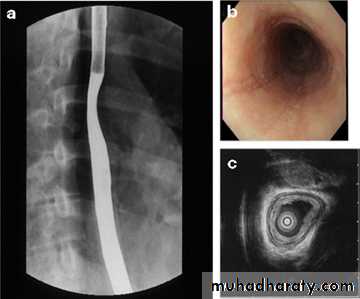
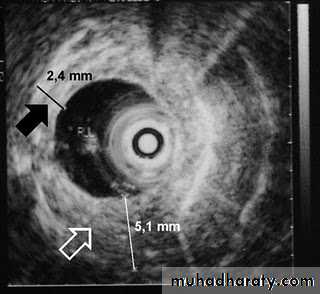
Radiology of G.I.TRadiological investigations1- Contrast examination Barium study Ba. Swallow, Ba. Meal, Ba. Follow through & Ba enema 2-Endoscopic Ultrasound .3- CT & MRI.4-Nuclear medicine (FDG-PET): flurodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography
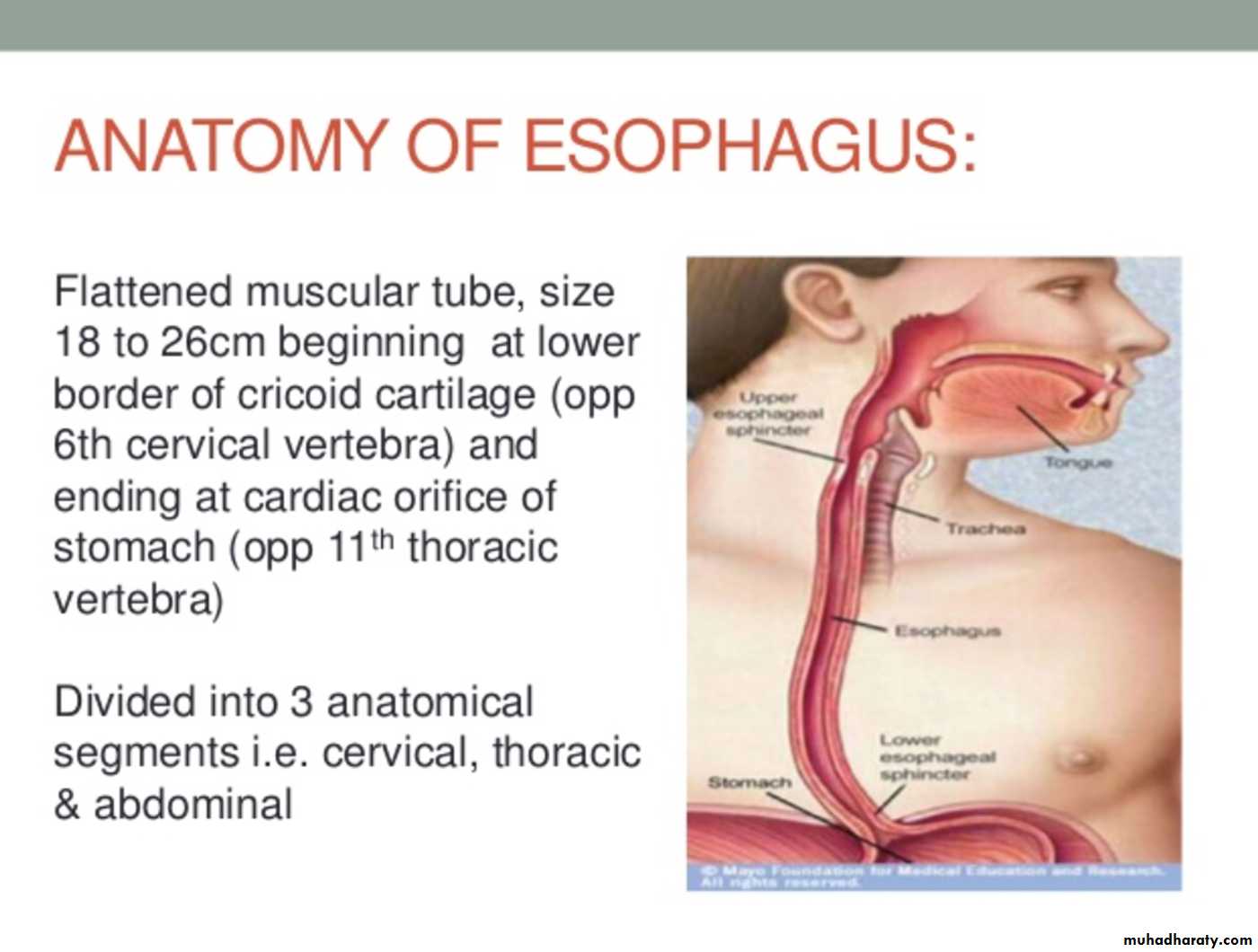
THE OESOPHAGUS
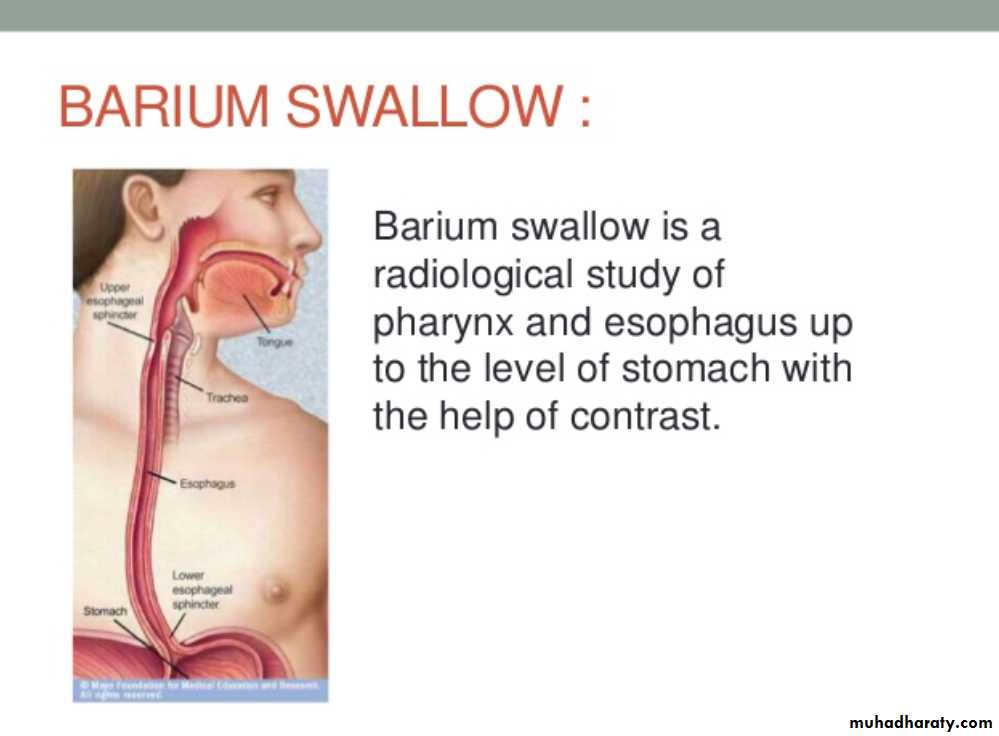
• THE OESOPHAGUSBarium Swallow:1. Conventional2. Double contrast (DC)3. Flouroscopy + spot films
Technique
1.Patient will need to be NPO after midnight before the exam2.The patient will have to swallow a contrast agent: Barium or Gastrografin
May also swallow sodium bicarbonate for double contrast barium swallow
3.X-ray tech will have the patient perform various maneuvers so that the barium can coat the GI tract
Indications
OdynaphagiaDysphagia
Hematemesis
Abdominal pain
Unexplained weight loss
The esophageal wall is composed of:
MucosaMusculature
Inner circular layerOuter longitudinal layer:
