Lens disorders
Marwan S.Salman M.D
Ass.Professor of Ophthalmology
Tikrit university , college of medicine

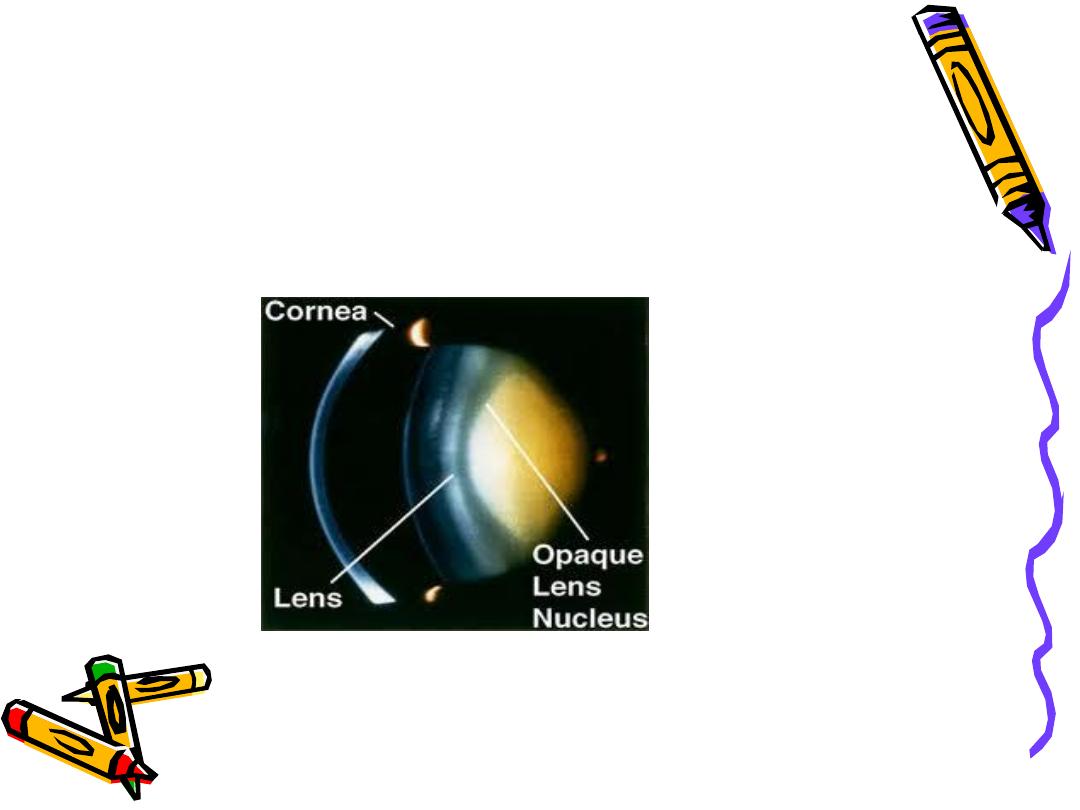
Anatomy of crystalline lens
Crystalline Lens Of Eye
• Transparent, biconvex, avascular structure enclosed by a
capsule(basement membrane secreted by lens epithelium)
• Approx. diameter is 10mm
• Lens measures approximately 10 mm in diameter and 4 mm thick
• Suspended by zonular fibres
• Parts Of Lens
• Capsule
• Cortex
• Nucleus
• Anatomy Of Lens
• CAPSULE
• ANT CAPSULE
• Basement membrane of ant lens epithelium
• POST CAPSULE
• Basement membrane of cell lens that have nuclei near lens equator
• Thickest basement membrane in the body

WHAT IS A CATARACT ?
• Any opacity in the lens or it’s capsule
whether developmental or acquired is
called cataract
OR
Loss of transparency of crystalline lens
is cataract
• Aging Changes
Nuclear changes (nuclear sclerosis)
• Hardening of nucleus starts as early as 20
years of age.
• Increase in insoluble proteins
• Cholesterol level increases while
phospholipid level decreases

Symptoms Of Cataracts
• Hazy, fuzzy or blurred vision
• Double vision
• Frequent changes in spectacle
prescriptions
• Feeling of having a film over the eye
• Colours appear dull
• Glare in bright daylight, and at night
from bright light sources

