PHARYNGITIS, AND
LARYNGITIS
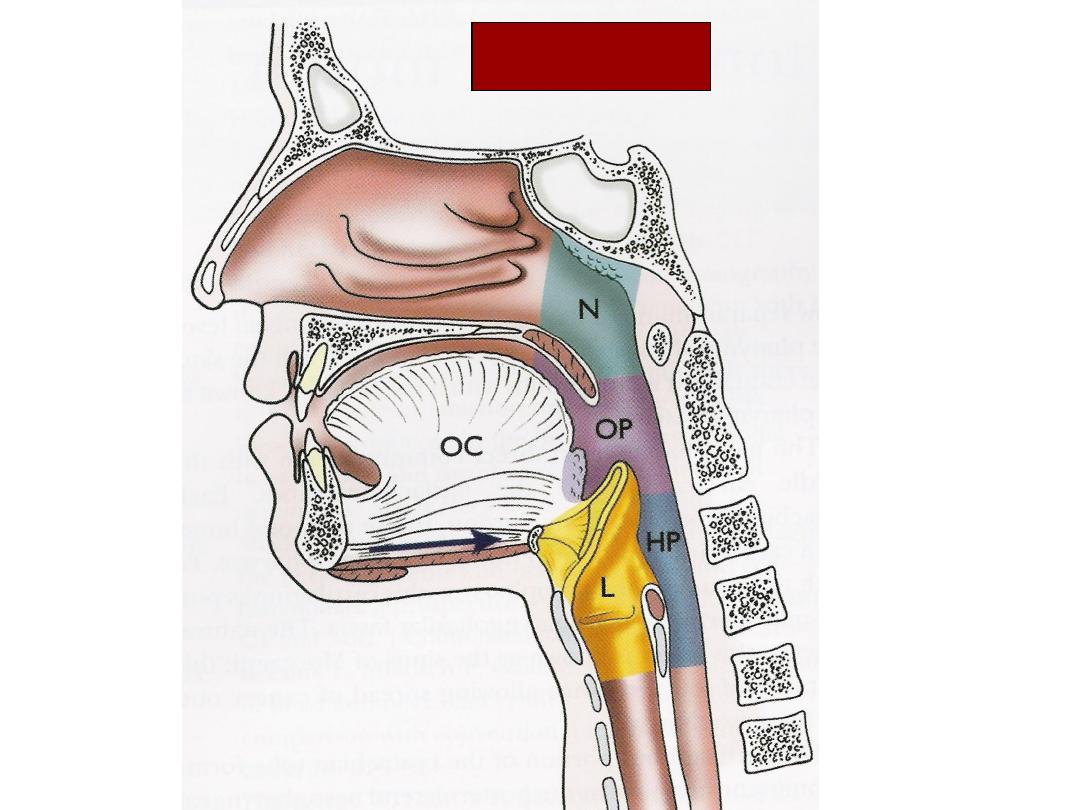
Anatomy

ACUTE PHARYNGITIS

ACUTE PHARYNGITIS
•
PATHOLOGY:
–
Frequently viral
–
may be secondary to sinonasal disease, caustic
injury, chronic allergy. Pharyngitis is a common
condition, particularly in children and young
adults

•
Types of pharyngitis
•
There are two types of pharyngitis - chronic
and acute.
•
Acute pharyngitis is common and is usually
caused by a viral infection. It's often caused by
the same viral infection that causes the
common cold
•
Chronic pharyngitis is a persistent sore throat

Acute Pharyngitis
•
Etiology
–
Viral >90%
•
Rhinovirus – common cold
•
Coronavirus – common cold
•
Adenovirus – pharyngoconjunctival fever;acute
respiratory illness
•
Parainfluenza virus – common cold; croup
•
Coxsackievirus - herpangina
•
EBV – infectious mononucleosis
•
HIV

