
Hemolytic Anemia
Is premature destruction of RBC (when rate of
destruction exceed the capacity of marrow to produce
RBC resulting in anemia.
(
RBC survival in adult is
110
—120 days
,
in term baby is
60-80 days
,
while in
preterm
is 40-60 days ) .
During hemolysis
– RBC survival is shortened – RBC
count is fall & erythropoietin is increased ---- stimulate
of B.M
– more RBC production & increase retic count.
The following are associated with hemolysis :----
1
- increased retic count .
2
- increase degradation rate of Hb results in increase
billiary excretion of heme pigment derivative & increase
urinary , fecal urobilinogen .
3
-elevation of unconjugate bilirubin & LDH .
4
- Decrease haptoglobin & hemopexin due to
increased their clearance .
5
- increase methemalbumine ( increase binding
oxidized heme to albumine )
6
-Hbemia & Hburia .

Classification of H.A
•
A-Cellular ;---resulting from
:--
•
1
- membrane defects ( spherocytosis , elliptocytosis)
•
2
- enzyme defects ( G6PD, pyruvate kinase )
•
3
- Hb pathy ( thalassemia, SCA )
•
B
-
Extracellular :-- as in
•
1-
auto
– immune H.A
•
2-
mechanical factor as in DIC, HUS, burn, thermal injury.( DIC : dissiminated intra
vascular coagulation) , HUS : hemolytic uremic
•
syndrome )
•
3-
plasma factors as in liver dis. , infection , wilson dis.
•
, abetalipoprotinemia
•
liver disease :-due to alteration in plasma cholesterol and phospho-lipid .
•
infection :-due to toxic effect on RBC .
•
wilson :- due to effect of copper on RBC membrane .
•
abetalipoproteinemia : due to absence of lipo protein .

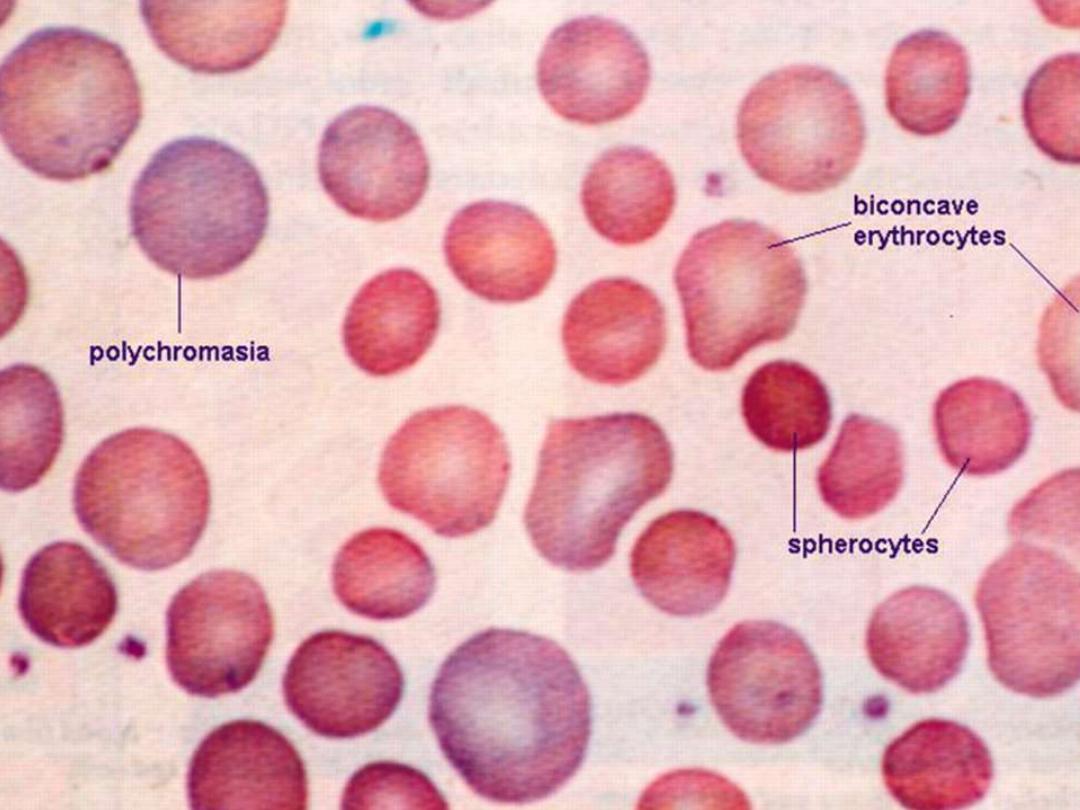
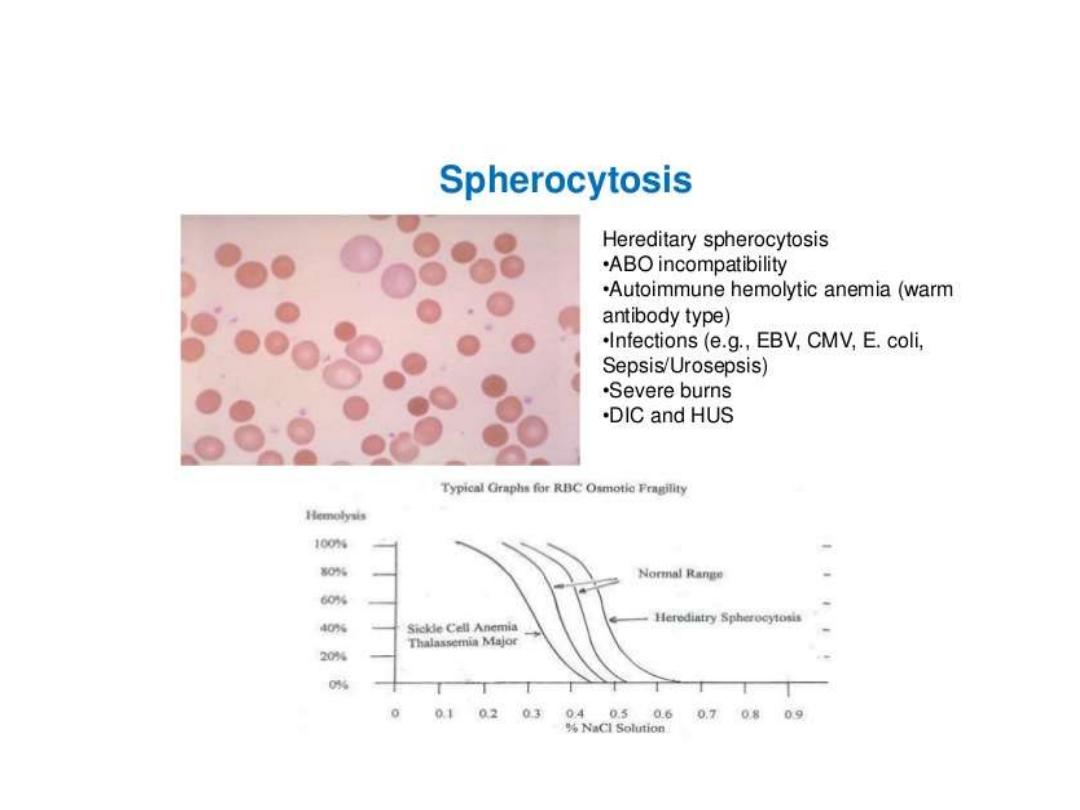
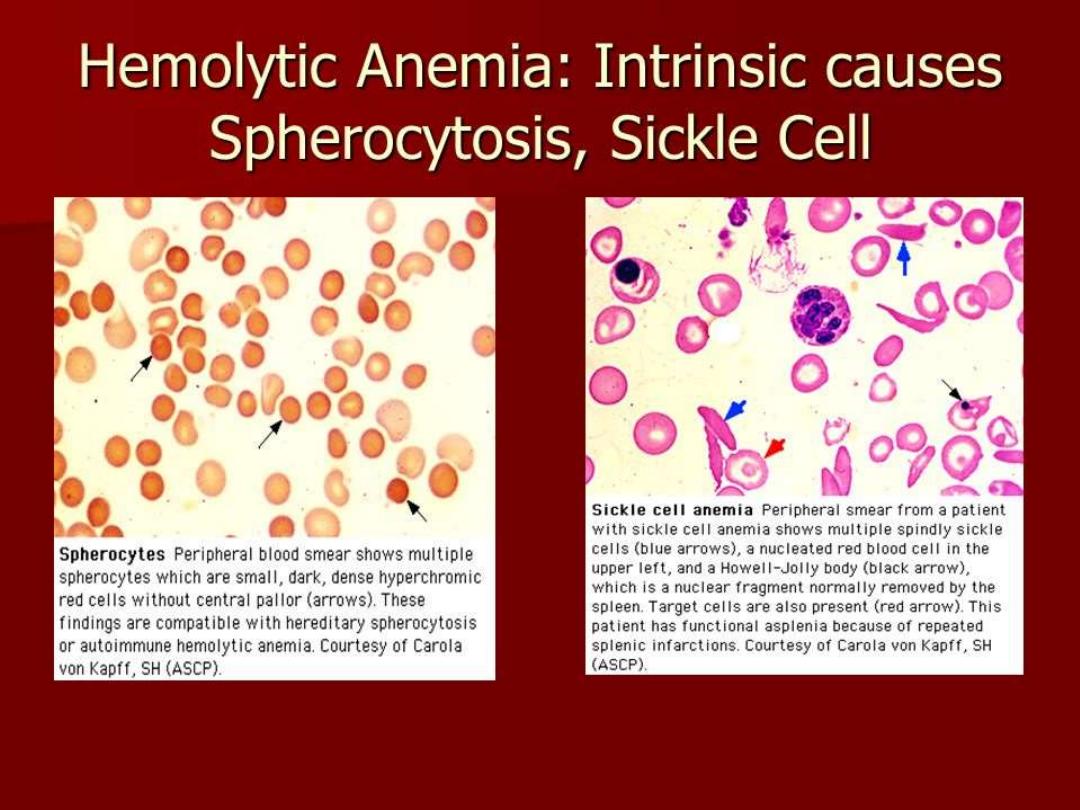
Hereditary spherocytosis
•
Resulting from abnormalities of
spectrin & ankyrin
which
are major components of cytoskelton responsible of
shape RBC causing
loss of membrane surface without
loss of volume causing of sphering of RBC(
and increasing in
cation permeability , cation transport leading to spherocyte cell resulting in destructing prematurely
in spleen ) .
•
IS