Persone with cataract

Acquired Cataract
• Senile cataract
• Presenile cataract
• Traumatic cataract
• Secondary cataract
• Age Related Cataract

Morphological classification
• Anterior subcapsular
• Posterior subcapsular
• Nuclear
• Cortical
• Christmas tree

SUBCAPSULAR CATARACT
Anterior subcapsular cataract
• Lies directly under lens capsule & there is associated
fibrous metaplasia of anterior epithelium of the Lens
Posterior subcapsular cataract
• Lies just in front of posterior capsule
• Associated with posterior migration of epithelial cells of
lens
• Patient troubled by headlights & bright sunlight
• Near vision is diminished more than distance Vision

NUCLEAR CATARACT
• Exaggeration of normal ageing
• May lead to
temporary myopia from increase in
refractive index of lens so patients
may be able to read again without
spectacles (second sight of the aged)

CORTICAL CATARACT
• Involves anterior, posterior or equatorial cortex.
• Opacities start as vacoules or clefts between lens fibers
• Later they may develop into radial spoke-like opacities
Christmas tree Cataract
• Uncommon
• Striking, polychromatic, needle-like deposits in the deep
cortex or nucleus
• May be solitary or associated with other opacities
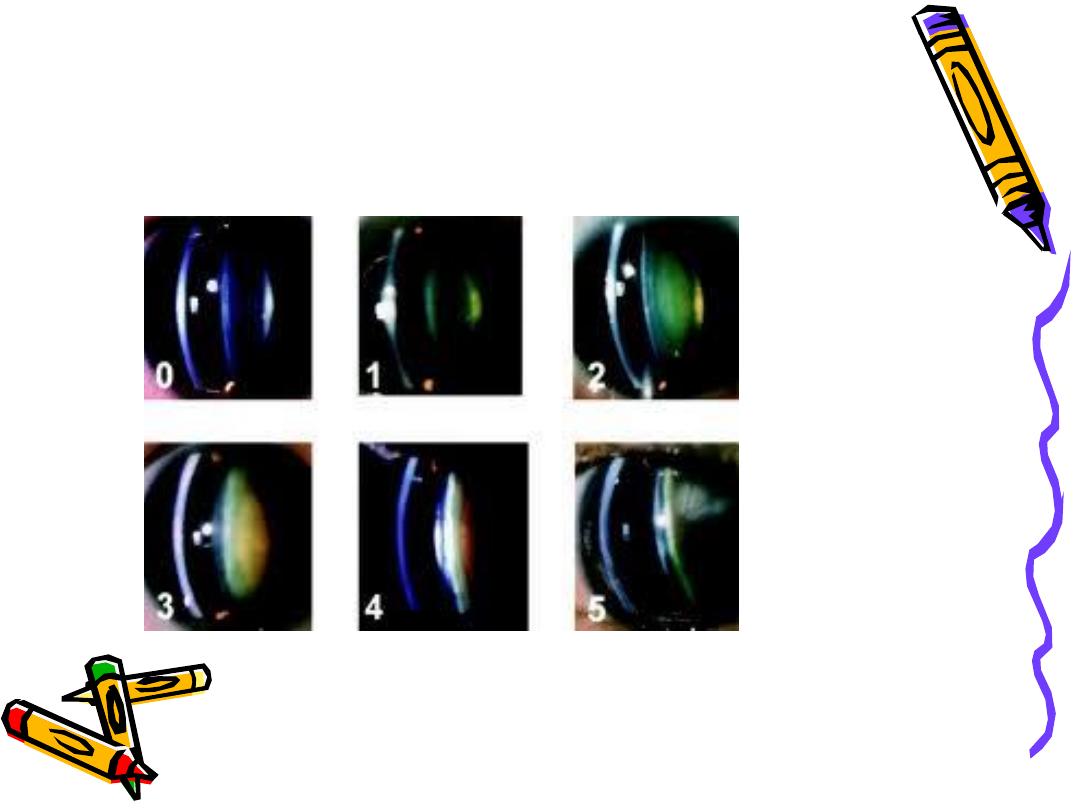