Acute Pharyngitis
•
Etiology
–
Bacterial
•
Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci (S. pyogenes)*
–
most common bacterial cause of pharyngitis
–
accounts for 15-30% of cases in children and 5-10% in
adults.
•
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
•
Arcanobacterium haemolyticum
•
Neisseria gonorrhea
•
Chlamydia pneumoniae

PHARYNGITIS
•
SIGNS AND
SYMPTOMS:
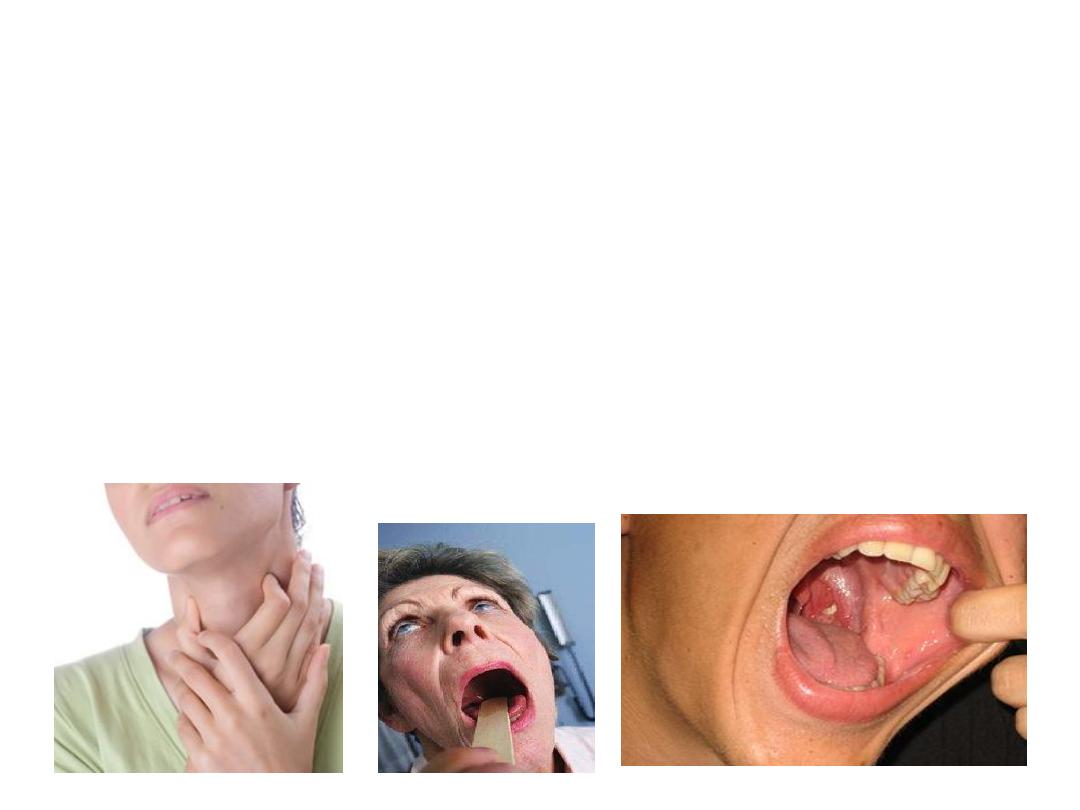
–
sore throat
–
odynophagia
–
otalgia (referred)
–
malaise
–
fever
–
erythema
–
cervical adenopathy

PHARYNGITIS
•
DIAGNOSIS:
–
clinical exam
–
consider throat cultures
–
viral smears rarely indicated