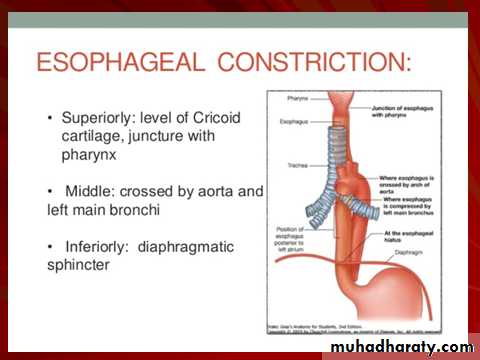
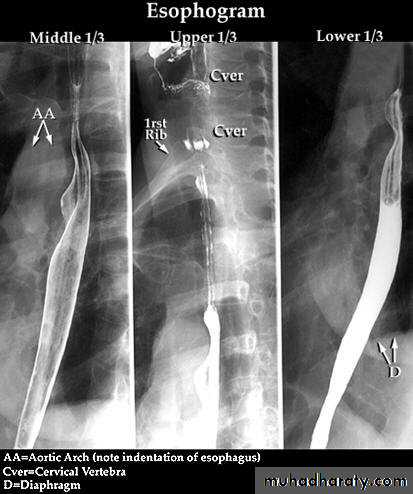
Upper 1/3 striated muscle
Middle 1/3 striated and smooth muscle
Lower 1/3 smooth muscle
No serosa
Esophagus mucosa: normal thin, parallel, uniform mucosal folds 3-4 in no.in double contrast examination
Esophageal peristalsis
Normal:Primary contraction: Propels bolus through the esophagus
Secondary contraction: Follows primary contraction and propels any remaining bolus from thoracic esophagus
Abnormal contraction :
Tertiary contractions,Diffuse esophageal spasm
crock screw o. ))Nutcracker esophagus
Decreased peristalsis
resulting from achalasia, scleroderma, dermatomyositis, polymyositis, esophagitis, and secondary to many other diseases
tertiary contractions
Diffuse esophageal spasm
Diffuse esophageal spasm produces intermittent contractions of the mid and distal esophageal smooth muscle, associated with chest symptoms• Congenital Anomalies
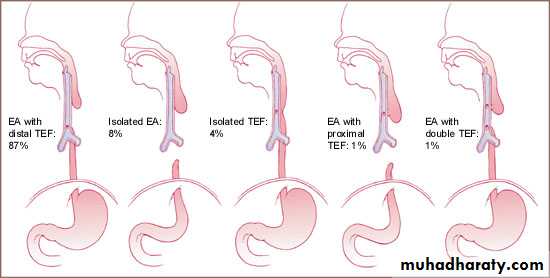
• 1- Artesia with or with out tracheo-oesophageal fistula (TEF).• 2- Congenital Short oesophagus.