• Nuclear sclerosis grading
• Nuclear cataract
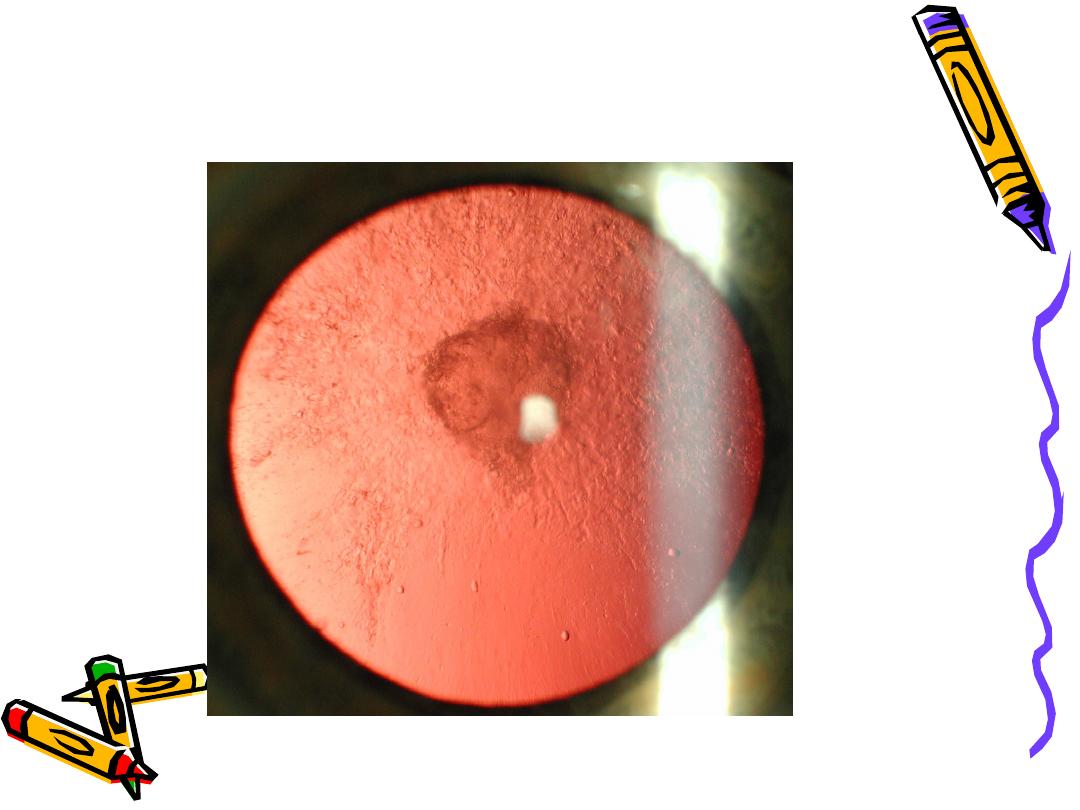