AD
&
less AR
,
25%
of all patients from
mutation
C|F:----
IS variable from
no
symptoms to
sever H.A
.
In neonate
may presents as anemia & hyperbilirubinemia
After infancy
, the spleen is usually enlarge & pigmentry
gall stone as early as 4-5 years
Liable of
aplastic crisis as result from parvo virus
Note :--
hemolysis may be more prominent in neonate because HbF bind
poorly with 2,3DPG causing more free 2,3DFG which destabilize interaction
of spectrin, ankyrin and protein 4.2 in RBC membrane .

Lab. Finding
•
1
- feature of hemolysis ( anemia & increase retic count )
•
2
- MCV is normal & MCHC often is increased(36-38)
•
3
- presence of spherocyte ( more than 15-20 % )
•
4
- erythroroid hyperplasia .
•
5-
gall stone
•
Diagnosis :--
•
1-
clinical examination .
•
2
-lab. Finding .
•
3-
incubated
osmotic fragility test .
•
D.D ;---other causes of spherocyte
;--
•
a
- iso & auto immune H.A.
•
b
- rare causes like thermal injury , clostredia infection, wilson dis.
•
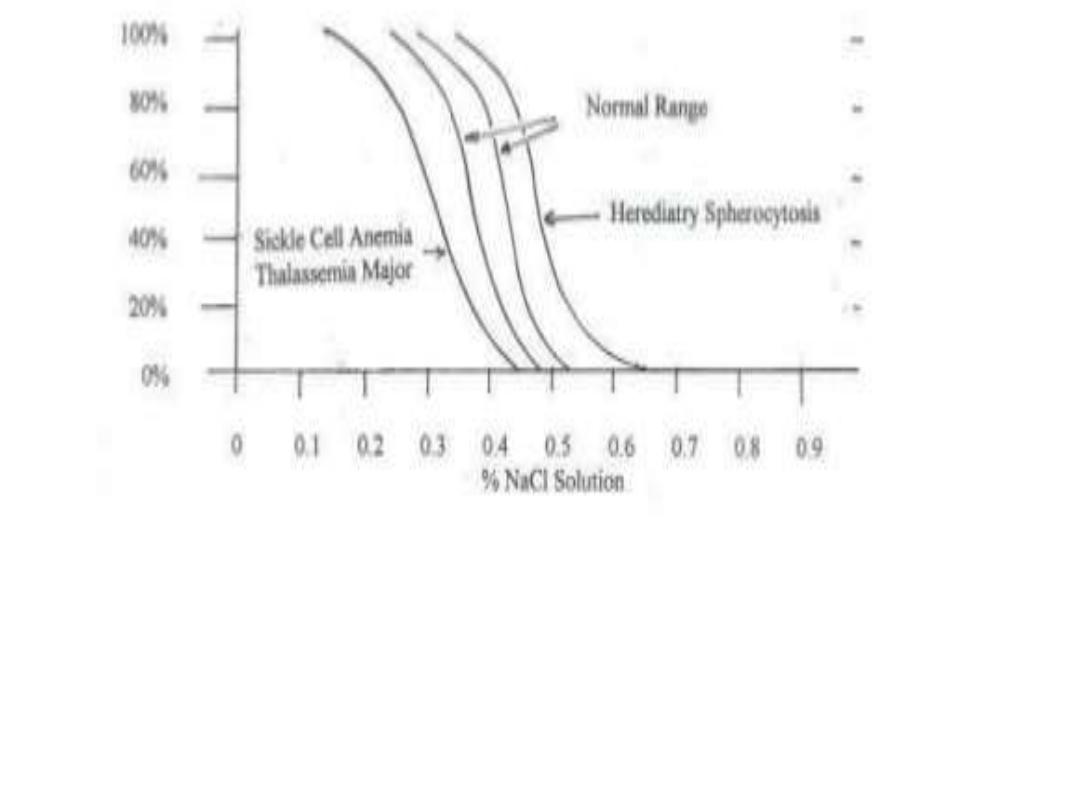