Suppurative Complications of Group A
Streptococcal Pharyngitis
•
Otitis media
•
Sinusitis
•
Peritonsillar and retropharyngeal abscesses
•
Suppurative cervical adenitis
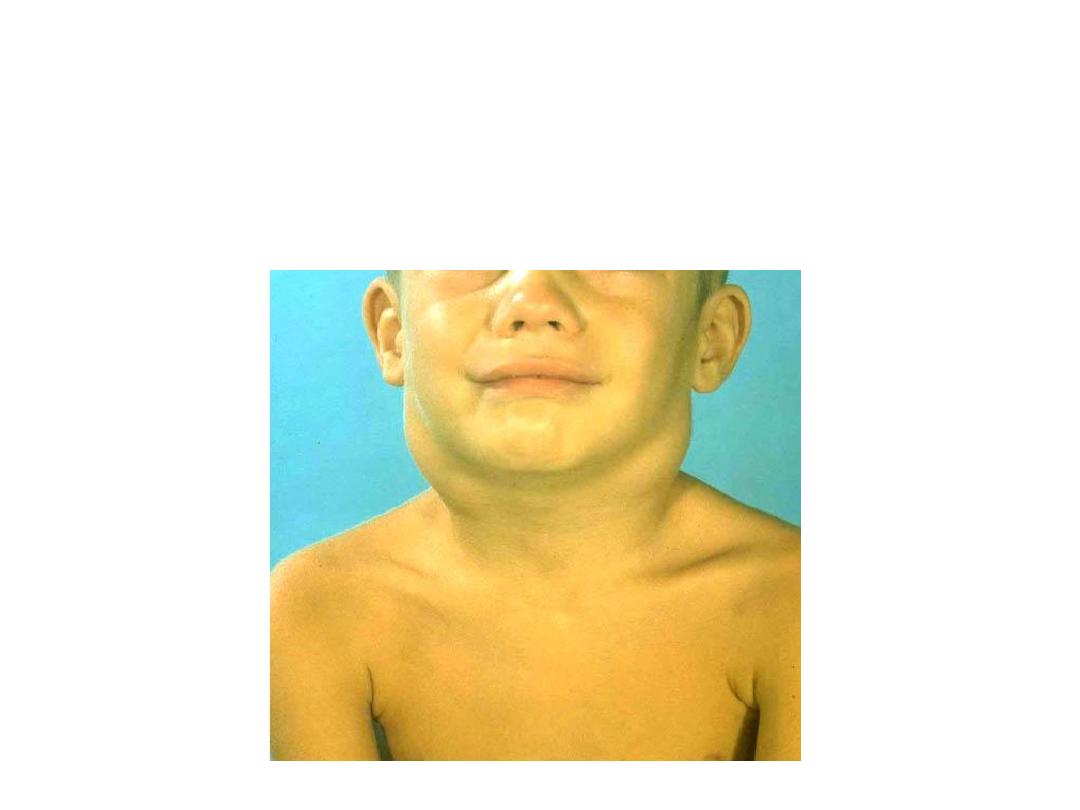
Streptococcal Cervical Adenitis

Nonsuppurative Complications of Group A
Streptococcus
•
Acute rheumatic fever
–
follows only streptococcal pharyngitis (not
group A strep skin infections)
•
Acute glomerulonephritis
–
May follow pharyngitis or skin infection
(pyoderma)

PHARYNGITIS
•
supportive care
–
bed rest
–
hydration
–
humidity
–
lozenges
–
anesthetic sprays
(cetacaine or
xylocaine) iodine
glyceride solutions
–
antipyretics
–
decongestants)
•
antibiotics for
suspected bacterial
infections

PHARYNGITIS
Other causes:
•
Candidiasis
•
Infectious Mononucleosis
•
Herpangina
•
Diphtheria
•
Scarlet Fever