• Posterior subcapsular cataract
• Abnormal red reflex
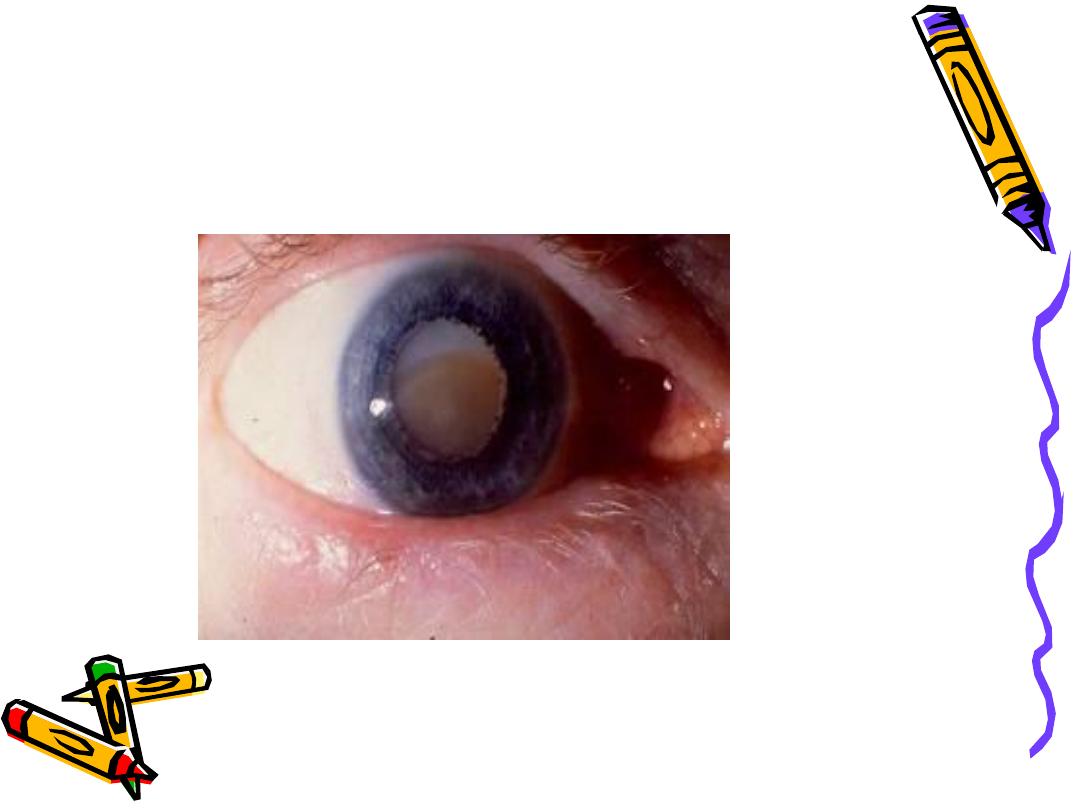
• Hypermature cataract