+incubated osmotic fragility test :-- RBC are incubated in progressive dilution of an
iso-osmotic buffered salt solution and when exposed to hypotonic saline cause the
RBC to swell called spherocyte which lyse more readily than biconcave and this is
accentuated by depriving the cells of glucose over night at 37c so called incubated
osmotic fragility test .
Osmotic fragility test in cong. spherocytosis

treatment
•
Depend on severity of anemia :---
•
A-
factor important in treatment (Hb, retic count, age ,
growth .
•
B-
Folic acid 1 mg daily
•
C-
prior splenectomy should immune against pneumo
coccal , meningo coccal & H. Influenza .
Should kept on pencillin
as 125 mg twice daily for those of less
than 5 years of age and 250 mg for above 5years of age .
Hb
–disorder
:---
•
Sickle cell anemia
:---
•
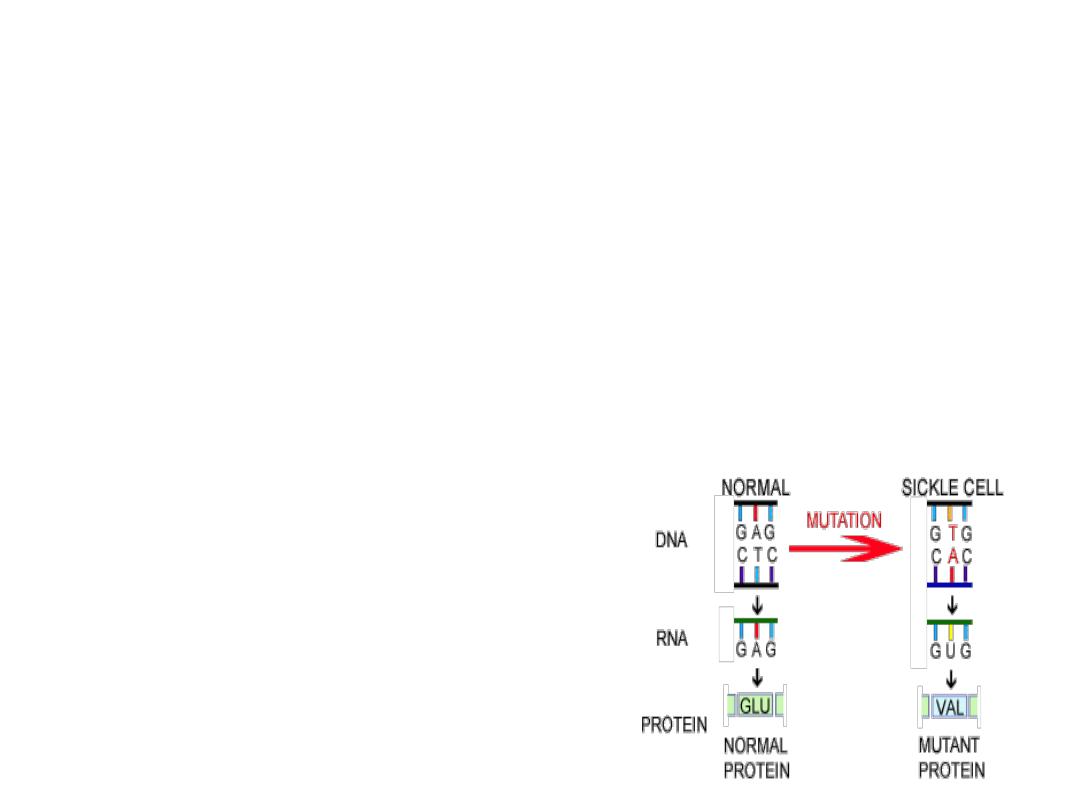
Hbs is
resulting from genetic mutation where by
glutamic acid
is replaced by
valine
at
position 6 on B-chain of Hb . This resulting in polymerization of Hb under condition of
hypoxia or acidosis
.