• 3- Congenital Duplication ( Neuro-enteric cyst )
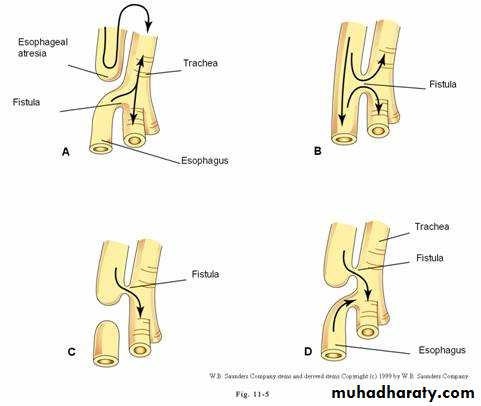
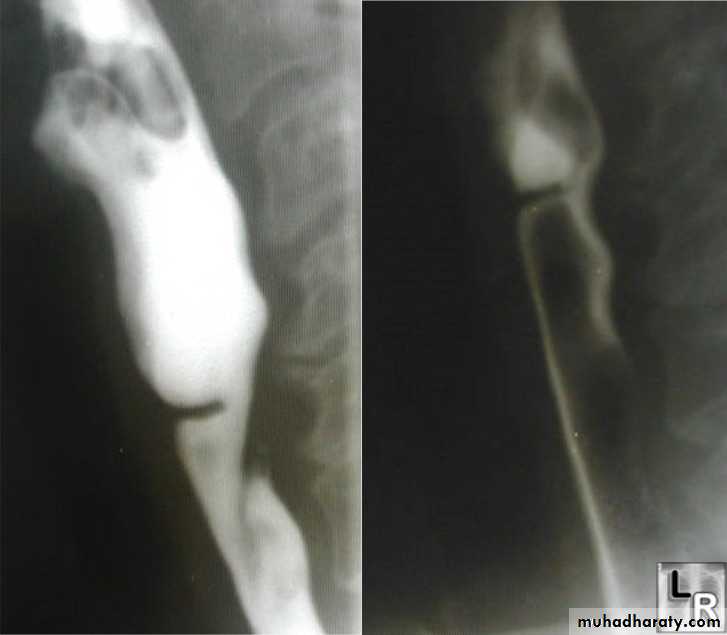
• ATRESIA:
• - Complete blockage of the lumen .
• - The diagnosis is suggested after birth by in ability of infant to feed or by choking during swallowing .
• - The blocked segment is mostly seen at level of thoracic inlet
Types of Fistula
Acquired Lesions
DYSPHAGIAdifficulty in swallowing causes
1- Carcinoma ( Malignant stricture).
2-Benign Stricture (Corrosive ).
3-Achalasia Cardia.
4-forgien body
5-osophagitis .
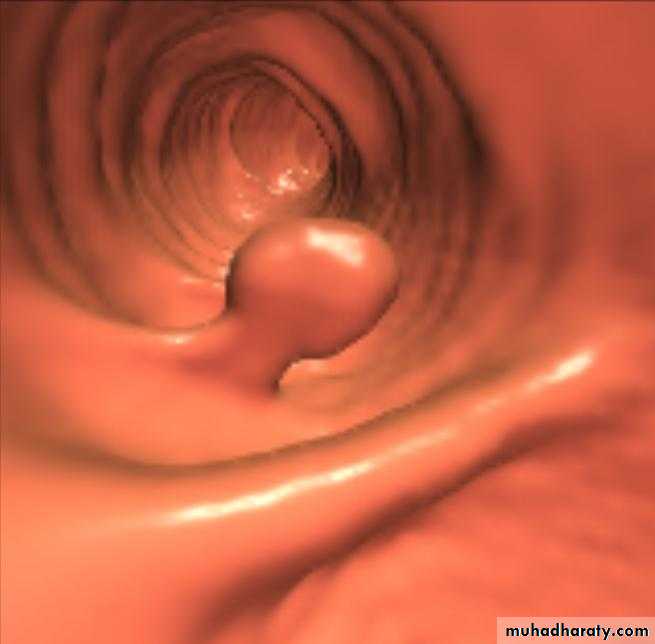
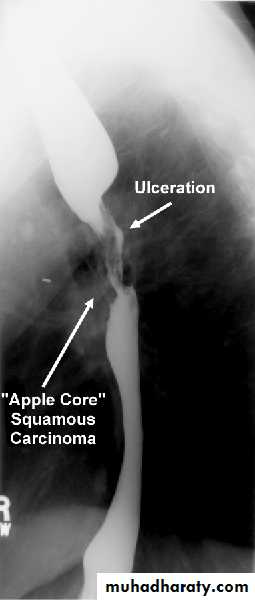
Malignant stricture
CA esophagus is the cause for the malignant stricture
The most common types of esophageal carcinoma are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma .
esophagography is unique among esophageal studies for assessing both morphology and motility. Barium esophagography remains the study of choice for characterization of esophageal strictures. Esophageal carcinoma may demonstrate a variety of appearances on barium esophagrams.