Morgagnion cataract
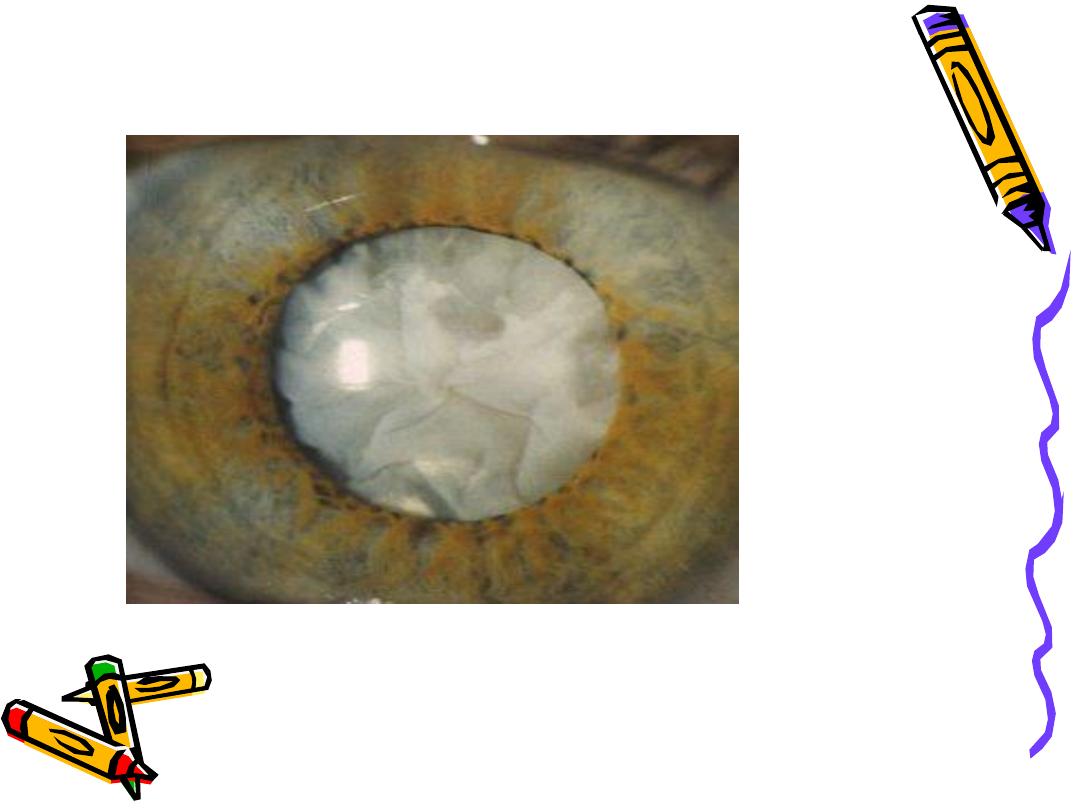
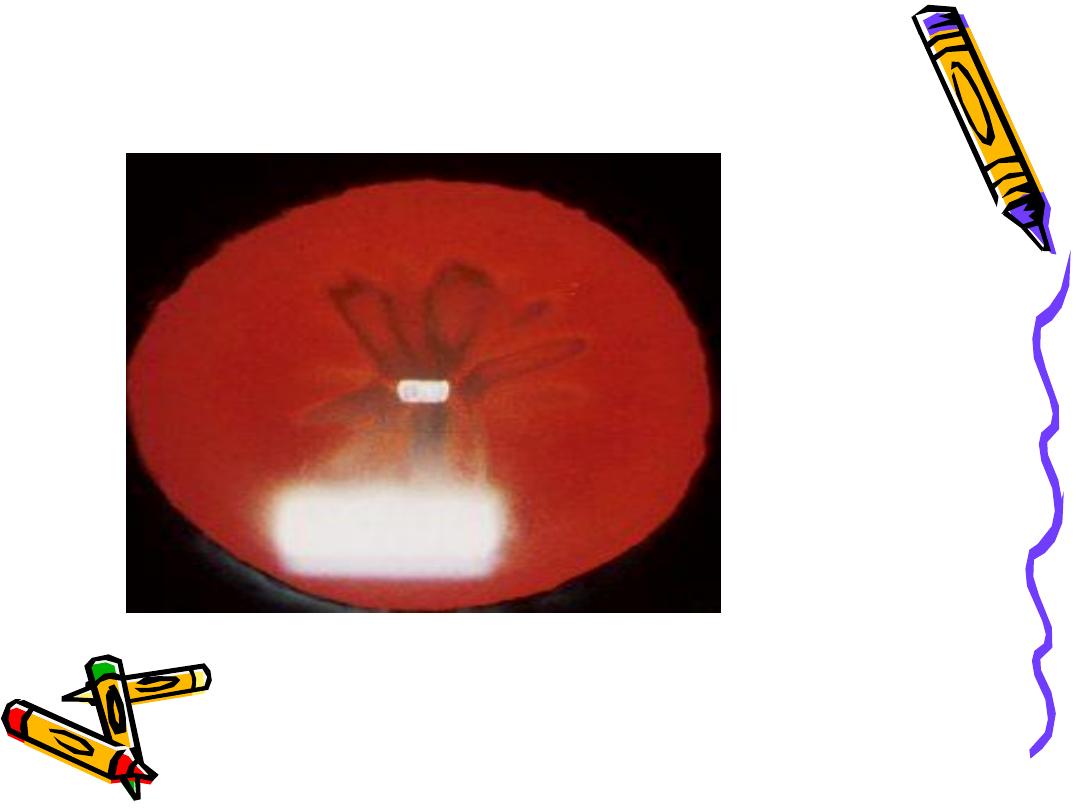