CHRONIC PHAYNGITIS

CHRONIC PHARYNGITIS
ETIOLOGIES
–
granulomatous
diseases
–
connective tissue
disorders
–
malignancies
–
postnasal drip
(chronic
rhinosinusitis)
–
Irritants
•
dust,
•
dry heat,
•
chemicals,
•
smoking,
•
alcohol
CHRONIC PHARYNGITIS
Signs and Symptoms
•
constant throat
clearing
•
dry throat
•
odynophagia
•
thickened and granular
pharyngeal wall
•
pharyngeal crusting
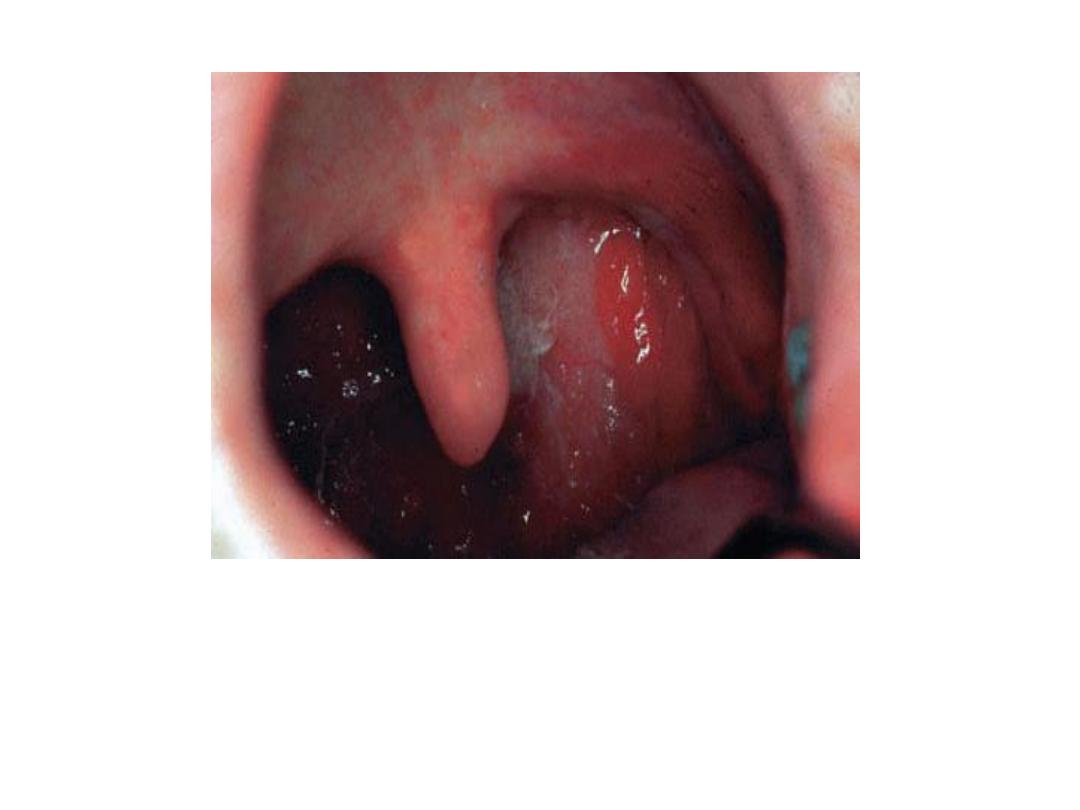
The typical appearance of a granulating
inflammation involving the posterior wall
of the pharynx (hypertrophic form).
CHRONIC PHARYNGITIS

CHRONIC PHARYNGITIS
•
clinical history and examination
•
culture and biopsy if failed empiric therapies

CHRONIC PHARYNGITIS
Treatment
•
address underlying etiology
•
avoidance of contributing factors
–
smoking
–
dust
–
dry environments
–
symptomatic treatment similar to acute
pharyngitis