Annular Carcinoma
Narrowing :1-Constant.
2-Irrigular .
3-Variable length.
4- Shouldering sign.
5-Fistula (double tract).
6-Soft tissue shadow of the mass
Computed Tomography
Contrast-enhanced CT plays an important role in the1.staging of esophageal carcinoma. to 2.determining the extent of the local tumor; 3.invasion of mediastinal structures; 4.involvement of supra clavicular, mediastinal, or upper abdominal lymph nodes
5. Assessment of the distant metastases
examination should extend from the thoracic inlet through the liver
Routine oral contrast material such as (gastrographine) or a negative intra luminalcontrast medium, such as water.
+/ - IV contrast injection
CT essential in the Dx & staging of the CA
CT finding of esophageal malignancy
1.Eccentric or circumferential wall thickening is greater than 5 mm.
2.Peri-esophageal soft tissue and fat stranding may be demonstrated.
3.A dilated fluid- and debris-filled esophageal lumen is proximal to an obstructing lesion.
4.Aortic invasion .
5.Osophageal CA is often metastatic at the time of presentation ( look for the LN & distal metastasis ) .
Barrett's esophagus
is a metaplastic disorder in which specialized columnar epithelium replaces healthy squamous epithelium.Barrett's metaplasia is the most common cause or precursor of esophageal carcinoma. The rate of esophageal adenocarcinoma is increasing in the Western world, and it is associated with a poor prognosis, mainly because individuals present with late-stage disease..
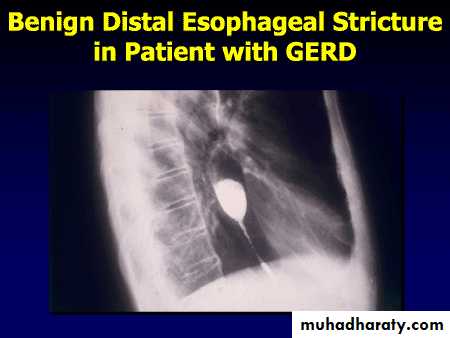
Benign Stricture
• Causes :
• Peptic esophagitis
• Corrosive
• Traumatic
• Ba. swallow :
• 1-Constant narrowing.
• 2- Long length (lower third).
• 3-Smooth and regular.
• 4-Mild proximal dilatation.
• 5-No shouldering sign.
• 6-Smooth tapering
• ( funnel shape).
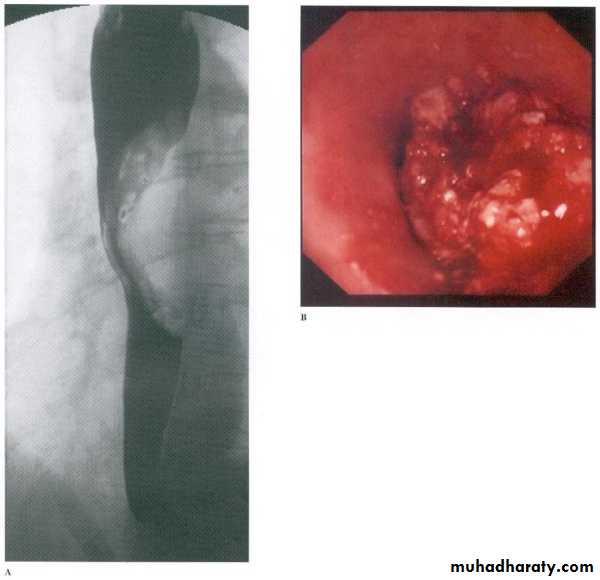
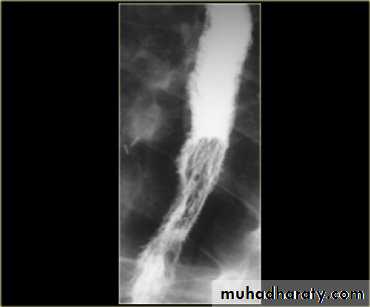
Infectious esophagitis
Candida esophagitis in patient with an infectious esophagitis due to candida , the barium shows numerous fine erosions & plaques causing shaggy outline of the osophagus due to Candida albicans in immunocompromised patient.middle year old female with a past medical history significant for HIV/AIDS comes in with complaint of loosing their weight over the past 2 weeks with pain & difficulty on swallowing …. Also feels like food is getting stuck in her throat
What is your diagnosis ??????????
