visual tooth contour in esthetic areas
The most frequent cause of overcontoured restorations is inadequate tooth preparation by the dentist, which forces the technician to produce a bulky restoration to provide room for the restorative material.
In areas of the mouth where esthetics are not critical, a flatter contour is always acceptable.
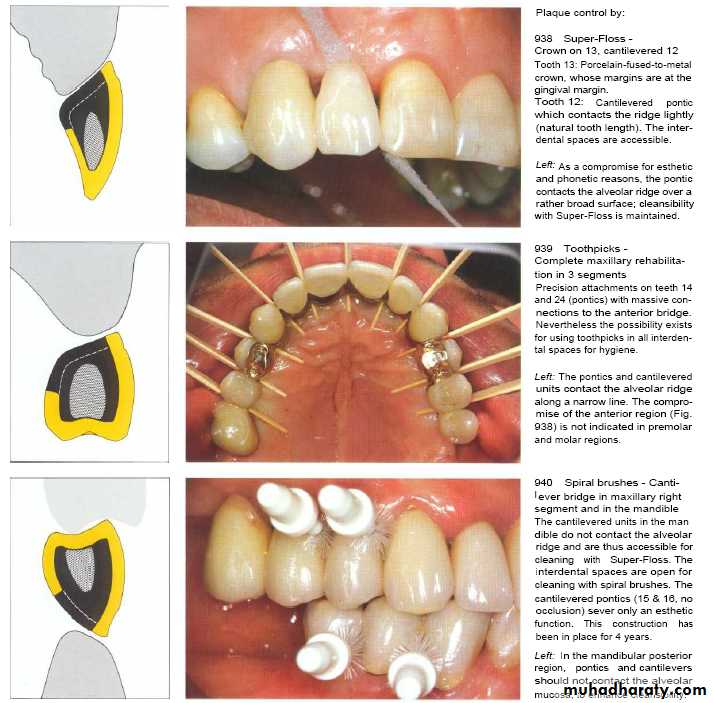
Contour of artificial crown or bridge or restoration should be cleansable so as to decrease plaque retention & gingival inflammation .
Materials
Restorative materials not injurious to tissue except cold cure acrylic.Its provide rough surface ,If its not polished well & accessible to cleaning.
The materials could be classified according to its smoothness from the smoother one which is ceramic ,gold, amalgum, composite, acrylic.
More importantly, tissues respond more to the differences in surface roughness of the material rather than the composition of the materials themselves.
The rougher the surface of the restoration subgingivally, the greater the plaque accumulation and gingival inflammation.
In clinical research,porcelain,highly polished gold, and highly polished resin all show similar plaque accumulation.
Regardless of the restorative material selected, a smooth surface is essential on all materials which are subgingivally placed.
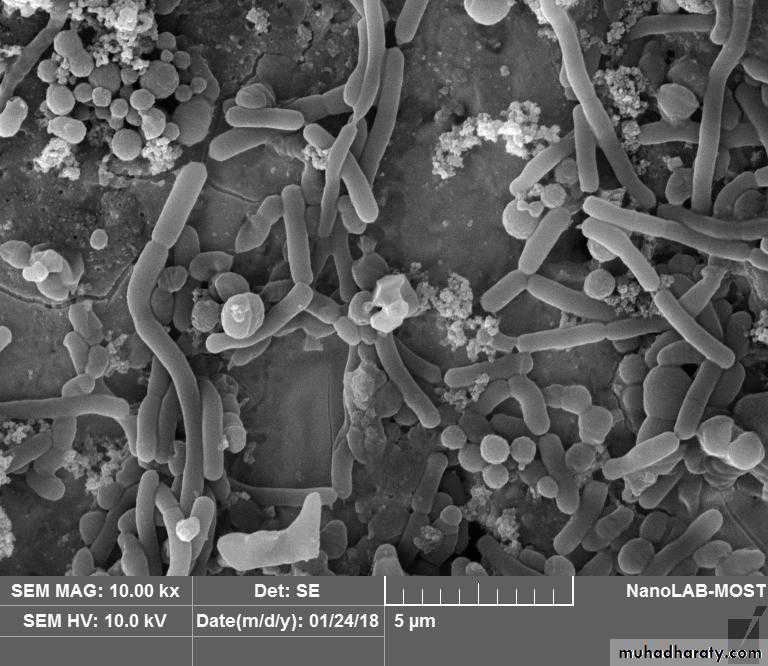
Biofilm x10.00
Biofilm x1.00• Biofilms and Application of Antibiofilms of Facklamia hominis and Streptococcus mutans on Amalgam surface
• s
• Extracellular poly• Biofilms and Application of Antibiofilms of Facklamia hominis and Streptococcus mutans on Amalgam surface
• s
• Biofilms and Application of Antibiofilms of Facklamia hominis and Streptococcus mutans on Amalgam surface• s
• Biofilm of S.mutans and F.homoinis on amalgam restoration• Biofilms and Application of Antibiofilms of Facklamia hominis and Streptococcus mutans on Amalgam surface
• s
Zirconia has mechanical properties similar to those of stainless steel.Dental research is nowadays directed towards metal-free prosthetic
Restorations.