•
2 group of SCS ( Sickle cell syndrome ):---
•
1- sickle cell trait
.
•
2- Hbss
.
•
Hbss ( sickle cell dis, or S. thalass.) :---
•
1
- affected newborn seldom exhibit C/F .
•
2
- H.A. gradually developed over 2-4 months paralleling of replacement of HbF by
HbS .
3-
infant has abnormal immune function as early as 6 months of age . Some children and
by 5 years of age have functional asplenia.
•
4- all
patients are at increases risk of infection
•
5
-dactylitis ( hand foot syndrome ).
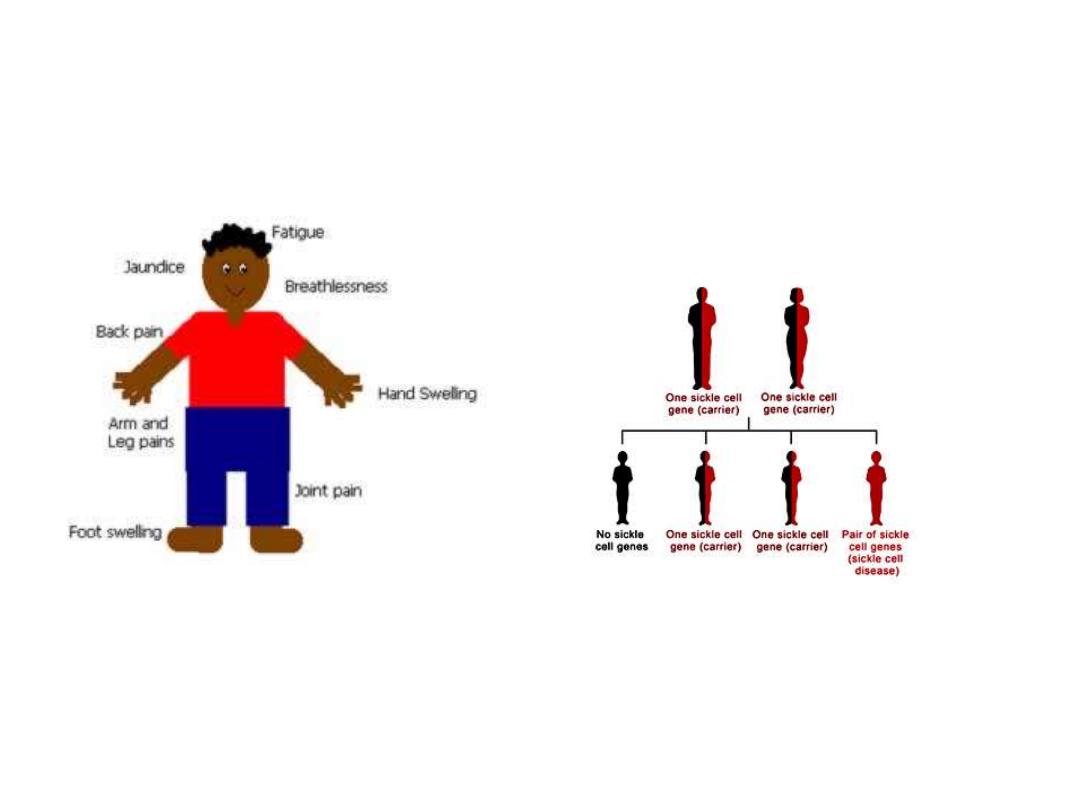
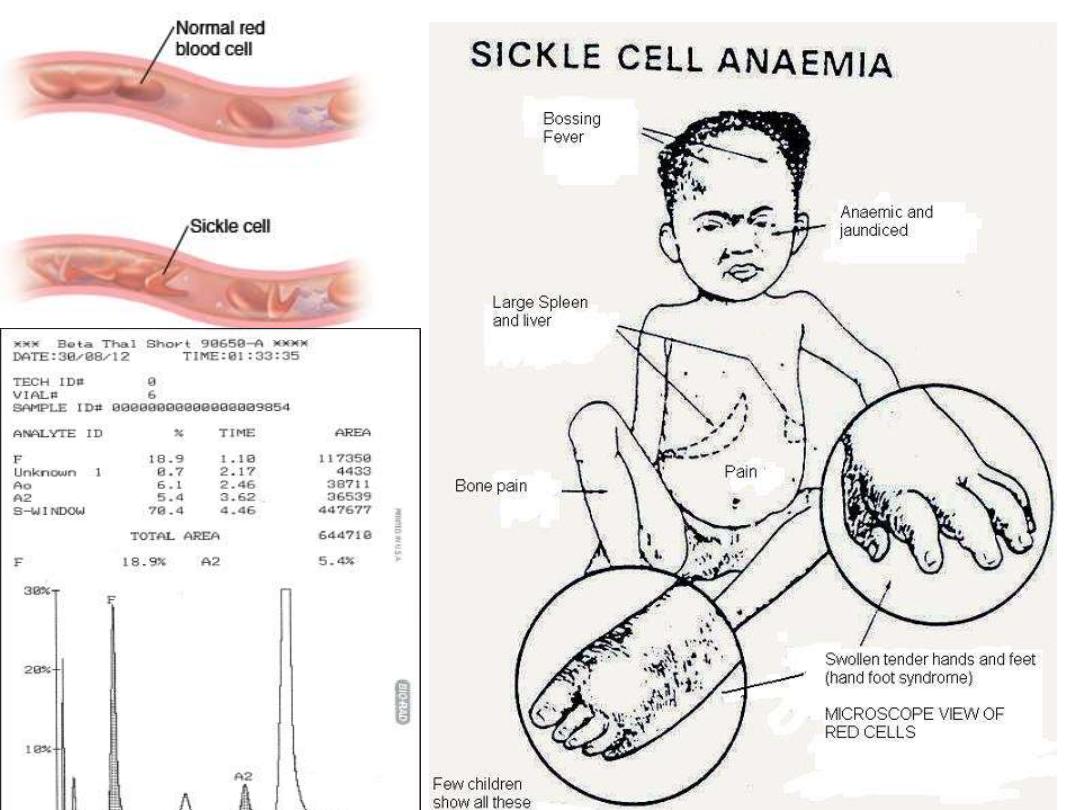
Sickle cell anemia
hereditary plus clinical features
Hereditary
.
•
.
.

Crisis in SCA
•
1
- acute painful crisis ( vaso-oclusive crisis ) .
•
2
-splenic sequestration .
•
3
- aplastic crisis .
•
4
-hemolytic crisis
•
Note 1-:
no evidence of blood transfusion decrease intensity or duration of episode of
painful crises . 2-multiple painful episode requiring hospitalization within one year &
pain episode required hospitalization of more than 7 days -----it needed evaluation for
comorbidities diseases or psycological stress .
.
•
Fever in SCA :---
•
IS MEDICAL EMERGENCY
that required prompt medical evaluation &
delivery of antibiotic because of high risk of bacterial infection & the
concomitant high fatality rate when infected .
•
Several clinical strategies have been developed ranging from ;--
•
1
- admitted all patients with fever for Intra.venous antibiotic .
TO-
-
•
2
- administration paranteral 3th generation cephalosporin in out patient
setting if no risk factors of occult bacteremia .
TO
—
•
3
- febrile patients with established risk factors for bacteremia : admission
to hospital .

The following associated with increased risk of bacteremia in SCA
patients( indication to hospital)
•
1
-severely ill patient .
2
- hypotension .
3
- poor capillary refilling(more than 4
second ) .
4
- temperature of more than 40.
•
5
- WBC of more than 30000 or less than 5000 .
•
6
-platelts count of less than 100 000 .
7
- Sever pain .
•
8
- history of pneumococcal sepsis .
9
- dehydration .
•
10
- Hb of less than 5gm\dl
•
with Blood culture should be aspirated to all patients with SCA associated
fever .