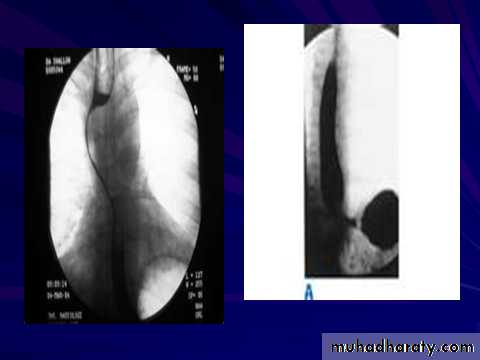
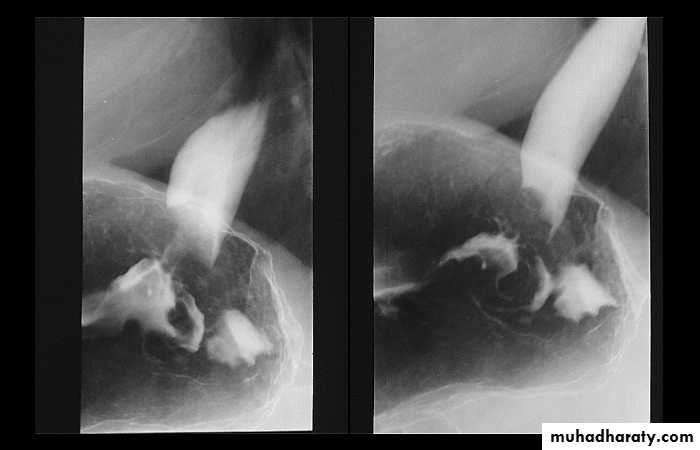
A chalasia Cardia
AchalasiaPresentation:
Equal M:F incidence, most common in middle-age
Slow progression of dysphasia to start with to solid material then to solid & water
Increased incidence of carcinoma
Etiology:
Unknown ??? absent or reduced esophageal ganglion cells at their distal lower sphincter
Incomplete or absent relaxation of LES with swallowing
Absent primary peristaltic waves
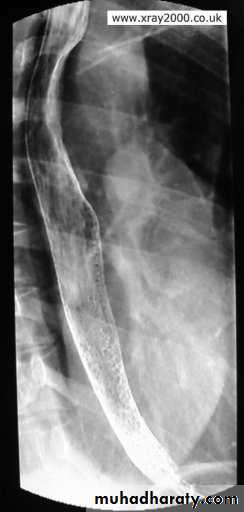
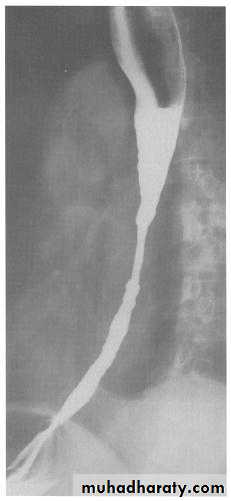
A chalasia Cardia
A : Absence
Chalasia : Relaxation
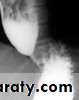
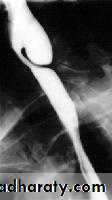
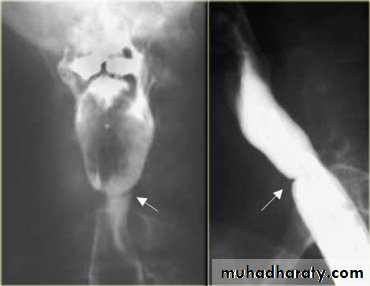
Narrowing :
1-the narrowing is Constant Short length (confined to cardia).
2-Regular and smooth.
3- No shouldering sign.
4-Tapering (Tip of pencil , cigar shape) Under left dome of diaphragm.
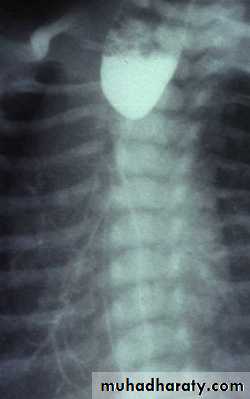
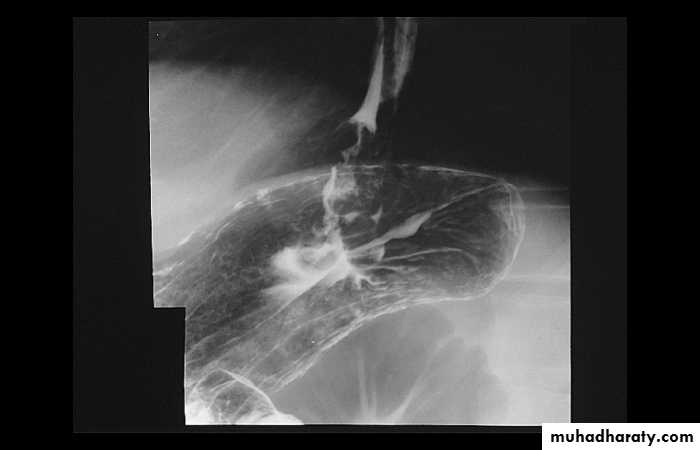
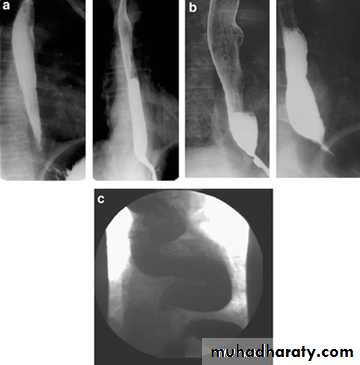
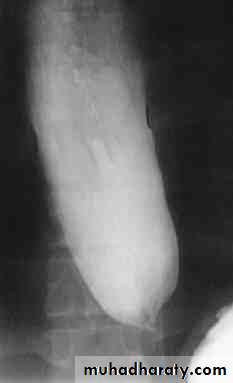
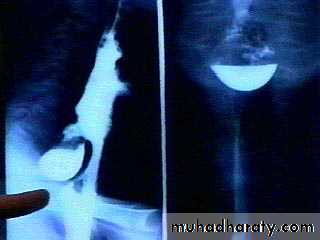
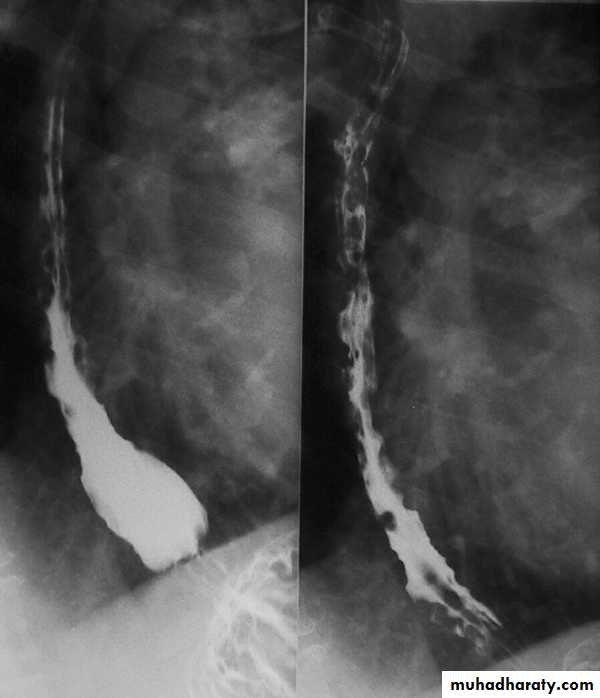
Achalasia continue
5. DILATATION (Sac like in proximal part )6-Undulating or spiky out line due to sluggish peristalsis.