It has less adherent to plaque than other restorative materials.
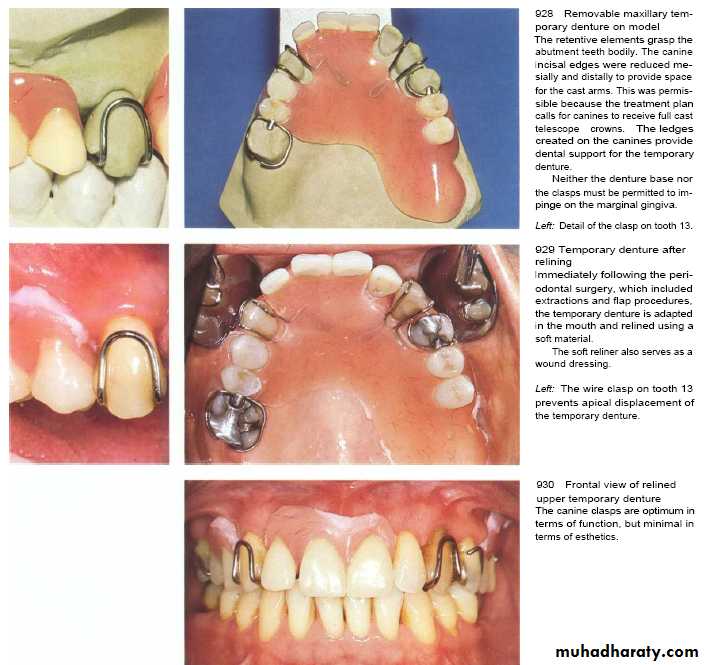
Design of Removable Partial Denture
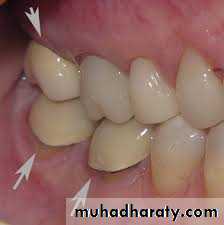
After the insertion of partial dentures, the mobility of the abutment teeth, gingival inflammation, and periodontal pocket formation increases. These occur due to :-1- retention of plaque.
2- its placement near or above gingival margin.
3- clasp(plaque retentive & exert lateral force ---torque force applied as no occlusal rest).
Partial dentures induce both quantative & qualitative changes in dental plaque(growth of spirochetes).
Chrome cobalt (casted partial dentures) is hygienic one whereas the acrylic is not as it is a temporary prosthesis.
During construction of removable partial dentures ,patient control & occlusal force must be taken in consideration
.
Design of Removable Partial Denture
Free end prosthesis induce damage to anterior teeth by application of leverage torque that result in increase teeth mobility. (dental implant is solution)Acrylic partial dentures should be wear for temporary period with its margin placed away at least 4mm from gingival margin.
Clasp should be constructed with occlusal rest & on canine tooth must construct a U-shape clasp.
In casted partial dentures---the presence of occlusal rest & margin away from gingiva are kept the adjacent periodontium healthy but also it may also increase gingival inflammation & periodontal pocket formation due to plaque accumulation especialy if its worn day & night .
Inflammed palatal gingivitis associated with max.acrylic partial denture.