LARYNGITIS
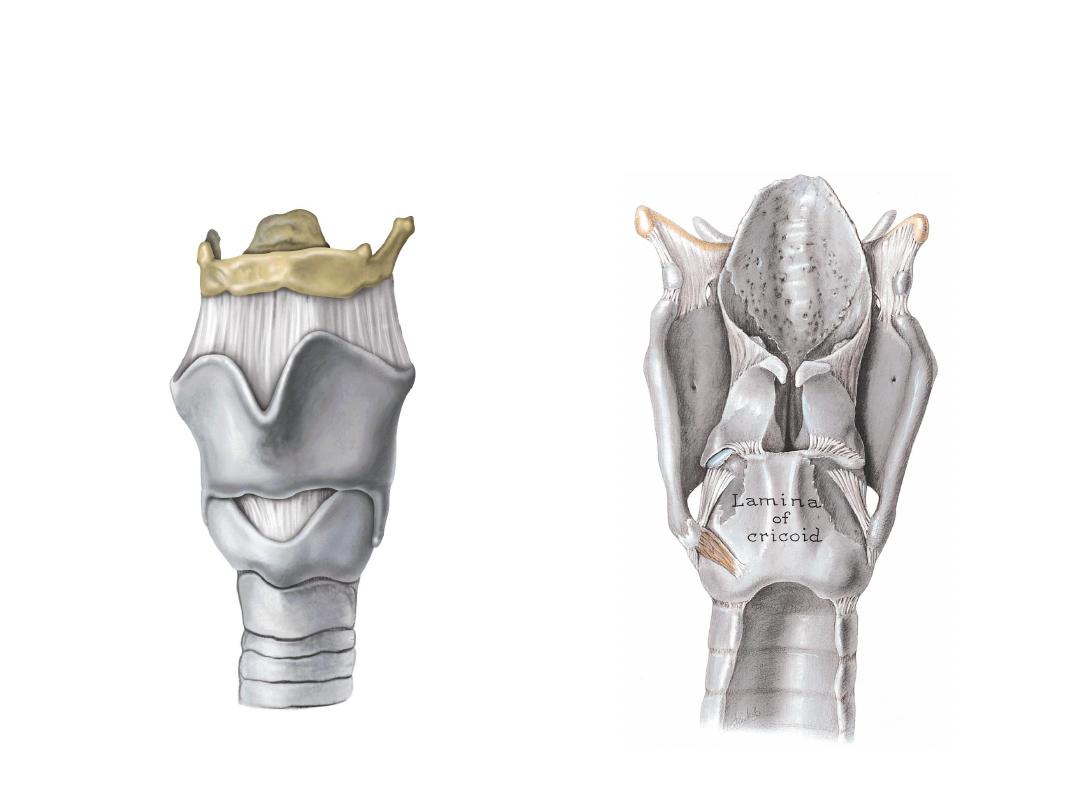
Anatomy

DEFINITION
It is the acute inflammation of larynx leading
to oedema of laryngeal mucosa and
underlying structures.

PAEDIATRIC CONCERNS
•
Lacks firm cartilaginous skeleton.
•
Flabby , easily collapses.
•
Glottic aperture , relatively smaller.
•
Mucosa swells up rapidly in response to
slightest trauma or infection.
•
Stridor is the most noticeable presentation.

AETIOLOGY
INFECTIOUS:
Viral
Bacterial
NON INFECTIOUS
Inhaled fumes
Allergy
Polluted atmospheric conditions
Vocal abuse
Iatrogenic trauma

CLINICAL PRESENTATION
•
Hoarseness or change in voice.
•
Husky, high pitched voice.
•
Discomfort in throat, pain.
•
Body aches.
•
Dysphagia, Dyspnoea.
•
Dry irritating paroxysmal cough.
•
Fever, Malaise.

CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS
•
Signs of acute URTI.
•
Dry thick sticky
secretions.
•
Dusky red and swallon
vocal cords.
•
Diffuse congestion of
laryngeal mucosa.

DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
•
Acute epiglottitis
•
Acute laryngo tracheo bronchitis.
•
Laryngeal perichondritis
•
Laryngeal oedema
•
Laryngeal diphtheria
•
Reinke’s oedema

TREATMENT
SUPPORTIVE
Voice rest.
Steam inhalation.
Cough suppressants.
Avoid smoking and cold.
Fluid intake.