7 Non- homogeneity of Barium due to food particles.
8-Air Barium level.
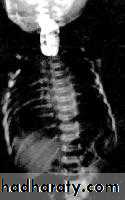
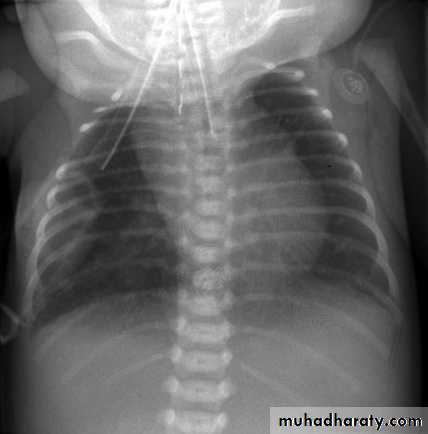
9- CXR shows widening of mediastinum.
10-Absence of fundal gas shadow.
7-Basal fibrosis in lungs due to repeated aspiration pneumonia .
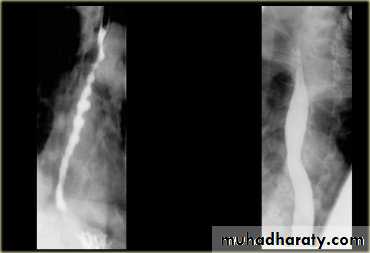
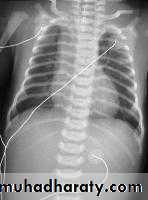
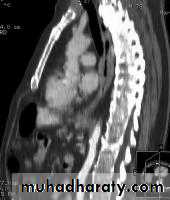
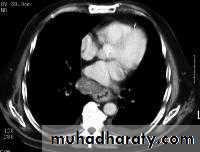
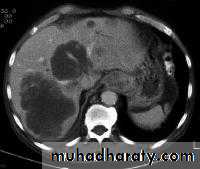
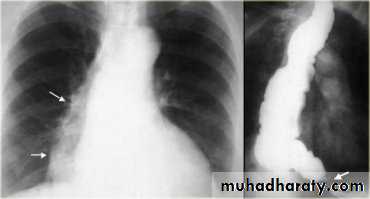
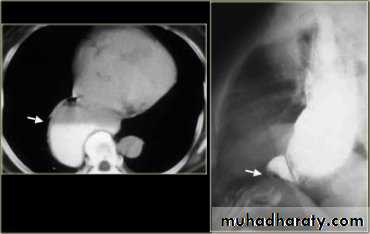
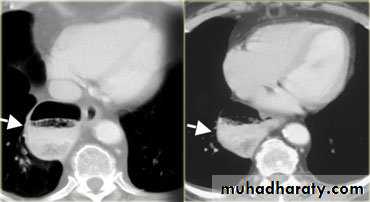
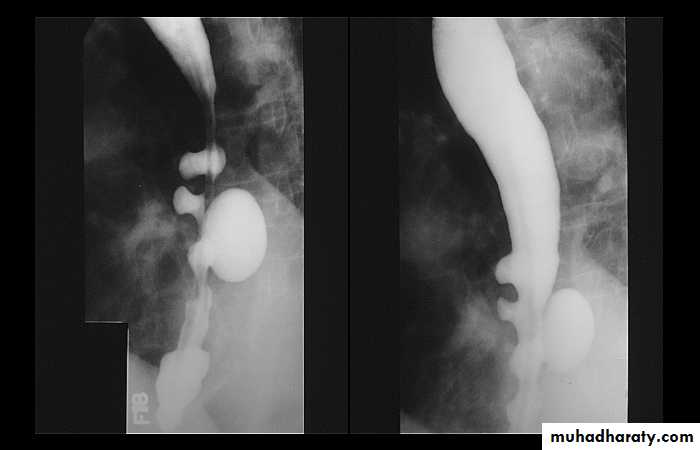
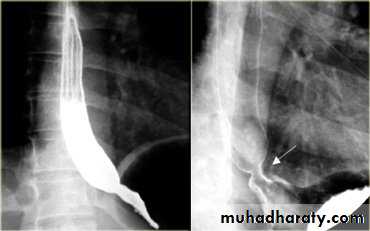
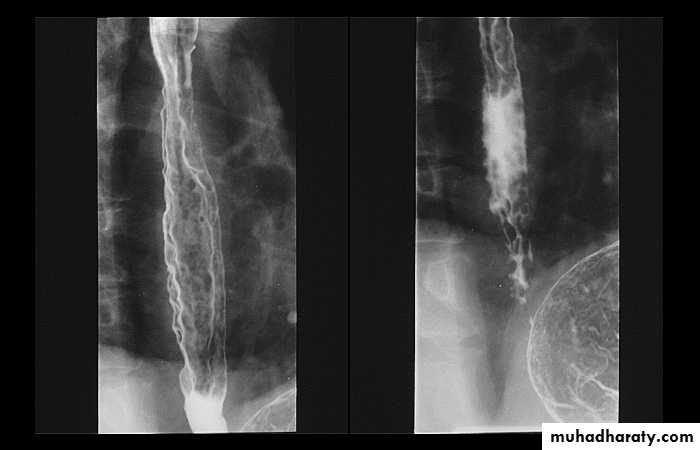
LEFT: Dilated esophagus (arrows) appears as long, well-defined structure paralleling heart RIGHT: Dilated esophagus usually deviates to right. Narrowing (arrow) at hiatus.
LEFT: CT shows dilated esophagus (arrow) that led to esophagram.RIGHT: Esophagram shows narrowing (arrow) at level of hiatus.
z
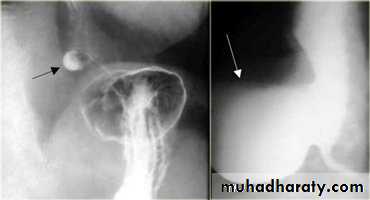
PULSION DIVERTICULUM
Due to raised intra-luminal tension
2- Chocking after meal .
3- In cervical portion at level of C5
4- Posteriorly (Killience dehiscent)
5- Lateral view show increased pre-vertebral space with air fluid level.