Classification According To Maturity
• Immature
• Mature
• Hypermature
• Morgagnian
• IMMATURE CATARACT
Lens is partially opaque
• MATURE CATARACT
Lens is completely opaque

HISTORY
• Age of Onset
• Decreased Vision
• Painless,
• Effecting daily routine activity?
• Trauma
• Any Ophthalmological Problems
• Drugs Intake
• Exposure to Radiations
• Systemic Diseases H.T DM etc.
• Skin disease, joint pains, etc.
• Family History

EXAMINATION
• GENERAL PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
• SYSTEMIC EXAMINATION
OCULAR EXAMINATION
• Visual Acuity
• Adnexa
• Iris
• Conjunctiva
• Cornea
• Anterior Chamber
• Pupil
• Lens
• Vitrous
• Retina

INVESTIGATIONS
• Blood Glucose
• ECG
• Chest x-rays (PA view)
• Blood Complete Picture
• Any specific relevant investigation (if
indicated)

OPTIMAL POST OP. REFRACTION
• If monocular correction is reqd.
In contralateral dense cataract or
amblyopia ?
best post op refraction is -1DS
• If binocular correction is reqd
difference between the two eyes
should not be more than 3DS.

SURGICAL TECHNIQUES
• ICCE
• ECCE
• ECCE with posterior chamber
IOL implant
• Phacoemulcification

CONGENITAL CATARACT
• An opacity in the crystalline lens,
present at the time of birth or
appears with in first three months of
life
• Occurs in about 3:10,000 live births
• 2/3 are bilateral
• Most common cause is genetic
mutation, usually autosomal dominant
(A.D)
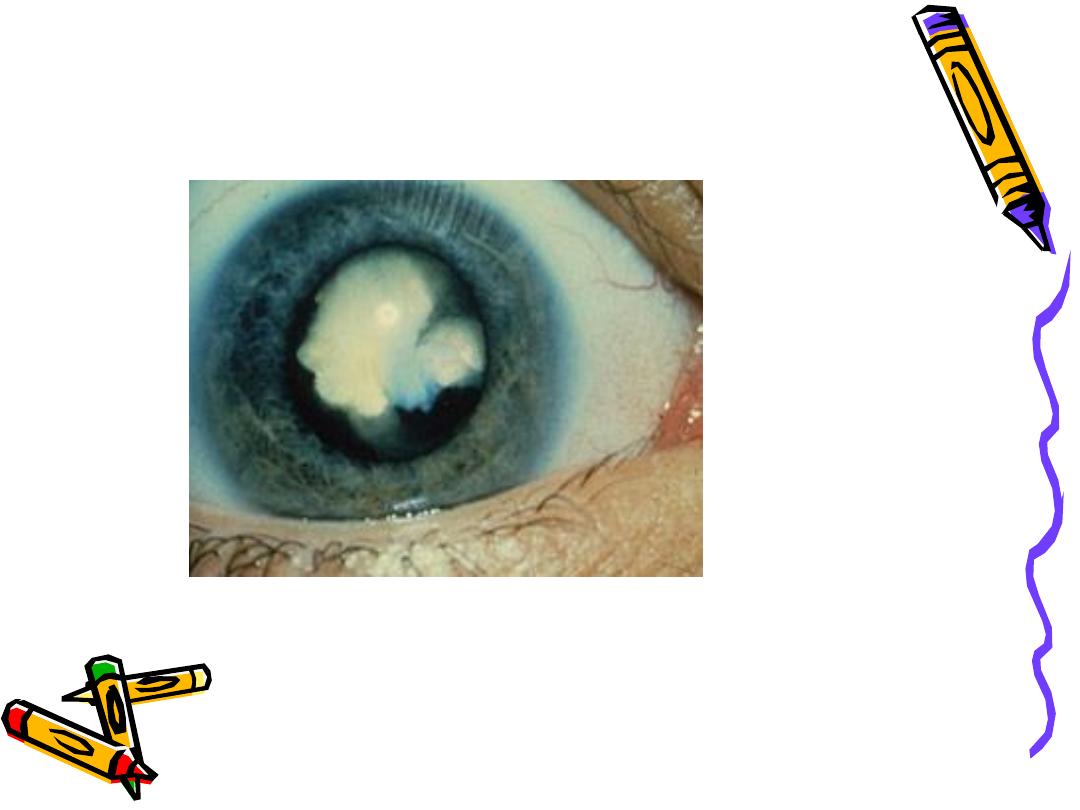
• Congenital cataract

AETIOLOGY
• IDIOPATHIC
35%
• HEREDITARY
25%
• INTRA-UTERINE CAUSES
20%
• Maternal infections
• Rubella
40-60%
• Mumps
10-22%
• Toxoplasmosis 5%
• Cytomegalovirus
• HSV
• Varicella
• Malnutrition
• Prematurity
• Drug induced

AETIOLOGY
• INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM
10%
• Lowe syndrome
• Galactosemia
• Mannasidosis
• Hypoparathyroidism
• Fabry disease
• Hypo/hyper glycemia
•

ASSOCIATED WITH OCULAR
ANOMALIES 05%
• Microphthalmia
• Aniridia
• Coloboma

AETIOLOGY
• CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITIES
03%
• Down’s syndrome
• Turner syndrome
• Trisomy 13 & 18
• BIRTH TRAUMA
02%
• SKELETAL SYNDROMES
• Hallermann-Streiff-Francois syndrome
• Nance-Horan syndrome