TREATMENT Cont
DEFINITIVE
•
ANTIBIOTICS
STEROIDS
ANALGESICS

Chronic Laryngitis
Presents as diffuse lesion or produce localized
effects in larynx
Chronic infections in the surrounding areas,vocal
abuse smoking, alcohal,irritant fumes are held
aetiological factors.
.
Chronic laryngitis has a
multifactorial etiology and is ofen
exacerbated by intercurrent viral
and bacterial infections
CAUSES OF CHRONIC LARYNGITIS

chronic laryngitis differential
Reinkes oedema
vocal nodules
vocal cord polyp
Contact ulcer
Hyperkeratosis and leukoplakia
Atrophic laryngitis
Laryngeal lupus
tuberculous laryngitis

Tuberculous laryngitis
•
Almost always to secondary to pulmonary TB
•
Infected sputum
•
Younger age group
•
Tubercle formation is characteristic
•
Infilteration stage followed by proliferative
stage
•
Posterior part of larynx involved
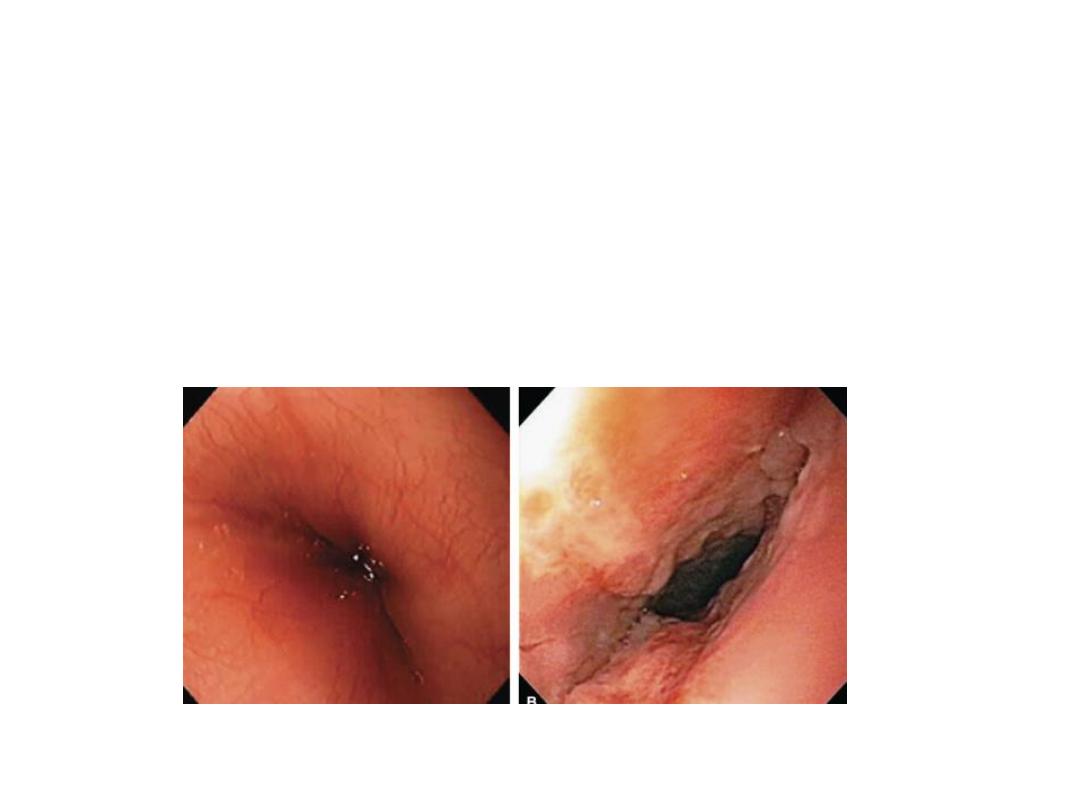
Reflux-Induced Laryngitis
•
inflammatory response of laryngeal mucosa
from Laryngopharyngeal Acid Reflux (LPR)