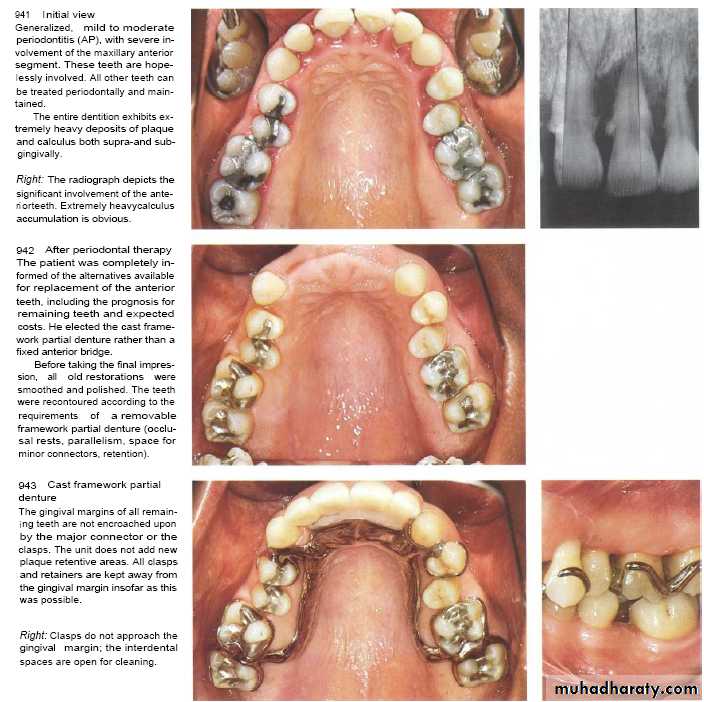
Restorative dental procedure
The use of rubber dam clamps, matrix bands, and burs in aggressive manner can lacerate the gingiva.They are transient injuries.
Forceful packing of a gingival retraction cord into the sulcus (to prepare subgingival margins on a tooth or for the purpose of obtaining an impression)may mechanically injure the periodontium.Malocclusion
Malocclusion may make plaque control more difficult.A positive correlation between crowding and periodontal disease.
Roots of teeth that are prominent in the arch ( as in bucco-or lingu- version, or within a high frenal attachment ).
Failure to replace missing posterior teeth may have adverse consequences on the periodontal support .
Tongue thrusting exerts excessive lateral pressure on the anterior teeth remaining teeth exhibit recession .
Occlusion
High spot lead to trauma of supporting tissue.Histological features;
1- widening of subcrestal periodental ligaments space.
2- reduction in collagen content of oblique & horizontal fibres.
3- Increase in vascularity & Leukocytes infiltration.
4- Increase in osteoclast on alvbone.
Arrangement of periodental tissue favors vertical force rather than lateral force which is very damaging to attachment apparatus .So ,carving of restoration very important to prevent force conversion into resultant damage.
If vertical force applied , all periodental fiber will resist this force but if lateral force is exerted , only horizontal fibres will resist which are of little amount So it will be destructed
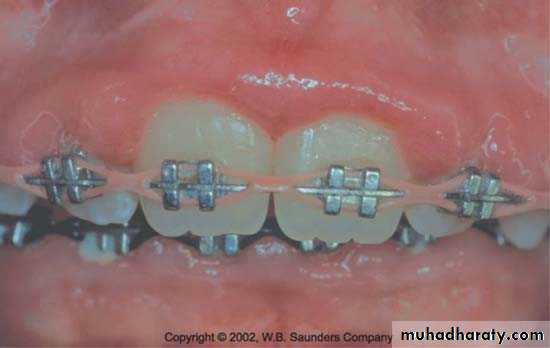
Periodontal Complications Associated with Orthodontic Therapy
Orthodontic therapy may affect the periodontium by favoringplaque retention, by directly injuring the gingiva as a result of overextended bands, and by creating excessive forces, unfavorable
forces, or both on the tooth and supporting structures.
Retention of plaque; Increase in Prevotella intermedia , Actinomyces odontolyticus, Actinobacillus actinomycetcomitans with decrease in aerobic facultative bacteria.
Oral hygiene improvement with evaluation of periodental diseases at each recall visits are mandetory from periodontal point of view.
Periodontal Complications Associated with Orthodontic Therapy
Irritation from orthodontic bands-start at early eruption of tooth .
-bands should not extend up to gingival tissue
-Forceful impingement lead to detachment of gingiva from tooth.
-The mean alveolar bone loss / adolescents patient underwent 2 years of orthodontic is 0.1 and 0.5 mm.
Excessive orthodontic forces also increase the risk of apical root resorption.
The prevalence of severe root resorption( as indicated by resorption of more than one third of the root length), during orthodontic therapy in adolescents has been reported at 3%.
It is important to avoid excessive force and too rapid tooth movement in orthodontic treatment.
Periodontal Complications Associated with Orthodontic Therapy
The dentoalveolar gingival fibers that are located within the marginal and attached gingiva are stretched when teeth are rotated during orthodontic therapy.Surgical severing or removal of these gingival fibers in combination with a brief period of retention may reduce the incidence of relapse after orthodontic treatment intended to realign rotated teeth
Gingivitis & enlargement associated with orthodontic treatment & poor oral hygiene .
Tissue injury from orthodontic force
Excessive force lead to necrosis of periodental fibers& bone, apical root resorption.Repair could be occurred if the periodental fiber is viable without infection.