Clinical Features
• Symptoms
– Decreased Vision
– Glare
• Signs
– Leukokoria
– Nystagmus
– Strabismus
– Amblyopia
– Microphthlamos

Morphological classification
• NUCLEAR CATARACT
• LAMELLAR (ZONULAR) CATARACT
• CORONARY CATARACT
• SUTURAL (STELLATE) CATARACT
• ANTERIOR POLAR CATARACT

CLINICAL FEATURES
• White pupillary reflex
• Poor Visual Acuity
• Nystagmus
• CLINICAL EVALUATION
• Purpose:
To know:
• Cataract density
• Type of cataract
• Condition of retina and optic nerve
• Any associated ocular anomaly
•
CLINICAL EVALUATION
• Purpose:
To know:
• Cataract density
• Type of cataract
• Condition of retina and optic nerve
• Any associated ocular anomaly

Steps:
• Torch examination
• Examination under Anesthesia
• Ophthalmoscopy direct / indirect
• Associated ocular pathology
• Corneal clouding
• Microphthalmos
• Glaucoma
• Persistent anterior fetal vasculature
• Chorioretinitis
• Rubella retinopathy
• Foveal or optic nerve hypoplasia
• PAEDIATRIC CONSULTATION
• Dysmorphic features or suspicion of associated
systemic diseases
LABORATORY
INVESTIGATIONS
• TORCH screening
• Blood Complete picture
• Blood Glucose levels
• Serum calcium and phosphorus
• Urine:for reducing substances after drinking milk
(glactosaemia) and chromatography for amino
acids (lowe syndrome ) .
• Chromosome analysis
• Refer for syspicious other systemic diseases

VISUAL FUNCTION
EVALUATION
• Visual Acuity
• Follows light or not
• Colour targets
• Reaction to occlusion
• Pupillary Reflexes
• Fixation Reflex
• Visual Evoked Potentials(VEP)

DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
• LEUKOCORIA
• Retinoblastoma
• Retinopathy of Prematurity
• Persistent Hyperplastic Primary Vitreous
• Retrolental Fibroplasia
• Toxocariasis
• Toxoplasmosis
• Incontinentia pigmenti
• Retinal Detachment
• Cytomegalovirus Retinitis
• RETINOBLASTOMA
• RETINAL DETACHMENT WITH A MITTENDORF SPOT
• PERSISTENT HYPERPLASTIC PRIMARY VITREOUS
• TOXOPLASMOSIS
• RETROLENTAL FIBROPLASIA

PROGNOSIS
• Visual morbidity may result from deprivation amblyopia,
refractive amblyopia, glaucoma (10% post surgical
removal), squint, secondary cataract and retinal
detachment
• Mental retardation, deafness, kidney disease, heart disease,
and metabolic disorders may be part of the presentation

Preoperative assessment for cataract surgery
• Visual symptoms
blur/glare ,distortion, color perception ,second sight
• POM
history of amblyopia, stabismus ,previous surgery e.g refractive
surgery, trauma ,concorrent eye disease.
• PMH
DM, HT,COAD, anasthetic history if GA considered .
• SH
occupation and daily task .
• DH
warfarin , antiplatelet agent,topical medication .
• VA
• Cover/uncover test.
• PUPILS
check RAPD , adequate dilitation
.
• Cataract
morphology ,density, maturity
• Others factors
• globe (deep set,small /large),
•
lids (blepharitis ,ectropion, entropion),
•
nasolacrimal (mucocele),
• Cornea (scarring ,guttata)
• Anterior champer depth

• IOP
• IRIS ( PXS,iridodonesis,posterior synchiae, inducable mydrasis .
• Lens (PXS, phacodonesis, sublxation,type of cataract )
• Optic disc e.g glaucoma, neuropathy, macula (AMD ),fundus .
• Complications
Intra operative :
• Posterior capsule rupture without vitreous loss (2%)
• Posterior capsule rupture with vitrous loss(1%)
• Anterior capsule problem
• Zonular dehiscence.
• Loss of nuclear fragment posteriorly 0.3%
• Choroidal haemorrhage 0.1%
Post operative early
• corneal odema
• Elevated IOP

