Dental management of patient with renal failure
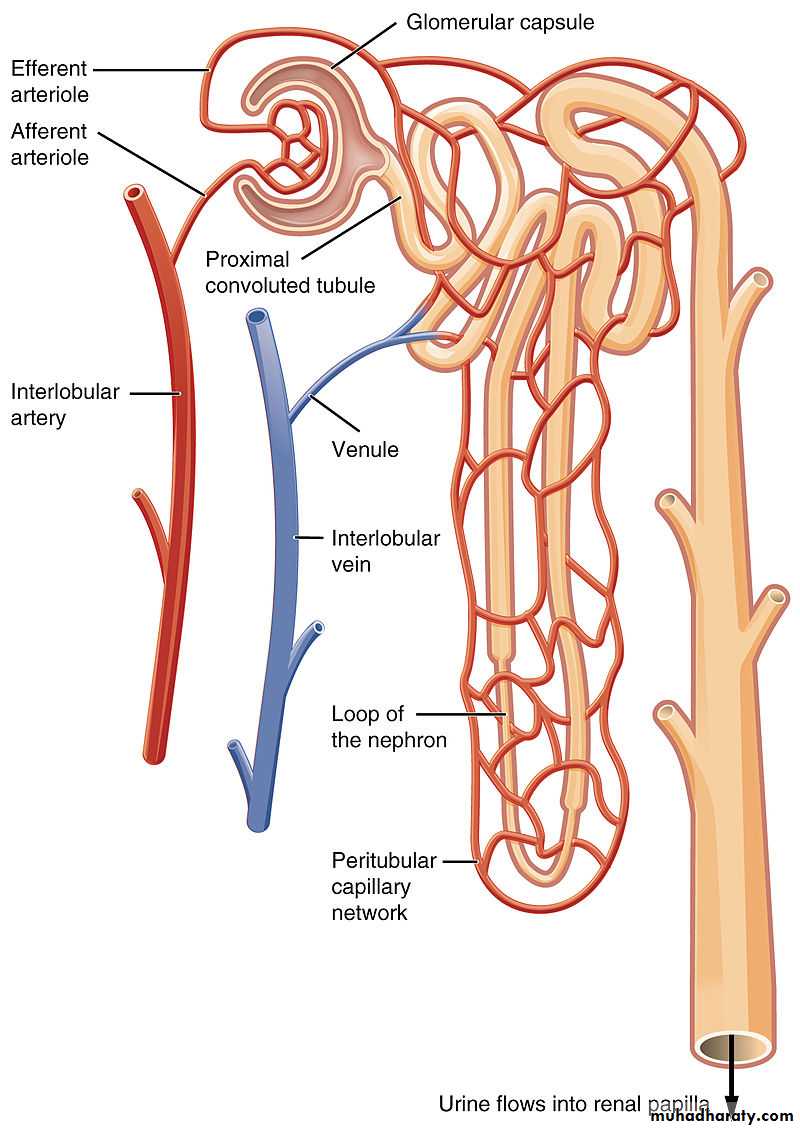
IntroductionEach human kidney is composed of about one million anatomical and functional units called nephrons. In turn, each nephron is composed of a glomerule and tubule. The glomerule consists of an interconnected network of capillaries which continues with the proximal convoluted tubule .
The kidney functions:
• Excretion of metabolic waste products.• Electrolyte regulation through the control of sodium, potassium and water excretion.
(c) vitamin D metabolism.
Classification of renal failure
When a nephron is destroyed it is unable to regenerate, and the kidneys compensate the loss through hypertrophy of the remaining nephrons, so that normal kidney function can be maintained until approximately half of all the existing nephrons have been destroyed. Once this point has been reached, symptoms of renal functional impairment begin to appear.Acute renal failure (ARF)
is characterized by a sudden reduction in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) lasting for hours or days.which may be due to:
Dehydration, a blockage in the urinary tract, or kidney damage
In general, renal function is restored once the underlying cause has been resolved.
Chronic renal failure (CRF)
is characterized by a gradual reduction in the number of functional nephrons. diabetes and high blood pressure are the most common causes.
leads to terminal or end-stage renal failure (ESRF)
Laboratory abnormalities which are commonly seen in patient with ESRD
1 – anemia2- elevated blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine .
3- hyponatremia and hyperkalemia
4- hyperphosphatemia and hypocalcaemia compromises of platelet function.The normal range of BUN is 10 – 20 mg /dl of blood and creatinine level is less than 1.5 mg /dl of blood .
patient usually do not have symptoms of renal dysfunction until the BUN is above 50 mg/dl or the creatinine level is above 5 mg/dl .
Treatment of ESRD may be
1- dialysis2- renal transplantation.