6- Confirmed by Ba. Swallow.
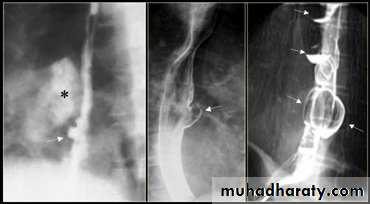
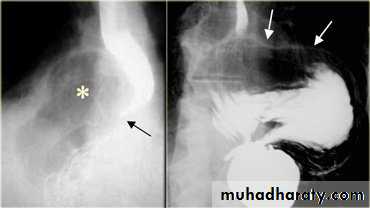
TRACTION DIVERTICULUM
Out pouching of lumen laterally due to fibrosis & adhesions( post-Tb.)
2-In the middle third at level of hilum
3- Up ward direction of diverticulum
4- Irregular base
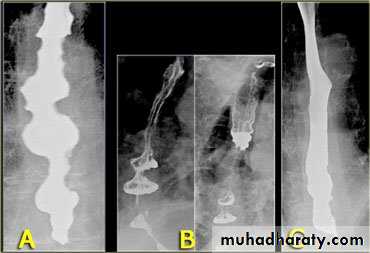
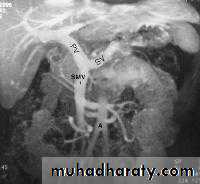
On the far left a traction diverticulum (arrow) due to hilar granulomatous disease. Calcified adenopathy (asterisk). In the middle a pulsion diverticulum (arrow) due to high intra luminal pressure.On the right multiple pulsion diverticula (arrows)
CONGENITAL DIVERTICULUM
1-Asymtomatic unless complicated.2-At lower part of esophagus above the diaphragm (Epi-phrenic)
3- Lateral or posterior in position.
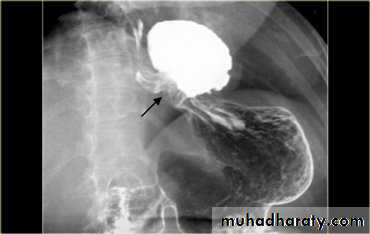
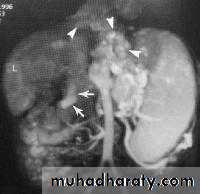
Sliding herniaOn the left initially, GE junction is below the esophageal hiatus. Later, stomach protrudes through hiatus
Para esophageal hernia
On the far left gas filled gastric funds (asterisk) protrudes through hiatus but GE junction (arrow) is below diaphragmThin mucosal fold (membrane)
2- Arise from anterior wall and extend Posteriorly .3- Lateral view Ba. Swallow show self like filling defect with proximal dilatation.