• Increase anterior inflammation
• Wound leake
• Iris prolapse
• Endophthalmitis
Post operative late
• Posterior capsule opacification
• Cystoid macular odema
• Retinal detachement
• Corneal decompensation
•

Ectopia lentis
Displacement of the lens from its normal position . Te lens may
be completely dislocated,rendering the pupil aphakic
(luxated) , or partially displaced still remaining in the
pupillary area (subluxated) ,ectopia lentis may be
herediatory or acquired . Acquired causes included trauma,
a large eye (i.e high myopia , buphthalmos), anterior uveal
tumor and hypermature cataract .
Without systemic association
1- familial ectopia lentis
2- ectopia lentis et pupillae
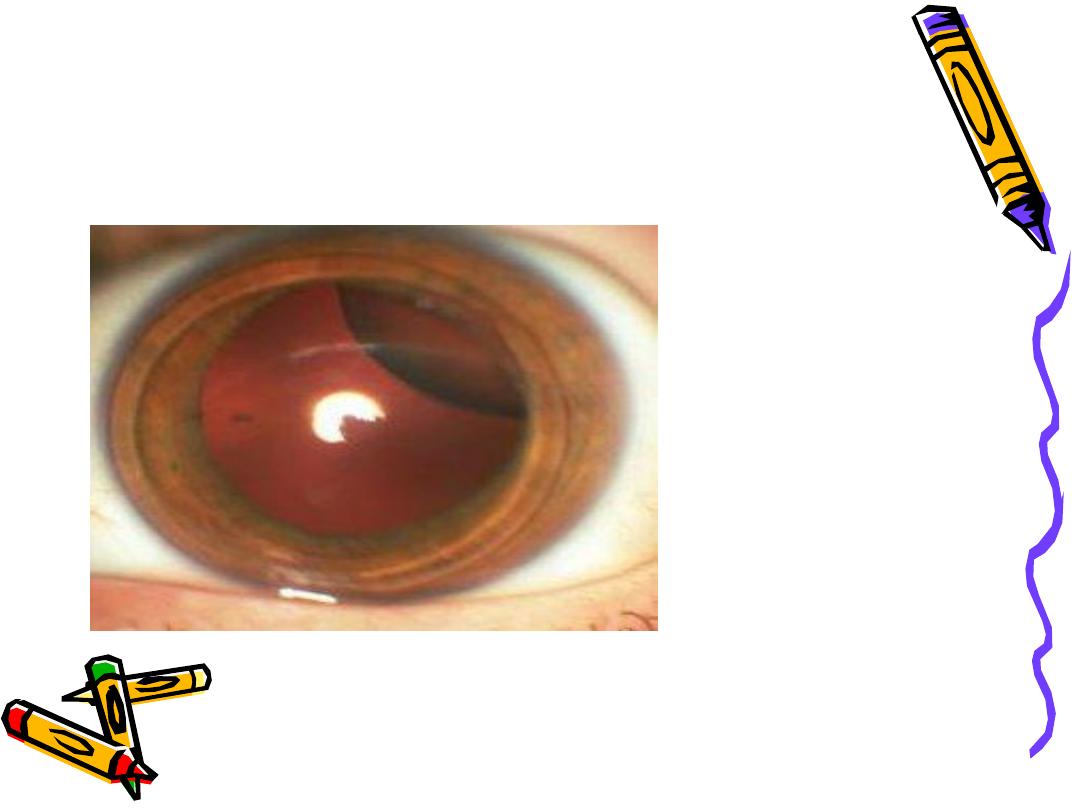
Ectopia lentis et pupillae

With systemic association
1- marfan syndrome
2- weill - marchesani syndrome
3-homocystineuria
4- hyperlysinaemia
5-stickler- syndrome

• Mangement
The main complication of ectopia lentis are a-
refractive error (lenticular myopia ) b-optical
distortion due to astigmatism c-glaucoma and
rarely d- lens induse uveitis
1- spectacele correction may correct astigmtism
induced by tilt or the edge effect in the eye with
mild subluxation aphakic correction may also
afford good visual result if significant portion of
visual axis is aphakic in the undilated state .
2-Surgical removal of lens is indicated for cataract ,
lens induced glaucoma ,uveitis or endothelial touch