Dialysis
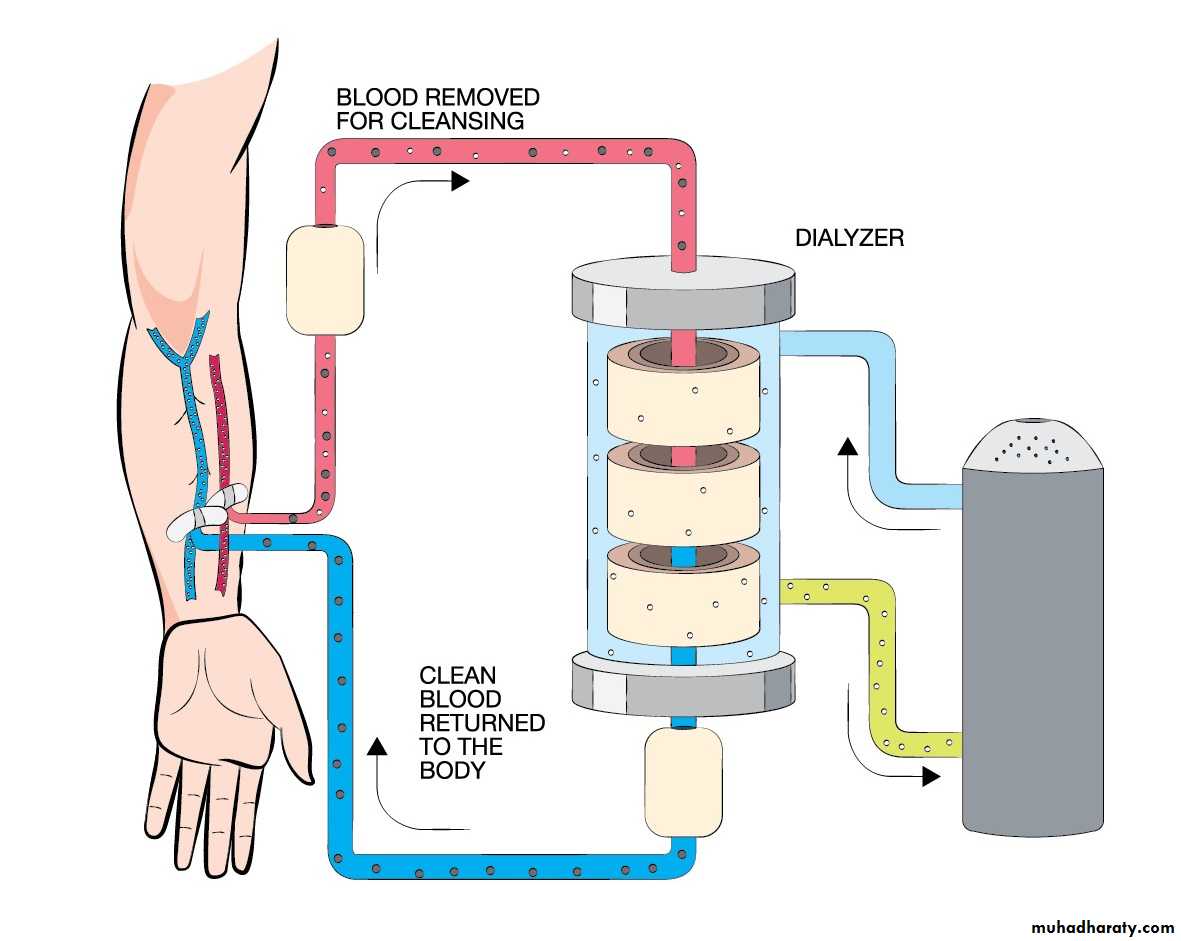
Dialysis is a medical procedure used to remove nitrogenous waste and excessive fluid from patients with severe renal insufficiency.
Type of dialysis
HemodialysisPeritoneal dialysis
Hemodialysisuses a man-made membrane (dialyzer) to filter wastes and remove extra fluid from the blood.
Peritoneal dialysis
uses the lining of the abdominal cavity (peritoneal membrane) and a solution (dialysate) to remove wastes and extra fluid from the body.
In patients with renal disease, the risk of caries formation is increased by poor oral hygiene and low salivary flow rate.
Dental management of renal failure patients
1- Consultation with the nephrologist provides information on the state of the disease, the type of treatment, the best timing of dental management.2- Prior to any dental treatment, complete blood count is to be obtained.
3- Blood pressure is to be monitored before and during treatment, with the administration of sedation to lessen anxiety4- The metabolism and elimination of certain drugs are altered in situations of renal failure.
The prescription of aminoglycoside antibiotics and tetracyclines is to be avoided, because of their nephrotoxicity.
Dialyzed patients
Patients on peritoneal dialysis require no special measures as regards dental treatment, beyond those already commented above. We therefore will center our attention on hemodialysis.1- dialyzed patients are at an increased risk of bleeding. It is advisable to provide dental treatment on non-dialysis days, to ensure the absence of circulating heparin, which has a half-life of about four hours
ensure that local hemostatic measures are available: mechanical compression, sutures and topical thrombin.
2- endocarditis is effectively a potential complication in dialyzed patients.
The recommended antibiotic regimen is 2 g of amoxicillin via the oral route one hour before the dental procedure. In the case of patients with allergy to penicillin, clindamycin is the drug of choice (600 mg via the oral route, one hour before the intervention).3- Dialyzed patients are subjected to numerous transfusions and blood exchanges, and this increased risk of infection in the form of HIV, HBV, HCV and tuberculosis.
Periodic monitoring is required, to avoid both personal cross-contamination in the dental clinic.
Renal transplant patients
1- It is important to conduct dental evaluation prior to renal transplantation.Teeth offering an uncertain prognosis are to be removed.
The potential for oral infections after transplantation is very high, since these patients receive immunosuppressive therapy.
2- Prophylactic antibiotic treatment is indicated before invasive dental procedures are carried out.
3- Prolonged corticosteroid therapy may make it necessary to administer a supplementary dose in situations of stress.
In the first 6 months after transplantation, patients should avoid any elective dental treatment