Reflux induced Laryngitis
Laryngeal Findings:
•
Erythema and edema
of
–
Posterior commissure
–
Arytenoids
–
Superior surface of
the vocal fold
–
Laryngeal surface of
the epiglottis

CHRONIC LARYNGITIS
Treatment:
•
Address etiology
–
stop smoking
–
voice rehabilitation
–
Treatrhinosinusitis
–
reflux regimen
–
Humidification
–
Mucolytics
–
Consider short course
of corticosteroids

Term applied to group of inflammatory
conditions involving larynx , trachea and
characterized by Triad :
Inspiratory stridor
Brassy cough
Hoarseness of voice +/_ resp.distress

Usually viral in origin
-
Parainfluenza virus (type 1)
- Influenza virus
- RSV , adenovirus , measles virus
It is the
most common
cause of Acute Airway
Obstruction in children
Age group 3m-3 years (peak 2years)
Affects boys more often than girls
Peak occurrence is in fall and winter

It is clinically diagnosed
Neck x-ray and CBC all should be done
in clinically stable pt .
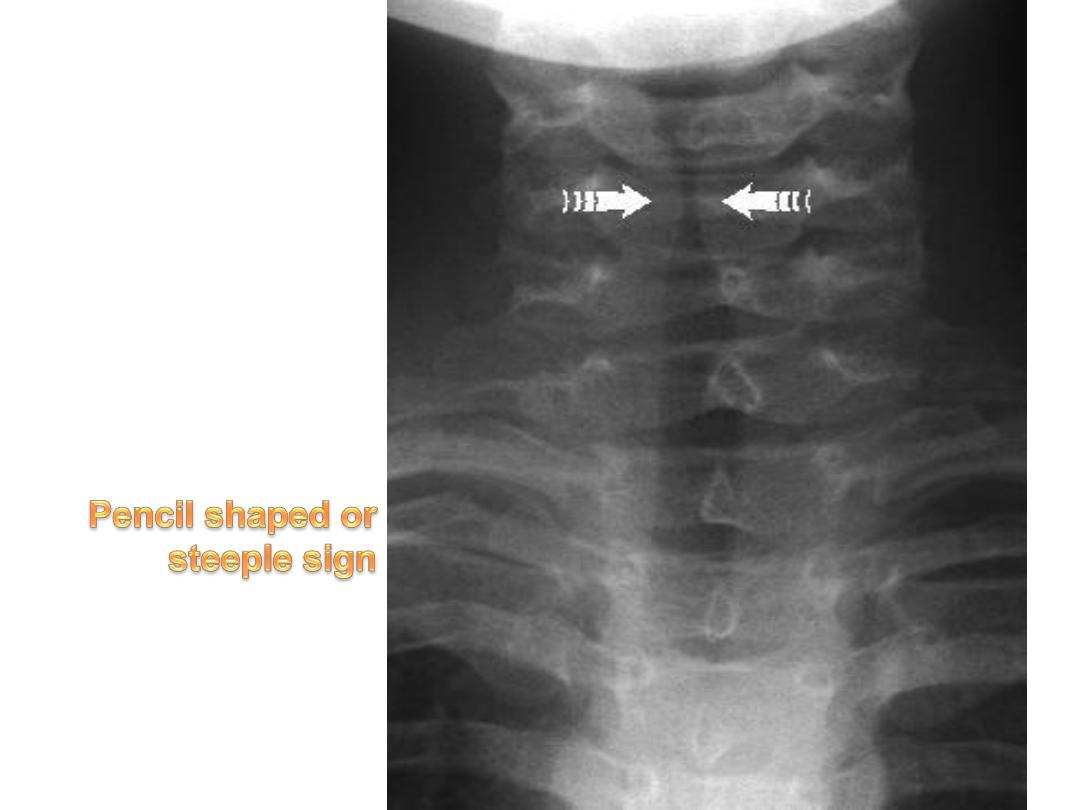
- AP neck film : show a pencil tip or
steeple sign of the subglottic trachea
- CBC , it may helps .