•
Complication of SCA:---
•
1
-Infection .
2
- acute chest syndrome
3
- sever anemia
•
4
-stroke ( 11% as overt stroke , 20% as silent stroke before 18 year)
•
5
-priapism . ( 20% 0f patient between 5-20 year of age )
•
6
- hyposthenuria 12% .
7
-skin ulcer
8
-avascular necrosis
•
10-
retinopathy 1-3%

Prevention of stroke ( primary prevention)
•
Can be accomplished by
transcranial doppler
(TCD) , Which asses
blood velocity in brain blood vesseles (if more than 200 cm\sec---
•
Transfusion threshold , prophylactic blood transfusion is instituted to
maintain Hbs of less than 30% .
•
Secondary prevention
;-- is accomplished by blood
transfusion to maintain Hbs of less than 30% in first 2 year of stroke
& less than 50% thereafter .
•
Lab. Finding :---
•
1-
retic count is increased 5-15%, Hb 5-9gm/dl, normal to increase
platelts, WBC 12000
—20 000 .
•
2
- blood film :--shows sickle cell, howell jolly body ,
•
3-
confirm diagnosis by Hb-electropheresis.
•
Several screening tests available include ;----
•
1-classic meta-bisulfite sickle cell
2- solubility tests which deoxygenated Hbs precipatated in a aqueous solution
•
3
-
hyperactive bone marrow
4
-X-ray in vertebral body ( osteoporosis ) and mild
expansion of B.M
.

Treatment of SCA
•
A-
is directed towards prevention of complication & optimization of health &
health coping strategies
by :---
1
- all patients should be immunized against pneumococcal , meningococcal &
annual adminstration influenza vaccine .
2-
pencillin prophylaxis ,
•
3
- folic acid 1 mg daily
•
4-
all febrile patients needs aspiration of blood culture & patients with risk
factor of bacteremia --- needs admission .
•
if well appearing patients & no risk factor
– given ceftriaxone &then
discharge to be if culture is staph or salmonella , should be evaluated for
osteomylitis )
)
seen 24hr later for rechecking & results of culture.
•
5-
to understanding of the family , how to palpate spleen to diagnosis early
sequestration crisis .
•
B
-
AVOID THE FOLLOWING
:---
•
1
- dehydration & acidosis .
2-
avoid vascular stasis .
•
3
-cold temperature .
•
C-
treatment of complication
:--
•
1
- pain killer
•
2-
blood transfusion in :- acute chest syndrome , stroke , stroke
prevention, sever
anemia before anesthesia

Chronic transfusion therapy used in
:--
1-still has TCA( transiant
cerebral ischemia . 2- avascular necrosis of hip & shoulder
3- drug therapy
:--
like hydroxy urea
:--
it is myelosuppressive drug.
its aims :--
a-
decrease rate of crisis of pain to 50% including acute chest syndrome
b-
decrease blood
transfusion to 50% in adult
Is safe and well tolerated in children older than 5 years of age .
if start in infants
:---
may preserve spleenic function
,
improve growth pattern
,
reduce incidence of
acute chest syndrome .
dose
15-20 mg\kg daily
with increase dose every 8 wk of 2.5-5mg|kg
(
max. dose is 35 mg |kg )
.
theraputic effects required several months
follow up of patient on hydroxyurea through measuring CBP( complete blood picture and blood urea (
stopped treatment if WBC of less than 2500 and platelets of less than 100000 , sever anemia ,
increased blood urea and liver injury ) .
•
4- B.M transplantation
.
•
Indication of hydroxy urea in SCA :
•
1- frequent episode of crises of more than 6 attack or more per year .
•
2- history of acute chest syndrome .
•
3- sever symptomatic anemia
•
4-history of stroke or high risk of stroke
•
5- sever unremitting chronic pain that not control by conservative measures .
•
6-history of other severe vaso occlusive events .

Sickle Cell Triat ( HbAS )
•
Hbs
is less than 50% and HbA of more than 50% .
•
Life span is normal & serious complication are very rare.
•
CBP :- within normal range .
•
Hb
–electropheresis is diagnostic
.
•
Complication include
:---
include
•
1-
sudden death during vigorious exercise .
•
2-
splenic infaraction at high attitude .
•
3-
hematuria , hyposthenuria & bacteruria .
•
4-
eye injury as hyphema .
•
Children with sickle cell trait should not have any restriction on
activities
.
•
thank you