4-Single or multiple.
ESOPHAGEAL WEB
10% incidence at autopsy
Can be congenital or acquiredMost in hypopharynx and proximal esophagus
Majority protrude from anterior esophageal wall
Symptoms if lumen > 50% compromised
Sideropenic dysphagia (Plummer-Vinson syndrome)
Iron deficiency anemia
Esophageal web with dysphagia
Increased incidence of carcinoma
Validity of syndrome debatable
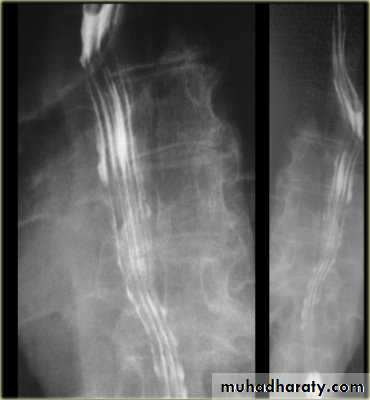
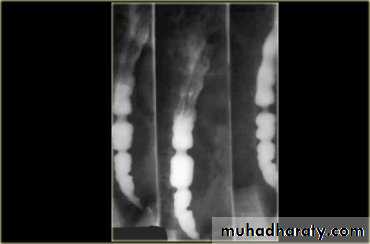
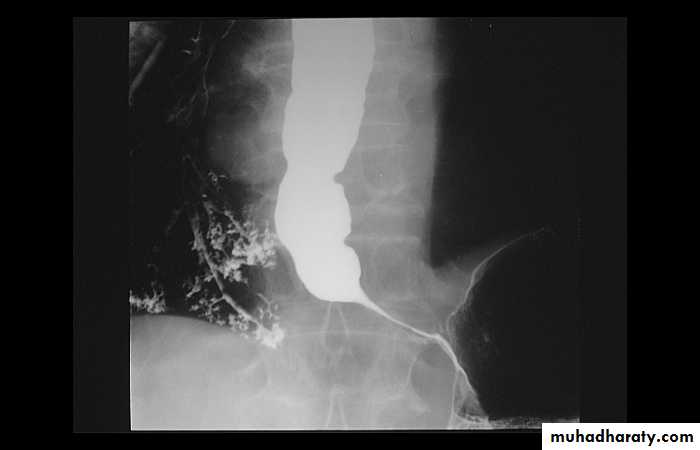
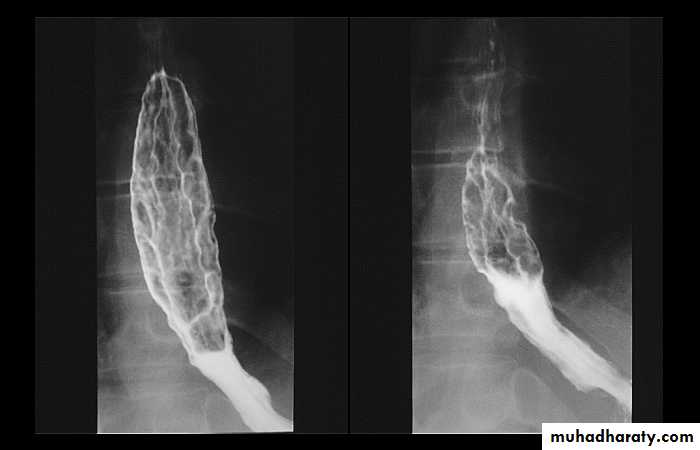
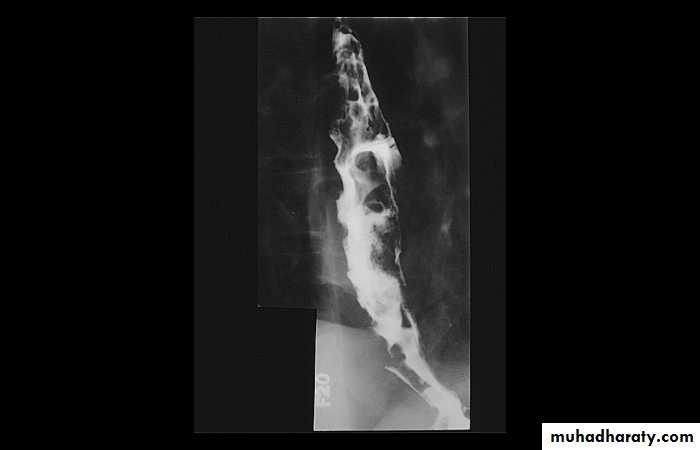
1-Dilatation of venous plexus in the wall of the esophagus due to increased pressure ( portal H.T.).
2-Important cause of Hematemesis .
3-Early changes seen in the mucosa (D.C.) loss of parallelism with thick and tortuous folds.
4-Later multiple small filling defects (fine cobble stone).
5-In advanced stage large filling defects ( coarse cobble stone ) .
6- More advanced stage elongated and worm like filling defect .
7-The changes are seen at lower third and gastric fundus.
Esophageal Varieces
Questions?