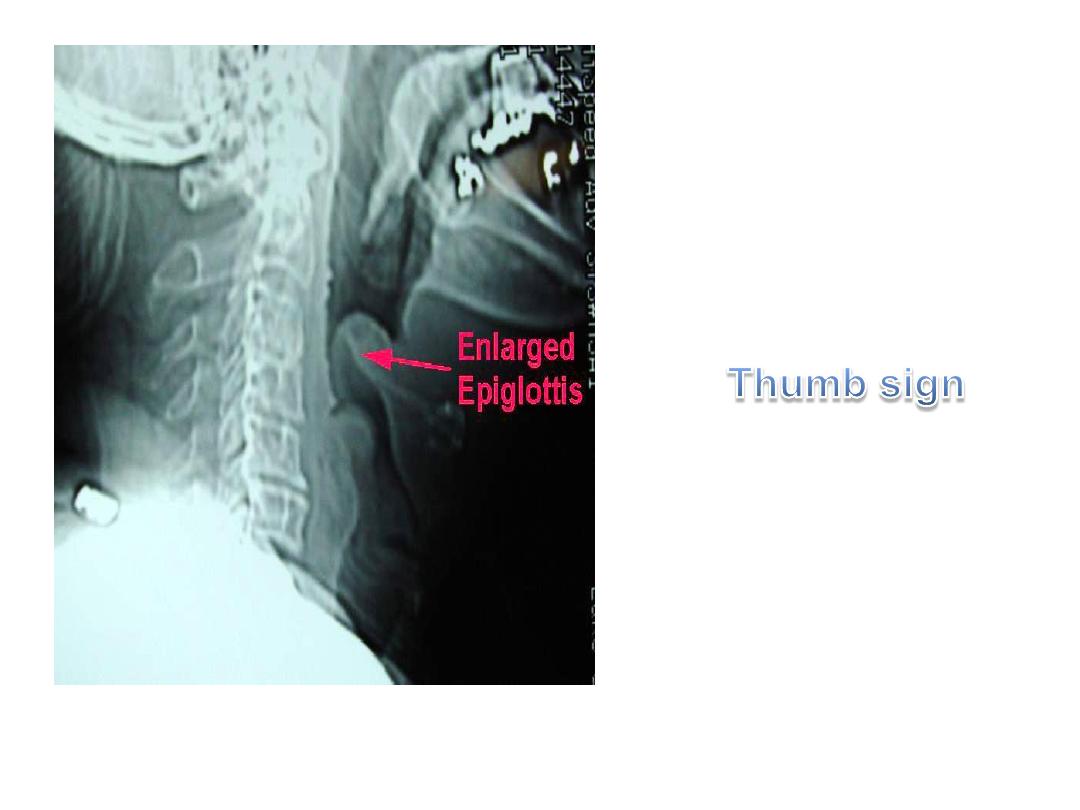
It is a rapidly progreesive bacterial infection
causing acute inflammation and edema of the
epiglottis and adjacent structures : aryepiglottic
folds and arytenoids
Also known as supraglottitis
It is life threatening condition may lead to
sudden and complete airway obstruction

Age : 2-6 years ( peak at 3 year)
Infant , older children and adult are
rarely affected
Causative agents :
-
HIB
- pneumococci , staphylococci,
streptococci

History
Presentation
Appearance of the child
Pharynx examination at this stage in ER
is absolutely contraindicated
Next step = admission in ICU
Neck x-ray : Not the priority
Do not leave the patient unattended

THANK YOU!!!
